A Novel Combination Therapy Tβ4/VIP Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Changes in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture of Human Telomerase-Immortalized Corneal Epithelial Cell Line
2.2. Conducting ECIS Experiments for Barrier Function and Cell Migration
2.3. Data Analysis and Modeling
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Immunostaining of Tight Junction Molecules
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
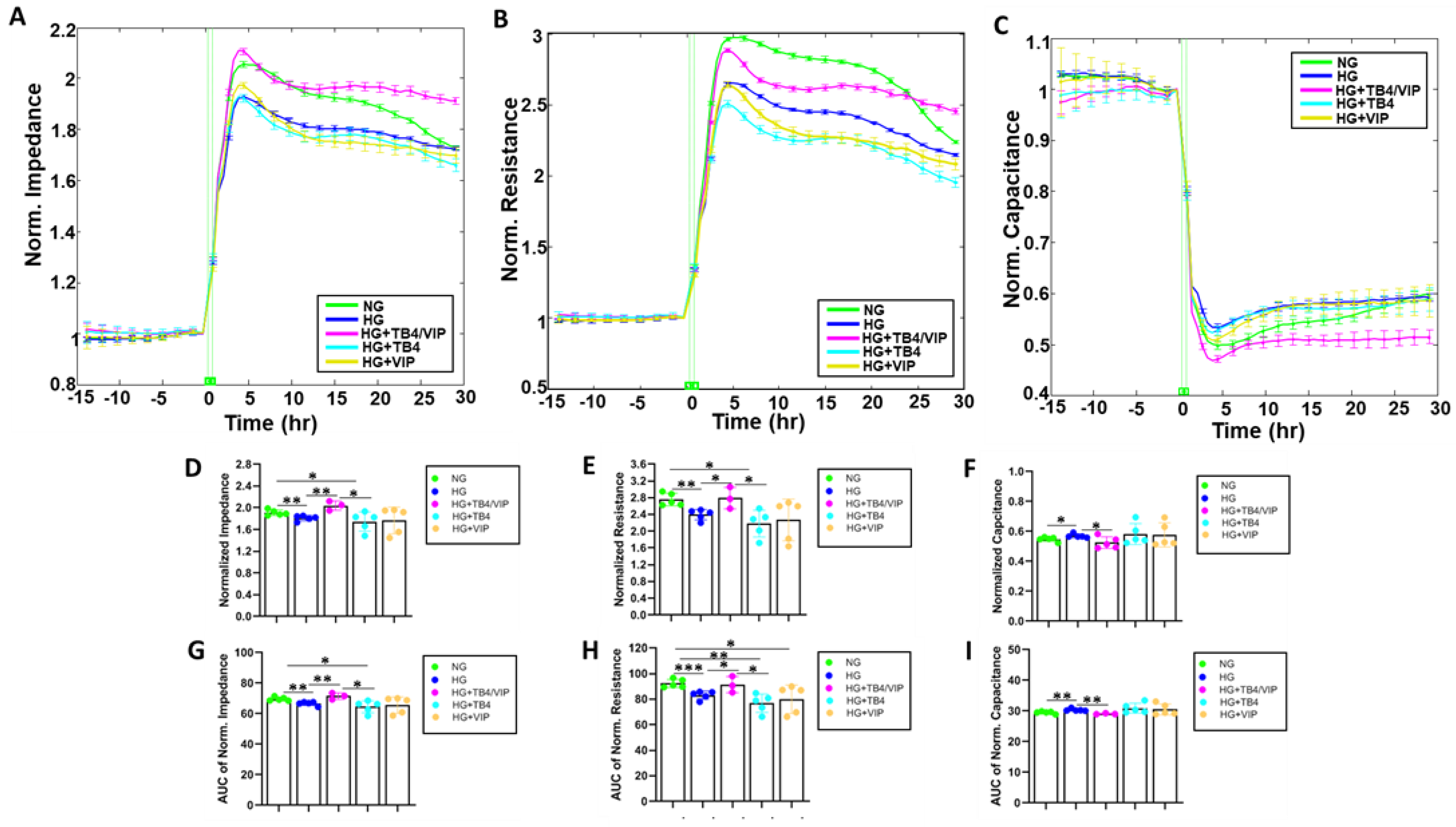
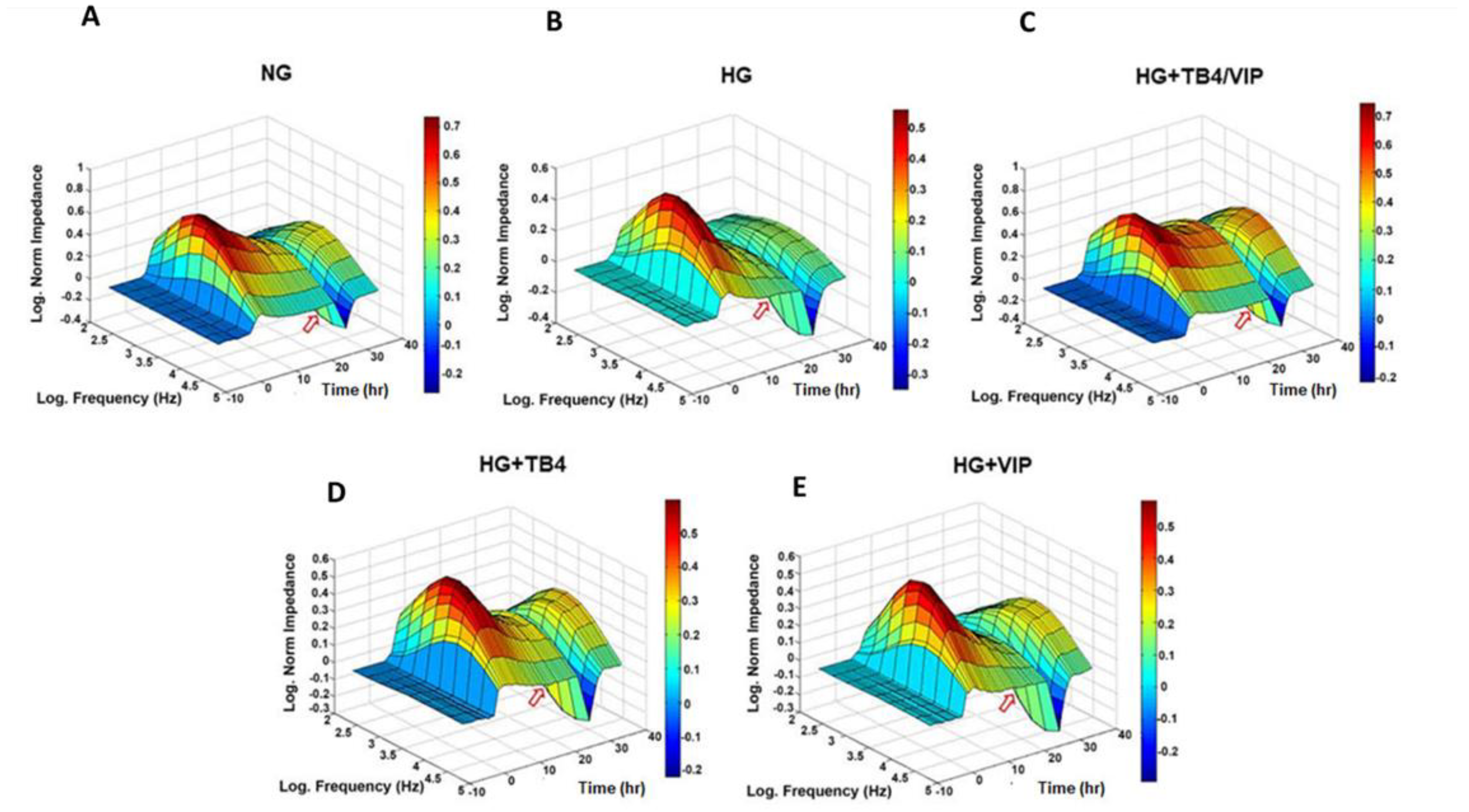
3.1. Bioimpedance Analysis of Barrier Function
3.2. Barrier Function Measurements
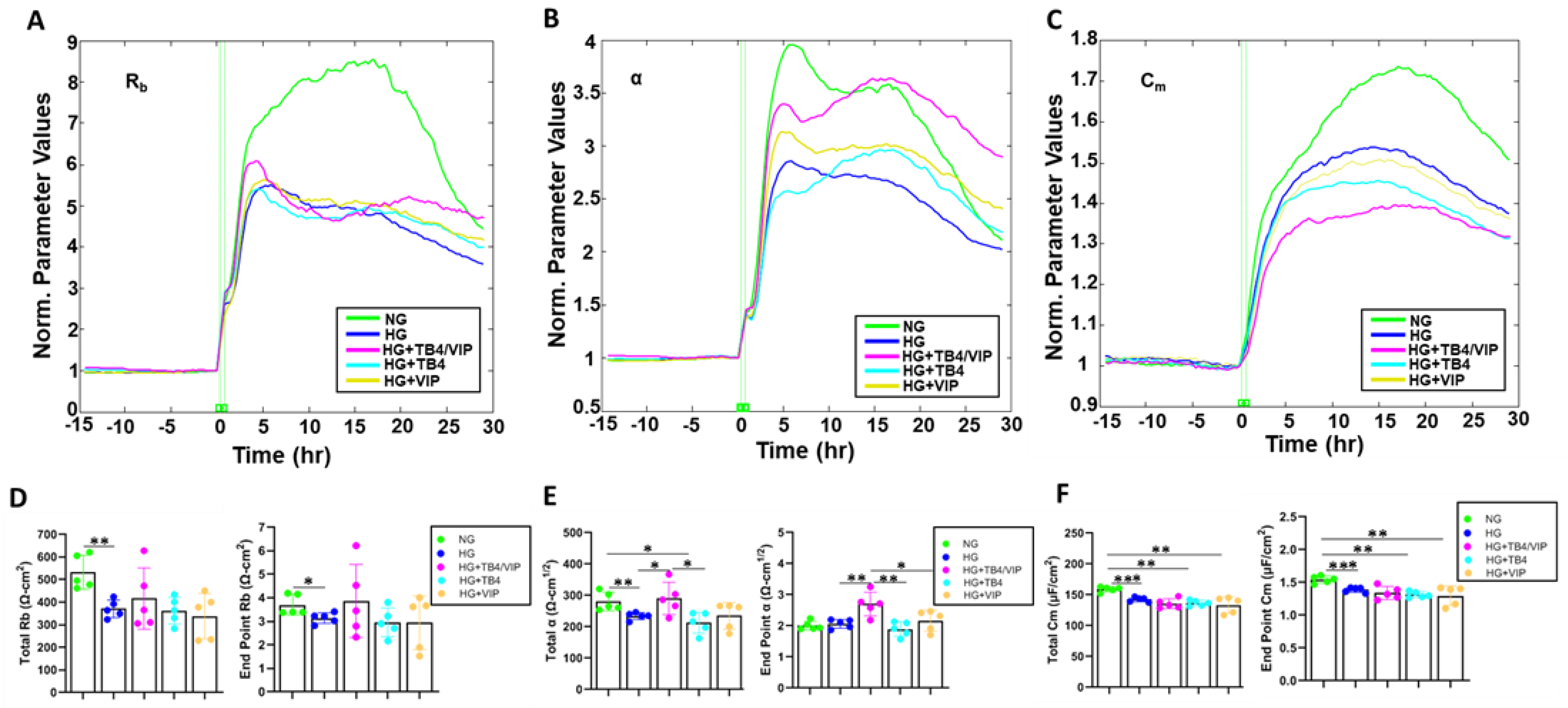
3.3. Mathematical Modeling Parameters of the R Data—α, Rb, and Cm
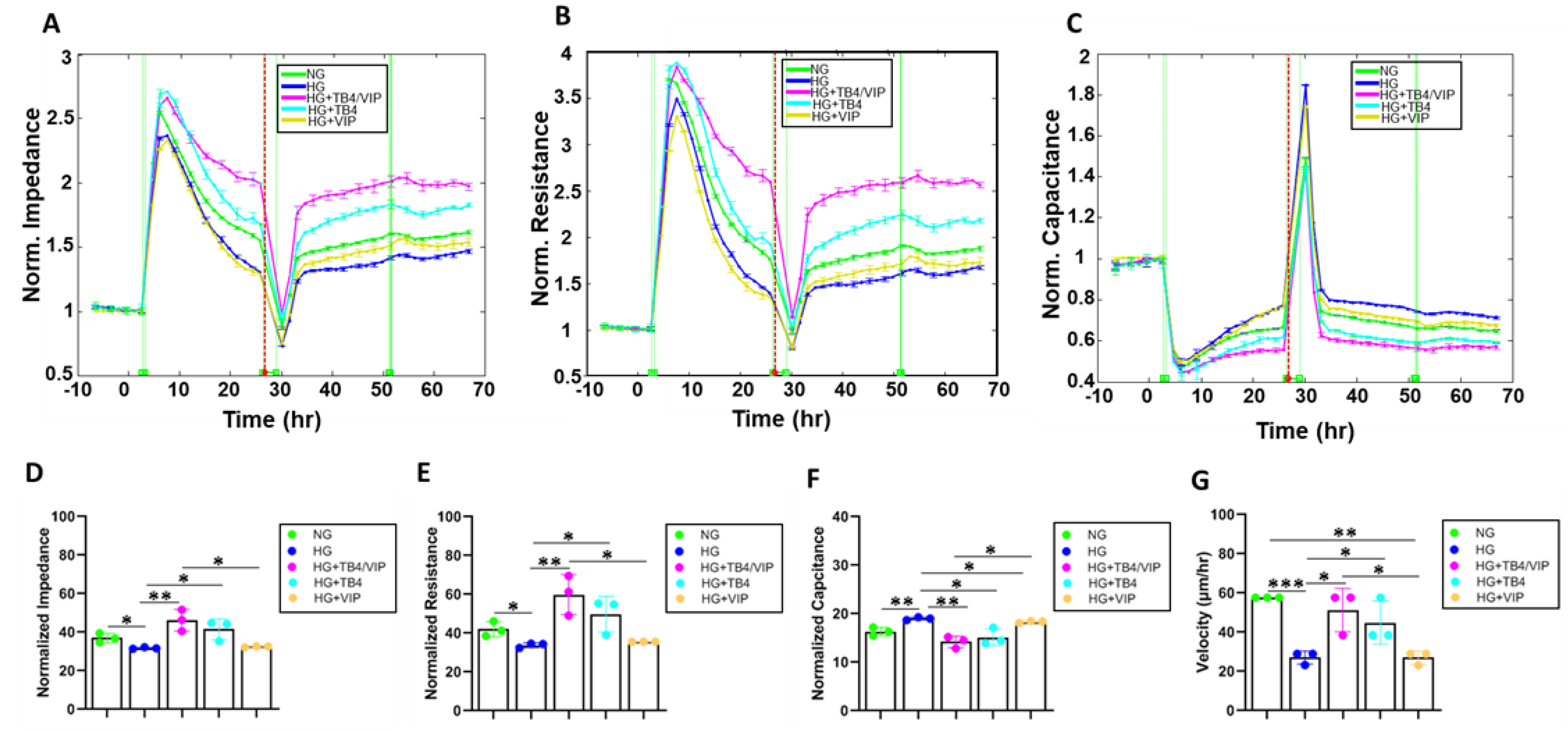
3.4. Bioimpedance Analysis of Wound Healing Response
3.5. Wound Healing Measurements
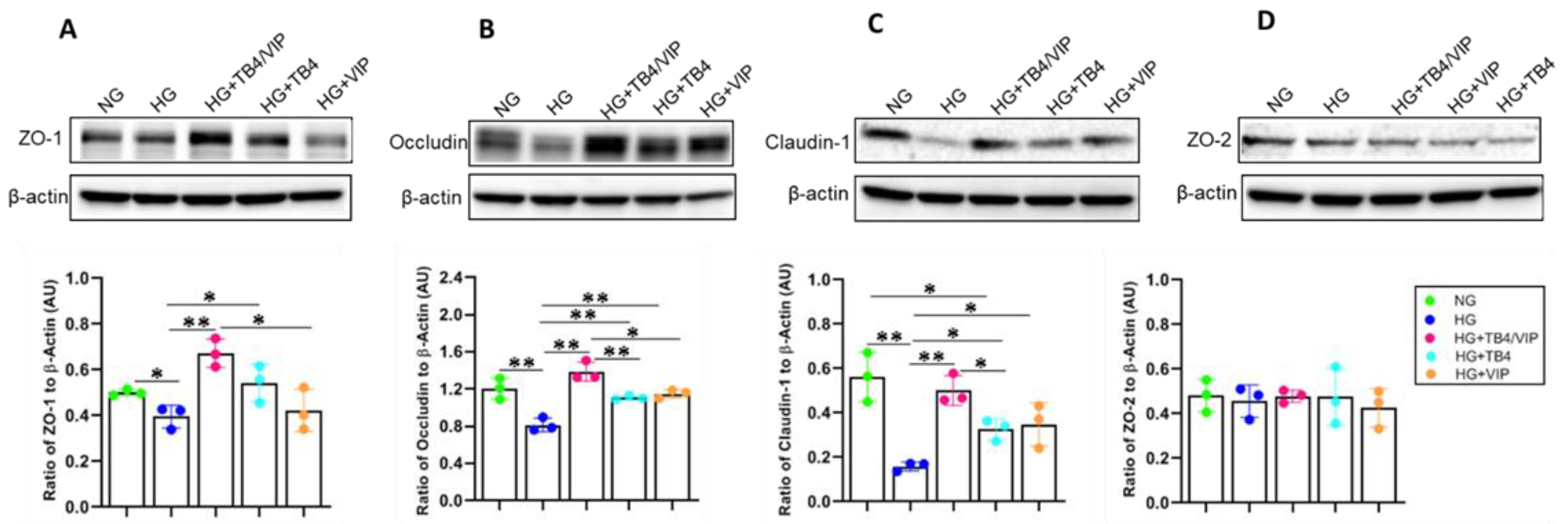
3.6. Western Blot Analysis of the Tight Junction Protein Complexes
3.7. IHC Assessment of the Tight Junction Protein Complexes
3.8. HUCL Cell Proliferation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECIS | electric cell–substrate impedance sensing |
| HG | high glucose (25 mM) |
| HUCLs | human telomerase-immortalized corneal epithelial cells |
| NG | normal glucose (5 mM) |
| ZO | zonula occludens |
References
- Schultz, R.O.; Van Horn, D.L.; Peters, M.A.; Klewin, K.M.; Schutten, W.H. Diabetic keratopathy. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1981, 79, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foundation ID. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; Foundation ID: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaji, Y. Prevention of diabetic keratopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 254–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutty, G.A. Effects of diabetes on the eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, ORSF81-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubimov, A.V. Diabetic complications in the cornea. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Potter, V.J.; Karamichos, D.; Lee, D.J. Ocular Complications of Diabetes and Therapeutic Approaches. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3801570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Feijoo, E.; Grau, A.E.; Abusleme, E.I.; Duran, J.A. Clinical presentation and causes of recurrent corneal erosion syndrome: Review of 100 patients. Cornea 2014, 33, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Zhu, M.; Petroll, W.M.; Koppaka, V.; Robertson, D.M. The impact of type 1 diabetes mellitus on corneal epithelial nerve morphology and the corneal epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ban, Y.; Kinoshita, S. Tight junction transmembrane protein claudin subtype expression and distribution in human corneal and conjunctival epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 36, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.M. Tight junctions/adherens junctions: Basic structure and function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, C.Y. Tight Junction in the Intestinal Epithelium: Its Association with Diseases and Regulation by Phytochemicals. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2645465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.S. Corneal epithelial tight junctions and their response to lipopolysaccharide challenge. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 4093–4100. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, H.; Zweimueller-Mayer, J.; Steinbacher, P.; Lametschwandtner, A.; Bauer, H.C. The dual role of zonula occludens (ZO) proteins. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 402593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.W.; Kaili, D.; Freeman, J.; Lei, C.Y.; Geng, B.C.; Tan, T.; He, J.F.; Shi, Z.; Ma, J.J.; Luo, Y.H.; et al. Diabetes inhibits corneal epithelial cell migration and tight junction formation in mice and human via increasing ROS and impairing Akt signaling. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-S.; Tai, M.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Chu, C.-C.; Wang, J.-J.; Tseng, S.-H.; Jan, R.-L. Risk of Corneal Ulcer in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Large-Scale Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannappel, E. Beta-Thymosins. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1112, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson-Viitanen, S.; Ruggieri, S.; Natalini, P.; Horecker, B.L. Distribution of thymosin beta 4 in vertebrate classes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1983, 221, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, D.; Kleinman, H.K. Animal studies with thymosin beta, a multifunctional tissue repair and regeneration peptide. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1194, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.H.; Chuang, C.H.; Ho, C.Y.; Shih, Y.R.; Lee, O.K.; Su, Y. Internalization is essential for the antiapoptotic effects of exogenous thymosin beta-4 on human corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.H.; Su, Y.; Chen, K.H.; Lee, O.K. Protection of thymosin beta-4 on corneal endothelial cells from UVB-induced apoptosis. Chin. J. Physiol. 2010, 53, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosne, G.; Kleinman, H.K. Primary Mechanisms of Thymosin beta4 Repair Activity in Dry Eye Disorders and Other Tissue Injuries. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5110–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carion, T.W.; Ebrahim, A.S.; Kracht, D.; Agrawal, A.; Strand, E.; Kaddurah, O.; McWhirter, C.R.; Sosne, G.; Berger, E.A. Thymosin Beta-4 and Ciprofloxacin Adjunctive Therapy Improves Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Keratitis. Cells 2018, 7, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Carion, T.W.; Ebrahim, A.S.; Sosne, G.; Berger, E.A. Adjunctive Thymosin Beta-4 Treatment Influences MPhi Effector Cell Function to Improve Disease Outcome in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Keratitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Carion, T.W.; Ebrahim, A.S.; Sosne, G.; Berger, E.A. Adjunctive Thymosin Beta-4 Treatment Influences PMN Effector Cell Function during Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Corneal Infection. Cells 2021, 10, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Zheng, X.; Mao, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yang, R.; Yu, R.; Chen, W. Recombinant Human Thymosin beta4 (rhTbeta4) Modulates the Anti-Inflammatory Responses to Alleviate Benzalkonium Chloride (BAC)-Induced Dry Eye Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosne, G.; Szliter, E.A.; Barrett, R.; Kernacki, K.A.; Kleinman, H.; Hazlett, L.D. Thymosin beta 4 promotes corneal wound healing and decreases inflammation in vivo following alkali injury. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghizadeh, M.; Kramerov, A.A.; Tajbakhsh, J.; Aoki, A.M.; Wang, C.; Chai, N.N.; Ljubimova, J.Y.; Sasaki, T.; Sosne, G.; Carlson, M.R.; et al. Proteinase and growth factor alterations revealed by gene microarray analysis of human diabetic corneas. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3604–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, S.I.; Mutt, V. Polypeptide with broad biological activity: Isolation from small intestine. Science 1970, 169, 1217–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.I.; Rosenberg, R.N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: Abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science 1976, 192, 907–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, R.J.; Sawmiller, D.R. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: Cardiovascular effects. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szliter, E.A.; Lighvani, S.; Barrett, R.P.; Hazlett, L.D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide balances pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected cornea and protects against corneal perforation. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, G.; D’Amico, A.G.; Gagliano, C.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Cavallaro, S.; D’Agata, V. VIP Family Members Prevent Outer Blood Retinal Barrier Damage in a Model of Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuderi, S.; D’Amico, A.G.; Castorina, A.; Imbesi, R.; Carnazza, M.L.; D’Agata, V. Ameliorative effect of PACAP and VIP against increased permeability in a model of outer blood retinal barrier dysfunction. Peptides 2013, 39, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, G.; D’Amico, A.G.; Saccone, S.; Federico, C.; Cavallaro, S.; D’Agata, V. PACAP and VIP Inhibit HIF-1α-Mediated VEGF Expression in a Model of Diabetic Macular Edema. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Carion, T.W.; Jiang, Y.; Steinle, J.J.; Berger, E.A. VIP protects human retinal microvascular endothelial cells against high glucose-induced increases in TNF-alpha and enhances RvD1. Prostagland. Other Lipid Mediat. 2016, 123, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, K.; Ambati, B.; Yu, F.S. Toll-like receptor 5-mediated corneal epithelial inflammatory responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4247–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, A.S.; Ebrahim, T.; Kani, H.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Carion, T.W.; Berger, E.A. Functional optimization of electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) using human corneal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.P.; Heidemann, D.G.; Chow, C.Y.; Crockford, D.; Turjman, N.; Angel, J.; Allan, C.B.; Sosne, G. Treatment of chronic nonhealing neurotrophic corneal epithelial defects with thymosin beta4. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1194, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.A.; McClellan, S.A.; Barrett, R.P.; Hazlett, L.D. VIP promotes resistance in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected cornea by modulating adhesion molecule expression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5776–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; McClellan, S.A.; Barrett, R.P.; Berger, E.A.; Zhang, Y.; Hazlett, L.D. VIP and growth factors in the infected cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6154–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.S.; Yin, J.; Lee, P.; Hwang, F.S.; McDermott, M. Sensory nerve regeneration after epithelium wounding in normal and diabetic cornea. Expert. Rev. Ophthalmol. 2015, 10, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yan, C.; Lee, P.; Sun, H.; Yu, F.S. Dendritic cell dysfunction and diabetic sensory neuropathy in the cornea. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1998–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, N.; Wu, L.; Lee, P.S.Y.; Me, R.; Dai, C.; Xie, L.; Yu, F.X. Role of VIP and Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathways in Mediating Epithelial Wound Healing, Sensory Nerve Regeneration and their Defects in Diabetic Corneas. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1549–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, M.; Garcia-Ramirez, M.; Corraliza, L.; Hernandez, C.; Simo, R. Effects of high glucose concentration on the barrier function and the expression of tight junction proteins in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Grosheva, I.; Zheng, D.; Soffer, E.; Blacher, E.; Braverman, S.; Tengeler, A.C.; Barak, O.; Elazar, M.; et al. Hyperglycemia drives intestinal barrier dysfunction and risk for enteric infection. Science 2018, 359, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Pfluger, T.; Ferreira, F.; Liang, J.; Navedo, M.F.; Zeng, Q.; Reid, B.; Zhao, M. Diabetic cornea wounds produce significantly weaker electric signals that may contribute to impaired healing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraih, S.; Barbarino, A.; Ross, C.; Shamloo, K.; Jhanji, V.; Zhang, M.; Sharma, A. Effect of High Glucose on Ocular Surface Epithelial Cell Barrier and Tight Junction Proteins. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukita, S.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, A. The Claudins: From Tight Junctions to Biological Systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunzel, D.; Yu, A.S. Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 525–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, P.M. Occludin: One protein, many forms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liao, R.; Wang, F.; Tang, S. Characteristics of Reconstituted Tight Junctions After Corneal Epithelial Wounds and Ultrastructure Alterations of Corneas in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Han, H.J.; Kim, S.; Kwon, J. Thymosin beta 4 attenuates PrP(106-126)-induced human brain endothelial cells dysfunction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 869, 172891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebrahim, A.S.; Carion, T.W.; Ebrahim, T.; Win, J.; Kani, H.; Wang, Y.; Stambersky, A.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Sosne, G.; Berger, E.A. A Novel Combination Therapy Tβ4/VIP Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Changes in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Biosensors 2023, 13, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110974
Ebrahim AS, Carion TW, Ebrahim T, Win J, Kani H, Wang Y, Stambersky A, Ibrahim AS, Sosne G, Berger EA. A Novel Combination Therapy Tβ4/VIP Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Changes in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Biosensors. 2023; 13(11):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110974
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbrahim, Abdul Shukkur, Thomas W. Carion, Thanzeela Ebrahim, Jeff Win, Hussein Kani, Yuxin Wang, Ashten Stambersky, Ahmed S. Ibrahim, Gabriel Sosne, and Elizabeth A. Berger. 2023. "A Novel Combination Therapy Tβ4/VIP Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Changes in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells" Biosensors 13, no. 11: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110974
APA StyleEbrahim, A. S., Carion, T. W., Ebrahim, T., Win, J., Kani, H., Wang, Y., Stambersky, A., Ibrahim, A. S., Sosne, G., & Berger, E. A. (2023). A Novel Combination Therapy Tβ4/VIP Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Changes in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Biosensors, 13(11), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13110974




