Challenges in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2: Evolution of the Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Valuable Tool for Viral Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2 Overview
3. Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2 in Brief
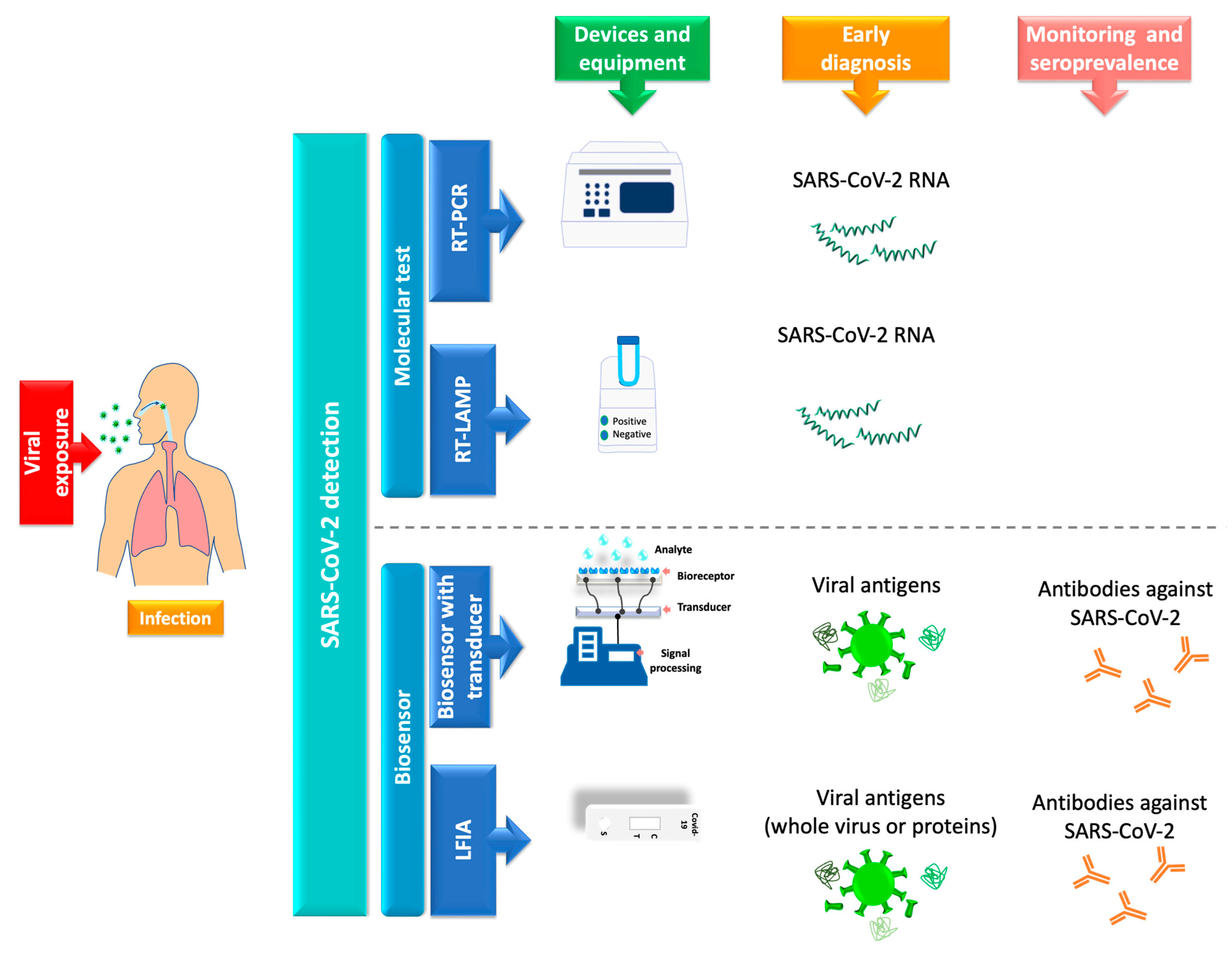
4. SARS-CoV-2 Detection
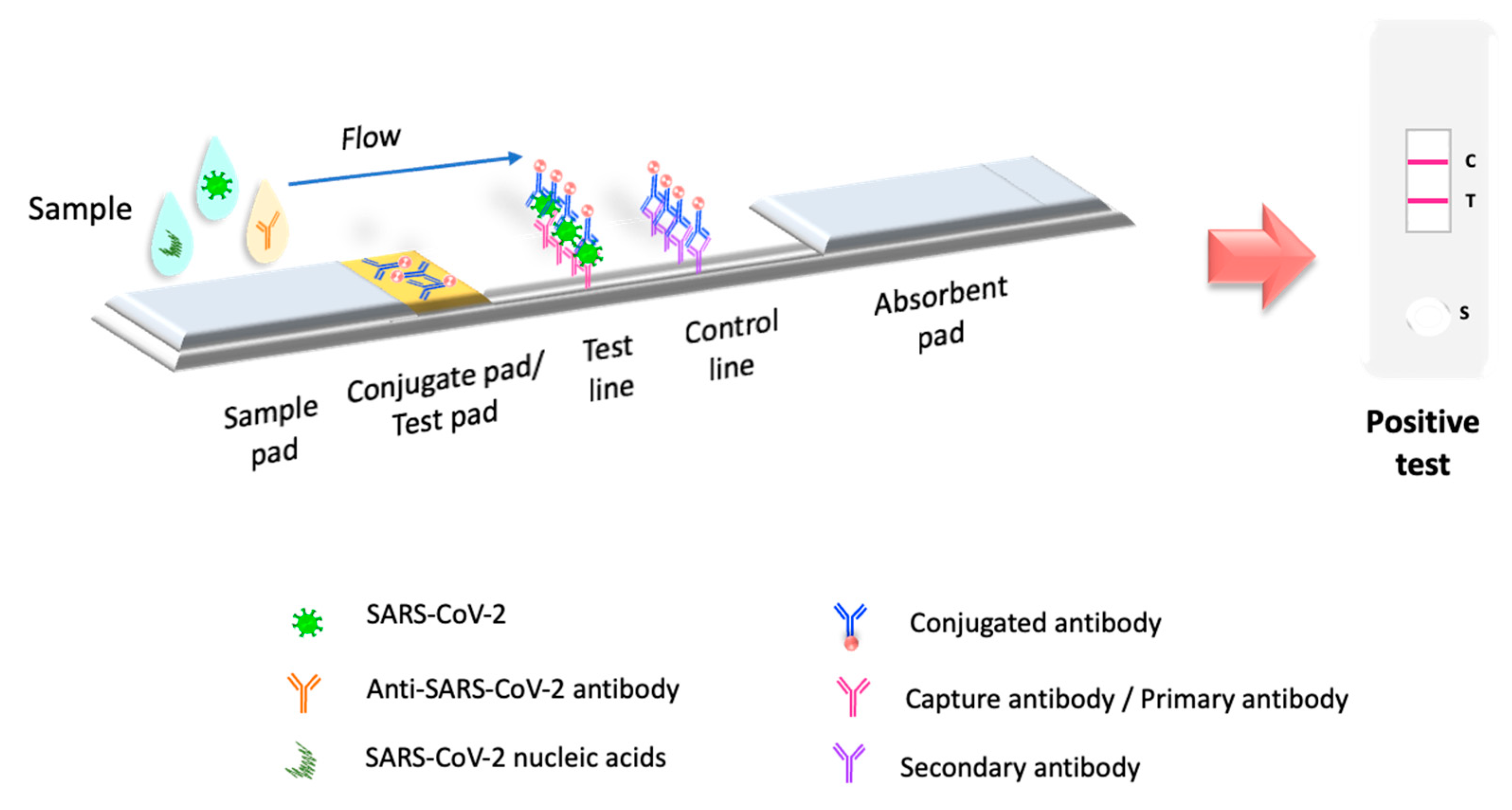
5. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Evolution in the Pandemic
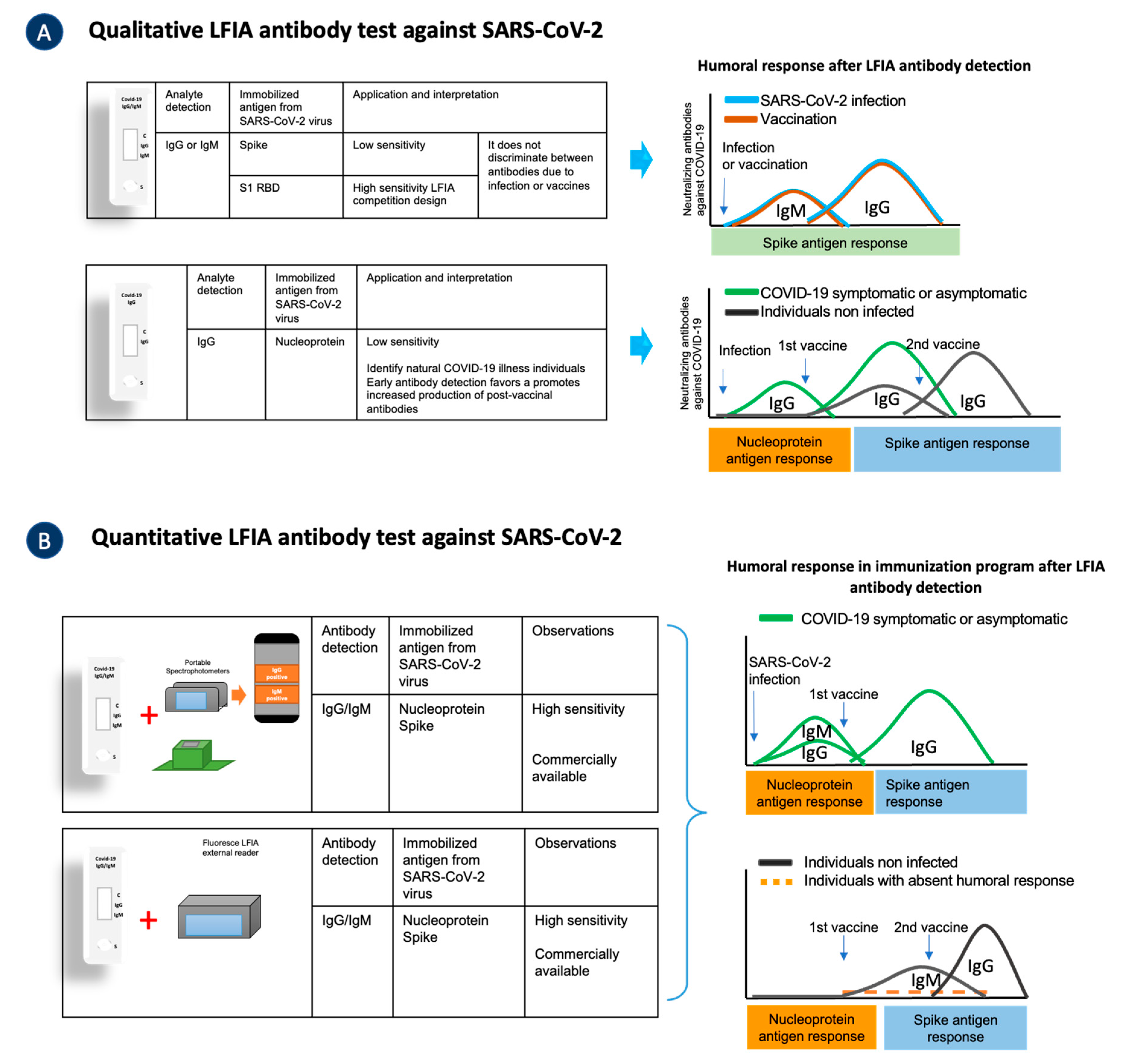
5.1. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Antibody Testing in COVID-19 Pandemic
LFIA Is a Quantitative Tool for Detecting Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
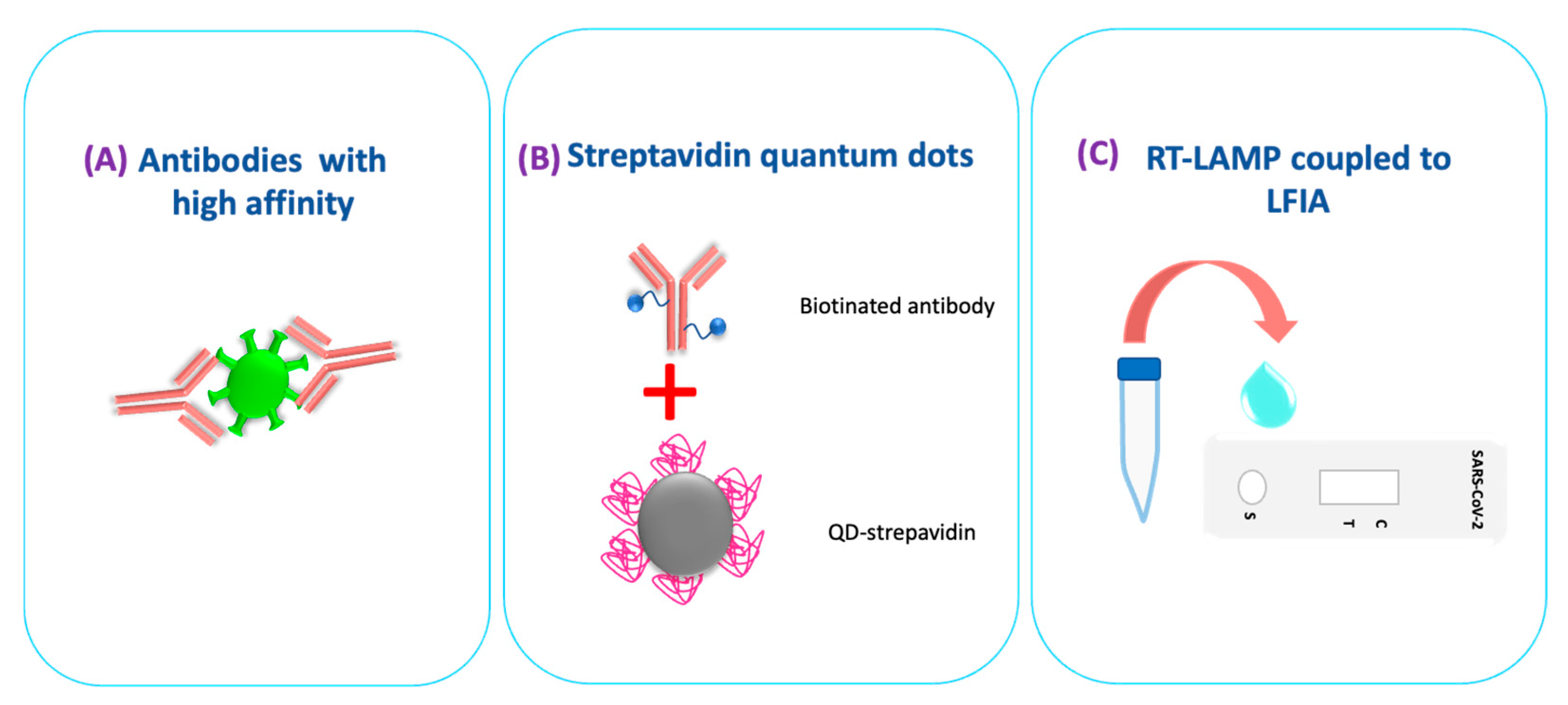
5.2. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Viral Antigen Testing for COVID-19
5.3. LFIA Simultaneously Detects Antigens and Antibodies
6. LFIA Detects Nucleic Acids of SARS-CoV-2
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. Laboratory Testing for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) in Suspected Human Cases. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/10665-331501 (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Ravi, N.; Cortade, D.L.; Ng, E.; Wang, S.X. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 Detection: A Comprehensive Review of the FDA-EUA COVID-19 Testing Landscape. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Babady, E.; Theel, E.S.; Storch, G.A.; Pinsky, B.A.; St George, K.; Smith, T.C.; Bertuzzi, S. Report from the American Society for Microbiology COVID-19 International Summit, 23 March 2020: Value of Diagnostic Testing for SARS–CoV-2/COVID-19. mBio 2020, 11, e00722-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Sakthivel, S.K.; Whitaker, B.; Murray, J.; Kamili, S.; Lynch, B.; Malapati, L.; Burke, S.A.; Harcourt, J.; et al. US CDC Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR Panel for Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouliou, D.S.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. False-Positive and False-Negative COVID-19 Cases: Respiratory Prevention and Management Strategies, Vaccination, and Further Perspectives. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meo, S.A.; Meo, A.S.; Al-Jassir, F.F.; Klonoff, D.C. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 New Variant: Global Prevalence and Biological and Clinical Characteristics. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 8012–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19—4 August 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-operational-update-on-covid-19---4-august-2021 (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in Biosensors: Principle, Architecture and Applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.A.; Ahmed Muneer, A.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.S.; Sattar, A.A.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F. Biosensors as a Future Diagnostic Approach for COVID-19. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobysh, M.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Viter, R.; Chen, C.-F.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Ramanavicius, A. Biosensors for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Virus and Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.; Asif, K.; Canzonieri, V.; Barai, H.R.; Rahman, M.d.M.; Daniele, S.; Rizzolio, F. Controlled, Partially Exfoliated, Self-Supported Functionalized Flexible Graphitic Carbon Foil for Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Yeh, H.-W.; Walls, A.C.; Wicky, B.I.M.; Sprouse, K.R.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Treger, R.; Quijano-Rubio, A.; Pham, M.N.; Kraft, J.C.; et al. Thermodynamically Coupled Biosensors for Detecting Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamhuri, S.A.; Soon, C.F.; Nordin, A.N.; Ab Rahim, R.; Sultana, N.; Khan, M.A.; Lim, G.P.; Tee, K.S. A Review on the Contamination of SARS-CoV-2 in Water Bodies: Transmission Route, Virus Recovery and Recent Biosensor Detection Techniques. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022, 36, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabowo, B.A.; Cabral, P.D.; Freitas, P.; Fernandes, E. The Challenges of Developing Biosensors for Clinical Assessment: A Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, L.; Bergeron, M.G. Diagnosing Infections—Current and Anticipated Technologies for Point-of-Care Diagnostics and Home-Based Testing. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, M.J.; Park, S.C.; Choi, M.; Lee, W.; Ku, K.B.; Kim, B.T.; Changkyun Park, E.; Kim, H.G.; et al. Development of a SARS-CoV-2-Specific Biosensor for Antigen Detection Using ScFv-Fc Fusion Proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Paper-Based Biosensors: Frontiers in Point-of-Care Detection of COVID-19 Disease. Biosensors 2021, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimayo, C.; Kaewnaphan, B.; Tanlieng, N.; Athipanyasilp, N.; Sirijatuphat, R.; Chayakulkeeree, M.; Angkasekwinai, N.; Sutthent, R.; Puangpunngam, N.; Tharmviboonsri, T.; et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Detection Assay in Comparison with Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Laboratory Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Thailand. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfossi, L.; Di Nardo, F.; Cavalera, S.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C. Multiplex Lateral Flow Immunoassay: An Overview of Strategies towards High-Throughput Point-of-Need Testing. Biosensors 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiskainen, I.; Juntunen, E.; Salminen, T.; Vuorenpää, K.; Bayoumy, S.; Vuorinen, T.; Khanna, N.; Pettersson, K.; Batra, G.; Talha, S.M. Double-Antigen Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-HIV-1 and -2 Antibodies Using Upconverting Nanoparticle Reporters. Sensors 2021, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Rong, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Magnetic SERS Strip for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Respiratory Viruses. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19495–19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, T.; Lefeuvre, C.; Serri, O.; Pivert, A.; Joubaud, F.; Dubée, V.; Kouatchet, A.; Ducancelle, A.; Lunel-Fabiani, F.; Le Guillou-Guillemette, H. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Serological Tests for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 through the Evaluation of Three Immunoassays: Two Automated Immunoassays (Euroimmun and Abbott) and One Rapid Lateral Flow Immunoassay (NG Biotech). J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. COVID-19 Testing Strategies and Objectives. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/covid-19-testing-strategies-and-objectives (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Hasöksüz, M.; Kiliç, S.; Saraç, F. Coronaviruses and SARS-COV-2. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, G.L. SARS, MERS and COVID-19—New Threats; Old Lessons. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 726–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.B.; Sukhramani, G.S.; Bishnoi, P.; Pable, A.A.; Barvkar, V.T. SARS-CoV-2, the Pandemic Coronavirus: Molecular and Structural Insights. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 180–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailany, R.A.; Safdar, M.; Ozaslan, M. Genomic Characterization of a Novel SARS-CoV-2. Gene Rep. 2020, 19, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, V.N.; Chang, H. The Architecture of SARS-CoV-2 Transcriptome. Cell 2020, 181, 914–921.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bačenková, D.; Trebuňová, M.; Špakovská, T.; Schnitzer, M.; Bednarčíková, L.; Živčák, J. Comparison of Selected Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and HCoV-NL63. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtipal, N.; Bharadwaj, S.; Kang, S.G. From SARS to SARS-CoV-2, Insights on Structure, Pathogenicity and Immunity Aspects of Pandemic Human Coronaviruses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Prather, K.A.; Tufekci, Z.; Fisman, D.; Schooley, R. Ten Scientific Reasons in Support of Airborne Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2021, 397, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, G.; Mallery, D.L.; Albecka, A.; Welch, L.G.; Cattin-Ortolá, J.; Luptak, J.; Paul, D.; McMahon, H.T.; Goodfellow, I.G.; Carter, A.; et al. Furin Cleavage of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Promotes but Is Not Essential for Infection and Cell-Cell Fusion. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, P.; Desikan, R.; Dixit, N.M. Targeting TMPRSS2 and Cathepsin B/L Together May Be Synergistic against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, K.; AlOmar, S.Y.; Almuqri, E.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Kumar, V. Genomics-Guided Identification of Potential Modulators of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Proteases, TMPRSS2 and Cathepsins B/L. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Entry Factors Are Highly Expressed in Nasal Epithelial Cells Together with Innate Immune Genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, S.; Chua, R.L.; Trefzer, T.; Kahn, N.C.; Schneider, M.A.; Muley, T.; Winter, H.; Meister, M.; Veith, C.; Boots, A.W.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Primarily Expressed in Bronchial Transient Secretory Cells. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, Z.; Castiglione, G.M.; Soiberman, U.S.; Eberhart, C.G.; Duh, E.J. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed on the Human Ocular Surface, Suggesting Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodoulian, L.; Tuberosa, J.; Rossier, D.; Boillat, M.; Kan, C.; Pauli, V.; Egervari, K.; Lobrinus, J.A.; Landis, B.N.; Carleton, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptors and Entry Genes Are Expressed in the Human Olfactory Neuroepithelium and Brain. iScience 2020, 23, 101839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Khandia, R.; Singhal, S.; Alqahtani, T.; Kamal, M.A.; El-Shall, N.A.; Nainu, F.; Desingu, P.A.; Dhama, K. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant, Salient Features, High Global Health Concerns and Strategies to Counter It amid Ongoing COVID-19 Pandemic. Environ. Res. 2022, 209, 112816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Smith, D.M. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Yonsei Med. J. 2021, 62, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.A.; Quandelacy, T.M.; Kada, S.; Prasad, P.V.; Steele, M.; Brooks, J.T.; Slayton, R.B.; Biggerstaff, M.; Butler, J.C. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission from People Without COVID-19 Symptoms. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2035057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Innate Immunity: The First Line of Defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boechat, J.L.; Chora, I.; Morais, A.; Delgado, L. The Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 Immunopathology—Current Perspectives. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, L.G.; Reuschl, A.-K.; Zuliani-Alvarez, L.; Whelan, M.V.X.; Turner, J.; Noursadeghi, M.; Jolly, C.; Towers, G.J. SARS-CoV-2 Sensing by RIG-I and MDA5 Links Epithelial Infection to Macrophage Inflammation. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severa, M.; Diotti, R.A.; Etna, M.P.; Rizzo, F.; Fiore, S.; Ricci, D.; Iannetta, M.; Sinigaglia, A.; Lodi, A.; Mancini, N.; et al. Differential Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Phenotype and Type I Interferon Response in Asymptomatic and Severe COVID-19 Infection. PLOS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisman, D.E.; Ronner, L.; Pinotti, R.; Taylor, M.D.; Sinha, P.; Calfee, C.S.; Hirayama, A.V.; Mastroiani, F.; Turtle, C.J.; Harhay, M.O.; et al. Cytokine Elevation in Severe and Critical COVID-19: A Rapid Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Comparison with Other Inflammatory Syndromes. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez, B.E.; González-Rojas, J.A.; Salazar, M.I.; Torres-Torres, C.; Castrejón-Jiménez, N.S. Taming the Autophagy as a Strategy for Treating COVID-19. Cells 2020, 9, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, A.; Joyner, M.J.; Pirofski, L.-A. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Antibody Responses: The Case for Convalescent Plasma Therapy. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 5112–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response up to 10 Months after Infection. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1832–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, D.; Ramadan, S.; Li, Y.; Klein, N. Facile Biosensors for Rapid Detection of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongchen, Z.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Y.; Gu, B. Different Longitudinal Patterns of Nucleic Acid and Serology Testing Results Based on Disease Severity of COVID-19 Patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herroelen, P.H.; Martens, G.A.; De Smet, D.; Swaerts, K.; Decavele, A.-S. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2: Comparative Clinical Performance of Seven Commercial Serology Tests. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.-X.; Liu, B.-Z.; Deng, H.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.-F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.-F.; et al. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, C.; Atyeo, C.; Fischinger, S.; Burke, J.; Slein, M.D.; Streeck, H.; Lauffenburger, D.; Ryan, E.T.; Charles, R.C.; Alter, G. Evolution of Early SARS-CoV-2 and Cross-Coronavirus Immunity. mSphere 2020, 5, e00622-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Jia, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; et al. The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 632814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyei-Barffour, I.; Addo, S.A.; Aninagyei, E.; Ghartey-Kwansah, G.; Acheampong, D.O. Sterilizing Immunity against COVID-19: Developing Helper T Cells I and II Activating Vaccines Is Imperative. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants Escape Neutralization by Vaccine-Induced Humoral Immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Veyer, D.; Baidaliuk, A.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Robillard, N.; Puech, J.; et al. Reduced Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Delta to Antibody Neutralization. Nature 2021, 596, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, N.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Ryo, A. Interpreting Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 323, 2249–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliendo, A.M.; Gilbert, D.N.; Ginocchio, C.C.; Hanson, K.E.; May, L.; Quinn, T.C.; Tenover, F.C.; Alland, D.; Blaschke, A.J.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Better Tests, Better Care: Improved Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, S139–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Bajwa, N.; Soni, D.; Das, S.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C. Authors’ Response: SARS-CoV-2 Detection by Real-Time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration. In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs—Antigen Diagnostic Tests for SARS-CoV-2; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- CDC. Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/clia/index.html (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- St John, A.; Price, C.P. Existing and Emerging Technologies for Point-of-Care Testing. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2014, 35, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Infectious Diseases Society of America. Antibody Testing. Available online: https://www.idsociety.org/covid-19-real-time-learning-network/diagnostics/antibody-testing/ (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- European Commission. COVID-19 In Vitro Diagnostic Devices and Test Methods Database. Available online: https://covid-19-diagnostics.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Van Elslande, J.; Houben, E.; Depypere, M.; Brackenier, A.; Desmet, S.; André, E.; Van Ranst, M.; Lagrou, K.; Vermeersch, P. Diagnostic Performance of Seven Rapid IgG/IgM Antibody Tests and the Euroimmun IgA/IgG ELISA in COVID-19 Patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.A.; Clemmensen, A.; Sparrewath, C.; Tetens, M.M.; Krogfelt, K.A. Children Naturally Evading COVID-19—Why Children Differ from Adults. COVID 2022, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotta, M.C.; David CN, d.e.; Varela, F.H.; Sartor, I.T.S.; Polese-Bonatto, M.; Fernandes, I.R.; Zavaglia, G.O.; Ferreira, C.F.; Kern, L.B.; Santos, A.P.; et al. Low Performance of a SARS-CoV-2 Point-of-Care Lateral Flow Immunoassay in Symptomatic Children during the Pandemic. J. Pediatr. 2022, 98, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.; Buchan, I.E.; Das, R.; Davis, E.L.; Fyles, M.; Hall, I.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; House, T.; Jay, C.; Medley, G.F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Testing: Weighing the False Positives against the Costs of Failing to Control Transmission. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andryukov, B.G. Six Decades of Lateral Flow Immunoassay: From Determining Metabolic Markers to Diagnosing COVID-19. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 280–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Huang, C.; Shi, F.-J.; Zeng, X.-Y.; Lu, T.; Ding, S.-N.; Jiao, Y.-J. Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strip for Rapid Detection of IgG Antibody against SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Analyst 2020, 145, 5345–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudinobar, F.; Britton, D.; Montclare, J.K. Protein-Based Lateral Flow Assays for COVID-19 Detection. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2021, 34, gzab010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Exinger, J.; Hartard, C.; Lafferrière, F.; Fenninger, C.; Charbonnière, L.J.; Jeulin, H. Evaluation of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay COVIDTECH® SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG Antibody Rapid Test. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral Flow Assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieri, M.; Nicolai, E.; Nuccetelli, M.; Sarubbi, S.; Tomassetti, F.; Pelagalli, M.; Minieri, M.; Terrinoni, A.; Bernardini, S. Validation of a Quantitative Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA)-Based Point-of-Care (POC) Rapid Test for SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, H.; Whitaker, M.; Flower, B.; Tang, S.N.; Atchison, C.; Darzi, A.; Donnelly, C.A.; Cann, A.; Diggle, P.J.; Ashby, D.; et al. Population Antibody Responses Following COVID-19 Vaccination in 212,102 Individuals. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. The Humoral Response and Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, O.; Rockstroh, A.; Borte, S.; Wolf, J. Evaluation of Simple Lateral Flow Immunoassays for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Vaccines 2022, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanne, J.H. Covid-19: FDA Approves Use of Convalescent Plasma to Treat Critically Ill Patients. BMJ 2020, 368, m1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Liu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Qu, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Meng, S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Effectiveness of Convalescent Plasma Therapy in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9490–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, Y.; Greig, M.; Liu, G.; Driedger, M.; Langlois, M.-A. Humoral Responses and Serological Assays in SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 610688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Spijker, R.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Adriano, A.; Beese, S.; Dretzke, J.; Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; et al. Antibody Tests for Identification of Current and Past Infection with SARS-CoV-2. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6, CD013652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, H.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of a Rapid Colloidal Gold Immunochromatography Assay for SARS-Cov-2 IgM/IgG. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novello, S.; Terzolo, M.; Paola, B.; Gianetta, M.; Bianco, V.; Arizio, F.; Brero, D.; Perini, A.M.E.; Boccuzzi, A.; Caramello, V.; et al. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Five Different Groups of Individuals at Different Environmental and Professional Risk of Infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Ko, C.-H.; Wang, C.J.; Chen, C.-W.; Chiu, W.-H.; Hong, C.; Cheng, H.-M.; Wang, I.-J. The Early Detection of Immunoglobulins via Optical-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay Platform in COVID-19 Pandemic. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochot, E.; Demey, B.; Touzé, A.; Belouzard, S.; Dubuisson, J.; Schmit, J.-L.; Duverlie, G.; Francois, C.; Castelain, S.; Helle, F. Anti-Spike, Anti-Nucleocapsid and Neutralizing Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Inpatients and Asymptomatic Individuals. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 584251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, L.L.; Smits, G.; van Hagen, C.C.E.; Wong, D.; Vos, E.R.A.; van Boven, M.; de Melker, H.E.; van Vliet, J.; Kuijer, M.; Woudstra, L.; et al. Seropositivity to Nucleoprotein to Detect Mild and Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Complementary Tool to Detect Breakthrough Infections after COVID-19 Vaccination? Vaccine 2022, 40, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, V.A.J.; Hernández-Carralero, E.; Paz-Cabrera, M.C.; Cabrera, E.; Hernández-Reyes, Y.; Hernández-Fernaud, J.R.; Gillespie, D.A.; Salido, E.; Hernández-Porto, M.; Freire, R. The Nucleocapsid Protein Triggers the Main Humoral Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 543, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.; Bouam, A.; Edouard, S.; Fenollar, F.; Di Pinto, F.; Mège, J.-L.; Drancourt, M.; Vitte, J. Evaluating ELISA, Immunofluorescence, and Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Assays. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 597529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochola, L.; Ogongo, P.; Mungai, S.; Gitaka, J.; Suliman, S. Performance Evaluation of Lateral Flow Assays for Coronavirus Disease-19 Serology. Clin. Lab. Med. 2022, 42, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Frew, E.; Cooper, J.; Humphrey, J.; Holden, M.; Mand, A.R.; Li, J.; Anderson, S.; Bi, M.; Hatler, J.; et al. Use of Lateral Flow Immunoassay to Characterize SARS-CoV-2 RBD-Specific Antibodies and Their Ability to React with the UK, SA and BR P.1 Variant RBDs. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-L.; Fu, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Hong, C.; Yang, W.-C.; Wang, I.-J.; Sun, J.-R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, C.-F.; Cheng, C.-M. A Lateral Flow Immunoassay Coupled with a Spectrum-Based Reader for SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Detection. Vaccines 2022, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.-F.; Hung, C.-H.; Hong, C.; Chen, S.-C.; Sun, Y.-C.; Wen, J.-W.; Kuo, C.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Cheng, C.-M. Quantitative Spectrochip-Coupled Lateral Flow Immunoassay Demonstrates Clinical Potential for Overcoming Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Screening Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Meng, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Ali, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Yi, M.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; et al. SERS-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG Antibodies by Using Gap-Enhanced Raman Nanotags. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurrab, F.M.; Younes, N.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Liu, N.; Qotba, H.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Nasrallah, G.K. Performance Evaluation of Novel Fluorescent-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) for Rapid Detection and Quantification of Total Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD Binding Antibodies in Infected Individuals. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 118, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, J.; Xun, J.; Dai, R.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Sui, G.; Cheng, X. Development of a Sensitive Immunochromatographic Method Using Lanthanide Fluorescent Microsphere for Rapid Serodiagnosis of COVID-19. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhao, H.; Bian, L.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG, Using Lanthanide-Doped Nanoparticles-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7226–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Fang, H.; Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Lai, W.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Development of a Rapid and Sensitive Quantum Dot Nanobead-Based Double-Antigen Sandwich Lateral Flow Immunoassay and Its Clinical Performance for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Total Antibodies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. Combination of Serological Total Antibody and RT-PCR Test for Detection of SARS-COV-2 Infections. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 283, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Berhane, S.; Taylor, M.; Adriano, A.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; Emperador, D.; Takwoingi, Y.; Cunningham, J.; et al. Rapid, Point-of-care Antigen Tests for Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, D.A.; Wang, J.Y.; Moeser, M.-E.; Starkey, T.; Lee, L.Y.W. A Systematic Review of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Lateral Flow Devices in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapari, A.; Braliou, G.G.; Papaefthimiou, M.; Mavriki, H.; Kontou, P.I.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Bagos, P.G. Performance of Antigen Detection Tests for SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peto, T.; Affron, D.; Afrough, B.; Agasu, A.; Ainsworth, M.; Allanson, A.; Allen, K.; Allen, C.; Archer, L.; Ashbridge, N.; et al. COVID-19: Rapid Antigen Detection for SARS-CoV-2 by Lateral Flow Assay: A National Systematic Evaluation of Sensitivity and Specificity for Mass-Testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 36, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giberti, I.; Costa, E.; Domnich, A.; Ricucci, V.; De Pace, V.; Garzillo, G.; Guarona, G.; Icardi, G. High Diagnostic Accuracy of a Novel Lateral Flow Assay for the Point-of-Care Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Antigen-Detection in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnosis-of-sars-cov-2infection-using-rapid-immunoassays (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- De Marinis, Y.; Pesola, A.-K.; Söderlund Strand, A.; Norman, A.; Pernow, G.; Aldén, M.; Yang, R.; Rasmussen, M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 by Rapid Antigen Tests on Saliva in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2021, 11, 1993535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivrane, A.; Igumnova, V.; Liepina, E.E.; Skrastina, D.; Leonciks, A.; Rudevica, Z.; Kistkins, S.; Reinis, A.; Zilde, A.; Kazaks, A.; et al. Development of Rapid Antigen Test Prototype for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva Samples. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2022, 127, e8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, L.; Li, B. Improvement in Detection Limit for Lateral Flow Assay of Biomacromolecules by Test-Zone Pre-Enrichment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, L.S.; Thulstrup, P.W. Gold Nanoparticle-Mediated Lateral Flow Assays for Detection of Host Antibodies and COVID-19 Proteins. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Jiao, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, X.; Fang, X.; Dai, X. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Coupled with Copper Enhancement for Rapid and Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, G.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y. Accuracy of a Nucleocapsid Protein Antigen Rapid Test in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 289.e1–289.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiro, V.V.; Gupta, A.; Singh, P.; Sharad, N.; Khurana, S.; Prakash, S.; Dar, L.; Malhotra, R.; Wig, N.; Kumar, A.; et al. Evaluation of COVID-19 Antigen Fluorescence Immunoassay Test for Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2021, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Lei, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; et al. Rapid Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Fluorescence Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Zheng, S.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. Ultrasensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Two Specific SARS-CoV-2 Antigens in Human Specimens Using Direct/Enrichment Dual-Mode Fluorescence Lateral Flow Immunoassay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40342–40353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X. A Colorimetric Sandwich-Type Bioassay for SARS-CoV-2 Using a HACE2-Based Affinity Peptide Pair. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-S.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.G. Versatile Role of ACE2-Based Biosensors for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Neutralizing Antibodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, J.C.; Bernuz, M.; Marfa, J.; Pallares-Rusiñol, A.; Martí, M.; Pividori, M.I. Comparative Study of Gold and Carbon Nanoparticles in Nucleic Acid Lateral Flow Assay. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Mesa Biotech, Inc., Recalls Certain Accula SARS-CoV-2 Tests for Risk of False Positives Caused by Contamination; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Warmt, C.; Henkel, J.; Schrick, L.; Nitsche, A.; Bier, F.F. Lateral Flow–Based Nucleic Acid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Enzymatic Incorporation of Biotin-Labeled DUTP for POCT Use. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, W.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Cao, B.; Jin, Q.; Cui, D. Rapid Developments in Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Nucleic Acid Detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M. Progress in Electrochemical Biosensing of SARS-CoV-2 Virus for COVID-19 Management. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castrejón-Jiménez, N.S.; García-Pérez, B.E.; Reyes-Rodríguez, N.E.; Vega-Sánchez, V.; Martínez-Juárez, V.M.; Hernández-González, J.C. Challenges in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2: Evolution of the Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Valuable Tool for Viral Diagnosis. Biosensors 2022, 12, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090728
Castrejón-Jiménez NS, García-Pérez BE, Reyes-Rodríguez NE, Vega-Sánchez V, Martínez-Juárez VM, Hernández-González JC. Challenges in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2: Evolution of the Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Valuable Tool for Viral Diagnosis. Biosensors. 2022; 12(9):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090728
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastrejón-Jiménez, Nayeli Shantal, Blanca Estela García-Pérez, Nydia Edith Reyes-Rodríguez, Vicente Vega-Sánchez, Víctor Manuel Martínez-Juárez, and Juan Carlos Hernández-González. 2022. "Challenges in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2: Evolution of the Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Valuable Tool for Viral Diagnosis" Biosensors 12, no. 9: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090728
APA StyleCastrejón-Jiménez, N. S., García-Pérez, B. E., Reyes-Rodríguez, N. E., Vega-Sánchez, V., Martínez-Juárez, V. M., & Hernández-González, J. C. (2022). Challenges in the Detection of SARS-CoV-2: Evolution of the Lateral Flow Immunoassay as a Valuable Tool for Viral Diagnosis. Biosensors, 12(9), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090728




