Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomedical Sensors: From Design to Application
Abstract
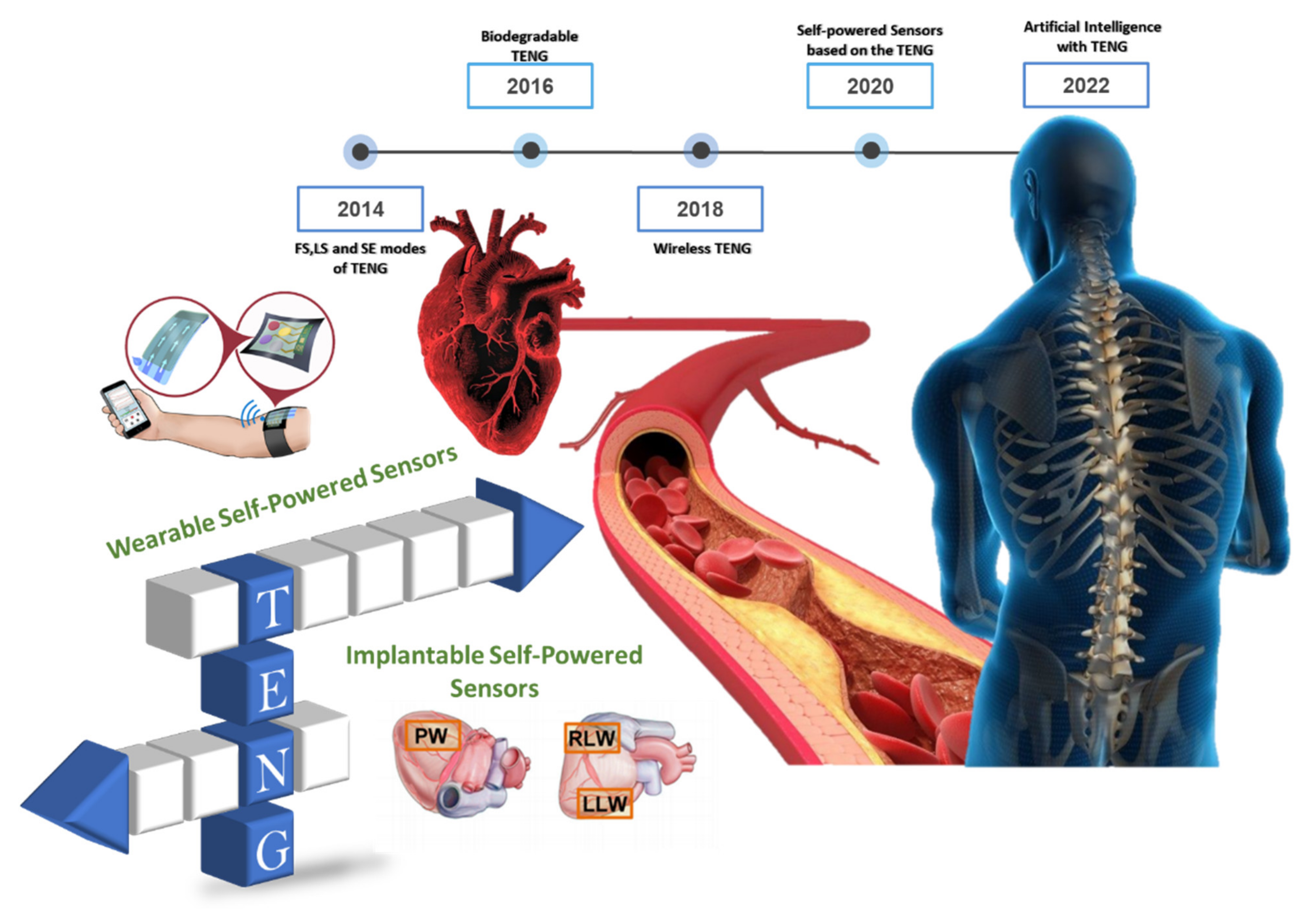
:1. Introduction
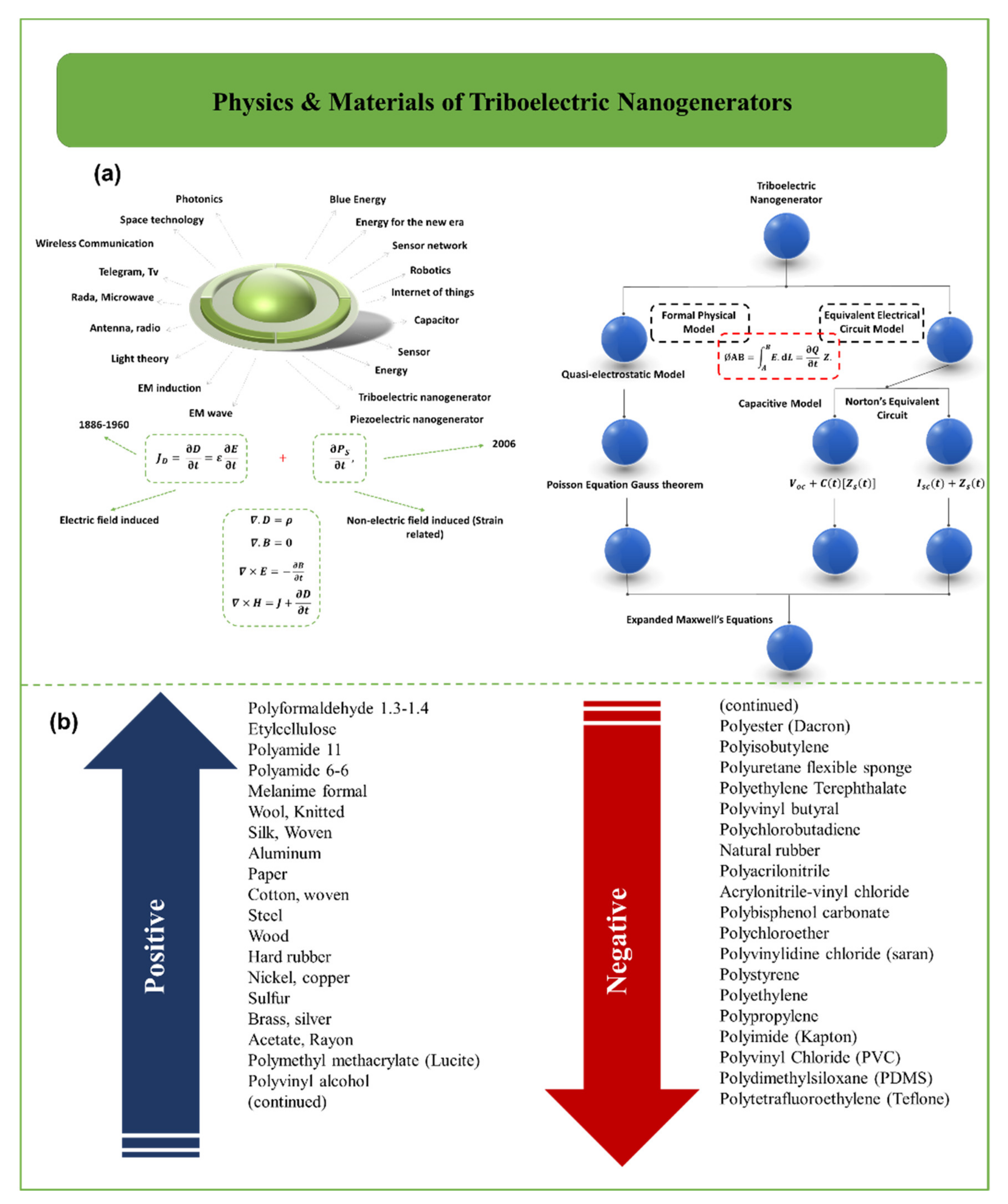
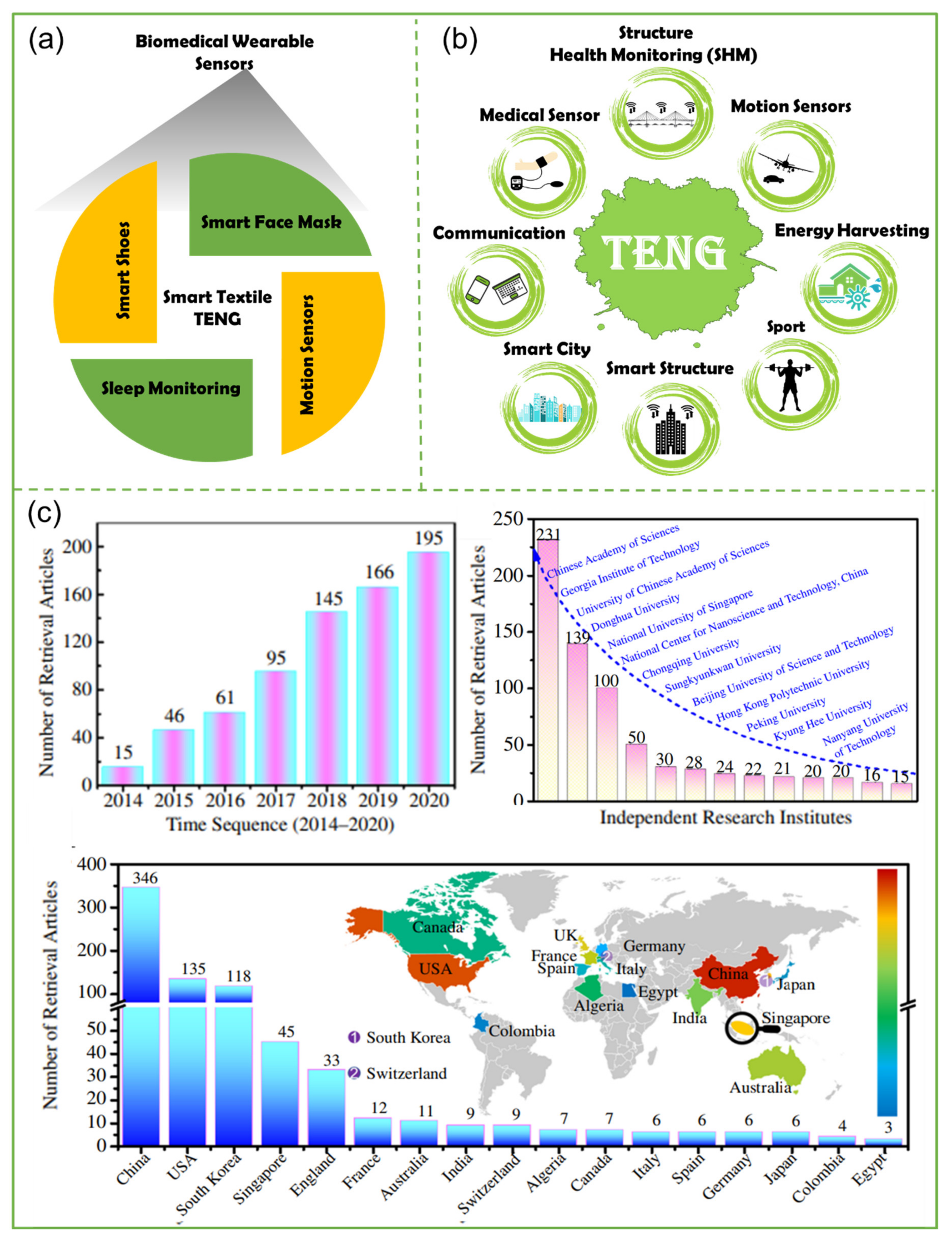
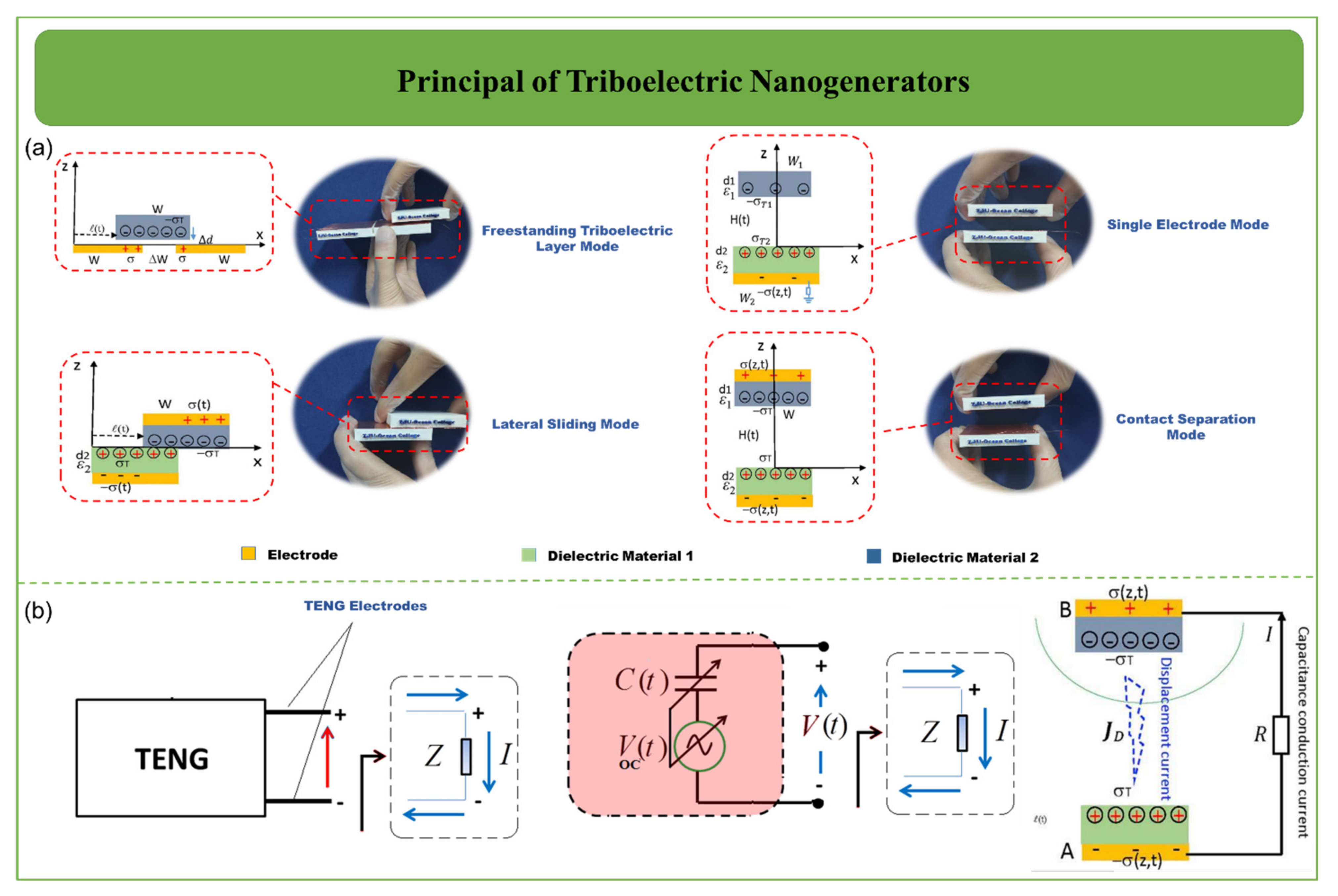
2. Overview of Self-Powered Sensors for Human Health Care
3. Implantable Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
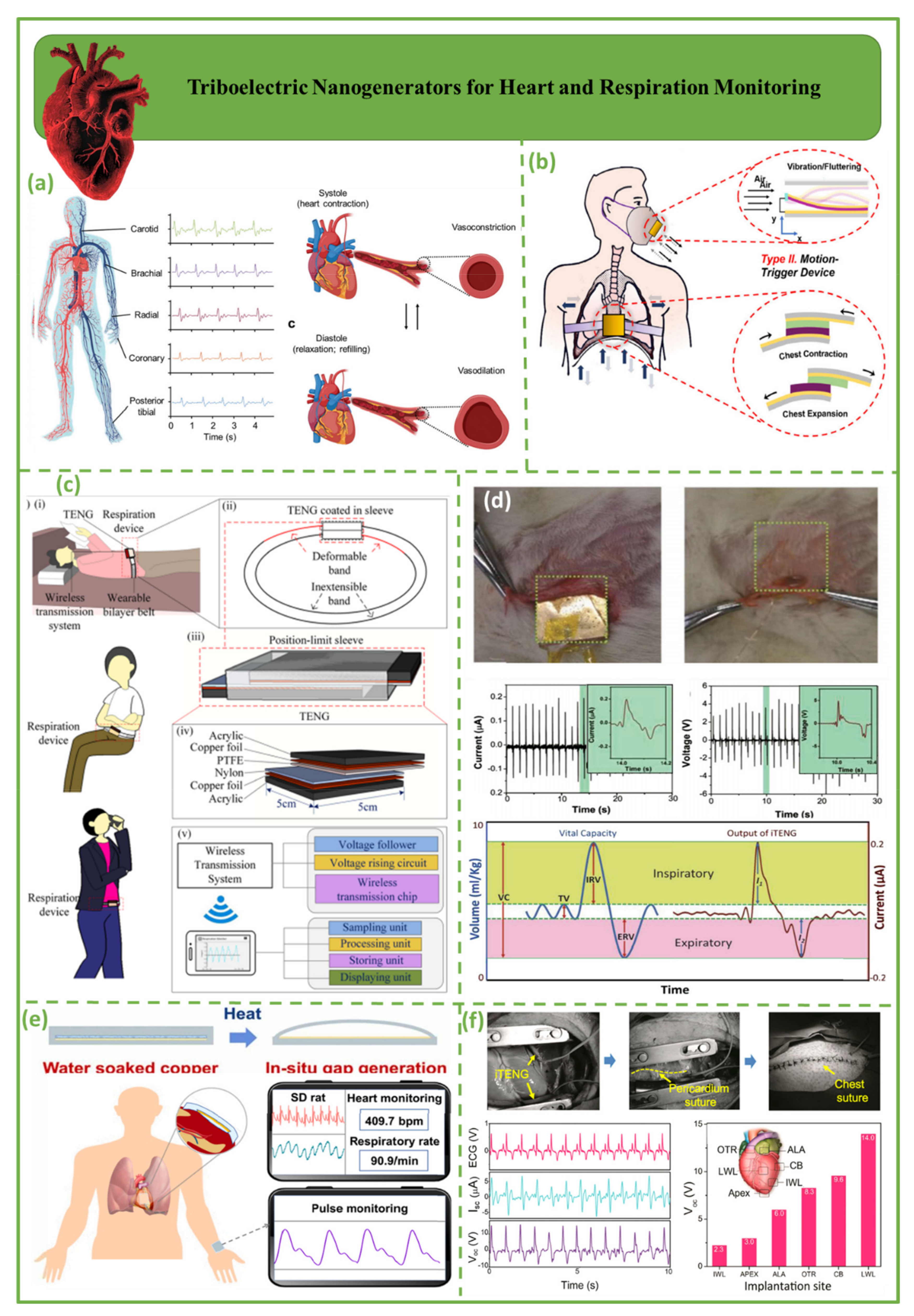
3.1. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Heart and Respiration Monitoring
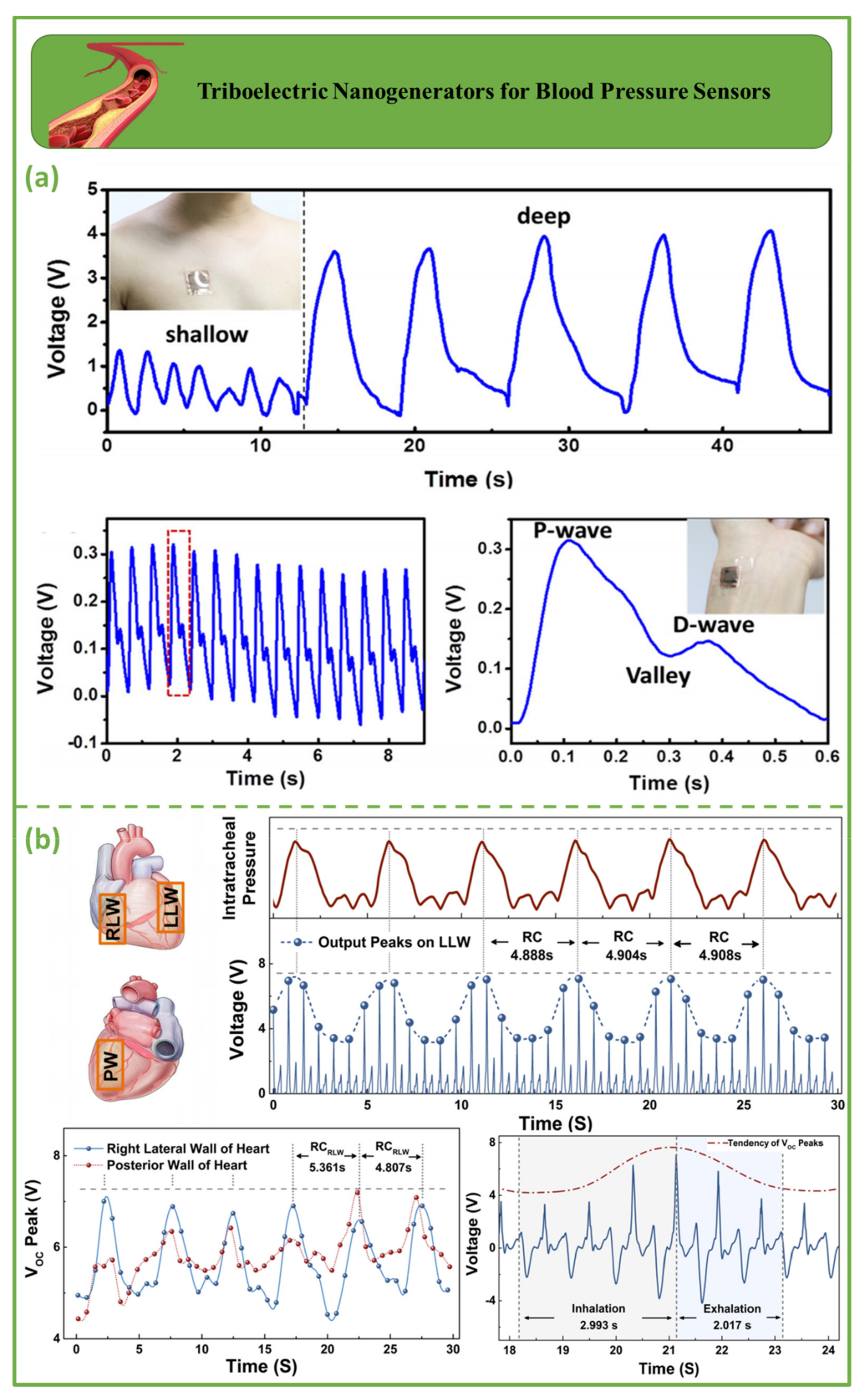
3.2. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Blood Pressure Sensors
4. Wearable Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
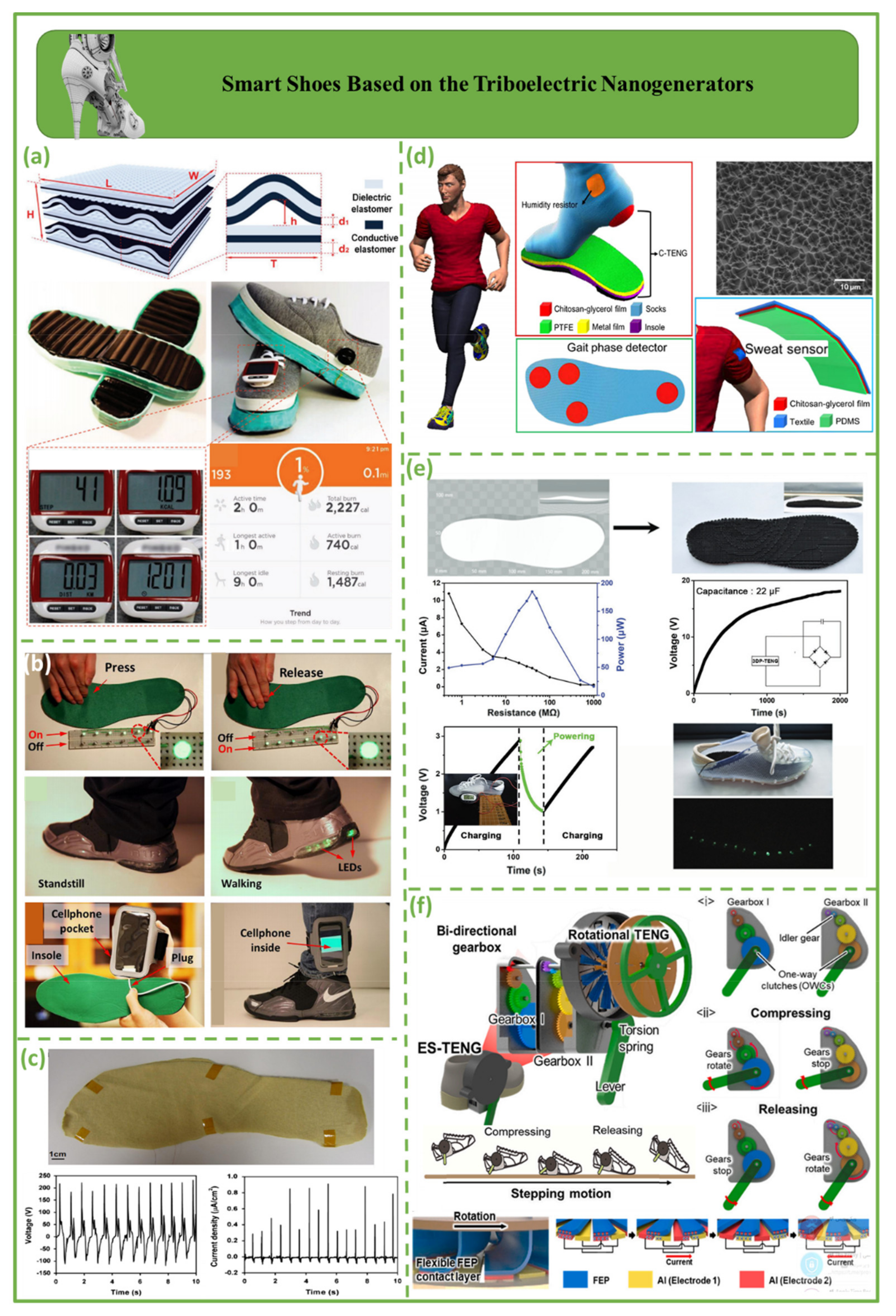
4.1. Smart Shoes Based on the Triboelectric Nanogenerators
4.2. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Motion Sensors
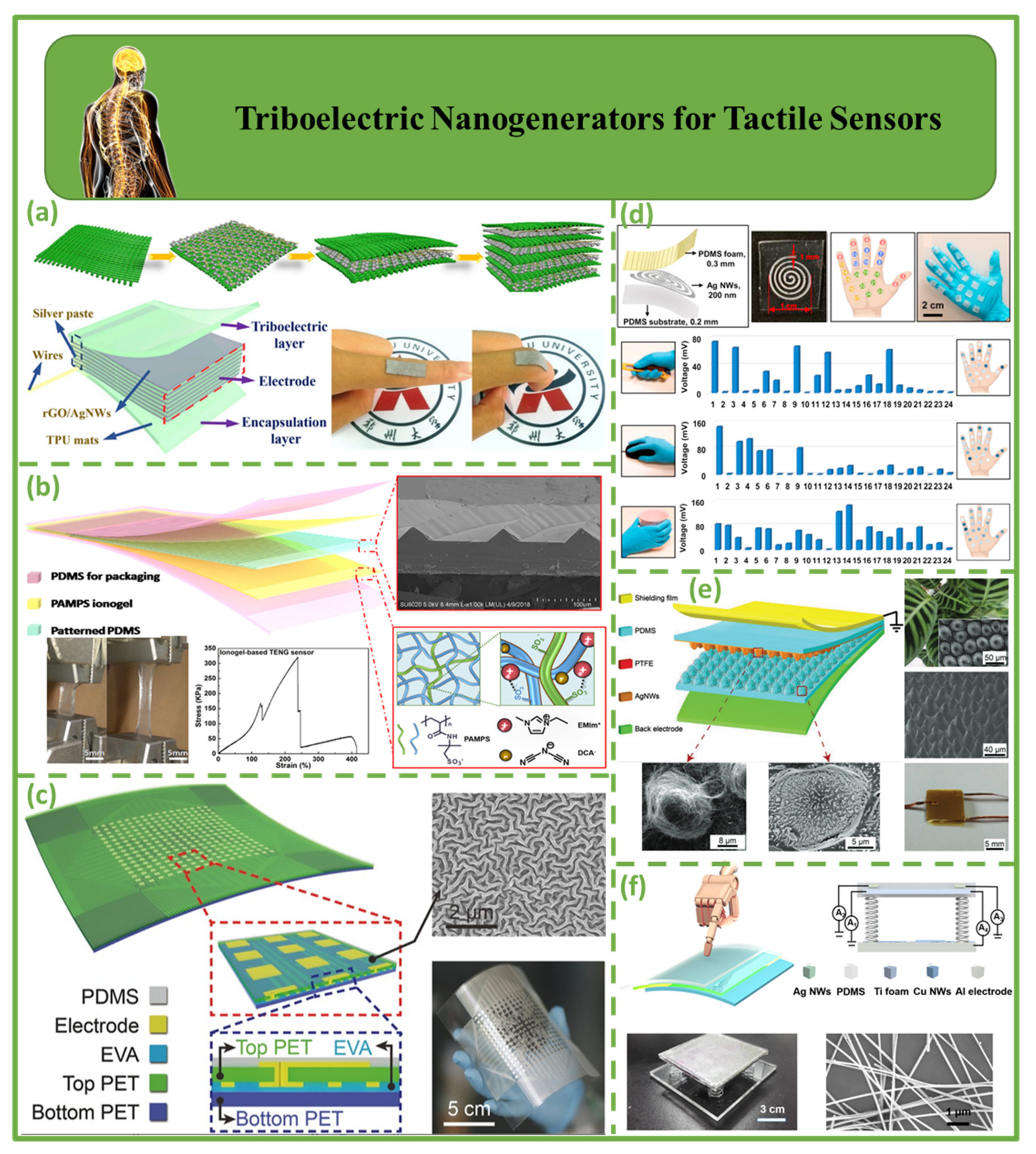
4.3. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Tactile Sensors
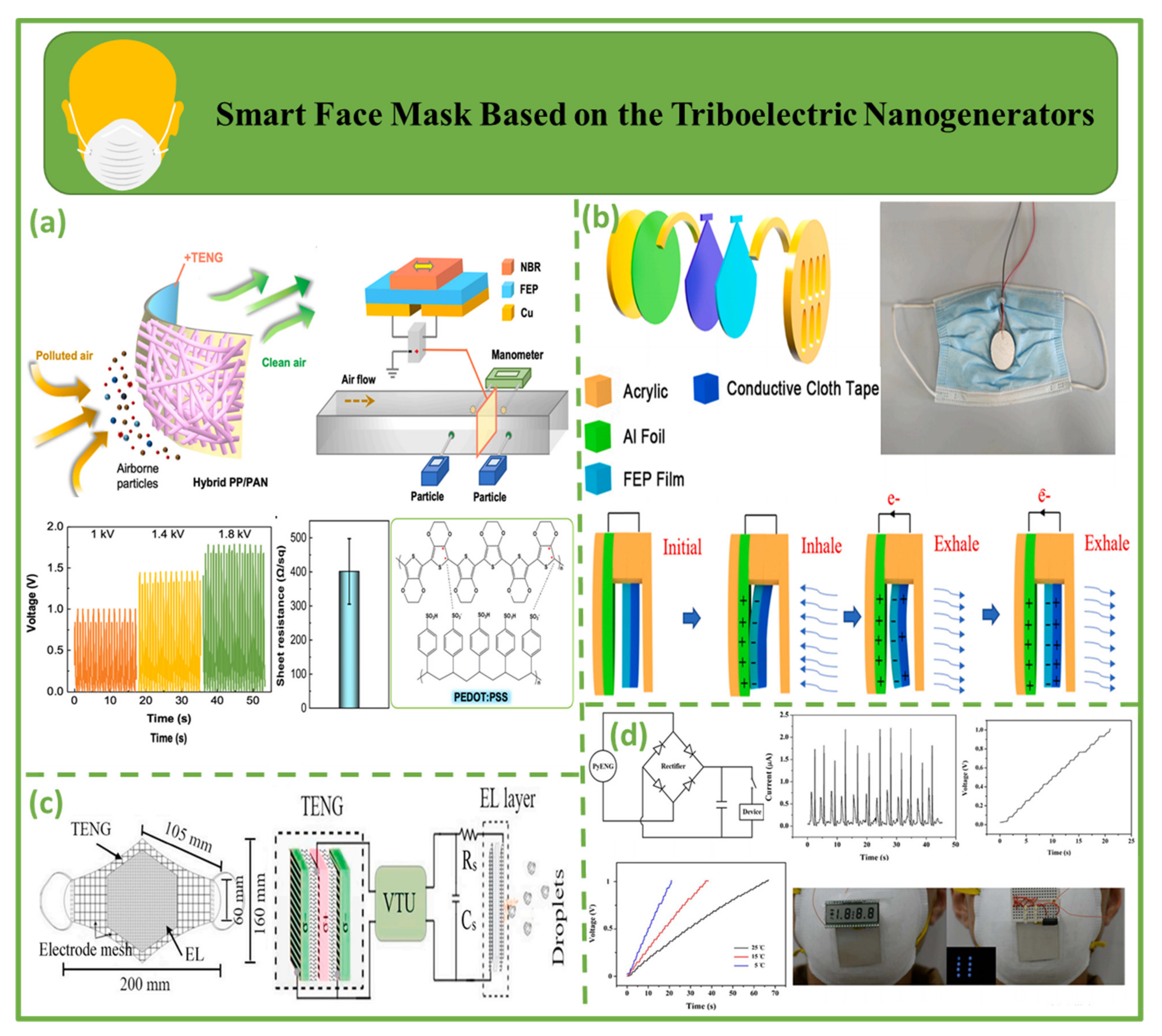
4.4. Smart Face Mask Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
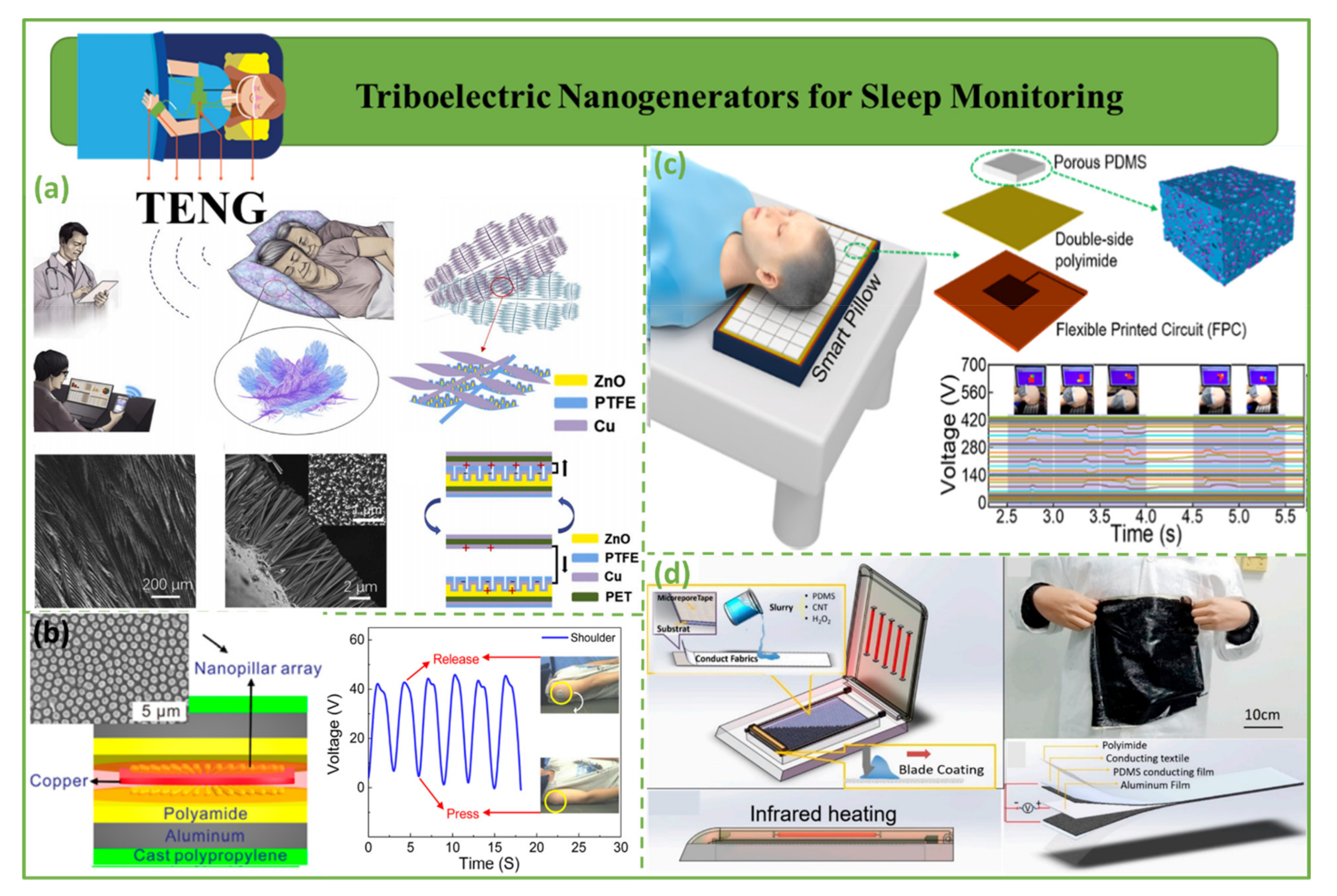
4.5. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Sleep Monitoring
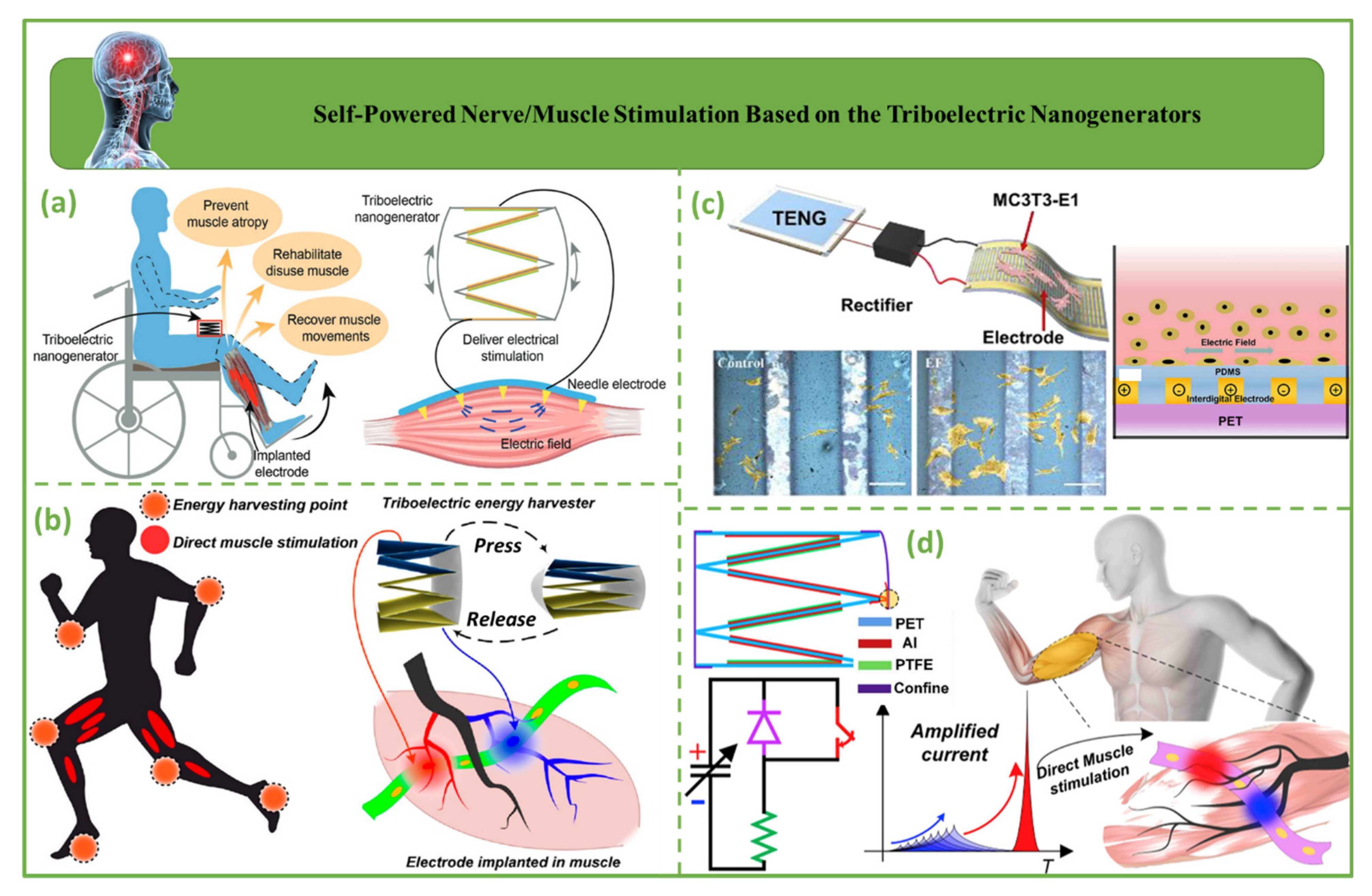
4.6. Self-Powered Nerve/Muscle Stimulation Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
5. Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends of TENGs for Biomedical Sensors
- Materials used in biomedical monitoring are anticipated to be flexible, light, stretchable, washable, attractive, skin-friendly, and even environmentally beneficial from the standpoint of wearability. As a result, researchers will gradually employ textile, rubber, hydrogel, shape-memory polymers, and other innovative functional materials to create well-designed TENG sensors.
- With respect to sensing techniques, quantification could replace traditional two-stage judgment (i.e., “0” and “1”) on a transient pulse with no intermediate state, particularly for the control step. Furthermore, the composite mechanism of the intermediate state in a human-like intelligent sensor should be investigated further.
- From the standpoint of technical integration, multiparameter systems can be built with advanced packaging and optimized modularization, and other novel technologies can be introduced to support the development of wearable biomedical monitors.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.-J.; Yim, E.-C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, J.-Y.; Oh, I.-K. Bacterial nano-cellulose triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Swetha, P.; Zhu, Y. Nanomaterial-enabled wearable sensors for healthcare. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawson, T.M.; Sharma, S.; Georgiou, P.; Holmes, A.; Cass, A.; O’Hare, D. Towards a minimally invasive device for beta-lactam monitoring in humans. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 82, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Q.; Kwon, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sharma, P.R.; Jin, L.; Li, X.; Xu, B. 3D printed microheater sensor-integrated, Drug-Encapsulated microneedle patch system for pain management. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1901170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Jiao, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Magnetic lifting triboelectric nanogenerators (ml-TENG) for energy harvesting and active sensing. APL Mater. 2021, 9, 091111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Jiao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Alavi, A.H. A new structural health monitoring approach based on smartphone measurements of magnetic field intensity. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2021, 24, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Matin Nazar, A.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Barri, K.; Alavi, A.H. Magnetic capsulate triboelectric nanogenerators. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Egbe, K.-J.I.; Matin Nazar, A.; Jiao, P.; Yang, Y.; Ye, X.; Wang, H. Vibrational turbine piezoelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting in multiphase flow fields. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6384–6393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varmaghani, A.; Matin Nazar, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Sharifi, A.; Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S.; Pourasad, Y. DMTC: Optimize energy consumption in dynamic wireless sensor network based on fog computing and fuzzy multiple attribute decision-making. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 9953416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Matin Nazar, A.; Wang, J.; Xia, K.; Wang, D.; Ji, X.; Jiao, P. Rolling Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerators (RS-TENG) under Low-Frequency Ocean Wave Action. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Nazar, A.M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H. Oscillatory magnetic piezoelectric nanogenerators under low-frequency and low-amplitude excitations. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2022, 52, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Xie, Y.; Matin Nazar, A.; Alavi, A.H. Piezoelectric sensing techniques in structural health monitoring: A state-of-the-art review. Sensors 2020, 20, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Alavi, A.H.; Asghari, A.; Niroomand, H.; Matin Nazar, A. An innovative approach for modeling of hysteretic energy demand in steel moment resisting frames. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Jiao, P.; Alavi, A.H. A novel multi-mode magnetic triboelectric nanogenerator energy harvesting system. In Proceedings of the Behavior and Mechanics of Multifunctional Materials XV; Harne, R.L., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabov, V.; Kopyl, S.; Soares dos Santos, M.P.; Kholkin, A.L. Natural and eco-friendly materials for triboelectric energy harvesting. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbe, K.-J.I.; Matin Nazar, A.; Jiao, P.; Alavi, A.H. Harnessing postbuckling instability of piezoelectric cylinders with corrugation for energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems XV, Virtual, 22 March 2021; pp. 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Rayegani, A.; Nouri, G. Application of Smart Dampers for Prevention of Seismic Pounding in Isolated Structures Subjected to Near-fault Earthquakes. J. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 26, 4069–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Smart textile triboelectric nanogenerators: Current status and perspectives. MRS Bull. 2021, 46, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, H.; Khajepour, A.; Khamesee, M.B.; Saadatnia, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators: Trends and impacts. Nano Today 2018, 22, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the first principle theory of nanogenerators from Maxwell’s equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tang, W.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.L. Power management and effective energy storage of pulsed output from triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecea, V.M.; Carlsson, J.-O.; Alm, O.; Boman, M. Out-of-plane vibrations of quartz resonators used in quartz crystal microbalance measurements in gas phase. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 125, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Guo, H.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.-H.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting low-frequency (<5 Hz) irregular mechanical energy: A possible killer application of triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4797–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayegani, A.; Nouri, G. Seismic collapse probability and life cycle cost assessment of isolated structures subjected to pounding with smart hybrid isolation system using a modified fuzzy based controller. Structures 2022, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Liu, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Yu, M.; Zhao, C.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Self-powered implantable electrical stimulator for osteoblasts’ proliferation and differentiation. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Z.L. The current development and future outlook of triboelectric nanogenerators: A survey of literature. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Lee, C. Self-powered triboelectric nanogenerator buoy ball for applications ranging from environment monitoring to water wave energy farm. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z.L. TriboPump: A low-cost, hand-powered water disinfection system. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadhel, A.; Kosel, J. Tactile sensors: Magnetic nanocomposite cilia tactile sensor (adv. mater. 47/2015). Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M.-G.; Song, W.J.; Park, J.-U.; Sun, J.-Y. Accelerated wound healing with an ionic patch assisted by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zheng, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Li, H.; Yan, L.; Shi, B.; Li, Z. A size-unlimited surface microstructure modification method for achieving high performance triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2016, 28, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Cylindrical rotating triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6361–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Segmentally structured disk triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting rotational mechanical energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.; Yang, Y.; Lin, L.; Lin, Z.-H.; Hwang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting pendulum oscillation energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Lan, L.; Zhao, F.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. All-electrospun flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on metallic MXene nanosheets. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectric nanogenerators for blue energy harvesting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6429–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, B.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Biodegradable triboelectric nanogenerator as a life-time designed implantable power source. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Self-powered direct muscle stimulation using a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) integrated with a flexible multiple-channel intramuscular electrode. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; He, T.; Li, Z.; Lee, C. Direct muscle stimulation using diode-amplified triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-J.; Song, W.-Z.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. A calibration-free self-powered sensor for vital sign monitoring and finger tap communication based on wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchet, R.; Yoon, H.-J.; Ryu, H.; Kim, M.-K.; Choi, E.-K.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, S.-W. Transcutaneous ultrasound energy harvesting using capacitive triboelectric technology. Science 2019, 365, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, S.-W. Nanogenerators to power implantable medical systems. Joule 2020, 4, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Broadband vibrational energy harvesting based on a triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.L. 3D mathematical model of contact-separation and single-electrode mode triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z. Theoretical foundations of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1087–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, S.; Zhou, H.; Xie, W.; Chen, J.; Qi, M.; Yu, H.; Mu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Enhancing the Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Grating-Electrode-Enabled Surface Plasmon Excitation (Adv. Energy Mater. 44/2019). Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1970177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.-Q.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.-L.; Kera, S.; Ueno, N.; Wee, A.T.S.; Yang, J.; Chen, W. Energy level realignment in weakly interacting donor–acceptor binary molecular networks. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1699–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Han, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, K.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, R.; Tao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Biodegradable, Super-Strong, and Conductive Cellulose Macrofibers for Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical modeling of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Radial piston triboelectric nanogenerator-enhanced cellulose fiber air filter for self-powered particulate matter removal. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.Q.; Han, C.B.; Lu, C.X.; He, C.; Jiang, T.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, C.J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator enhanced nanofiber air filters for efficient particulate matter removal. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6211–6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric actuators 2008: Key factors for commercialization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Materials—Smart/Intelligent Materials and Nano Technology, (SmartMat-ȁ08) and 2nd International Workshop on Functional Materials and Nanomaterials (IWOFM-2), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 22–25 April 22 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical systems of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, S.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Simulation method for optimizing the performance of an integrated triboelectric nanogenerator energy harvesting system. Nano Energy 2014, 8, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhu, H.; Lu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Design of biodegradable wheat-straw based triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered sensor for wind detection. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Yi, F.; Yin, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z. Simulation and structure optimization of triboelectric nanogenerators considering the effects of parasitic capacitance. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.D.I.G.; Jayawardena, K.; Mills, C.; Deane, J.; Anguita, J.; Dorey, R.; Silva, S. Triboelectric nanogenerators: Providing a fundamental framework. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1801–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Jiang, T.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Quantifying the power output and structural figure-of-merits of triboelectric nanogenerators in a charging system starting from the Maxwell’s displacement current. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Liu, D.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Three-dimensional modeling of alternating current triboelectric nanogenerator in the linear sliding mode. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmasena, R.; Jayawardena, K.; Mills, C.; Dorey, R.; Silva, S. A unified theoretical model for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayegba, B.O.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Matin Nazar, A.; Huang, M.; Hariri-Ardebili, M.A. Resource Efficiency and Thermal Comfort of 3D Printable Concrete Building Envelopes Optimized by Performance Enhancing Insulation: A Numerical Study. Energies 2022, 15, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Wang, H.; Matin Nazar, A.; Jiao, P.; Zhu, R. A Numerical Study on 3D Printed Cementitious Composites Mixes Subjected to Axial Compression. Materials 2021, 14, 6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Idala Egbe, K.-J.; Abdollahi, A.; Hariri-Ardebili, M.A. Triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting in ocean: A review on application and hybridization. Energies 2021, 14, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüegg, M.; Blum, R.; Boero, G.; Brugger, J. Biodegradable Frequency-Selective Magnesium Radio-Frequency Microresonators for Transient Biomedical Implants. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Saxena, M.; Padmanabhan, D.; Jayachandra, M.; Pandya, H.J. Futuristic medical implants using bioresorbable materials and devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; He, W.; Chen, J.; Wen, C.; Yin, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zou, S. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy for accelerating tooth movement during orthodontic treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lasers Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermann, L.; Jain, R.; Chen, L.; Maarouf, M.; Barbe, M.T.; Allert, N.; Brücke, T.; Kaiser, I.; Beirer, S.; Sejio, F. Multiple-source current steering in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease (the VANTAGE study): A non-randomised, prospective, multicentre, open-label study. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Song, C.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, T.; Shin, K.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T.; Kim, D.-H. Wearable/disposable sweat-based glucose monitoring device with multistage transdermal drug delivery module. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Han, D.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, S. Oppositely charged polyurethane microspheres with tunable zeta potentials as an injectable dual-loaded system for bone repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25808–25817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Tian, L.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, S.; Tang, Y.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y. Washable textile-structured single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19143–19150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Thangavel, G.; Cai, G.; Zhou, X.; Park, S.; Xiong, J.; Lee, P.S. Extremely stretchable and self-healing conductor based on thermoplastic elastomer for all-three-dimensional printed triboelectric nanogenerator. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, A.C.; He, J.-H.; Wang, Z.L.; Alshareef, H.N. MXene electrochemical microsupercapacitor integrated with triboelectric nanogenerator as a wearable self-charging power unit. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrastretchable, transparent triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gong, S.; Wang, X. Sequential infiltration synthesis of doped polymer films with tunable electrical properties for efficient triboelectric nanogenerator development. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4938–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, N.; Dai, C.; Liu, J.; Gu, L.; Ge, R.; Du, T.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y. Increasing the output charge quantity of triboelectric nanogenerators via frequency multiplication with a multigap-structured friction layer. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Single-crystal nanorings formed by epitaxial self-coiling of polar nanobelts. Science 2004, 303, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Self-powered wireless smart sensor node enabled by an ultrastable, highly efficient, and superhydrophobic-surface-based triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9044–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Fitzpatrick, V.; Ibrahim, A.; Zwierstra, M.J.; Hanna, P.; Lechtig, A.; Nazarian, A.; Lin, S.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Design of biodegradable, implantable devices towards clinical translation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, W.E.; Timms, D.L.; Frazier, O. Total artificial hearts: Past, present, and future. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2015, 12, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Wearable triboelectric nanogenerators for heart rate monitoring. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 5871–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Respiration-driven triboelectric nanogenerators for biomedical applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Xuan, W.; Dong, S.; Luo, J. A portable triboelectric nanogenerator for real-time respiration monitoring. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Kim, J.U.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, J.H.; Jung, W.; Ok, J.; Kim, T.i. Injectable Electronics: Injectable Biomedical Devices for Sensing and Stimulating Internal Body Organs. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2070125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, T.; Boveda, S.; Defaye, P.; Rosier, A.; Sadoul, N.; Bordachar, P.; Klug, D.; Ritter, P.; Belhameche, M.; Babuty, D. Role of medical reaction in management of inappropriate ventricular arrhythmia diagnosis: The inappropriate Therapy and HOme monitoRiNg (THORN) registry. EP Europace 2019, 21, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Feig, V.R.; Bao, Z. Conjugated polymer for implantable electronics toward clinical application. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Shi, B.; Fan, F.; Wang, X.; Yan, L.; Yuan, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. In vivo powering of pacemaker by breathing-driven implanted triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5851–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhuo, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, L. Eco-friendly in-situ gap generation of no-spacer triboelectric nanogenerator for monitoring cardiovascular activities. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shi, B.; Xue, X.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; An, Z. In vivo self-powered wireless cardiac monitoring via implantable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6510–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; You, X.; Gong, H.; Yang, Y.; Bai, T.; Wang, W.; Guo, W.; Liu, X.; Ye, M.; Stretchable, B. Multifunctional silk fibroin-based hydrogels toward wearable strain/pressure sensors and triboelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6442–6450. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y. Expandable microsphere-based triboelectric nanogenerators as ultrasensitive pressure sensors for respiratory and pulse monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Gu, Y.; Chen, J.; Bahrani, A.A.; Jawdeh, E.G.A.; Bada, H.S.; Saatman, K.; Yu, G.; Chen, L. A wearable fiberless optical sensor for continuous monitoring of cerebral blood flow in mice. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, B.; Xue, X.; Ji, W.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zou, Y.; An, Z. Self-powered, one-stop, and multifunctional implantable triboelectric active sensor for real-time biomedical monitoring. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, W.; Lin, L.; Zi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Sustainable energy source for wearable electronics based on multilayer elastomeric triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602832. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Power-generating shoe insole based on triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered consumer electronics. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.-C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside shoe insole for harvesting walking energy. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, Y.-T.; Yang, P.-K.; Chiu, C.-M.; Lin, Y.-J.; Chen, S.-W.; Choi, D.; Lin, Z.-H. A textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with humidity-resistant output characteristic and its applications in self-powered healthcare sensors. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Zuo, H.; Qian, S.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L.; Lei, D.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, B.; He, C. A single integrated 3D-printing process customizes elastic and sustainable triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Jang, S.; Cho, S.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D. Exo-shoe triboelectric nanogenerator: Toward high-performance wearable biomechanical energy harvester. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin Nazar, A.; Egbe, K.J.I.; Jiao, P. Hybrid Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Walking Sensing. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2200063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zheng, N.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric nanogenerator for human motion tracking and gesture recognition. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106601. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wen, T.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cho, J.; Chou, X.; Xue, C. Core–shell coaxially structured triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and motion sensing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 2950–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, J. High output triboelectric nanogenerator based on PTFE and cotton for energy harvester and human motion sensor. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2021, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gogurla, N.; Roy, B.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, S. Skin-contact actuated single-electrode protein triboelectric nanogenerator and strain sensor for biomechanical energy harvesting and motion sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Sohn, M.; Ma, R.; Kang, D.J. Flexible single-electrode triboelectric nanogenerators with MXene/PDMS composite film for biomechanical motion sensors. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105383. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Han, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Xing, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, X. Self-powered implantable electronic-skin for in situ analysis of urea/uric-acid in body fluids and the potential applications in real-time kidney-disease diagnosis. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Xing, L.; Xue, X. Self-powered implantable skin-like glucometer for real-time detection of blood glucose level in vivo. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, Y.; Feng, Z.; Kim, J.; Robertson, J.L.; Jia, X.; Johnson, B.N. 3D printed stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator fibers and devices. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104973. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsunari, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Matsushima, M.; Kawabe, T.; Shikida, M. Development of small-footprint thermal sensor detecting airflow at mouth in baby. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2017, 1, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Closson, A.B.; Jin, C.; Nie, Y.; Cabe, A.; Escobedo, D.; Huang, S.; Trase, I.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z. Cardiac Energy Harvesting: Multifunctional Pacemaker Lead for Cardiac Energy Harvesting and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2070031. [Google Scholar]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, J.S. Triboelectric nanogenerators with gold-thin-film-coated conductive textile as floating electrode for scavenging wind energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, M.S.; Fang, H.; Wang, H. An integrated wearable sensor for unobtrusive continuous measurement of autonomic nervous system. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; Li, L.; Song, H.; Du, C.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, C.; Cao, G.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. A self-charging power unit by integration of a textile triboelectric nanogenerator and a flexible lithium-ion battery for wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Pan, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator as high-sensitive and self-powered electronic skins for energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104546. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, N.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, M.; Pan, C.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Torres, D.; Díaz, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Lin Wang, Z.; Sepúlveda, N. Nanogenerator-based dual-functional and self-powered thin patch loudspeaker or microphone for flexible electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Lee, J.; Hyeon, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.H. Fabric-based integrated energy devices for wearable activity monitors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6329–6334. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Gao, Z.; Yao, K.; Hou, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; He, J.; Huang, X.; Song, E.; Yu, J. Thin, soft, skin-integrated foam-based triboelectric nanogenerators for tactile sensing and energy harvesting. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100657. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.; Xu, L.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Wu, H. Bioinspired triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered electronic skin for robotic tactile sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Zou, J.; Xing, F.; Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. From dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator to smart tactile sensor: A multiplexing design. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3950–3956. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Bian, Y.; Lim, C.K.; Niu, Z.; Lee, P.K.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Daoud, W.A.; Zi, Y. Tribo-charge enhanced hybrid air filter masks for efficient particulate matter capture with greatly extended service life. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106015. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Xue, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Intelligent facemask based on triboelectric nanogenerator for respiratory monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 91, 106612. [Google Scholar]
- Ghatak, B.; Banerjee, S.; Ali, S.B.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Das, N.; Mandal, D.; Tudu, B. Design of a self-powered triboelectric face mask. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Luo, W.; Wang, W.; Lin, M.; Liang, D.; Luo, Q. A wearable pyroelectric nanogenerator and self-powered breathing sensor. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Yao, G.; Yan, Z.; Huang, L.; Chen, S.; Pan, T.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Self-powered, wireless, remote meteorologic monitoring based on triboelectric nanogenerator operated by scavenging wind energy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32649–32654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Xiang, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Tao, C.; Yang, S.; Fan, X. Imperceptible sleep monitoring bedding for remote sleep healthcare and early disease diagnosis. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104664. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Nanogenerator, T. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG)—Sparking an Energy and Sensor Revolution. Adv. Energy Mater 2020, 10, 2000137. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Gan, B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, A.; Yuan, H.; Chen, N.; Sun, C.; Wang, Z.L. Nanopillar arrayed triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered sensitive sensor for a sleep monitoring system. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8097–8103. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, H.; Wang, H.; Cheng, R.; Liao, Y.; Shi, X.; Luo, J.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.L. Smart Pillow Based on Flexible and Breathable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Head Movement Monitoring during Sleep. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23998–24007. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Large scale triboelectric nanogenerator and self-powered flexible sensor for human sleep monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 1713. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, G.; Yang, R.; Wang, A.C.; Wang, Z.L. Muscle-driven in vivo nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2534–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; He, T.; He, B.; Thakor, N.V.; Lee, C. Investigation of low-current direct stimulation for rehabilitation treatment related to muscle function loss using self-powered TENG system. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900149. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Pu, X.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Huang, Z.; Hu, C. A strategy to promote efficiency and durability for sliding energy harvesting by designing alternating magnetic stripe arrays in triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104087. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Jia, X.; Liu, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding triboelectric nanogenerator enables noncontact motion-tracking and positioning. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, C.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric-generator-driven pulse electrodeposition for micropatterning. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4960–4965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. Hybrid electromagnetic–triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting vibration energy. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, X.; Lin, Z.-H.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting wind energy and as self-powered wind vector sensor system. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9461–9468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Structure | Year | Authors | Applied Tribolayer | Electrode Type | Max Open-Circuit Voltage (V ) | Max Short-Circuit Current | Current Density | Surface Power Density | Power Density and Power | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart and respiration monitoring | 2021 | Shen et al. [81] | Kapton/PDMS | Cu | 109 | 2.73 µA | - | - | - | Monitors the condition of the heart and respiration system/Incompatible with the cellular tissues of the heart in some cases |
| 2020 | Li et al. [82] | PTFE | Cu | 0.2–45 | 0.5–18 µA | - | 0.6–15 W/m2 | - | ||
| 2019 | Zhang et al. [83] | PTFE/nylon | Cu | 40 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2014 | Zheng [87] | Kapton/PDMS | Al/Au | 12 | 0.8 µA | - | 8.44 mW/m2 | - | ||
| 2021 | Zhao et al. [88] | Silicone rubber | Cu | 3.67 | 51.74 nA | - | - | - | ||
| 2016 | Zheng et al. [89] | PTFE/Kapton/PDMS | Al/Cu | 90 | 12 µA | - | 107 mW/m2 | - | ||
| Blood pressure sensors | 2019 | Liu et al. [91] | PDMS/FEP | Cu | ~70 | - | - | - | - | Prevention of heart attack and stroke |
| 2016 | Ma et al. [93] | Kapton/PDMS/PTFE | Al/Au | ~15 | 4 µA | - | - | - | ||
| Smart shoes | 2017 | Li et al. [94] | Dielectric elastomer | Conductive Elastomer | 50 | 16.2 µA | ~8 mA/m2 | 0.1 W/m2 | - | Energy harvesting/increased vulnerability of shoes |
| 2013 | Zhu et al. [95] | Kapton/PTFE | Al | 220 | 600 µA | - | - | - | ||
| 2013 | Hou et al. [96] | PDMS/ITO | Cu/PET | 220 | 40 µA | ~0.08 mA/cm2 | - | 1.4 mW | ||
| 2018 | Jao et al. [97] | PTFE | Metal/chitosan-glycerol | 130 | 15 µA | 10 mA/m2 | - | - | ||
| 2018 | Chen et al. [98] | PGS/CNTs | Salt | 170 | 11 µA | 200 mA/m2 | - | 185.2 µW | ||
| 2021 | Yun et al. [99] | FEP | Al | 3 k | 20 µA | - | - | 3 mW | ||
| Motion sensors | 2022 | Matin Nazar et al. [100] | Kapton | Al/Cu | 21.9 | - | - | - | 70 µW | Monitors walking behavior and helps to improve the treatment process/exposed sensors subject to increased vulnerability |
| 2022 | Zeng et al. [101] | FEP/silicone/PTFE/nylon | Carbon black/Al | 468 | 10.4 µA | - | - | 1.25 mW | ||
| 2018 | Tian et al. [102] | Silicone | Ni/conductive silicone | 380 | 11 µA | - | - | 1.638 mW | ||
| 2021 | Zhang et al. [103] | PTFE/cotton | Conductive cotton | 556 | 26 µA | - | 0.66 mW/cm2 | - | ||
| 2019 | Gogurla et al. [104] | PDMS/silicone | AgNWs/Al/Cu/PET | 110 | ~0.1 µA | - | 2 mW/m2 | - | ||
| 2020 | He et al. [105] | MXene/PDMS | Cu–Ni/textile | 225 | - | 30 µA/cm2 | 10 mW/cm2 | - | ||
| Tactile sensors | 2020 | Zhou et al. [115] | TPU mats | AgNWs/rGO | 202.4 | - | - | 6 mW/m2 | - | Increase efficiency, energy harvesting and aids in the diagnosis of disease/challenges associated with washing; can cause skin sensitivity and discomfort in some users |
| 2019 | Zhao et al. [116] | PDMS | PAMPS ionogel | 3.3 | 2.3 nA | - | - | - | ||
| 2016 | Wang et al. [78] | PDMS/Kapton | PET | ~60 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2021 | Wu et al. [119] | PDMS | AgNWs | 78.7 | 26.5 µA | - | 33.75 W/m2 | - | ||
| 2019 | Yao et al. [120] | PDMS | AgNWs | 3.48 | 26.29 nA | - | - | - | ||
| 2017 | Li et al. [121] | PDMS | AgNWs/CuNWs/Al | 90 | 9 µA | - | - | - | ||
| Smart face masks | 2021 | Wang et al. [122] | FEP/NBR | Cu/AgNW | 1.8 k | - | - | - | - | Increases performance and efficiency/can cause skin sensitivity in some users |
| 2022 | Lu et al. [123] | FEP/acrylic | Al | 8 | 0.8 µA | - | - | - | ||
| 2021 | Ghatak et al. [124] | PVC/PP/latex rubber/PI | Nylon/Pu | ~90 | ~25 mA | - | - | 400 mW | ||
| 2017 | Xue et al. [125] | PVDF | Al | 42 | 2.5 µA | - | - | 8.31 µW | ||
| Sleep monitoring | 2020 | Zhang et al. [127] | PTFE | Cu | ~350 | ~40 µA | - | - | 11.6 mW | Improves the treatment of insomnia and sleep disorders |
| 2016 | Song et al. [129] | CPP/PA | Al/Cu | 55 | 0.9 µA | - | ~120 mW/m2 | - | ||
| 2022 | Kou et al. [130] | PDMS/Kapton | Al | ~65 | ~0.7 µA | - | - | - | ||
| 2018 | Ding et al. [131] | PDMS | Al/textile electrode | ~16 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Self-powered nerve/muscle stimulation | 2019 | Wang et al. [133] | PTFE | Al | - | 55 µA | - | - | - | Monitoring the condition of the nerve/muscle stimulation system/incompatible with the cellular tissues in some people |
| 2019 | Wang et al. [38] | PTFE | Al | 47 | 35 µA | - | - | 95 µW | ||
| 2019 | Tian et al. [25] | PTFE/PDMS | Au/PET | 100 | 1.6 µA | - | - | - | ||
| 2019 | Wang et al. [39] | PTFE | Al | - | 40 µA | - | - | ~500 µW |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahimi Sardo, F.; Rayegani, A.; Matin Nazar, A.; Balaghiinaloo, M.; Saberian, M.; Mohsan, S.A.H.; Alsharif, M.H.; Cho, H.-S. Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomedical Sensors: From Design to Application. Biosensors 2022, 12, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090697
Rahimi Sardo F, Rayegani A, Matin Nazar A, Balaghiinaloo M, Saberian M, Mohsan SAH, Alsharif MH, Cho H-S. Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomedical Sensors: From Design to Application. Biosensors. 2022; 12(9):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090697
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahimi Sardo, Fatemeh, Arash Rayegani, Ali Matin Nazar, Mohammadali Balaghiinaloo, Mohammadhossein Saberian, Syed Agha Hassnain Mohsan, Mohammed H. Alsharif, and Ho-Shin Cho. 2022. "Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomedical Sensors: From Design to Application" Biosensors 12, no. 9: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090697
APA StyleRahimi Sardo, F., Rayegani, A., Matin Nazar, A., Balaghiinaloo, M., Saberian, M., Mohsan, S. A. H., Alsharif, M. H., & Cho, H.-S. (2022). Recent Progress of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Biomedical Sensors: From Design to Application. Biosensors, 12(9), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12090697










