Portable Vertical Graphene@Au-Based Electrochemical Aptasensing Platform for Point-of-Care Testing of Tau Protein in the Blood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
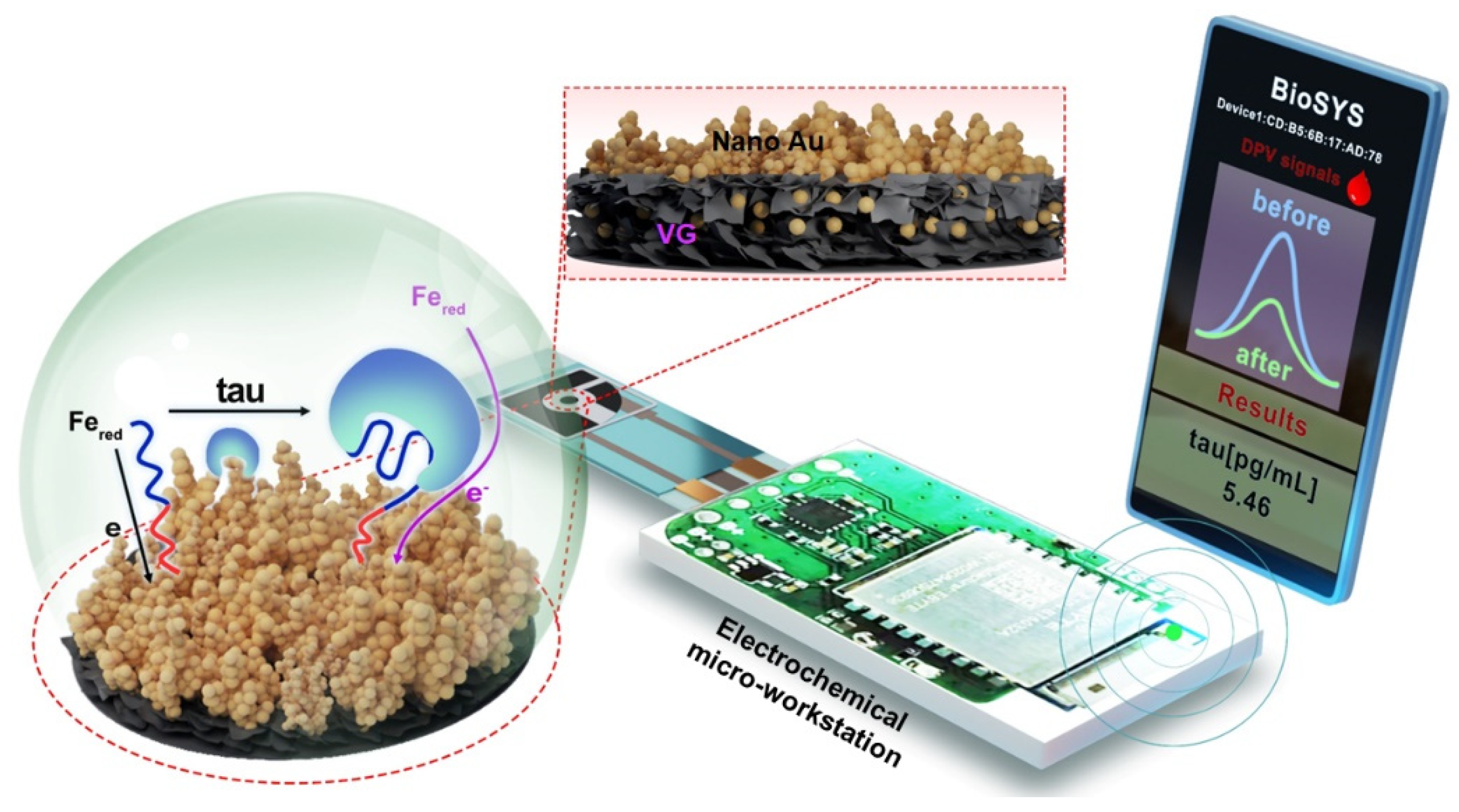
2.3. Preparation of VG@Au Electrode
2.4. Fabrication and Analytical Performace of Portable Sensing Platform
2.5. Detection of Clinical Serum Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of VG@Au
3.2. Fabrication and Analytical Performance of Portable Electrochemical Sensing Platform
3.3. Selectivity and Stability
3.4. Application of Portable Electrochemcial Aptasensing Platform in Clinical Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheltens, P.; de Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C.E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Haber, A.; Preuss, C.; John, C.; Uyar, A.; Yang, H.S.; Logsdon, B.A.; Philip, V.; Karuturi, R.K.M.; Carter, G.W.; et al. Transfer learning-trained convolutional neural networks identify novel MRI biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease progression. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 13, e12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanseeuw, B.J.; Betensky, R.A.; Jacobs, H.I.L.; Schultz, A.P.; Sepulcre, J.; Becker, J.A.; Cosio, D.M.O.; Farrell, M.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Mormino, E.C.; et al. Association of Amyloid and Tau With Cognition in Preclinical Alzheimer Disease: A Longitudinal Study. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Limorenko, G.; Lashuel, H.A. Revisiting the grammar of Tau aggregation and pathology formation: How new insights from brain pathology are shaping how we study and target Tauopathies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 513–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscoso, A.; Karikari, T.K.; Grothe, M.J.; Ashton, N.J.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Snellman, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Schöll, M. CSF biomarkers and plasma p-tau181 as predictors of longitudinal tau accumulation: Implications for clinical trial design. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yang, C.; Luo, H. Current trends in blood biomarker detection and imaging for Alzheimer’s disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 210, 114278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, S.; Scarano, S.; Fedeli, S.; Pascale, E.; Cicchi, S.; Ravelet, C.; Peyrin, E.; Minunni, M. Toward sensitive immuno-based detection of tau protein by surface plasmon resonance coupled to carbon nanostructures as signal amplifiers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbi, K.; Uk, L.J.; Soohyun, K.; Sojin, S.; Jun, S.S. A nanoplasmonic Biosensor for Ultrasensitive detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarker using a Chaotropic agent. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Han, X.X.; Ozaki, Y.; Zhao, B. In-situ fingerprinting phosphorylated proteins via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Single-site discrimination of Tau biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongsung, P.; Hyun, K.J.; Jin, K.H.; Dongtak, L.; David, S.L.; Sung, Y.D.; Seon, H.K. Multiplexed femtomolar detection of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in biofluids using a reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112505. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, K.S.; Dongwoo, K.; Mijin, Y.; Gon, S.J.; Hyun, L.S. The role of graphene patterning in field-effect transistor sensors to detect the tau protein for Alzheimer’s disease: Simplifying the immobilization process and improving the performance of graphene-based immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113519. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, C.; Jiao, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, D.; Ning, L.; Xiang, Y.; Li, G. Polyvalent Biotinylated Aptamer Scaffold for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Tau Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15162–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-N.; Xu, D.; Ho, S.-L.; Wong, M.S.; Li, H.-W. Ultra-sensitive detection of protein biomarkers for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4012–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, K.; Guo, W.; Dai, B.; Liang, Y.; Dai, J.; Cui, M. Novel D-A-D based near-infrared probes for the detection of beta-amyloid and Tau fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8717–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X. Integrated individually electrochemical array for simultaneously detecting multiple Alzheimer’s biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 162, 112253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Xu, T. Portable electrochemical micro-workstation platform for simultaneous detection of multiple Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javad, Z.; Zahra, K.; Khalil, A.; Mohammad, T.S.; Hossein, H.; Mohammd, D.N. Current progress in aptamer-based sensing tools for ultra-low level monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 210, 114278. [Google Scholar]
- Sailapu, S.K.; Dutta, D.; Simon, A.T.; Ghosh, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Smartphone controlled interactive portable device for theranostics in vitro. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Pereira, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Cardoso, V.F. Biodegradable polymer-based microfluidic membranes for sustainable point-of-care devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennareddy, S.; Kalagara, R.; Smith, C.; Matsoukas, S.; Kellner, C.P. Abstract TP106: Diagnostic Capability Of An Emerging Portable Stroke Detection Device In Clinical Practice. Stroke 2022, 53, ATP106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, K.; Geng, X.; Guan, Y. Portable instruments for on-site analysis of environmental samples. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 154, 116653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Moon, D.; An, J.E.; Park, S.J.; Seo, S.E.; Ha, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Phyo, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Wireless portable bioelectronic nose device for multiplex monitoring toward food freshness/spoilage. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 215, 114551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambhir, S.S.; Ge, T.J.; Vermesh, O.; Spitler, R.; Gold, G.E. Continuous health monitoring: An opportunity for precision health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Barnaghi, P.; Nilforooshan, R.; Rostill, H.; Soreq, E.; Sharp, D.J.; Scott, G. Home monitoring of vital signs and generation of alerts in a cohort of people living with dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 17, e055151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y.; Ma, X.; Ding, S.-N. Bipolar electrochemiluminescence sensors: From signal amplification strategies to sensing formats. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W. The Era of Digital Health: A Review of Portable and Wearable Affinity Biosensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1906713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, N.F.B.; Santos, M.S.F.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Wang, J.; Angnes, L. Screen-Printed Technologies Combined with Flow Analysis Techniques: Moving from Benchtop to Everywhere. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cui, X.; Gong, Y.; Xu, X.; Gao, B.; Wen, T.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Portable microfluidic and smartphone-based devices for monitoring of cardiovascular diseases at the point of care. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, H.S. Diagnostic methods and potential portable biosensors for coronavirus disease 2019. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, C.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, Y.; Gu, M.B. Aptamer duo-based portable electrochemical biosensors for early diagnosis of periodontal disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Tripathy, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.; Chaudhury, G.; Singh, S.G. Towards point-of-care diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Multi-analyte based portable chemiresistive platform for simultaneous detection of beta-amyloid (1-40) and (1-42) in plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, X.; Fu, W. Review of Vertical Graphene and its Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 9561–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Shan, J.J.; Cui, L.Z.; Qi, Y.; Hu, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, Z.F. Direct Plasma-Enhanced-Chemical-Vapor-Deposition Syntheses of Vertically Oriented Graphene Films on Functional Insulating Substrates for Wide-Range Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 2202026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, I.T.; Li, X.; Yadikar, H.A.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Lyu, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, K.K.; Tan, W. Identification and Characterization of DNA Aptamers Specific for Phosphorylation Epitopes of Tau Protein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14314–14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzino, C.A.; Serafín, V.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Calero, M.; Lobo, A.O.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; et al. An electrochemical immunosensor using gold nanoparticles-PAMAM-nanostructured screen-printed carbon electrodes for tau protein determination in plasma and brain tissues from Alzheimer patients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yola, B.B.; Karaman, C.; Özcan, N.; Atar, N.; Polat, I.; Yola, M.L. Electrochemical Tau Protein Immunosensor Based on MnS/GO/PANI and Magnetite-incorporated Gold Nanoparticles. Electroanal. 2022, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.; Shui, B.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Song, S.; Guo, Z. Development of a Label-Free Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of Tau381 and its Preliminary Application in AD and Non-AD Patients’ Sera. Biosensors 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hun, X.; Kong, X. An enzyme linked aptamer photoelectrochemical biosensor for Tau-381 protein using AuNPs/MoSe2 as sensing material. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 192, 113666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Methods | Biomarkers | LOD | Linear Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemistry | T-tau | 0.142 pg/mL | 0.1–1000 pg/mL | [16] |
| Electrochemistry | T-tau | 0.059 pg/mL | 0.1–100 pg/mL | [15] |
| Electrochemistry | tau | 1.7 pg/mL | 0–2.5 ng/mL | [35] |
| Electrochemistry | tau | 0.46 pg/mL | 4.6 pg/mL–4.6 μg/mL | [36] |
| Electrochemistry | Tau381 | 28 pg/mL | 40–4000 pg/mL | [37] |
| FET sensors | tau | 0.01 pg/mL | 10 fg/mL–1ng/mL | [11] |
| FET sensors | tau | 1.003 pg/mL | 0.1pg/mL–100 ng/mL | [10] |
| Photoelectrochemistry | Tau381 | 0.013 pg/mL | 0–40 ng/mL | [38] |
| Fluorescence | Tau441 | 0.56 pg/mL | 0–46 pg/mL | [13] |
| LSPR | tau | 46 ng/mL | 23–575 ng/mL | [7] |
| Electrochemistry | tau | 0.034 pg/mL | 0.1 pg/mL–1 ng/mL | This work |
| Sample | Biomarkers | This Sensor (pg/mL) | Quanterix Co. (pg/mL) | Margin of Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tau | 2.19 ± 0.15 | 2.08 ± 0.08 | +5.29% |
| 2 | tau | 4.12 ± 0.11 | 3.93 ± 0.12 | +4.83% |
| 3 | tau | 4.28 ± 0.18 | 4.37 ± 0.09 | −2.06% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Q.; Xu, T. Portable Vertical Graphene@Au-Based Electrochemical Aptasensing Platform for Point-of-Care Testing of Tau Protein in the Blood. Biosensors 2022, 12, 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080564
Liu Y, Liu X, Li M, Liu Q, Xu T. Portable Vertical Graphene@Au-Based Electrochemical Aptasensing Platform for Point-of-Care Testing of Tau Protein in the Blood. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):564. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080564
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yibiao, Xingyun Liu, Mifang Li, Qiong Liu, and Tailin Xu. 2022. "Portable Vertical Graphene@Au-Based Electrochemical Aptasensing Platform for Point-of-Care Testing of Tau Protein in the Blood" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080564
APA StyleLiu, Y., Liu, X., Li, M., Liu, Q., & Xu, T. (2022). Portable Vertical Graphene@Au-Based Electrochemical Aptasensing Platform for Point-of-Care Testing of Tau Protein in the Blood. Biosensors, 12(8), 564. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080564







