Highly Sensitive Love Mode Acoustic Wave Platform with SiO2 Wave-Guiding Layer and Gold Nanoparticles for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Finite Element Analysis
2.2. Fabrication Process of SAW Device
2.3. Preparation of AuNPs–Antibody Conjugates
2.4. Surface Functionalization of the Love Wave Sensor
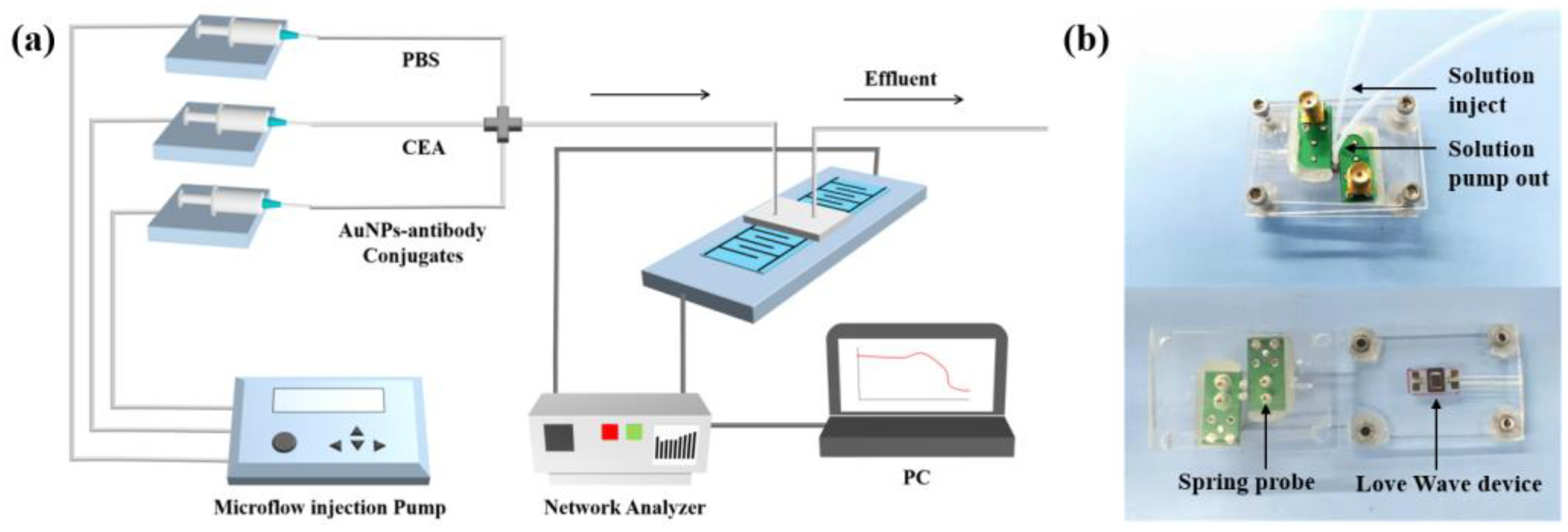
2.5. Biosensing System
2.6. Detection Strategy of CEA
3. Results and Discussion
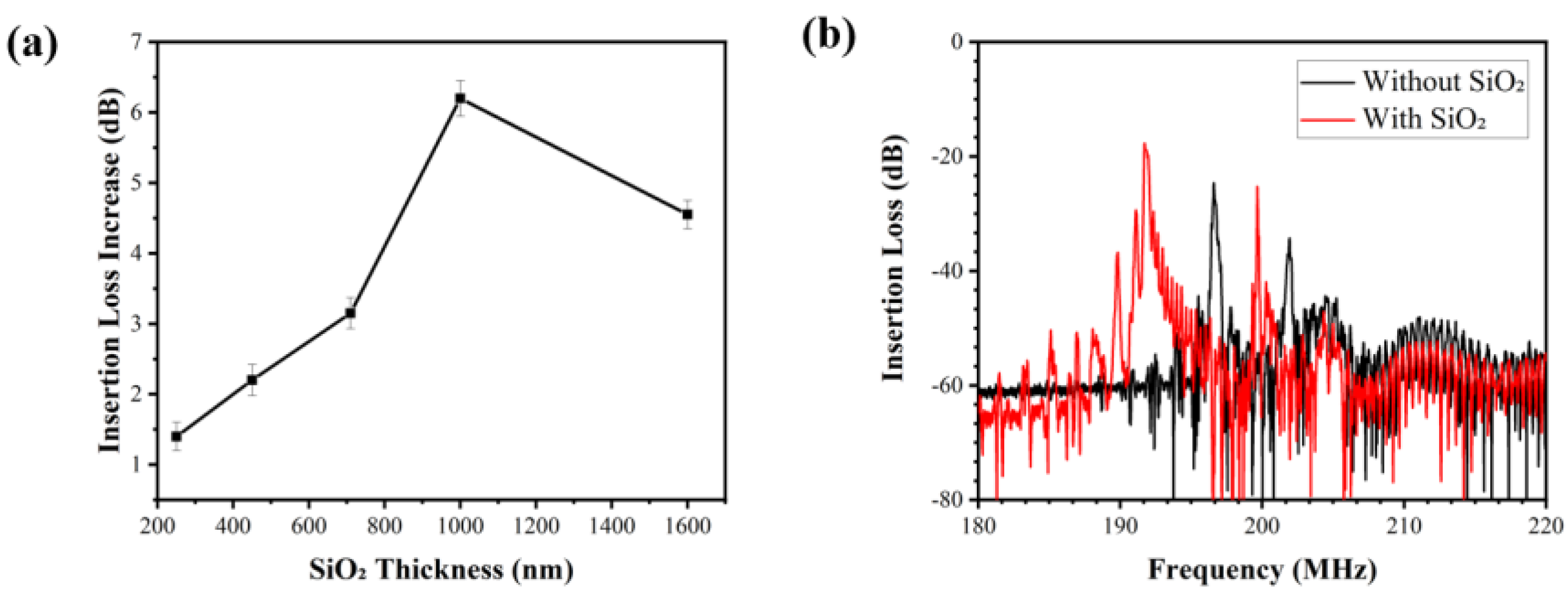
3.1. Optimized Parameters of Wave-Guiding Layer
3.2. Characterization of AuNPs and Surface Functionalization
3.3. Sensing Performance for CEA Detection
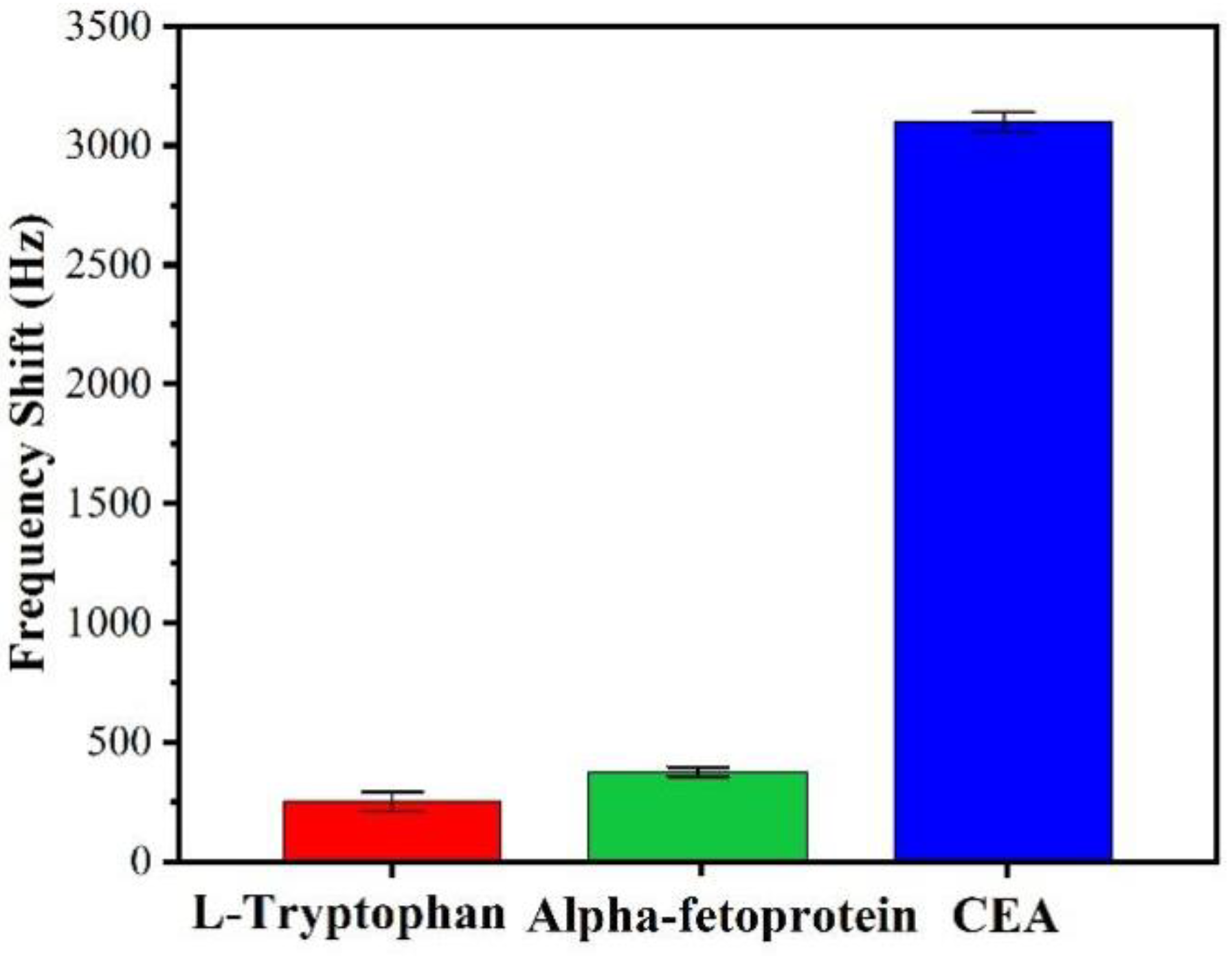
3.4. Interferences of Nonspecific Adsorptions
4. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noor, M.M.; Narwal, V. Machine learning approaches in cancer detection and diagnosis: Mini review. IJ Mutil Re App St 2017, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Crosbie, P.A.; Shah, R.; Summers, Y.; Dive, C.; Blackhall, F. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in early stage NSCLC: CTCs and serum/plasma markers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.W.; Peng, Y.H.; Chen, B.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Shen, J.H.; Xu, L.Y. Autoantibodies as potential biomarkers for the early detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steward, A.M.; Nixon, D.; Zamcheck, N.; Aisenberg, A. Carcinoembryonic antigen in breast cancer patients: Serum levels and disease progress. Cancer 1974, 33, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibalhossaini, F.; Ebadi, P. Evidence for CEA release from human colon cancer cells by an endogenous GPI-PLD enzyme. Cancer Lett. 2006, 234, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunnet, M.; Sorensen, J.B. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamcheck, N.; Martin, E.W. Factors controlling the circulating CEA levels in pancreatic cancer: Some clinical correlations. Cancer 1981, 47, 1620–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.; Kellen, J.A.; Lickrish, G.M.; Bush, R.S. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and other tumor markers in ovarian and cervical cancer. Cancer 1978, 42, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, T.P.; Jaeger, P.H.; Bertholet, M.M.; Ruegsegger, C.H.; Loosli, R.M.; Pettavel, J. Detection of recurrence of large-bowel carcinoma by radioimmunoassay of circulating carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). Lancet 1974, 304, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousserie, G.; Grinevich, R.; Brazhnik, K.; Even-Desrumeaux, K.; Reveil, B.; Tabary, T.; Sukhanova, A. Detection of carcinoembryonic antigen using single-domain or full-size antibodies stained with quantum dot conjugates. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Wang, M.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H. Sensitive sandwich ELISA based on a gold nanoparticle layer for cancer detection. Analyst 2012, 137, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.J.; Niu, D.J.; Xie, W.Z.; Wang, W. A disposable electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on nano-Au/multi-walled carbon nanotubes–chitosans nanocomposite film modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, Z.; Su, F.; Gao, L.; Pang, X.; Cao, W.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay for CEA through host–guest interaction of β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene and Cu@ Ag core–shell nanoparticles with adamantine-modified antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cushing, S.K.; Zhang, J.; Suri, S.; Evans, R.; Petros, W.P.; Wu, N. Three-dimensional hierarchical plasmonic nano-architecture enhanced surface-enhanced Raman scattering immunosensor for cancer biomarker detection in blood plasma. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4967–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Fu, A. An ultra-sensitive chemiluminescence immunosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen using HRP-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as labels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Overview of piezoelectric biosensors, immunosensors and DNA sensors and their applications. Materials 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, R.M.; Mekalanos, J.J.; Jacobs, M.B.; Lubrano, G.J.; Guilbault, G.G. Quartz crystal microbalance detection of Vibrio cholerae O139 serotype. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 187, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, S.; Hauck, S.; Yacoub-George, E.; Wolf, H.; Koch, S.; Kößlinger, C.; Hieber, K. Application of bioactive layers for chemical sensors and analysis systems. Mater. Sci. Forum 1998, 287–288, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, S.; Qazi, H.I.A.; Luo, J.; Fu, C.; Tao, R.; Rauf, S.; Fu, Y. Ultrasensitive Leaky Surface Acoustic Wave Immunosensor for Real-Time Detection of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Biological Fluids. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruhl, F.J.; Rapp, B.E.; Rapp, M.; Länge, K. Surface acoustic wave (SAW) biosensor chip system-a promising alternative for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.; Quan, A.; Li, C.; Fu, C.; Fu, Y.Q. Graphene oxide-Au nano particle coated quartz crystal microbalance biosensor for the real time analysis of carcinoembryonic antigen. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 4118–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.; Quan, A.; Qiu, C.; Cao, W.; Fu, C.; Fu, Y.Q. Highly selective and label-free Love-mode surface acoustic wave biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection using a self-assembled monolayer bioreceptor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 518, 146061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Tran, V.T.; Pudasaini, S.; Gautam, A.; Lee, J.M.; Fu, Y.Q.; Du, H. Large-Scale Fabrication of 3D Scaffold-Based Patterns of Microparticles and Breast Cancer Cells using Reusable Acoustofluidic Device. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Ao, D.; Li, W.; Zu, X.; Li, S.; Fu, Y.Q. NH3 sensing property and mechanisms of quartz surface acoustic wave sensors deposited with SiO2, TiO2, and SiO2-TiO2 composite films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matatagui, D.; Moynet, D.; Fernández, M.J.; Fontecha, J.; Esquivel, J.P.; Gràcia, I.; Horrillo, M.C. Detection of bacteriophages in dynamic mode using a Love-wave immunosensor with microfluidics technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournel, F.; Baco, E.; Mamani-Matsuda, M.; Degueil, M.; Bennetau, B.; Moynet, D.; Rebière, D. Love wave biosensor for real-time detection of okadaic acid as DSP phycotoxin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 170, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Jung, J.; Hahn, Y.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.S. A centrifugally actuated point-of-care testing system for the surface acoustic wave immunosensing of cardiac troponin I. Analyst 2013, 138, 2558–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandas, P.J.; Luo, J.; Prabakaran, K.; Chen, F.; Fu, Y.Q. Highly stable, love-mode surface acoustic wave biosensor using Au nanoparticle-MoS2-rGO nano-cluster doped polyimide nanocomposite for the selective detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiersten, H.F. Elastic surface waves guided by thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 40, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Venema, A. Theoretical comparison of sensitivities of acoustic shear wave modes for (bio) chemical sensing in liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 61, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Lubking, G.W.; Vellekoop, M.J.; Venema, A. Love waves for (bio)-chemical sensing in liquids. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1992 Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings, Tuscon, AZ, USA, 20–23 October 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby, B.; Vellekoop, M.J. Properties of Love waves: Applications in sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 1997, 6, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizeli, E.; Stevenson, A.C.; Goddard, N.J.; Lowe, C.R. Acoustic Love plate sensors: Comparison with other acoustic devices utilizing surface SH waves. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 14, 638–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmusson, A.; Gizeli, E. Comparison of poly (methylmethacrylate) and Novolak waveguide coatings for an acoustic biosensor. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 5911–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Harding, G.L. A multilayer structure for Love-mode acoustic sensors. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 1998, 65, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondoh, J.; Shiokawa, S. A liquid sensor based on a shear horizontal SAW device. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 1993, 76, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandas, P.J.; Prabakaran, K.; Luo, J.; Fu, C.; Fu, Y.Q.; MG, D.H. Ti3C2Tx MXene-Au nanoparticles doped polyimide thin film as a transducing bioreceptor for real-time acoustic detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 112998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Su, Y.; Fan, C.; Bhethanabotla, V.R. Gold nanoparticle-based low limit of detection Love wave biosensor for carcinoembryonic antigens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 95, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šetka, M.; Bahos, F.A.; Matatagui, D.; Potoček, M.; Kral, Z.; Drbohlavová, J.; Vallejos, S. Love wave sensors based on gold nanoparticle-modified polypyrrole and their properties to ammonia and ethylene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yuan, Y.J. Quantification of Staphylococcus aureus using surface acoustic wave sensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8411–8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zou, Y.; An, C.; Ying, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, P. Sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in exhaled breath condensate using surface acoustic wave immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 217, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kal-Koshvandi, A.T. Recent advances in optical biosensors for the detection of cancer biomarker α-fetoprotein (AFP). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerbrey, G. Verwendung von Schwingquarzen zur Wägung dünner Schichten und zur Mikrowägung. Z. Für Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X. Film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) as biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzak, K.A.; Gizeli, E. Love Wave Biosensors; Handbook of Biosensors and Biochips; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, J.; Bufacchi, R.; Kondoh, J.; Duffy, D.M.; McKendry, R.A. Determining biosensing modes in SH-SAW device using 3D finite element analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiełczyński, P. Sensitivity of Love surface waves to mass loading. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Harding, G.L.; Ogilvy, J.A.; Dencher, P.R.; Lake, M. A study of Love-wave acoustic sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1996, 56, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabar, K.C.; Brown, K.R.; Keating, C.D.; Stranick, S.J.; Tang, S.L.; Natan, M.J. Nanoscale characterization of gold colloid monolayers: A comparison of four techniques. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, V.; Surwade, S.P.; Ammu, S.; Agnihotra, S.R.; Jain, S.; Roberts, K.E.; Manohar, S.K. All-organic vapor sensor using inkjet-printed reduced graphene oxide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2154–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Luo, J.; Fu, C.; Tao, R.; Li, H.; Fu, Y. Highly Sensitive Love Mode Acoustic Wave Platform with SiO2 Wave-Guiding Layer and Gold Nanoparticles for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens. Biosensors 2022, 12, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070536
Li C, Zhang J, Xie H, Luo J, Fu C, Tao R, Li H, Fu Y. Highly Sensitive Love Mode Acoustic Wave Platform with SiO2 Wave-Guiding Layer and Gold Nanoparticles for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070536
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chong, Jikai Zhang, Haiyu Xie, Jingting Luo, Chen Fu, Ran Tao, Honglang Li, and Yongqing Fu. 2022. "Highly Sensitive Love Mode Acoustic Wave Platform with SiO2 Wave-Guiding Layer and Gold Nanoparticles for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070536
APA StyleLi, C., Zhang, J., Xie, H., Luo, J., Fu, C., Tao, R., Li, H., & Fu, Y. (2022). Highly Sensitive Love Mode Acoustic Wave Platform with SiO2 Wave-Guiding Layer and Gold Nanoparticles for Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigens. Biosensors, 12(7), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070536





