Emerging Methods of Monitoring Volatile Organic Compounds for Detection of Plant Pests and Disease
Abstract
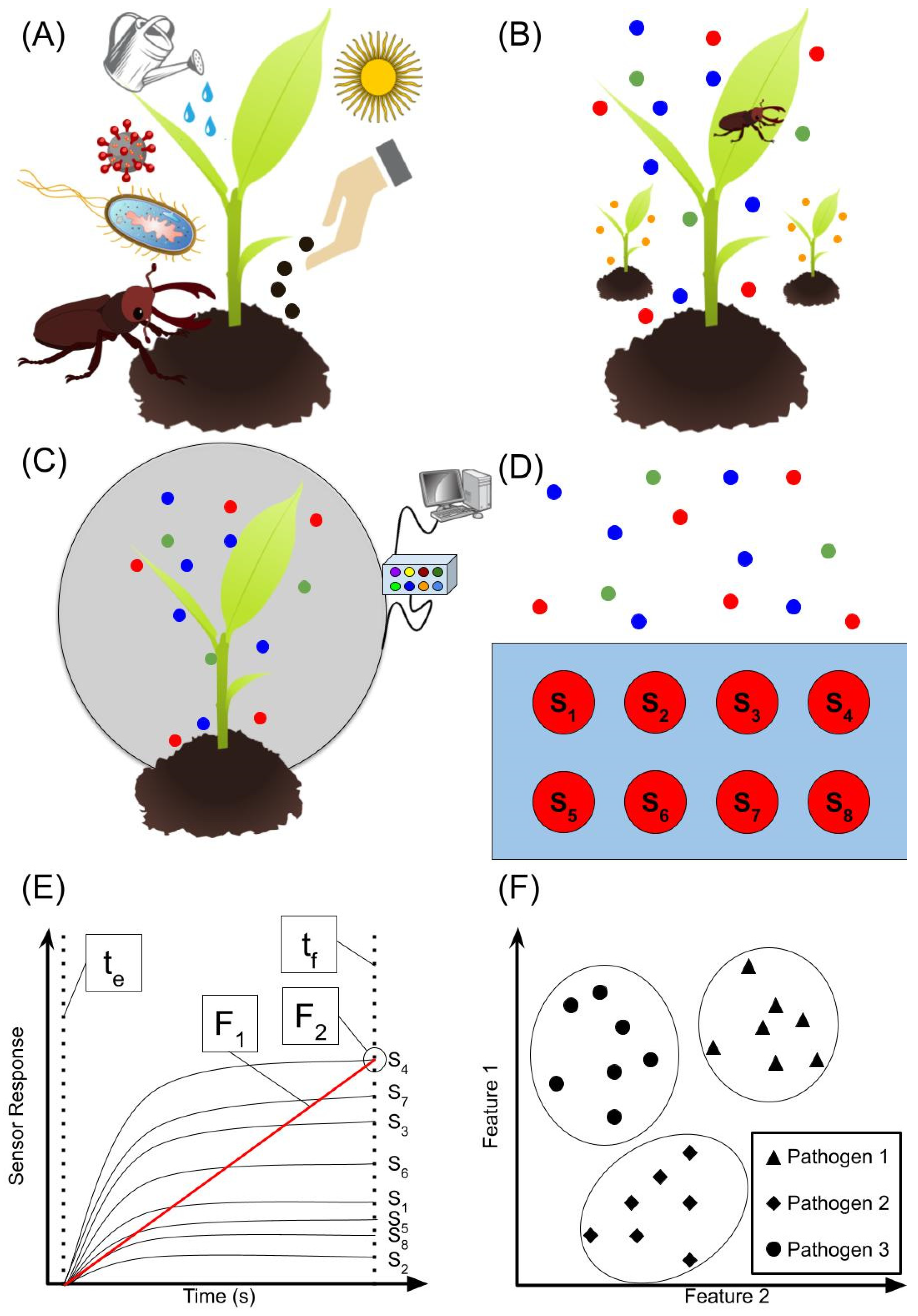
1. Introduction
2. Emerging VOC Sensing Methods
2.1. Methods with Electrical Variation
2.1.1. MOS Sensors
2.1.2. CP Sensors
2.1.3. Electrochemical Sensors
2.2. Methods with Variance in Other Properties
3. Challenges and Future Improvements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natural Resources Canada. Forest Pest Management. Available online: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/forests-forestry/wildland-fires-insects-disturban/forest-pest-management/13361 (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency. Plant Pest Surveillance. Available online: https://www.inspection.gc.ca/plant-health/plant-pests-invasive-species/plant-pest-surveillance/eng/1344466499681/1344466638872 (accessed on 17 January 2020).
- Poland, T.M.; Rassati, D. Improved biosecurity surveillance of non-native forest insects: A review of current methods. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Molden, D.J.; Makin, I.W. Remote sensing for irrigated agriculture: Examples from research and possible applications. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 46, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azfar, S.; Nadeem, A.; Basit, A. Pest detection and control techniques using wireless sensor network: A review. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. JEZS 2015, 3, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Everitt, J.H.; Escobar, D.E.; Appel, D.N.; Riggs, W.G.; Davis, M.R. Using airborne digital imagery for detecting oak wilt disease. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankin, R.W.; Smith, M.T.; Tropp, J.M.; Atkinson, E.B.; Jong, D.Y. Detection of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) Larvae in Different Host Trees and Tissues by Automated Analyses of Sound-Impulse Frequency and Temporal Patterns. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.; Ray, A.; Dash, S.; Mishra, A.; Achary, K.G.; Nayak, S.; Singh, S. Fungal disease detection in plants: Traditional assays, novel diagnostic techniques and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banga, K.S.; Kotwaliwale, N.; Mohapatra, D.; Giri, S.K. Techniques for insect detection in stored food grains: An overview. Food Control 2018, 94, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.D.; Marcotte, M.; Noseworthy, M.; Ramsfield, T. Forest Biosecurity in Canad—An Integrated Multi-Agency Approach. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2021, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, I.; Sabella, E.; Monteduro, A.G.; Chiriacò, M.S.; De Bellis, L.; Luvisi, A.; Maruccio, G. Advances in plant disease detection and monitoring: From traditional assays to in-field diagnostics. Sensors 2021, 21, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ramasamy, R.P. Current and prospective methods for plant disease detection. Biosensors 2015, 5, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laothawornkitkul, J.; Moore, J.P.; Taylor, J.E.; Possell, M.; Gibson, T.D.; Hewitt, C.N.; Paul, N.D. Discrimination of plant volatile signatures by an electronic nose: A potential technology for plant pest and disease monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8433–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effah, E.; Holopainen, J.K.; McCormick, A.C. Potential roles of volatile organic compounds in plant competition. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2019, 38, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.J.; Smith, L.; Baig, N. An overview of plant volatile metabolomics, sample treatment and reporting considerations with emphasis on mechanical damage and biological control of weeds. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholl, D.; Boland, W.; Hansel, A.; Loreto, F.; Rö Se, U.S.R.; Schnitzler, J.R.-P. Practical approaches to plant volatile analysis. Plant J. 2006, 45, 540–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tholl, D.; Hossain, O.; Weinhold, A.; Röse, U.S.; Wei, Q. Trends and applications in plant volatile sampling and analysis. Plant J. 2021, 106, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrueta, L.A.; Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Héberger, K. Supervised pattern recognition in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1158, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Ling, P.; Zhu, H.; Keener, H.M. Plant pest detection using an artificial nose system: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Farha, F.; Li, Q.; Wan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ning, H. Review on smart gas sensing technology. Sensors 2019, 19, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Applications of electronic-nose technologies for non-invasive early detection of plant, animal and human diseases. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, A.; Blasioli, S.; Biondi, E.; Bertaccini, A.; Braschi, I.; Spinelli, F. Potential applications and limitations of electronic nose devices for plant disease diagnosis. Sensors 2017, 17, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, R.; Ryu, C.M. Biogenic Volatile Compounds for Plant Disease Diagnosis and Health Improvement. Plant Pathol. J. 2018, 34, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, A.; Spinelli, F.; Donati, I.; Ryu, C.M.; Kloepper, J.W. Bacterial volatile compound-based tools for crop management and quality. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, D.; Ning, H. A survey on gas sensing technology. Sensors 2012, 12, 9635–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemistry LibreTexts. 3.4: Selecting an Analytical Method. Available online: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/BethuneCookman_University/B-CU%3A_CH-345_Quantitative_Analysis/Book%3A_Analytical_Chemistry_2.1_(Harvey)/03%3A__The_Vocabulary_of_Analytical_Chemistry/3.04%3A_Selecting_an_Analytical_Method (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Operating Principle—MOS-Type Gas Sensor. Available online: https://www.figarosensor.com/technicalinfo/principle/mos-type.html (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, E.; Blasioli, S.; Galeone, A.; Spinelli, F.; Cellini, A.; Lucchese, C.; Braschi, I. Detection of potato brown rot and ring rot by electronic nose: From laboratory to real scale. Talanta 2014, 129, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, H.; Luo, X.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Estimation of the Age and Amount of Brown Rice Plant Hoppers Based on Bionic Electronic Nose Use. Sensors 2014, 14, 18114–18130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzolo, A.; Bianchi, G.; Lucido, P.; Cangelosi, B.; Pozzi, L.; Villa, G.; Clematis, F.; Pasini, C.; Curir, P. Electronic nose for the early detection of red palm weevil (rhynchophorus ferrugineous olivier) infestation in palms: Preliminary results. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1099, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, A.; Biondi, E.; Blasioli, S.; Rocchi, L.; Farneti, B.; Braschi, I.; Savioli, S.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Biasioli, F.; Spinelli, F. Early detection of bacterial diseases in apple plants by analysis of volatile organic compounds profiles and use of electronic nose. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2016, 168, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutolo, M.F.; Iliescu, D.; Clarkson, J.P.; Covington, J.A. Early identification of potato storage disease using an array of metal-oxide based gas sensors. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 116, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, S. Discrimination among tea plants either with different invasive severities or different invasive times using MOS electronic nose combined with a new feature extraction method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 143, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y. Detection of pest species with different ratios in tea plant based on electronic nose. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2019, 174, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, Q. Evaluation of E-nose data analyses for discrimination of tea plants with different damage types. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2019, 126, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, S. Early Diagnosis of Botrytis Cinerea Infestation of Tomato Plant by Electronic Nose. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Srivastava, S.; Panda, B.K.; Mishra, H.N. Prediction of Sitophilus granarius infestation in stored wheat grain using multivariate chemometrics & fuzzy logic-based electronic nose analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 152, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zheng, L.; Dong, S.; Gong, Z.; Sang, M.; Long, X.; Luo, M.; Peng, H. Rapid detection and classification of citrus fruits infestation by Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) based on electronic nose. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 147, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Inocente, E.A.A.; Acosta, N.; Keener, H.M.; Zhu, H.; Ling, P.P. Development of fast e-nose system for early-stage diagnosis of aphid-stressed tomato plants. Sensors 2019, 19, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Gu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Evaluation of trunk borer infestation duration using MOS E-nose combined with different feature extraction methods and GS-SVM. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowik, P.; Adamowicz, L.; Tarakowski, R.; Wacławik, P.; Oszako, T.; Ślusarski, S.; Tkaczyk, M. Application of a low-cost electronic nose for differentiation between pathogenic oomycetes pythium intermedium and phytophthora plurivora. Sensors 2021, 21, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, N.; Mao, S.; Tu, K. Early detection and classification of pathogenic fungal disease in post-harvest strawberry fruit by electronic nose and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liang, G.; Tian, H.; Sun, J.; Wan, C. Electronic nose-based technique for rapid detection and recognition of moldy apples. Sensors 2019, 19, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Early discrimination and growth tracking of Aspergillus spp. contamination in rice kernels using electronic nose. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchorab, Z.; Frąc, M.; Guz, Ł.; Oszust, K.; Łagód, G.; Gryta, A.; Bilińska-Wielgus, N.; Czerwiński, J. A method for early detection and identification of fungal contamination of building materials using e-nose. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, B.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Rafiee, S. Quality detection of pomegranate fruit infected with fungal disease. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazaika, S.; Choudhury, R.; Saikia, S.; Sarma, U. Pathogen Detection in Khasi Mandarin Orange using Serological and Electronic Nose Diagnostic Technique. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 9, 2981–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresnawaty, I.; Mulyatni, A.S.; Eris, D.D.; Prakoso, H.T.; Tri-Panji; Triyana, K.; Widiastuti, H. Electronic nose for early detection of basal stem rot caused by Ganoderma in oil palm. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 468, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, M.J.; Abu-Khalaf, N.; Molina-Cabrera, C.; Ruiz-Canales, A.; Ramos, J.; Bahder, B.W. Detection of Lethal Bronzing Disease in Cabbage Palms (Sabal palmetto) Using a Low-Cost Electronic Nose. Biosensors 2020, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.C.; Steinthal, G.; Sunshine, S. Conductive polymer-carbon black composites-based sensor arrays for use in an electronic nose. Sens. Rev. 1999, 19, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Pitt, W.G.; McGrath, L.K.; Ho, C.K. Modeling carbon black/polymer composite sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, T.D.; Prosser, O.; Hulbert, J.N.; Marshall, R.W.; Corcoran, P.; Lowery, P.; Ruck-Keene, E.A.; Heron, S. Detection and simultaneous identification of microorganisms from headspace samples using an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gitaitis, R.; Tollner, B.; Sumner, P.; MacLean, D. Onion sour skin detection using a gas sensor array and support vector machine. Sens. Instrum. Food Qual. Saf. 2009, 3, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Krewer, G.; Kays, S.J. Blueberry Postharvest Disease Detection Using an Electronic Nose; Written for presentation at the 2009 ASABE annual international meeting, Reno, NV, USA, 21–24 June 2009; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2009; Volume 8, pp. 5289–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, W.G.; Khalilian, A.; Han, Y.J.; Greene, J.K.; Degenhardt, D.C. Detecting stink bugs/damage in cotton utilizing a portable electronic nose. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Schmidt, N.E.; Gitaitis, R. Detection of onion postharvest diseases by analyses of headspace volatiles using a gas sensor array and GC-MS. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, D.C.; Greene, J.K.; Khalilian, A. Temporal dynamics and electronic nose detection of stink bug-induced volatile emissions from cotton bolls. Psyche 2012, 2012, 236762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, R.; Laothawornkitkul, J.; Iliescu, D.; Hines, E.; Leeson, M.; Napier, R.; Moore, J.P.; Paul, N.D.; Hewitt, C.N.; Taylor, J.E. Plant pest and disease diagnosis using electronic nose and support vector machine approach. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2012, 119, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.; Nascimento, H.M.; Yamauchi, E.Y.; Li, R.W.C.; Esteves, C.H.A.; Rehder, G.P.; Gaylarde, C.C.; Shirakawa, M.A. A conductive polymer based electronic nose for early detection of Penicillium digitatum in post-harvest oranges. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 2766–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Bacterial Wetwood Detection in Fagus grandifolia and Prunus serotina Sapwood using a Conducting Polymer Electronic-nose Device. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Sensor Device Technologies and Applications, Lisbon, Portugal, 16–20 November 2014; pp. 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lampson, B.D.; Degenhardt, D.C.; Greene, J.K.; Khalilian, A.; Han, Y.J. Development of a Portable Electronic Sensor for Detection of the Kudzu Bug, Megacopta cribraria (Fabricius) (Hemiptera: Plataspidae). Adv. Entomol. 2017, 05, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Operating Principle—Electrochemical-Type Gas Sensor. Available online: https://www.figarosensor.com/technicalinfo/principle/electrochemical-type.html (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Venkatasetty, H.V. Electrochemical amperometric gas sensors for environmental monitoring and control. SAE Tech. Pap. 1990, 901296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutolo, M.F.; Clarkson, J.P.; Covington, J.A. The use of an electronic nose to detect early signs of soft-rot infection in potatoes. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 167, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.; Scott, S.M.; Ali, Z.; O’Hare, W.T. Chemical sensors for electronic nose systems. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, M.C.; Ponder, J.B.; Bailey, D.P.; Ingison, C.K.; Suslick, K.S. Colorimetric sensor arrays for volatile organic compounds. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. The Optoelectronic Nose: Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensor Arrays. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 231–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P. Introduction to biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutolo, M.; Covington, J.A.; Clarkson, J.; Iliescu, D. Detection of potato storage disease via gas analysis: A pilot study using field asymmetric ion mobility spectrometry. Sensors 2014, 14, 15939–15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.T.; Boock, J.J.; Kemperman, R.H.J.; Wei, M.S.; Beekman, C.R.; Yost, R.A. Portable FAIMS: Applications and future perspectives. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 422, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Khot, L.R.; Schroeder, B.K. FAIMS based sensing of Burkholderia cepacia caused sour skin in onions under bulk storage condition. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Khot, L.R.; Schroeder, B.K.; Si, Y. Rapid and non–destructive detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing soft rot in stored potatoes through volatile biomarkers sensing. Crop Prot. 2017, 93, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ramasamy, R.P. A Portable Electrochemical System for Plant Volatile Detection. ECS Trans. 2018, 85, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Paul, R.; Ba Tis, T.; Saville, A.C.; Hansel, J.C.; Yu, T.; Ristaino, J.B.; Wei, Q. Non-invasive plant disease diagnostics enabled by smartphone-based fingerprinting of leaf volatiles. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Gu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Discrimination of wood borers infested Platycladus orientalis trunks using quartz crystal microbalance gas sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalupowicz, D.; Veltman, B.; Droby, S.; Eltzov, E. Evaluating the use of biosensors for monitoring of Penicillium digitatum infection in citrus fruit. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 311, 127896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Sang, M.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Gong, Z.; Tang, X.; Long, X.; Xiong, H.; Peng, H. Rapid detection of d-limonene emanating from citrus infestation by Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) using a developed gas-sensing system based on QCM sensors coated with ethyl cellulose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 328, 129048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.M.C.; Wildt, J.; Kappers, I.F.; Bouwmeester, H.J.; Hofstee, J.W.; van Henten, E.J. Detection of Diseased Plants by Analysis of Volatile Organic Compound Emission. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, T.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G.; Freund, M.S.; Shafai, C.; Thomson, D.J. Characterization of volatile organic compounds released by granivorous insects in stored wheat. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2012, 48, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cornelio, R.; Cantor, F.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Rodríguez, D. Tools in the Investigation of Volatile Semiochemicals on Insects: From Sampling to Statistical Analysis. Insects 2019, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
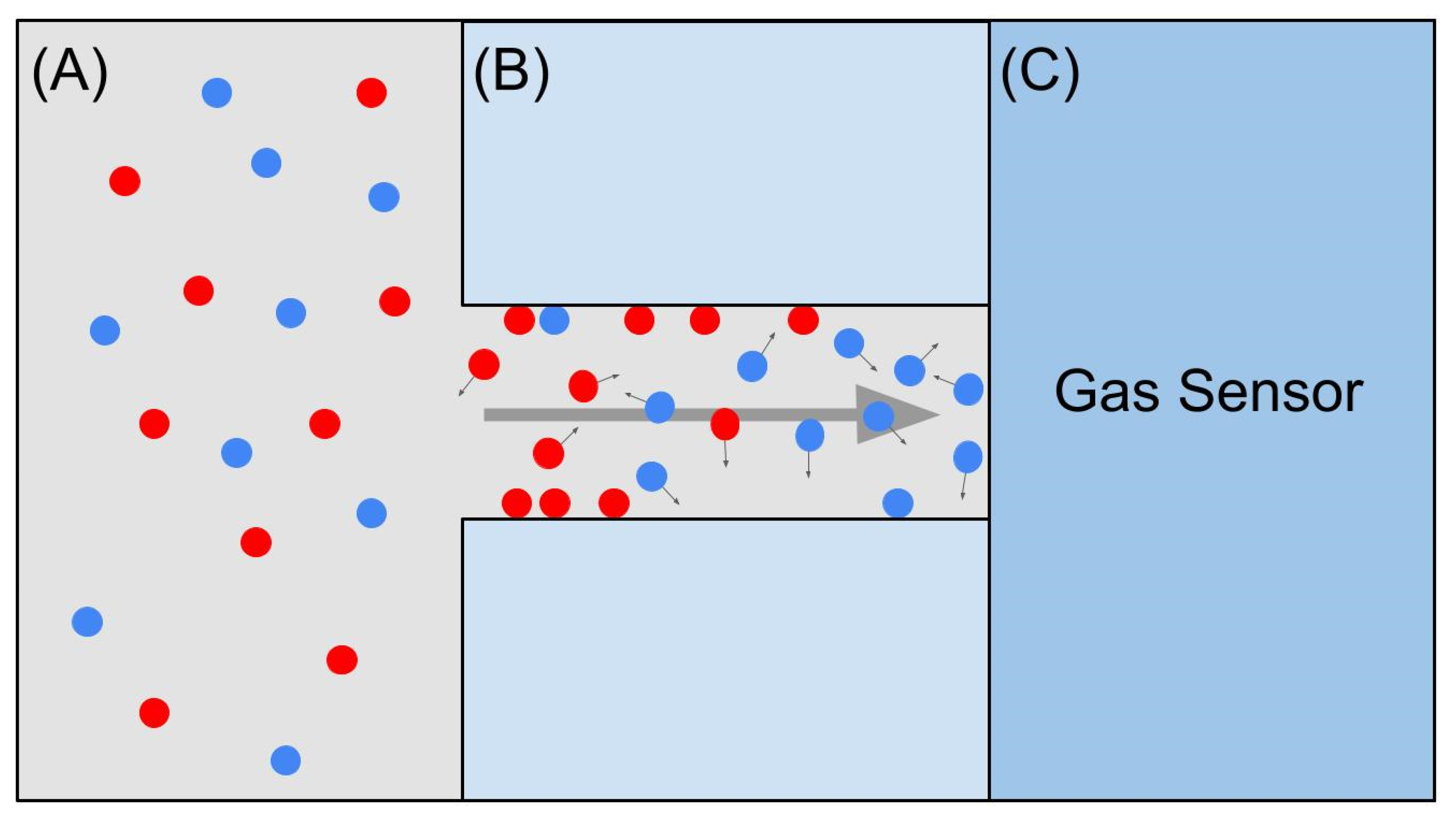
- Paknahad, M.; Bachhal, J.S.; Hoorfar, M. Diffusion-based humidity control membrane for microfluidic-based gas detectors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1021, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, V.; Bernardini, S.; Bendahan, M.; Aguir, K.; Perrier, P.; Graur, I. Fabrication and characterization of gas detection microfluidic system. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Ghafarinia, V. Gas analysis by monitoring molecular diffusion in a microfluidic channel. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8349–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Paknahad, M.; Ghafarinia, V. A miniature gas analyzer made by integrating a chemoresistor with a microchannel. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Babaei, F.; Amini, A. Recognition of complex odors with a single generic tin oxide gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabi, P.; Hui, J.; Montazeri, M.M.; Nguyen, K.T.; Logel, A.; O’Brian, A.; Hoorfar, M. Smelling Through Microfluidic Olfaction Technology. In CSME Conference Proceedings; YorkSpace: Denver, Colorado, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknahad, M.; Bachhal, J.S.; Ahmadi, A.; Hoorfar, M. Characterization of channel coating and dimensions of microfluidic-based gas detectors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paknahad, M.; Mcintosh, C.; Hoorfar, M. Selective detection of volatile organic compounds in microfluidic gas detectors based on “like dissolves like”. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janfaza, S.; Kim, E.; O’Brien, A.; Najjaran, H.; Nikkhah, M.; Alizadeh, T.; Hoorfar, M. A Nanostructured Microfluidic Artificial Olfaction for Organic Vapors Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paknahad, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Rousseau, J.; Nejad, H.R.; Hoorfar, M. On-Chip Electronic Nose for Wine Tasting: A Digital Microfluidic Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 4322–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, E.J.; Pauls, G.; Rillig, M.C.; Hansson, B.S.; Hilker, M.; Reinecke, A. Novel Set-Up for Low-Disturbance Sampling of Volatile and Non-volatile Compounds from Plant Roots. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deasy, W.; Shepherd, T.; Alexander, C.J.; Birch, A.N.E.; Evans, K.A. Development and Validation of a SPME-GC-MS Method for in situ Passive Sampling of Root Volatiles from Glasshouse-Grown Broccoli Plants Undergoing Below-Ground Herbivory by Larvae of Cabbage Root Fly, Delia radicum L. Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kfoury, N.; Scott, E.; Orians, C.; Robbat, A. Direct Contact Sorptive Extraction: A Robust Method for Sampling Plant Volatiles in the Field. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8501–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sensing Mechanism | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOS |
| ||
| CP |
| ||
| Electrochemical |
| ||
| Colorimetric |
|
| |
| FAIMS |
| ||
| Biosensing | |||
| QCM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacDougall, S.; Bayansal, F.; Ahmadi, A. Emerging Methods of Monitoring Volatile Organic Compounds for Detection of Plant Pests and Disease. Biosensors 2022, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040239
MacDougall S, Bayansal F, Ahmadi A. Emerging Methods of Monitoring Volatile Organic Compounds for Detection of Plant Pests and Disease. Biosensors. 2022; 12(4):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040239
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacDougall, Samantha, Fatih Bayansal, and Ali Ahmadi. 2022. "Emerging Methods of Monitoring Volatile Organic Compounds for Detection of Plant Pests and Disease" Biosensors 12, no. 4: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040239
APA StyleMacDougall, S., Bayansal, F., & Ahmadi, A. (2022). Emerging Methods of Monitoring Volatile Organic Compounds for Detection of Plant Pests and Disease. Biosensors, 12(4), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040239






