Digital Microfluidics-Powered Real-Time Monitoring of Isothermal DNA Amplification of Cancer Biomarker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
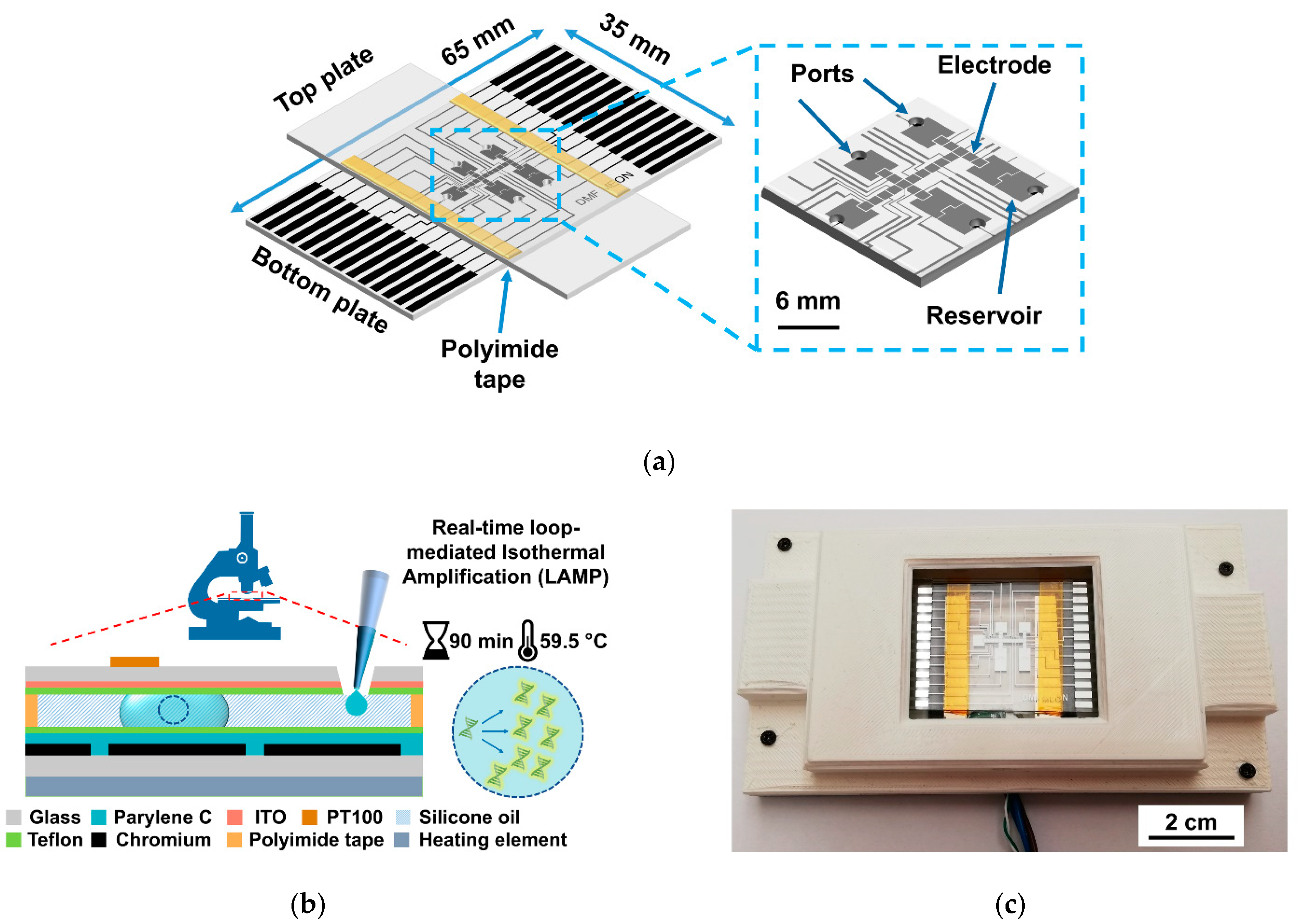
2.1. DMF Chip Design and Production
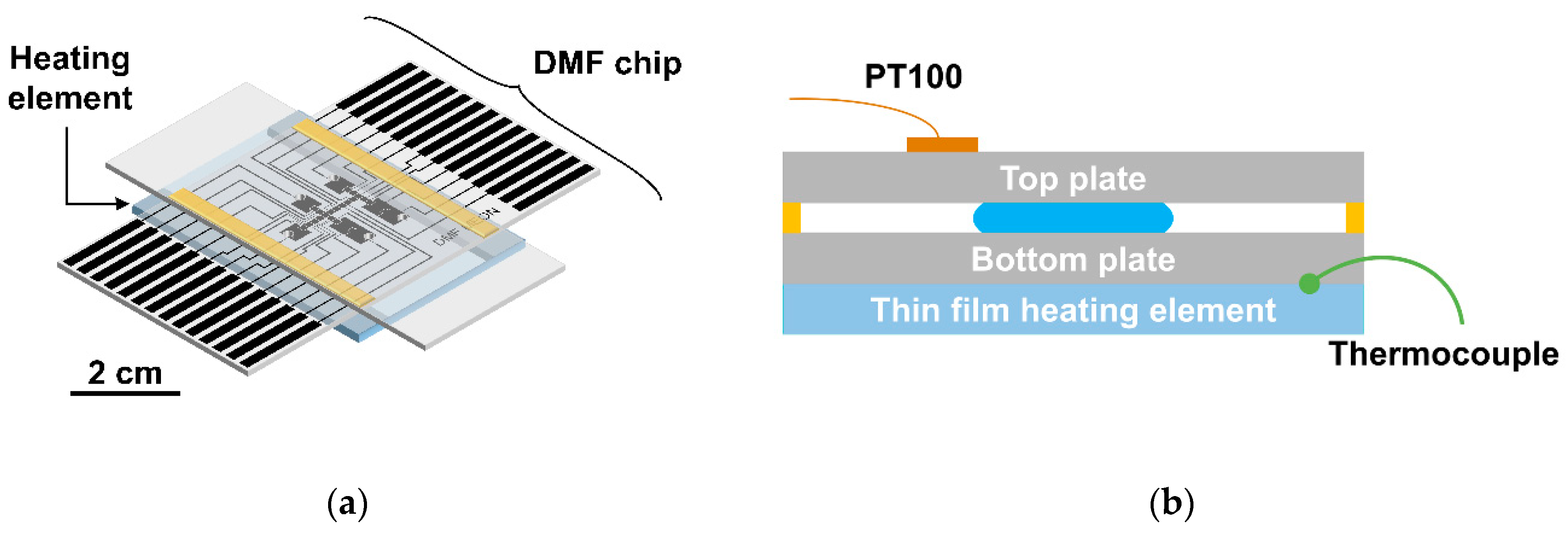
2.2. DMF Platform: Electrode Pattern and DMF Device Support System
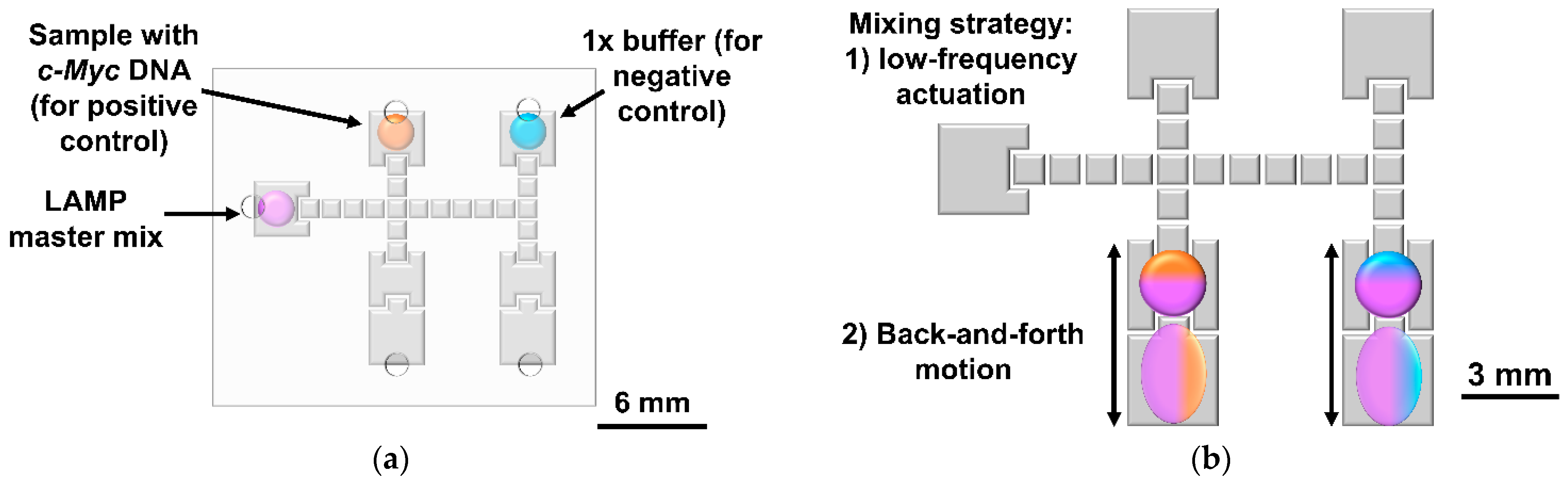
2.3. DMF Droplet Driving System
2.4. Temperature Control System
2.5. Loop-Mediated Isothermal (LAMP) Reaction
2.6. On-Chip LAMP Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temperature Monitoring for On-Chip LAMP
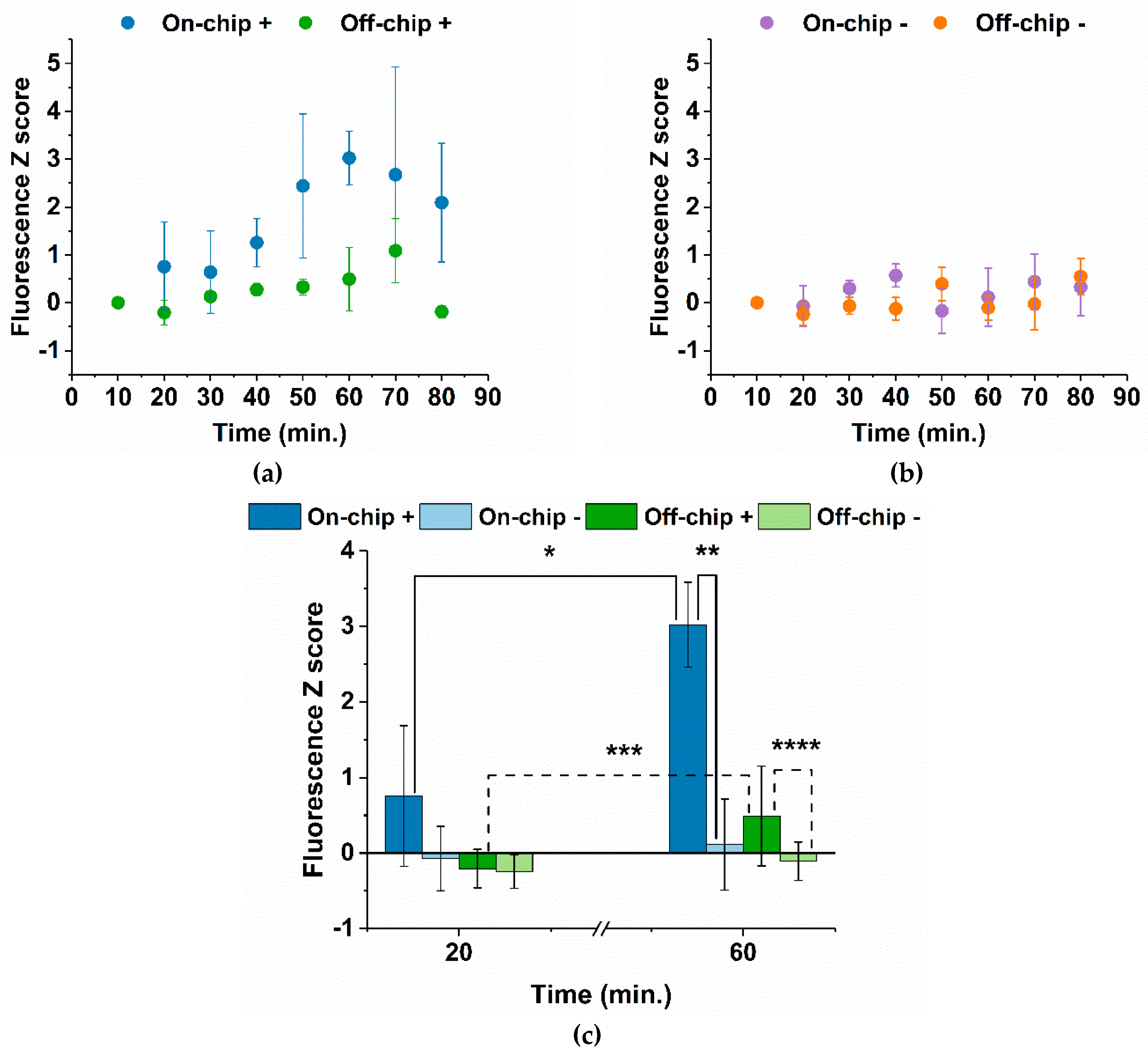
3.2. On-Chip LAMP
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 4 May 2021).
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer Statistics for the Year 2020: An Overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossmann, S.H.; Troyer, D.L. Point-of-Care Routine Rapid Screening: The Future of Cancer Diagnosis? Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gubala, V.; Harris, L.F.; Ricco, A.J.; Tan, M.X.; Williams, D.E. Point of Care Diagnostics: Status and Future. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 487–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Kricka, L.J. Current and Emerging Trends in Point-of-Care Technology and Strategies for Clinical Validation and Implementation. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, P.; Domingo, G.J.; Gerdes, J. Point-of-Care Diagnostics for Global Health. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauglitz, G. Point-of-Care Platforms. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, N.L.; Hayes, D.F. Cancer Biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordente, A.; Meucci, E.; Martorana, G.; Silvestrini, A. Cancer Biomarkers Discovery and Validation: State of the Art, Problems and Future Perspectives. In Advances in Cancer Biomarkers: From Biochemistry to Clinic for a Critical Revision; Scatena, R., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.S.D.S.; Islam, A.; Muench, D.; Sedoris, K. C-Myc and Cancer Metabolism. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5546–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V.; Le, A.; Gao, P. MYC-Induced Cancer Cell Energy Metabolism and Therapeutic Opportunities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6479–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. MYC, Metabolism, Cell Growth, and Tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a014217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the Path to Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC Activation Is a Hallmark of Cancer Initiation and Maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Chang-Yen, D.A.; Yarnell, L.E.; Pearson, E.L.; Oleksak, C.M.; Fischer, A.T.; Luoma, R.P.; Robinson, J.M.; et al. Automated Digital Microfluidic Platform for Magnetic-Particle-Based Immunoassays with Optimization by Design of Experiments. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9638–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital Microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgawad, B.M.; Wheeler, A.R.; Abdelgawad, M.; Wheeler, A.R. The Digital Revolution: A New Paradigm for Microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sista, R.; Hua, Z.; Thwar, P.; Sudarsan, A.; Srinivasan, V.; Eckhardt, A.; Pollack, M.; Pamula, V. Development of a Digital Microfluidic Platform for Point of Care Testing. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 2091–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafia, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Hoorfar, M.; Najjaran, H. Ultra-Portable Smartphone Controlled Integrated Digital Microfluidic System in a 3D-Printed Modular Assembly. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.H.C.; Fobel, R.; Fobel, C.; Lamanna, J.; Rackus, D.G.; Summers, A.; Dixon, C.; Dryden, M.D.M.; Lam, C.; Ho, M.; et al. A Digital Microfluidic System for Serological Immunoassays in Remote Settings. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, aar6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklavounos, A.A.; Lamanna, J.; Modi, D.; Gupta, S.; Mariakakis, A.; Callum, J.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital Microfluidic Hemagglutination Assays for Blood Typing, Donor Compatibility Testing, and Hematocrit Analysis. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, B.J.; Veigas, B.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Águas, H.; Igreja, R.; Baptista, P.V. Digital Microfluidics for Nucleic Acid Amplification. Sensors 2017, 17, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, B.J.; Veigas, B.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Baptista, P.P.V.; Igreja, R. A Digital Microfluidics Platform for Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebrail, M.J.; Wheeler, A.R. Let’s Get Digital: Digitizing Chemical Biology with Microfluidics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebrail, M.J.; Bartsch, M.S.; Patel, K.D.; Jebrail, J.; Bartsch, M.S.; Patel, K.D.; Jebrail, M.J.; Bartsch, M.S. Digital Microfluidics: A Versatile Tool for Applications in Chemistry, Biology and Medicine. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Jung, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, K. Active Digital Microfluidic Paper Chips with Inkjet-Printed Patterned Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fobel, R.; Kirby, A.E.; Ng, A.H.C.C.; Farnood, R.R.; Wheeler, A.R. Paper Microfluidics Goes Digital. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelgawad, M. Digital Microfluidics: Automation of Liquid Handling on the Microscale. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2020, 14, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP): Principle, Features, and Future Prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veigas, B.; Branquinho, R.; Pinto, J.V.; Wojcik, P.J.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Baptista, P.V. Ion Sensing (EIS) Real-Time Quantitative Monitorization of Isothermal DNA Amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veigas, B.; Pinto, J.; Vinhas, R.; Calmeiro, T.; Martins, R.; Fortunato, E.; Baptista, P.V. Quantitative Real-Time Monitoring of RCA Amplification of Cancer Biomarkers Mediated by a Flexible Ion Sensitive Platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.; Pamula, V.K.; Pollack, M.G.; Fair, R.B. Electrowetting-Based Droplet Mixers for Microfluidic Systems. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. Rapid Droplet Mixers for Digital Microfluidic Systems. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugele, F.; Baret, J.C.; Steinhauser, D. Microfluidic Mixing through Electrowetting-Induced Droplet Oscillations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 204106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dong, C.; Law, M.K.; Jia, Y.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. Hydrodynamic-Flow-Enhanced Rapid Mixer for Isothermal DNA Hybridization Kinetics Analysis on Digital Microfluidics Platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, E.; De Leon Derby, M.D.; Van Den Berg, A.; Hoorfar, M. An Electrohydrodynamic Technique for Rapid Mixing in Stationary Droplets on Digital Microfluidic Platforms. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Sen, P. Mixing Enhancement by Degenerate Modes in Electrically Actuated Sessile Droplets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugele, F.; Staicu, A.; Bakker, R.; Van Den Ende, D. Capillary Stokes Drift: A New Driving Mechanism for Mixing in AC-Electrowetting. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.J. Enhancement of Mixing by Droplet-Based Microfluidics. In Proceedings of the Technical Digest. MEMS 2002 IEEE International Conference. Fifteenth IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 January 2002; pp. 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kalsi, S.; Valiadi, M.; Tsaloglou, M.; Parry-jones, L.; Jacobs, A.; Watson, R.; Turner, C.; Amos, R.; Hadwen, B.; Buse, J.; et al. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Antibiotic Resistance on a Programmable Digital Microfluidic Platform. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Lee, G.-B.; Huang, F.-C.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Lin, J.-L. Integrated Polymerase Chain Reaction Chips Utilizing Digital Microfluidics. Biomed. Microdevices 2006, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Rouse, J.L.; Eckhardt, A.E.; Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Schell, W.A.; Benton, J.L.; Mitchell, T.G.; Pollack, M.G. Multiplexed Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction on a Digital Microfluidic Platform. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norian, H.S.; Shepard, K.; Kymissis, J.; Field, R. An Integrated CMOS Quantitative-Polymerase-Chain-Reaction Lab-on-Chip for Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4076–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rival, A.; Jary, D.; Delattre, C.; Fouillet, Y.; Castellan, G.; Bellemin-Comte, A.; Gidrol, X. An EWOD-Based Microfluidic Chip for Single-Cell Isolation, MRNA Purification and Subsequent Multiplex QPCR. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Leung, W.Y.; Xin, X. Characterization of EvaGreen and the Implication of Its Physicochemical Properties for QPCR Applications. BMC Biotechnol. 2007, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremers, T.; Thelen, S.; Bosbach, N.; Schnakenberg, U. PortaDrop: A Portable Digital Microfluidic Platform Providing Versatile Opportunities for Lab-On-A-Chip Applications. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, T.; Dong, C.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.Z.; Lun, Z.R.; Jia, Y.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. LampPort: A Handheld Digital Microfluidic Device for Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP). Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sci-Bots DropBot DB3-120 Kit. Available online: https://shop.sci-bots.com/product/dropbot-db3-120-kit/ (accessed on 17 March 2022).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coelho, B.J.; Veigas, B.; Bettencourt, L.; Águas, H.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R.; Baptista, P.V.; Igreja, R. Digital Microfluidics-Powered Real-Time Monitoring of Isothermal DNA Amplification of Cancer Biomarker. Biosensors 2022, 12, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040201
Coelho BJ, Veigas B, Bettencourt L, Águas H, Fortunato E, Martins R, Baptista PV, Igreja R. Digital Microfluidics-Powered Real-Time Monitoring of Isothermal DNA Amplification of Cancer Biomarker. Biosensors. 2022; 12(4):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040201
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoelho, Beatriz Jorge, Bruno Veigas, Luís Bettencourt, Hugo Águas, Elvira Fortunato, Rodrigo Martins, Pedro V. Baptista, and Rui Igreja. 2022. "Digital Microfluidics-Powered Real-Time Monitoring of Isothermal DNA Amplification of Cancer Biomarker" Biosensors 12, no. 4: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040201
APA StyleCoelho, B. J., Veigas, B., Bettencourt, L., Águas, H., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Baptista, P. V., & Igreja, R. (2022). Digital Microfluidics-Powered Real-Time Monitoring of Isothermal DNA Amplification of Cancer Biomarker. Biosensors, 12(4), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040201









