A Novel Peptide as a Specific and Selective Probe for Klebsiella pneumoniae Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture
2.2. Biopanning of Phage-Displayed Peptides
2.3. Preparation of Biotinylated Peptide
2.4. Phage Binding ELISA Assay
2.5. Binding Specificity of KP Peptide
2.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.7. Binding of KP Peptide to Lipopolysaccharide
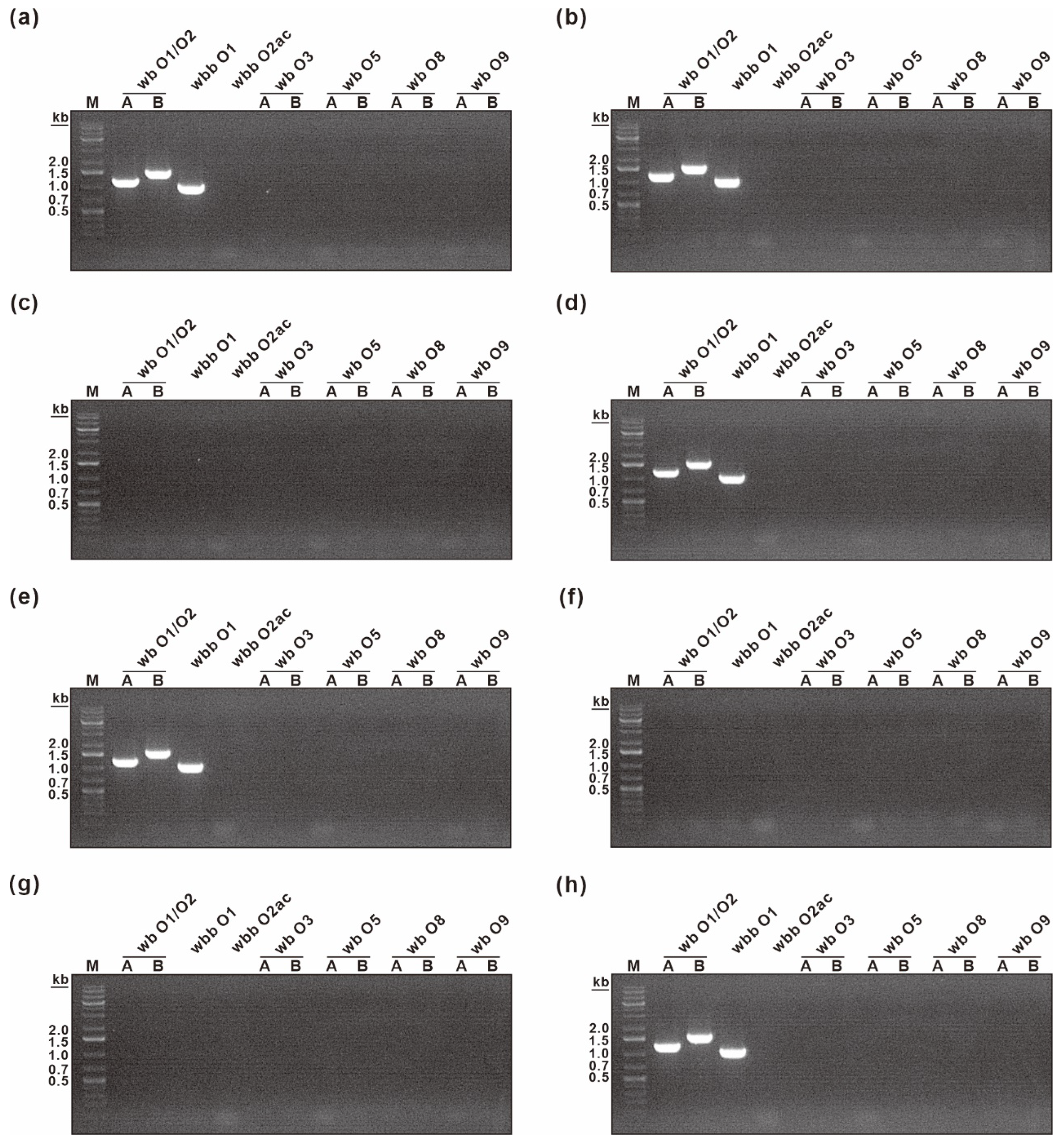
2.8. K. pneumoniae O Antigen Typing
2.9. Comparison of Specificity and Sensitivity of KP Peptide with Commercially Available Anti-Klebsiella spp. Antibodies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biopanning of a Phage Display Library against K. pneumoniae
3.2. Specificity of Phage Binding to K. pneumoniae
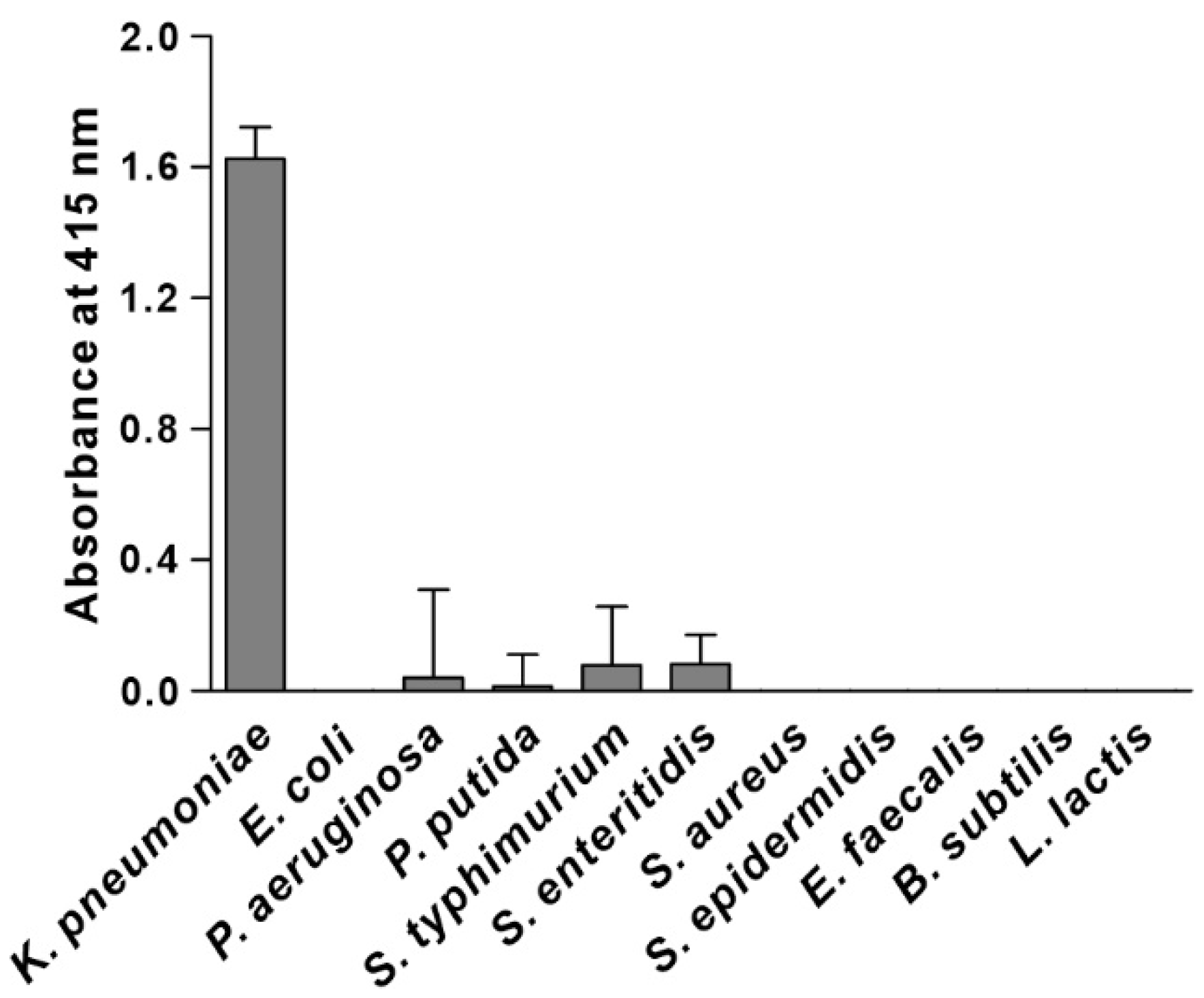
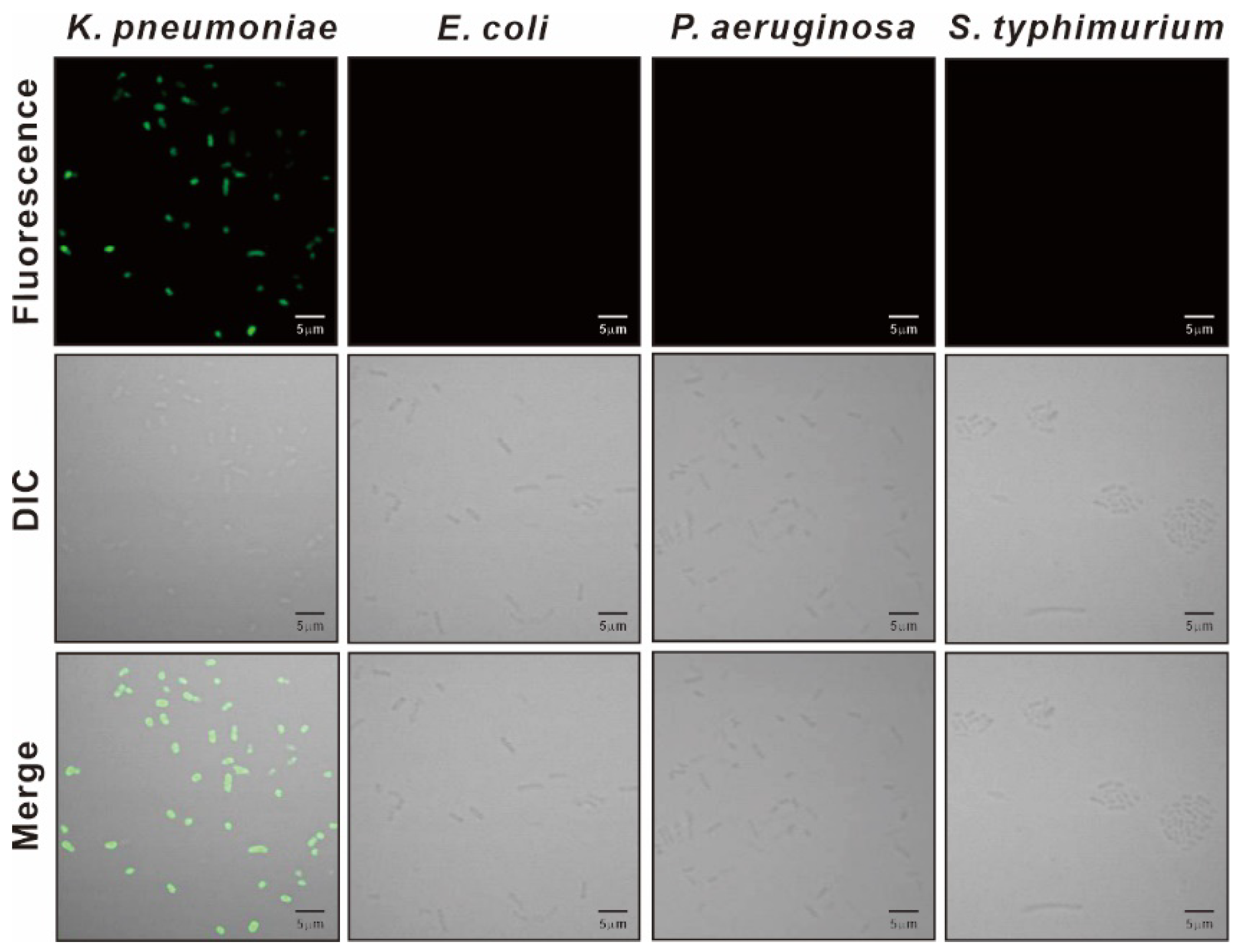
3.3. Specificity of KP Peptide Binding to K. pneumoniae
3.4. Characterization of the Binding Specificity of KP Peptide
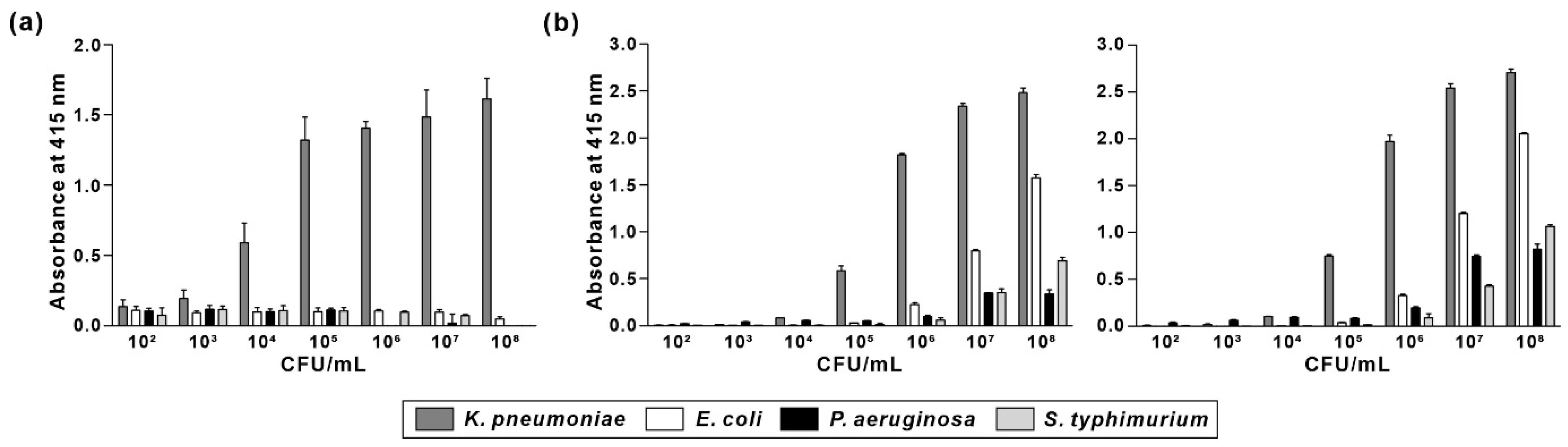
3.5. Comparison of Specificity and Sensitivity of KP Peptide with Commercially Available Anti-Klebsiella spp. Antibodies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Abu Bakar, M. Healthcare-associated infections—An overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczosa, M.K.; Mecsas, J. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, T.T.; Liebenthal, D.; Tran, T.K.; Ngoc Thi Vu, B.; Ngoc Thi Nguyen, D.; Thi Tran, H.K.; Thi Nguyen, C.K.; Thi Vu, H.L.; Fox, A.; Horby, P.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae oropharyngeal carriage in rural and urban Vietnam and the effect of alcohol consumption. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, C.P.; Lin, Y.T.; Lin, J.C.; Chen, T.L.; Yeh, K.M.; Chang, F.Y.; Chuang, H.C.; Wu, H.S.; Tseng, C.P.; Siu, L.K. Klebsiella pneumoniae in gastrointestinal tract and pyogenic liver abscess. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1322–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrie, C.L.; Mirceta, M.; Wick, R.R.; Edwards, D.J.; Thomson, N.R.; Strugnell, R.A.; Pratt, N.F.; Garlick, J.S.; Watson, K.M.; Pilcher, D.V.; et al. Gastrointestinal Carriage Is a Major Reservoir of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection in Intensive Care Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snitkin, E.S.; Zelazny, A.M.; Thomas, P.J.; Stock, F.; Group, N.C.S.P.; Henderson, D.K.; Palmore, T.N.; Segre, J.A. Tracking a hospital outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with whole-genome sequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 148ra116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.M.; Bray, A.S.; Nagpal, R.K.; Caudell, D.L.; Yadav, H.; Zafar, M.A. Animal Model to Study Klebsiella pneumoniae Gastrointestinal Colonization and Host-to-Host Transmission. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00071-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, C.; Pujol, M.; Ardanuy, C.; Ricart, A.; Pallares, R.; Linares, J.; Ariza, J.; Gudiol, F. Epidemiology and successful control of a large outbreak due to Klebsiella pneumoniae producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1998, 42, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, R.A.; Hujer, A.M.; Marshall, S.H.; Perez, F.; Hujer, K.M.; Briceno, D.F.; Dul, M.; Jacobs, M.R.; Grossberg, R.; Toltzis, P.; et al. “Silent” dissemination of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates bearing K. pneumoniae carbapenemase in a long-term care facility for children and young adults in Northeast Ohio. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, M.; Phillips, I. Hands as route of transmission for Klebsiella species. Br. Med. J. 1977, 2, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, H.; Bozidis, P.; Ilia, A.; Mpekoulis, G.; Papadopoulou, C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Pathogens and Detection of Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Hospital Wastewater. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, J.R.; Kitchel, B.; Driebe, E.M.; MacCannell, D.R.; Roe, C.; Lemmer, D.; de Man, T.; Rasheed, J.K.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Keim, P.; et al. Genomic Analysis of the Emergence and Rapid Global Dissemination of the Clonal Group 258 Klebsiella pneumoniae Pandemic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Baek, J.Y.; Peck, K.R.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, Y.E.; Kim, S.H.; Huh, H.J.; Lee, N.Y.; Kang, C.I.; Chung, D.R.; et al. Discrepant susceptibility to gentamicin despite amikacin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae by VITEK 2 represents false susceptibility associated with the armA 16S rRNA methylase gene. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1448–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Gao, Q.; Hou, Y.; Huang, X. PCR detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae in infant formula based on 16S-23S internal transcribed spacer. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.S.; Lee, K.S.; Heo, S.H.; Seo, J.H.; Choi, Y.K. Rapid identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Corynebacterium kutscheri, and Streptococcus pneumoniae using triplex polymerase chain reaction in rodents. Exp. Anim. 2013, 62, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shannon, K.E.; Lee, D.Y.; Trevors, J.T.; Beaudette, L.A. Application of real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of selected bacterial pathogens during municipal wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.J.; Lee, E.H.; Hwang, D.H.; Lee, H.; Baek, J.H.; Jeong, S.H. Direct detection of intact Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases produced by Enterobacterales using MALDI-TOF MS. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, K.; Li, C. Rapid detection of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in China based on MALDI-TOF MS. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 192, 106385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelcbuch, L.; Yitzhaki, E.; Nissan, O.; Gidron, E.; Buchshtab, N.; Kario, E.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Zak, N.B.; Bassan, M. Luminescent Phage-Based Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae: From Engineering to Diagnostics. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Kamaladini, H.; Haddadi, F.; Sharifmoghadam, M.R. Thiol-Capped Gold Nanoparticle Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Visual Colorimetric Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Fluoresc. 2018, 28, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, T. Rapid detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Raoultella ornithinolytica and other related bacteria in food by lateral-flow test strip immunoassays. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 147, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, W.; Ullah, M.W.; Farooq, U.; Aziz, A.; Wang, S. Bacteriophage-based advanced bacterial detection: Concept, mechanisms, and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Hirst, N.A.; Millner, P.A. Biosensors for whole-cell bacterial detection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, R.C.; Sato, A.K.; Gorzelany, J.; de Souza, M. Phage display-derived peptides as therapeutic alternatives to antibodies. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.P.; Cropek, D.M.; Banta, S. High affinity peptides for the recognition of the heart disease biomarker troponin I identified using phage display. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 105, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.M.; Heo, N.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Ryu, M.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Park, T.J.; Huh, Y.S.; Park, J.P. Selection of affinity peptides for interference-free detection of cholera toxin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Plano, L.M.; Carnazza, S.; Messina, G.M.L.; Rizzo, M.G.; Marletta, G.; Guglielmino, S.P.P. Specific and selective probes for Staphylococcus aureus from phage-displayed random peptide libraries. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 157, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Mohan, K.V.; Gao, Y.; Atreya, C.D. Identification and evaluation of a novel peptide binding to the cell surface of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 168, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnazza, S.; Foti, C.; Gioffre, G.; Felici, F.; Guglielmino, S. Specific and selective probes for Pseudomonas aeruginosa from phage-displayed random peptide libraries. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Kulabhusan, P.K.; Joshi, M.; Bodas, D.; Paknikar, K.M. A high affinity phage-displayed peptide as a recognition probe for the detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 231, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokulova, I.B.; Olsen, E.V.; Chen, I.H.; Fiebor, B.; Barbaree, J.M.; Vodyanoy, V.J.; Chin, B.A.; Petrenko, V.A. Landscape phage probes for Salmonella typhimurium. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 63, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainath Rao, S.; Mohan, K.V.; Nguyen, N.; Abraham, B.; Abdouleva, G.; Zhang, P.; Atreya, C.D. Peptides panned from a phage-displayed random peptide library are useful for the detection of Bacillus anthracis surrogates B. cereus 4342 and B. anthracis Sterne. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 395, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, J.H. Development of a novel hybrid antimicrobial peptide for targeted killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 185, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.J.; Ning, Y.J.; Liu, H.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. A Novel Lipopolysaccharide Recognition Mechanism Mediated by Internalization in Teleost Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.T.; Shih, Y.J.; Cheong, C.M.; Yi, W.C. Rapid and Accurate Determination of Lipopolysaccharide O-Antigen Types in Klebsiella pneumoniae with a Novel PCR-Based O-Genotyping Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, X.; Xiao, W.; Lam, K.S. Tumor-targeting peptides from combinatorial libraries. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Liu, I.J.; Lu, R.M.; Wu, H.C. Advancement and applications of peptide phage display technology in biomedical science. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, H.D.; Coppock, M.B.; Idso, M.N.; Lai, B.T.; Liang, J.; McCarthy-Torrens, A.M.; Warren, C.M.; Heath, J.R. Protein-Catalyzed Capture Agents. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9950–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Lim, J.; Jee, J.E.; Aw, J.H.; Lee, S.S. Peptide-Peptide Co-Assembly: A Design Strategy for Functional Detection of C-peptide, A Biomarker of Diabetic Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaar, T.; Lettow, M.; Remmler, D.; Börner, H.G.; Weller, M.G. Efficient Screening of Combinatorial Peptide Libraries by Spatially Ordered Beads Immobilized on Conventional Glass Slides. High Throughput 2019, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, Z.P.; Vinogradov, A.A.; Quartararo, A.J.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Choo, Z.N.; Evans, E.D.; Halloran, K.H.; Mijalis, A.J.; Mong, S.K.; Simon, M.D.; et al. Xenoprotein engineering via synthetic libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5298–E5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arato, V.; Raso, M.M.; Gasperini, G.; Berlanda Scorza, F.; Micoli, F. Prophylaxis and Treatment against Klebsiella pneumoniae: Current Insights on This Emerging Anti-Microbial Resistant Global Threat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, E.; Perry, M.B. Structural analysis of the core region of the lipopolysaccharides from eight serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 335, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regue, M.; Izquierdo, L.; Fresno, S.; Pique, N.; Corsaro, M.M.; Naldi, T.; De Castro, C.; Waidelich, D.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. A second outer-core region in Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, E.; Cedzynski, M.; Ziolkowski, A.; Swierzko, A. The structure of the core region of the lipopolysaccharide from Klebsiella pneumoniae O3. 3-deoxy-alpha-D-manno-octulosonic acid (alpha-Kdo) residue in the outer part of the core, a common structural element of Klebsiella pneumoniae O1, O2, O3, O4, O5, O8, and O12 lipopolysaccharides. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Chen, C.; Han, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xia, X.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J. Rapid, Visual Detection of Klebsiella pneumoniae Using Magnetic Nanoparticles and an Horseradish Peroxidase-Probe Based Immunosensor. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wuzhen, G.C.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, M.; Lin, J. Optical Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Salmonella typhimurium Based on Porous Gold@Platinum Nanocatalysts and a 3D Fluidic Chip. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| O Type Detected | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | PCR Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| O1/O2 | wb O1/O2-A-F | CGCTATAAGAGCAGCATGCTAG | 1251 |
| wb O1/O2-A-R | CGATATCACCTACTGCCAGA | ||
| wb O1/O2-B-F | TTGTTGAGCCTGACAGGATC | 1589 | |
| wb O1/O2-B-R | GCCATTGCTTGCTTGTACAG | ||
| O1 | wbb O1-F | GATTTCACTTTCCGGGCAAC | 1075 |
| wbb O1-R | GGCTTGCTGAATCACAAGAC | ||
| O2ac | wbb O2ac-F | AAACATCGCTGACTCGAGTC | 1046 |
| wbb O2ac-R | CGACTATGATCGTACCAACG | ||
| O3 | wb O3-A-F | CTATCGCTACCGTGGCTTTA | 767 |
| wb O3-A-R | TCTCGTCCACAATATCAGCG | ||
| wb O3-B-F | GCCTACAGTATCTACCTCTG | 903 | |
| wb O3-B-R | CGGTAAAGTCAGGATGGAAG | ||
| O5 | wb O5-A-F | GCTACCAAACCAGTATGCTG | 1821 |
| wb O5-A-R | AGGTGCGTACTGGAAGTATG | ||
| wb O5-B-F | GGTGATGAAAGCCAGAATGC | 1423 | |
| wb O5-B-R | CAGTGCCTGAAACAGTTTGC | ||
| O8 | wb O8-A-F | CGTGGCAATGGTTTGCTAGT | 1230 |
| wb O8-A-R | TCAATCCACACAACTCGGTC | ||
| wb O8-B-F | GCTAGTTCGGCAACTAACTCAC | 841 | |
| wb O8-B-R | AGTTCCAGCATCGAAGCAACTC | ||
| O9 | wb O9-A-F | CGCGCTCAGTTATTCCATTG | 973 |
| wb O9-A-R | CTGGCTGATGACAGAGAATC | ||
| wb O9-B-F | GCATTCCTGTTCGTGTATGG | 949 | |
| wb O9-B-R | ATGTCACCGACAGCAAGTAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Jang, J.H.; Jung, I.Y.; Cho, J.H. A Novel Peptide as a Specific and Selective Probe for Klebsiella pneumoniae Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030153
Kim H, Jang JH, Jung IY, Cho JH. A Novel Peptide as a Specific and Selective Probe for Klebsiella pneumoniae Detection. Biosensors. 2022; 12(3):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030153
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun, Ju Hye Jang, In Young Jung, and Ju Hyun Cho. 2022. "A Novel Peptide as a Specific and Selective Probe for Klebsiella pneumoniae Detection" Biosensors 12, no. 3: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030153
APA StyleKim, H., Jang, J. H., Jung, I. Y., & Cho, J. H. (2022). A Novel Peptide as a Specific and Selective Probe for Klebsiella pneumoniae Detection. Biosensors, 12(3), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030153




