Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticles–PDMS Composite Stamps as a Platform for Micro-Contact Printing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Glass Slides Cleaning and Surface Modification with DMOAP
2.3. Preparation of PDMS Stamps
2.4. U.V. Treatment of PDMS Stamp and DMOAP-Coated Slide
2.5. Preparation of AuNPs–PDMS Composite Stamp
2.6. Immobilisation of B40t77 Aptamer on AuNPs–PDMS Stamp
2.7. Characterisation of Prepared Solid Stamp Materials
2.8. Patterning of Target Protein through Micro-Contact Printing
2.9. Fabrication of LCs Optical Cell
2.10. Stability Check of the Prepared AuNPs–PDMS Stamp
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proposed Scheme of μCP of Gp-120 Protein Based on AuNPs–PDMS Composite Stamp
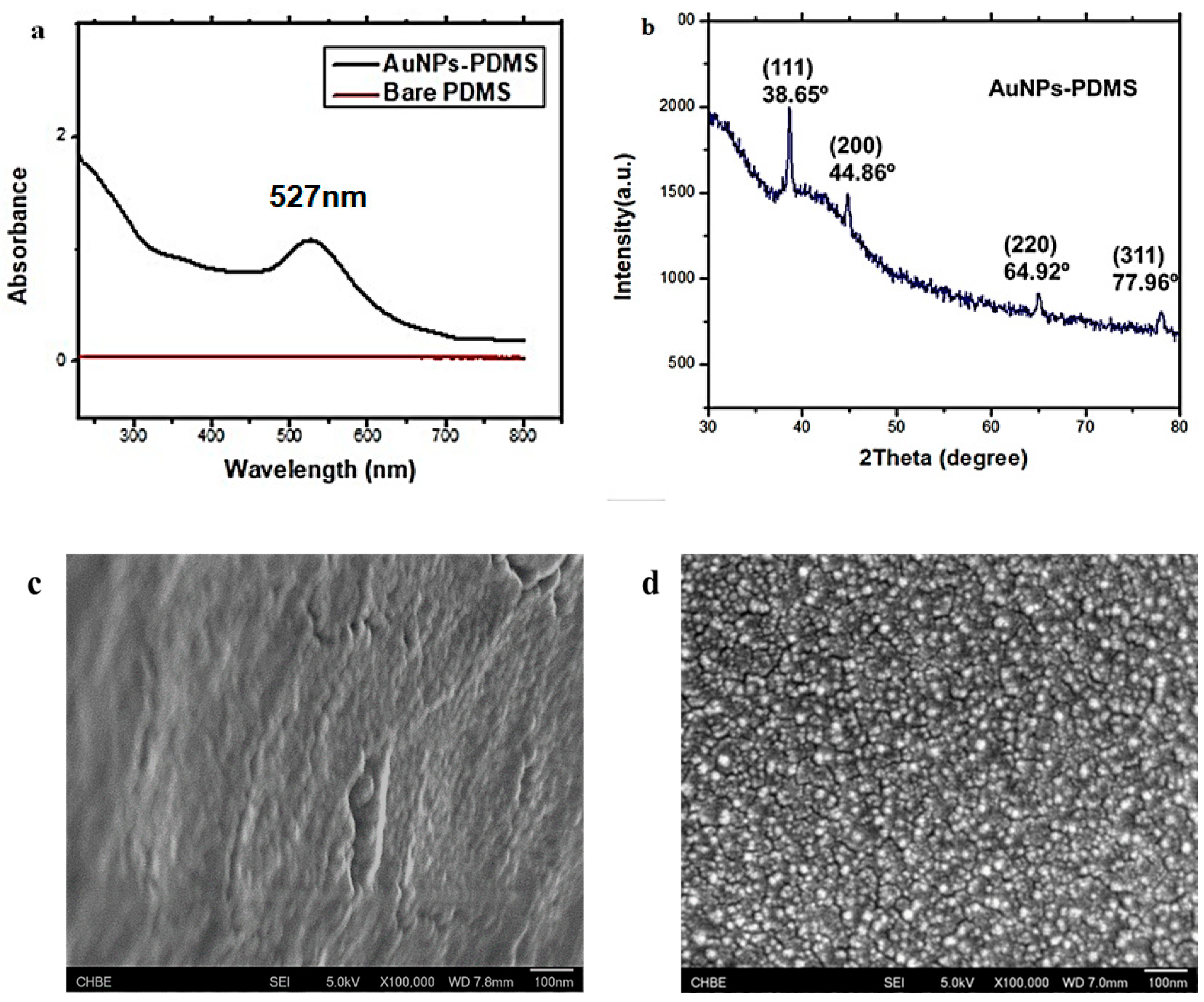
3.2. Characterisation of AuNPs–PDMS Composite Stamp
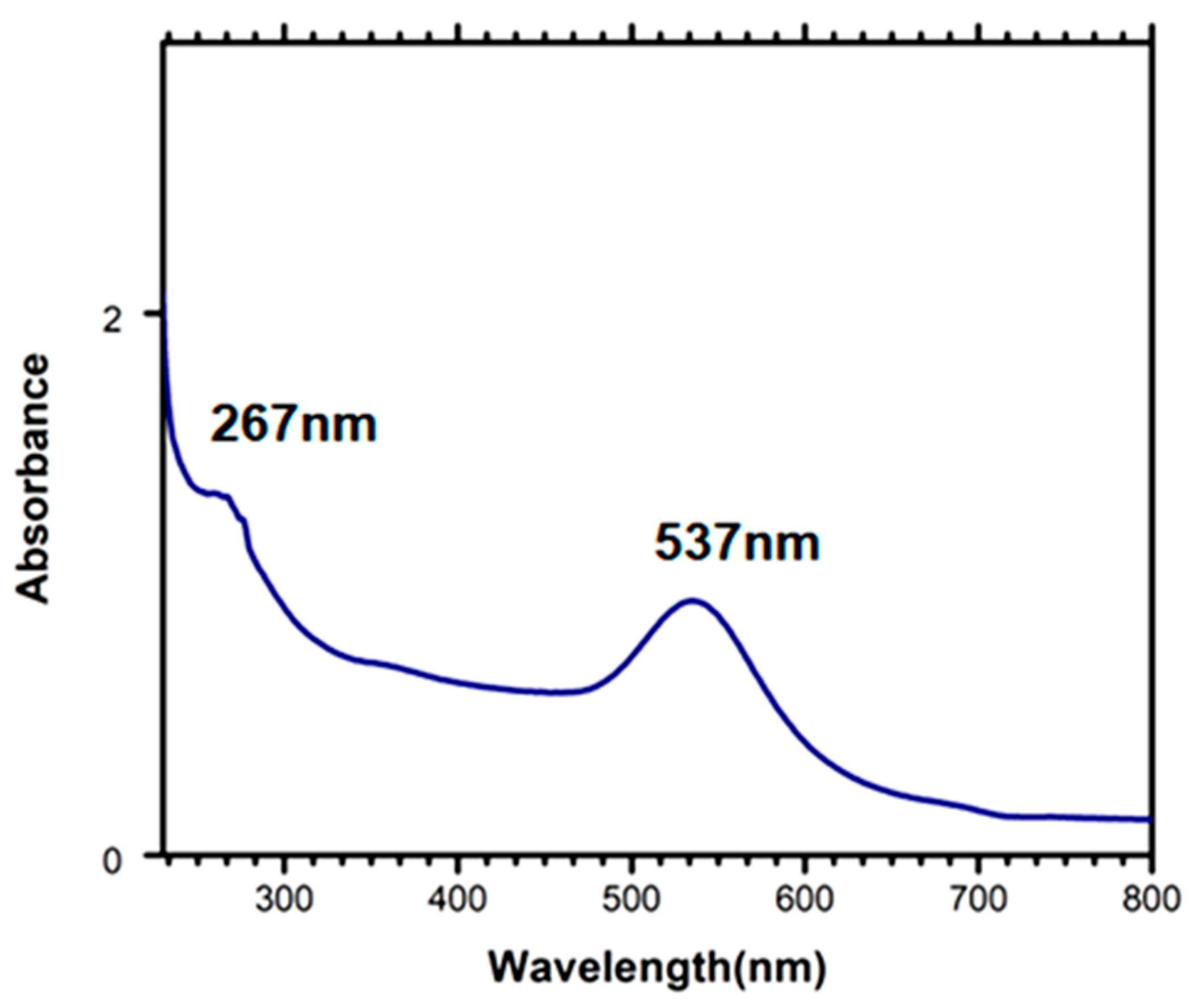
3.3. Characterisation of Aptamer Immobilised on PDMS–AuNPs Composite Stamps
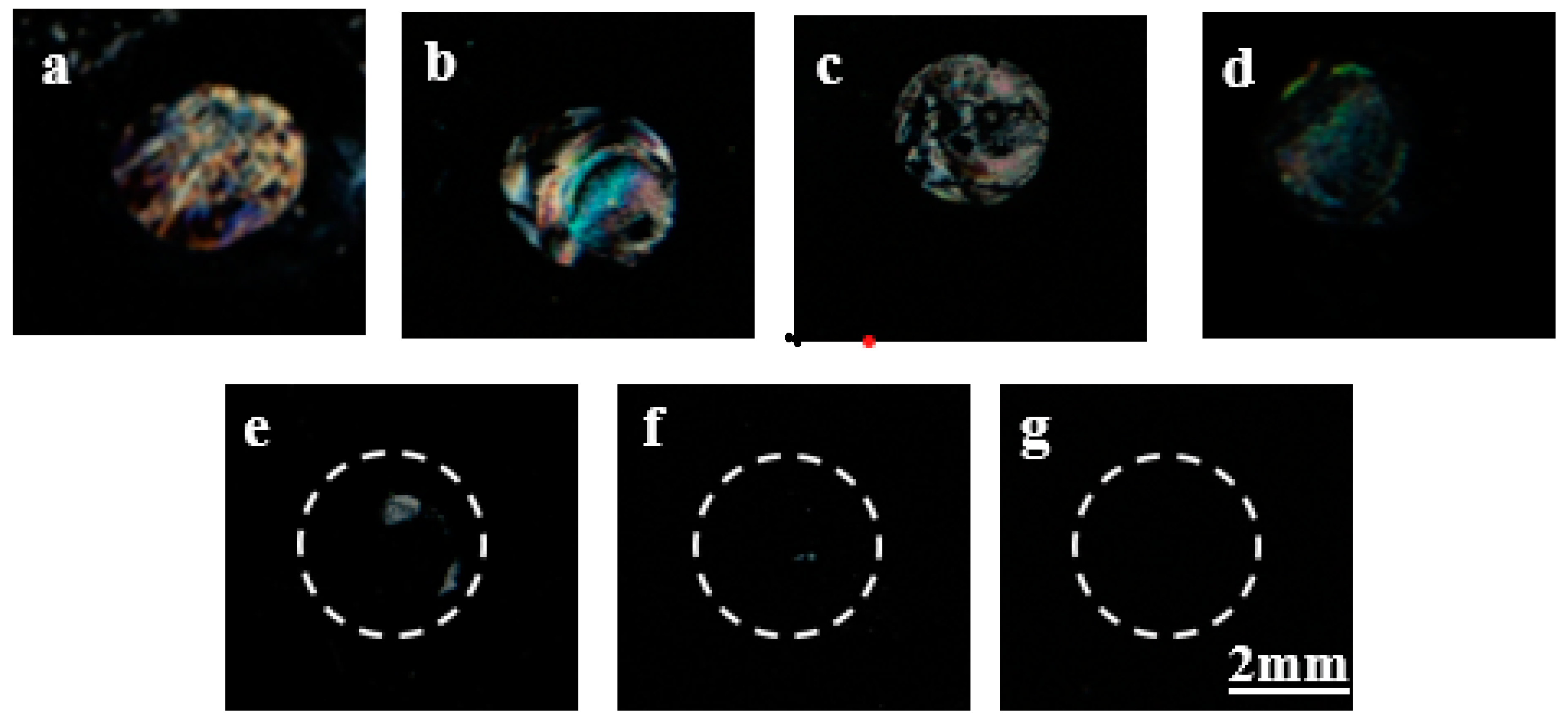
3.4. Detection of Gp-120 Target Protein through µCP by Using LCs
3.5. Capturing Desired Target Protein (Gp-120) in a Protein Mixture Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Chen, G.Y.J.; Yao, S.Q. Review Recent Advances in Microarray Technologies for Proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hölz, K.; Schaudy, E.; Lietard, J.; Somoza, M.M. Multi-level patterning nucleic acid photolithography. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogaki, R.; Alexander, M.; Kingshott, P. Chemical patterning in biointerface science Patterning of surfaces with different chemistries provides novel insights of new chemically patterned surfaces is highlighted. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamarche, E.; Pereiro, I.; Kashyap, A.; Kaigala, G.V. Biopatterning: The Art of Patterning Biomolecules on Surfaces. Langmuir 2021, 37, 9637–9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste-Dolz, A.; Avella-Oliver, M.; Puchades, R.; Maquieira, A. Indirect microcontact printing to create functional patterns of physisorbed antibodies. Sensors 2018, 18, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, A.; Renault, J.P.; Michel, B.; Bosshard, H.R.; Delamarche, E. Microcontact printing of proteins. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, K.L. Improving protein transfer efficiency and selectivity in affinity contact printing by using UV-modified surfaces. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, I.; Souza, A.; Sousa, P.; Ribeiro, J.; Castanheira, E.M.S.; Lima, R.; Minas, G. Properties and applications of PDMS for biomedical engineering: A review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökaltun, A.; Kang, Y.B.; Yarmush, M.L.; Usta, O.B.; Asatekin, A. Simple Surface Modification of Poly(dimethylsiloxane) via Surface Segregating Smart Polymers for Biomicrofluidics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, Q.; Wang, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, W.; Ren, L.; Shen, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Surface modification of poly(dimethylsiloxane) and its applications in microfluidics-based biological analysis. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 31, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhong, X.; Wang, W.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, J.J. Aptamer-based PDMS-gold nanoparticle composite as a platform for visual detection of biomolecules with silver enhancement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3110–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.Y. In-situ synthesis of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-gold nanoparticles composite films and its application in microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, X.; Riaud, A. Optimization of synthesis conditions of gold nanoparticlespolydimethylsiloxane composite for ultrasound generation. Nanotechnology 2021, 3, 2850–2857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Ali, S.; Xu, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. A SERS aptasensor based on AuNPs functionalized PDMS film for selective and sensitive detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Y.; Fostier, A.H.; Santos, E.B. In situ formation of gold and silver nanoparticles on uniform PDMS films and colorimetric analysis of their plasmonic color. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 607, 125463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusty, M.; Shirage, P.M. Gold nanoparticle-cellulose/PDMS nanocomposite: A flexible dielectric material for harvesting mechanical energy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 10097–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SadAbadi, H.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Wüthrich, R. Integration of gold nanoparticles in PDMS microfluidics for lab-on-a-chip plasmonic biosensing of growth hormones. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, W. Quantifying thiol-gold interactions towards the efficient strength control. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.Y.; Bian, Z.P.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.J. PDMS gold nanoparticle composite film-based silver enhanced colorimetric detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Ling, L.; Xue, C.Y.; Chin, S.Y.; Khan, S.A.; Yang, K.L.; Tu, Q.; Wang, J.C.J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Recent developments in aptasensors for diagnostic applications. Langmuir 2018, 18, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.D.; Hussain, Z.; Yang, K.L. Aptamer laden liquid crystals biosensing platform for the detection of HIV-1 glycoprotein-120. Molecules 2021, 26, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Wu, W. Graphene-Based Steganographic Aptasensor for Information Computing and Monitoring Toxins of Biofilm in Food. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, A.D.; Hussain, Z.; Liaqat, U.; Arif, D.; Yang, K.-L. Liquid Crystal Based Binding Assay for Detecting HIV-1 Surface Glycoprotein. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.K.; Griffiths, C.; Lea, S.M.; James, W. Structural characterization of an anti-gp120 RNA aptamer that neutralizes R5 strains of HIV-1. RNA 2005, 11, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, R.; Liu, M.; Yao, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, N.; Yuan, Z.; Jin, M.; Shui, L. A label-free optical immunoassay based on birefringence of liquid crystal for insulin-like growth factor-I sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Hsu, W.T.; Hwang, S.J. Real-time liquid crystal-based creatinine sensor using a micro-patterned flexible substrate. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 48, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Ma, C.; Munir, S.; Yu, L.; Hu, Q. Liquid crystal-based sensors for the detection of biomarkers at the aqueous/LC interface. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.T.K.; Jang, C.H. Simple, sensitive technique for α-amylase detection facilitated by liquid crystal-based microcapillary sensors. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Cheng, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, R.; Lin, J.M.; Hu, Q. A portable digital optical kanamycin sensor developed by surface-anchored liquid crystal droplets. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SadAbadi, H.; Badilescu, S.; Packirisamy, M.; Wuẗhrich, R. PDMS-gold nanocomposite platforms with enhanced sensing properties. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.V.; Khati, M.; Mamba, B.B.; Arotiba, O.; Rotherham, L.S. Towards HIV detection: Novel Poly (propylene) dendrimer-streptavidin platform for electrochemical DNA and gp-120 aptamer biosensors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 5425–5437. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbasi, A.D.; Hussain, Z.; Yang, K.-L. Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticles–PDMS Composite Stamps as a Platform for Micro-Contact Printing. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121067
Abbasi AD, Hussain Z, Yang K-L. Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticles–PDMS Composite Stamps as a Platform for Micro-Contact Printing. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121067
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbasi, Amna Didar, Zakir Hussain, and Kun-Lin Yang. 2022. "Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticles–PDMS Composite Stamps as a Platform for Micro-Contact Printing" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121067
APA StyleAbbasi, A. D., Hussain, Z., & Yang, K.-L. (2022). Aptamer-Based Gold Nanoparticles–PDMS Composite Stamps as a Platform for Micro-Contact Printing. Biosensors, 12(12), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121067





