Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Imprinting Technology for Protein Recognition
2.1. Protein Imprinting
2.2. Removal of Protein Template
2.3. Heterogeneity of Imprinted Sites
3. Conductive Polymers for Electrosythesized MIPs
- Template removal (i.e., “leaching” or “bleeding”), when it occurs, can damage the MIP (both conventional or electrosynthesized-based); this step often requires long term optimization;
- Unsatisfactory selectivity of the imprinted cavities, i.e., they may also interact with commonly present interfering analogues;
- No significant difference in the measured signal between eMIP and the corresponding non-imprinted polymer (i.e., a polymer prepared identically to eMIP without the addition of a template) [99].
3.1. Polypyrrole (Ppy)
3.2. Polyaminophenyl Boronic Acid (PAPBA)
3.3. Polyaniline (PANI) and Related Compounds
3.3.1. Polyaniline (PANI)
3.3.2. Poly(o-phenylenediamine) (PPD)
3.4. Polyphenol-Related Compounds
3.5. Polyscopoletin
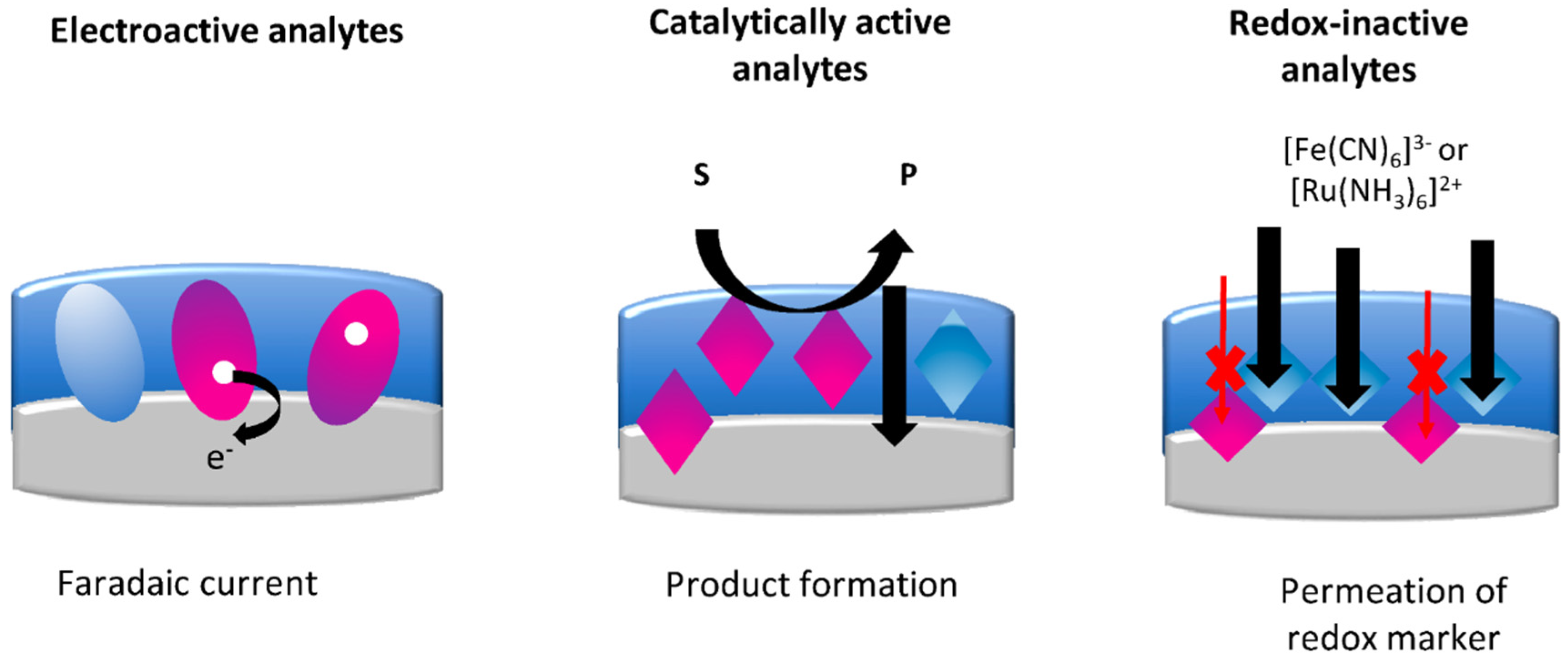
4. Electrochemical Readout
- The flow of a redox probe: the signal, regulated by the target binding, is detected at the underlying electrode surface;
- Enzymatic activity: enzymatic activity is detected by the formation of a redox-active product at the underlying electrode; this pathway applies to catalytically active targets (enzyme targets, or enzyme-labelled targets, catalytically active MIPs);
- Direct electron transfer (DET): faradaic current is recorded due to DET between the redox-active target and the underlying electrode.
4.1. Redox-Active Analytes
4.2. Catalytic Active Analytes
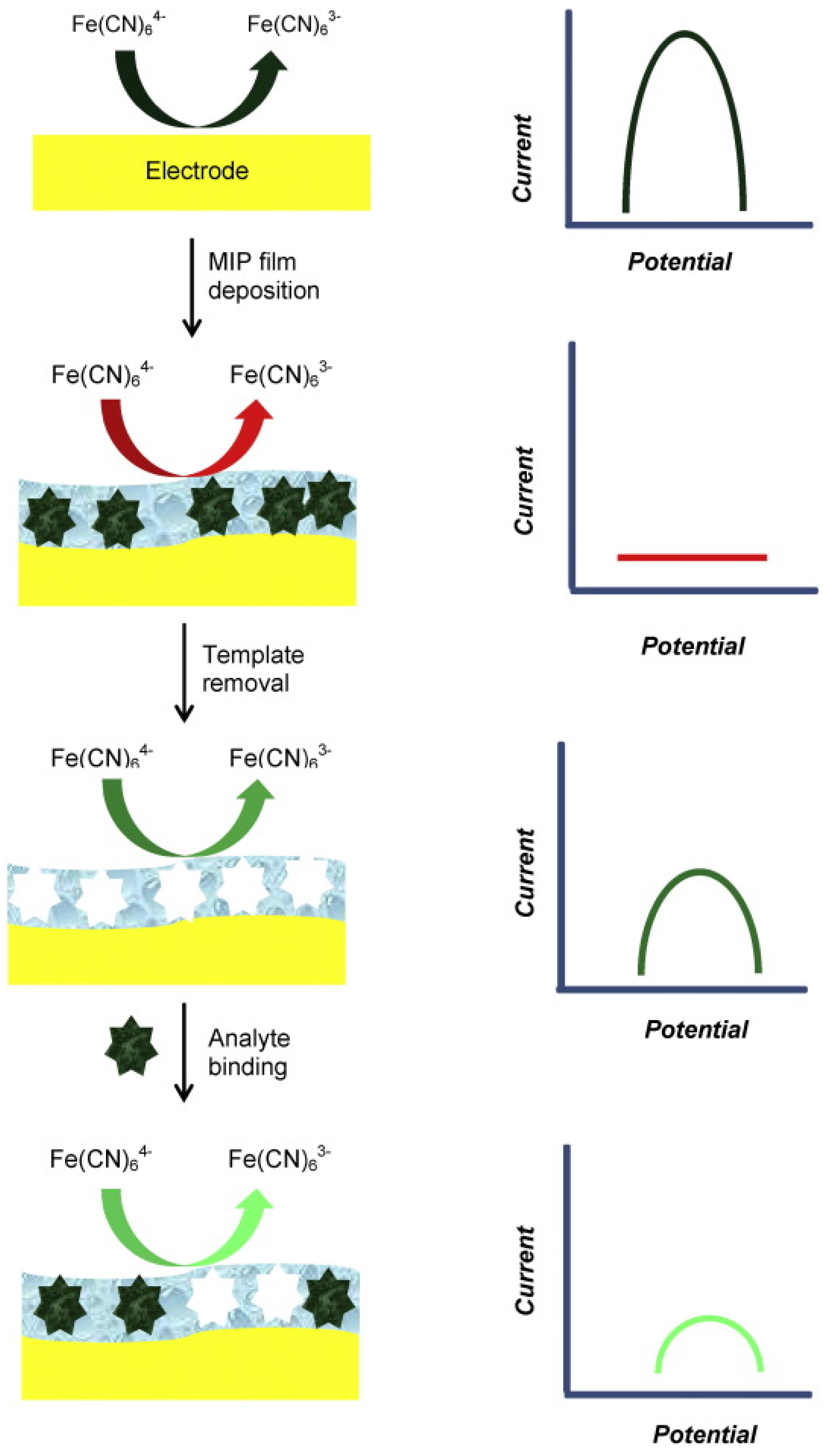
4.3. Redox-Inactive Analytes
5. Gate Effect
5.1. Diffusion-Controlled Mechanism
5.1.1. Shrinking and Swelling of MIP Film
5.1.2. Physical Cavity Blocking by Analyte Molecules
5.2. Electronic Property-Controlled Mechanism
5.3. The Electrical Double Layer Model
6. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3-APBA | 3-aminophenyl boronic acid |
| 3-NT | 3-nitrotyrosine |
| AC | alternating current |
| ANI | aniline |
| APBA | aminophenyl boronic acid |
| AuSPE | gold screen-printed electrode |
| Au-TFE | gold thin film electrode |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| BTC | butyrylthiocholine iodide |
| BuChE | butyrylcholinesterase |
| CA15-3 | cancer antigen 15-3 |
| CNT | carbon nanotube |
| CS | chitosan solution |
| CV | cyclic voltammetry |
| cyt c | cytochrome c |
| DET | direct electron transport |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DPA | dipicolinic acid |
| DPV | differential pulse voltammetry |
| EGTA | ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid |
| EIS | electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| eMIP | electro synthesized molecularly imprinted polymer |
| EP | epinephrine |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| GCE | glassy carbon electrode |
| GSPE | graphene screen-printed electrode |
| HER2-ECD | extracellular domain of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HTHP | hexameric tyrosine-coordinated heme protein |
| ITO | indium-tin-oxide |
| LBL | layer-by-layer |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| MIP | molecularly imprinted polymer |
| mPD | m-phenylenediamine |
| MUA | mercaptoundecanoic acid |
| MWCNT | multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| ncovNP | SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein |
| NE | norepinephrine |
| NIP | non-molecular imprinted polymer |
| NP | nanoparticle |
| o-PD | o-phenylenediamine |
| OS | oxidative stress |
| PANI | polyaniline |
| PAPBA | polyaminophenylboronic acid |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PmPD | poly-m-phenylenediamine |
| POC | point-of-care |
| PPD | poly(o-phenylenediamine) |
| PPy | polypyrrole |
| Py | pyrrole |
| RAFT | reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SAM | self-assembly monolayer |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| SWV | square-wave voltammetry |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Artificial biosensors: How can molecular imprinting mimic biorecognition? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 922–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Zebger, I.; Scheller, F.W. Simple and Robust: The Claims of Protein Sensing by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 330, 129369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, D.; Aggour, M.G.; Farghali, A.A.; Mahajan, R.; Wiklander, J.G.; Nicholls, I.A.; Piletsky, S.A. Strategies for molecular imprinting and the evolution of MIP nanoparticles as plastic antibodies—Synthesis and applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Peeters, M.; Tridente, A.; Banks, C.E. Molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical biosensors: Overcoming the challenges of detecting vital biomarkers and speeding up diagnosis. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasco, M.F.; Truta, L.A.; Sales, M.G.F.; Moreira, F.T. Imprinting technology in electrochemical biomimetic sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays–An overview of the current status quo. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. How Reliable Is the Electrochemical Readout of MIP Sensors? Sensors 2020, 20, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, O.S.; Bedwell, T.S.; Esen, C.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers in electrochemical and optical sensors. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Cowie, A.C. Progress in molecularly imprinted polymers for biomedical applications. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2019, 22, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z. Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Akgönüllü, S.; Yavuz, H.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based sensors for medical applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igarzabal, C.I.A.; Martinelli, M.; Brunetti, V.; Strumia, M.C. Adaptation of Biopolymers to Specific Applications. In Surface Modification of Biopolymers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 84–112. [Google Scholar]
- Anantha-Iyengar, G.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Nallal, M.; Lee, K.-P.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Lakshmi, D.; Sai-Anand, G. Functionalized conjugated polymers for sensing and molecular imprinting applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 1–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskierko, Z.; Sharma, P.S.; Bartold, K.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; Noworyta, K.; Kutner, W. Molecularly imprinted polymers for separating and sensing of macromolecular compounds and microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.P. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Jagminas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Advances in molecularly imprinted polymers based affinity sensors. Polymers 2021, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikay, G.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W.; Ozkan, S.A. Au-Pt nanoparticles based molecularly imprinted nanosensor for electrochemical detection of the lipopeptide antibiotic drug Daptomycin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, G.; Bottari, F.; Sleegers, N.; Florea, A.; Cowen, T.; Moretto, L.M.; Piletsky, S.; De Wael, K. Conductive imprinted polymers for the direct electrochemical detection of β-lactam antibiotics: The case of cefquinome. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, I.-A.; Iacob, B.-C.; Dudaș, C.-L.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Bogdan, D.; Marian, I.O.; Bodoki, E.; Oprean, R. Biomimetic electrochemical sensor for the highly selective detection of azithromycin in biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Kim, K.-H. Recent advances in nanomaterial-based electrochemical detection of antibiotics: Challenges and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 153, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Niu, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, R. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted composite membrane of poly (o-aminothiophenol) with gold nanoparticles for sensitive determination of herbicide simazine in environmental samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Mazzotta, E.; Picca, R.A.; Poma, A.; Chianella, I.; Piletsky, S.A. MIP sensors–the electrochemical approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1827–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Daneshi, M.; Marty, J.L. Recent developments in non-enzymatic (bio) sensors for detection of pesticide residues: Focusing on antibody, aptamer and molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 2021, 232, 122397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Ozkan, S.A.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical MIP-sensors for drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P.; Tamboli, V.; Harniman, R.L.; Estrela, P.; Allender, C.J.; Bowen, J.L. Aptamer–MIP hybrid receptor for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, N.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Jamaludin, N.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based DNA biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, B.; Freund, M.S. Saccharide imprinting of poly (aniline boronic acid) in the presence of fluoride. Analyst 2003, 128, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehit, E.; Drzazgowska, J.; Buchenau, D.; Yesildag, C.; Lensen, M.; Altintas, Z. Ultrasensitive nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, A.; Bouchikhi, B.; El Bari, N. A nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer and its application in measuring saliva glucose. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetzschmann, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.W. Label-Free MIP Sensors for Protein Biomarkers. In Label-Free Biosensing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 291–321. [Google Scholar]
- Erdőssy, J.; Horváth, V.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheller, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for biopolymers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 14, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Z.; Li, J.; Lu, W.; Li, B.; Yang, G.; Bi, Y.; Arabi, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, L. Molecularly imprinted polymers based materials and their applications in chromatographic and electrophoretic separations. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 146, 116504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based microfluidic systems for point-of-care applications. Micromachines 2019, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical sensors based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spychalska, K.; Zając, D.; Baluta, S.; Halicka, K.; Cabaj, J. Functional polymers structures for (Bio) sensing application—A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beluomini, M.A.; da Silva, J.L.; de Sá, A.C.; Buffon, E.; Pereira, T.C.; Stradiotto, N.R. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymer on nanostructured carbon materials: A review. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 840, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical detection and analysis: Progress and perspectives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12568–12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Ji, Y.; Li, R. Molecularly imprinted polymer-enhanced biomimetic paper-based analytical devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1148, 238196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiech, M.; Luliński, P.; Wieczorek, P.P.; Marć, M. Quantum and carbon dots conjugated molecularly imprinted polymers as advanced nanomaterials for selective recognition of analytes in environmental, food and biomedical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, M.M. Advancements of chiral molecularly imprinted polymers in separation and sensor fields: A review of the last decade. Talanta 2021, 224, 121794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasseb, A.A.; Shehab, O.R.; El Nashar, R.M. Application of molecularly imprinted polymers for electrochemical detection of some important biomedical markers and pathogens. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 31, 100848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Barton, S.J.; Wren, S.P.; Barker, J. Review on molecularly imprinted polymers with a focus on their application to the analysis of protein biomarkers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Medina Rangel, P.X.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Antibody mimics for bioimaging and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczura, M.; Luliński, P.; Sobiech, M. Imprinting Technology for Effective Sorbent Fabrication: Current State-of-Art and Future Prospects. Materials 2021, 14, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Sarhan, A.; Zabrocki, K. Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of racemates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1973, 14, 4329–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, F.H. The preparation of specific adsorbents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1949, 35, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickey, F.H. Specific adsorption. J. Phys. Chem. 1955, 59, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, G.; Vesper, W.; Grobe-Einsler, R.; Sarhan, A. Enzyme-analogue built polymers, 4. On the synthesis of polymers containing chiral cavities and their use for the resolution of racemates. Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1977, 178, 2799–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagishi, T.; Klotz, I.M. Macromolecule-small molecule interactions; introduction of additional binding sites in polyethyleneimine by disulfide cross–linkages. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 1972, 11, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrlöw, O.; Glad, M.; Mosbach, K. Acrylic polymer preparations containing recognition sites obtained by imprinting with substrates. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 299, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshady, R.; Mosbach, K. Synthesis of substrate-selective polymers by host-guest polymerization. Makromol. Chem. 1981, 182, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, L.; Sellergren, B.; Mosbach, K. Imprinting of amino acid derivatives in macroporous polymers. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 5211–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlatakis, G.; Andersson, L.I.; Müller, R.; Mosbach, K. Drug assay using antibody mimics made by molecular imprinting. Nature 1993, 361, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Sole, R.D.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; Grinsven, B.v.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent advances in electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymer sensing platforms for bioanalyte detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Chianella, I.; Larcombe, L.; Piletsky, S.A.; Noble, J.; Porter, R.; Horgan, A. The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1547–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kryscio, D.R.; Fleming, M.Q.; Peppas, N.A. Protein conformational studies for macromolecularly imprinted polymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenbach, V.; Hosseinpour, S.; Peukert, W. Isoelectric Point of Proteins at Hydrophobic Interfaces. Front. Chem. 2021, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, H.R.; Peppas, N.A. Protein-imprinted polymers: The shape of things to come? Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 5753–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Thomas, J.L.; Wang, S.-E.; Chen, H.-C.; Chou, T.-C. The microcontact imprinting of proteins: The effect of cross-linking monomers for lysozyme, ribonuclease A and myoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menaker, A.; Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Horváth, V.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized surface-imprinted conducting polymer microrods for selective protein recognition. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2271–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ye, J.; Bie, Z.; Liu, Z. Affinity-tunable specific recognition of glycoproteins via boronate affinity-based controllable oriented surface imprinting. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.-r.; Ni, Y.-l.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.-q.; Zhang, J. Detection of glycoprotein through fluorescent boronic acid-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 960, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjerten, S.; Liao, J.-L.; Nakazato, K.; Wang, Y.; Zamaratskaia, G.; Zhang, H.-X. Gels mimicking antibodies in their selective recognition of proteins. Chromatographia 1997, 44, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Heényi, C.; Bikadi, Z.; Gao, J.-P.; Hjerten, S. Some studies of the chromatographic properties of gels (‘artificial antibodies/receptors’) for selective adsorption of proteins. Chromatographia 2001, 54, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Turner, A.P. Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng-Jun, Z.; Xiong-Hui, M.; Jian-Ping, L. An insulin molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on epitope imprinting. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Rachkov, A.; Minoura, N. Recognition of oxytocin and oxytocin-related peptides in aqueous media using a molecularly imprinted polymer synthesized by the epitope approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 889, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaskar, A.; Kulkarni-Kale, U. Prediction of three-dimensional structure and mapping of conformational epitopes of envelope glycoprotein of Japanese encephalitis virus. Virology 1999, 261, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, N.W.; Wright, B.E.; Hlady, V.; Britt, D.W. Formation of protein molecular imprints within Langmuir monolayers: A quartz crystal microbalance study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ambrosini, S.; Tamahkar, E.; Rossi, C.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Toward a universal method for preparing molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles with antibody-like affinity for proteins. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczko, E.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletska, E.; Piletsky, S. PEG-stabilized core–shell surface-imprinted nanoparticles. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9891–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moczko, E.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; de Vargas Sansalvador, I.P.; Caygill, S.; Canfarotta, F.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S. Surface-modified multifunctional MIP nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, A.G.; Haq, I.; Cowen, T.; Di Masi, S.; Trivedi, S.; Alanazi, K.; Piletska, E.; Mujahid, A.; Piletsky, S.A. Design and fabrication of a smart sensor using in silico epitope mapping and electro-responsive imprinted polymer nanoparticles for determination of insulin levels in human plasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, G.; Ozgur, E.; Rad, A.Y.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Rapid real-time detection of procalcitonin using a microcontact imprinted surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Analyst 2013, 138, 6422–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular imprinting techniques used for the preparation of biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liang, R.; Qin, W. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based potentiometric sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepa, J.; Šišoláková, I.; Vojtko, M.; Trnková, L.; Nagy, G.; Maskaľová, I.; Oriňak, A.; Oriňaková, R. NiO Nanoparticles for Electrochemical Insulin Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, G.; Haschick, R.; Chiad, K.; Klapper, M.; Müllen, K.; Biffis, A. Molecularly imprinted nanospheres by nonaqueous emulsion polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their advances toward industrial use: A review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menger, M.; Yarman, A.; Erdőssy, J.; Yildiz, H.B.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. MIPs and aptamers for recognition of proteins in biomimetic sensing. Biosensors 2016, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, Z.; Erdőssy, J.; Keltai, K.; Scheller, F.W.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polyscopoletin nanofilms for human serum albumin detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 977, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yazdani, Z.; Yadegari, H.; Heli, H. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical nanobiosensor for prostate specific antigen determination. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 566, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.G.; Silva, M.S.; Freitas, M.; Nouws, H.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the point-of-care detection of a breast cancer biomarker (CA 15-3). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Erdossy, J.; Katz, S.; Zebger, I.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Altintas, Z.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Scheller, F.W. Electrosynthesized MIPs for transferrin: Plastibodies or nano-filters? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 105, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpleby, R.J., II; Baxter, S.C.; Rampey, A.M.; Rushton, G.T.; Chen, Y.; Shimizu, K.D. Characterization of the heterogeneous binding site affinity distributions in molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 804, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, B.r.C.; O’Mahony, J.; Karlsson, J.G.; Bengtsson, H.; Eriksson, L.A.; Nicholls, I.A. Structure and dynamics of monomer—Template complexation: An explanation for molecularly imprinted polymer recognition site heterogeneity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 13297–13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Karim, K.; Piletsky, S. Computational approaches in the design of synthetic receptors–A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Turner, A.P. Electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2002, 14, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K. Molecularly imprinted polymers in analytical chemistry. Analyst 2001, 126, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, F.; Liu, Z.; Wu, G.L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Willner, I. Surface imprinting in layer-by-layer nanostructured films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.M. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers (e-MIPs), perceptions based in recent literature for soon-to-be world-class scientists. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Lopez, M.; Gutierrez-Fernandez, S.; Lobo-Castanon, M.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Electrochemical sensing with electrodes modified with molecularly imprinted polymer films. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, M.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Niu, L.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Liu, W. Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer/reduced graphene oxide composite for simultaneous determination of uric acid and tyrosine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahcen, A.A.; Amine, A. Recent advances in electrochemical sensors based on molecularly imprinted polymers and nanomaterials. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benachio, I.; Lobato, A.; Gonçalves, L.M. Employing molecularly imprinted polymers in the development of electroanalytical methodologies for antibiotic determination. J. Mol. Recognit. 2021, 34, e2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, X.; Liu, B.; Fu, L.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, G.; Tang, D.J.E. Molecular imprint for electrochemical detection of streptomycin residues using enzyme signal amplification. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Cristalli, A.; Nagy, G.; Nagy, L.; Corder, C.; Pendley, B.D.; Ufer, S.; Nagle, H.T.; Neuman, M.R.; Lindner, E. Analytical performance characteristics of thin and thick film amperometric microcells. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 369, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regasa, M.B.; Soreta, T.R.; Femi, O.E.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Subbiahraj, S. Novel multifunctional molecular recognition elements based on molecularly imprinted poly (aniline-co-itaconic acid) composite thin film for melamine electrochemical detection. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 27, 100318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-based synthetic receptor for direct detection of bovine leukemia virus glycoproteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, A.; Warriner, K. Microbial imprinted polypyrrole/poly (3-methylthiophene) composite films for the detection of Bacillus endospores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, X.-T.; Zhou, J.-P.; Liu, G.-Z.; Zhang, S.-Y. Electrochemical preparation of surface molecularly imprinted poly (3-aminophenylboronic acid)/MWCNTs nanocomposite for sensitive sensing of epinephrine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikay, G.; Kurbanoglu, S.; Zhang, X.; Kosak Soz, C.; Wollenberger, U.; Ozkan, S.A.; Yarman, A.; Scheller, F.W. Electrochemical MIP sensor for butyrylcholinesterase. Polymers 2019, 11, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bozal-Palabiyik, B.; Lettieri, M.; Uslu, B.; Marrazza, G. Electrochemical detection of vascular endothelial growth factor by molecularly imprinted polymer. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziq, A.; Kidakova, A.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Development of a portable MIP-based electrochemical sensor for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wei, X. A sensitive and selective sensor for dopamine determination based on a molecularly imprinted electropolymer of o-aminophenol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasta, H.; Goyal, R.N. Molecularly imprinted sensor based on o-aminophenol for the selective determination of norepinephrine in pharmaceutical and biological samples. Talanta 2014, 125, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, J.G.; Rebelo, P.; Freitas, M.; Nouws, H.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Breast cancer biomarker (HER2-ECD) detection using a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.V.; Marques, A.C.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Paper-based (bio)sensor for label-free detection of 3-nitrotyrosine in human urine samples using molecular imprinted polymer. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2020, 28, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosserdt, M.; Gajovic-Eichelman, N.; Scheller, F.W.J.A. Modulation of direct electron transfer of cytochrome c by use of a molecularly imprinted thin film. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6437–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomo, G.; Waryo, T.; Feleni, U.; Baker, P.; Iwuoha, E. Functional Polymers. In Electrochemical Polymerization; Jafar Mazumder, M.A., Sheardown, H., Al-Ahmed, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 105–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, X.; Xing, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Zhou, H. Molecularly imprinted polymers based electrochemical sensor for bovine hemoglobin recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 168, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Xia, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, F.; Bi, S.; Shi, G.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. An ionic liquid-modified graphene based molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for sensitive detection of bovine hemoglobin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, J.; Szűcs, J.; Dorkó, Z.; Horváth, V.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Nanosphere lithography as a versatile method to generate surface-imprinted polymer films for selective protein recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4703–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceolin, G.; Orbán, Á.; Kocsis, V.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Kézsmárki, I.; Horváth, V. Electrochemical template synthesis of protein-imprinted magnetic polymer microrods. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5209–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramanavičius, A.; Ramanavičienė, A.; Malinauskas, A. Electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymer—Polypyrrole. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6025–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, A.; Oztekin, Y.; Ramanaviciene, A. Electrochemical formation of polypyrrole-based layer for immunosensor design. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, T.; Raya, A.; Barrero, M.J.; Garreta, E.; Consiglio, A.; Gonzalez, F.; Vassena, R.; Bilić, J.; Pekarik, V.; Tiscornia, G. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryanarayanan, V.; Wu, C.T.; Ho, K.C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1795–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurlock, L.D.; Jaramillo, A.; Praserthdam, A.; Lewis, J.; Brajter-Toth, A. Selectivity and sensitivity of ultrathin purine-templated overoxidized polypyrrole film electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 336, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deore, B.; Chen, Z.; Nagaoka, T. Potential-induced enantioselective uptake of amino acid into molecularly imprinted overoxidized polypyrrole. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3989–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Menaker, A.; Gyurcsányi, R.E.; Öpik, A. Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polypyrrole films for enantioselective recognition of L-aspartic acid. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yao, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole prepared by electrodeposition for the selective recognition of tryptophan enantiomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1952–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, L.; Şahin, Y. Determination of paracetamol based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 127, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkorucuklu, S.P.; Sahin, Y.; Alsancak, G. Voltammetric behaviour of sulfamethoxazole on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted overoxidized polypyrrole. Sensors 2008, 8, 8463–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebarvia, B.S.; Cabanilla, S.; Sevilla, F., III. Biomimetic properties and surface studies of a piezoelectric caffeine sensor based on electrosynthesized polypyrrole. Talanta 2005, 66, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, L.; Sahin, M.; Sahin, Y. Electrochemical preparation of a molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-modified pencil graphite electrode for determination of ascorbic acid. Sensors 2008, 8, 5792–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.-W.; Chang, H.-J.; Lee, N.; Kim, J.-H.; Chun, H.S. Detection of mycoestrogen zearalenone by a molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, C.-L.; Milne, W.I. Dynamic modulation of detection window in conducting polymer based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, P.; Pasha, S.K.; Snipes, S.A.; Bhansali, S. A reusable electrochemical biosensor for monitoring of small molecules (cortisol) using molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 164, B54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Finkelsteinas, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for sensor design. Mater. Sci. 2004, 10, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Gharbi, O.; Vivier, V.; Gao, M.; Orazem, M.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabi, M.; Kuralay, F.; Jager, E.W.; Beni, V.; Turner, A.P.J.B. Electrochemical bacterial detection using poly (3-aminophenylboronic acid)-based imprinted polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rick, J.; Chou, T.-C. Using protein templates to direct the formation of thin-film polymer surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, X. Synthesis of hydrophilic and conductive molecularly imprinted polyaniline particles for the sensitive and selective protein detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.K.; Dhand, C.; Malhotra, B.D. Molecularly imprinted polyaniline film for ascorbic acid detection. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xie, D.; Cai, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.N.; Yao, S.Z. Surface-Imprinting Sensor Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Graphene Composite for Determination of Bovine Serum Albumin. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, A. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensor for tyrosinase. Turk. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaie, N.; Daneshpour, M.; Azimzadeh, M.; Mahshid, S.; Khoshfetrat, S.M.; Jahanpeyma, F.; Gholaminejad, A.; Omidfar, K.; Foruzandeh, M. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on the use of polyaniline and its nanocomposites: A review on recent advances. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidenko, P.S.; Pidenko, S.A.; Skibina, Y.S.; Zacharevich, A.M.; Drozd, D.D.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Burmistrova, N.A. Molecularly imprinted polyaniline for detection of horseradish peroxidase. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 6509–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heineman, W.R.; Wieck, H.J.; Yacynych, A.M. Polymer film chemically modified electrode as a potentiometric sensor. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, K.; Ohsaka, T.; Ohnuki, Y.; Oyama, N. Electrochemical preparation of a ladder polymer containing phenazine rings. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1987, 219, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Palmisano, F.; Torsi, L.; Zambonin, P.G. Glucose fast-response amperometric sensor based on glucose oxidase immobilized in an electropolymerized poly (o-phenylenediamine) film. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Losito, I.; Zambonin, P.G. Molecularly imprinted electrosynthesized polymers: New materials for biomimetic sensors. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Doblhoff-Dier, O.; Takeuchi, T. A molecularly imprinted synthetic polymer receptor selective for atrazine. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 4404–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Madhuri, R.; Tiwari, M.P.; Sharma, P.S. Imprinting molecular recognition sites on multiwalled carbon nanotubes surface for electrochemical detection of insulin in real samples. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 9146–9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretjakov, A.; Syritski, V.; Reut, J.; Boroznjak, R.; Öpik, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer film interfaced with Surface Acoustic Wave technology as a sensing platform for label-free protein detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 902, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, A.; Hillman, A.R.; Ryder, K.S.; Cihangir, S. Highly Efficient Defluoridation of Water through Reusable poly (aniline-co-o-aminophenol) Copolymer Modified Electrode Using Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 022502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetterström, T.; Sharp, T.; Marsden, C.; Ungerstedt, U. In vivo measurement of dopamine and its metabolites by intracerebral dialysis: Changes after d-amphetamine. J. Neurochem. 1983, 41, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella, P.; Ghasemzadeh, B.; Mitchell, K.; Adams, R.N. Nafion-coated carbon fiber electrodes for neurochemical studies in brain tissue. Electroanalysis 1990, 2, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, S.J.; Macpherson, J.V. Enhancing square wave voltammetry measurements via electrochemical analysis of the non-faradaic potential window. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7935–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajovic-Eichelmann, N.; Ehrentreich-Förster, E.; Bier, F.F. Directed immobilization of nucleic acids at ultramicroelectrodes using a novel electro-deposited polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechtrirat, D.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Stöcklein, W.F.; Scheller, F.W.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N. Protein rebinding to a surface-confined imprint. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5231–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, T.; Mazzotta, E.; Malitesta, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polyscopoletin for the Electrochemical Detection of the Chronic Disease Marker Lysozyme. Biosensors 2021, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Yarman, A.; Jetzschmann, K.J.; Jeoung, J.-H.; Schad, D.; Dobbek, H.; Wollenberger, U.; Scheller, F.W. Molecularly imprinted electropolymer for a hexameric heme protein with direct electron transfer and peroxide electrocatalysis. Sensors 2016, 16, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.M.; Sette, G.; Phan, Q. Electrochemical probing of selective haemoglobin binding in hydrogel-based molecularly imprinted polymers. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9203–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazurenko, I.; Hitaishi, V.P.; Lojou, E. Recent advances in surface chemistry of electrodes to promote direct enzymatic bioelectrocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 19, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Díaz, G.; Antuña-Jiménez, D.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. New materials for analytical biomimetic assays based on affinity and catalytic receptors prepared by molecular imprinting. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 33, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Garcia-Cruz, A.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Kutner, W. ‘Gate effect’in molecularly imprinted polymers: The current state of understanding. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Ohdaira, R.; Iiyama, C.; Sakai, K. “Gate effect” of thin layer of molecularly-imprinted poly (methacrylic acid-co-ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 73, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, P.; Cieplak, M.; Majewska, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Sharma, P.S.; Kutner, W. “Gate Effect” in p-Synephrine Electrochemical Sensing with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Redox Probes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7546–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerdurai, V.; Cieplak, M.; Noworyta, K.R.; Gajda, M.; Ziminska, A.; Sosnowska, M.; Piechowska, J.; Borowicz, P.; Lisowski, W.; Shao, S. Electrochemical sensor for selective tyramine determination, amplified by a molecularly imprinted polymer film. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 138, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, T.F. Structural and conformational chemistry from electrochemical molecular machines. Replicating biological functions. A review. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 788–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
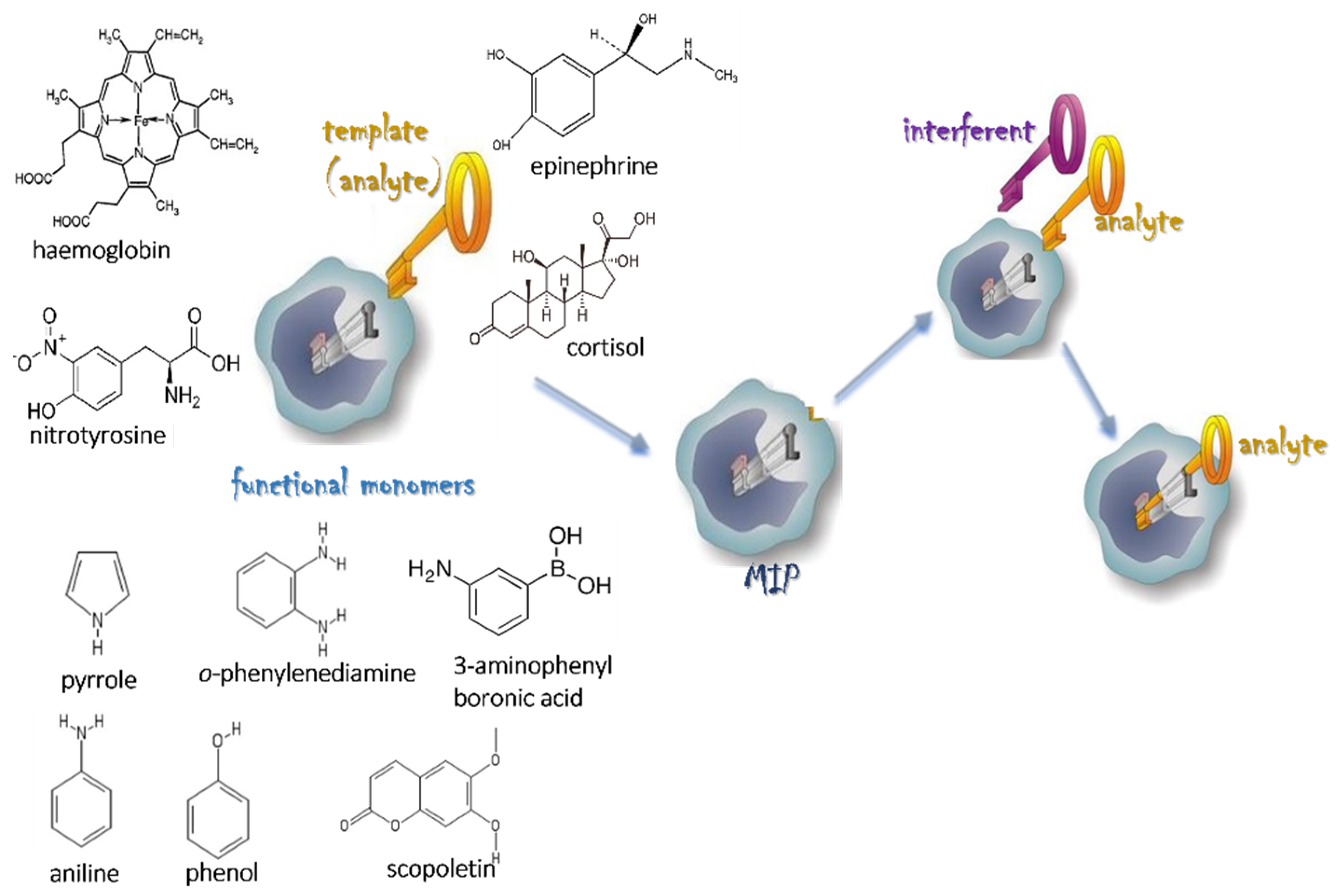
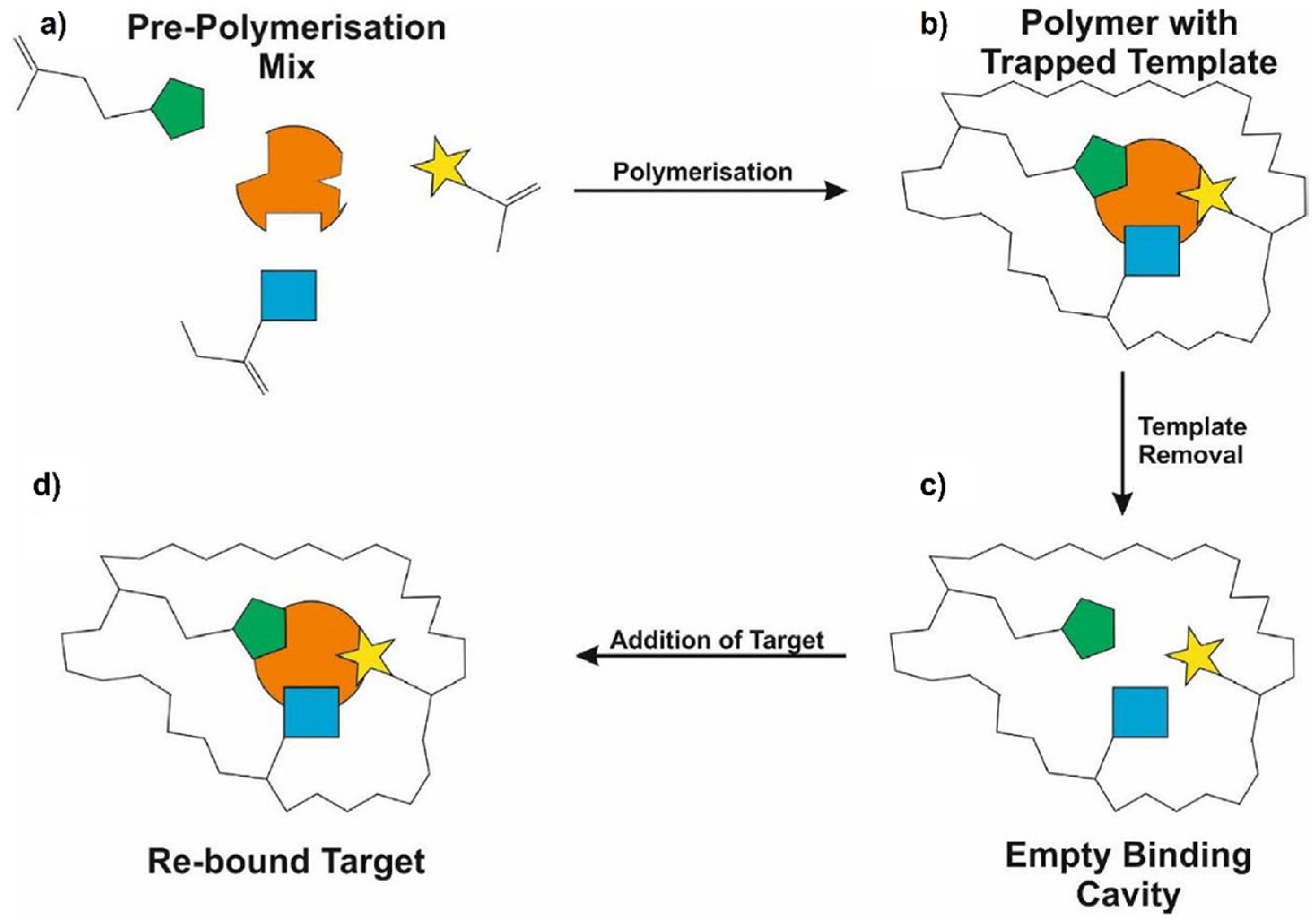
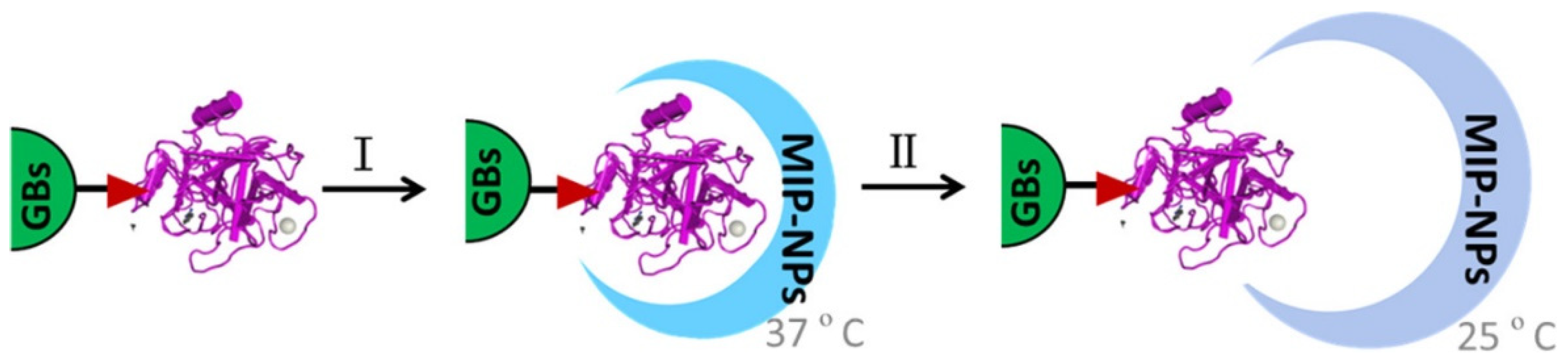
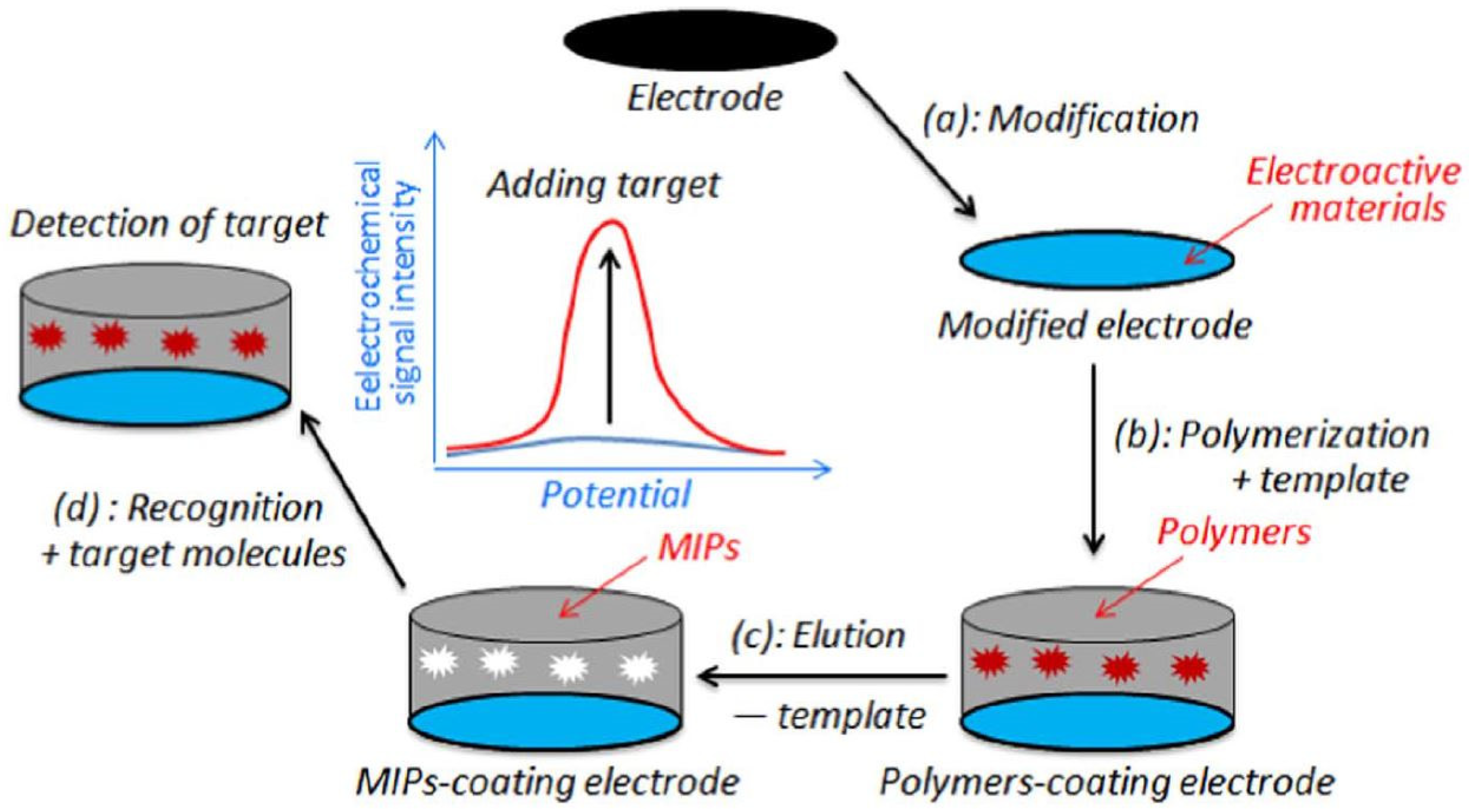
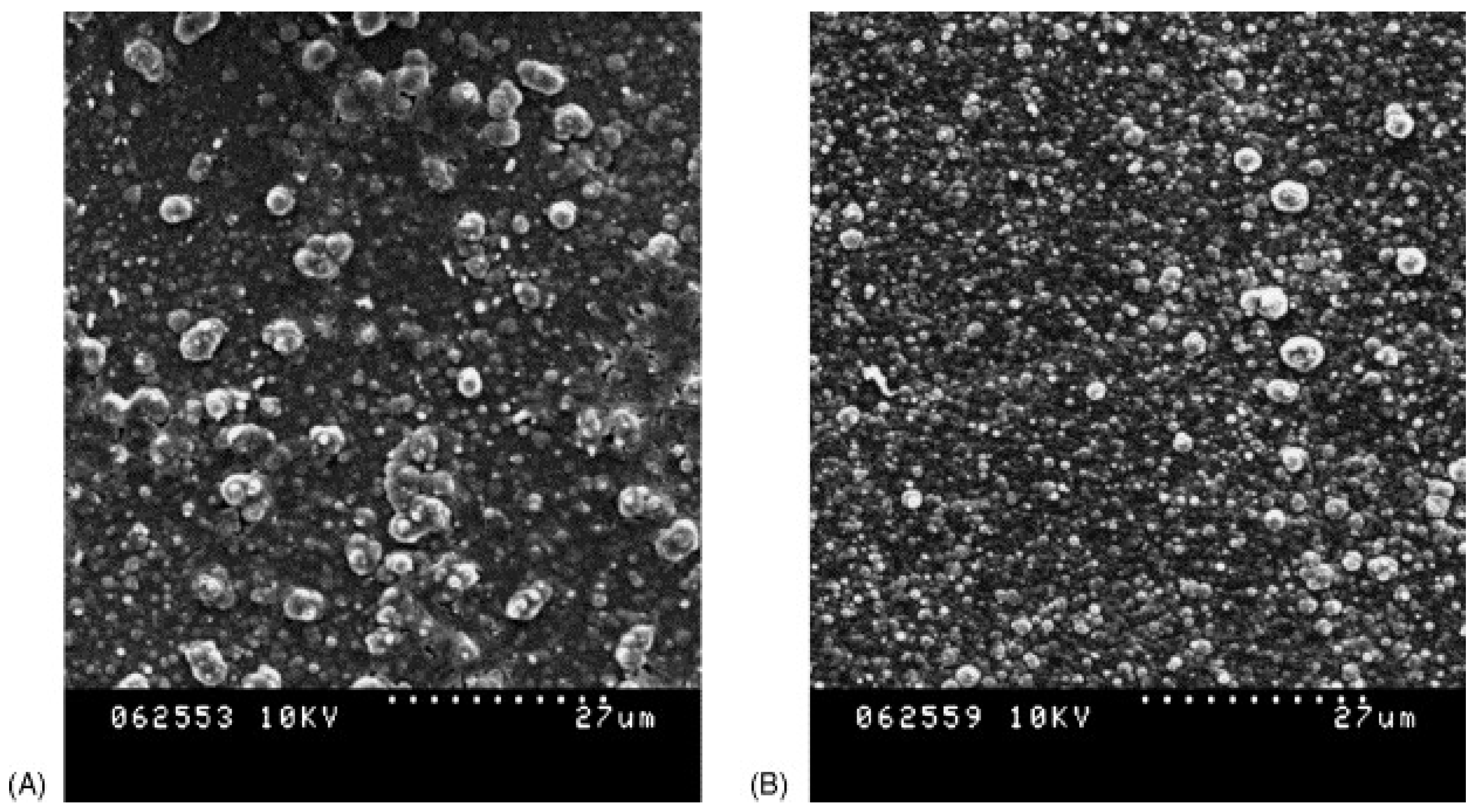
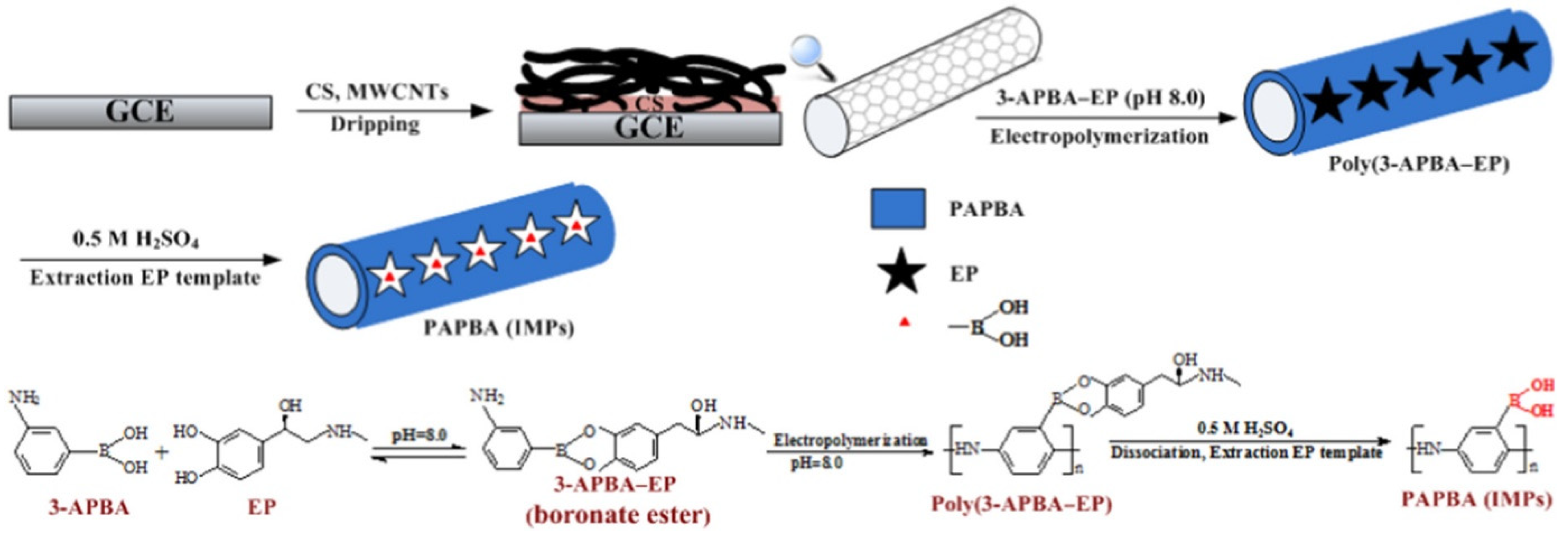


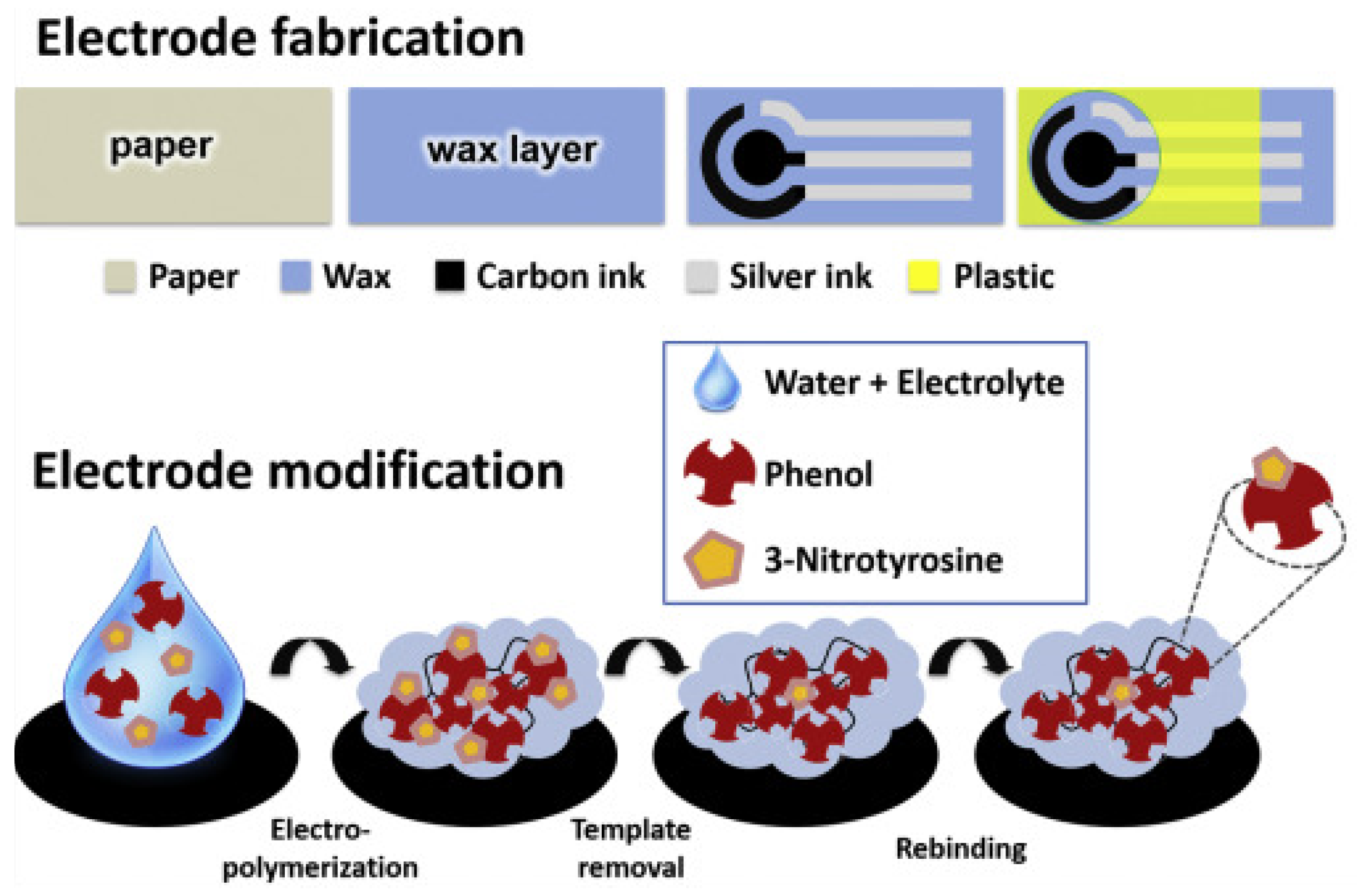
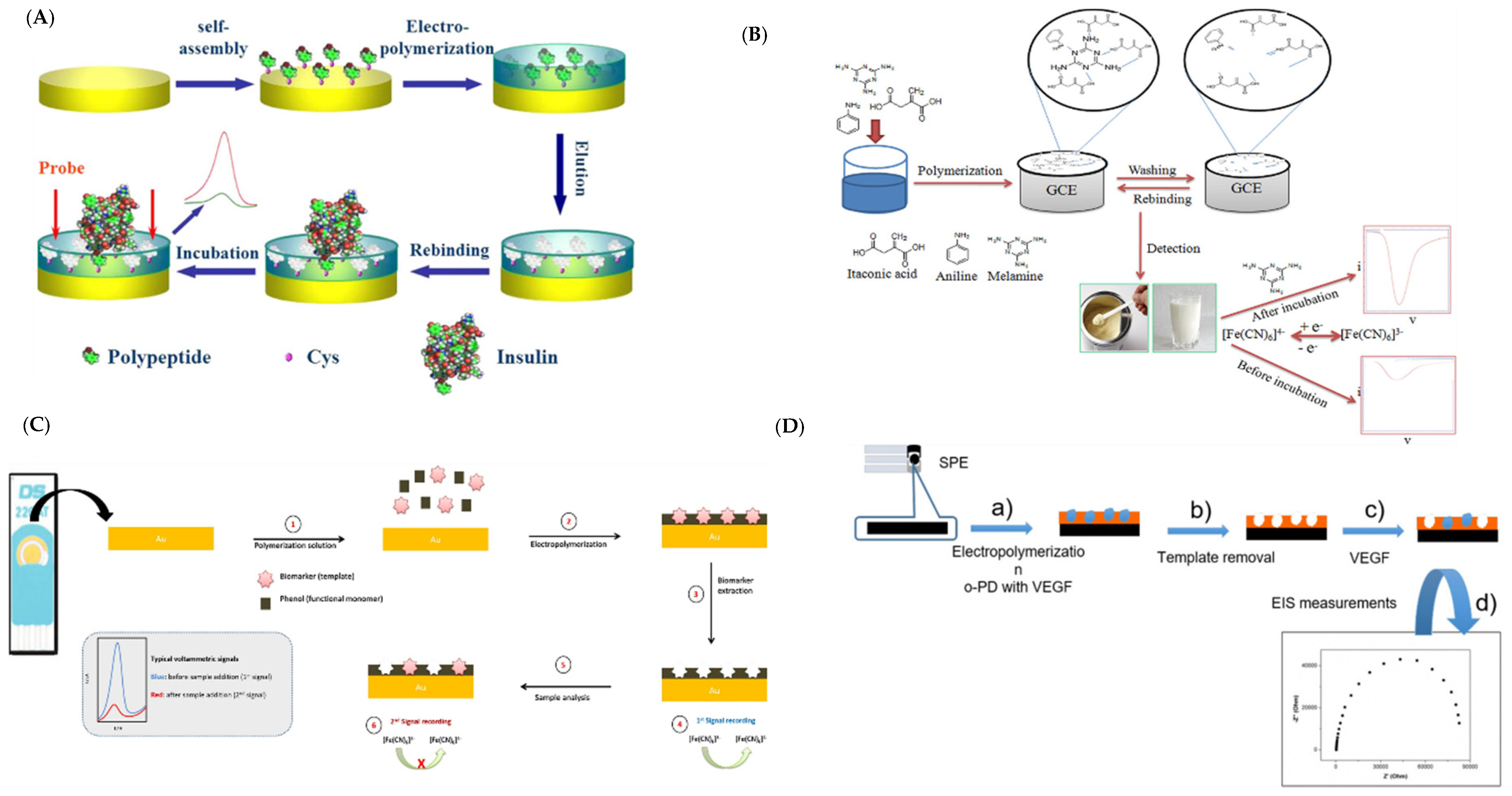

| Imprinting Method | Features |
|---|---|
| Bulk imprinting |
|
| Surface imprinting |
|
| Microcontact imprinting |
|
| Polymer-brush imprinting |
|
| Surface grafting |
|
| Epitope imprinting |
|
| Electropolymerization |
|
| Target | MIP | Electrode Material | Detection Method | Linear Centration Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gp51 | Ppy | Pt | PDA (Photodiode-Array) | - | - | [107] |
| B. subtilis endospores | Ppy/poly (3-methylthiophene) | GCE | EIS (electrochemical impedance spectroscopy) | 104–106 CFU/mL | 102 CFU/mL | [108] |
| EP | PAPBA | MWCNTs/GCE | DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) | 0.2–800 µM | 35 nM | [109] |
| Insulin | PPD | GCE | DPV | 10−14–5 · 10−13 M | 7.24 10−15 M | [71] |
| BuCHE | PPD | GCE | CV, amperometry | 0.05–2 nM | 14.7 pM | [110] |
| VEGF | PPD | SPE | EIS | 20–200 pg/mL | 0.08 pg/mL | [111] |
| ncovNP | PPD | Au-TFE | DPV | ≤111 fM | 15 fM | [112] |
| dopamine | poly(o-aminophenol) | Au | DPV | 20–250 nM | 1.98 nM | [113] |
| NE | poly(o-aminophenol) | GCE | SWV | 0.05–10 µM | 0.49 nM | [114] |
| CA15-3 | poly(2-aminophenol) | AuSPE | DPV | 5–50 U/mL | 1.5 U/mL | [90] |
| HER2-ECD | polyphenol | AuSPE | DPV | 10–70 ng/mL | 1.6 ng/mL | [115] |
| 3-NT | polyphenol | Paper-based with carbon ink | DPV | 500 nM–1 mM | 22.3 nM | [116] |
| cyt c | polyscopoletin | Au/MUA | CV, chronoamperometry | - | - | [117] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zidarič, T.; Finšgar, M.; Maver, U.; Maver, T. Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies. Biosensors 2022, 12, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010044
Zidarič T, Finšgar M, Maver U, Maver T. Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies. Biosensors. 2022; 12(1):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010044
Chicago/Turabian StyleZidarič, Tanja, Matjaž Finšgar, Uroš Maver, and Tina Maver. 2022. "Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies" Biosensors 12, no. 1: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010044
APA StyleZidarič, T., Finšgar, M., Maver, U., & Maver, T. (2022). Artificial Biomimetic Electrochemical Assemblies. Biosensors, 12(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12010044








