A Sarcopenia Detection System Using an RGB-D Camera and an Ultrasound Probe: Eye-in-Hand Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The arc curve fitting method of the angular surface of the subject’s thigh with an RGB-D camera with piecewise arcs [26] was changed to accommodate the eye-in-hand configuration. Moreover, in the proposed method, algebraic and geometric fitting methods [29,30,31,32] are both used to render the curve fitting result more quickly than the previous method (enhanced piecewise arc curve fitting method).
- An in-vitro test with bean curd-gelatin phantom was performed to validate the system and the proposed method. In opposition to the single-point muscle thickness measurements using ultrasound images in previous work [26], multiple-point bean curd thickness was measured.
2. Materials and Methods
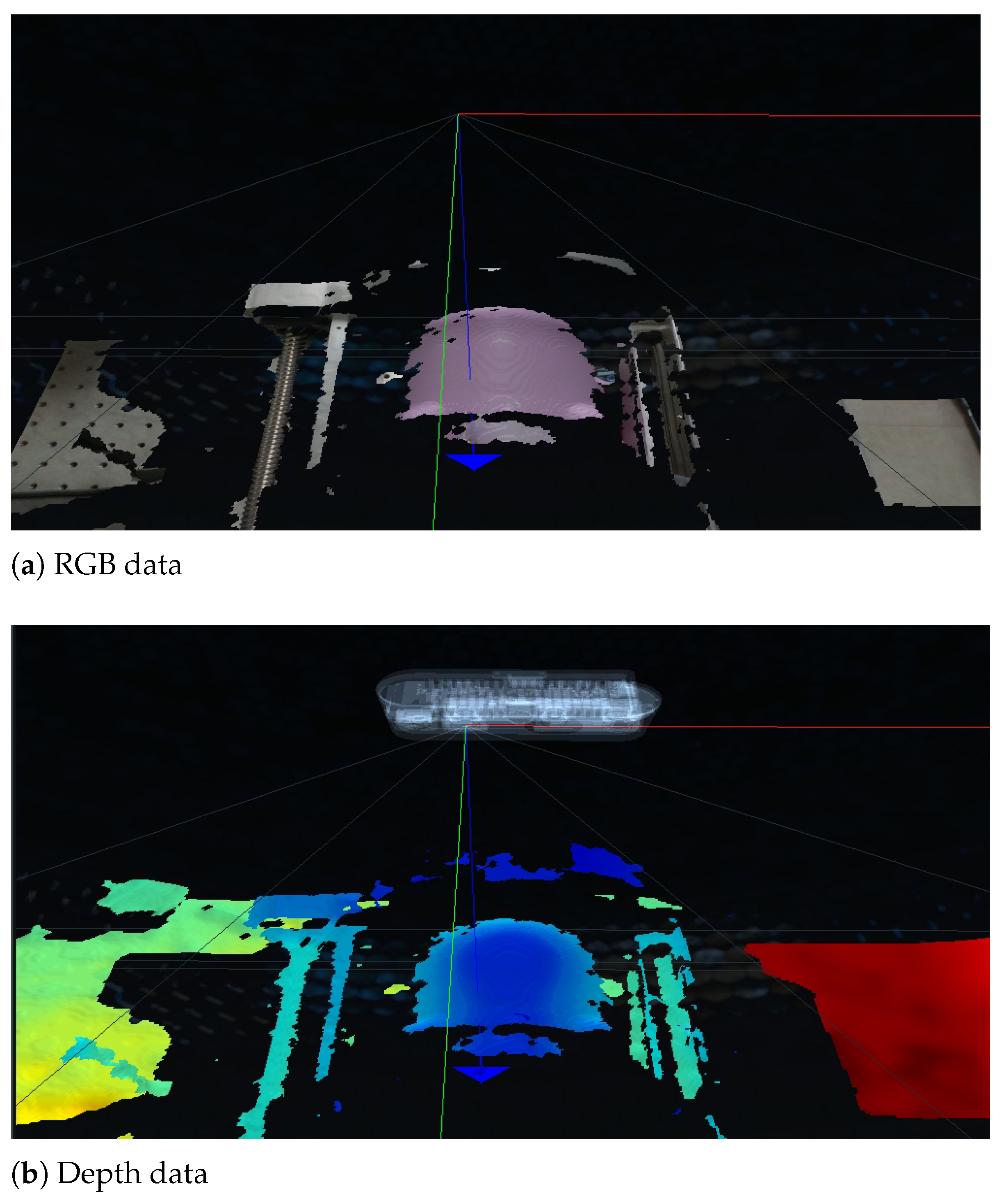
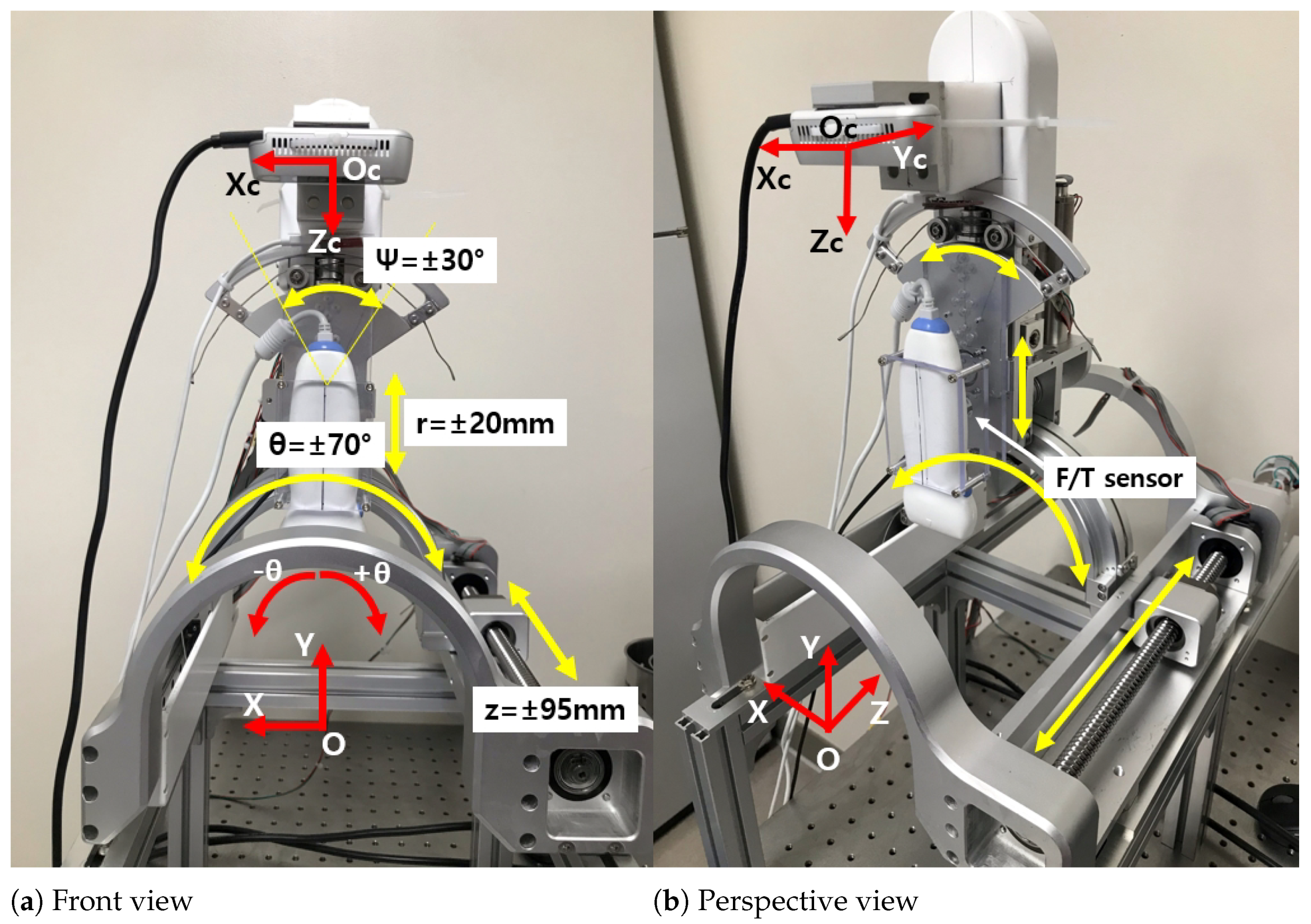
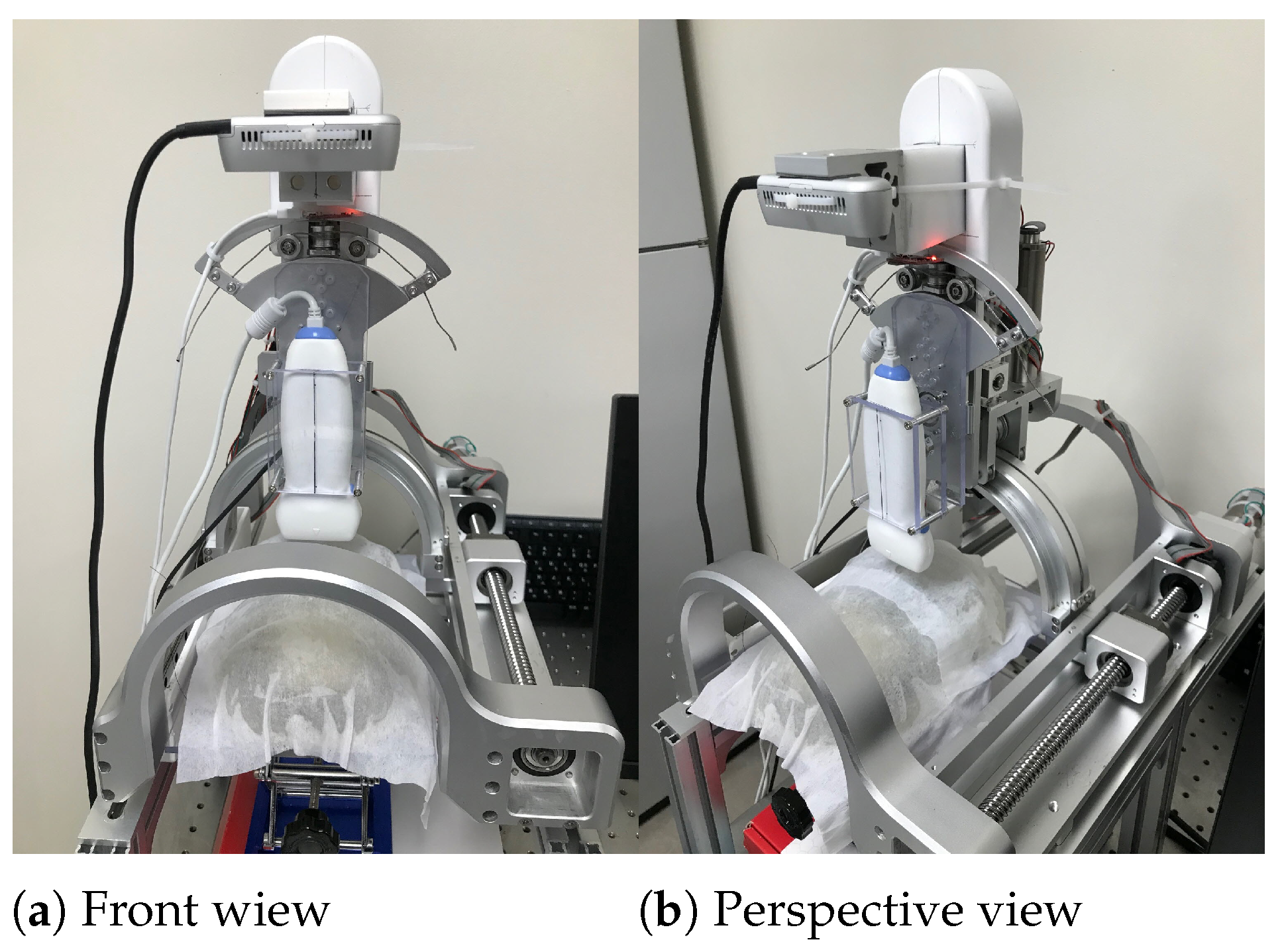
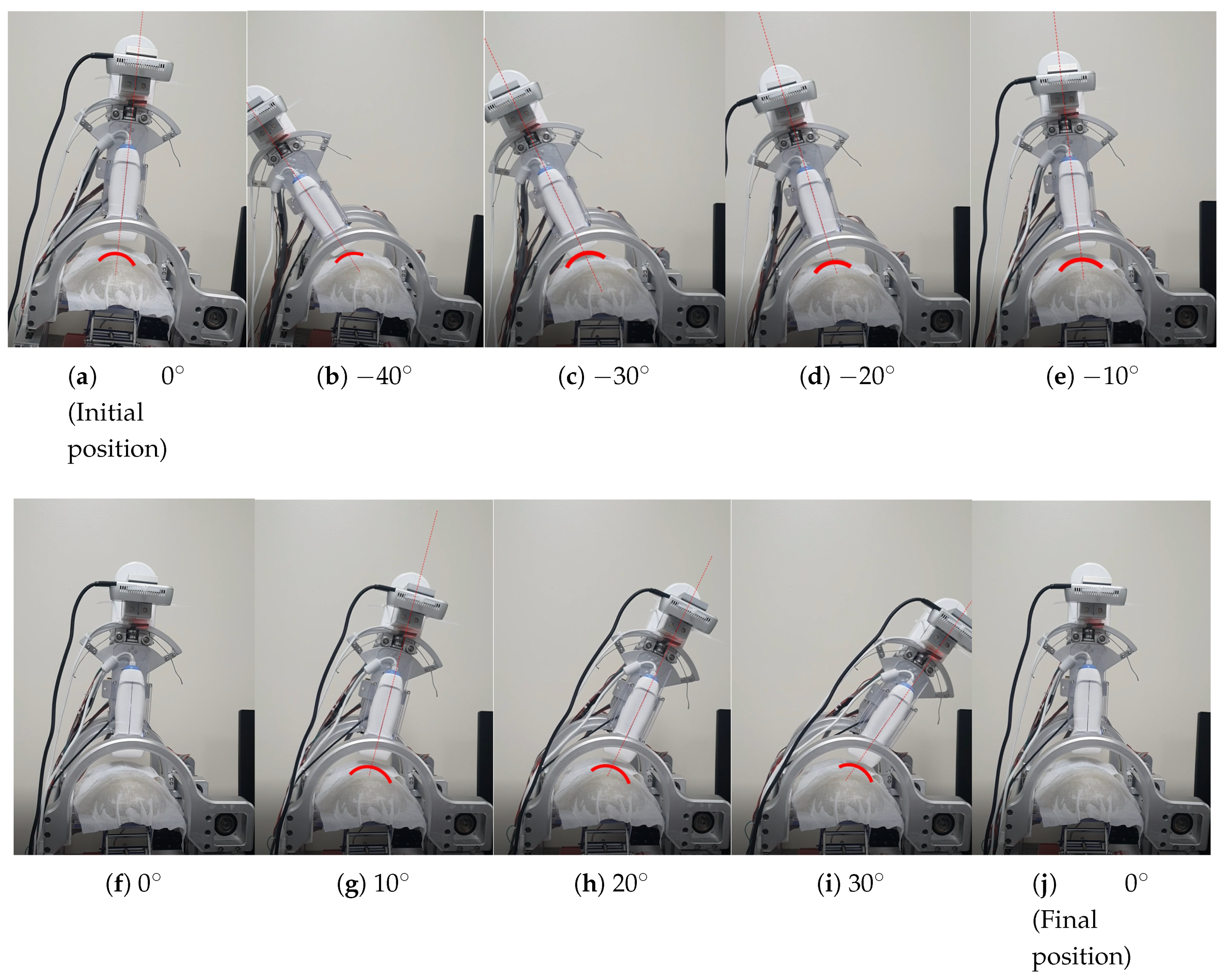
2.1. The Modified Sarcopenia Detection System
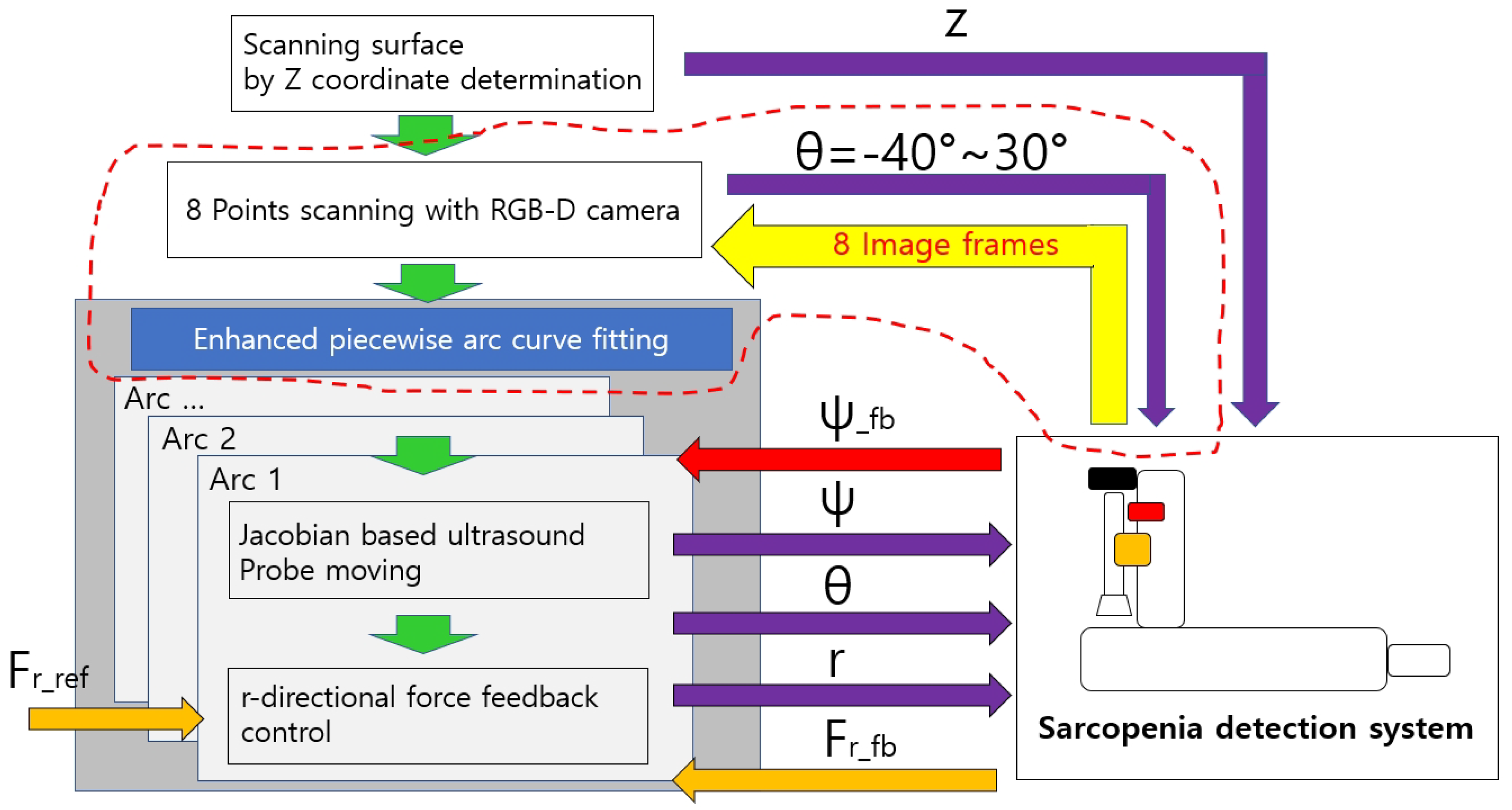
2.2. Modified Overall Control Flow Diagram
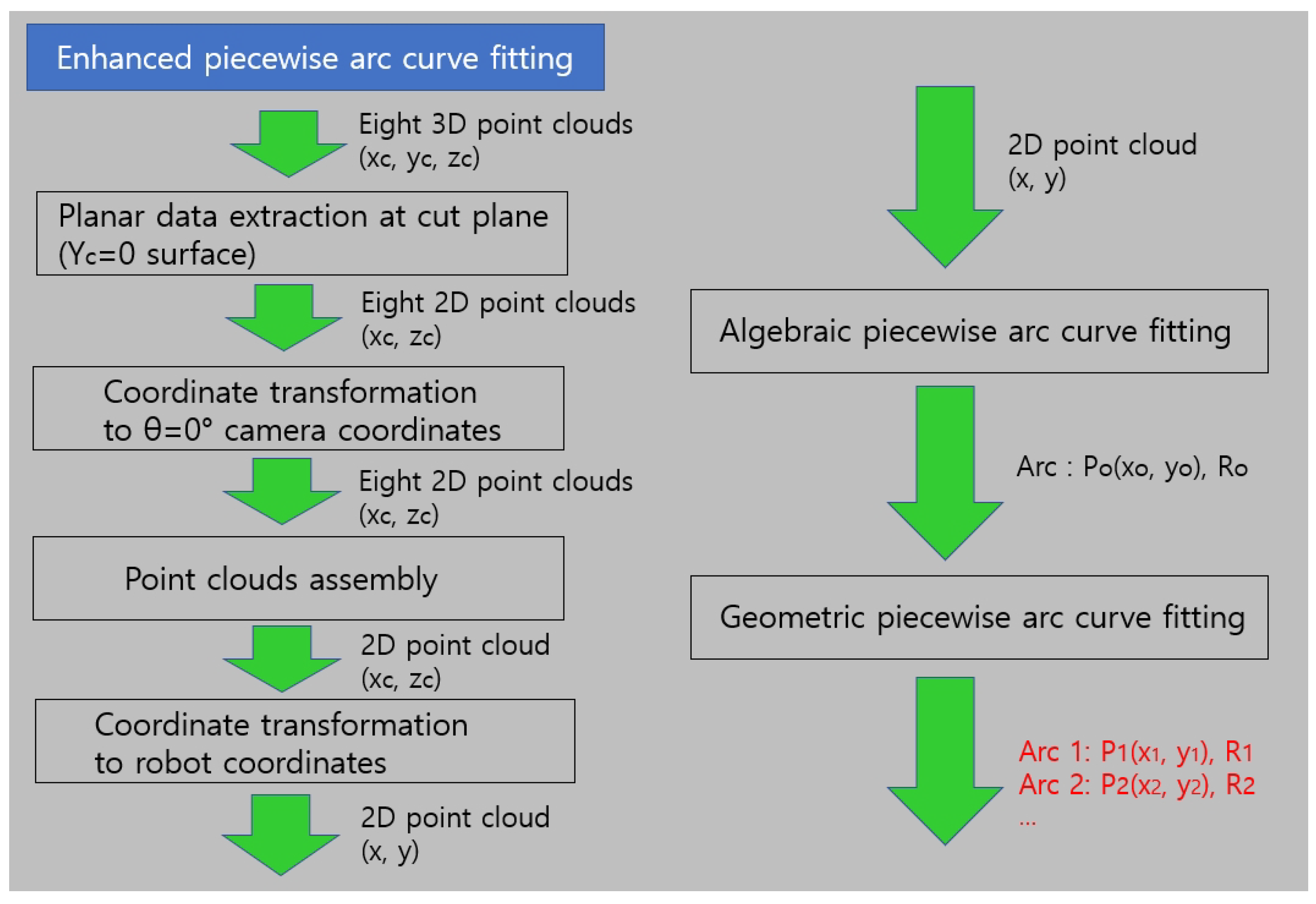
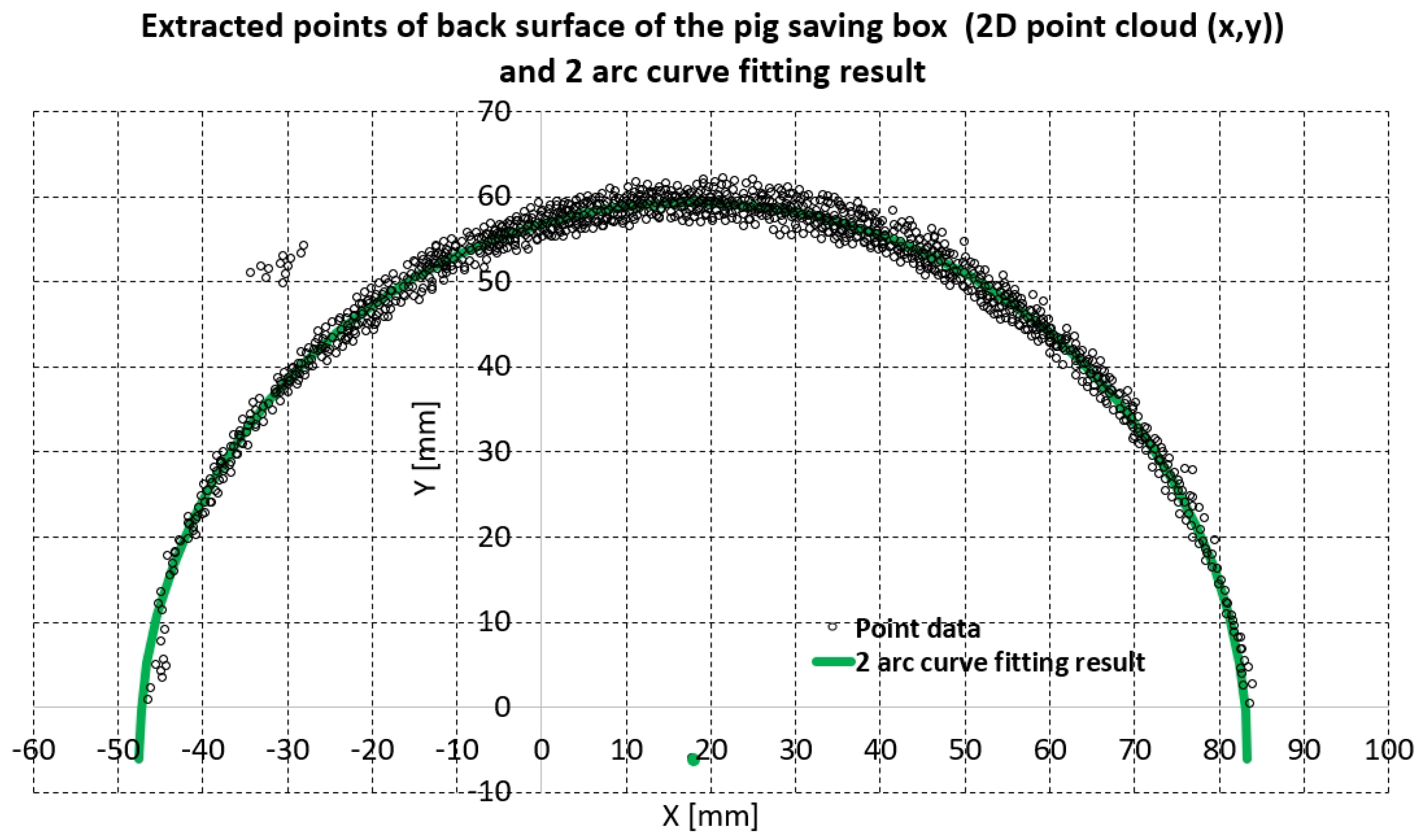
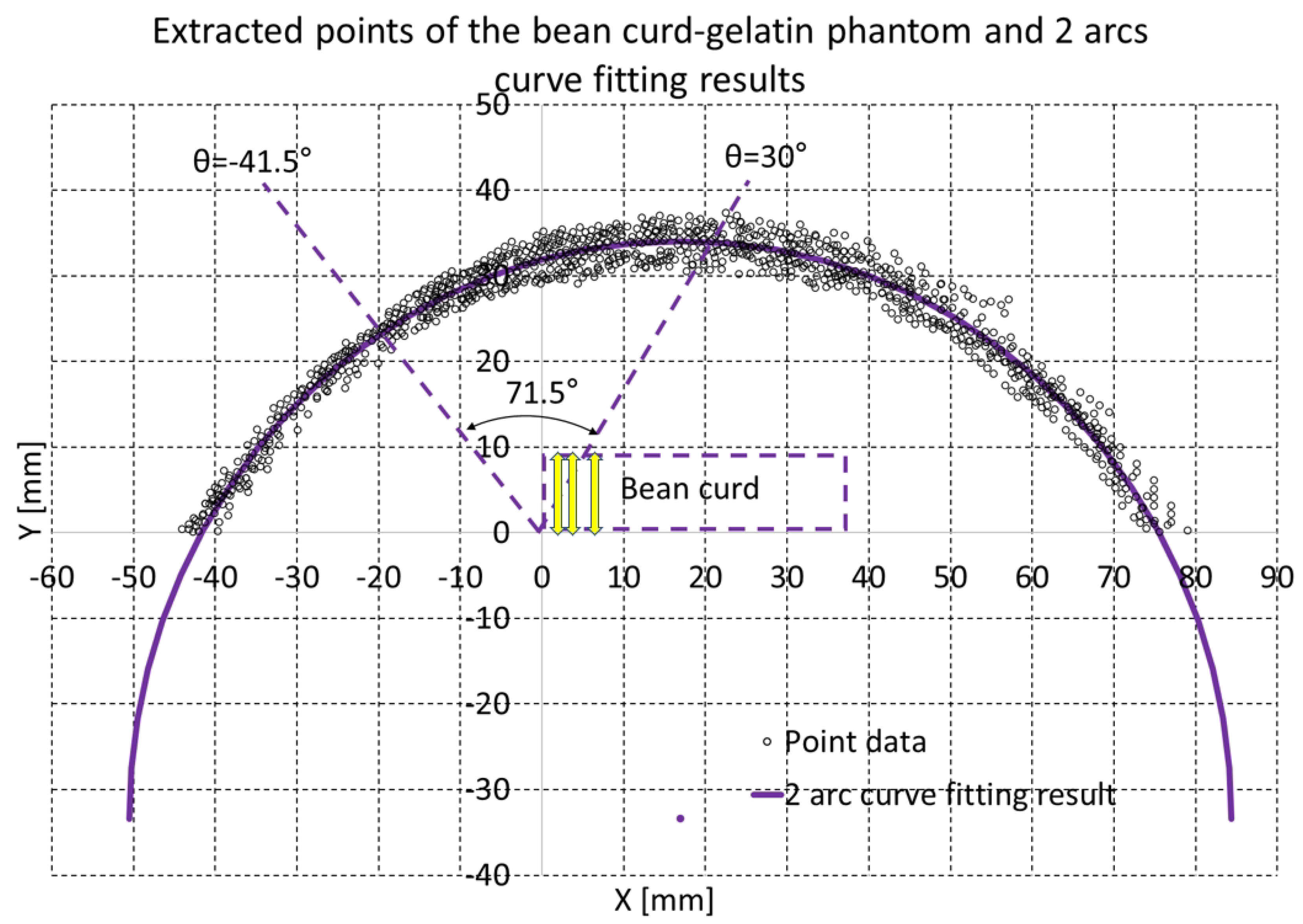
2.3. The Enhanced Piecewise Arc Curve Fitting Method
2.3.1. Details of the Enhanced Piecewise Arc Curve Fitting Method
2.3.2. A Comparison of the Enhanced Piecewise Arc Curve Fitting with the Piecewise Arc Curve Fitting
3. Results
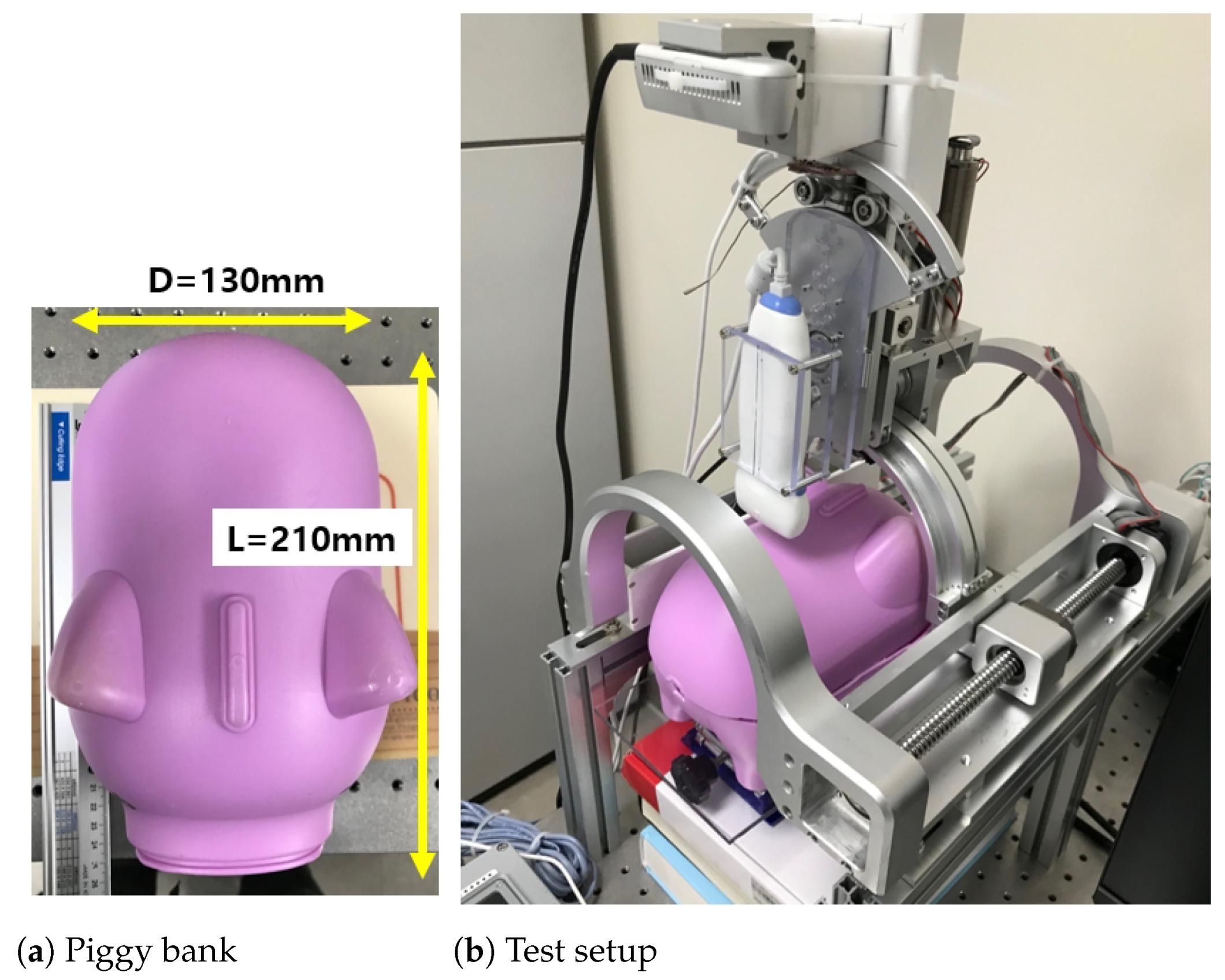
3.1. Bean Curd-Gelatin Phantom
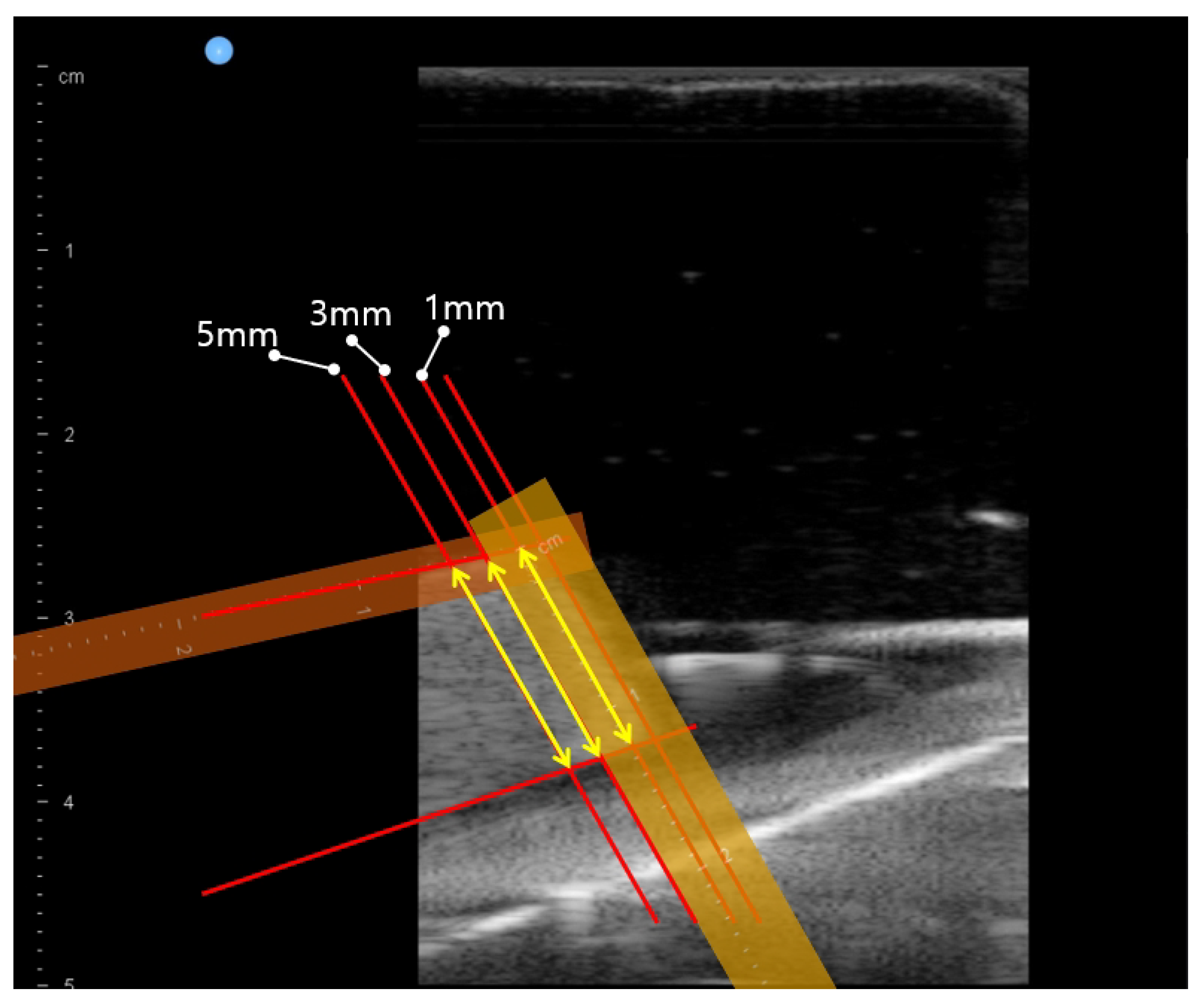
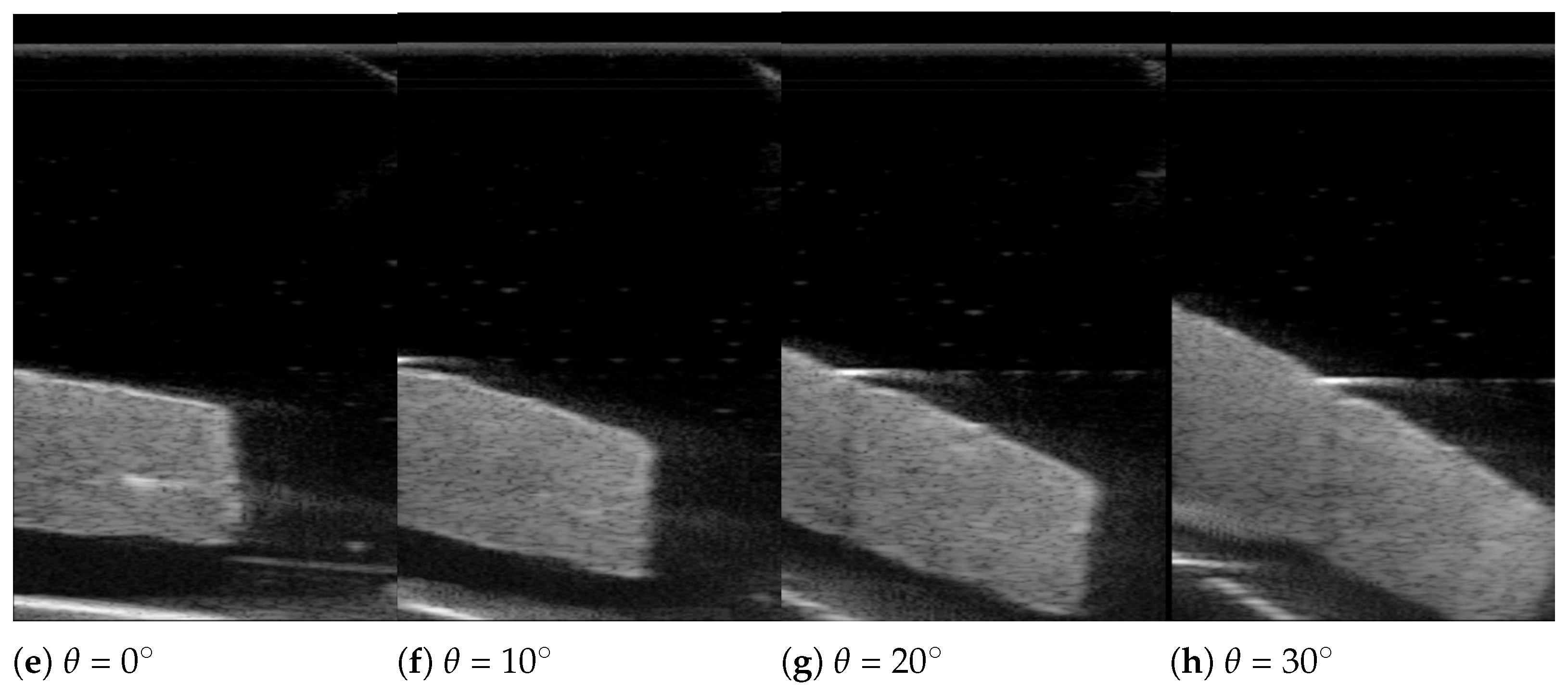
3.2. In-Vitro Bean Curd-Gelatin Phantom Test Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Geometric Piecewise Arc Curve Fitting Details

References
- Santilli, V.; Bernetti, A.; Mangone, M.; Paoloni, M. Clinical definition of sarcopenia. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2014, 11, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrager, M.A.; Metter, E.J.; Simonsick, E.; Ble, A.; Bandinelli, S.; Lauretani, F.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity and inflammation in the InCHIANTI study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Shepard, D.S.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Roubenoff, R. The Healthcare Costs of Sarcopenia in the United States. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.A.A.; Lima, T.B.; Do, M.; Ietsugu, V.; De Carvalho Nunes, H.R.; Qi, X.; Romeiro, F.G. Anthropometric measures associated with sarcopenia in outpatients with liver cirrhosis. Wiley Online Libr. 2019, 76, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Zepeda, M.; Sánchez-Garrido, N.; González-Lara, M.; Gutiérrez-Robledo, L.M. Sarcopenia Prevalence Using Simple Measurements and Population-Based Cutoff Values. 2016. Available online: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Martin, A.D.; Spenst, L.F.; Drinkwater, D.T.; Clarys, J.P. Anthropometric Estimation of Muscle Mass in Men. 1990. Available online: europepmc.org (accessed on 15 July 2021).
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N.; Manzato, E. Measurement of lean body mass using bioelectrical impedance analysis: A consideration of the pros and cons. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.C.; Heymsfield, S.B. Bioelectrical impedance analysis for diagnosing sarcopenia and cachexia: What are we really estimating? J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.H.; Jun, M.A. Comparative analysis of the multi-frequency bio-impedance and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry on body composition in obese subjects. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Recio-Boiles, A.; Galeas, J.N.; Goldwasser, B.; Sanchez, K.; Man, L.M.W.; Gentzler, R.D.; Gildersleeve, J.; Hollen, P.J.; Gralla, R.J. Enhancing evaluation of sarcopenia in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by assessing skeletal muscle index (SMI) at the first lumbar (L1) level on routine chest computed tomography (CT). Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, E.Y.; Jin, W. Prognostic significance of CT-determined sarcopenia in patients with advanced gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozynek, M.; Kucybała, I.; Urbanik, A.; Wojciechowski, W. The use of artificial intelligence in the imaging of sarcopenia: A narrative review of current status and perspectives. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirón Mombiela, R.; Vucetic, J.; Rossi, F.; Tagliafico, A.S. Ultrasound Biomarkers for Sarcopenia: What Can We Tell so Far? Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2020, 24, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Aging, G.T.-C. Ultrasound measurements of gastrocnemius muscle thickness in older people with sarcopenia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hida, T.; Ando, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ito, K.; Tsushima, M.; Kobayakawa, T.; Morozumi, M.; Tanaka, S.; Machino, M.; Ota, K.; et al. Ultrasound measurement of thigh muscle thickness for assessment of sarcopenia. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 519–527. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, E.M.; Draskovits, T.; Praschak, M.; Quittan, M.; Graf, A. Association between ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness, pennation angle, echogenicity and skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. Age 2013, 35, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minetto, M.A.; Caresio, C.; Menapace, T.; Hajdarevic, A.; Marchini, A.; Molinari, F.; Maffiuletti, N.A. Ultrasound-Based Detection of Low Muscle Mass for Diagnosis of Sarcopenia in Older Adults. PM&R 2016, 8, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustani, K.; Kundisova, L.; Capecchi, P.; Nante, N.; Bicchi, M. Ultrasound measurement of rectus femoris muscle thickness as a quick screening test for sarcopenia assessment. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 83, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.; Qi, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, A.; Cai, J.; Lai, B.; Sheng, Y.; Ding, G. The correlation of muscle thickness and pennation angle assessed by ultrasound with sarcopenia in elderly Chinese community dwellers. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salim, S.; Al-Khathiri, O.; Tandon, P.; Baracos, V.E.; Churchill, T.A.; Warkentin, L.M.; Khadaroo, R.G. Thigh ultrasound used to identify frail elderly patients with sarcopenia undergoing surgery: A pilot study. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 256, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajowski, G.; Pałac, M.; Wolny, T.; Linek, P. Lateral Abdominal Muscles Shear Modulus and Thickness Measurements under Controlled Ultrasound Probe Compression by External Force Sensor: A Comparison and Reliability Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris-Love, M.O.; Monfaredi, R.; Ismail, C.; Blackman, M.R.; Cleary, K. Quantitative ultrasound: Measurement considerations for the assessment of muscular dystrophy and sarcopenia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Love, M.O.; Ismail, C.; Monfaredi, R.; Hernandez, H.J.; Pennington, D.; Woletz, P.; McIntosh, V.; Adams, B.; Blackman, M.R. Interrater reliability of quantitative ultrasound using force feedback among examiners with varied levels of experience. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-de-Araujo, R.; Harris-Love, M.O.; Miljkovic, I.; Fragala, M.S.; Anthony, B.W.; Manini, T.M. The Need for Standardized Assessment of Muscle Quality in Skeletal Muscle Function Deficit and Other Aging-Related Muscle Dysfunctions: A Symposium Report. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, J. Sarcopenia Detection System Using RGB-D Camera and Ultrasound Probe: System Development and Preclinical In-Vitro Test. Sensors 2020, 20, 4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://orbbec3d.com/astra-mini-series/ (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Available online: https://www.intelrealsense.com/depth-camera-d435i/ (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Available online: https://people.cas.uab.edu/~mosya/cl/CircleFitByPratt.cpp (accessed on 13 May 2021).
- Chernov, N.; Lesort, C. Least squares fitting of circles. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2005, 23, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, N. Fitting circles to scattered data: Parameter estimates have no moments. Metrika 2011, 73, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharadqah, A.; Chernov, N. Error analysis for circle fitting algorithms. Electron. J. Stat. 2009, 3, 886–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.intelrealsense.com/sdk-2/ (accessed on 13 May 2021).



| Fitting Name | Center Point | Radius | Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X [mm] | Y [mm] | R [mm] | Total Error | Average Error | ||
| Algebraic | arc | 17.839 | −6.194 | 65.576 | 75.66 | 0.07 |
| Geometric | 1st arc | 17.869 | −6.114 | 65.436 | 80.32 | 0.069 |
| 2nd arc | 17.909 | −6.114 | 65.466 | |||
| Method Name | Center Point | R [mm] | Error [mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X [mm] | Y [mm] | Total Error | Average Error | |||
| Method in [26] | 1st arc | −2.2 | −56.89 | 73.62 | 1.22 | 0.04 |
| 2nd arc | −5.79 | −35.85 | 51.42 | |||
| Enhanced method | 1st arc | −3.15 | −50.92 | 70.11 | 2.38 | 0.07 |
| 2nd arc | −7.41 | −39.12 | 57.33 | |||
| Method name | Elapsed Time [ms] | |||||
| Method in [26] | 9475 | |||||
| Enhanced method | 9 | |||||
| Fitting Name | Center Point | Radius | Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X [mm] | Y [mm] | R [mm] | Total Error | Average Error | ||
| Algebraic | arc | 16.932 | −33.350 | 67.464 | 67.96 | 0.069 |
| Geometric | 1st arc | 16.942 | −33.421 | 67.444 | 66.98 | 0.068 |
| 2nd arc | 16.922 | −33.371 | 67.454 | |||
| Measuring Condition | Average of = −40∼30 | Std. Deviation of = −40∼30 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mm | 3 mm | 5 mm | 1 mm | 3 mm | 5 mm | |
| Operator #1 | 12.64 | 12.80 | 12.84 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.24 |
| Operator #2 | 12.54 | 12.74 | 12.74 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Operator #3 | 12.59 | 12.74 | 12.73 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.34 |
| Operator #4 | 12.56 | 12.73 | 12.74 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.36 |
| Operator #5 | 12.57 | 12.73 | 12.77 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
| Average | 12.58 | 12.75 | 12.77 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, J.; Moon, J.; Sung, K.R.; Choi, J. A Sarcopenia Detection System Using an RGB-D Camera and an Ultrasound Probe: Eye-in-Hand Approach. Biosensors 2021, 11, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070243
Kim Y-J, Choi J, Moon J, Sung KR, Choi J. A Sarcopenia Detection System Using an RGB-D Camera and an Ultrasound Probe: Eye-in-Hand Approach. Biosensors. 2021; 11(7):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070243
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeoun-Jae, Jueun Choi, Jungwoo Moon, Kyung Rim Sung, and Jaesoon Choi. 2021. "A Sarcopenia Detection System Using an RGB-D Camera and an Ultrasound Probe: Eye-in-Hand Approach" Biosensors 11, no. 7: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070243
APA StyleKim, Y.-J., Choi, J., Moon, J., Sung, K. R., & Choi, J. (2021). A Sarcopenia Detection System Using an RGB-D Camera and an Ultrasound Probe: Eye-in-Hand Approach. Biosensors, 11(7), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070243