Subtle Application of Electrical Field-Induced Lossy Mode Resonance to Enhance Performance of Optical Planar Waveguide Biosensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. ITO Thin-Film Coating
2.3. EF-LMR Biosensor Assembly
2.4. LMR Experiment Setup
3. Results and Discussions
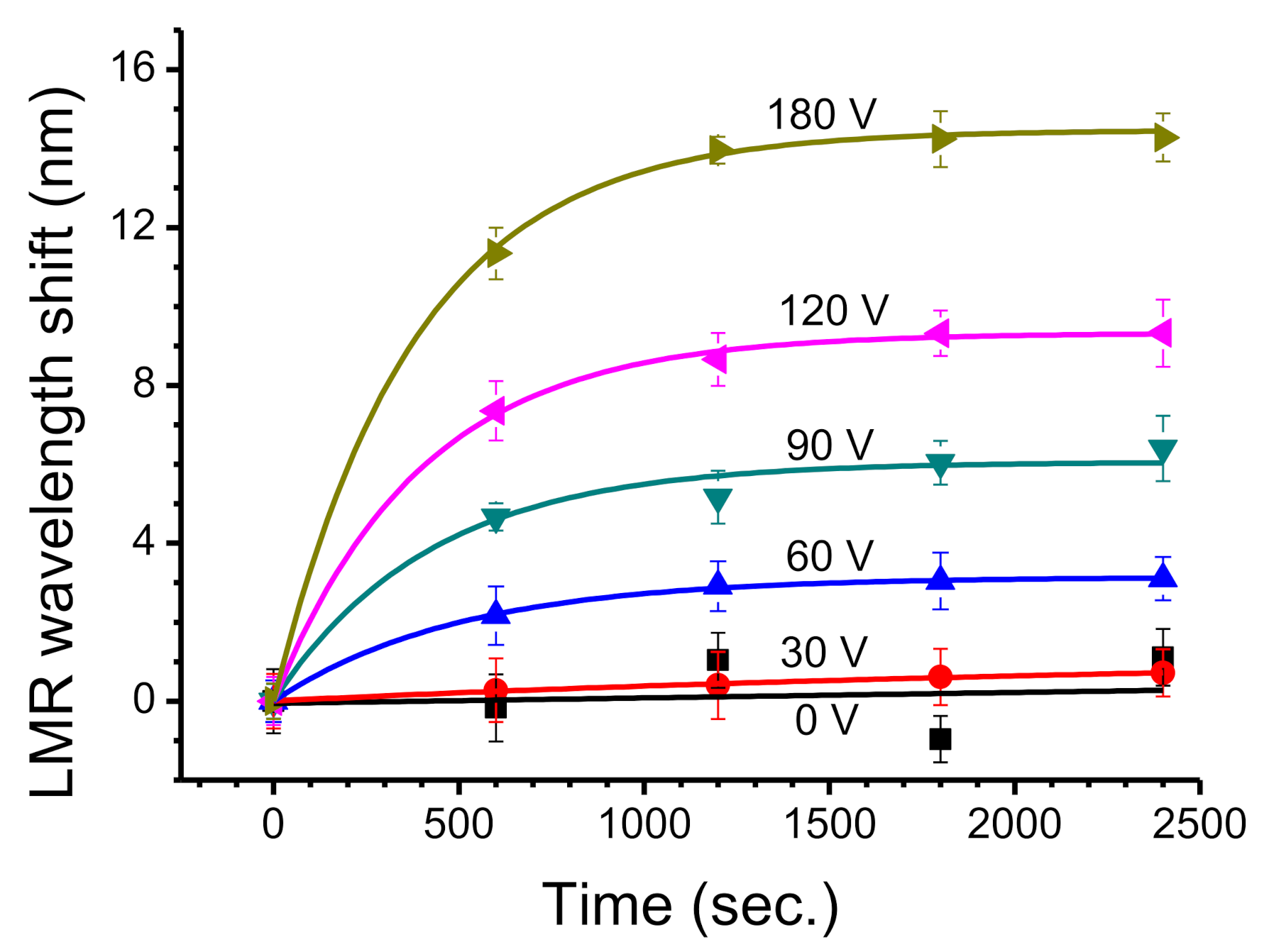
3.1. Observations with Short-Term Applied Voltage
3.2. Observations with Long-Term Applied Voltage
3.3. Sensitivity and Molecular Kinetics
3.4. Molecular Desorption with No Applied Voltage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nylander, C.; Liedberg, B.; Lind, T. Gas detection by means of surface plasmon resonance. Sens. Actuators 1982, 3, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, N.A.S.; Fen, Y.W.; Saleviter, S.; Kamil, Y.M.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Abdullah, J.; Mahdi, M.A. Experimental evaluation on surface plasmon resonance sensor performance based on sensitive hyperbranched polymer nanocomposite thin films. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Niu, L.-Y.; Fan, X.-C. Enhanced sensitivity of bimetallic optical fiber SPR sensor based on MoS2 nanosheets. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 128, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, C.; González-Rubio, G.; Mulvaney, P.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Rodríguez, F. Monodisperse Gold Nanorods for High-Pressure Refractive Index Sensing. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliarik, M.; Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors: Approaching their limits? Opt. Express 2009, 17, 16505–16517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinibaldi, A.; Fieramosca, A.; Rizzo, R.; Anopchenko, A.; Danz, N.; Munzert, P.; Magistris, C.; Barolo, C.; Michelotti, F. Combining label-free and fluorescence operation of Bloch surface wave optical sensors. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2947–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.K.; Pal, S. Design analysis of Bloch surface wave based sensor for haemoglobin concentration measurement. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 3639–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zheng, Z.; Wan, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, J. High-sensitivity sensing based on intensity-interrogated Bloch surface wave sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryga, M.; Ciprian, D.; Hlubina, P. Bloch Surface Wave Resonance Based Sensors as an Alternative to Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniak, M.; Grzegorzewski, J.; Szustakowski, M. Analysis of lossy mode cut-off conditions in planar waveguides with semiconductor guiding layer. IEE Proc. J. Optoelectron. 1993, 140, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Villar, I.; Zamarreno, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Arregui, F.J.; Matias, I.R. Lossy Mode Resonance Generation With Indium-Tin-Oxide-Coated Optical Fibers for Sensing Applications. J. Light. Technol. 2009, 28, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.; Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernaez, M.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical fiber refractometers based on Lossy Mode Resonances by means of SnO2 sputtered coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohorquez, D.L.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Matias, I.R. Generation of lossy mode resonances in a broadband range with multilayer coated coverslips optimized for humidity sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Mullaney, K.; Korposh, S.; James, S.W.; Lee, S.-W.; Tatam, R.P. An ammonia sensor based on Lossy Mode Resonances on a tapered optical fibre coated with porphyrin-incorporated titanium dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubiate, P.; Zamarreño, C.; Sánchez, P.; Matias, I.; Arregui, F. High sensitive and selective C-reactive protein detection by means of lossy mode resonance based optical fiber devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Qi, K. Simulation of a microstructure fiber pressure sensor based on lossy mode resonance. AIP Adv. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossy Mode Resonance Excitation in Fiber-Optics: Applications in Biosensing. Proceedings of Asia Communications and Photonics Conference/International Conference on Information Photonics and Optical Communications 2020 (ACP/IPOC), Beijing, China, 24–27 October 2020; p. S4G.1.
- Ozcariz, A.; Vitoria, I.; Arregui, F.J.; Zamarreño, C.R. Copper oxide coated D-shaped optical fibers for the development of LMR refractometers. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Sensors, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 25–28 October 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.-M.; Jin, S. Lossy mode resonance-based fiber optic sensor using layer-by-layer SnO2 thin film and SnO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 492, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Urrutia, A.; Goicoechea, J.; Arregui, F.J. Optical fiber humidity sensors based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) and Lossy-mode resonance (LMR) in overlays loaded with silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Pang, F.; Huang, S.; Zou, F.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T. High sensitivity refractive index sensor based on adiabatic tapered optical fiber deposited with nanofilm by ALD. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 13880–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.-L.; Lin, H.-Y.; Su, S.-H. High Sensitivity Refractive Index Sensor by D-Shaped Fibers and Titanium Dioxide Nanofilm. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.; Franzena, S.; Maria, J.-P.; Losego, M.; Leonard, D.N.; Laughlin, B.; Duscher, G.; Weibel, S. Surface plasmon resonance in conducting metal oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 054905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Theoretical assessment of D-shaped optical fiber chemical sensor associated with nanoscale silver strip operating in near-infrared region. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2020, 52, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, O.; Del Villar, I.; Corres, J.M.; Matias, I.R. Lossy mode resonance sensors based on lateral light incidence in nanocoated planar waveguides. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, M. Optical properties of soda lime silica glasses. Sol. Energy Mater. 1985, 12, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-W.; Chen, C.-K.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, L.-Y. Determination of Schistosoma japonicum circulating antigens in dilution serum by piezoelectric immunosensor and S/N enhancement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Geyer, P.; Holdt, L.M.; Teupser, D.; Mann, M. Revisiting biomarker discovery by plasma proteomics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-M.; Do, V.Q.; Seo, Y.-S.; Duong, M.T.H.; Ahn, H.-C.; Huh, H.J.; Lee, M.-Y. Application of Fisetin to the Quantitation of Serum Albumin. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Va (Volt.) | Short-Term | Long-Term | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δλshort (nm) | αshort | Δλmax (nm) | αlong | k | R2 | |
| 30 | 0.585 | 0.019 | 1.177 | 0.039 | 0.0005 | 0.980 |
| 60 | 2.224 | 0.037 | 3.862 | 0.064 | 0.0014 | 0.933 |
| 90 | 4.080 | 0.045 | 6.862 | 0.076 | 0.0019 | 0.970 |
| 120 | 6.756 | 0.056 | 9.788 | 0.081 | 0.0023 | 0.993 |
| 180 | 11.247 | 0.062 | 14.796 | 0.082 | 0.0024 | 0.997 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, L.-Y. Subtle Application of Electrical Field-Induced Lossy Mode Resonance to Enhance Performance of Optical Planar Waveguide Biosensor. Biosensors 2021, 11, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030086
Lin Y-C, Chen L-Y. Subtle Application of Electrical Field-Induced Lossy Mode Resonance to Enhance Performance of Optical Planar Waveguide Biosensor. Biosensors. 2021; 11(3):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030086
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu-Cheng, and Liang-Yü Chen. 2021. "Subtle Application of Electrical Field-Induced Lossy Mode Resonance to Enhance Performance of Optical Planar Waveguide Biosensor" Biosensors 11, no. 3: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030086
APA StyleLin, Y.-C., & Chen, L.-Y. (2021). Subtle Application of Electrical Field-Induced Lossy Mode Resonance to Enhance Performance of Optical Planar Waveguide Biosensor. Biosensors, 11(3), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030086






