Development, Optimization, Characterization, and Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Nickel Ions in Food
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.2.1. Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV)
2.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
2.3. Receptor Immobilization on Screen Printed Electrodes (SPEs)
2.4. Testing Biosensor Performance on Nickel Detection in Food
2.5. Atomic Adsorption Spectrometry Method (AAS)
3. Results
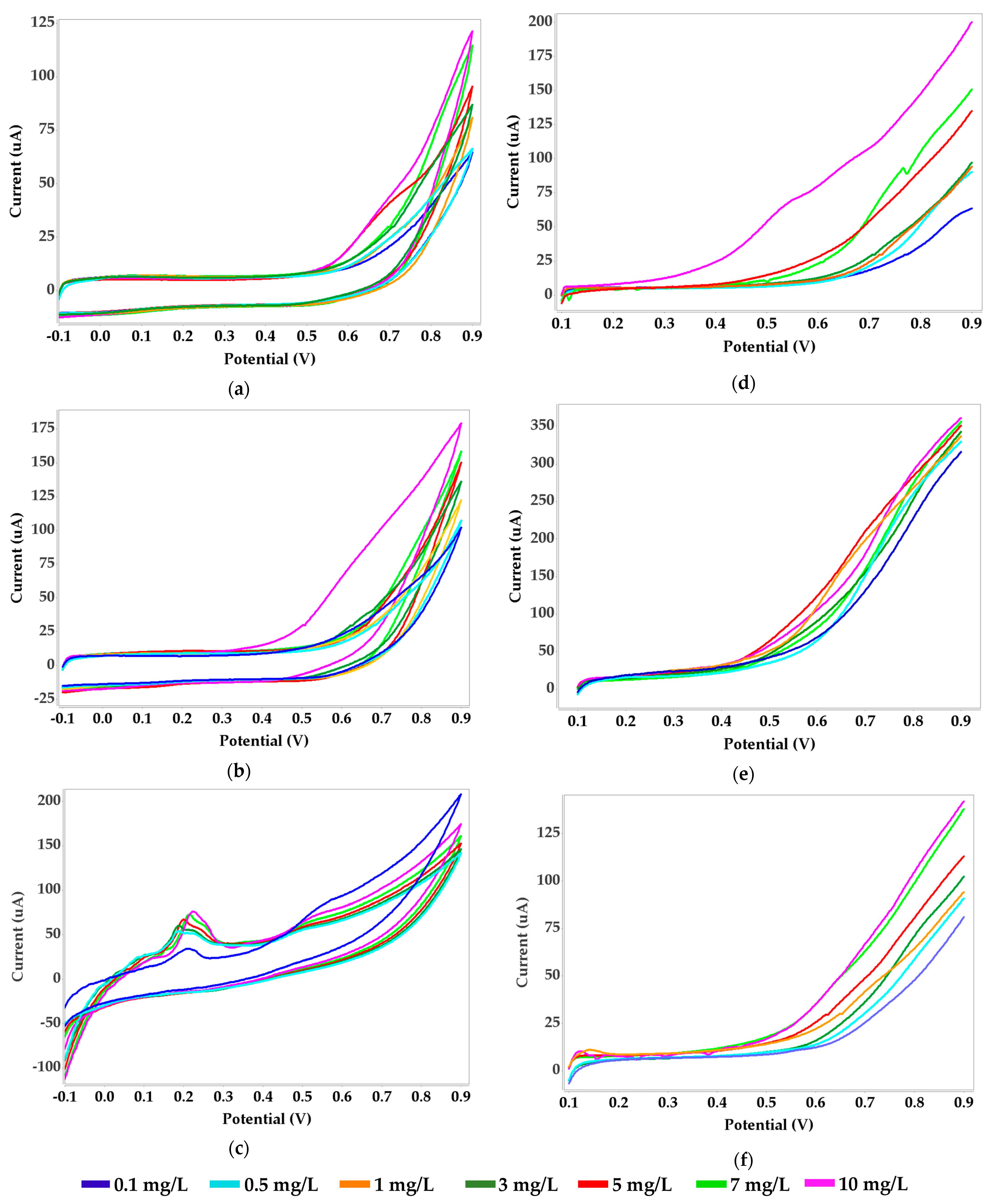
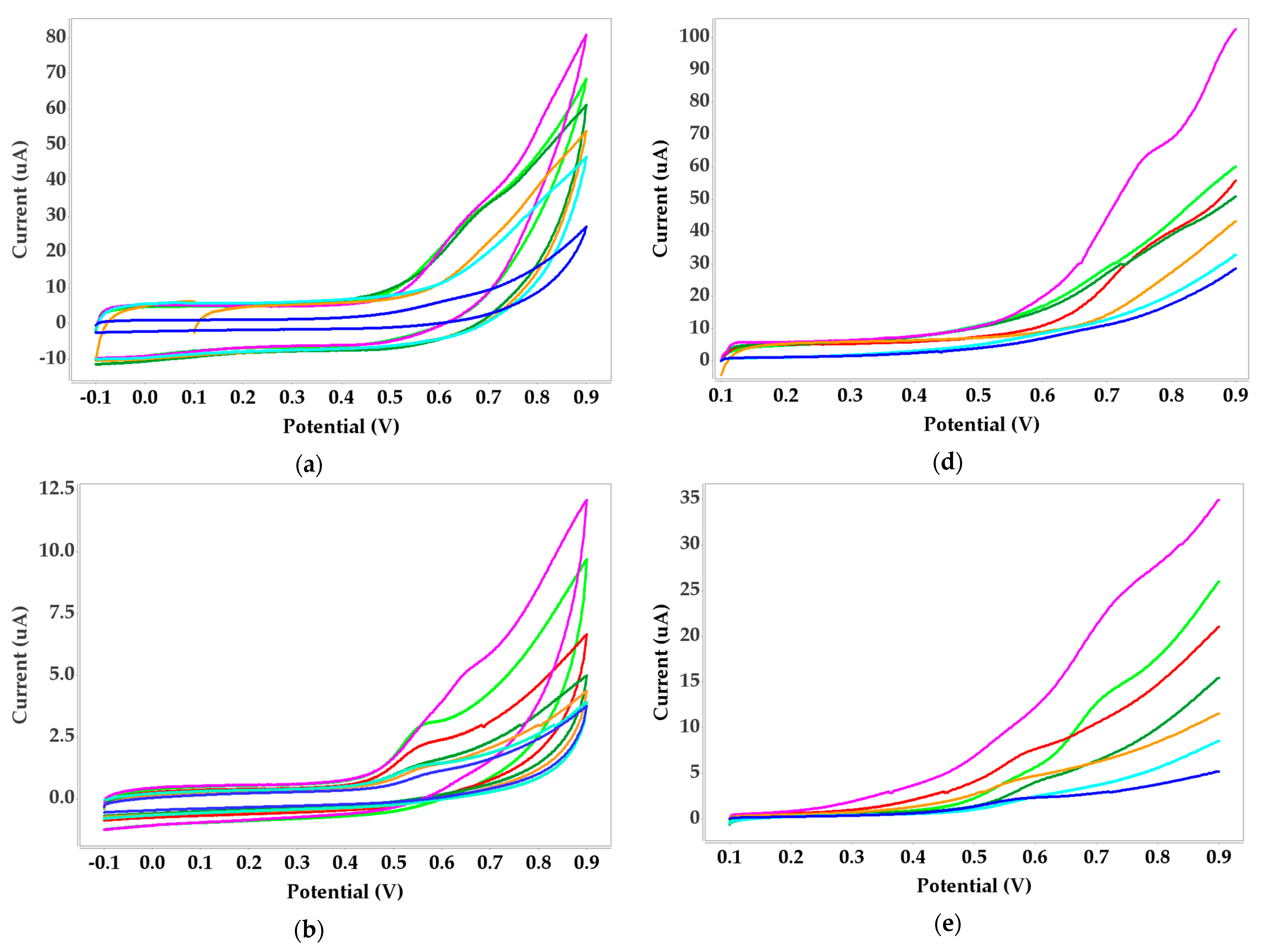
3.1. Protein A-Agarose and Nickel(II) Voltammetric Measurements
3.2. Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) and Nickel(II) Voltammetric Measurements
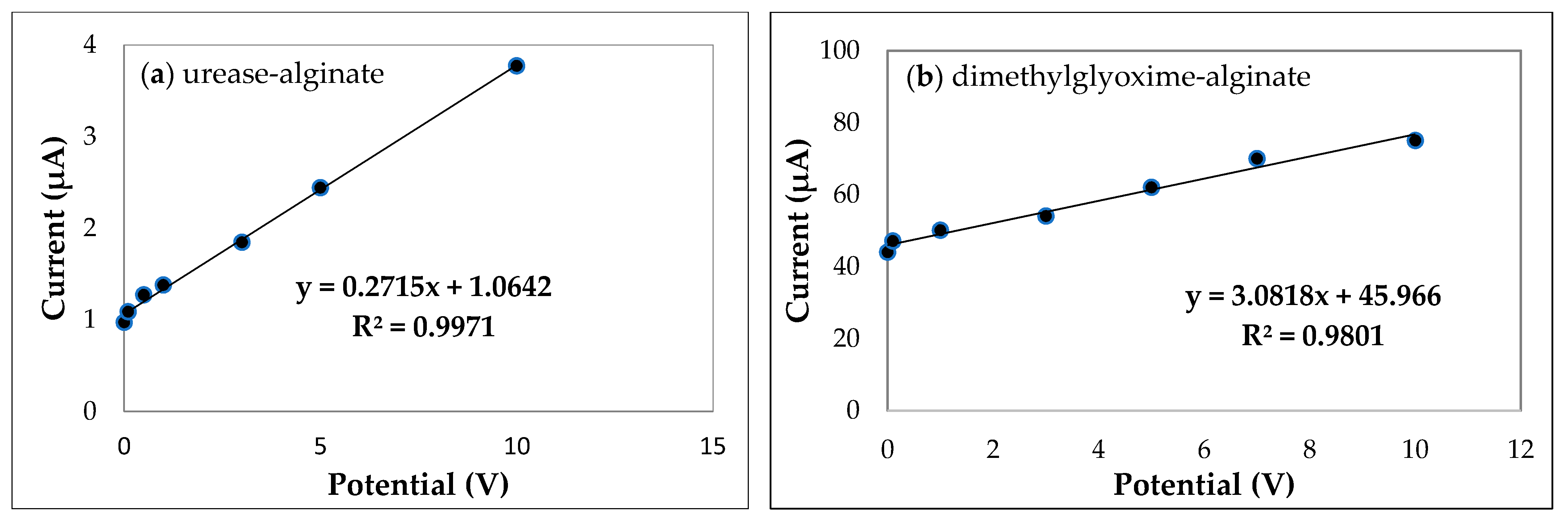
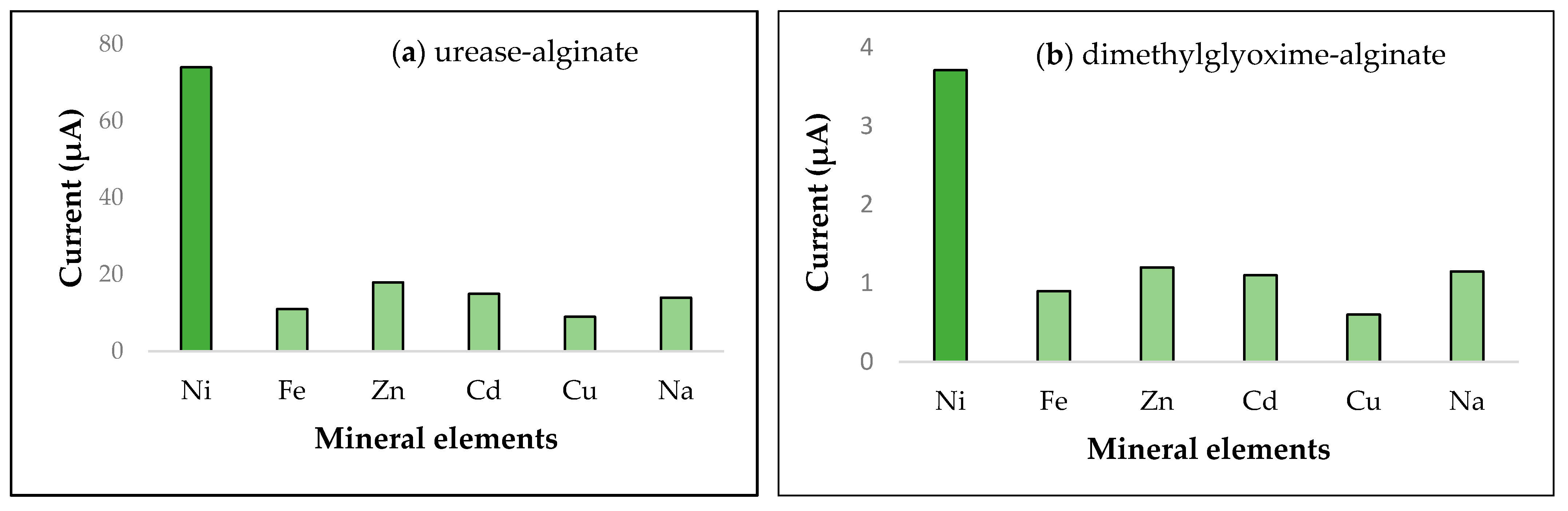
3.2.1. Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) Immobilized with Alginate
3.2.2. Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) Immobilized with Benzophenone
3.3. Urease and Nickel(II) Voltammetric Measurements
3.4. Ethylenediamine and Nickel(II) Voltammetric Measurements
3.5. Analytical Performance Characteristics of the Five Biosensors
3.6. Biosensors Optimization
3.7. Testing the Biosensors for Food Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Alcamo, A.; Mansueto, P.; Soresi, M.; Iacobucci, R.; La Blasca, F.; Geraci, G.; Cavataio, F.; Fayer, F.; Arini, A.; Di Stefano, L.; et al. Contact Dermatitis Due to Nickel Allergy in Patients Suffering from Non-Celiac Wheat Sensitivity. Nutrients 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duda-Chodak, A.; Blaszczyk, U. The impact of nickel on human health. J. Elem. 2008, 13, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Kruszewski, B.; Obiedziński, M.W.; Kowalska, J. Nickel, cadmium and lead levels in raw cocoa and processed chocolate mass materials from three different manufacturers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 66, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, R.F.D.S.; Alcântara, M.A.K.D.; Izário Filho, H.J. Evaluation of sample preparation methods and optimization of nickel determination in vegetable tissues. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2011, 35, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Singh, M. A Bacillus sphaericus Based Biosensor for Monitoring Nickel Ions in Industrial Effluents and Foods. J. Autom. Methods Manag. Chem. 2006, 2006, 83427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human health and environmental toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antico, A.; Soana, R. Nickel sensitization and dietary nickel are a substantial cause of symptoms provocation in patients with chronic allergic-like dermatitis syndromes. Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 6, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodman, J.E.; Prueitt, R.L.; Dodge, D.G.; Thakali, S. Carcinogenicity assessment of water-soluble nickel compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2009, 39, 365–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusi, E.A.; Di Ciommo, V.M.; Patrissi, T.; Guarascio, P. High prevalence of nickel allergy in an overweight female population: A pilot observational analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, C. Food Hypersensitivity: Diagnosing and Managing Food Allergies and Intolerances. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 576017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakur, M.S.; Ragavan, K.V. Biosensors in food processing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, P.J.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Guilbault, G.G. Biosensors for food analysis. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2000, 39, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Monošík, R.; Stred’anský, M.; Tkac, J.; Šturdík, E. Application of Enzyme Biosensors in Analysis of Food and Beverages. Food Anal. Methods 2012, 5, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.K.; Barfidokht, A.; Tehrani, F.; Mishra, R.K. Food Safety Analysis Using Electrochemical Biosensors. Foods 2018, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neethirajan, S.; Ragavan, V.; Weng, X.; Chand, R. Biosensors for sustainable food engineering: Challenges and perspectives. Biosensors 2018, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meshram, B.D.; Agrawal, A.K.; Adil, S.; Ranvir, S.; Sande, K.K. Biosensor and its application in food and dairy industry: A review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci 2018, 7, 3305–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.A.; Mazaheri, L.; Ashkenani, H.; Mohadesi, A.; Afzali, D. Determination of nickel in water, food, and biological samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration on modified carbon nanotubes. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Katz, E. Biosensors—Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Sensors 2020, 20, 6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattison, R.L.; Bowyer, A.A.; New, E.J. Small molecule optical sensors for nickel: The quest for a universal nickel receptor. Coord. Chem. Rev 2020, 425, 213522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Recommendation (EU) 2016/1111 of 6 July 2016 on the Monitoring of Nickel in Food (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32016H1111&from=FR (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Forzani, E.S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Tao, N. Detection of heavy metal ions in drinking water using a high-resolution differential surface plasmon resonance sensor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.F.; Zhang, X.W.; Kuang, H.Z.; Li, Q.Q.; Li, Y. Study on simultaneous determination of Ni, Pb and Cd by ion chromatography. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 146, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.N.; Kanchi, S.; Sabela, M.I.; Bisetty, K.; Jyothi, N.V.V. Spectrophotometric determination of nickel (II) in waters and soils: Novel chelating agents and their biological applications supported by DFT method. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Singh, M.; Chandra, S. A new macrocyclic ligand-based sensor for nickel (II) ions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 70, 2995–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.M.; Jin, H.G.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, G.L.; He, Q.G. Recent advances in black phosphorus-based electrochemical sensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1170, 338480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.C.; Morrin, A. Electroanalytical sensor technology. In Electrochemistry; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almaquer, F.E.P.; Ricacho, J.S.Y.; Ronquillo, R.L.G. Simple and rapid colorimetric sensing of Ni(II) ions in tap water based on aggregation of citrate-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuswandi, B.; Verboom, W.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Tripodal receptors for cation and anion sensors. Sensors 2006, 6, 978–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozitsina, A.N.; Svalova, T.S.; Malysheva, N.N.; Okhokhonin, A.V.; Vidrevich, M.B.; Brainina, K.Z. Sensors Based on Bio and Biomimetic Receptors in Medical Diagnostic, Environment, and Food Analysis. Biosensors 2018, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McConnell, E.M.; Nguyen, J.; Li, Y. Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.; Cheung, Y.-W.; Wang, L.; Lee, M.; Figueroa-Miranda, G.; Liang, S.; Mayer, D.; Tanner, J.A. An electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor targeting Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II for malaria diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 192, 113472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.P.; Ostapczuk, P. Nickel and cobalt determination by constant current potentiometry. Fresenious’ J. Anal. Chem. 1993, 346, 952–956. [Google Scholar]
- Hopîrtean, E.; Cosma, V.; Coroian, A. Potentiometric determination of nickel impurities in brasses. Chem. Anal. 1992, 37, 741. [Google Scholar]
- González, P.; Cortınez, V.A.; Fontán, C.A. Determination of nickel by anodic adsorptive stripping voltammetry with a cation exchanger-modified carbon paste electrode. Talanta 2002, 58, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaf, E.; Suyani, H.; Zein, R.; Pardi, H. Simultaneous Determination of Trace Amounts of Iron, Cobalt, Nickel and Chromium in Water Samples with Calcon as Complexing Agent by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry. Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 3978–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouarram, A.; Galindo-Riaño, M.D.; García-Vargas, M.; Stitou, M.; El Yousfi, F.; Espada-Bellido, E. An efficient approach to designing and optimizing the analysis of Ni(II) by AdCSV in seawater. Talanta 2010, 82, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokpas, K.; Jahed, N.; Baker, P.G.; Iwuoha, E.I. Complexation-based detection of nickel (II) at a gra-phene-chelate probe in the presence of cobalt and zinc by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Sensors 2017, 17, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mettakoonpitak, J.; Miller-Lionberg, D.; Reilly, T.; Volckens, J.; Henry, C.S. Low-cost reusable sensor for cobalt and nickel detection in aerosols using adsorptive cathodic square-wave stripping voltammetry. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 805, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, A.; Królicka, A.; Maczuga, M.; Zarębski, J. A novel screen-printed electrode modified with lead film for adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of cobalt and nickel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochab, M.; Gęca, I.; Korolczuk, M. The new Micro-set for Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetric Simultaneous Determination of Nickel and Cobalt Traces in Aqueous Media. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.; Garcia, M.B.Q.; Lima, J.L. Square wave adsorptive stripping voltammetry of nickel and cobalt at wall-jet electrodes in continuous flow. Electroanalysis 1996, 8, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, Q.; Mao, C.J.; Niu, H.L.; Jin, B.K.; Zhang, S.Y. Electrochemical biosensor for Ni2+ detection based on a DNAzyme-CdSe nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.K.; Kabiri, M. Determination of trace amounts of nickel by differential pulse adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry using calconcarboxylic acid as a chelating agent. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2005, 2, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Arshad, M.N.; Asiri, A.M. Electrochemical detection of Ni2+ ions using synthesized (E)-N′-Chlorobenzylidene-4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide derivatives modified with a Nafion matrix. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 7455–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharkiva, A.M.; Shumar, S.V. Potentiometric determination of nickel (II) with sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (NaDEDC). J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1611, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sett, A.; Das, S.; Sharma, P.; Bora, U. Aptasensors in health, environment and food safety monitoring. Open J. Appl. Biosens. 2012, 1, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odobašić, A.; Šestan, I.; Begić, S. Biosensors for determination of heavy metals in waters. In Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.L.; dos Santos, W.N.; Lemos, V.A. On-line preconcentration system for nickel determination in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 445, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türke, N. Stability Constants of Mixed Ligand Complexes of Nickel (II) with Adenine and Some Amino Acids. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasmin, J.; Ahmed, M.R.; Cho, B.-K. Biosensors and their Applications in Food Safety: A Review. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 41, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucca, P.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Sanjust, E. Agarose and Its Derivatives as Supports for Enzyme Immobilization. Molecules 2016, 21, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, W.S.; Dias, V.L.N.; Costa, W.M.; de Araujo Rodrigues, I.; Marques, E.P.; Sousa, A.G.; Boaventura, J.; Bezerra, C.W.B.; Song, C.; Liu, H.; et al. Nickel-dimethylglyoxime complex modified graphite and carbon paste electrodes: Preparation and catalytic activity towards methanol/ethanol oxidation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalek, J.; Hradecky, J.; Adam, V.; Krystofova, O.; Huska, D.; Masarik, M.; Trnkova, L.; Horna, A.; Klosova, K.; Adamek, M. Spectrometric and voltammetric analysis of urease–Nickel nanoelectrode as an electrochemical sensor. Sensors 2007, 7, 1238–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavares, M.C.; Oliveira, K.A.; de Fátima, A.; Coltro, W.K.; Santos, J.C.C. Paper-based analytical device with colorimetric detection for urease activity determination in soils and evaluation of potential inhibitors. Talanta 2021, 230, 122301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, L.; Musiani, F.; Ciurli, S. The structure-based reaction mechanism of urease, a nickel dependent enzyme: Tale of a long debate. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 25, 829–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norocel, L.; Gutt, G. Screen-Printed Voltammetric Biosensors for the Determination of Copper in Wine. Sensors 2019, 19, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norocel, L.; Gutt, G. Development and performance testing of an electrochemical sensor for determination of iron ions in wine. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2019, 25, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.M.S.; Magalhaes, J.M.; Soares, H. Simultaneous Determination of Nickel and Cobalt Using a Solid Bismuth Vibrating Electrode by Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, V.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Determination of Trace Levels of Nickel (II) by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry Using a Disposable and Low-Cost Carbon Screen-Printed Electrode. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nickel Biosensor | SPE | Technique | R2 | Sensitivity [µA Mm−1 cm−2] | Limit of Detection (LOD) [mg/L] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A-agarose | Carbon | CV | 0.9376 | 1.4753 | 0.050 |
| Bismuth | 0.9242 | 0.4038 | 0.018 | ||
| Silver | 0.9742 | 1.8433 | 0.019 | ||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.9261 | 0.5189 | 0.090 | |
| Bismuth | 0.8607 | 0.4064 | 0.026 | ||
| Silver | 0.9329 | 0.6584 | 0.012 | ||
| Dimethylglyoxime -alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.9779 | 0.1444 | 0.010 |
| Bismuth | 0.9605 | 0.0984 | 0.028 | ||
| Silver | 0.9801 | 0.2850 | 0.080 | ||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.9556 | 0.0575 | 0.092 | |
| Bismuth | 0.8516 | 0.1720 | 0.098 | ||
| Silver | 0.9482 | 0.1165 | 0.050 | ||
| Dimethylglyoxime- benzophenone | Carbon | CV | 0.7824 | 0.1107 | 0.100 |
| Bismuth | 0.8751 | 0.0682 | 0.150 | ||
| Silver | 0.8678 | 0.5175 | 0.092 | ||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.9415 | 0.0769 | 0.120 | |
| Bismuth | 0.9574 | 0.0815 | 0.100 | ||
| Silver | 0.9757 | 0.6978 | 0.060 | ||
| Urease-alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.8569 | 0.1725 | 0.050 |
| Bismuth | 0.9782 | 0.8737 | 0.020 | ||
| Silver | 0.9971 | 2.1921 | 0.005 | ||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.9112 | 0.1099 | 0.040 | |
| Bismuth | 0.9846 | 0.2767 | 0.026 | ||
| Silver | 0.9226 | 0.2562 | 0.030 | ||
| Ethylenediamine -alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.9343 | 0.1066 | 0.050 |
| Bismuth | 0.9578 | 0.0812 | 0.100 | ||
| Silver | 0.9328 | 0.1513 | 0.080 | ||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.8831 | 0.1388 | 0.076 | |
| Bismuth | 0.9430 | 0.2005 | 0.050 | ||
| Silver | 0.9112 | 0.1382 | 0.080 |
| Biosensor for Ni | SPEs | Technique | Nickel Content [mg/kg] | AAS [mg/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A-agarose | Carbon | CV | 8.68 | 7.98 |
| Bismuth | 8.23 | |||
| Silver | 8.32 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.52 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.60 | |||
| Silver | 8.18 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-alginate | Carbon | CV | 8.38 | |
| Bismuth | 8.44 | |||
| Silver | 8.56 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.26 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.03 | |||
| Silver | 8.17 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-benzophenone | Carbon | CV | 8.76 | |
| Bismuth | 8.25 | |||
| Silver | 8.81 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.48 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.74 | |||
| Silver | 8.16 | |||
| Urease-alginate | Carbon | CV | 8.29 | |
| Bismuth | 8.16 | |||
| Silver | 8.51 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.35 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.42 | |||
| Silver | 8.11 | |||
| Ethylenediamine-alginate | Carbon | CV | 8.31 | |
| Bismuth | 8.62 | |||
| Silver | 8.34 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.50 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.64 | |||
| Silver | 8.43 |
| Biosensor for Ni | SPEs | Technique | Nickel Content [mg/kg] | AAS [mg/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A-agarose | Carbon | CV | 0.92 | 0.80 |
| Bismuth | 1.26 | |||
| Silver | 1.02 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.89 | ||
| Bismuth | 0.98 | |||
| Silver | 1.14 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.91 | |
| Bismuth | 0.72 | |||
| Silver | 0.88 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.98 | ||
| Bismuth | 1.22 | |||
| Silver | 1.28 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-benzophenone | Carbon | CV | 1.26 | |
| Bismuth | 1.08 | |||
| Silver | 1.10 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 1.32 | ||
| Bismuth | 1.18 | |||
| Silver | 1.04 | |||
| Urease-alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.97 | |
| Bismuth | 0.96 | |||
| Silver | 0.84 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 0.78 | ||
| Bismuth | 0.90 | |||
| Silver | 0.86 | |||
| Ethylenediamine-alginate | Carbon | CV | 0.92 | |
| Bismuth | 0.98 | |||
| Silver | 1.28 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 1.20 | ||
| Bismuth | 1.22 | |||
| Silver | 1.06 |
| Biosensor for Ni | SPEs | Technique | Nickel Content [mg/kg] | AAS [mg/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A-agarose | Carbon | CV | 7.68 | 7.11 |
| Bismuth | 8.21 | |||
| Silver | 7.42 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 7.62 | ||
| Bismuth | 7.89 | |||
| Silver | 7.98 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-alginate | Carbon | CV | 8.11 | |
| Bismuth | 8.02 | |||
| Silver | 7.68 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 7.56 | ||
| Bismuth | 7.28 | |||
| Silver | 7.72 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-benzophenone | Carbon | CV | 7.82 | |
| Bismuth | 7.51 | |||
| Silver | 8.68 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 7.94 | ||
| Bismuth | 7.84 | |||
| Silver | 7.32 | |||
| Urease-alginate | Carbon | CV | 7.62 | |
| Bismuth | 7.46 | |||
| Silver | 7.18 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 7.48 | ||
| Bismuth | 7.54 | |||
| Silver | 7.28 | |||
| Ethylenediamine-alginate | Carbon | CV | 7.83 | |
| Bismuth | 7.78 | |||
| Silver | 7.44 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 8.20 | ||
| Bismuth | 8.12 | |||
| Silver | 8.36 |
| Biosensor for Ni | SPEs | Technique | Nickel Content [mg/kg] | AAS [mg/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein A-agarose | Carbon | CV | 2.98 | 2.35 |
| Bismuth | 3.06 | |||
| Silver | 3.11 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 2.85 | ||
| Bismuth | 2.93 | |||
| Silver | 2.96 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-alginate | Carbon | CV | 2.17 | |
| Bismuth | 3.08 | |||
| Silver | 3.29 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 3.44 | ||
| Bismuth | 3.27 | |||
| Silver | 3.38 | |||
| Dimethylglyoxime-benzophenone | Carbon | CV | 3.02 | |
| Bismuth | 3.16 | |||
| Silver | 2.71 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 2.92 | ||
| Bismuth | 3.10 | |||
| Silver | 3.01 | |||
| Urease-alginate | Carbon | CV | 2.74 | |
| Bismuth | 2.61 | |||
| Silver | 2.41 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 2.49 | ||
| Bismuth | 2.72 | |||
| Silver | 2.81 | |||
| Ethylenediamine-alginate | Carbon | CV | 2.79 | |
| Bismuth | 2.98 | |||
| Silver | 2.92 | |||
| Carbon | LSV | 3.05 | ||
| Bismuth | 3.14 | |||
| Silver | 2.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anchidin-Norocel, L.; Savage, W.K.; Gutt, G.; Amariei, S. Development, Optimization, Characterization, and Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Nickel Ions in Food. Biosensors 2021, 11, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120519
Anchidin-Norocel L, Savage WK, Gutt G, Amariei S. Development, Optimization, Characterization, and Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Nickel Ions in Food. Biosensors. 2021; 11(12):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120519
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnchidin-Norocel, Liliana, Wesley K. Savage, Gheorghe Gutt, and Sonia Amariei. 2021. "Development, Optimization, Characterization, and Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Nickel Ions in Food" Biosensors 11, no. 12: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120519
APA StyleAnchidin-Norocel, L., Savage, W. K., Gutt, G., & Amariei, S. (2021). Development, Optimization, Characterization, and Application of Electrochemical Biosensors for Detecting Nickel Ions in Food. Biosensors, 11(12), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11120519





