A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Bacteria
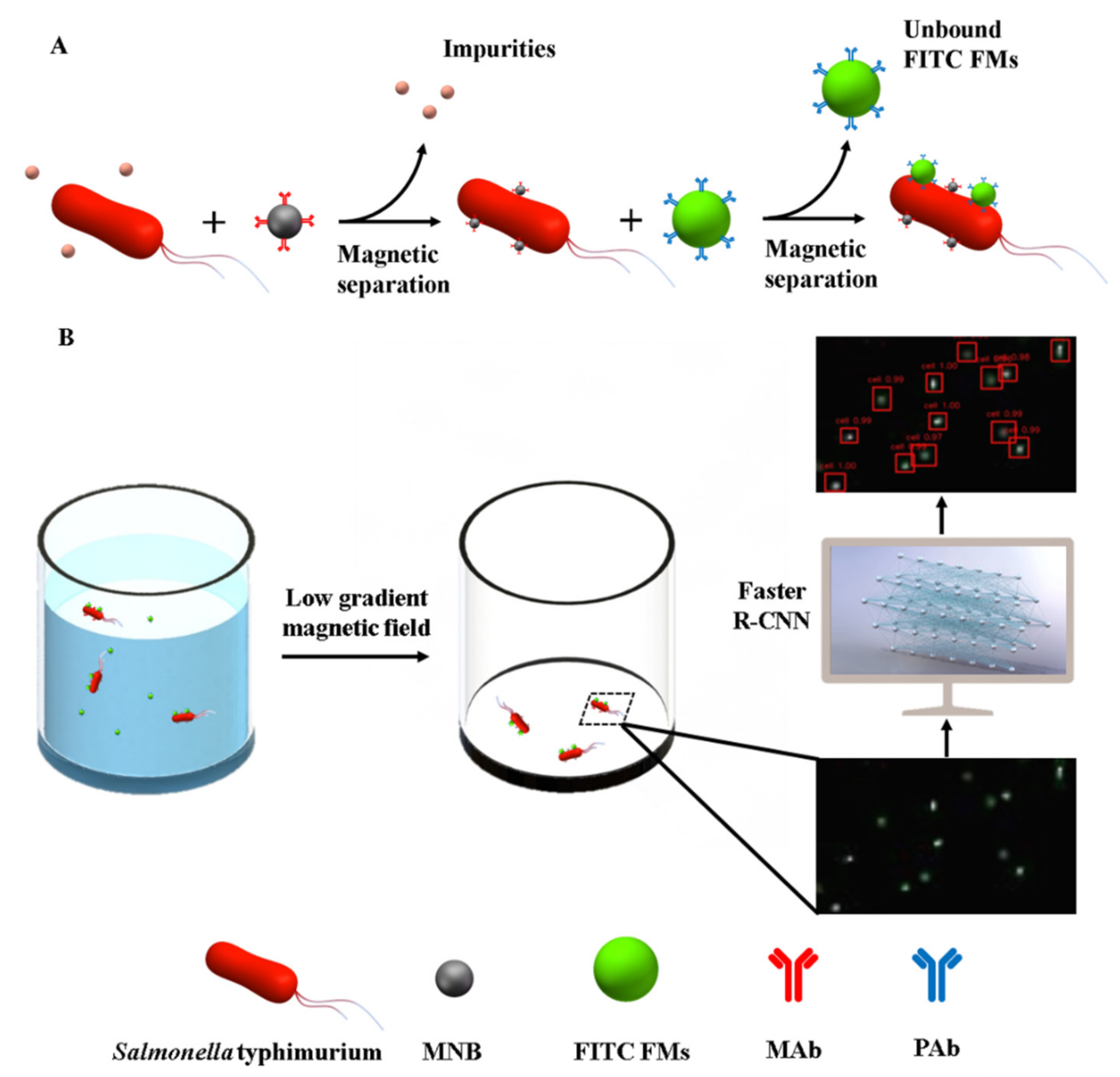
2.3. Preparation of the Immune FITC FMs
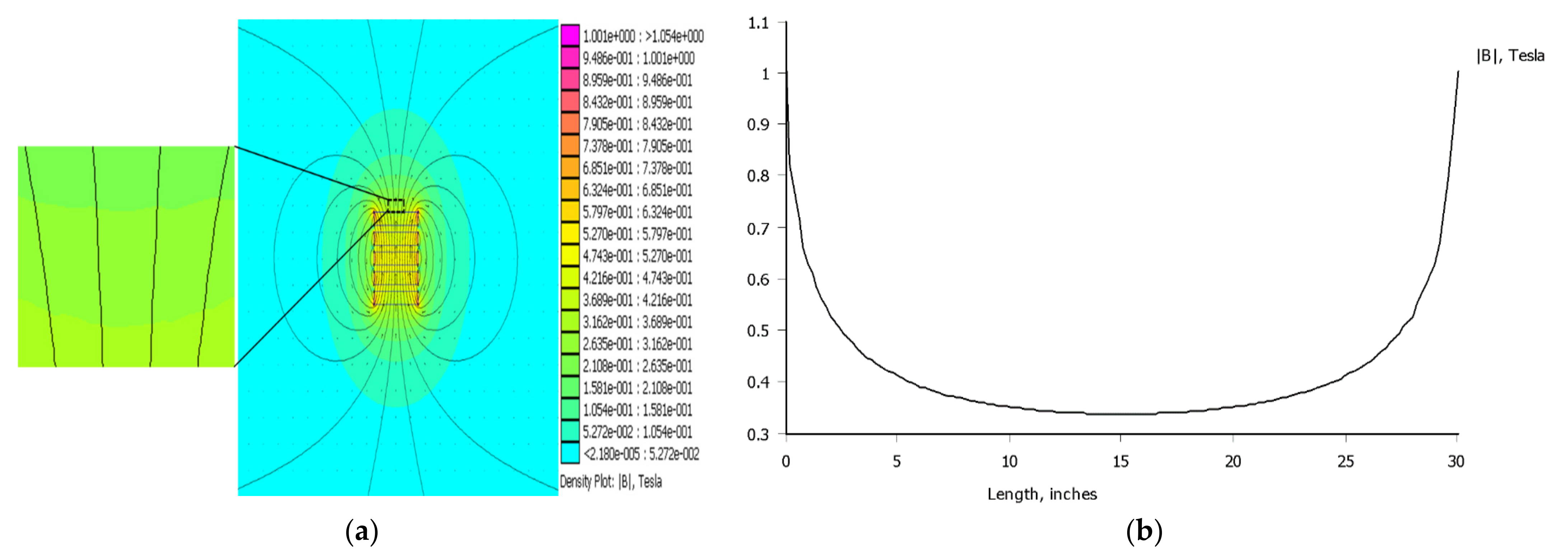
2.4. Development of the Low-Gradient Magnetic Field
2.5. Acquisition of Fluorescent Images and Preparation of the DataSet
2.6. The Establishment of the Faster R-CNN Model
2.7. Separation, Identification and Detection of Target Bacteria
2.8. Detection of Target Bacteria in Spiked Milk
3. Results and Discussion
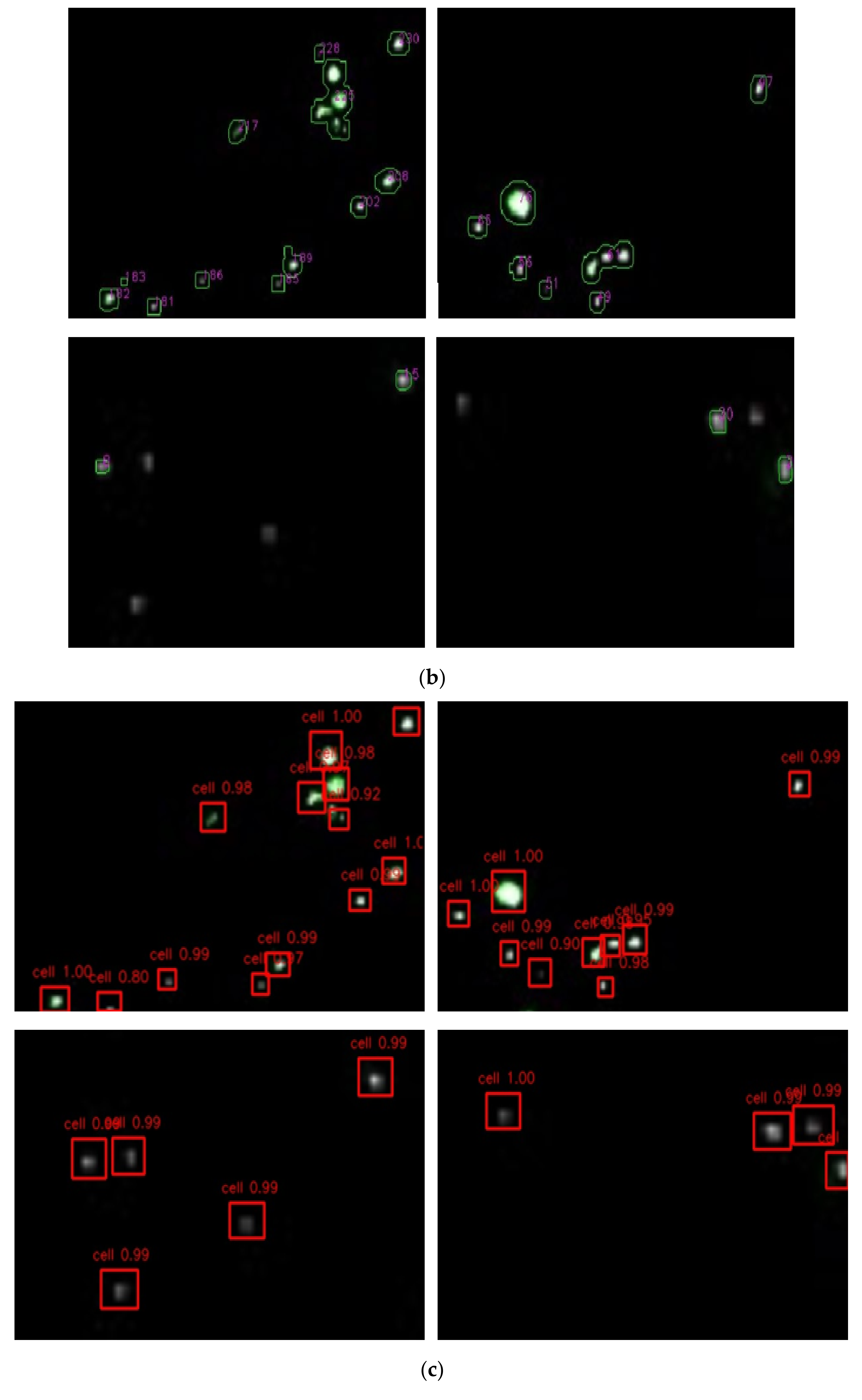
3.1. Identification of Fluorescent Spots Using the Faster R-CNN Model
3.2. Transformation of the Fluorescent Bacteria from Spatial to Planar
3.3. Optimization of the Faster R-CNN Deep Learning Algorithm
3.4. Detection of Target Bacteria Using This Fluorescent Biosensor
3.5. Detection of Target Bacteria in Milk Sample
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Barrere, V.; Tompkins, E.; Armstrong, M.; Bird, P.; Bastin, B.; Goodridge, L. Optimization of Salmonella detection in garlic, onion, cinnamon, red chili pepper powders and green tea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 316, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R.; Gast, R.K.; Regmi, P.; Ward, G.E.; Anderson, K.E.; Karcher, D.M. Pooling of Laying Hen Environmental Swabs and Efficacy of Salmonella Detection. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzwghaibi, A.B.; Yahyaraeyat, R.; Fasaei, B.N.; Langeroudi, A.G.; Salehi, T.Z. Rapid molecular identification and differentiation of common Salmonella serovars isolated from poultry, domestic animals and foodstuff using multiplex PCR assay. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, M.; Gerger, M.; Wakatsuki, T. Automated Cell Culture System and Method. U.S. Patent 10,202,568, 12 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Deng, X.; Brown, E.W.; Hammack, T.S.; Ma, L.M.; Zhang, G. Evaluation of Roka Atlas Salmonella method for the detection of Salmonella in egg products in comparison with culture method, real-time PCR and isothermal amplification assays. Food Control 2018, 94, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liao, T.; Zhou, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, X.; Chen, X. Colorimetric method for Salmonella spp. detection based on peroxidase-like activity of Cu(II)-rGO nanoparticles and PCR. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 615, 114068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdi-Amirkhiz, S.; Anzabi, Y.; Mahmazi, S. Evaluation of rapid detection and investigation of the presence of spv operon virulence genes in isolated Salmonella by using simplex PCR and multiplex PCR as molecular methods. J. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 14, fa237–fa250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ali, L.; Gill, V.; Tatavarthy, A.; Deng, X.; Hu, L.; Brown, E.W.; Hammack, T.S. Development and Validation of a Cultural Method for the Detection and Isolation of Salmonella in Cloves. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.-J.; Sha, R.-c.; Feng, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-C. Comparison of double antigen sandwich and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus antibodies. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.M.; Lee, S.Y. Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical biosensors: An exhaustive and comprehensive review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y. Biosensors Coupled with Signal Amplification Technology for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria: A Review. Biosensors 2021, 11, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.A.; Altemimi, A.B.; Alhelfi, N.; Ibrahim, S.A. Application of Biosensors for Detection of Pathogenic Food Bacteria: A Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-C.; Kim, M.-S.; Yoo, K.-C.; Ha, N.-R.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Yoon, M.-Y. Sensitive fluorescent imaging of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium using a polyvalent directed peptide polymer. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewska-Nowak, A.; Raczynski, T.; Pijanowska, D.G.; Janczak, D.; Jakubowska, M. Evaluation of Fluorescein as a Label in Electrochemical and Optical Measurements; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reshma, V.G.; Mohanan, P.V. Quantum dots: Applications and safety consequences. J. Lumin. 2019, 205, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; Pu, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots: From Chemistry and Physics to Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Y.; Qu, C.; Song, Y.; Zhou, D.; Qu, S.; et al. Cell-based fluorescent microsphere incorporated with carbon dots as a sensitive immunosensor for the rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157 in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satterly, N.G.; Voorhees, M.A.; Ames, A.D.; Schoepp, R.J. Comparison of MagPix Assays and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ferrari, M.; Qin, L. Point-of-care technologies for molecular diagnostics using a drop of blood. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsang, M.K.; Ye, W.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Hao, J. Ultrasensitive Detection of Ebola Virus Oligonucleotide Based on Upconversion Nanoprobe/Nanoporous Membrane System. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; He, B.; Fu, Y.; Song, Y. A self-powered microfluidic chip integrated with fluorescent microscopic counting for biomarkers assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 291, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yichen, W.; Yair, R.; Hongda, W.; Yilin, L.; Eyal, B.-D.; Laurent, A.B.; Christian, P.; Aydogan, O. Three-dimensional virtual refocusing of fluorescence microscopy images using deep learning. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woźniak, M.; Połap, D.; Kośmider, L.; Cłapa, T. Automated fluorescence microscopy image analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria in alive and dead stadium. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 67, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S.; Jean, N.; Hogan, C.A.; Blackmon, L.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Holodniy, M.; Banaei, N.; Saleh, A.A.E.; Ermon, S.; Dionne, J. Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman spectroscopy and deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Liu, T.; Cui, J.; Borole, P.; Benjamin, A.; Kording, K.; Issadore, D. A web-based automated machine learning platform to analyze liquid biopsy data. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafeef, M.; Srivastava, I.; Pan, D. Machine-learning for Precision Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prediction of the Nanoparticles Cellular internalization. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, C.; Verma, R. Novel Methods Based on CNN for Improved Bacteria Classification; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakasabapathy, M.K.; Thirumalaraju, P.; Bormann, C.L.; Kandula, H.; Dimitriadis, I.; Souter, I.; Yogesh, V.; Kota Sai Pavan, S.; Yarravarapu, D.; Gupta, R.; et al. Development and evaluation of inexpensive automated deep learning-based imaging systems for embryology. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 4139–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.01497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kutlu, H.; Avci, E.; Ozyurt, F. White blood cells detection and classification based on regional convolutional neural networks. Med. Hypotheses. 2020, 135, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wu, T. Novel neural network application for bacterial colony classification. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2018, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielinski, B.; Plichta, A.; Misztal, K.; Spurek, P.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Ochonska, D. Deep learning approach to bacterial colony classification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DIBaS. 2021. Available online: http://misztal.edu.pl/software/databases/dibas/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Yun, C. Simple-Faster-Rcnn-Pytorch. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Darrenl. LabelImg. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg (accessed on 7 November 2021).






| No. | Added Bacteria (CFU/mL) | Detected Bacteria (CFU/mL) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69 | 59 | 85.31 | 7.56 |
| 2 | 138 | 152 | 110.48 | 6.38 |
| 3 | 275 | 277 | 100.59 | 3.86 |
| 4 | 550 | 590 | 107.33 | 2.57 |
| 5 | 1100 | 1210 | 109.99 | 2.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Q.; Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y. A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Biosensors 2021, 11, 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110447
Hu Q, Wang S, Duan H, Liu Y. A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Biosensors. 2021; 11(11):447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110447
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Qiwei, Siyuan Wang, Hong Duan, and Yuanjie Liu. 2021. "A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network" Biosensors 11, no. 11: 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110447
APA StyleHu, Q., Wang, S., Duan, H., & Liu, Y. (2021). A Fluorescent Biosensor for Sensitive Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Low-Gradient Magnetic Field and Deep Learning via Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Biosensors, 11(11), 447. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11110447





