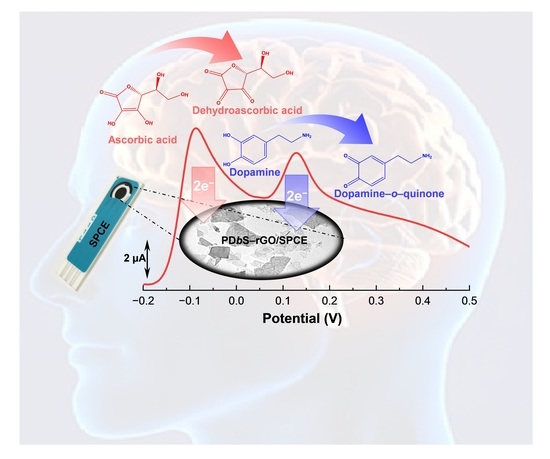
Disposable Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Block Copolymer-Dispersed Graphene for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid in Ex Vivo Mouse Brain Tissue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of PolyDMAEMA Macro-RAFT Agent
2.3. Synthesis of Poly(DMAEMA-b-styrene) Copolymer
2.4. Functionalization of rGO Using Polymer Dispersant
2.5. Preparation of PDbS–rGO-Modified SPCE
2.6. Instrument and Measurements
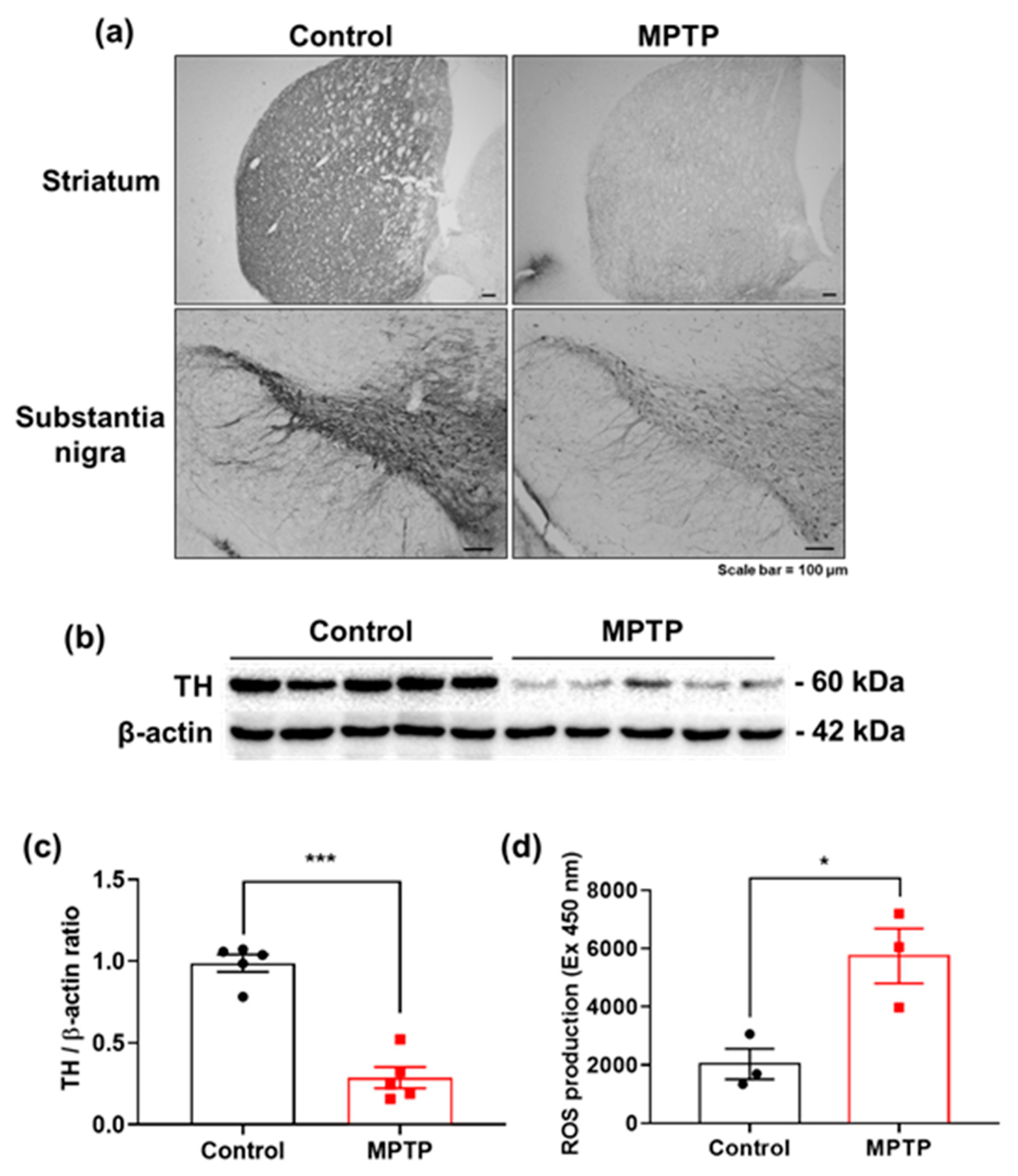
2.7. MPTP-Induced PD Mouse Model
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
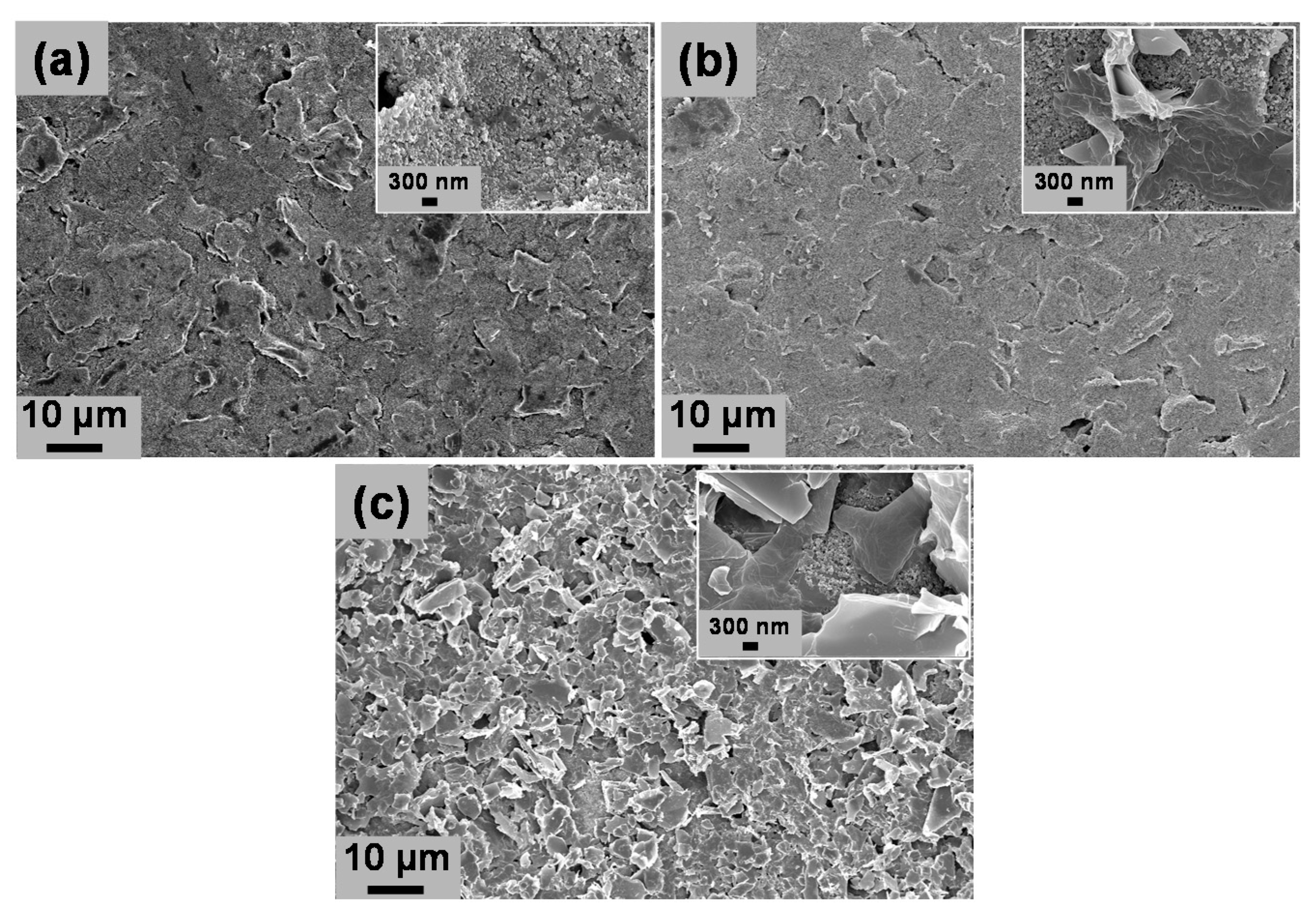
3.1. Physical Characterization of PDbS–rGO
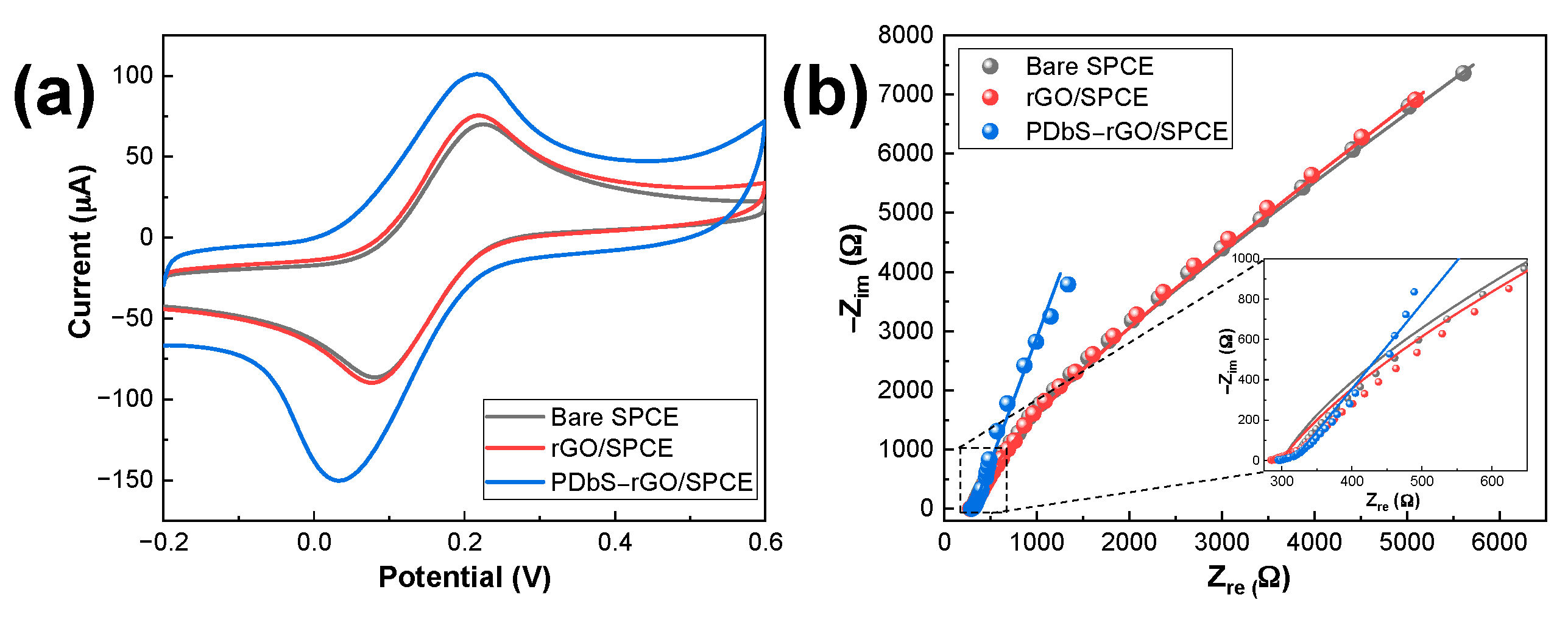
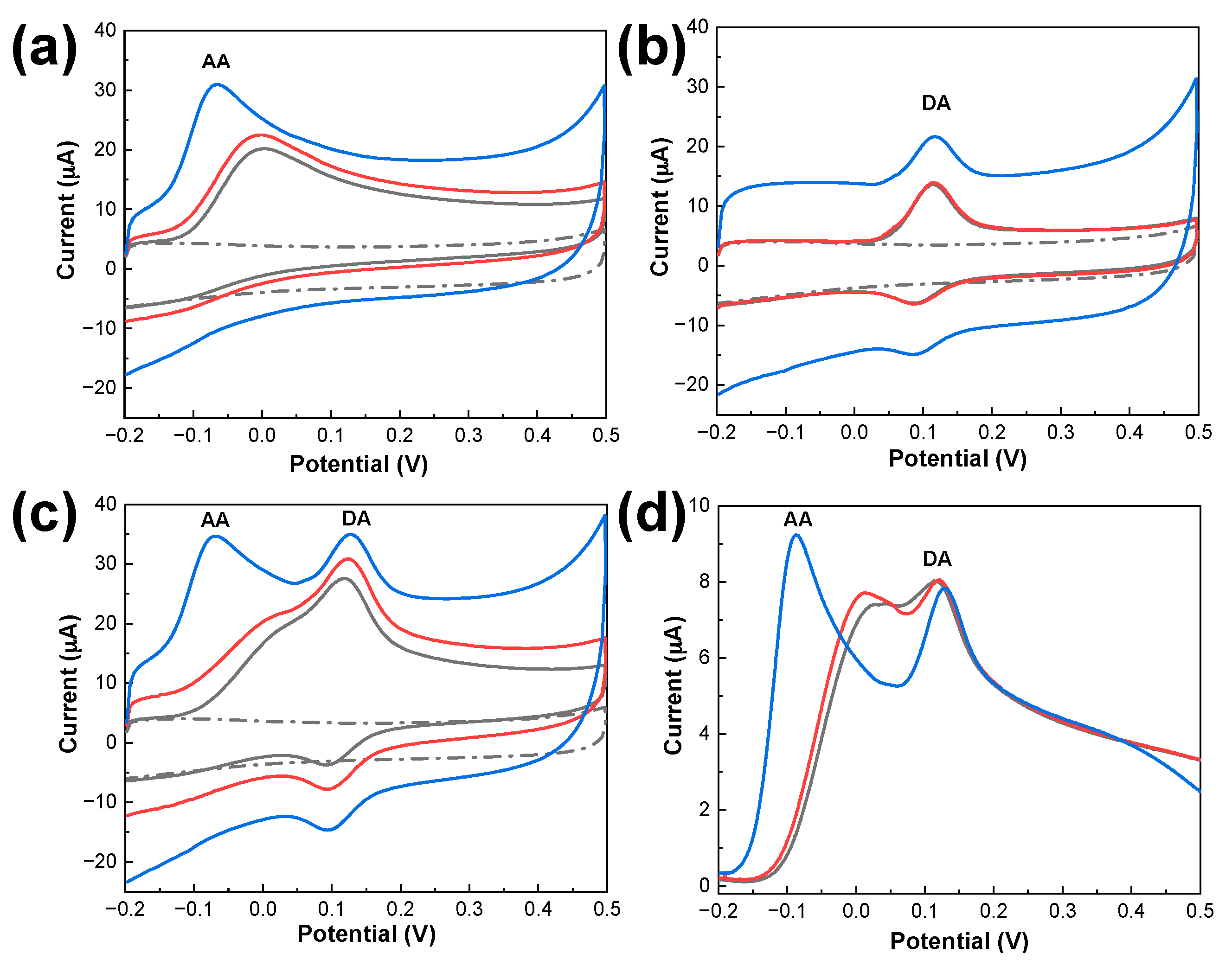
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Modified Electrodes
3.3. Optimization of pH
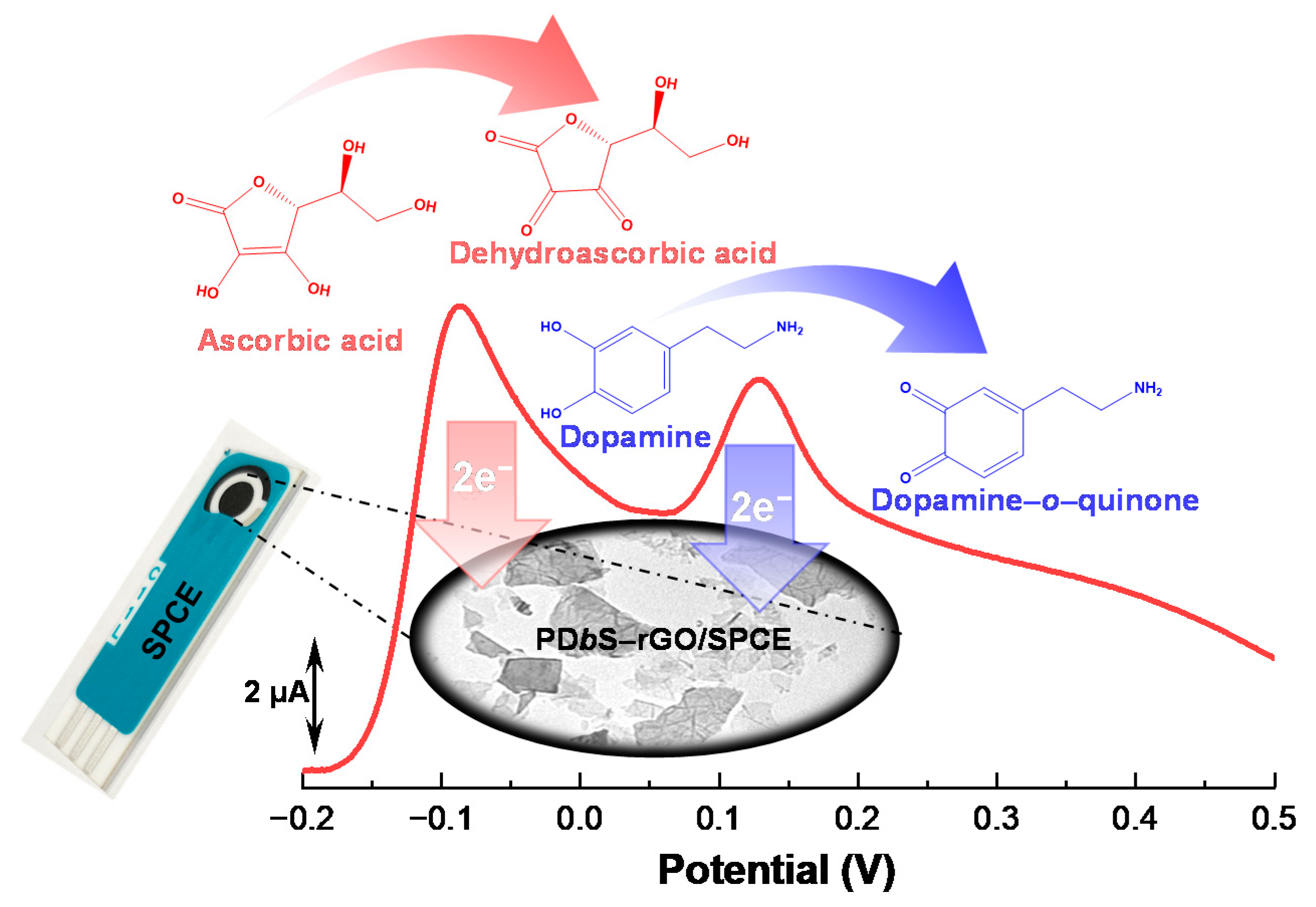
3.4. Electrochemical Response of PDbS−rGO/SPCE to DA and AA
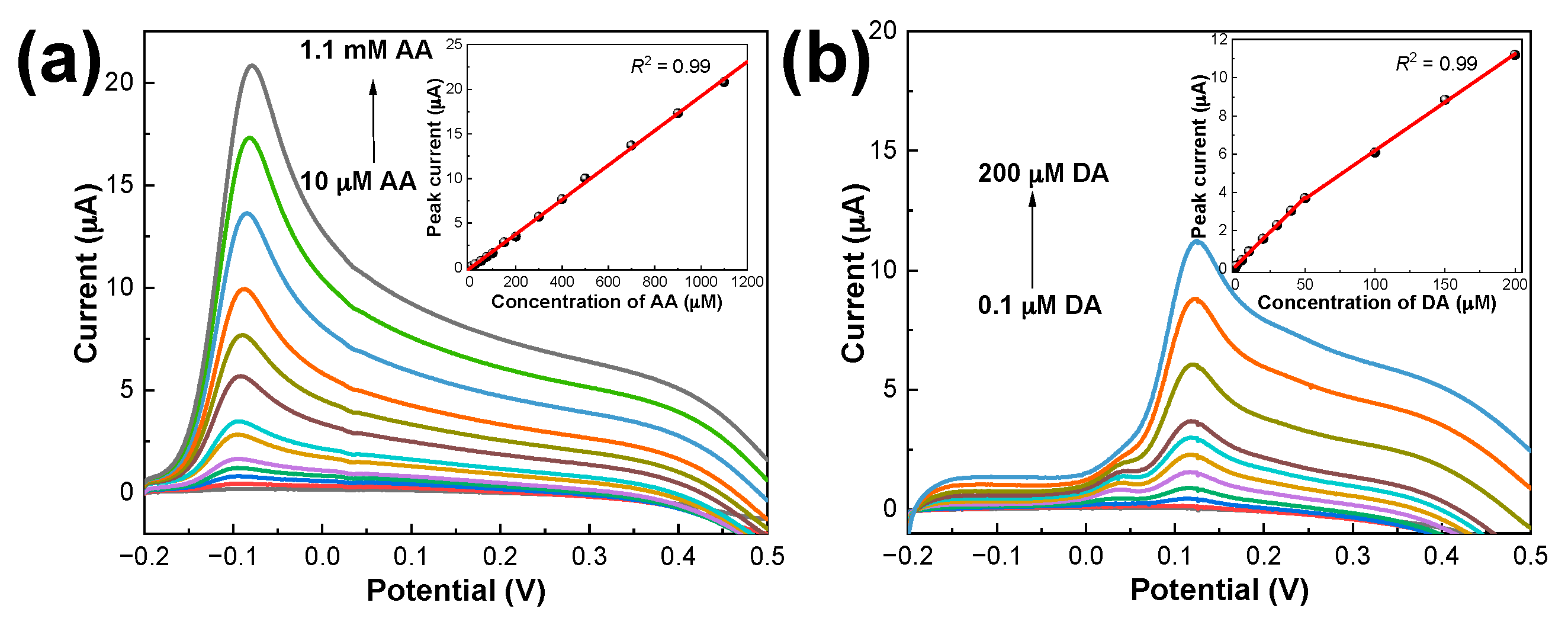
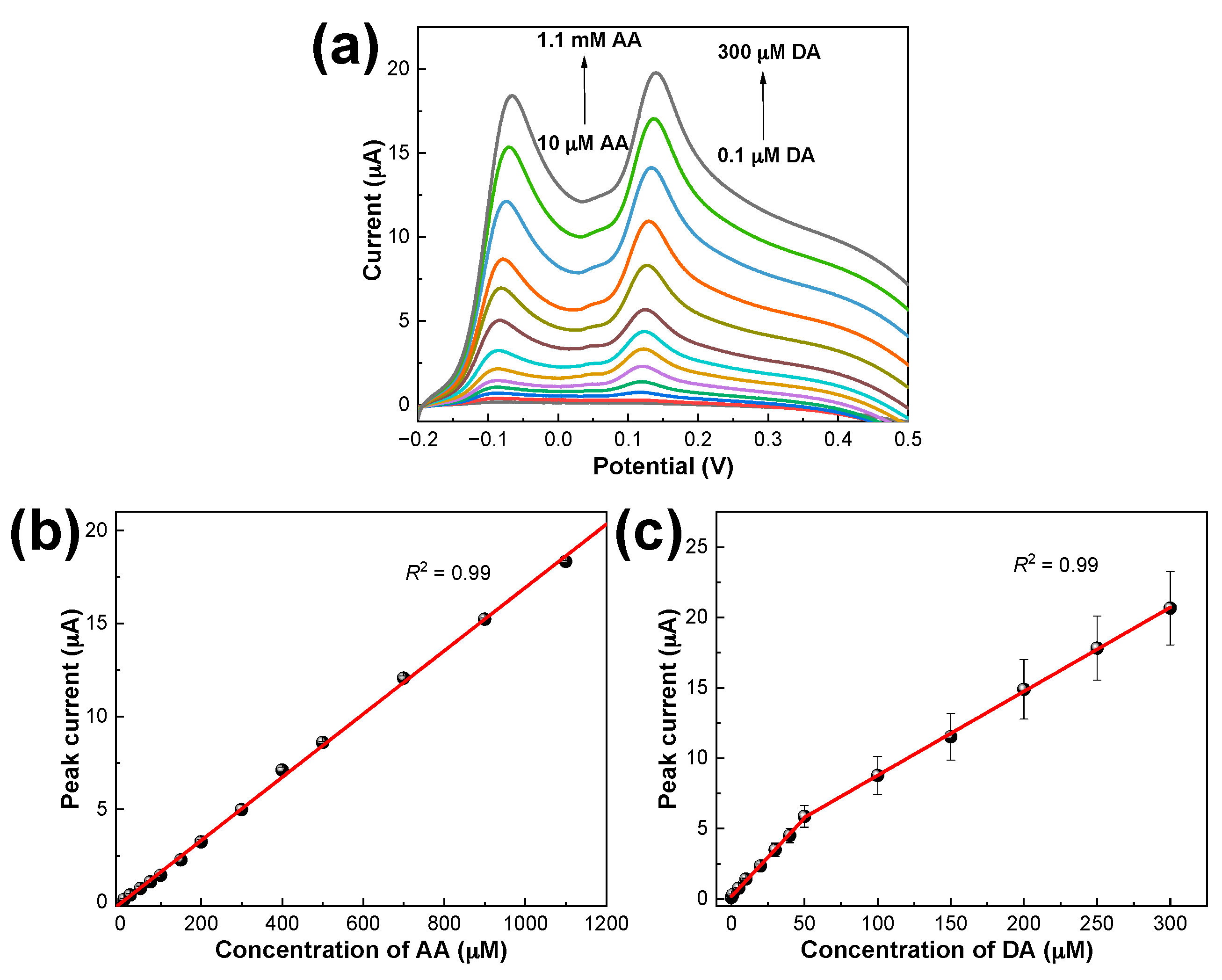
3.5. Simultaneous Determination of DA and AA Using PDbS−rGO/SPCE
3.6. Interference Study
3.7. Reproducibility and Stability Studies
3.8. Analysis of Brain Tissue Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kogularasu, S.; Akilarasan, M.; Chen, S.-M.; Chen, T.-W.; Lou, B.-S. Urea-based morphological engineering of ZnO; for the biosensing enhancement towards dopamine and uric acid in food and biological samples. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 227, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias-Pinto, A.; Acuña, A.I.; Beltrán, F.A.; Torres-Díaz, L.; Castro, M.A. Old things new view: Ascorbic acid protects the brain in neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28194–28217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, C.C.; da Encarnação, T.G.; Domith, I.; dos Santos Rodrigues, A.; de Oliveira, N.A.; Socodato, R.; Paes-de-Carvalho, R. Dopamine-induced ascorbate release from retinal neurons involves glutamate release, activation of AMPA/kainate receptors and downstream signaling pathways. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, S.N.; Schou-Pedersen, A.M.V.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Spatial memory dysfunction induced by vitamin C deficiency is associated with changes in monoaminergic neurotransmitters and aberrant synapse formation. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, F.E.; May, J.M. Vitamin C function in the brain: Vital role of the ascorbate transporter SVCT2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadon, N.; Jain, R.; Sharma, S.; Singh, K. Recent trends in electrochemical sensors for multianalyte detection—A review. Talanta 2016, 161, 894–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.R.; Imran, S.; Ye, W.; Weng, H.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. Simultaneous voltammetric detection of six biomolecules using a nanocomposite of titanium dioxide nanorods with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 362, 137094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jin, C.; Miao, X.; Shen, Y. Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid on a MoS2-CPtNPs nanocomposite-modified electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 3969–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Hou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C. Preparation of electrochemical sensor based on zinc oxide nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of AA, DA, and UA. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 592538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranmanesh, T.; Foroughi, M.M.; Jahani, S.; Zandi, M.S.; Nadiki, H.H. Green and facile microwave solvent-free synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticle-decorated CNTs as a quadruplet electrochemical platform for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and acetaminophen. Talanta 2020, 207, 120318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liang, H.; Zhu, M.; Lai, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Ye, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, W. Electrochemical dual signal sensing platform for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and glucose based on copper and cerium bimetallic carbon nanocomposites. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 139, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ding, D.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Diao, G. Three-dimensional nitrogen-doped graphene-based metal-free electrochemical sensors for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, and acetaminophen. Analyst 2021, 146, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chang, Z.; Ge, M.; Mei, Q.; Dong, W.-F. Simultaneous recognition of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of ascorbic acid via an intercalated MXene/PPy nanocomposite. Sensors 2021, 21, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papanikolaou, I.; de Souza, L.R.; Litina, C.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Investigation of the dispersion of multi-layer graphene nanoplatelets in cement composites using different superplasticiser treatments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Jiang, X.; Hong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Zhu, D. Recent developments concerning the dispersion methods and mechanisms of graphene. Coatings 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perumal, S.; Park, K.T.; Lee, H.M.; Cheong, I.W. PVP-b-PEO block copolymers for stable aqueous and ethanolic graphene dispersions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 464, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Perumal, S.; Cheong, I.W. Amphiphilic fluorinated block copolymer synthesized by RAFT polymerization for graphene dispersions. Polymers 2016, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perumal, S.; Lee, H.M.; Cheong, I.W. A study of adhesion forces between vinyl monomers and graphene surfaces for non-covalent functionalization of graphene. Carbon 2016, 100, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y.R. Exfoliation and noncovalent functionalization of graphene surface with poly-N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone by in situ polymerization. Molecules 2021, 26, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, S.; Yasin, S.; Ramzan, N.; Iqbal, T.; Akhtar, M.N. Preparation of stable dispersion of graphene using copolymers: Dispersity and aromaticity analysis. Soft Mater. 2019, 17, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarathinam, T.; Kwon, M.; Thirumalai, D.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Paik, H.-j.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Ha, H.K.; et al. Polymer-dispersed reduced graphene oxide nanosheets and Prussian blue modified biosensor for amperometric detection of sarcosine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1175, 338749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, D.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Chang, S.-C. Reagentless amperometric pyruvate biosensor based on a Prussian blue- and enzyme nanoparticle-modified screen-printed carbon electrode. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 30123–30129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Suh, Y.J.; Yang, S.; Hong, D.G.; Ishigami, A.; Kim, H.; Hur, J.-S.; Chang, S.-C.; Lee, J. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of evernic acid in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Ferreira, E.H.M.; Stavale, F.; Achete, C.A.; Capaz, R.B.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Quantifying defects in graphene via Raman spectroscopy at different excitation energies. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohmad, G.; Sarkar, S.; Biswas, A.; Roy, K.; Dey, R.S. Polymer-assisted electrophoretic synthesis of N-doped graphene-polypyrrole demonstrating oxygen reduction with excellent methanol crossover impact and durability. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 12664–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.J.; McCarthy, B.D.; Rountree, E.S.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2018, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 833. [Google Scholar]
- Konopka, S.; McDuffie, B. Diffusion coefficients of ferri-and ferrocyanide ions in aqueous media, using twin-electrode thin-layer electrochemistry. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Son, S.H.; Sharma, R.; Won, Y.-Y. A Discussion of the pH-dependent protonation behaviors of poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) and poly(ethylenimine-ran-2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (P(EI-r-EOz)). J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocak, J.; Bond, A.M.; Mitchell, S.; Scollary, G. A statistical overview of standard (IUPAC and ACS) and new procedures for determining the limits of detection and quantification: Application to voltammetric and stripping techniques (technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 1997, 69, 297–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jia, Z.; Huo, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhong, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, M.; Bian, M.; Hou, C. In-situ growth of gold nanoparticles on a 3D-network consisting of a MoS2/rGO nanocomposite for simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyong, P.; Rawlinson, S.; Davis, J. A voltammetric sensor based on chemically reduced graphene oxide-modified screen-printed carbon electrode for the simultaneous analysis of uric acid, ascorbic acid and dopamine. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinesh, B.; Vilian, A.E.; Kwak, C.H.; Huh, Y.S.; Saraswathi, R.; Han, Y.-K. The facile and simple synthesis of poly (3,4ethylenedioxythiophene) anchored reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for biochemical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1077, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghnegahdar, N.; Tarighat, M.A.; Dastan, D. Curcumin-functionalized nanocomposite AgNPs/SDS/MWCNTs for electrocatalytic simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid, and guanine in co-existence of ascorbic acid by glassy carbon electrode. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 5602–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Faraj, Y.; Liu, L.-Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.-J.; Wei, J.; Chu, L.-Y. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, uric acid and estriol in maternal urine samples based on the synergetic effect of reduced graphene oxide, silver nanowires and silver nanoparticles in their ternary 3D nanocomposite. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S. Electrochemical sensors based on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide for the simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 842, 155873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.; Jerome, R.; Preethika, M.; Sundaramurthy, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. 2D-titanium carbide (MXene) based selective electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 72, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Cao, T.; Fan, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Tong, Z. Synthesis of polyfluorinated azobenzene intercalated tantalum tungstate nanocomposite for determination of dopamine and ascorbic Acid. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 037516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Ha, S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Hur, J.-S.; Lee, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of usnic acid in an MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2020, 1730, 146642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.-F. Consideration of sample matrix effects and “biological” noise in optimizing the limit of detection of biosensors. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3290–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyakul, N.; Baeumner, A.J. Combining electrochemical sensors with miniaturized sample preparation for rapid detection in clinical samples. Sensors 2015, 15, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.F.; David, S.N.; Newport, G.D.; Cadet, J.L.; Slikker, W., Jr. MPTP-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity are age-dependent: Evidence from measures of reactive oxygen species and striatal dopamine levels. Synapse 1994, 18, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Electrodes | Dynamic Linear Range (µM) | Limit of Detection (µM) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | AA | DA | AA | ||
| 3D-MoS2/rGO/Au/GCE | 0.30–198.3 | 2.0–5400 | 0.11 | 0.93 | [32] |
| rGO/SPCE | 0.20–80 | 100–2500 | 0.10 | 50 | [33] |
| PEDOT/rGO/GCE | 0.10–901 | 0.20–907 | 0.60 | 1.5 | [34] |
| CM/AgNPs/SDS/MWCNTs/GCE | 12–200 | - | 0.14 | - | [35] |
| rGO/AgNWs/ AgNPs/SPCE | 0.60–50 | - | 0.16 | - | [36] |
| N-rGO/GCE | 1.0–60 | 100–4000 | 0.10 | 9.6 | [37] |
| Ti-C-Tx/GCE | 0.50–50 | 100–1000 | 0.060 | 4.6 | [38] |
| C3F7-azo+-TaWO6/GCE | 50–310 | 50–310 | 0.81 | 1.6 | [39] |
| PDbS–rGO/SPCE | 0.10–300 | 10–1100 | 0.134 | 0.88 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thirumalai, D.; Lee, S.; Kwon, M.; Paik, H.-j.; Lee, J.; Chang, S.-C. Disposable Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Block Copolymer-Dispersed Graphene for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid in Ex Vivo Mouse Brain Tissue. Biosensors 2021, 11, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100368
Thirumalai D, Lee S, Kwon M, Paik H-j, Lee J, Chang S-C. Disposable Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Block Copolymer-Dispersed Graphene for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid in Ex Vivo Mouse Brain Tissue. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100368
Chicago/Turabian StyleThirumalai, Dinakaran, Seulah Lee, Minho Kwon, Hyun-jong Paik, Jaewon Lee, and Seung-Cheol Chang. 2021. "Disposable Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Block Copolymer-Dispersed Graphene for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid in Ex Vivo Mouse Brain Tissue" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100368
APA StyleThirumalai, D., Lee, S., Kwon, M., Paik, H.-j., Lee, J., & Chang, S.-C. (2021). Disposable Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Block Copolymer-Dispersed Graphene for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Ascorbic Acid in Ex Vivo Mouse Brain Tissue. Biosensors, 11(10), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100368