Bio-Specific Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters for Sensitive SERS Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
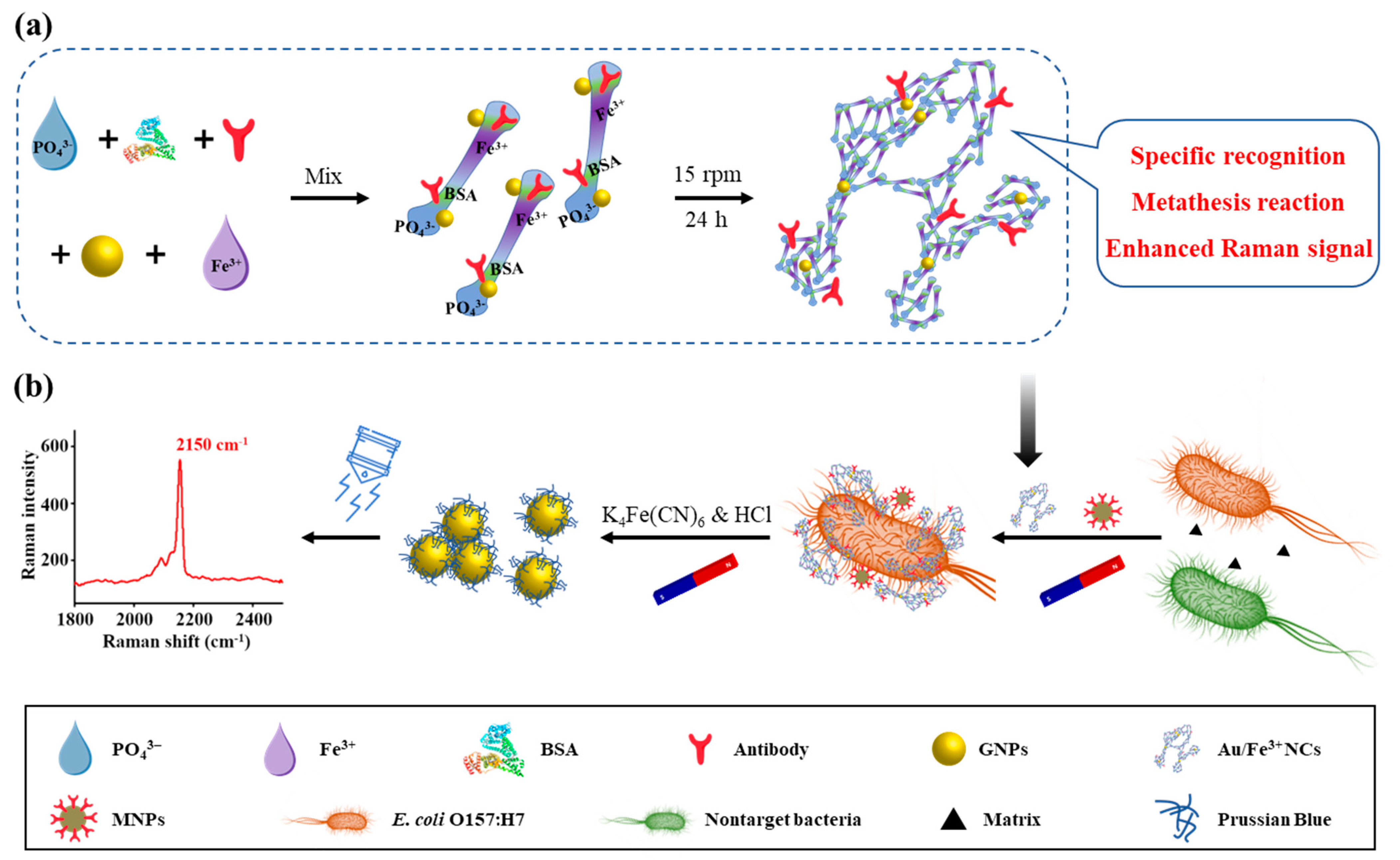
2.2. Preparation of Novel Au/Fe3+ Nanoclusters
2.3. Characterization of Au/Fe3+ Nanoclusters
2.4. Separation and Detection of Bacteria
2.5. Optimization of the Au/Fe3+ Nanoclusters-Based Biosensor
2.6. Performance Evaluation of the Biosensor
2.7. Analyses of Food Samples
2.8. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
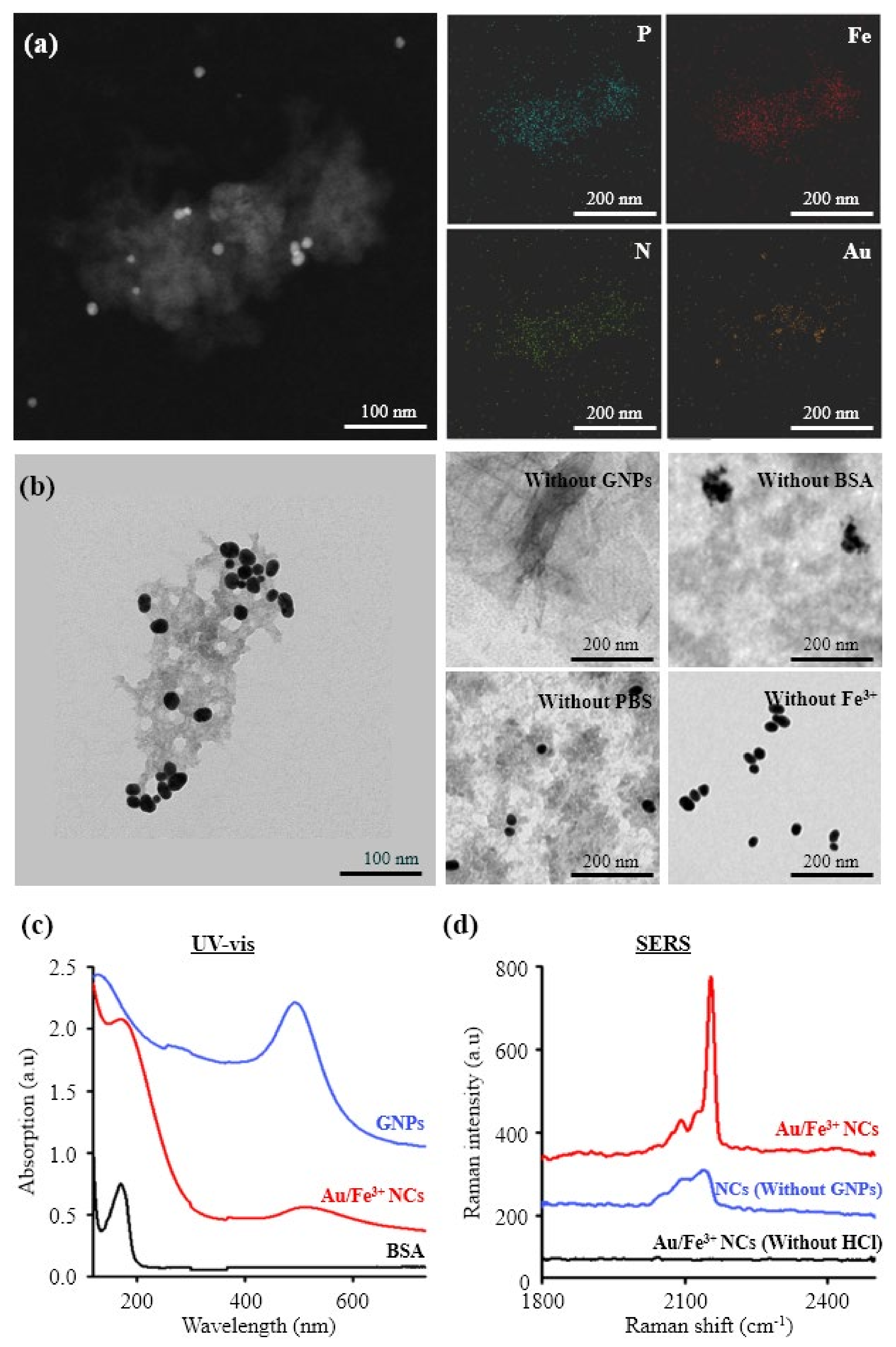
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters
3.2. Formation Mechanism of Au/Fe3+ Nanoclusters
3.3. Optimization of Au/Fe3+ NCs-Based SERS Biosensor
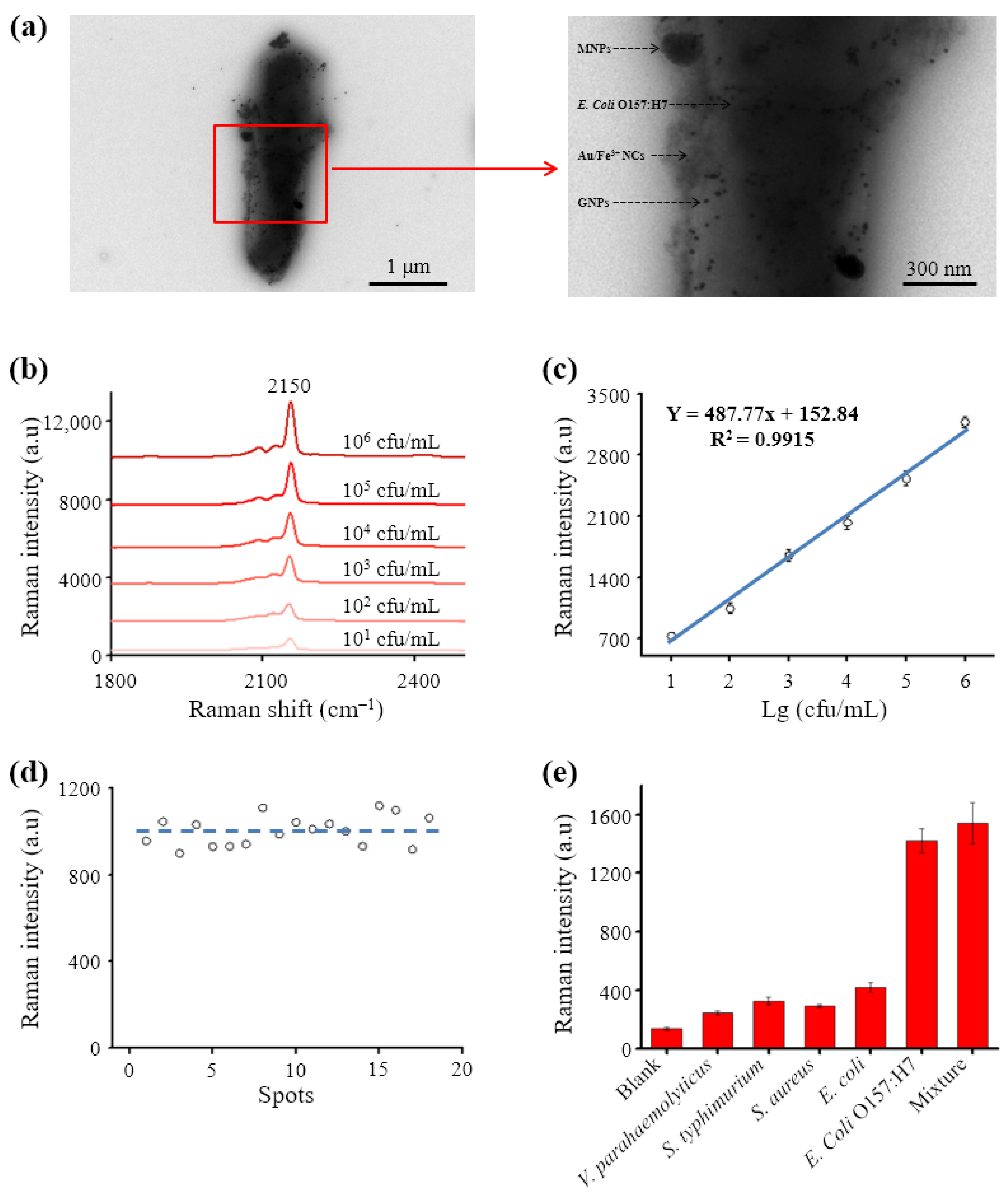
3.4. High-Performance SERS Detection of E. coli O157:H7
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, T.; Song, Y.; Wei, T.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Zhu, M.J.; Lin, Y. Sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using Pt-Au bimetal nanoparticles with peroxidase-like amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Blacker, B.F.; Rao, P.C.; Brown, A.; Atherly, D.E.; Brewer, T.G.; Engmann, C.M.; Houpt, E.R.; Kang, G.; et al. Morbidity and mortality due to shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: The Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H. Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeni, F.; Acar, S.; Polat, Ö.G.; Soyer, Y.; Alpas, H. Rapid and standardized methods for detection of foodborne pathogens and mycotoxins on fresh produce. Food Control 2014, 40, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Yong, Q.; Wang, W.; Hua, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based ELISA to detect Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Agric. Immunol. 2013, 24, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Andler, S.M.; Goddard, J.M.; Nugen, S.R.; Rotello, V.M. Integrating recognition elements with nanomaterials for bacteria sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.J.; Zheng, J.K.; He, L.L. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) combined techniques for high-performance detection and characterization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.K.; He, L.L. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the chemical analysis of food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, H.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.W. Recent developments in Raman spectral analysis of microbial single cells: Techniques and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tang, L.H.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.Z.; Liu, J.W.; Zheng, J.K. DNA-encoded bimetallic Au-Pt dumbbell nanozyme for high-performance detection and eradication of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 187, 113327–113337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Qin, T.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, L. Graphene oxide wrapped SERS tags: Multifunctional platforms toward optical labeling, photothermal ablation of bacteria, and the monitoring of killing effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Bi, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, A.; Liang, S. Highly surface-roughened caterpillar-like Au/Ag nanotubes for sensitive and reproducible substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45856–45861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Wu, X.J.; Wang, C.W.; Rong, Z.; Ding, H.M.; Li, H.; Li, S.H.; Shao, N.S.; Dong, P.T.; Xiao, R.; et al. Facile synthesis of au-coated magnetic nanoparticles and their application in bacteria detection via a sers method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19958–19967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamer, U.; Boyac, I.H.; Temur, E.; Zengin, A.; Dincer, I.; Elerman, Y. Fabrication of magnetic gold nanorod particles for immunomagnetic separation and SERS application. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.P.; Xu, B.C. Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Ren, W.; Zhu, L.; Irudayaraj, J. Prosperity to challenges: Recent approaches in SERS substrate fabrication. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 36, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yin, H.; Ma, W.; Kuang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive SERS detection of mercury based on the assembled gold nanochains. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.S.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.Z.; Xue, L.; Zhao, C.Y.; Tian, G.F.; Bao, Y.M.; Tang, L.H.; Lin, J.H.; Zheng, J.K. Gold nanobones enhanced ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering aptasensor for detecting Escherichia coli O157:H7. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Lu, C.; Zhou, S.S.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Gao, F.; Fan, B.; Lin, J.H.; Wang, F.Z.; Zheng, J.K. Sensitive and simultaneous detection of different pathogens by surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on aptamer and Raman reporter co-mediated gold tags. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 317, 128182–128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Xue, L.; Huang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, N.; Lin, J.H. A capillary biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella using Fe-nanocluster amplification and smart phone imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurier, K.G.; Vermoortele, F.; Ameloot, R.; De Vos, D.E.; Hofkens, J.; Roeffaers, M.B. Iron(III)-based metal-organic frameworks as visible light photocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14488–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.P.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ying, J.Y. Protein-directed synthesis of highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 888–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lei, J.; Zare, R.N. Protein-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.C.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Liao, M.; Lin, J.H. Rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using magnetic nanoparticle immunoseparation, nanocluster signal amplification and smartphone image analysis. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 284, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Yin, Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, W.; Yang, H. Facile synthesis of enzyme-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers and its application as a colorimetric platform for visual detection of hydrogen peroxide and phenol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10775–10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Lan, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Niu, Z. Multi-enzyme co-embedded organic-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers: Synthesis and application as a colorimetric sensor. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, G.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, D.; Gou, D.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. A new biosensor based on the recognition of phages and the signal amplification of organic-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers for discriminating and quantitating live pathogenic bacteria in urine. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 258, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huo, X.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, J. Exploring protein-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers and immune magnetic nanobeads to detect Salmonella typhimurium. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.; Yu, M.; Fu, F.; Han, W.; Li, G.; Xie, J.; Song, Y.; Swihart, M.T.; Song, E. Dual recognition strategy for specific and sensitive detection of bacteria using aptamer-coated magnetic beads and antibiotic-capped gold nanoclusters. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Q.; Ma, S.; Liu, H.; Dong, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, D. Prussian blue as a highly sensitive and background-free resonant Raman reporter. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. The formation of colloidal gold. J. Phys. Chem. C 1953, 57, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, G.P.; Kneipp, J. Different binding sites of serum albumins in the protein corona of gold nanoparticles. Analyst 2018, 143, 6061–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matei, I.; Buta, C.M.; Turcu, I.M.; Culita, D.; Munteanu, C.; Ionita, G. Formation and stabilization of gold nanoparticles in bovine serum albumin solution. Molecules 2019, 24, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidson, A.M.; Brust, M.; Cooper, D.L.; Volk, M. Sensitive analysis of protein adsorption to colloidal gold by differential centrifugal sedimentation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6807–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dokmanic, I.; Sikic, M.; Tomic, S. Metals in proteins: Correlation between the metal-ion type, coordination number and the amino-acid residues involved in the coordination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2008, 64, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Cooper, D.R.; Porebski, P.J.; Shabalin, I.G.; Handing, K.B.; Minor, W. CheckMyMetal: A macromolecular metal-binding validation tool. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2017, 73, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Spiked Concentration (cfu/mL) | Plate Counting Method (cfu/mL) | This Method (cfu/mL) | Recovery Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 1000 | 906 ± 70 | 968 ± 89 | 93.60 |
| Lettuce | 1500 | 1486 ± 30 | 1418 ± 113 | 95.25 |
| Chicken | 1500 | 1633 ± 31 | 1674 ± 83 | 97.50 |
| Methods | Materials | Target | LOD (cfu/mL) | Detection Time | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERS | AuMNPs core/shell nanocomposites | S. aureus | 10 | ~120 min | [13] |
| SERS | Gold nanoparticles | S. typhimurium & S. aureus | 15 & 35 | ~150 min | [15] |
| Electrochemical biosensor | GOx&HRP-Cu3(PO4)2 hybrid nanoflowers | E. coli | 1 | ~140 min | [7] |
| Hue-saturation-lightness color space | Fe-nanoclusters | S. typhimurium | 14 | — | [20] |
| Hue-saturation-lightness color space | Immune GOx–nanoclusters | S. typhimurium | 16 | — | [24] |
| SERS | Nanocluster | E. coli O157:H7 | 2 | ~30 min | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Gao, F.; Lu, C.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Zheng, J. Bio-Specific Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters for Sensitive SERS Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosensors 2021, 11, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100354
Li Y, Gao F, Lu C, Fauconnier M-L, Zheng J. Bio-Specific Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters for Sensitive SERS Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosensors. 2021; 11(10):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100354
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuzhi, Fei Gao, Chang Lu, Marie-Laure Fauconnier, and Jinkai Zheng. 2021. "Bio-Specific Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters for Sensitive SERS Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7" Biosensors 11, no. 10: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100354
APA StyleLi, Y., Gao, F., Lu, C., Fauconnier, M.-L., & Zheng, J. (2021). Bio-Specific Au/Fe3+ Porous Spongy Nanoclusters for Sensitive SERS Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosensors, 11(10), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11100354






