A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for On-Site Authentication of Cephalopod Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Dataset Assembling for Primers Design, and DNA Extraction
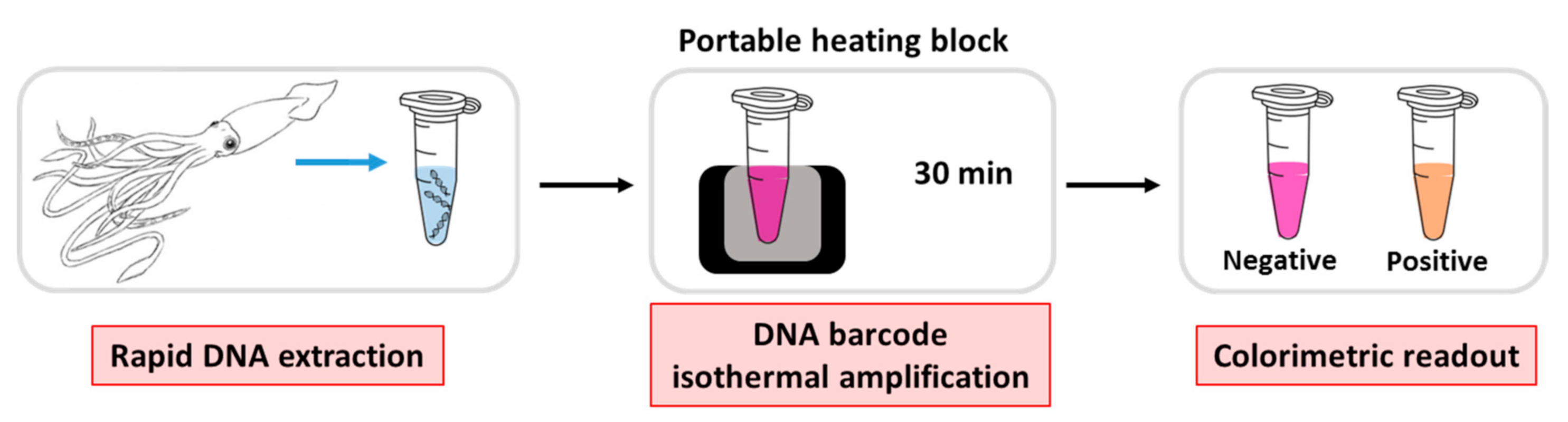
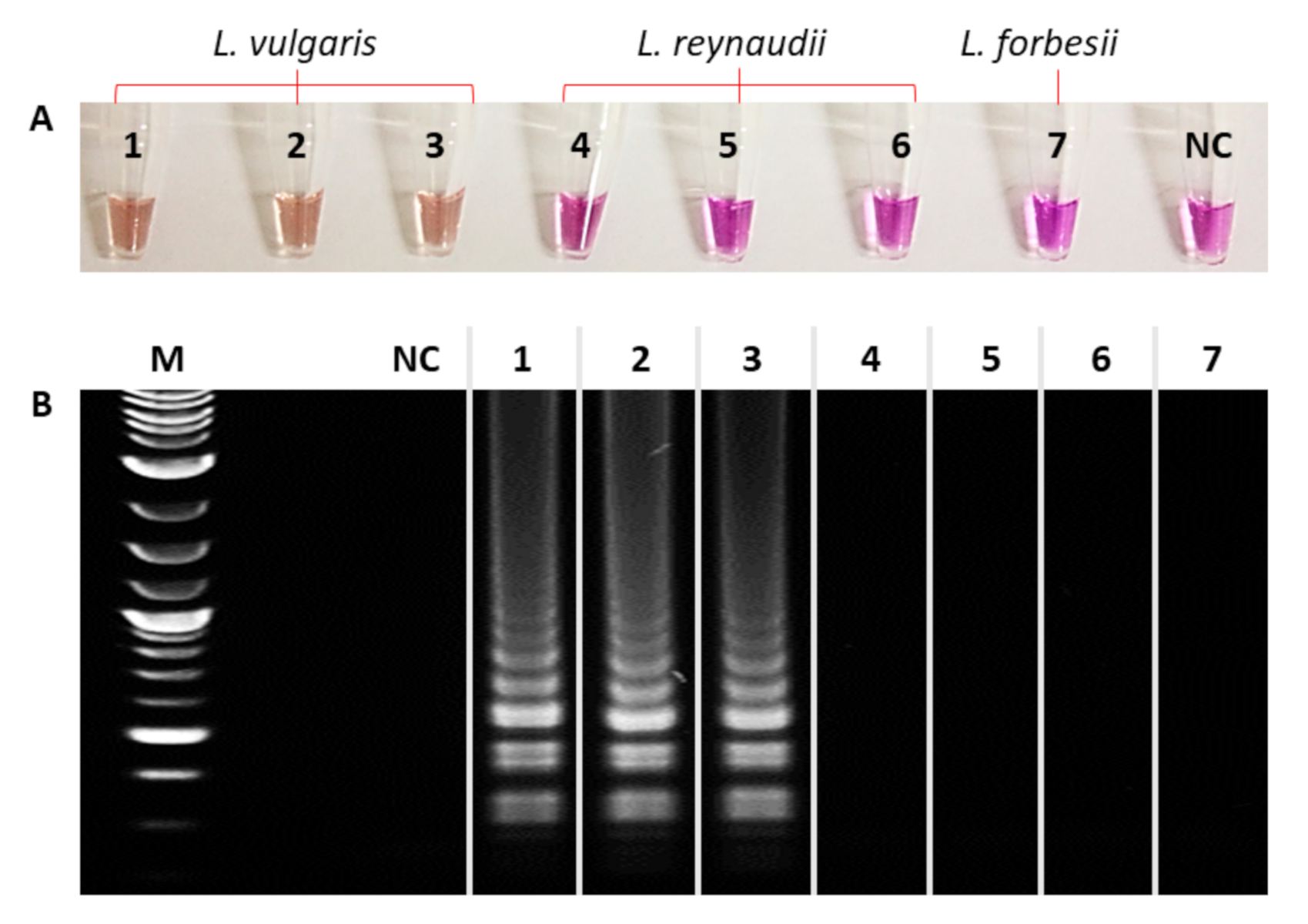
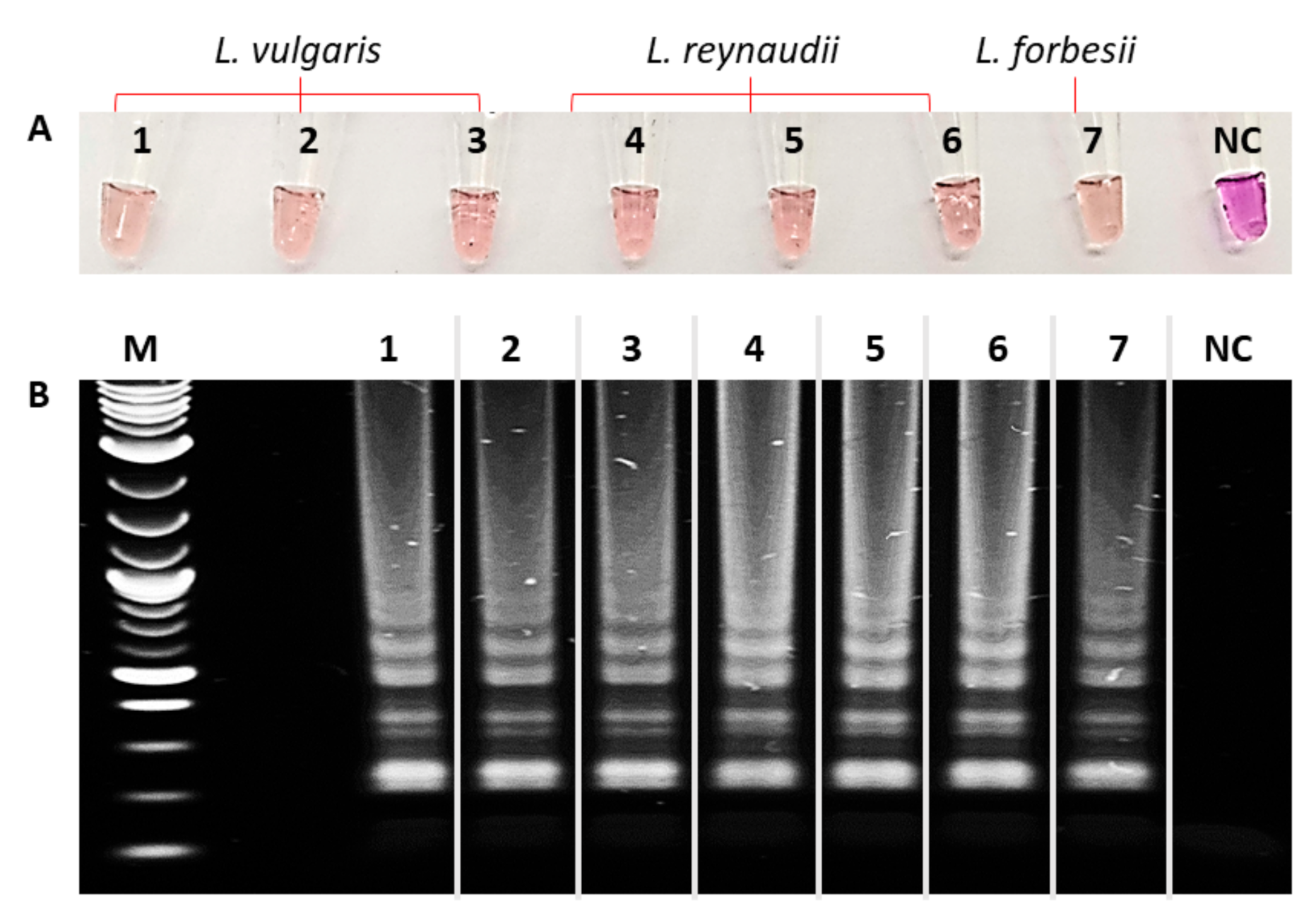
2.2. Colorimetric LAMP Reaction
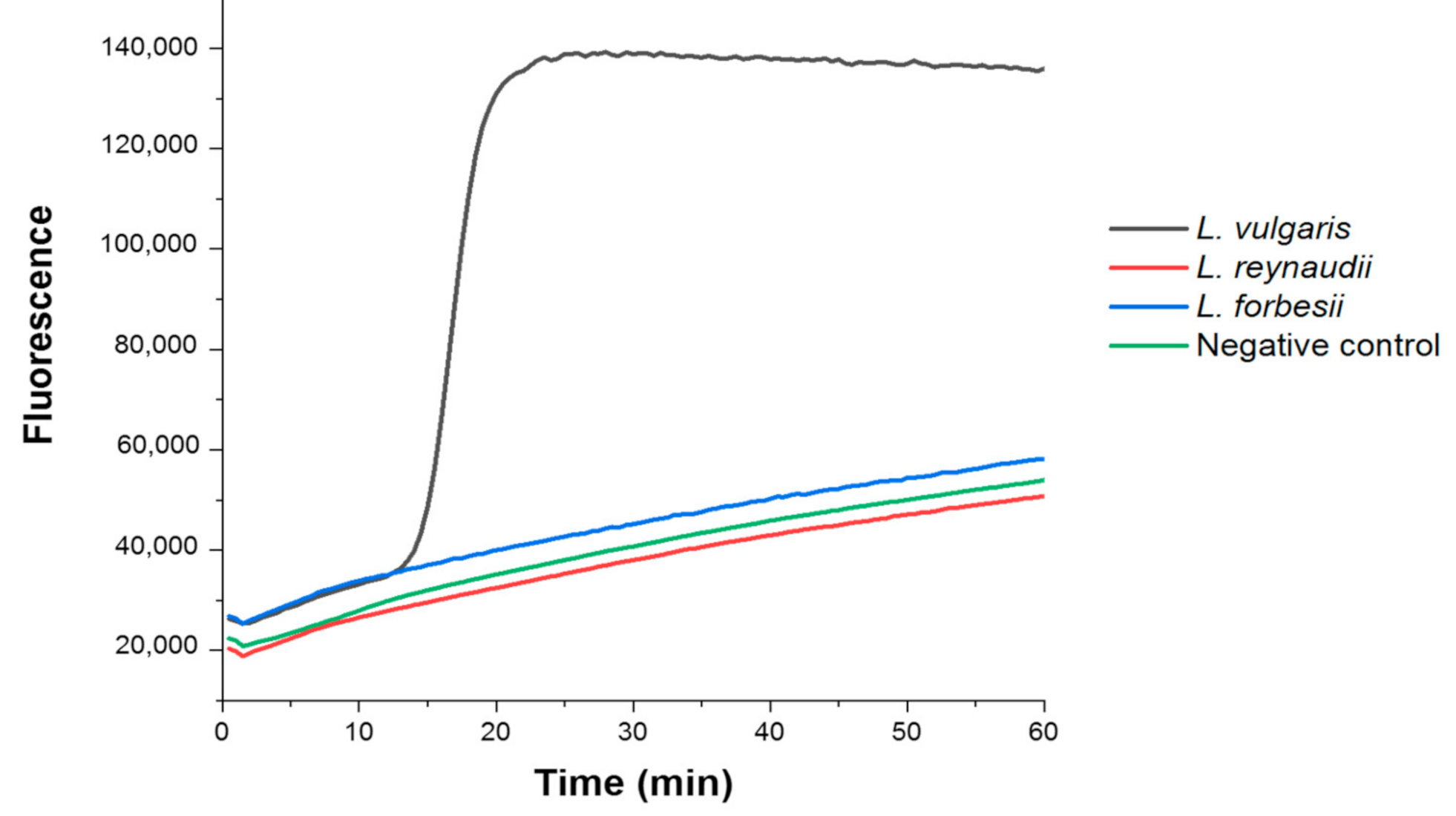
2.3. Fluorimetric LAMP Reaction
2.4. LAMP-AGE Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naaum, A.M.; Warner, K.; Mariani, S.; Hanner, R.H.; Carolin, C.D. Seafood Mislabeling Incidence and Impacts. In Seafood Authenticity and Traceability, 1st ed.; Naaum, A.M., Hanner, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, M.; Mitchell, M.; Dean, M.; Elliott, C.; Campbell, K. The seafood supply chain from a fraudulent perspective. Food Sec. 2018, 10, 939–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, A.; De Mattia, F.; Losa, A.; Bruni, I.; Federici, S.; Casiraghi, M.; Martellos, S.; Labra, M. DNA barcoding as a new tool for food traceability. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; Casiraghi, M.; Bruni, I.; Guzzetti, L.; Cortis, P.; Berterame, N.M.; Labra, M. From DNA barcoding to personalized nutrition: The evolution of food traceability. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, H.F.; Zemlak, T.S.; Mason, J.A.; Washington, J.D.; Tenge, B.J.; Nguyen, N.-L.T.; Barnett, J.D.; Savary, W.E.; Hill, W.E.; Moore, M.M.; et al. Potential use of DNA barcodes in regulatory science: Applications of the Regulatory Fish Encyclopedia. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handy, S.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hanner, R.H.; Ormnos, A.; Weigt, L.A.; Moore, M.M.; Yancy, H.F. A single-laboratory validated method for the generation of DNA barcodes for the identification of fish for regulatory compliance. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeds, J.R.; Handy, S.M.; Fry, F., Jr.; Granade, H.; Williams, J.; Powers, M.; Shipp, R.; Weigt, L.A. Protocol for building a reference standard sequence library for DNA-based seafood identification. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The barcode of life data system (https://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, F.; Cerioli, M.; Colombo, M.M.; Marchisio, E.; Malandra, R.; Renon, P. A simple polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method for the differentiation of cephalopod mollusc families Loliginidae from Ommastrephidae, to avoid substitutions in fishery field. Food Control 2002, 13, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuto, M.; Galimberti, A.; Ferri, E.; Labra, M.; Malandra, R.; Galli, P.; Casiraghi, M. DNA barcoding reveals fraudulent substitutions in shark seafood products: The Italian case of “palombo” (Mustelus spp.). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, A.; Ramilo-Fernández, G.; Sotelo, C.G. A real-time PCR method for the authentication of common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) in food products. Foods 2020, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, P.; Galimberti, A.; Mezzasalma, V.; De Mattia, F.; Casiraghi, M.; Labra, M.; Pompa, P.P. DNA barcoding meets nanotechnology: Development of a smart universal tool for food authentication. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 8094–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggioni, D.; Tatulli, G.; Montalbetti, E.; Tommasi, N.; Galli, P.; Labra, M.; Pompa, P.P.; Galimberti, A. From DNA barcoding to nanoparticle-based colorimetric testing: A new frontier in cephalopod authentication. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Fan, C. Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12491–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, M.; Horioke, K.; Ishida, H.; Dash, P.K.; Saxena, P.; Jana, A.M.; Islam, M.A.; Inoue, S.; Hosaka, N.; Morita, K. Rapid detection and differentiation of dengue virus serotypes by a real-time reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, C.C.; Nabeta, P.; Henostroza, G.; Raqib, R.; Rahim, Z.; Gerhardt, M.; Sanga, E.; Hoelscher, M.; Notomi, T.; Hase, T.; et al. Operational feasibility of using loop-mediated isothermal amplification for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in microscopy centers of developing countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1936–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic method for infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 2009, 15, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroenram, W.; Cecere, P.; Pompa, P.P. Xylenol orange-based loop-mediated DNA isothermal amplification for sensitive naked-eye detection of Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 156, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.E.; Lim, B.; Hsu, C.-C.; Xiong, D.; Wu, W.; Yu, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Ji, M.; et al. RT-LAMP for rapid diagnosis of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaagt, F.; Haase, I.; Fischer, M. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)-based method for rapid mushroom species identification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulmawjood, A.; Grabowski, N.; Fohler, S.; Kittler, S.; Nagengast, H.; Klein, G. Development of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid and sensitive identification of ostrich meat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Hong, Y.; Kim, H.-Y. Development of a rapid on-site detection method for pork in processed meat products using real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Food Control 2016, 66, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Feng, J.; Dai, Z.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Application of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Jumbo Flying Squid Dosidicus gigas (D’Orbigny, 1835). Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yu, R.; Xiang, M.; Xia, G. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Real-time methods for the detection of the survivin gene in cancer cells. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 6277–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y. Development of a real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay and visual LAMP assay for detection of African swine fever virus (ASFV). J. Virol. Methods 2020, 276, 113775–113782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Nagamine, K.; Tomita, N.; Notomi, T. Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Honda, E.; Ogura, A.; Nomoto, A.; Hanaki, K. Colorimetric detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by using hydroxy naphthol blue. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.A.; Zhang, Y.; Evans, T.C. Visual detection of isothermal nucleic acid amplification using pH-sensitive dyes. BioTechniques 2015, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, V.M.; Lopes, A.R.; Costa, P.; Rosa, R. Cephalopods as vectors of harmful algal bloom toxins in marine food webs. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3381–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Jen, H.-C.; Jian, S.-J.; Hwang, D.-F. Toxin and species identification of toxic octopus implicated into food poisoning in Taiwan. Toxicon 2014, 91, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| F3 | 5′-ACTGTTAAATGACGATCAACTATAC-3′ |
| B3 | 5′-GGCTAAATCTACAGACGGT-3′ |
| FIP | 5′-AGCGAAGGGGGAAGTAATCAAACGGAAACTGATTAGTGCCTA-3′ |
| BIP | 5′-TCTGCTGTAGAAAGAGGAGCTGCTGCGTGAGAAAGATTTCTAGA-3′ |
| LF | 5′-CTATATCTGGCGCACCTAGTATTA-3′ |
| LB | 5′-GTACAGGATGAACAGTCTACCC-3′ |
| Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| F3-pc | 5′-TCCCTATGGTAACTATATTATAAGCA-3′ |
| B3-pc | 5′-ACAGCTGCGGTATTTTAAC-3′ |
| FIP-pc | 5′-ATTTTCATAGTGAAAAAGCTTGAATTTTTTAAAGGTCCTTAATCACCCCAATTAAAATTTATATAT-3′ |
| BIP-pc | 5′-TTTCTAAAAAATAAAATAGAGACAGATTAACCTTCGTGTACTAAGGTAGCATAATAATTTGCC-3′ |
| LF-pc | 5′-GACGAGAAGACCCTACTGAG-3′ |
| LB-pc | 5′-CAAACCATTCATTCTAGCCTCAAATTAT-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tatulli, G.; Cecere, P.; Maggioni, D.; Galimberti, A.; Pompa, P.P. A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for On-Site Authentication of Cephalopod Species. Biosensors 2020, 10, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120190
Tatulli G, Cecere P, Maggioni D, Galimberti A, Pompa PP. A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for On-Site Authentication of Cephalopod Species. Biosensors. 2020; 10(12):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120190
Chicago/Turabian StyleTatulli, Giuseppina, Paola Cecere, Davide Maggioni, Andrea Galimberti, and Pier Paolo Pompa. 2020. "A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for On-Site Authentication of Cephalopod Species" Biosensors 10, no. 12: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120190
APA StyleTatulli, G., Cecere, P., Maggioni, D., Galimberti, A., & Pompa, P. P. (2020). A Rapid Colorimetric Assay for On-Site Authentication of Cephalopod Species. Biosensors, 10(12), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10120190









