Development of a Novel SPR Assay to Study CXCR4–Ligand Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression of CXCR4 in Sf9 Cells
2.2. Membrane Preparation and Solubilization
2.3. CXCR4 Immobilization and Stability Test
2.4. Nanobody-Fc Binding to CXCR4 Using SPR
2.5. CXCR4 Virus-Like Particle Analysis Using SPR
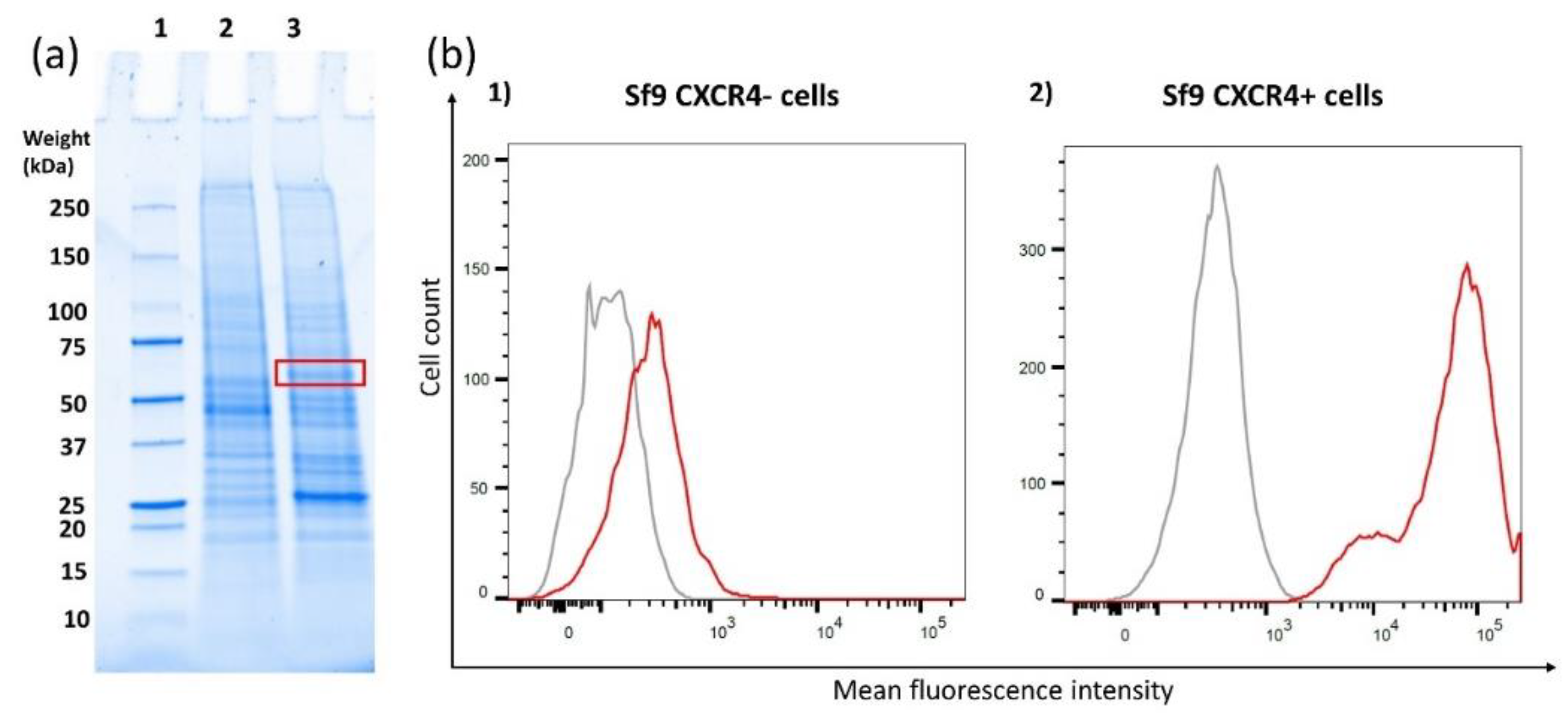
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Calcium Mobilization Assay
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CXCR4 Expression Level in Sf9-Transfected Cells
3.2. CXCR4 Immobilization
3.3. CXCR4 Functionality
3.4. CXCR4 Nb-Fc Binding Using SPR
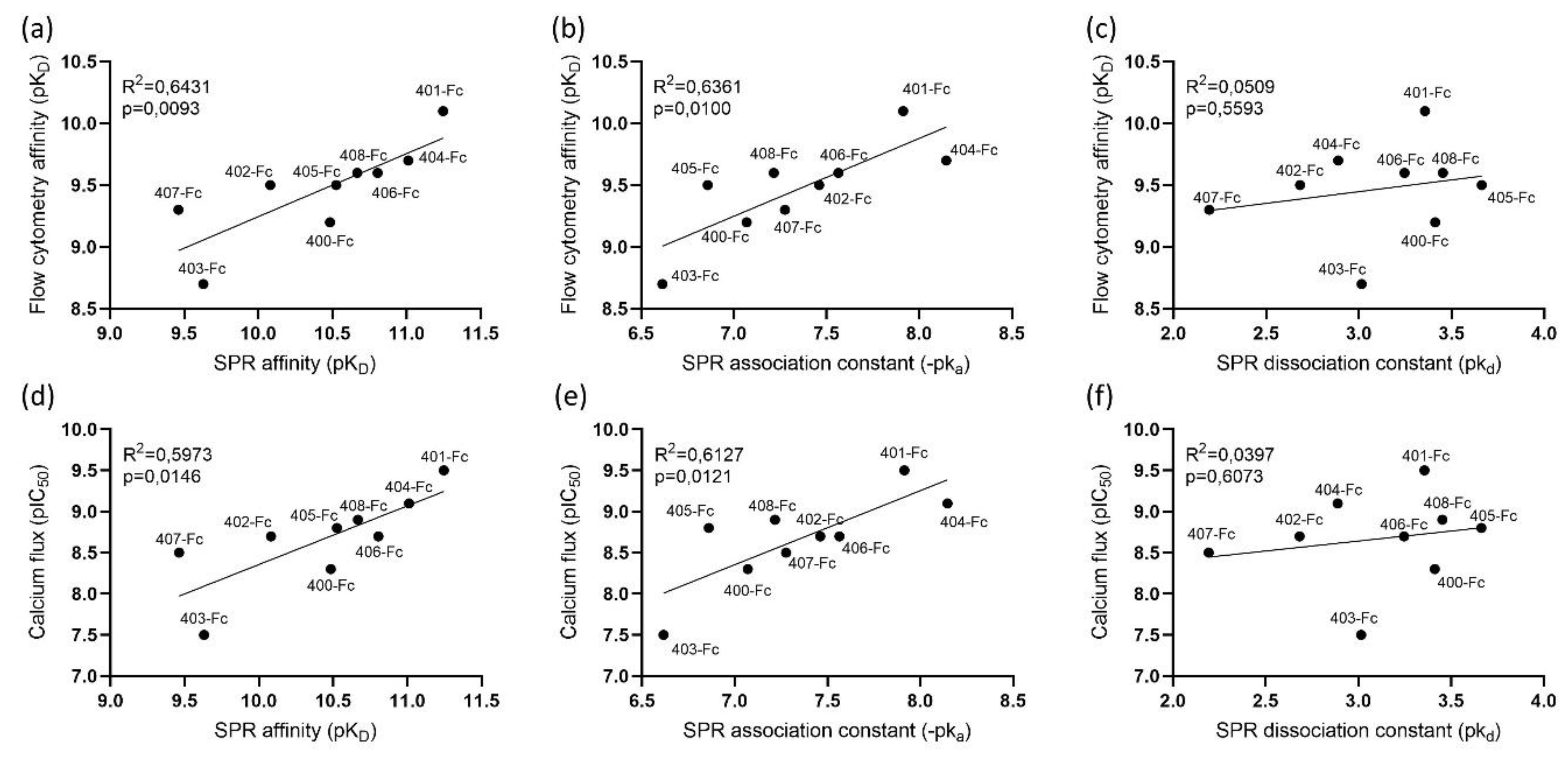
3.5. Comparison of the Monovalent and Bivalent Nanobody
3.6. Comparison of SPR Data with Cell-Based Assays
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauser, A.S.; Chavali, S.; Masuho, I.; Jahn, L.J.; Martemyanov, K.A.; Gloriam, D.E.; Babu, M.M. Pharmacogenomics of GPCR Drug Targets. Cell 2018, 172, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Pillarisetti, K. Cutting edge: CXCR4-Lo: Molecular cloning and functional expression of a novel human CXCR4 splice variant. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2368–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Sand, L.; Jochemsen, A.; Beletkaia, E.; Schmidt, T.; Hogendoorn, P.; Szuhai, K. Novel splice variants of CXCR4 identified by transcriptome sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapham, C.K.; Romantseva, T.; Petricoin, E.; King, L.R.; Manischewitz, J.; Zaitseva, M.B.; Golding, H. CXCR4 heterogeneity in primary cells: Possible role of ubiquitination. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Azad, B.B.; Nimmagadda, S. The intricate role of CXCR4 in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 124, 31–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.-R.; Kottmann, A.H.; Kuroda, M.; Taniuchi, I.; Littman, D.R. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 1998, 393, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, K.; Hirota, S.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshida, H.; Kawabata, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshida, N.; Nishikawa, S.-I. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is essential for vascularization of the gastrointestinal tract. Nature 1998, 393, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, T.; Hirota, S.; Tachibana, K.; Takakura, N.; Nishikawa, S.-I.; Kitamura, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Kikutani, H.; Kishimoto, T. Defects of B-cell lymphopoiesis and bone-marrow myelopoiesis in mice lacking the CXC chemokine PBSF/SDF-1. Nature 1996, 382, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busillo, J.M.; Benovic, J.L. Regulation of CXCR4 signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, C.J.; Koglin, M.; Marshall, F.H. Therapeutic antibodies directed at G protein-coupled receptors. MAbs 2010, 2, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Rosensweig, C.J.; Faden, L.B.; Dewitz, M.C. Monoclonal antibody successes in the clinic. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jähnichen, S.; Blanchetot, C.; Maussang, D.; Gonzalez-Pajuelo, M.; Chow, K.Y.; Bosch, L.; De Vrieze, S.; Serruys, B.; Ulrichts, H.; Vandevelde, W.; et al. CXCR4 nanobodies (VHH-based single variable domains) potently inhibit chemotaxis and HIV-1 replication and mobilize stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hout, A.; Klarenbeek, A.; Bobkov, V.; Doijen, J.; Arimont, M.; Zhao, C.; Heukers, R.; Rimkunas, R.; de Graaf, C.; Verrips, T.; et al. CXCR4-targeting nanobodies differentially inhibit CXCR4 function and HIV entry. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobkov, V.; Zarca, A.M.; Van Hout, A.; Arimont, M.; Doijen, J.; Bialkowska, M.; Toffoli, E.; Klarenbeek, A.; van der Woning, B.; van der Vliet, H.J.; et al. Nanobody-Fc constructs targeting chemokine receptor CXCR4 potently inhibit signaling and CXCR4-mediated HIV-entry and induce antibody effector functions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, W.; Frazer, J.; Unett, D. Functional assays for screening GPCR targets. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.N. Surfactants in membrane solubilisation. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 177, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homola, J.; Piliarik, M. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensors. In Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors; Homola, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 4, pp. 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttenrauch, F.; Nitzki, A.; Lin, F.T.; Höning, S.; Oppermann, M. β-arrestin binding to CC chemokine receptor 5 requires multiple C-terminal receptor phosphorylation sites and involves a conserved Asp-Arg-Tyr sequence motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30769–30777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, E.G.; Persuh, M.; Thompson, D.A.D.; Lin, S.W.; Sakmar, T.P.; Olson, W.C.; Dragic, T. Specific interaction of CCR5 amino-terminal domain peptides containing sulfotyrosines with HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Möbius, K.; Haußner, C.; Donhauser, N.; Schmidt, B.; Eichler, J. Mimicking Protein–Protein Interactions through Peptide–Peptide Interactions: HIV-1 gp120 and CXCR4. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, Z.; Wang, Y.; Soulages, J.L.; Brown, M.F.; Tollin, G. Surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy studies of membrane proteins: Transducin binding and activation by rhodopsin monitored in thin membrane films. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, P.J.; Hadingham, T.C.; McDonnell, J.M.; Watts, A. Direct analysis of a GPCR-agonist interaction by surface plasmon resonance. Eur. Biophys. J. 2006, 35, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, R.; Reczek, D.; Brondyk, W. Capture-stabilize approach for membrane protein SPR assays. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofuku, Y.; Yoshiura, C.; Ueda, T.; Terasawa, H.; Hirai, T.; Tominaga, S.; Hirose, M.; Maeda, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Terashima, Y.; et al. Structural basis of the interaction between chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12 and its G-protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35240–35250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navratilova, I.; Dioszegi, M.; Myszka, D.G. Analyzing ligand and small molecule binding activity of solubilized GPCRs using biosensor technology. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 355, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, B.; Calle, A.; Sánchez, A.; Lechuga, L.M.; Ortiz, A.M.; Armelles, G.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M. Real-time detection of the chemokine CXCL12 in urine samples by surface plasmon resonance. Talanta 2013, 109, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navratilova, I.; Besnard, J.; Hopkins, A.L. Screening for GPCR Ligands Using Surface Plasmon Resonance. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Muñoz, L.; Barroso, R.; Paredes, A.G.; Mellado, M.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M. Methods to Immobilize GPCR on the Surface of SPR Sensors. In G Protein-Coupled Receptor Screening Assays: Methods and Protocols; Prazeres, D.M.F., Martins, S.A.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, B.; Muñoz, L.M.; Holgado, B.L.; Lucas, P.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Calle, A.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J.L.; Lechuga, L.M.; Rodríguez, J.F.; Gutiérrez-Gallego, R.; et al. Technical Advance: Surface plasmon resonance-based analysis of CXCL12 binding using immobilized lentiviral particles. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Dolezal, O.; Cao, B.; Nilsson, S.K.; See, H.B.; Pfleger, K.D.; Roche, M.; Gorry, P.R.; Pow, A.; Viduka, K.; et al. i-bodies, Human Single Domain Antibodies That Antagonize Chemokine Receptor CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 12641–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navratilova, I.H.; Aristotelous, T.; Bird, L.E.; Hopkins, A.L. Surveying GPCR solubilisation conditions using surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 556, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Partridge, A.; Wu, Y. Improving nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance detection of small molecules by reducing steric hindrance via molecular linkers. Talanta 2019, 198, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Chien, E.Y.T.; Mol, C.D.; Fenalti, G.; Liu, W.; Katritch, V.; Abagyan, R.; Brooun, A.; Wells, P.; Bi, F.C.; et al. Structures of the CXCR4 Chemokine GPCR with Small-Molecule and Cyclic Peptide Antagonists. Science 2010, 330, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navratilova, I.; Sodroski, J.; Myszka, D.G. Solubilization, stabilization, and purification of chemokine receptors using biosensor technology. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 339, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornhorst, J.A.; Falke, J.J. Purification of proteins using polyhistidine affinity tags. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 326, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, S.; Ricklin, D.; Eberle, A.N.; Ernst, B. Oligohis-tags: Mechanisms of binding to Ni2+-NTA surfaces. J. Mol. Recognit. 2009, 22, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Farzan, M.; Sodroski, J. Ligand-independent dimerization of CXCR4, a principal HIV-1 coreceptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3378–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Affinity KD (pM) | Association Rate Constant ka (106) (M−1·s−1) | Dissociation Rate Constant kd (10−4) (s−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VUN400-Fc | 33.57 ± 7.37 | 11.7 ± 1.16 | 3.87 ± 0.53 |
| VUN401-Fc | 5.72 ± 0.80 | 82.03 ± 34.80 | 4.41 ± 1.33 |
| VUN402-Fc | 87.97 ± 26.84 | 28.87 ± 17.43 | 20.73 ± 6.74 |
| VUN403-Fc | 236.33 ± 26.89 | 4.12 ± 0.47 | 9.66 ± 1.12 |
| VUN404-Fc | 9.82 ± 1.41 | 139.83 ± 74.57 | 12.92 ± 5.22 |
| VUN405-Fc | 30.27 ± 5.52 | 7.23 ± 0.73 | 2.17 ± 0.35 |
| VUN406-Fc | 16.03 ± 3.51 | 36.67 ± 11.69 | 5.68 ± 1.34 |
| VUN407-Fc | 353.67 ± 80.18 | 18.87 ± 4.21 | 64.23 ± 8.67 |
| VUN408-Fc | 21.70 ± 2.63 | 16.47 ± 2.15 | 3.53 ± 0.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boonen, A.; Singh, A.K.; Hout, A.V.; Das, K.; Loy, T.V.; Noppen, S.; Schols, D. Development of a Novel SPR Assay to Study CXCR4–Ligand Interactions. Biosensors 2020, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100150
Boonen A, Singh AK, Hout AV, Das K, Loy TV, Noppen S, Schols D. Development of a Novel SPR Assay to Study CXCR4–Ligand Interactions. Biosensors. 2020; 10(10):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100150
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoonen, Arnaud, Abhimanyu K. Singh, Anneleen Van Hout, Kalyan Das, Tom Van Loy, Sam Noppen, and Dominique Schols. 2020. "Development of a Novel SPR Assay to Study CXCR4–Ligand Interactions" Biosensors 10, no. 10: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100150
APA StyleBoonen, A., Singh, A. K., Hout, A. V., Das, K., Loy, T. V., Noppen, S., & Schols, D. (2020). Development of a Novel SPR Assay to Study CXCR4–Ligand Interactions. Biosensors, 10(10), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100150






