Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
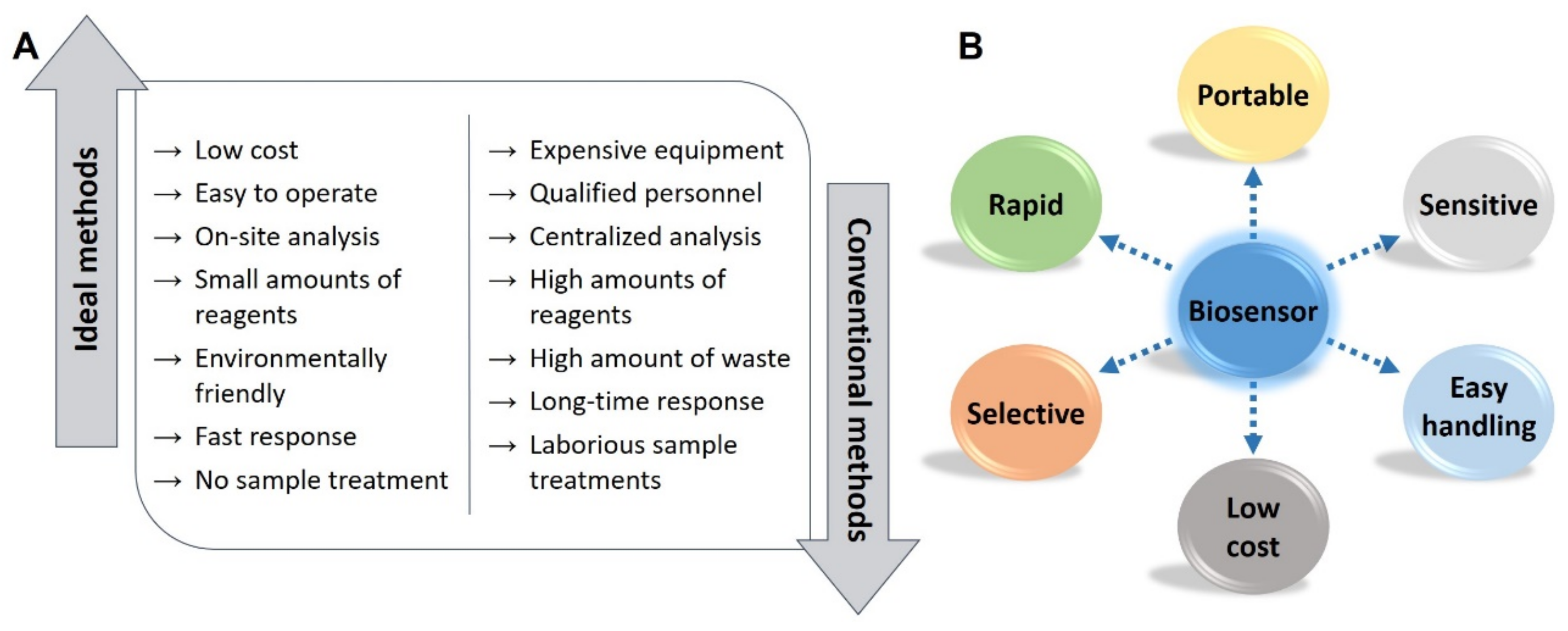
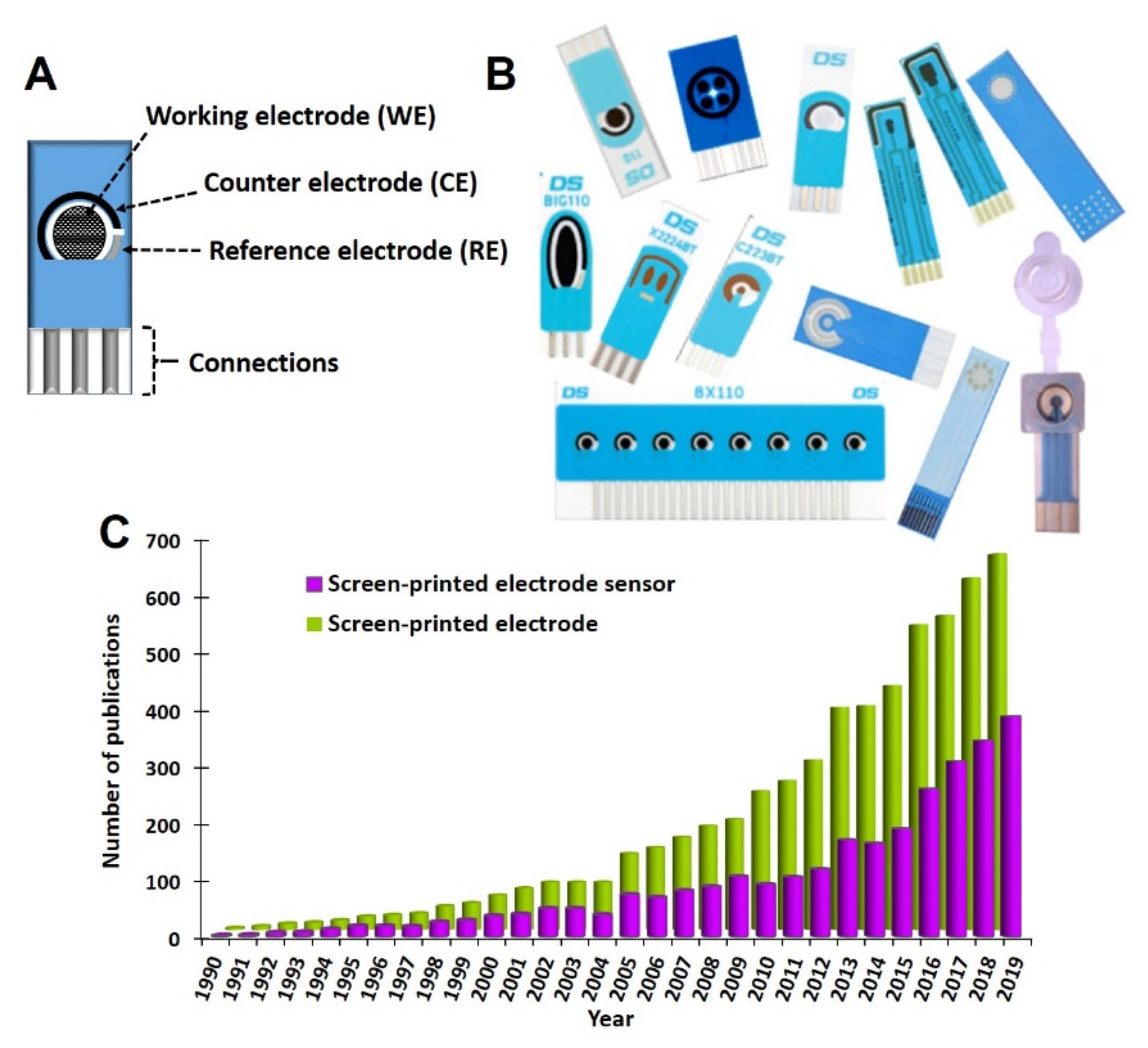
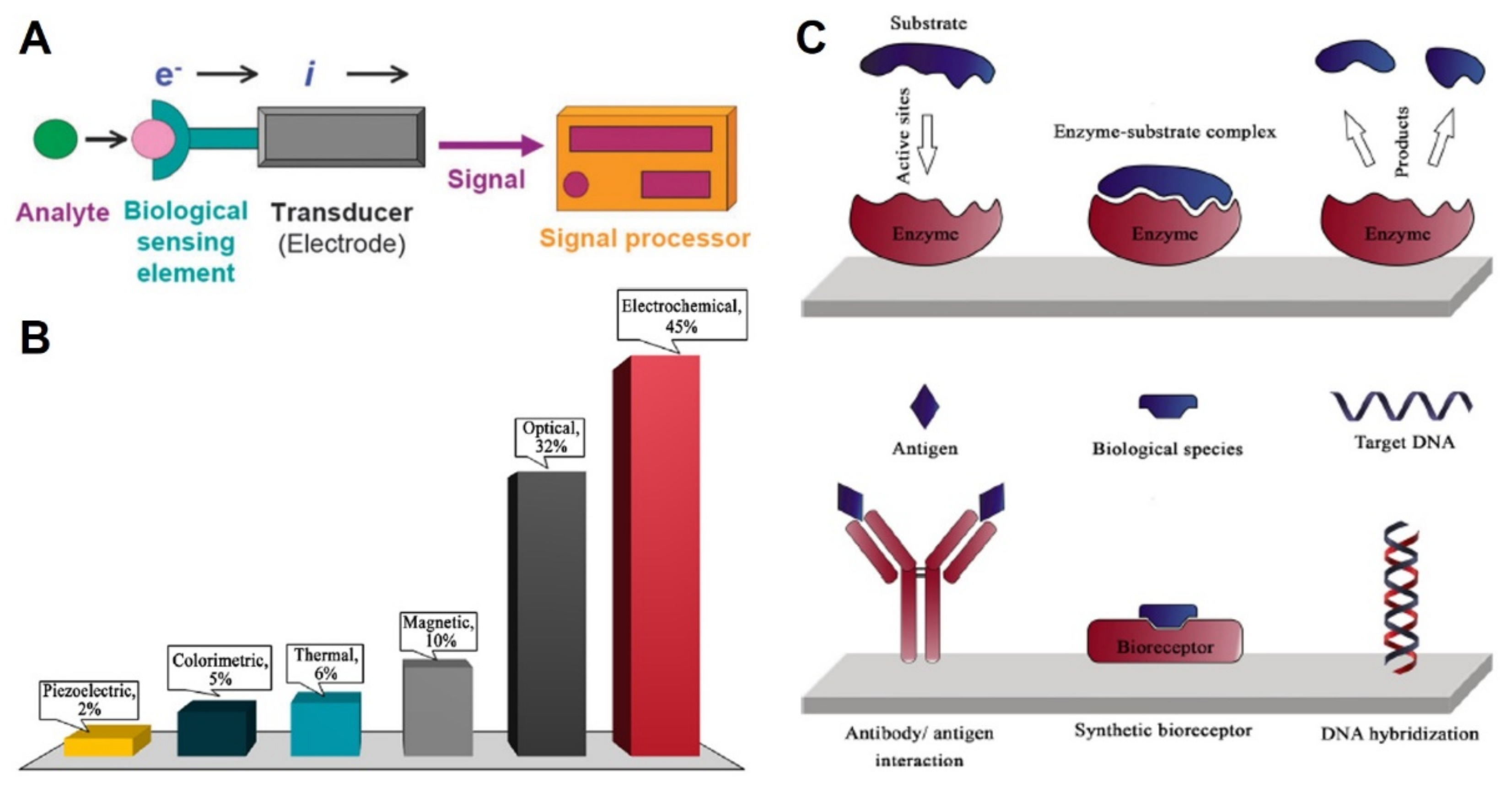
2. Screen-Printed Electrodes as Transducers
2.1. Production and Design of Screen-Printed Electrodes
2.2. (Bio)Sensors Based on SPEs
3. Parameters Related to Food Spoilage
3.1. Bacteria
3.2. Biogenic Amines
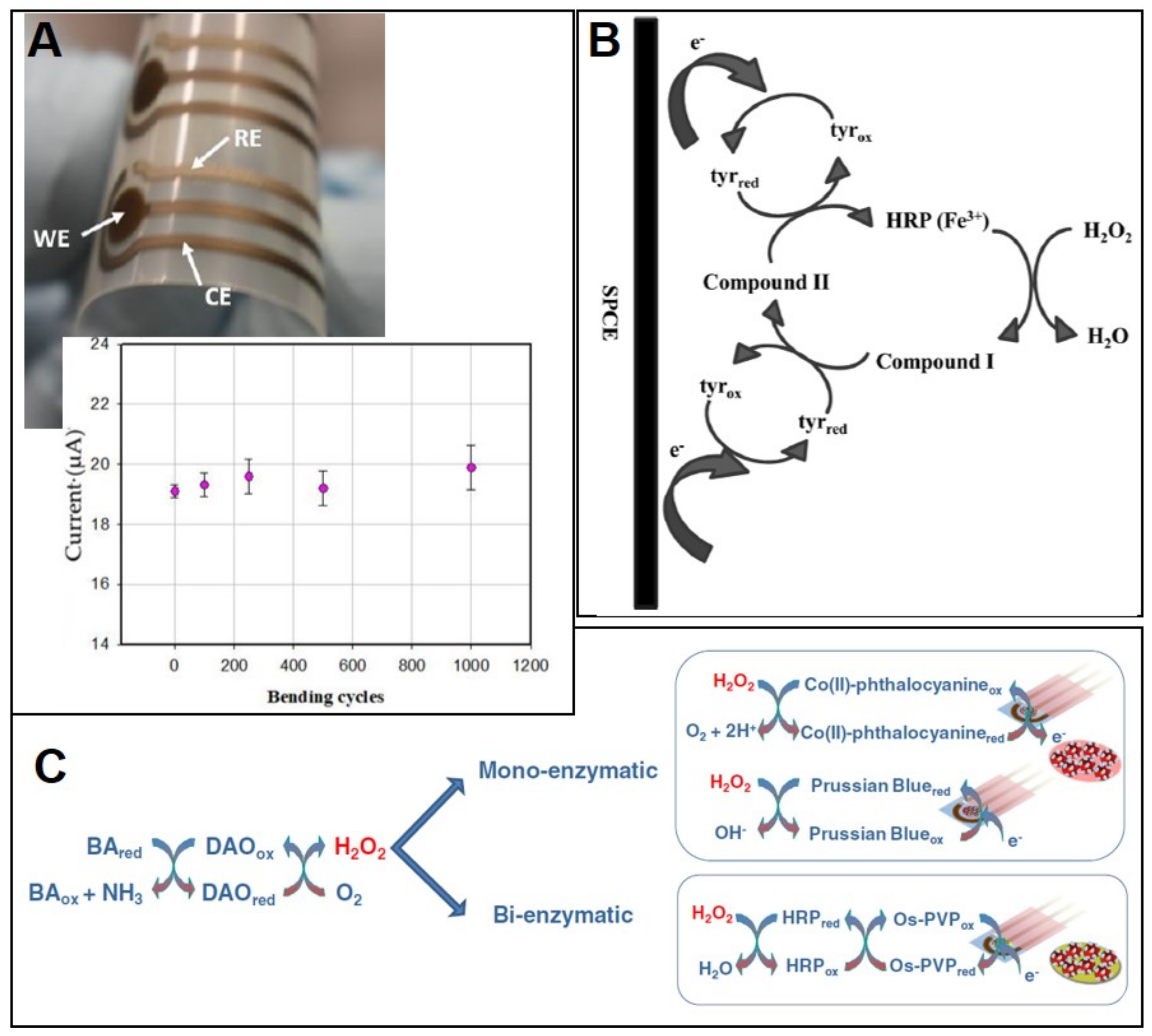
4. SPE-Based (Bio)Sensors for the Determination of Food Spoilage Parameters
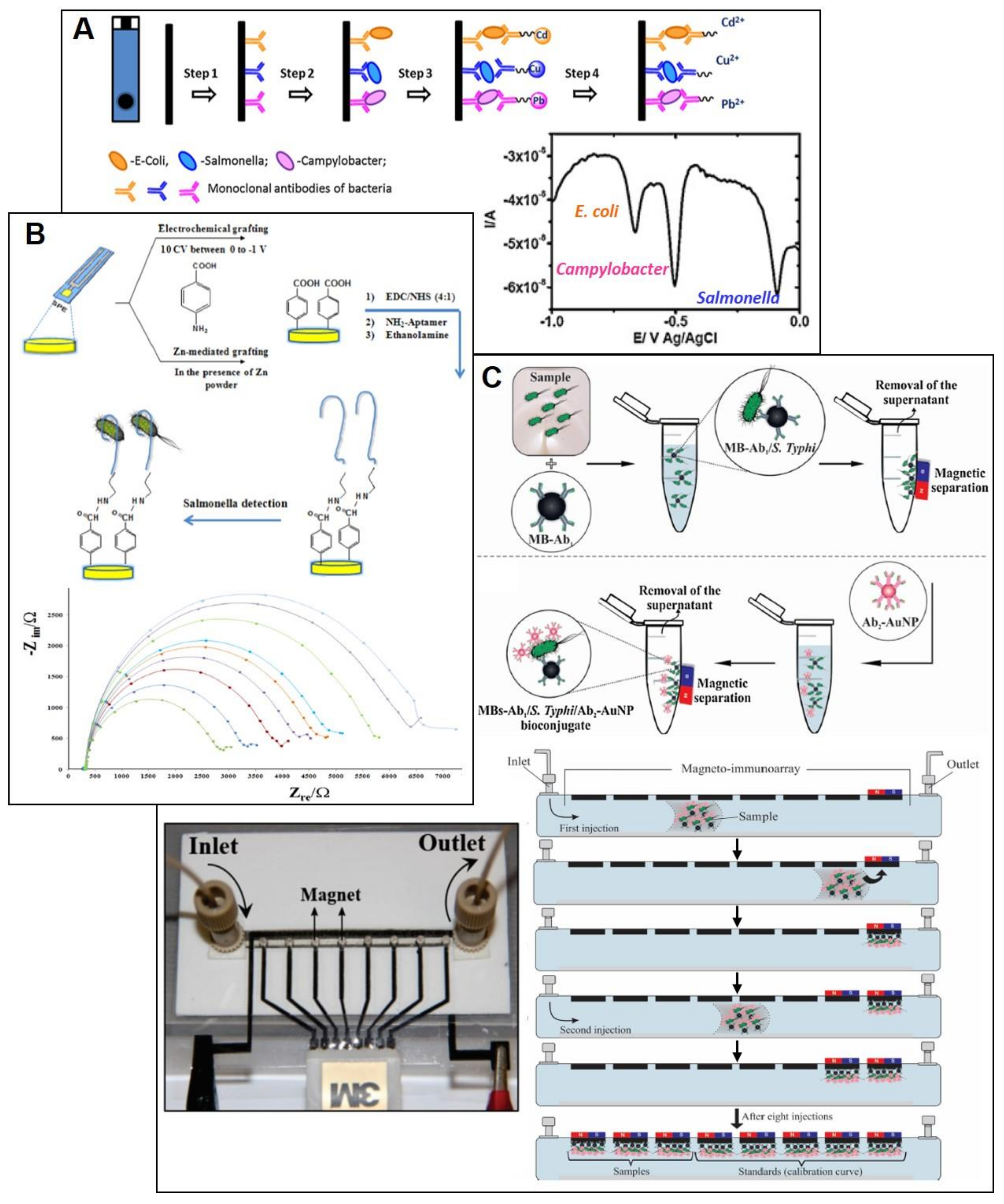
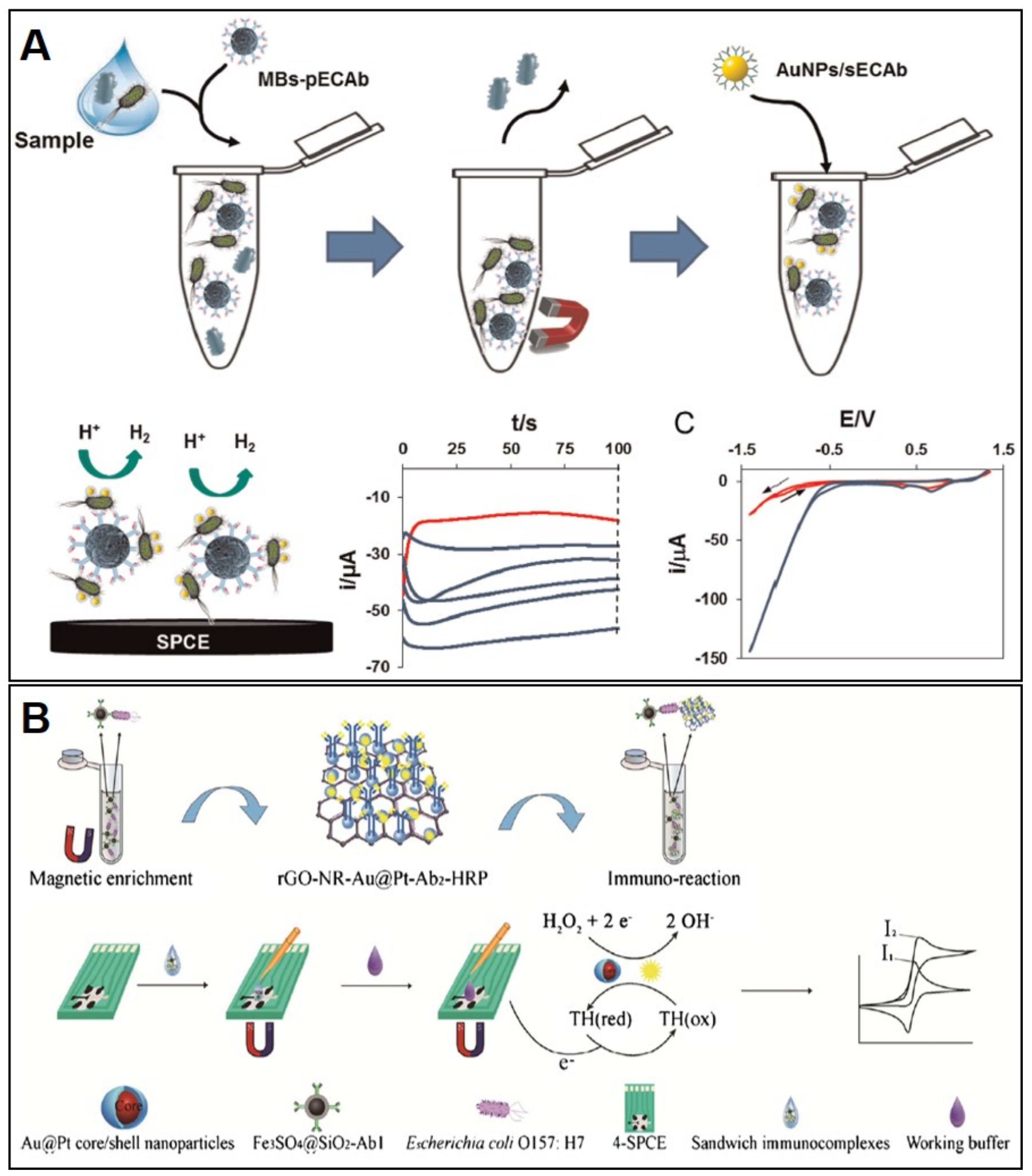
4.1. SPE-Based (Bio)Sensors for Bacteria Detection
4.2. SPE-Based (Bio)Sensors for Biogenic Amines Detection
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/food-safety (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Den Besten, H.M.W.; Wells-Bennik, M.H.J.; Zwietering, M.H. Natural Diversity in Heat Resistance of Bacteria and Bacterial Spores: Impact on Food Safety and Quality. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.; Al-Khaldi, S.; Assimon, S.A.; Beuadry, C.; Benner, R.A.; Bennett, R.; Binet, R.; Cahill, S.M.; Burkhardt, W., III. Bad Bud Book. In Handbook of Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Introduction, 2nd ed.; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780323401814. [Google Scholar]
- Naila, A.; Flint, S.; Fletcher, G.; Bremer, P.; Meerdink, G. Control of biogenic amines in food—Existing and emerging approaches. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R139–R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H. Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). BIOHAZ Scientific Opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biji, K.B.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Mohan, C.O.; Gopal, T.K.S. Biogenic amines in seafood: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairath, G.; Singh, P.K.; Dabur, R.S.; Rani, M.; Chaudhari, M. Biogenic amines in meat and meat products and its public health significance: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6835–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, M.; Lambropoulou, D.; Morrison, C.; Kłodzińska, E.; Namieśnik, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Literature update of analytical methods for biogenic amines determination in food and beverages. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köse, S.; Kaklikkaya, N.; Koral, S.; Tufan, B.; Buruk, K.C.; Aydin, F. Commercial test kits and the determination of histamine in traditional (ethnic) fish products-evaluation against an EU accepted HPLC method. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Nunes, G.S.; Souto, L.; Marty, J.L. Screen printed technology—An application towards biosensor development. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 487–498. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, A.; Crew, A.; Pemberton, R.; Hughes, G.; Doran, O.; Hart, J.P. Screen-printed carbon based biosensors and their applications in agri-food safety. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 127, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, A.; Nunes, G.; Hayat, A.; Latif, U.; Marty, J.L. Electrochemical affinity biosensors based on disposable screen-printed electrodes for detection of food allergens. Sensors 2016, 16, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Cruz, J.M.; Serrano, N.; Pérez-Ràfols, C.; Ariño, C.; Esteban, M. Electroanalysis from the past to the twenty-first century: Challenges and perspectives. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, G.; Age, S.; Simon, S. History’s Influence on Screen Printing’s Future Explore How Screenprinting’s Past Will Shape Its Future. Screen Print. February 2006. Available online: https://www.screenweb.com/content/historys-influence-screen-printings-future (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Couto, R.A.S.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Quinaz, M.B. Recent developments, characteristics and potential applications of screen-printed electrodes in pharmaceutical and biological analysis. Talanta 2016, 146, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Micheli, L.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Piermarini, S.; Ricci, F.; Volpe, G. Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: Recent applications in clinical analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rama, E.C.; Costa-García, A. Screen-printed Electrochemical Immunosensors for the Detection of Cancer and Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1700–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.T.; Li, D.W.; Long, Y.T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Disposable screen printed electrochemical sensors: Tools for environmental monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 10432–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cano-Raya, C.; Denchev, Z.Z.; Cruz, S.F.; Viana, J.C. Chemistry of solid metal-based inks and pastes for printed electronics–A review. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical (bio)sensors: Promising tools for green analytical chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, A.; Jalali, M.; Raeissi, K.; Karimzadeh, F.; Kharaziha, M.; Mahshid, S.S.; Mahshid, S. A review on recent advancements in electrochemical biosensing using carbonaceous nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metrohm DropSens. Available online: http://www.dropsens.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Micrux Technologies. Available online: http://www.micruxfluidic.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Pine Research. Available online: https://pineresearch.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Gwent Group. Available online: http://www.gwent.org/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- PalmSens. Available online: https://www.palmsens.com/ (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Rusens. Available online: http://www.rusens.com/indexeng.html (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Putzbach, W.; Ronkainen, N.J. Immobilization techniques in the fabrication of nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Sensors (Basel) 2013, 13, 4811–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antuña-Jiménez, D.; González-García, M.B.; Hernández-Santos, D.; Fanjul-Bolado, P. Screen-printed electrodes modified with metal nanoparticles for small molecule sensing. Biosensors 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffy, G.F.; Moore, E.J. Electrochemical Immunosensors for Food Analysis: A Review of Recent Developments. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Parkhomovsky, S.; Wang, J. Stamp transfer electrodes for electrochemical sensing on non-planar and oversized surfaces. Analyst 2012, 137, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Hubble, L.J.; Martín, A.; Kumar, R.; Barfidokht, A.; Kim, J.; Musameh, M.M.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Wang, J. Wearable flexible and stretchable glove biosensor for on-site detection of organophosphorus chemical threats. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, C.; Marquette, C.A.; Blum, L.J.; Doumèche, B. Paper electrodes for bioelectrochemistry: Biosensors and biofuel cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, G.; Bottari, F.; Van Loon, J.; Du Bois, E.; De Wael, K.; Moretto, L.M. Disposable electrodes from waste materials and renewable sources for (bio)electroanalytical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.M.P.S.; González-García, M.B.; Hernández-Santos, D.; Fanjul-Bolado, P. Screen-Printed Electrochemical 96-Well Plate: A High-Throughput Platform for Multiple Analytical Applications. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2764–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermarini, S.; Micheli, L.; Ammida, N.H.S.; Palleschi, G.; Moscone, D. Electrochemical immunosensor array using a 96-well screen-printed microplate for aflatoxin B1 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification1International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Physical Chemistry Division, Commission I.7 (Biophysical Chemistry); Analytical Chemistry Division, Commission V.5 (Electroanalytical). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Mutharasan, R. Review of biosensors for foodborne pathogens and toxins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 183, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Immobilization strategies to develop enzymatic biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent advances in electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymer sensing platforms for bioanalyte detection. Sensors (Switzerland) 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tudorache, M.; Bala, C. Biosensors based on screen-printing technology, and their applications in environmental and food analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Adornetto, G.; Palleschi, G. A review of experimental aspects of electrochemical immunosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesewski, E.; Johnson, B.N. Electrochemical biosensors for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duncan, T.V. Nanoscale sensors for assuring the safety of food products. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Neves, M.M.P.S.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Emerging electrochemical biosensing approaches for detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food samples: An overview. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical biosensors for Salmonella: State of the art and challenges in food safety assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.-H.; Yang, W.-Z.; Feng, X.-S. A review of pretreatment and analytical methods of biogenic amines in food and biological samples since 2010. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1605, 360361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A comprehensive review on freshness of fish and assessment: Analytical methods and recent innovations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/salmonella-most-common-cause-foodborne-outbreaks-european-union (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). ECDC The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2015. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D.J. Campylobacter virulence and survival factors. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. As a foodborne pathogen: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabiani, L.; Delibato, E.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; De Medici, D.; Palleschi, G. Development of a sandwich ELIME assay exploiting different antibody combinations as sensing strategy for an early detection of Campylobacter. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allocati, N.; Masulli, M.; Alexeyev, M.F.; Di Ilio, C. Escherichia coli in Europe: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 6235–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, S.K.; Pusparajah, P.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Ser, H.L.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandre, D.L.; Melo, A.M.A.; Furtado, R.F.; Borges, M.F.; Figueiredo, E.A.T.; Biswas, A.; Cheng, H.N.; Alves, C.R. A Rapid and Specific Biosensor for Salmonella Typhimurium Detection in Milk. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; Delibato, E.; Palleschi, G. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of foodborne Salmonella: A critical overview. Sensors (Switzerland) 2017, 17, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, R.L.; Gorris, L.G.M.; Hayman, M.M.; Jackson, T.C.; Whiting, R.C. A review of Listeria monocytogenes: An update on outbreaks, virulence, dose-response, ecology, and risk assessments. Food Control 2017, 75, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.A.; De Vries, E.G.E.; Kema, I.P. Current status and future developments of LC-MS/MS in clinical chemistry for quantification of biogenic amines. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Mohammed, G.I.; Al-Eryani, D.A.; Saigl, Z.M.; Alyoubi, A.O.; Alwael, H.; Bashammakh, A.S.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; El-Shahawi, M.S. Biogenic Amines Formation Mechanism and Determination Strategies: Future Challenges and Limitations. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 0, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.L.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.D.C.; Callejón, R.M. Recent trends in the determination of biogenic amines in fermented beverages—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Viswanathan, S.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Iron oxide/gold core/shell nanomagnetic probes and CdS biolabels for amplified electrochemical immunosensing of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afonso, A.S.; Pérez-López, B.; Faria, R.C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Hernández-Herrero, M.; Roig-Sagués, A.X.; Maltez-da Costa, M.; Merkoçi, A. Electrochemical detection of Salmonella using gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dou, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Enzyme-functionalized electrochemical immunosensor based on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide and polyvinyl alcohol-polydimethylsiloxane for the detection of Salmonella pullorum & Salmonella gallinarum. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57733–57742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Dou, W.; Zhao, G. A sandwich electrochemical immunosensor for Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum based on a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with an ionic liquid and electrodeposited gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutreja, R.; Jariyal, M.; Pathania, P.; Sharma, A.; Sahoo, D.K.; Suri, C.R. Novel surface antigen based impedimetric immunosensor for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in water and juice samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheryan, Z.; Raoof, J.B.; Golabi, M.; Turner, A.P.F.; Beni, V. Diazonium-based impedimetric aptasensor for the rapid label-free detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ngoensawat, U.; Rijiravanich, P.; Surareungchai, W.; Somasundrum, M. Electrochemical Immunoassay for Salmonella Typhimurium Based on an Immuno-magnetic Redox Label. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, T.R.; Martucci, D.H.; Faria, R.C. Simple disposable microfluidic device for Salmonella typhimurium detection by magneto-immunoassay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonsawat, W.; Limvongjaroen, S.; Supromma, S.; Panphut, W.; Ruecha, N.; Ratnarathorn, N.; Dungchai, W. A paper-based conductive immunosensor for the determination of Salmonella Typhimurium. Analyst 2020, 145, 4637–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murasova, P.; Kovarova, A.; Kasparova, J.; Brozkova, I.; Hamiot, A.; Pekarkova, J.; Dupuy, B.; Drbohlavova, J.; Bilkova, Z.; Korecka, L. Direct culture-free electrochemical detection of Salmonella cells in milk based on quantum dots-modified nanostructured dendrons. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 863, 114051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Rani, C.; Ho, J.A.H.A. Electrochemical immunosensor for multiplexed detection of food-borne pathogens using nanocrystal bioconjugates and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2012, 94, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Pastucha, M.; Kovář, D.; Lacina, K.; Skládal, P. Rapid Immunosensing of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: The Effect of Sample Treatment. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibato, E.; Volpe, G.; Stangalini, D.; De Medici, D.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Development of SYBR-green real-time PCR and a multichannel electrochemical immunosensor for specific detection of Salmonella enterica. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratiwi, F.W.; Rijiravanich, P.; Somasundrum, M.; Surareungchai, W. Electrochemical immunoassay for Salmonella Typhimurium based on magnetically collected Ag-enhanced DNA biobarcode labels. Analyst 2013, 138, 5011–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, F.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium in foods using an electrochemical immunosensor based on screen-printed interdigitated microelectrode and immunomagnetic separation. Talanta 2016, 148, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Materón, E.M.; Ibáñez-Redín, G.; Faria, R.C.; Correa, D.S.; Oliveira, O.N. Electrical detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples using information visualization methods with a sensor based on magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with antimicrobial peptides. Talanta 2019, 194, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, J.; Dou, W.; Zhao, G. A sandwich electrochemical immunoassay for Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum based on a AuNPs/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbing antibody and 4 channel screen printed carbon electrode electrodeposited gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74548–74556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, Q.; Huo, H.; Bai, S.; Cai, G.; Lai, W.; Lin, J. Efficient separation and quantitative detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on screen-printed interdigitated electrode, urease and magnetic nanoparticles. Food Control 2017, 73, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolba, M.; Ahmed, M.U.; Tlili, C.; Eichenseher, F.; Loessner, M.J.; Zourob, M. A bacteriophage endolysin-based electrochemical impedance biosensor for the rapid detection of Listeria cells. Analyst 2012, 137, 5749–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Shen, T.Y.; Chang, C.A.; Lin, C.S. Disposable amperometric immunosensing strips fabricated by Au nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of foodborne pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.R.H.A.A.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Merkoçi, A. Highly sensitive and rapid determination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in minced beef and water using electrocatalytic gold nanoparticle tags. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. A sensitive and regenerative electrochemical immunosensor for quantitative detection of: Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on stable polyaniline coated screen-printed carbon electrode and rGO-NR-Au@Pt. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. A non-enzymatic electrochemical immunoassay for quantitative detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using Au@Pt and graphene. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 559, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. Electrochemical sandwich immunoassay for Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles and graphene functionalized with electrocatalytically active Au@Pt core/shell nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. A Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Modified with AuNPs for Quantitative Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 7960–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. Electropolymerization of Stable Leucoemeraldine Base Polyaniline Film and Application for Quantitative Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 6507–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimafonte, M.; Fulgione, A.; Gaglione, R.; Papaianni, M.; Capparelli, R.; Arciello, A.; Censi, S.B.; Borriello, G.; Velotta, R.; Ventura, B. Della Screen printed based impedimetric immunosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli in drinking water. Sensors 2020, 20, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Lum, J.; Callaway, Z.; Lin, J.; Bottje, W.; Li, Y. A label-free impedance immunosensor using screen-printed interdigitated electrodes and magnetic nanobeads for the detection of E. coli O157:H7. Biosensors 2015, 5, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. An electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of: E. coli O157:H7 with highly efficient bi-functional glucose oxidase-polydopamine nanocomposites and Prussian blue modified screen-printed interdigitated electrodes. Analyst 2016, 141, 5441–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shkodra, B.; Abera, B.D.; Cantarella, G.; Douaki, A.; Avancini, E.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Flexible and printed electrochemical immunosensor coated with oxygen plasma treated SWCNTs for histamine detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.X.; Yang, J.Y.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Mao, C.; Sun, Y.M.; Lei, H.T.; Shen, Y.D.; Beier, R.C.; Xu, Z.L. Portable amperometric immunosensor for histamine detection using Prussian blue-chitosan-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite films. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veseli, A.; Vasjari, M.; Arbneshi, T.; Hajrizi, A.; Švorc, L.; Samphao, A.; Kalcher, K. Electrochemical determination of histamine in fish sauce using heterogeneous carbon electrodes modified with rhenium(IV) oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Sari, M.I.; Hsieh, Y. A disposable non-enzymatic histamine sensor based on the nafion-coated copper phosphate electrodes for estimation of fish freshness. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 283, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Lopes, P.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Amperometric enzyme sensor for the rapid determination of histamine. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, R.; Costa-rama, E.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Diamine oxidase-modified screen-printed electrode for the redox-mediated determination of histamine. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 3, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.; Bartrolí, J.; Fàbregas, E. Amperometric biosensor for the determination of histamine in fish samples. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Apetrei, C. Amperometric biosensor based on diamine oxidase/platinum nanoparticles/graphene/chitosan modified screen-printed carbon electrode for histamine detection. Sensors 2016, 16, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. A screen-printed disposable biosensor for selective determination of putrescine. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Cascalheira, J.F.; Dias-Cabral, A.C.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Characterization of a Disposable Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Putrescine Oxidase from Micrococcus rubens for the Determination of Putrescine. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, P.E.; Erdoğan, Z.Ö.; Öztürk, F.; Koçoğlu, İ.O.; Kılıç, E. Amperometric Biosensors for Tyramine Determination Based on Graphene Oxide and Polyvinylferrocene Modified Screen-printed Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Apetrei, C. The biocomposite screen-printed biosensor based on immobilization of tyrosinase onto the carboxyl functionalised carbon nanotube for assaying tyramine in fish products. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lai, C.-W.; Chang, Y.-F.; Chan, H.-Y.; Tsai, C.-F.; Ho, J.A.; Wu, L. Tyramine detection using PEDOT:PSS/AuNPs/1-methyl-4-mercaptopyridine modified screen-printed carbon electrode with molecularly imprinted polymer solid phase extraction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkıran, B.; Erden, P.E.; Kaçar, C.; Kılıç, E. Disposable Amperometric Biosensor Based on Poly-L-lysine and Fe3O4 NPs-chitosan Composite for the Detection of Tyramine in Cheese. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Pérez, A.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Disposable amperometric biosensor for the determination of tyramine using plasma amino oxidase. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Pérez, A.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Disposable Horseradish Peroxidase Biosensors for the Selective Determination of Tyramine. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, C.; Erden, P.E.; Dalkiran, B.; İnal, E.K.; Kiliç, E. Amperometric biogenic amine biosensors based on Prussian blue, indium tin oxide nanoparticles and diamine oxidase—Or monoamine oxidase–modified electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; Román, L.D.T.-D.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Dual enzymatic biosensor for simultaneous amperometric determination of histamine and putrescine. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Asunción Alonso-Lomillo, M.; Julia Arcos-Martínez, M. Simultaneous determination of cadaverine and putrescine using a disposable monoamine oxidase based biosensor. Talanta 2013, 117, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Campàs, M. Electrochemical enzyme sensor arrays for the detection of the biogenic amines histamine, putrescine and cadaverine using magnetic beads as immobilisation supports. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Matos, P.; Arcos-Martínez, M.J. Disposable biosensors for determination of biogenic amines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 665, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fusco, M.; Federico, R.; Boffi, A.; MacOne, A.; Favero, G.; Mazzei, F. Characterization and application of a diamine oxidase from Lathyrus sativus as component of an electrochemical biosensor for the determination of biogenic amines in wine and beer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telsnig, D.; Kalcher, K.; Leitner, A.; Ortner, A. Design of an Amperometric Biosensor for the Determination of Biogenic Amines Using Screen Printed Carbon Working Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.; Wittmann, C. Enzyme sensor array for the determination of biogenic amines in food samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 372, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classification | Name | Molecular Formula | Structure | Molecular Weight (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterocyclic | Histamine (HIS) | C5H9N3 |  | 111.15 |
| Tryptamine (TRYP) | C10H12N2 |  | 160.21 | |
| Aromatic | Phenylethylamine (PHEN) | C8H11N |  | 121.18 |
| Tyramine (TYR) | C8H11NO | 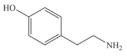 | 137.18 | |
| Aliphatic | Spermidine (SPD) | C10H26N4 |  | 145.25 |
| Spermine (SPM) | C7H19N3 | 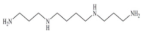 | 202.34 | |
| Cadaverine (CAD) | C5H14N2 | 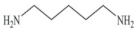 | 102.18 | |
| Putrescine (PUT) | C4H12N2 | 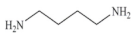 | 88.15 |
| Serotype | Sensor Construction | Detect. Tech. | Conc. Range | LOD | Analysis Time | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmonella Pullorum and Salmonella Gallinarum | Immunoassay; HRP as indirect label; ERGO/PVA-PDMS/SPCE | CV | 10–109 CFU/mL | 1.61 CFU/mL | ≈31 min | Chicken, eggs | [70] |
| Salmonella Pullorum and Salmonella Gallinarum | Immunoassay (sandwich); HRP as label; IL/Ab/AuNP/SPCE | CV | 104–109 CFU/mL | 3 × 103 CFU/mL | ≈81 min | Chicken, eggs | [71] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); Ab-coated MB; Ag measurement; Avidin-SPCE | DPASV | 10–106 CFU/mL | 12.6 CFU/mL | ≈105 min | Milk, green bean sprouts, eggs | [81] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay; Au-coated MB/SAM/Ab; CdSNP as label; SPCE | SWASV | 10–106 cell/mL | 13 cells/mL | ≈40 min | Milk | [68] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); Ab on MB-MWCNT-Methylene Blue (which is the label); Avidin-SPCE | DPV | 10–106 CFU/mL in buffer and milk | 7.9 CFU/mL in buffer; 17.3 CFU/mL in milk | ≈55 min | Milk | [74] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on MB; AuNP as label; SPCE | DPV | 103–106 cell/mL | 143 cells/mL | ≈95 min | Milk | [69] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay; Label free; Ferrocyanide measurement; rG-GO/SPCE | EIS | − | 101 CFU/mL in samples | ≈15 min | Water, orange juice | [72] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Aptasensor; Label free; diazonium salt- modified SPCE | EIS | 10–108 CFU/mL | 6 CFU/mL | ≈45 min | Apple juice | [73] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Paper-based immunoassay (sandwich); AuNP as label; SPCE | C | 10–108 CFU/mL | 10 CFU/mL | ≈35 min | Water | [76] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); HRP as label; SPAuE | CA | 10–107 CFU/mL | ≈20 CFU/mL | ≈150 min | Chicken | [82] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); HRP as label; SAM/Protein A/SPAuE | CA | − | 10 CFU/mL | ≈125 min | Milk | [62] |
| Salmonella (no serotype) | Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on MB; QD (CdTe) dendron as label; BiSPCE | SWASV | − | 4 CFU/mL | ≈80 min | Milk | [77] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay; Label free; SAM/GA/Ab/2-SPAuE | EIS | 103–108 CFU/mL | 103 CFU/mL | ≈20 min | Milk | [79] |
| Salmonella. Typhimurium (and E. coli O157:H7) | Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture biotinylated Ab on stretavidin-MB; GOX-as label; SP-IDME (gold) | EIS | 102–106 CFU/mL for both | 1.66 × 103 CFU/mL (3.90 × 102 CFU/mL for E. coli) | ≈180 min | Chicken carcass (ground beef for E. coli) | [83] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella aureus (and E. coli) | Antimicrobial petide melittin on MB; SP-IDME (silver) | EIS | 10–104 CFU/mL; 10–106 CFU/mL (1–106 CFU/mL for E. coli) | 10 CFU/mL for both (1 CFU/mL for E. coli) | ≈30 min | Water, apple juice | [84] |
| Salmonella Pullorum and Salmonella Gallinarum | Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on AuNP-modified MB (SiO2/Fe3O4); HRP as label; 4-SPCE | CV | 102–106 CFU/mL | 32 CFU/mL | ≈70 min | Chicken | [85] |
| Salmonella Typhimurium | Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on MB; AuNP as label; µFD-8-SPCE | DPV | 10.0–100.0 cell/mL in milk | 7.7 cells/mL | ≈75 min | Milk | [75] |
| Salmonella (no serotype) | Immunoassay (sandwich); HRP as label; 96-well SPCE plate | IPA | 5 × 106–5 × 108 CFU/mL | 2 × 106 CFU/mL | ≈100 min | Pork, chicken, beef | [80] |
| Salmonella (no serotype) (Multiplexed: E. coli, Campylobacter) | Immunoassay (sandwich); specific nanolabel for each specie (CuS, CdS, PbS); MWCNT-PAH/SPCE | SWASV | 103–5 × 105 cell/mL | 400 cells/mL for Salmonella and Campylobacter; 800 cells/mL for E. coli | ≈70 min | Milk | [78] |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Immunoassay (sandwich); Ab capture on MB; Ab detection/urease (as label) modified AuNP; SP-IDE (gold) | EIS | 1.9 × 103–1.9 × 106 CFU/mL | 1.6 × 103 CFU/mL | ≈115 min | Lettuce | [86] |
| Listeria innocua Serovar 6b | Label-free; Bacteriophage endolysin CBD500 covalent immobilized on SPAuE | EIS | 104–109 CFU/mL | 1.1 × 104 CFU/mL | ≈25 min | Milk | [87] |
| Sensor Construction | Detect. Tech. | Conc. Range | LOD | Analysis Time | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunoassay (sandwich); HRP as label; AuNP/FeDC-SPCE | CA | 102 to 107 CFU/mL | 600 CFU/mL | ≈35 min | Milk | [88] |
| Immunoassay (sandwich); Ab capture on MB; AuNP as label (catalysing HER); SPCE | CA | 102–105 CFU/mL in samples | 309 CFU/mL in tap water, 457 CFU/mL in minced beef | ≈70 min | Water, minced beef | [89] |
| Immunoassay (sandwich); rGO-NR-Au@Pt nanocomposite-detection Ab (measurement of H2O2 reduction); AuNP/PANI-SPCE | CV | 8.9 × 103–8.9 × 109 CFU/mL | 2840 CFU/mL | ≈110 min | Milk, pork | [90] |
| Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on MB; rGO-NR-Au@Pt nanocomposite-detection Ab (measurement of H2O2 reduction); Thionine as mediator; SPCE | CV | 4 × 103–4 × 108 CFU/mL | 450 CFU/mL | ≈115 min | Milk, pork | [91] |
| Immunoassay (sandwich); Capture Ab on MB; rGO-NR-Au@Pt nanocomposite HRP-modified detection-Ab; HRP as label; Thionine as mediator; 4-SPCE | CV | 4 × 102–4 × 108 CFU/mL | 91 CFU/mL | ≈135 min | Milk, pork | [92] |
| Immunoassay; Label-free (measurement of Fe(CN)63−/4−); AuNP-SPCE | CV | 1.19 × 103–1.19 × 109 CFU/mL | 594 CFU/mL | ≈55 min | Milk powder | [93] |
| Immunoassay; Label-free (measurement of Fe(CN)63−/4−); AuNP/PANI-SPCE | DPV | 4 × 104–4 × 109 CFU/mL | 7980 CFU/mL | ≈45 min | Milk | [94] |
| Immunoassay (sandwich); Ab photochemical immobilization; Label free; SPAuE | EIS | 102–103 CFU/mL in drinking water | 30 CFU/mL | ≈70 min | Drinking water | [95] |
| Immunoassay; Capture Ab on MB; Label free; SP-IDME of gold | EIS | 104–107 CFU/mL | 104.45 CFU/mL | ≈60 min | Ground beef | [96] |
| Immunoassay; Ab on AuNP/MB-GOX@PDA; Filtration step; GOX as label; Prussian Blue-modified SP-IDME of gold | A | 103–106 CFU/g in ground beef | 190 CFU/g | ≈75 min | Ground beef | [97] |
| Biogenic Amines | Sensor Construction | Detect. Tech. | Conc. Range | LOD | Analysis Time | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIS | Rhenium (IV) oxide-SPCE | A | 4.5–90 µM | 1.8 µM | ≈3 min | Fish sauce | [100] |
| HIS | Nafion/Cu3(PO4)2NP/SPCE | A | 0.045–4.5 mM | 0.027 mM | ≈3 min | Fish | [101] |
| HIS | Immunoassay (competitive); Histamine labelled with HRP; Capture Ab on SWCNT/SPE (flexible with a silver WE) | CA | 0.045–450 nM | 0.022 nM | ≈140 min | Fish | [98] |
| HIS | Immunoassay (competitive); HRP-labelled detection Ab; Histamine-ovalbumin conjugate on PB/chitosan/AuNP/SPCE | CV | 0.09–900 µM | 0.01 nM | ≈130 min | Fish | [99] |
| HIS | DAO on SPCE | CA | 9–675 µM | 4.5 µM | ≈1 min | Fish (hake, mackerel) | [102] |
| HIS | DAO on SPCE; [Fe(CN)6]3− in solution as mediator | CA | 45–675 µM | 8.7 µM | ≈7 min | Fish (tuna, mackerel) | [103] |
| HIS | DAO and HRP on polysulfone/ MWCNT/ferrocene membrane/SPCE; SPCE with two WE, ferrocene as mediator | A | 0.3–20 µM | 0.17 µM | ≈2 min | Fish (anchovy, tuna, sardine, mackerel, shrimp, grater weever) | [104] |
| HIS | DAO on PtNP/rGO/chitosan/SPCE | A | 0.1–300 µM | 25.4 nM | ≈2 min | Fish (carp, tench, catfish, perch) | [105] |
| PUT | MAO on TTF-SPCE; TTF as mediator | A | 16–101 µM | 17.2 µM | ≈2 min | Anchovy, Courgette | [106] |
| PUT | PUO on TTF-SPCE; TTF as mediator | A | 10–74 µM | 10.1 µM | ≈2 min | Octopus, courgette | [107] |
| TYR | DAO on GO/PVF-modified SPCE | A | 0.99–120 µM | 0.41 µM | ≈2 min | Cheese | [108] |
| MAO on GO/PVF-modified SPCE | 0.9–110 µM | 0.61 µM | |||||
| TYR | Ty on SWCNT/SPCE | A | 5–180 µM | 0.62 µM | ≈2 min | Fish | [109] |
| TYR | 1-methyl-4-mercaptopyridine/AuNP/PEDOT:PSS/SPCE | DPV | 5–100 nM | 2.31 nM | ≈6 min | Milk | [110] |
| TYR | Nafion/Ty/Fe3O4-chitosan/poly-L-lysine/SPCE | A | 0.49–63 µM | 0.075 µM | ≈2 min | Cheese | [111] |
| TYR | PAO on SPCE (hydroxymethylferrocene in cell solution as mediator) | A | 2–164 µM | 2.0 µM | ≈2 min | Cheese | [112] |
| TYR | HRP on SPCE | A | 2–456 µM | 2.1 µM | ≈2 min | Cheese | [113] |
| HIS | DAO on PB/ITO nanoparticles/SPCE | A | 6.0–690 µM | 1.9 µM | ≈2 min | Cheese | [114] |
| CAD | MAO on PB/ITO nanoparticles/SPCE | 3–1000 µM | 0.9 µM | ||||
| HIS | HMD and PUO respectively on TTF-SPCE (with 4 WE); TTF as mediator | A | − | 8.1 µM | ≈2 min | Octopus | [115] |
| PUT | − | 10 µM | |||||
| PUT | MAO (for PUT) or MAO/AuNPs (for PUT and CAD) on TTF-SPCE (with two WE); TTF as mediator | A | 9.9–74.1 µM | 9.9 µM | ≈2 min | Octopus | [116] |
| CAD | 19.6–107.1 µM | 19.9 µM | |||||
| Total biogenic amines (calibration with HIS, PUT, CAD) | DAO on MB; PB-SPCE | CA | 0.01–1 mM for HIS, PUT, CAD | 4.8 µM for HIS; 0.9 µM for PUT; 0.67 µM for CAD | ≈15 min | Fish (sea bass) | [117] |
| Total biogenic amines (calibration with HIS) | DAO and HRP on aryl diazonium salt/SPCE | A | 0.2–1.6 µM | 0.18 µM | ≈2 min | Fish (anchovy) | [118] |
| Total biogenic amines (calibration with PUT) | DAO on polyazetidine prepolimer/SPE (with two WE of gold) | A | 8–227 µM | 2.3 µM | ≈2 min | Wine, beer | [119] |
| Total biogenic amines (calibration with CAD, PUT, TYR, HIS) | Nafion/DAO/MnO2-SPCE (MnO2 as mediator) | A | 1–50 µM for CAD and PUT; 10–300 µM for TYR and HIS | 0.3 µM for CAD and PUT; 3.0 µM for TYR and HIS | ≈5 min | Chicken meat | [120] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torre, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection. Biosensors 2020, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100139
Torre R, Costa-Rama E, Nouws HPA, Delerue-Matos C. Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection. Biosensors. 2020; 10(10):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100139
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorre, Ricarda, Estefanía Costa-Rama, Henri P. A. Nouws, and Cristina Delerue-Matos. 2020. "Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection" Biosensors 10, no. 10: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100139
APA StyleTorre, R., Costa-Rama, E., Nouws, H. P. A., & Delerue-Matos, C. (2020). Screen-Printed Electrode-Based Sensors for Food Spoilage Control: Bacteria and Biogenic Amines Detection. Biosensors, 10(10), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10100139