Polycrystalline-Diamond MEMS Biosensors Including Neural Microelectrode-Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction

| Organic Substances | Inorganic Substances |
|---|---|
| adenosine, ascorbic acid, caffeine, carbamate pesticides, catecholamines, cephalexin, chlorophenols, chlorpromazine, p-cresol, cysteine, dopamine, formaldehyde, flavonoids, glucose, glutathione, guanosine, histamine, indoles, NADH, nitrophenol, nucleic acids, oxalic acid, penicillamine, phenol, polyamines, purine, pyrimidine, serotonin, sulfa drugs, tetracycline antibiotics, theobromine, theophylline, tiopronin and xanthine | azide anion, hydrazine, hydrogen peroxide, iodide, nitrate, nitrite, dissolved oxygen, dissolved ozone, peroxodisulfate, sulfate, sulfide, Ag+, As(III), Cd2+, Cu2+, Hg+, Mn2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Sn4+ and Zn2+ |
2. Development and Fabrication of Poly-C Micro-Electrode Arrays
2.1. Development of Poly-C Neural Recording Probes
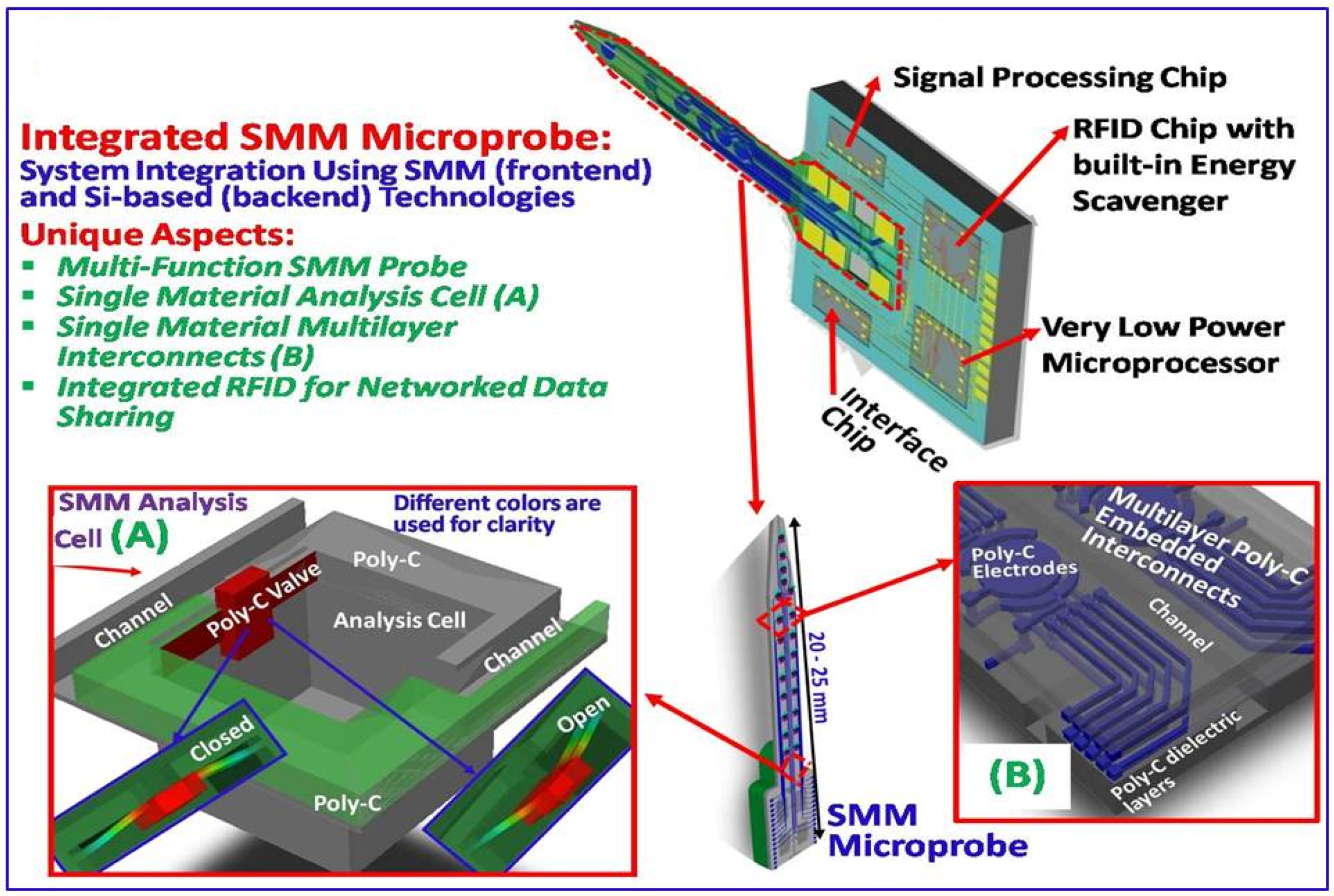
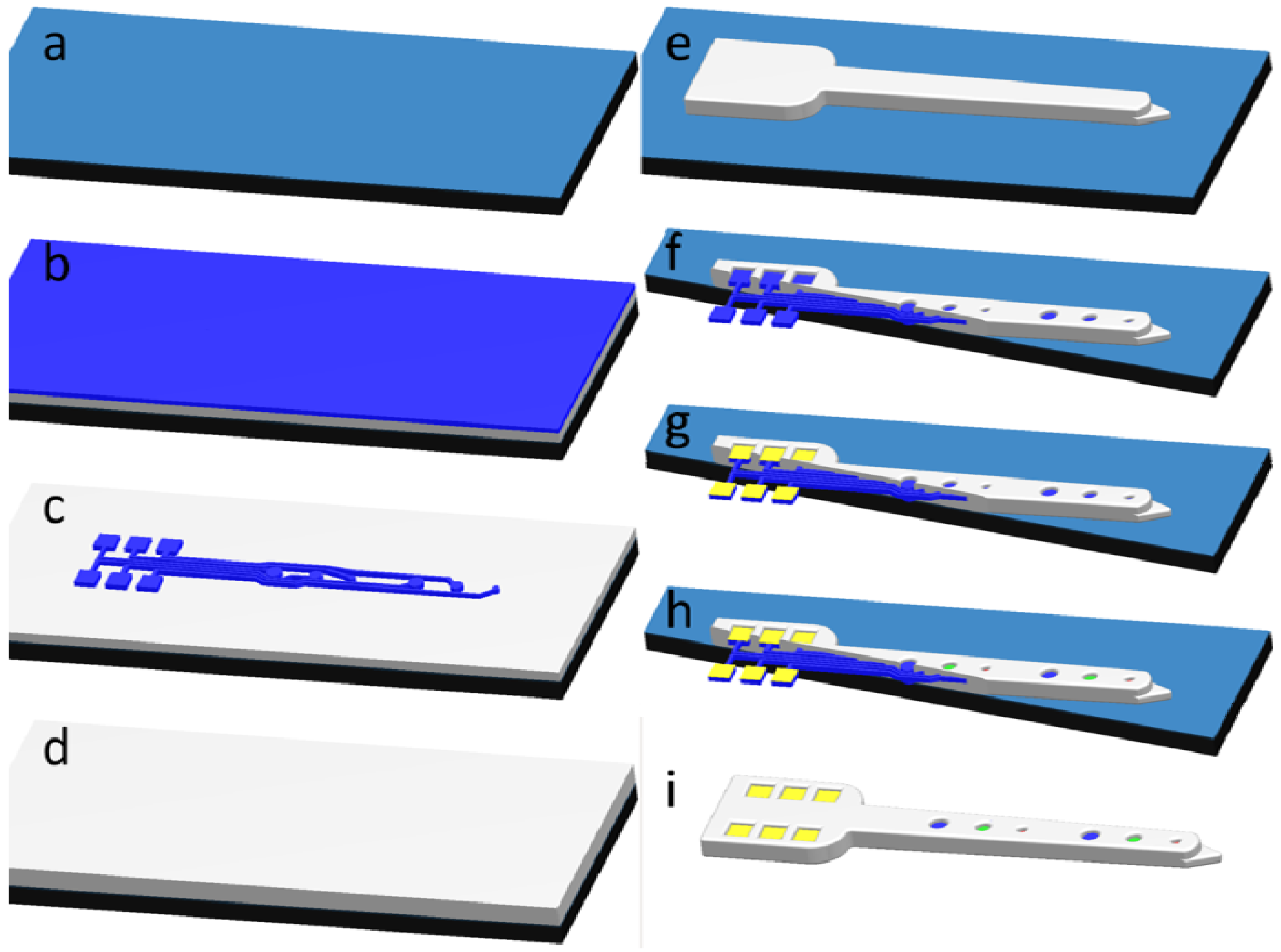
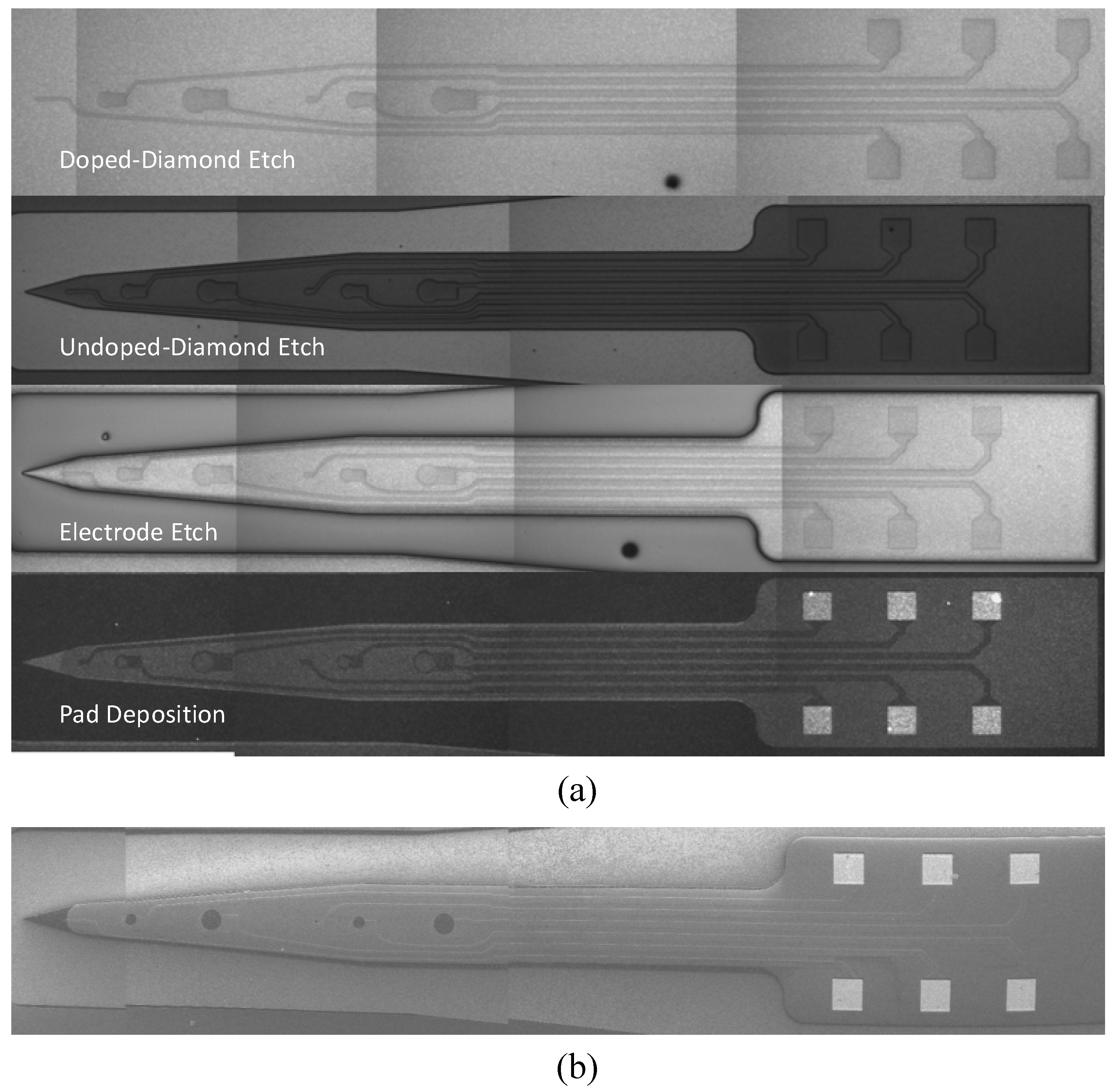
2.2. Development of All-Diamond Neural Recording Probes Using the Single Material MEMS (SMM) Concept
3. Experiments and Results
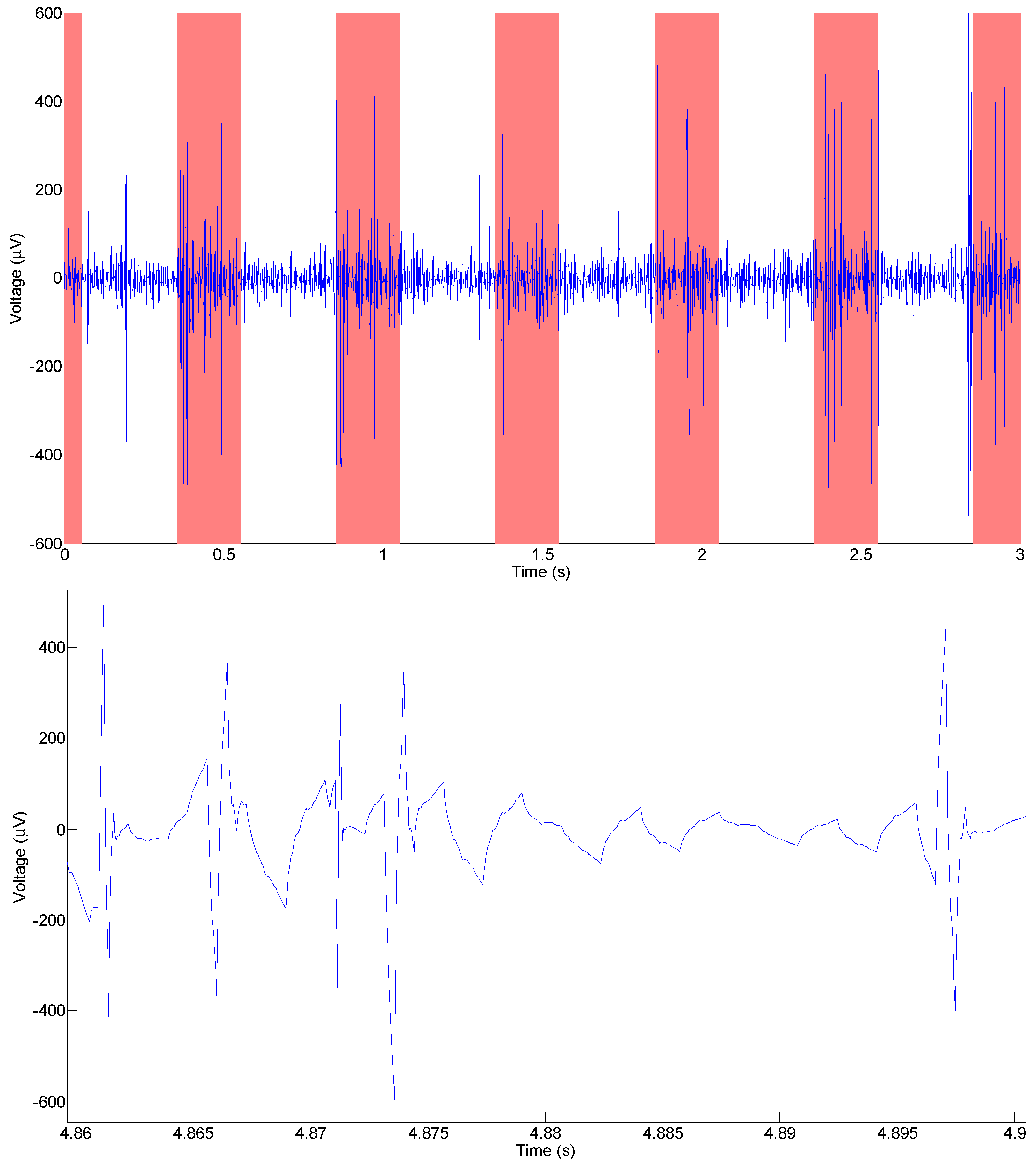
3.1. In Vivo Electrical Neural Recordings
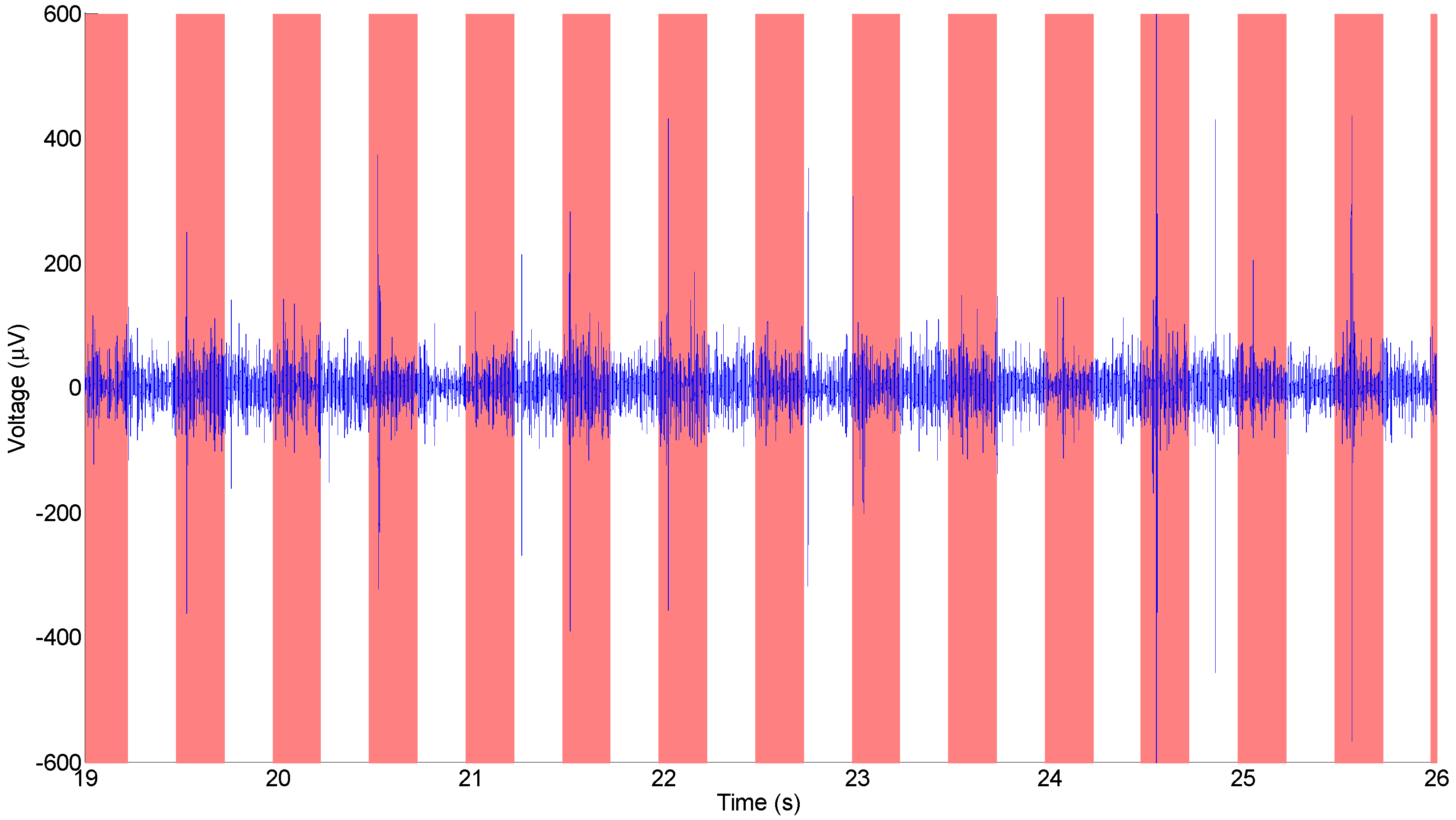
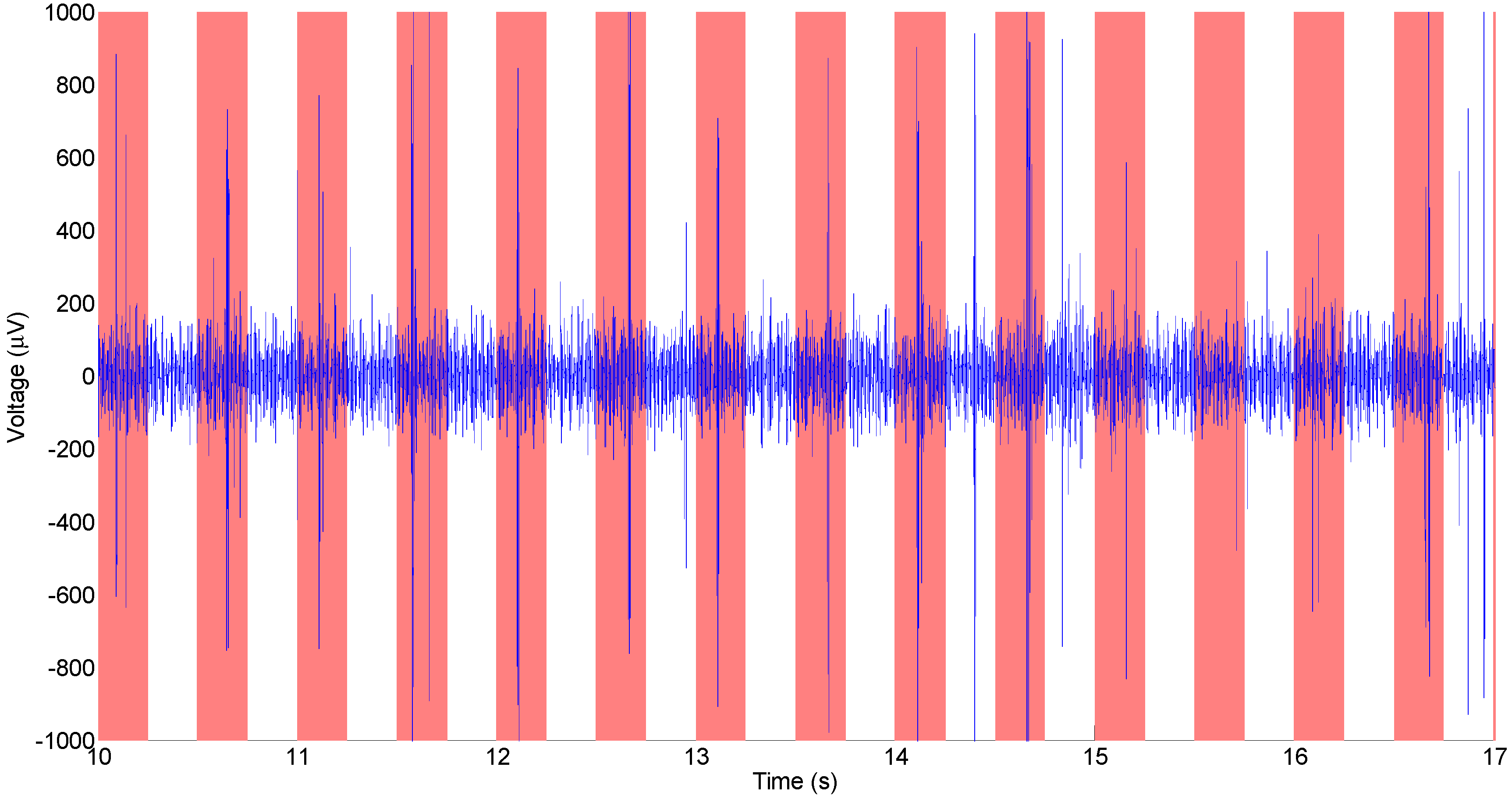
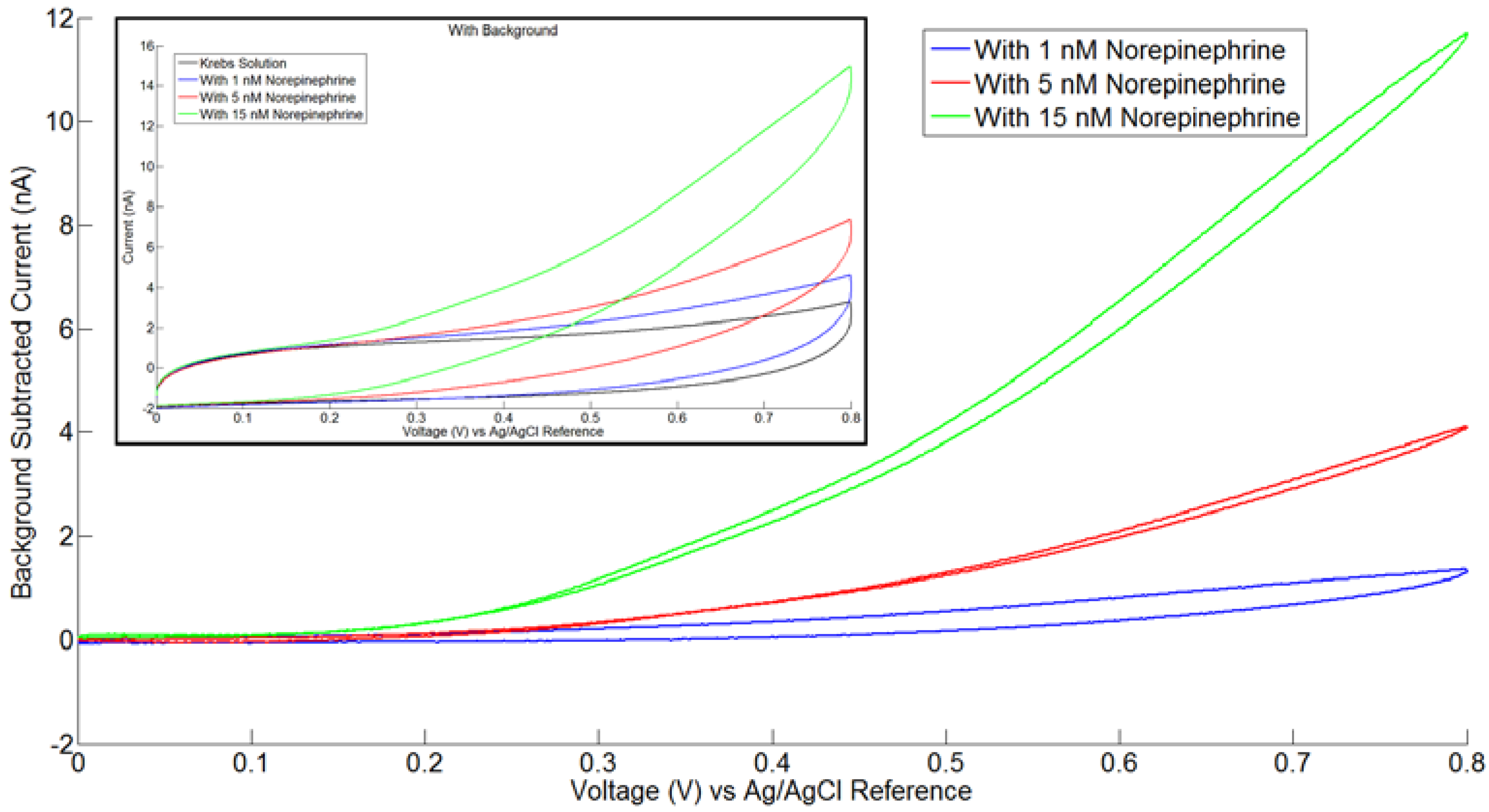
3.2. In Vitro Electrochemical Detection with Poly-C Micro-Electrode Arrays

4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Lazcka, O.; Campo, F.J.; Munoz, F.X. Pathogen detection: A perspective of traditional methods and biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Electroanalytical biosensors and their potential for food pathogen and toxin detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Aslam, D.M.; Tang, Y.; Stark, B.H.; Najafi, K. The fabrication of all-diamond packaging panels with built-in interconnects for wireless integrated Microsystems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2004, 13, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Aslam, D.M. CVD diamond thin film technology for MEMS packaging. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Aslam, D.M.; Sullivan, J.P. The application of polycrystalline diamond in a thin film packaging process for MEMS resonators. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 2068–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Butler, J.E.; Hsu, D.S.Y.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. CVD polycrystalline diamond high-Q microme-chanical resonators. In Proceedings of the 15th International IEEE Microelectromechanical Systems Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, January 2002; pp. 657–660.
- Wang, J.; Butler, V.; Feygelson, T.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. Microwave-assisted palladium catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of sodium tetraphenylborate with carboxylic anhydrides. In Proceedings of 17th International IEEE Micro-electromechanical Systems Conference, Masstricht, The Netherlands, 25–29 January 2004; pp. 641–642.
- Sepulveda, N.; Aslam, D.M.; Sullivan, J.P. Polycrystalline diamond MEMS resonator technology for sensor applications. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, N.; Lu, J.; Aslam, D.M.; Sullivan, J.P. High-performance polycrystalline diamond micro- and nanoresonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imboden, M.; Mohanty, P.; Gaidarzhy, A.; Rankin, J.; Sheldon, B.W. Scaling of dissipation in megahertz-range micromechanical diamond oscillators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Aslam, D.M. Study of polycrystalline diamond piezoresistive position sensors for application in cochlear implant probe. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-Y.; Aslam, D.M.; Wiler, J.; Casey, B. A novel diamond microprobe for neuro-chemical and electrical recording in neural prosthesis. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2009, 18, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, I.; Aslam, D.M.; Tamor, M.A.; Potter, T.J.; Elder, R.C. Piezoresistive microsensors using p-type CVD diamond films. Sens. Actuat. 1994, 45, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.L.; Wur, D.R.; Kang, W.P.; Kinser, D.L.; Kerns, D.V. Polycrystalline diamond pressure microsensor. Diamond Relat. Mater. 1996, 15, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A.; Nawachi, N.; Tsutsumoto, T.; Nishiie, H.; Asahi, T. Pressure and vibration sensors using piezoresistive effect of polycrystalline diamond film. New Diamond Front. Carbon Technol. 2005, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A.; Nawachi, N.; Tsutsumoto, T.; Terayama, A. Pressure sensor using p-type polycrys-talline diamond piezoresistors. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.S.; Aslam, D.M. Single-structure heater and temperature sensor using a p-type poly-crystalline diamond resistor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1996, 17, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.G.; Zheng, C.Q.; Ren, J.; Hong, S.M. Properties and texture of B-doped diamond films as thermal sensor. Diamond Relat. Mater. 1993, 2, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.P.; Gurbuz, Y.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. New hydrogen sensor using a polycrystalline diamond-based Schottky diode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 2231–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, Y.; Kang, W.P.; Davidson, J.L.; Kinser, D.L.; Kerns, D.V. Diamond microelectronic gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. 1996, 33, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, Y.; Kang, W.P.; Davidson, J.L.; Kerns, D.V. Diamond microelectronic gas sensor for detection of benzene and toluene. Sens. Actuat. 2004, 99, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Aslam, D.M. Poly-diamond gated field-emitter display cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1999, 46, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, K.; Kang, W.P.; Davidson, J.L. A monolithic nanodiamond lateral field emission vacuum transistor. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2008, 29, 1259–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.R.; Wu, T.H.; Jou, S.; Chen, W.R.; Hsu, J.F.; Yeh, C.S. Effect of triode structure on field emission properties of nanocrystalline diamond films. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2009, 18, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesham, R.; Roppel, T.; Ellis, C. Fabrication of microchannels in synthetic polycrystalline diamond thin films for heat sinking applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 1706–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaudeu, S.; Zhu, X.; Aslam, D.M. Fabrication of 2-um wide poly-crystalline diamond channels using silicon molds for micro-fluidic applications. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J.A.; Auciello, O. Ultrananocrystalline diamond. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2003, 29, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.-Y.; Varney, M.; Aslam, D.M.; Wise, K.D. Fabrication and characterization of all-diamond microprobes for electrochemical analysis. In Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Sanya, China, 6–9 January 2008; pp. 532–535.
- Cao, Z.; Aslam, D. Fabrication technology for single-material MEMS using polycrystalline diamond. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.A.; Tender, L.M.; Feldstein, M.J.; Golden, J.P.; Scruggs, S.B.; MacCraith, B.D.; Cras, J.J.; Ligler, F.S. Array biosensor for simultaneous identification of bacterial, viral, and protein analytes. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Erf, G.F. Interdigitated array microelectrode based electrochemical impedance immunosensor for detection of Escherichia Coli O157:H7. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Butler, J.E.; Russell, J.N., Jr.; Hamers, R.J. Direct electrical detection of antigen-antibody binding on diamond and silicon substrates using electrical impedance spectroscopy. Analyst 2006, 132, 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, E.; Male, K.B.; Luong, J.H.T. Boron doped diamond biosensor for detection of Escherichia Coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7691–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Zhang, G.-J.; Nakamura, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Hiraki, T.; Yang, J.-H.; Funatsu, T.; Ohdomari, I.; Kawarada, H. Label-free DNA sensors using ultrasensitive diamond field-effect transistors in solution. Phys. Rev. E 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Uetsuka, H.; Osawa, E.; Nebel, C.E. Vertically aligned diamond nanowires for DNA sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5183–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, A. Doped diamond: A compact review on a new, versatile electrode material. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2007, 2, 355–385. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.; Sarada, B.V.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Application of diamond microelectrodes for end-column electrochemical detection in capillary. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvacka, J.; Quaiserova, V.; Park, J.; Show, Y.; Muck, A.; Swain, G.M. Boron-doped diamond microelectrodes for use in capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, P.S.; Loh, K.P.; Poh, W.C.; Zhang, H. Biosensing properties of nanocrystalline diamond film grown on polycrystalline diamond electrodes. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2004, 14, 426–431. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Mocko, V.Q.; Peckova, K.; Galligan, J.J.; Fink, G.D.; Swain, G.M. Fabrication, characterization, and application of a diamond microelectrode for electrochemical measurement of nore-pinephrine release from the sympathetic nervous system. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herlambang, O.; Sarada, B.V.; Rao, T.N. Miniturization of diamond microsensor system for in vivo detection. Chem. Sens. B 2002, 18, 121–123. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, J.M.; Xie, S.; Sutton, G.P.; Higashikubo, B.T.; Chetek, C.A.; Lu, H.; Chiel, H.J.; Martin, H.B. Diamond electrodes for neurodynamic studies in Aplysia californica. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarada, B.V.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Electrochemical oxidation of histamine and serotonin at highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2002, 72, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, T.N.; Yagi, I.; Miwa, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Electrochemical oxidation of NADH at highly boron-doped diamond electrode. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Shafer, G.; Wilson, C.G.; Martin, H.B. In vitro adenosine detection with a diamond-based sensor. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.K.; Lee, K.-R. Biomedical applications of diamond-like carbon coatings: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2007, 83B, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tsai, C.; Gerberich, W.W.; Kruckebeu, L.; Kania, D.R. Biocompatibility of chemical-vapour-deposited diamond. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.F.; Loh, K.P.; Vedula, S.R.K.; Lim, C.T.; Sternschulte, H.; Steinmuller, D.; Sheu, F.-S.; Zhong, Y.L. Cell adhesion properties on photochemically functionalized diamond. Langmuir 2007, 23, 5615–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, X.; Krueger, T.B.; Lago, N.; Micera, S.; Stieglitz, T.; Dario, P. A critical review of interfaces with the peripheral nervous system for the control of neuroprostheses and hybrid bionic systems. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005, 10, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, M.A.; Nicolelis, M.A.L. Brain-machine interfaces: Past, present and future. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, E.; Lang, E.A. Criteria for deep-brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: Review and analysis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2006, 6, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewley, D.T.; Hills, M.D.; Borkholder, D.A.; Opris, I.E.; Maluf, N.I.; Storment, C.W.; Kovacs, G.T.A. Plasma-etched neural probes. Sens. Actuat. A 1997, 58, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Mabuchi, K.; Fujita, H. 3D flexible multichannel neural probe array. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipke, D.R. Implantable neural probe systems for cortical neuroprosthesis. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2004, 7, 5344–5347. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Q.; Wise, K.D. Single-unit neural recording with active microelectrode arrays. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlin, P.; Kindlundh, M.; Mouroux, A.; Yoshida, K.; Hofmann, U.G. A 32-site neural recording probe fabricated by DRIE of SOI substrates. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2002, 12, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.K.; Jones, K.E.; Huber, R.J.; Horch, K.W.; Normann, R.A. A silicon-based three-dimensional neural interface: manufacturing process for an intracortical electrode array. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindlundh, M.K.; Norlin, P.; Hofmann, U.G. A neural probe process enabling variable electrode configurations. Sens. Actuat. B 2004, 12, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.H.; Hwang, E.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Parl, S.J.; Oh, S.J.; Jung, S.C.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, S.J. A micro-machined silicon depth probe for multichannel neural recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutten, W.L.C.; Vanwier, H.J.; Put, J.H.M. Sensitivity and selectivity of intraneural stimulation using a silicon electrode array. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1991, 38, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueng, K.; Gun, L.; Djupsund, K.; Yang, D.; Lee, L.P. A new neural probe using SOI wafers with topological interlocking mechanism. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine and Biology, Lyon, France, 12–14 October 2000; pp. 507–511.
- Motta, P.S.; Judy, J.W. Multielectrode microprobes for deep-brain stimulation fabricated with a customizable 3-D electroplating process. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, L.; Tang, W.C.; Zeng, F.G. Micromachined electrode arrays with form-fitting profile for auditory nerve prostheses. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2005, 5, 5260–5263. [Google Scholar]
- Wise, K.D.; Sodagar, A.M.; Yao, Y.; Gulari, M.N.; Perlin, G.E.; Najafi, K. Microelectrode, micro-electronics, and implantable neural Microsystem. Proc. IEEE 2008, 96, 1184–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarowski, D.H.; Andersen, M.D.; Retterer, S.; Spence, A.J.; Isaacson, M.; Craighead, H.G.; Turner, J.N.; Shain, W. Brain responses to micromachined silicon devices. Brain Res. 2003, 983, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.K.; Johnson, M.D.; Scott, K.A.; Shim, J.H.; Nam, H.; Kipke, D.R.; Brown, R.B. Iridium oxide reference electrodes for neurochemical sensing with MEMS microelectrode arrays. IEEE Sens. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, G.M.; Ramesham, R. The electrochemical activity of boron-doped polycrystalline diamond thin film electrode. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-Y.; Aslam, D.M.; Wang, S.H.; Swain, G.M.; Wise, K.D. Fabrication and testing of a novel all-diamond neural probe for chemical detection and electrical sensing applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Tucson, AZ, USA, 13–17 January 2008; pp. 244–247.
- Cao, Z.; Aslam, D.M. MEMS structures using polycrystalline diamond single-material micro technologies. In Presented at the IEEE Nano Electro Mechanical Systems, Xiamen, China, 20–23 January 2010.
- Cao, Z.; Varney, M.W.; Aslam, D.M. Single-material MEMS using polycrystalline diamond. In Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hong Kong, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 51–54.
- Varney, M.W.; Cao, Z.; Aslam, D.M. Fabrication and testing of a novel all-diamond neural probe for chemical detection and electrical sensing applications. In Presented at the IEEE Nano Electro Mechanical Systems, Xiamen, China, 20–23 January 2010.
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Varney, M.W.; Aslam, D.M.; Janoudi, A.; Chan, H.-Y.; Wang, D.H. Polycrystalline-Diamond MEMS Biosensors Including Neural Microelectrode-Arrays. Biosensors 2011, 1, 118-133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1030118
Varney MW, Aslam DM, Janoudi A, Chan H-Y, Wang DH. Polycrystalline-Diamond MEMS Biosensors Including Neural Microelectrode-Arrays. Biosensors. 2011; 1(3):118-133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1030118
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarney, Michael W., Dean M. Aslam, Abed Janoudi, Ho-Yin Chan, and Donna H. Wang. 2011. "Polycrystalline-Diamond MEMS Biosensors Including Neural Microelectrode-Arrays" Biosensors 1, no. 3: 118-133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1030118
APA StyleVarney, M. W., Aslam, D. M., Janoudi, A., Chan, H.-Y., & Wang, D. H. (2011). Polycrystalline-Diamond MEMS Biosensors Including Neural Microelectrode-Arrays. Biosensors, 1(3), 118-133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios1030118





