Highly Efficient Wideband Microwave Absorbers Based on Zero-Valent Fe@γ-Fe2O3 and Fe/Co/Ni Carbon-Protected Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles Supported on Graphene Oxide
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of the Citric Acid to Ethylene Glycol (CA:EG) and Metal Precursor (CA:M) Ratios
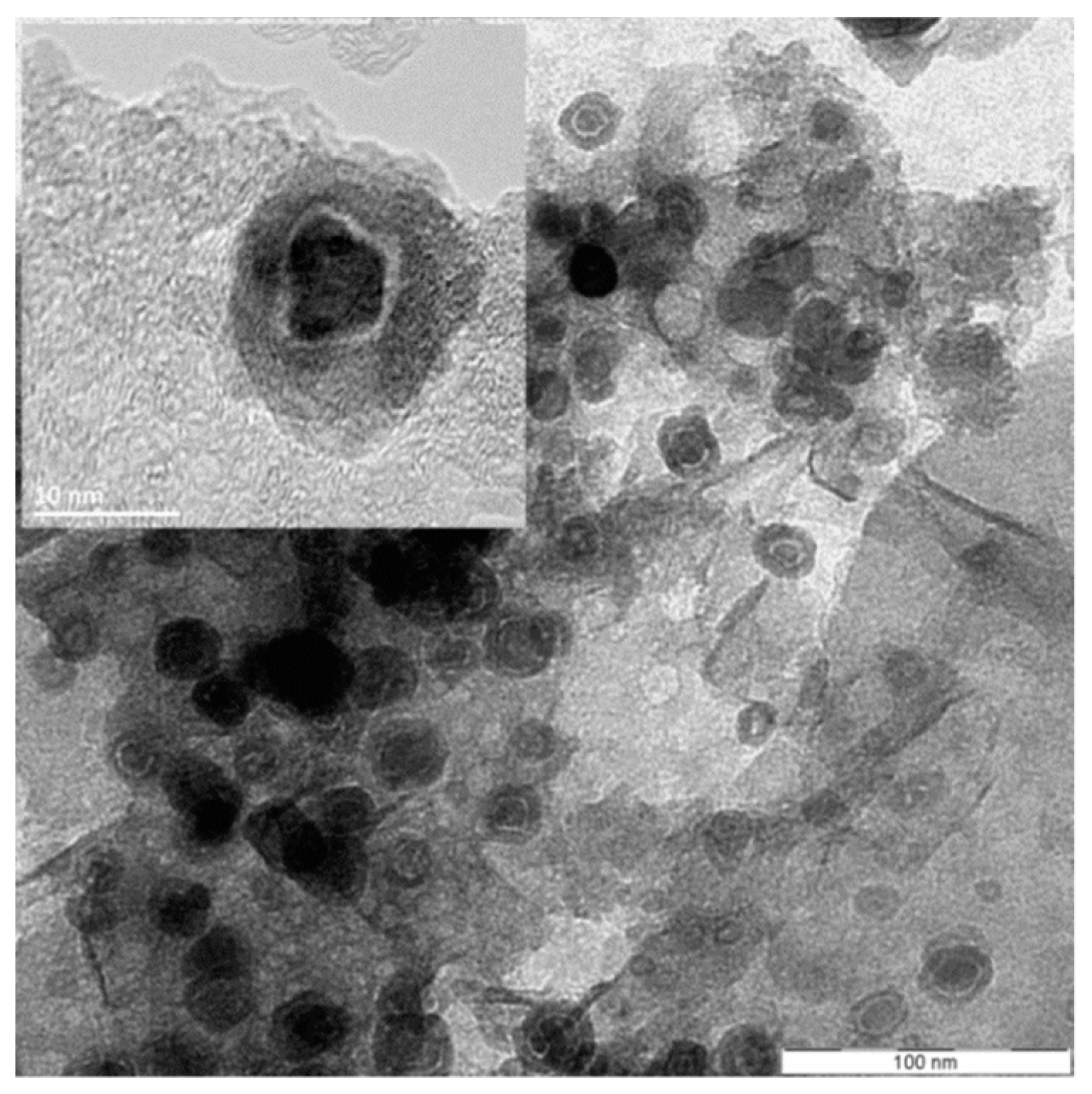
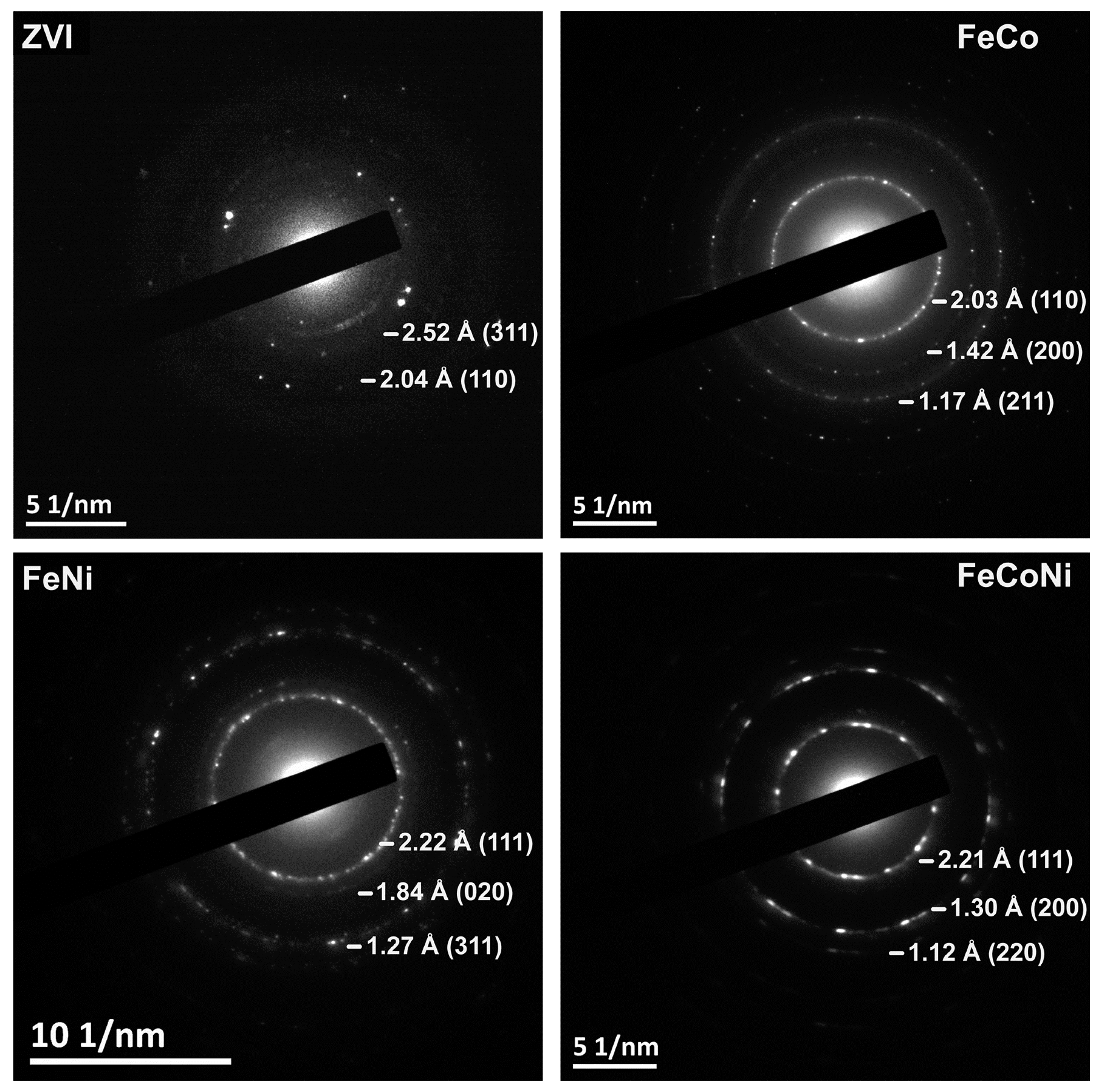
3.2. Characterization of the Chemical Composition of the ZVI Nanoparticles Deposited onto rGO
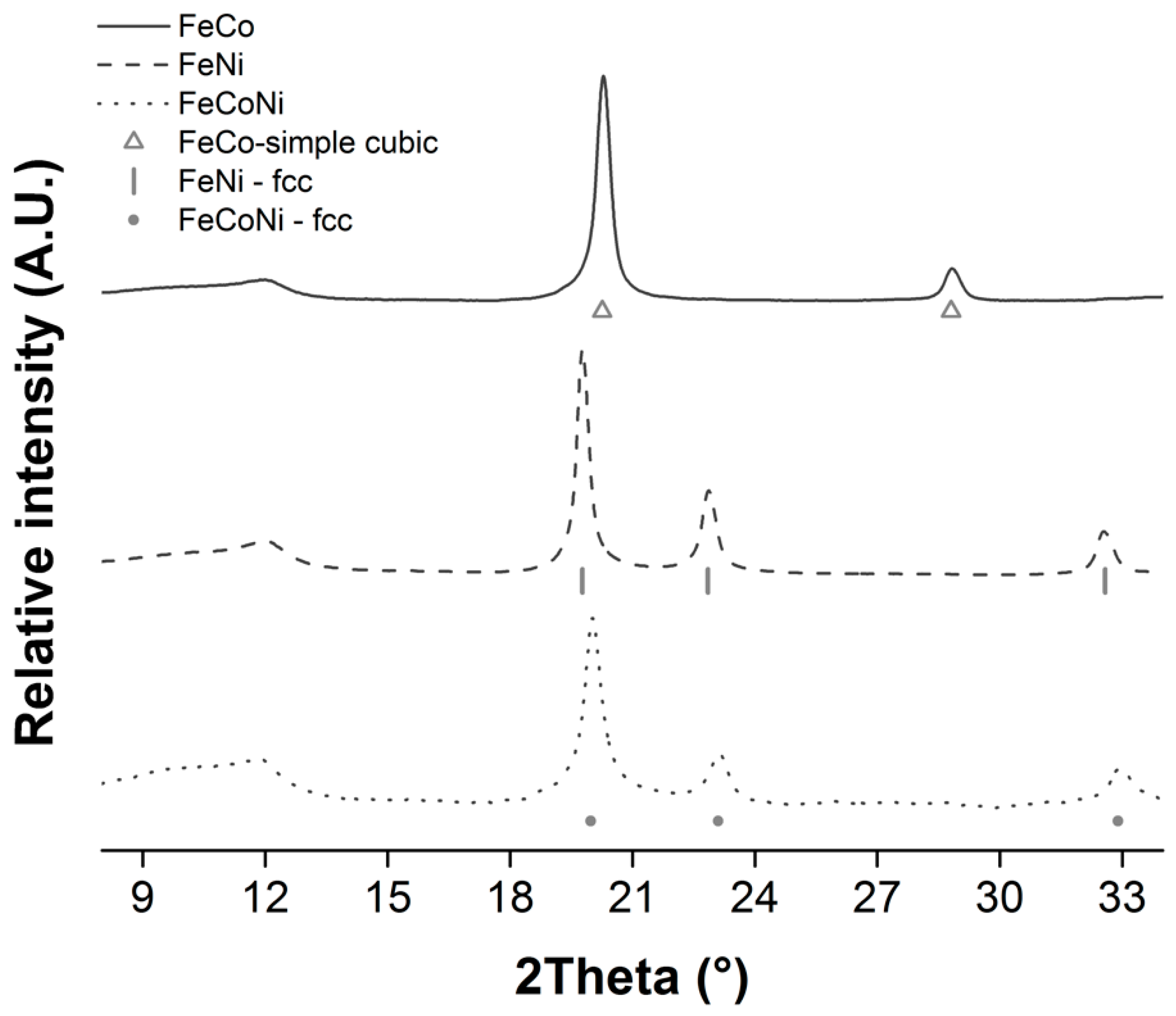
3.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Fe/Co/Ni Alloy NPs Deposited onto rGO
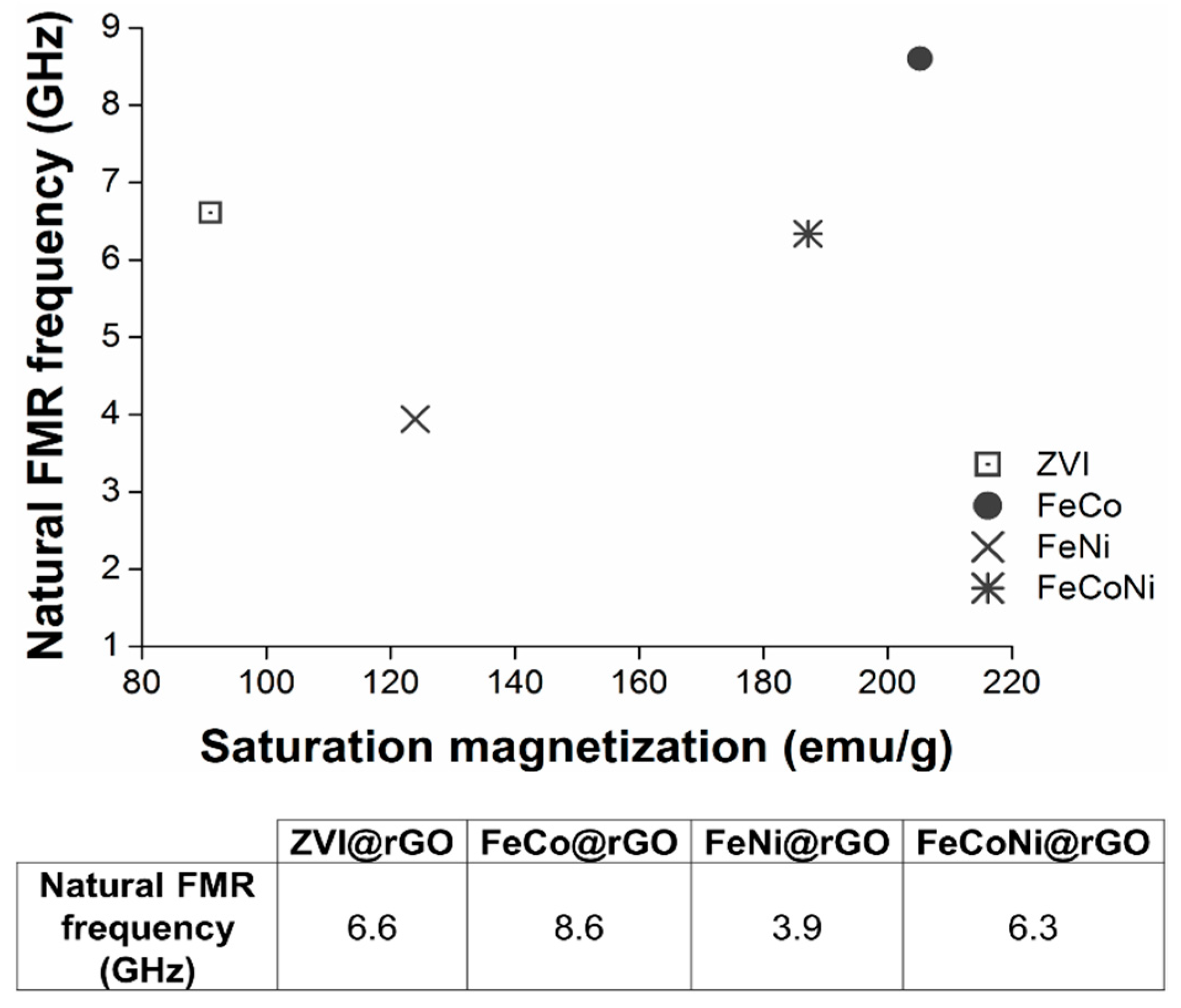
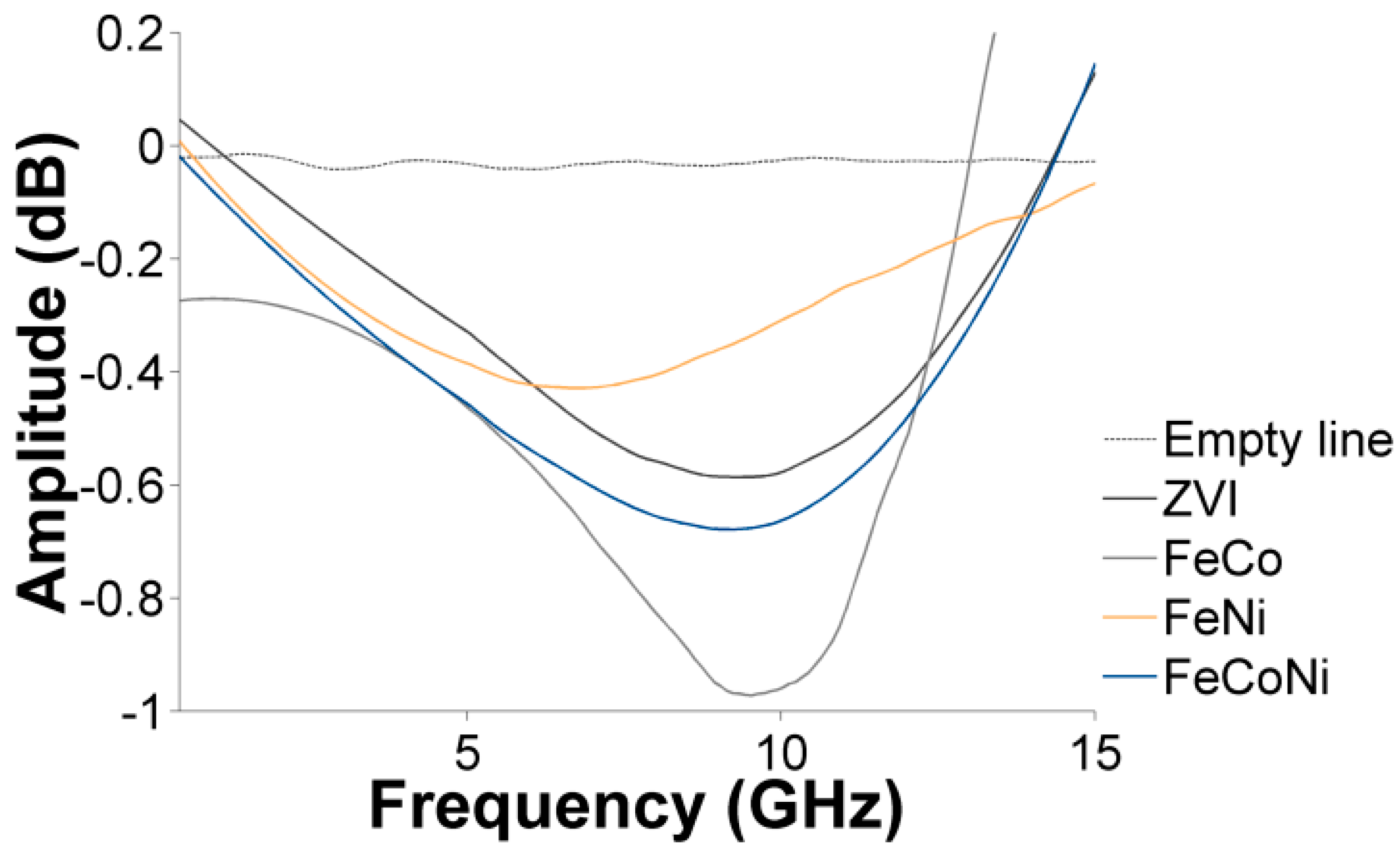
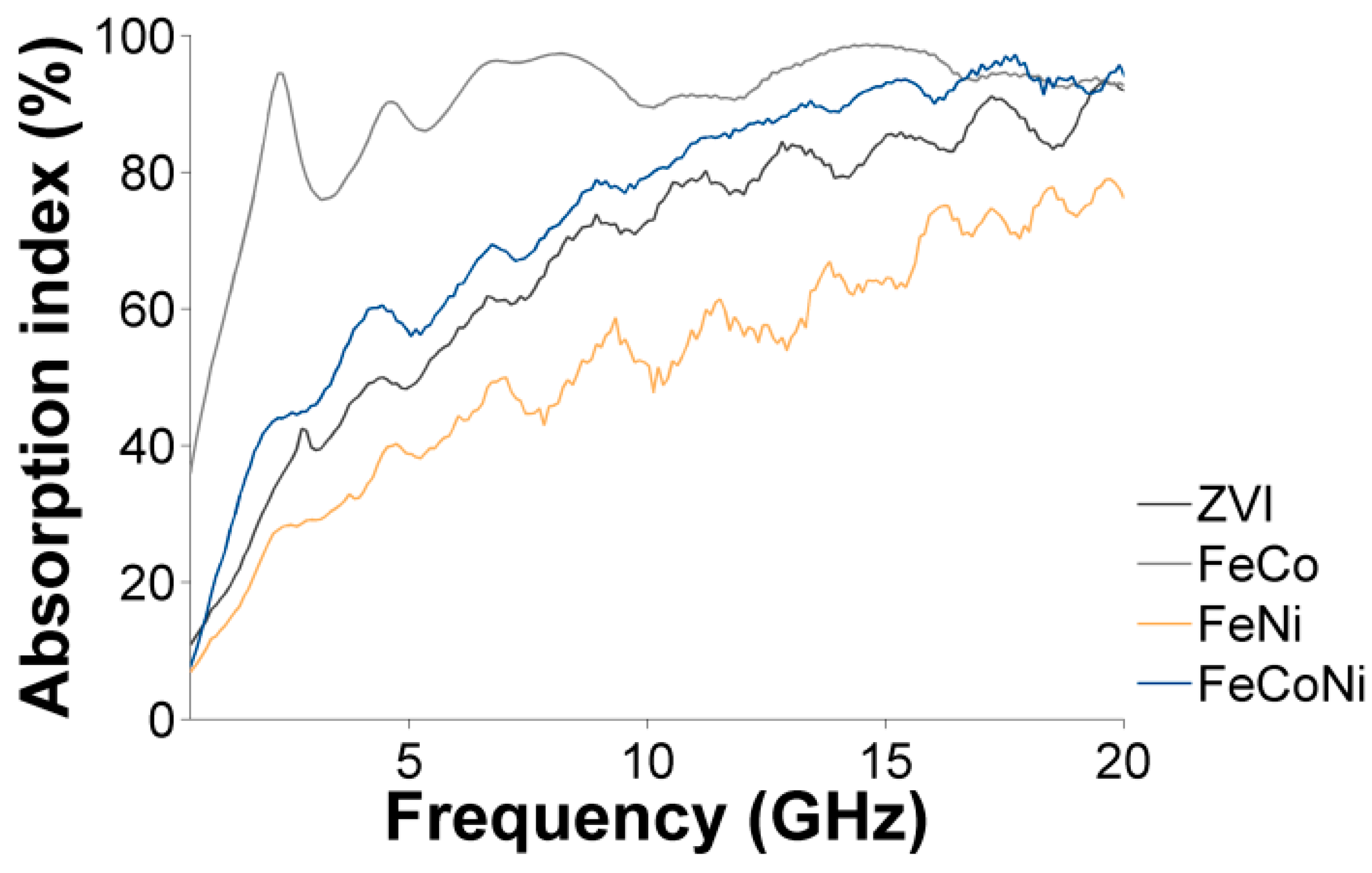
3.4. Characterization of the Nanocomposites Magnetic Properties and Microwave Absorption Behavior
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomassin, J.-M.; Jérôme, C.; Pardoen, T.; Bailly, C.; Huynen, I.; Detrembleur, C. Polymer/carbon based composites as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2013, 74, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks, European Commission, Opinion on Potential Health Effects of Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF). 2015. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/scientific_committees/emerging/docs/scenihr_o_041.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2019).
- Hemming, L.H. Architectural Electromagnetic Shielding Handbook: A Design and Specification Guide; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.B.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, T. Magnetic Nanomaterials: Fundamentals, Synthesis and Applications; Hou, Y., Sellmyer, D.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2017; Chapter 15; pp. 473–514. [Google Scholar]
- Timonen, J.V.I.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O.; Oksanen, M.; Seppälä, E.; Chalapat, K.; Li, J.; Paraoanu, G.S. Trends in Nanophysics: Theory, Experiment and, Technology; Aldea, A., Bârsan, V., Eds.; Springer Science: London, UK, 2010; Chapter 11; pp. 257–285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xi, K.; Cao, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Du, Y. Excellent microwave absorption property of Graphene-coated Fe nanocomposites. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Park, B.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.B. Magnetic and dispersible FeCoNi-graphene film produced without heat treatment for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, F.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Hollow N-doped carbon polyhedron containing CoNi alloy nanoparticles embedded within few-layer N-doped graphene as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 24920–24929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Long, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Optimization of porous FeNi3/N-GN composites with superior microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zha, W.; Kang, M.; Lu, S.; Cui, L.; Li, S. Microwave absorption response of nickel/graphene nanocomposites prepared by electrodeposition. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 8060–8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Bae, K.-M.; Sil Lee, Y.S.; Ana, K.-H.; Park, S.-J. EMI shielding behaviors of Ni-coated MWCNTs-filled epoxy matrix nanocomposites. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 42, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Q.; Xu, J.; Shen, X. Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16905–16914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos-Henry, F.; Pichon, B.; Tchuitio Yagang, Y.; Delcorte, A.; Bailly, C.; Huynen, I.; Hermans, S. Decoration of nanocarbon solids with magnetite nanoparticles: towards microwave metamaterial absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 3, 3290–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlée, Y.; Huynen, I.; Bailly, C. Thin smart multilayer microwave absorber based on hybrid structure of polymer and carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 213105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlée, Y.; Huynen, I.; Bailly, C. Thin and flexible multilayer polymer composite structures for effective control of microwave electromagnetic absorption. Comp. Sci. Tech. 2014, 100, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesfin, H.M.; Baudouin, A.C.; Hermans, S.; Delcorte, A.; Huynen, I.; Bailly, C. Frequency selective microwave absorption induced by controlled orientation of graphene-like nanoplatelets in thin polymer films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 103105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, W.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. One-pot synthesis of urchinlike Ni nanoparticles/RGO composites with extraordinary electromagnetic absorption properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, N.L.V.; Escote, M.T.; Valentini, A.; McCafferty, L.; Stolojan, V.; Beliatis, M.; Mills, C.A.; Rhodes, R.; Smith, C.T.G.; Silva, S.R.P. Adsorbent 2D and 3D carbon matrices with protected magnetic iron nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechini, M.P. Sprague Electric Co, assignee. Patent US 3330697 A, 11 July 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Galceran, M.; Pujol, M.C.; Aguiló, M.; Díaz, F. Sol-gel modified Pechini method for obtaining nanocrystalline KRE(WO4)2 (RE = Gd and Yb). J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Shi, Z.-X.; Qian, S.-M. Structure and performance of YBa2Cu3O7 prepared by sol-gel methods. Gongneng Cailiao/J. Funct. Mater. 2004, z1, 898–902. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, M.E.; Betancourt, I.; Arellano-Jimenez, M.J.; Sánchez-Llamazares, J.L.; Sánchez-Valdés, C.F. Magnetocaloric response of submicron (LaAg)MnO3 manganite obtained by Pechini method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol 2015, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Seo, H.J. A visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of vanadate garnet AgCa2Ni2V3O12 nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh-Oghaz, M.; Razavi, R.S.; Barekat, M.; Naderi, M.; Malekzadeh, S.; Rezazadeh, M. Synthesis and characterization of Y2O3 nanoparticles by sol–gel process for transparent ceramics applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol–gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, E.; Liu, B.; Fan, W.Y. Preparation of Graphite-Coated Iron Nanoparticles Using Pulsed Laser Decomposition of Fe3(CO)12 and PPh3 in Hexane. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 3845–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides. Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Darmstadt, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Kang, F.-Y.; Gu, J.-L. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of FeCoNi alloy particles/graphite flaky composites. J. Inorg. Mater. 2010, 25, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Ji, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Du, Y. Cross-Linking-Derived Synthesis of Porous CoxNiy/C Nanocomposites for Excellent Electromagnetic Behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 38814–38823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arief, I.; Biswas, S.; Bose, S. FeCo-Anchored Reduced Graphene Oxide Framework-Based Soft Composites Containing Carbon Nanotubes as Highly Efficient Microwave Absorbers with Excellent Heat Dissipation Ability. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 19202–19214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.P.; Jin, C.; Lv, Y. Enhanced microwave absorption of flower-like FeNi@C nanocomposites by dual dielectric relaxation and multiple magnetic resonance. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 22710–22715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos-Henry, F.; Hermans, S.; Huynen, I. Coplanar waveguide method for microwave and ferromagnetic resonance characterization of nanocarbon powders decorated with magnetic nanoparticles. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017, 59, 2330–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos-Henry, F.; Hermans, S.; Huynen, I. Microwave Characterization of Metal-Decorated Carbon Nanopowders Using a Single Transmission Line. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrykin, V.; Kakihana, M. Chemistry and Applications of Polymeric Gel Precursors. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology: Processing, Characterization and Applications; Sakka, S., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: London, UK, 2005; Chapter 4; pp. 77–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mashreghi, A.; Davoudi, F. The effect of ethylene glycol/citric acid molar ratio in the initial precursor of TiO2 nanoparticle paste synthesized by a polymerizable complex method on the photovoltaic properties of dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 30, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Agarwal, V.; Liu, M.; Rees, W.S. Investigation of the mechanism of sol-gel formation in the Sr(NO3)2/citric acid/ethylene glycol system by solution state 87Sr nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaee, M.Z.; Motamedi, E.; Majdi, M. Magnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide/polystyrene: Fabrication and characterization of a promising nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuz Johra, F.; Lee, J.-W.; Jung, W.-G. Facile and safe graphene preparation on solution based platform. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 2883–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide studied by the XRD, TEM and electron spectroscopy methods. J. Electron. Spectrosc. 2014, 195, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Das, S.; Patra, M.; Thakur, M. Iron nanoparticles from an electrochemical route. Nanosci. Methods 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, I.N.; Shipilin, M.A.; Alekseev, V.P.; Shipilin, A.M. Mössbauer study of maghemite nanoparticles. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2012, 38, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Shima, M.; Pati, R.; Nayak, S.K.; Singh, D.J.; Ma, R.; Li, Y.; Bando, Y.; Nasu, S.; Ajayan, P.M. Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism in Doped Face-Centered Cubic Fe Nanoparticles. Small 2006, 2, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.M.; Socolovsky, L.M.; Goya, G.F.; Knobel, M.; Zanchet, D. Structural, magnetic, and Mossbauer characterization of size-controlled iron-iron oxide nanoparticles obtained by chemical methods. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 2681–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Gibb, T.C. Mössbauer Spectroscopy; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, the Netherlands, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Kobe, B.A.; McIntyre, M.S. Examination of the oxidation of iron by oxygen using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and QUASESTM. Surf. Sci. 2004, 565, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, H.; Oudar, J. Material Concepts in Surface Reactivity and Catalysis; Dover Publications INC: Mineola, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zero-valent iron Powder Diffraction File (PDF) 00-006-0696 (2017) and γ-Fe2O3 PDF 00-039-1346 (2017); International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2017.
- Balaban, A.T.; Klein, D.J. Local interconversions between graphite and diamond structures. Carbon 1997, 35, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM Handbook Volume 3: Alloy. Phase Diagrams; Okamoto, H., Schlesinger, M.E., Mueller, E.M., Eds.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlfarth, E.P. Ferromagnetic Materials: A Handbook on the Properties of Magnetically Ordered Substances, Vol. 2; North Holland Pub. Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- FeCo Powder Diffraction File (PDF) 00-049-1568 (2017) and FeNi PDF 04-009-3507 (2017) and FeCoNi PDF 04-016-6385; International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD): Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2017.
- de Mayo, B.; Forester, D.W.; Spooner, S. Structure and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline (Fe1−xCox)90Zr7B2Cu1 (0 ⩽ x ⩽ 0.6). J. Appl. Phys. 1970, 41, 1319. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanasamy, A.; Nagarajan, T.; Muthukumarasamy, P.; Radhakrishnan, T.N. Hyperfine field distribution in disordered binary alloys. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1979, 9, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, D.; Shinoda, K.; Sato, K.; Konno, Y.; Joseyphus, R.J.; Motomiya, K.; Takahashi, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Sato, Y.; Tohji, K.; et al. Chemical Synthesis of sub-micrometer- to nanometer-sized magnetic FeCo dice. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djekoun, A.; Bouzabata, B.; Otmani, A.; Greneche, J.M. X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer studies of nanocrystalline FeNi alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Catal. Today 2004, 89, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guittoum, A.; Layadi, A.; Bourzami, A.; Tafat, H.; Souami, N.; Boutarfaia, S.; Lacour, D. X-ray diffraction, microstructure, Mössbauer and magnetization studies of nanostructured Fe50Ni50 alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, H.N.; Han, M.S. Mössbauer studies on the superparamagnetic behavior of 69–31 at.% FeNi fine particles. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 1932–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, C.M.; Nogueira Martins, A.F.; Costa, B.C.; Soares Ribeiro, T.; Pinheiro Braga, T.; Soares, J.M.; Sasaki, J.M. Synthesis of FeNi Alloy Nanomaterials by proteic sol-gel method: crystallographic, morphological, and magnetic Properties. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1637091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinjo, T.; Itoh, F.; Takaki, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Shikazono, N. Fe57 Mössbauer effect in Fe2B, FeB and Fe3C. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1964, 19, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinga, M.; Maeda, Y.; Nakamura, Y. Mössbauer Effect of invar type Fe-Ni-C and Fe-Ni-Mn alloys in the critical concentration. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1974, 37, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvalis, A.P.; Zboril, R.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Tucek, J.; Spyridi, S.; Bakas, T. A facile synthetic route toward air-stable magnetic nanoalloys with Fe-Ni/Fe-Co core and iron oxide shell. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaziz, W.; Pichon, B.P.; Fleutot, S.; Liu, Y.; Lefevre, C.; Greneche, J.-M.; Toumi, M.; Mhiri, T.; Begin-Colin, S. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Reproducible Tuning of the Size and Nanosized-Dependent Composition, Defects, and Spin Canting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3795–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaleyrat, F.; Ammar, M.; Lobue, M.; Bonnet, J.P.; Audebert, P.; Wang, G.Y.; Champion, Y.; Hÿtch, M.; Snoeck, E. Silica coated nanoparticles: synthesis, magnetic properties and spin structure. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 483, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guimarães, A.P. Principles of Nanomagnetism; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Pichon, B.P.; Ulhaq, C.; Lefèvre, C.; Grenèche, J.-M.; Bégin, D.; Bégin-Colin, S. Systematic Study of Exchange Coupling in Core–Shell Fe3−δO4@CoO Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 4073–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, H.; Takahashi, M.; Ogawa, T. Synthesis of Monodisperse Iron Nanoparticles with a High Saturation Magnetization Using an Fe(CO)x−Oleylamine Reacted Precursor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 5835–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Surface and Colloid Science; Matijevic, E., Borkovec, M., Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Chapter 2; pp. 27–81. [Google Scholar]
- Culity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, R.H. Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhatkar, A.G.; Jamison, A.C.; Litvinov, D.; Willson, R.C.; Lee, T.R. Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 15977–16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusak, K.E.; Johnston-Peck, A.C.; Wu, W.-C.; Anderson, B.D.; Tracy, J.B. Size and Composition Control of CoNi Nanoparticles and Their Conversion into Phosphides. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C. On the theory of ferromagnetic resonance absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charilaou, M.; Sahu, K.K.; Faivre, D.; Fischer, A.; García-Rubio, I.; Gehring, A.U. Magnetic anisotropy of non-interacting collinear nanocrystal-chains. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 182504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.P. Coplanar Waveguide: a surface strip transmission line suitable for nonreciprocal gyromagnetic device applications. IEEE T. Microw. Theory 1969, 17, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saib, A.; Huynen, I. Transmission lines on periodic bandgap metamaterials: from microwaves to optics applications. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Op. 2005, 7, S124–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saib, A.; Huynen, I.; Vanhoenacker-Janvier, D. Design of a stopband filter based on a Magnetic Photonic Bandgap Material. In Proceedings of the 33th European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 6–10 October 2003; pp. 809–812. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, F.; Peng, H.-X. Ferromagnetic microwires enabled multifunctional composite materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 183–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhong, W.-H. Polymer Nanocomposites for Dielectrics; Zhong, K., Li, B., Eds.; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd: Singapore, 2017; Chapter 8; pp. 171–192. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Ji, G.; Ma, J.; Ouyang, P.; Gong, H.; Xu, G.; Du, Y. Strong Electromagnetic Wave Response Derived from the Construction of Dielectric/Magnetic Media Heterostructure and Multiple Interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 9964–9974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
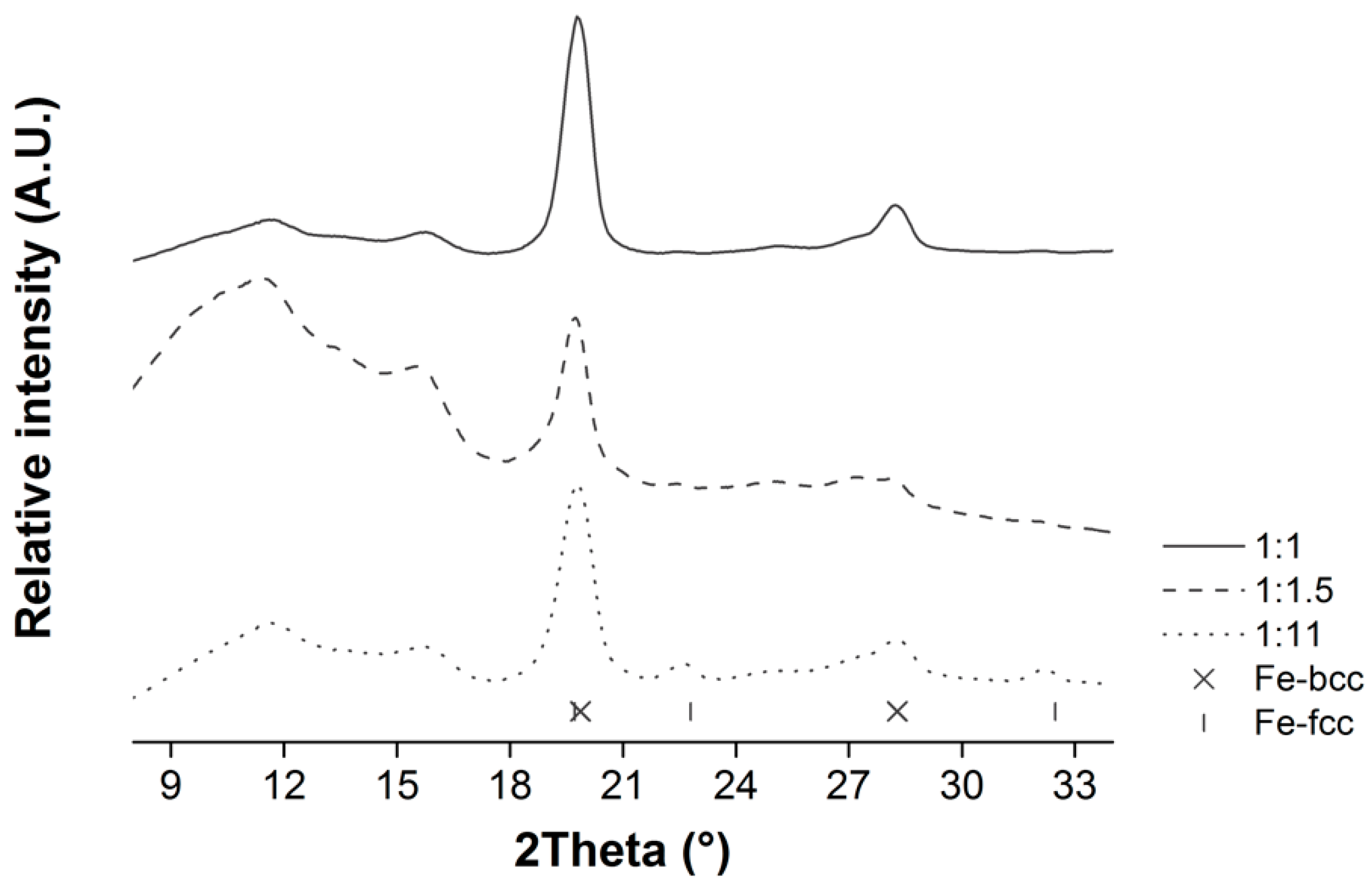


| CA:M Ratio | ||
|---|---|---|
| CA:EG Ratio | 3:1 | 6:1 |
| 1:1 | 16.8 ± 6.5 nm | 14.8 ± 4.7 nm |
| 1:1.5 | 17.9 ± 8.1 nm | 14.3 ± 7.2 nm |
| 1:11 | 18.3 ± 9.6 nm | 19.7 ± 10.4 nm |
| Nanocomposite | T | δ | ε, ΔEQ | Bhf | Г/2 | Relative Area | Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [K] | [mm/s] | [mm/s] | [Tesla] | [mm/s] | [%] | ||
| ZVI@rGO | 77 | 0.05(1) | – | – | 0.18 * | 4 | γ-Fe (fcc) |
| 0.11(1) | 0 | 34.1 | 0.21(1) | 86 | α-Fe (bcc) | ||
| 0.43(1) | 0 | 39 | 0.28 * | 10 | γ-Fe2O3 | ||
| FeCo@rGO | 77 | 0.12(1) | 0 | 34.6 | 0.22(1) | 100 | FeCo alloy |
| FeNi@rGO | 77 | 0.16(1) | 0.35(1) | – | 0.15 * | 6 | superparamagnetic phase |
| 0.027(1) 0.06(2) | −0.018(1) 0.01(1) | 34.1 31.5 | 0.20(1) 0.29(1) | 24 70 | FeNi (fcc) alloy | ||
| FeCoNi@rGO | 77 | 0.35(1) | −0.07(1) | 21.2 | 0.40(1) | 30 | Fe carbide |
| 0.15(1) | −0.05(1) | 32 | 0.17(1) | 70 | FeCoNi (fcc) alloy |
| EDX | ICP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy NPs | % Fe | % Co | % Ni | % Fe | % Co | % Ni |
| FeCo | 47 ± 4 | 53 ± 6 | – | 49 | 51 | – |
| FeNi | 48 ± 3 | – | 52 ± 3 | 52 | – | 48 |
| FeCoNi | 30 ± 8 | 36 ± 5 | 34 ± 6 | 32 | 34 | 34 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mederos-Henry, F.; Mahin, J.; Pichon, B.P.; Dîrtu, M.M.; Garcia, Y.; Delcorte, A.; Bailly, C.; Huynen, I.; Hermans, S. Highly Efficient Wideband Microwave Absorbers Based on Zero-Valent Fe@γ-Fe2O3 and Fe/Co/Ni Carbon-Protected Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091196
Mederos-Henry F, Mahin J, Pichon BP, Dîrtu MM, Garcia Y, Delcorte A, Bailly C, Huynen I, Hermans S. Highly Efficient Wideband Microwave Absorbers Based on Zero-Valent Fe@γ-Fe2O3 and Fe/Co/Ni Carbon-Protected Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(9):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091196
Chicago/Turabian StyleMederos-Henry, Francisco, Julien Mahin, Benoit P. Pichon, Marinela M. Dîrtu, Yann Garcia, Arnaud Delcorte, Christian Bailly, Isabelle Huynen, and Sophie Hermans. 2019. "Highly Efficient Wideband Microwave Absorbers Based on Zero-Valent Fe@γ-Fe2O3 and Fe/Co/Ni Carbon-Protected Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide" Nanomaterials 9, no. 9: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091196
APA StyleMederos-Henry, F., Mahin, J., Pichon, B. P., Dîrtu, M. M., Garcia, Y., Delcorte, A., Bailly, C., Huynen, I., & Hermans, S. (2019). Highly Efficient Wideband Microwave Absorbers Based on Zero-Valent Fe@γ-Fe2O3 and Fe/Co/Ni Carbon-Protected Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nanomaterials, 9(9), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9091196








