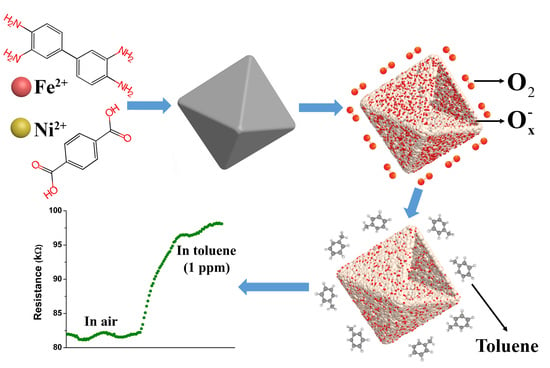
MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
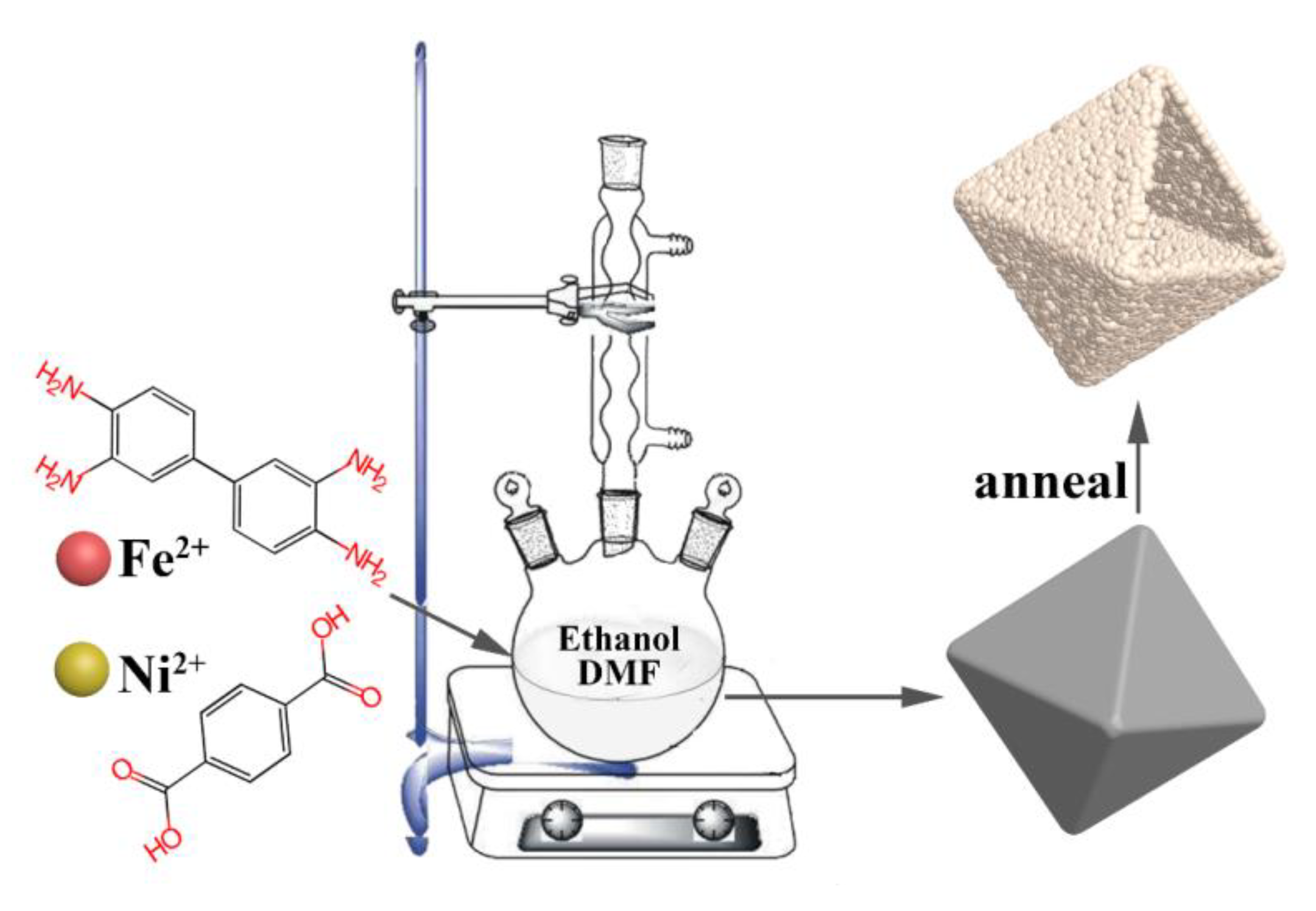
2.1. Materials Synthesis
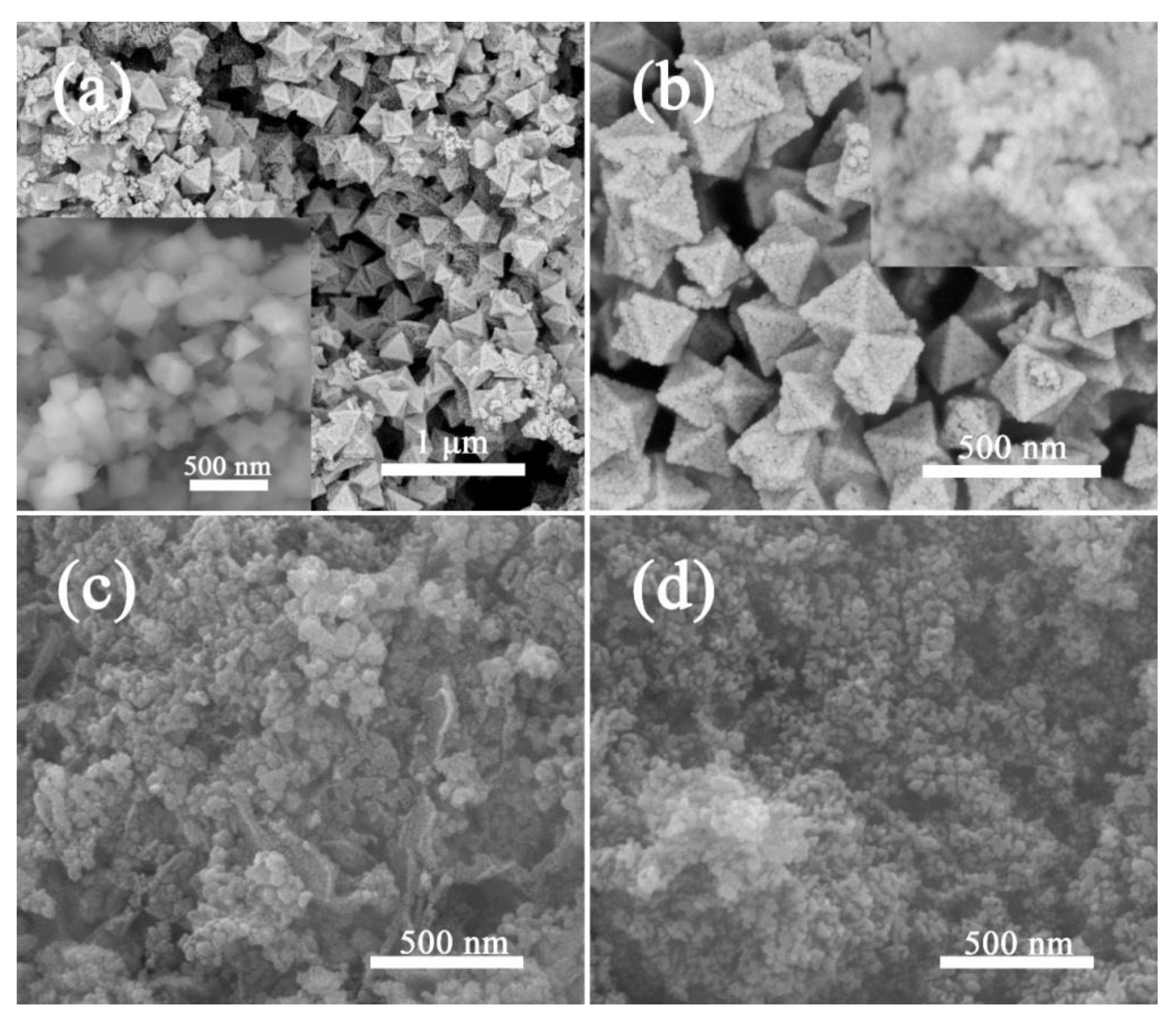
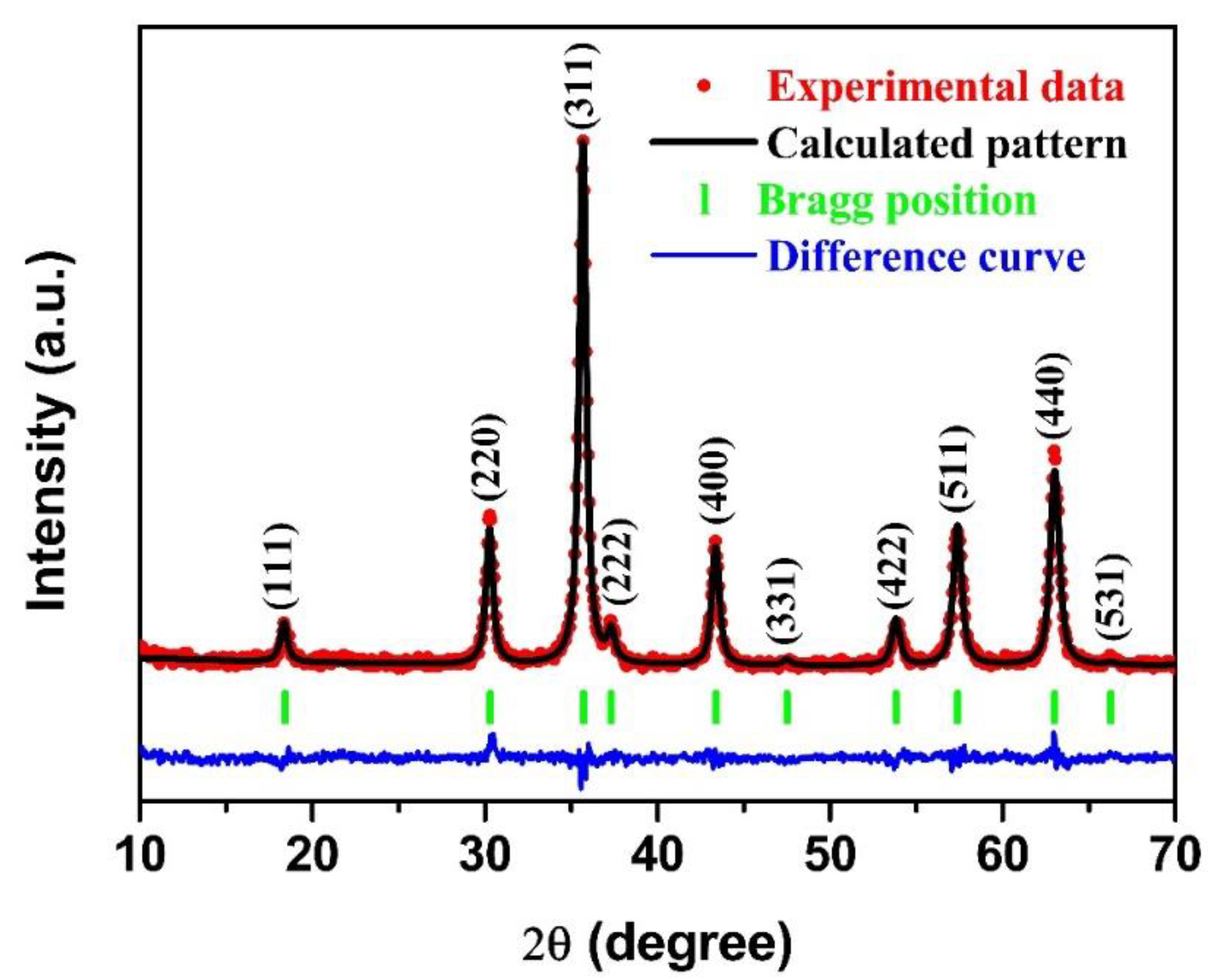
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Fabrication and Measurement of the Gas Sensor
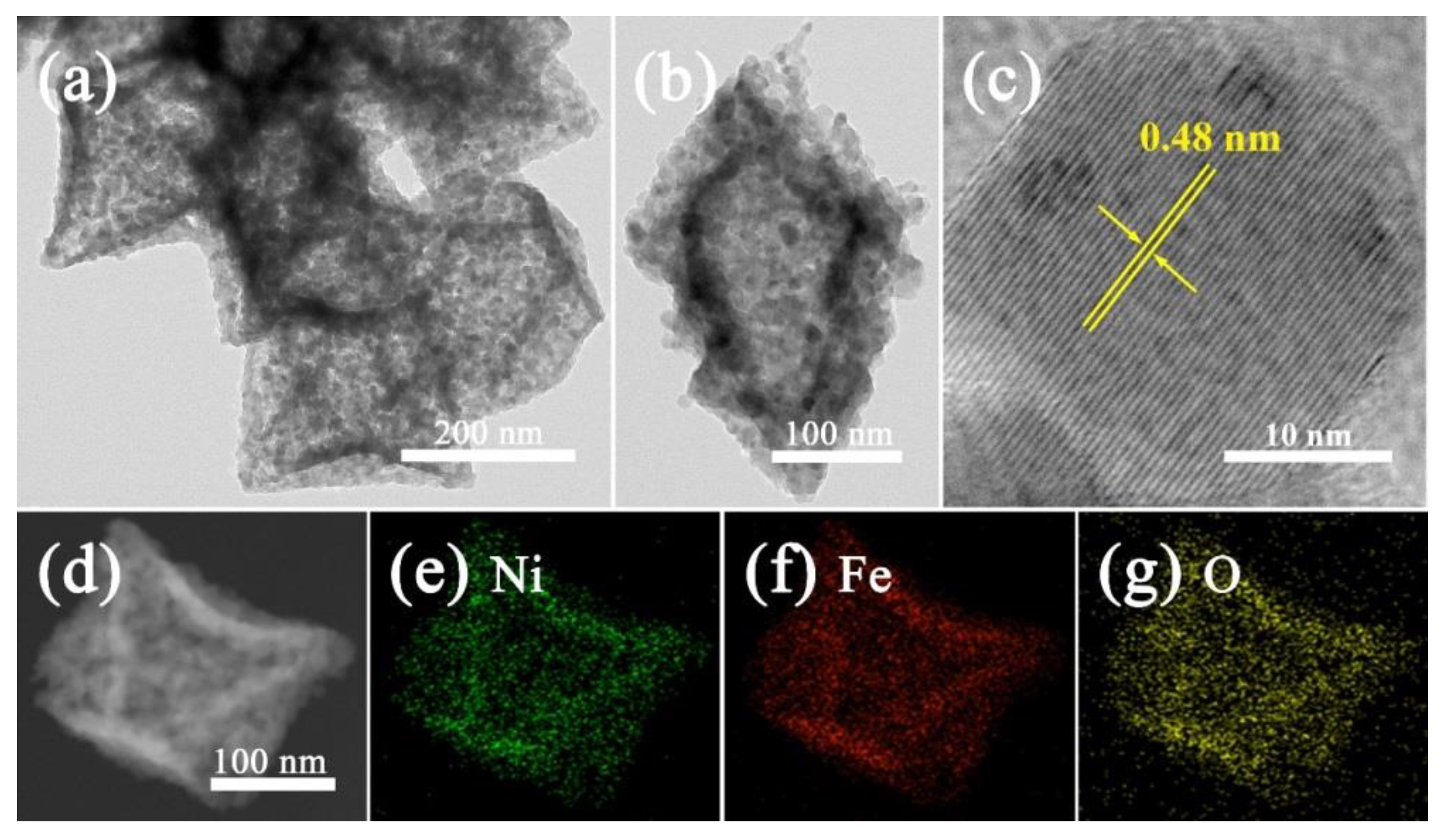
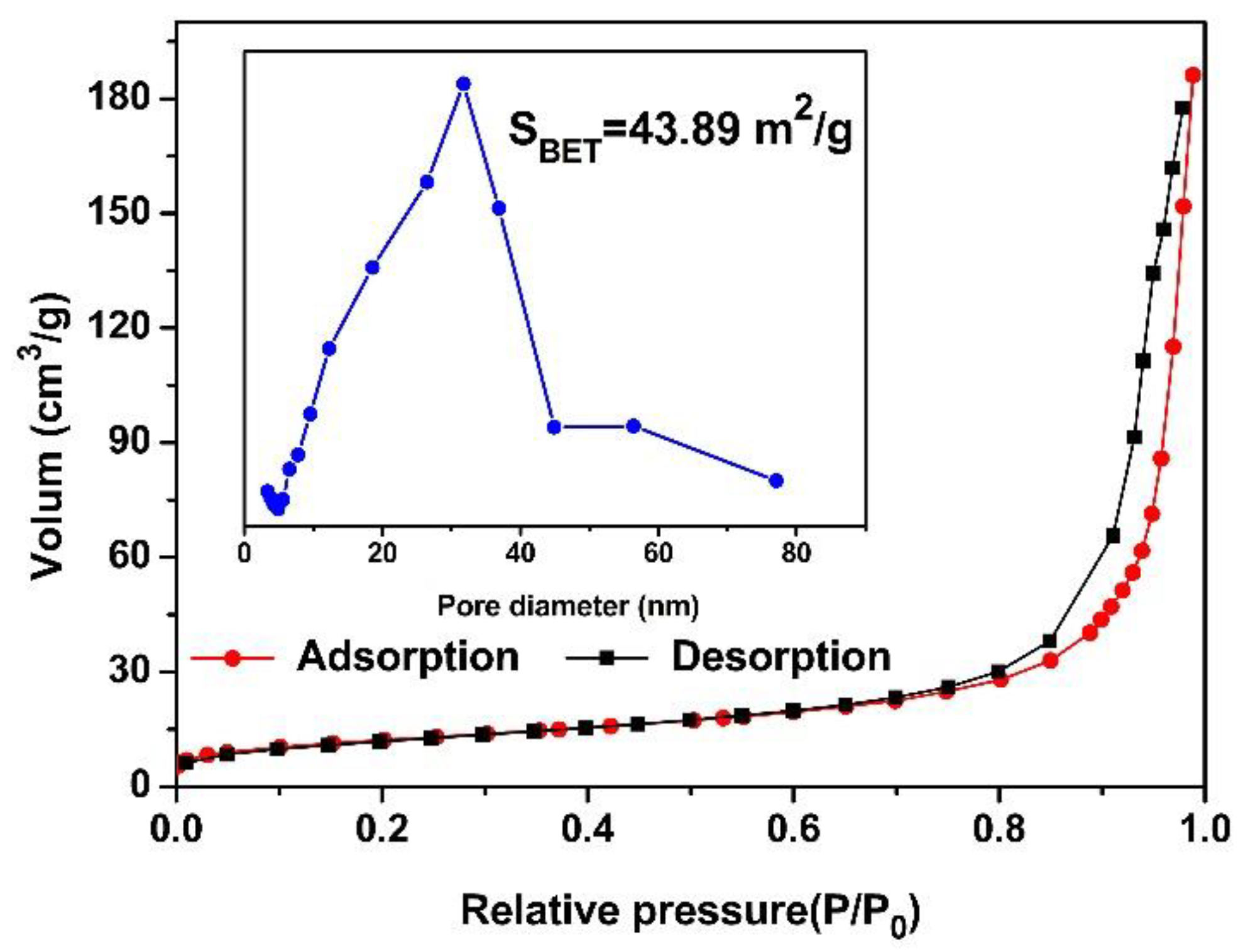
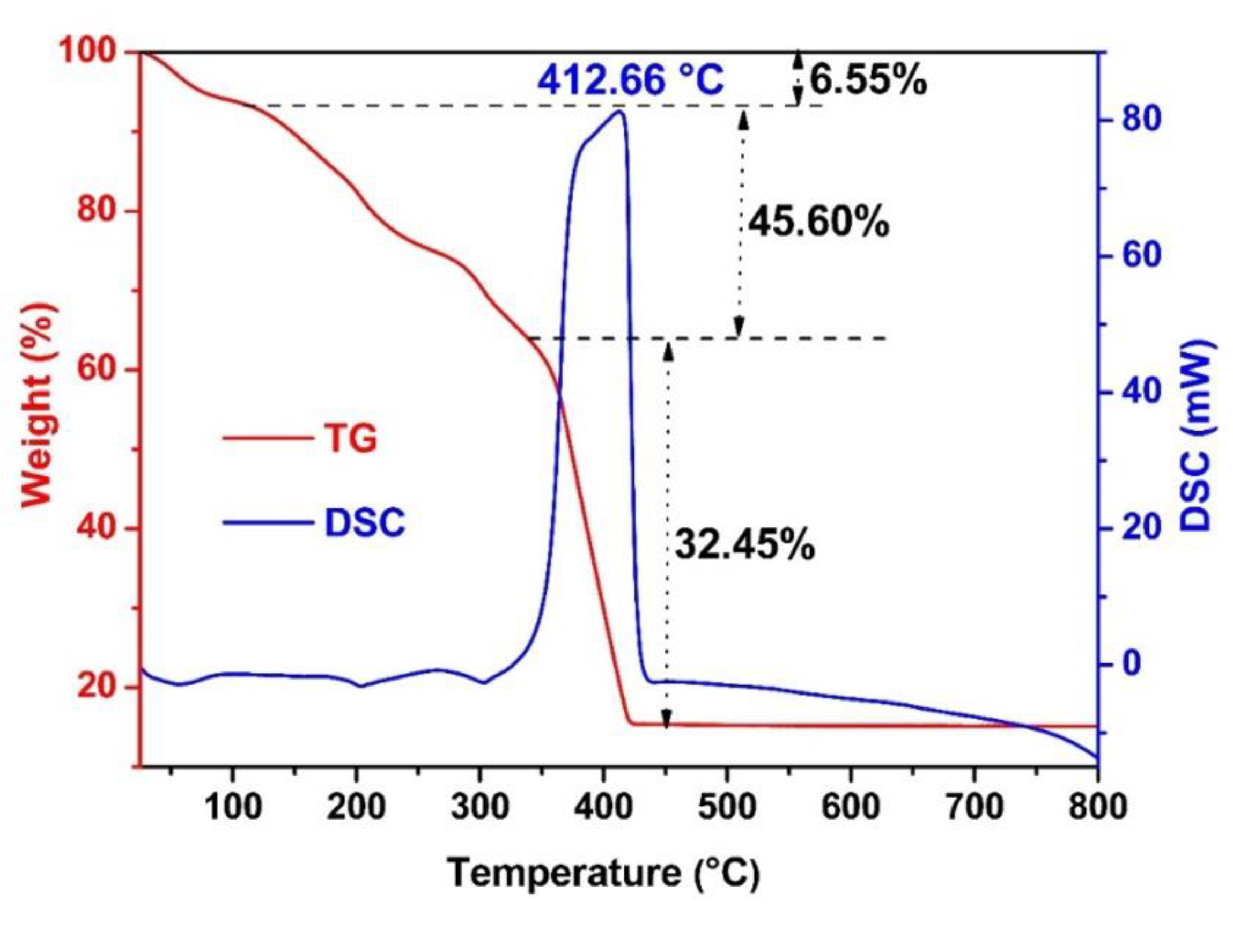
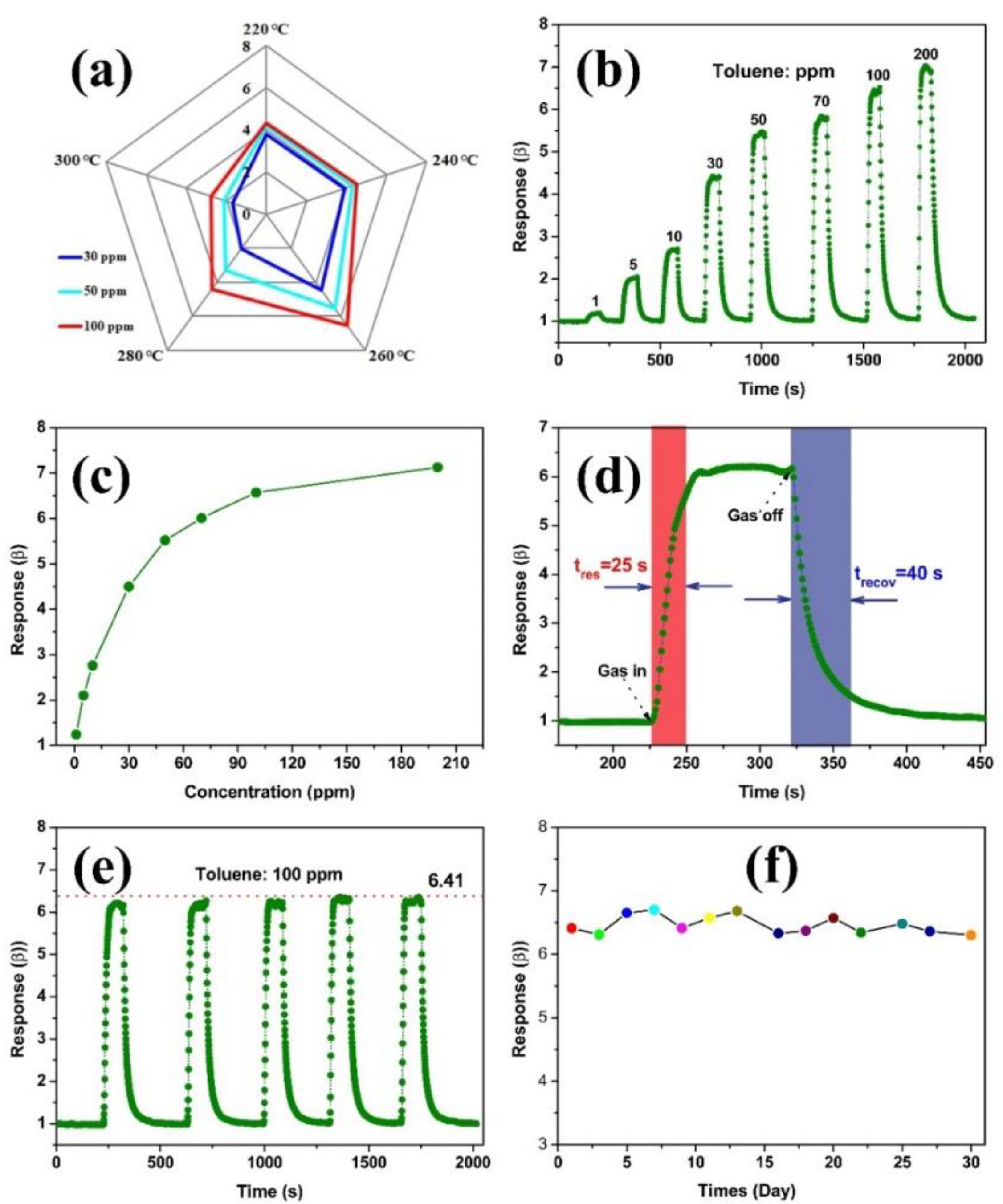
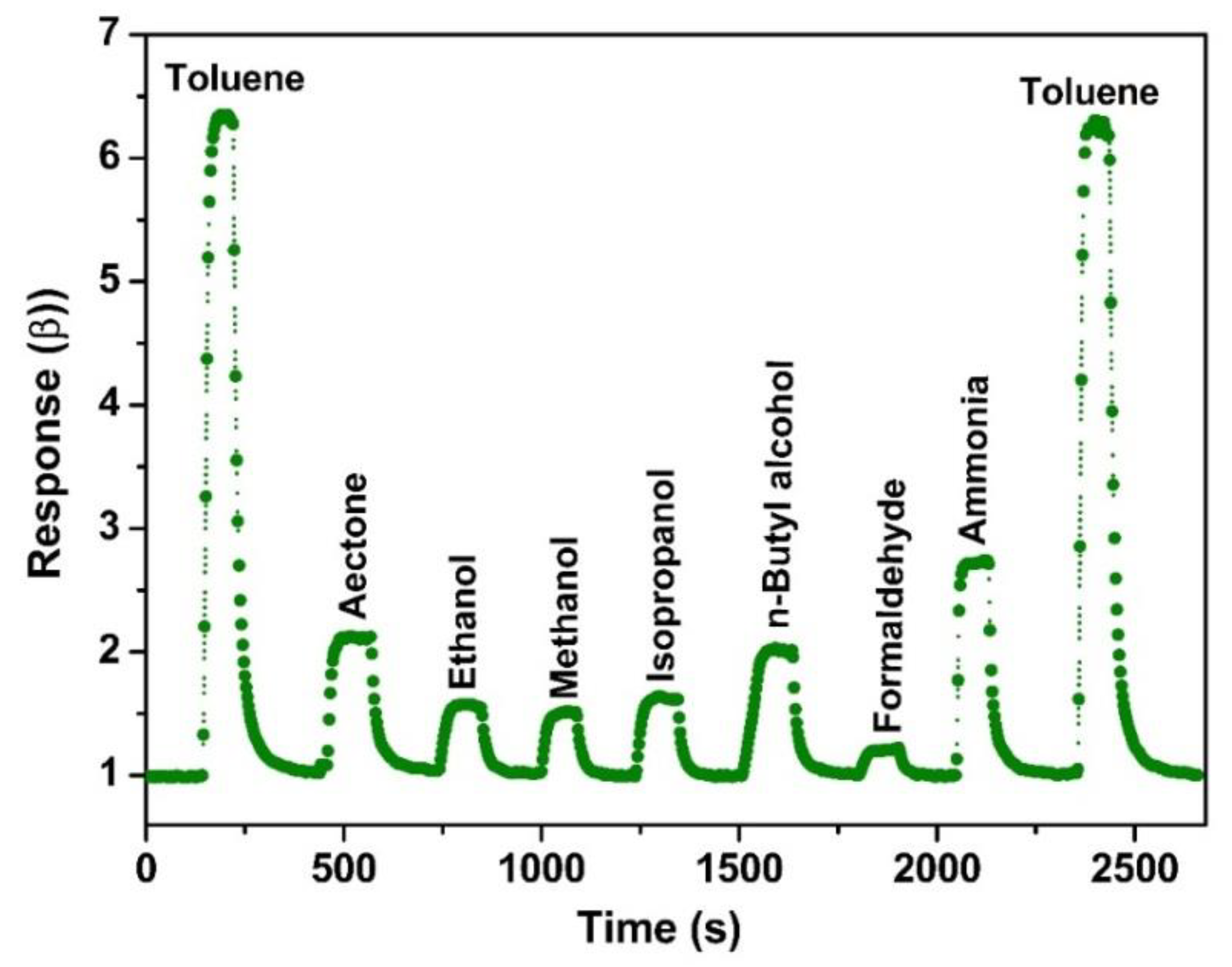
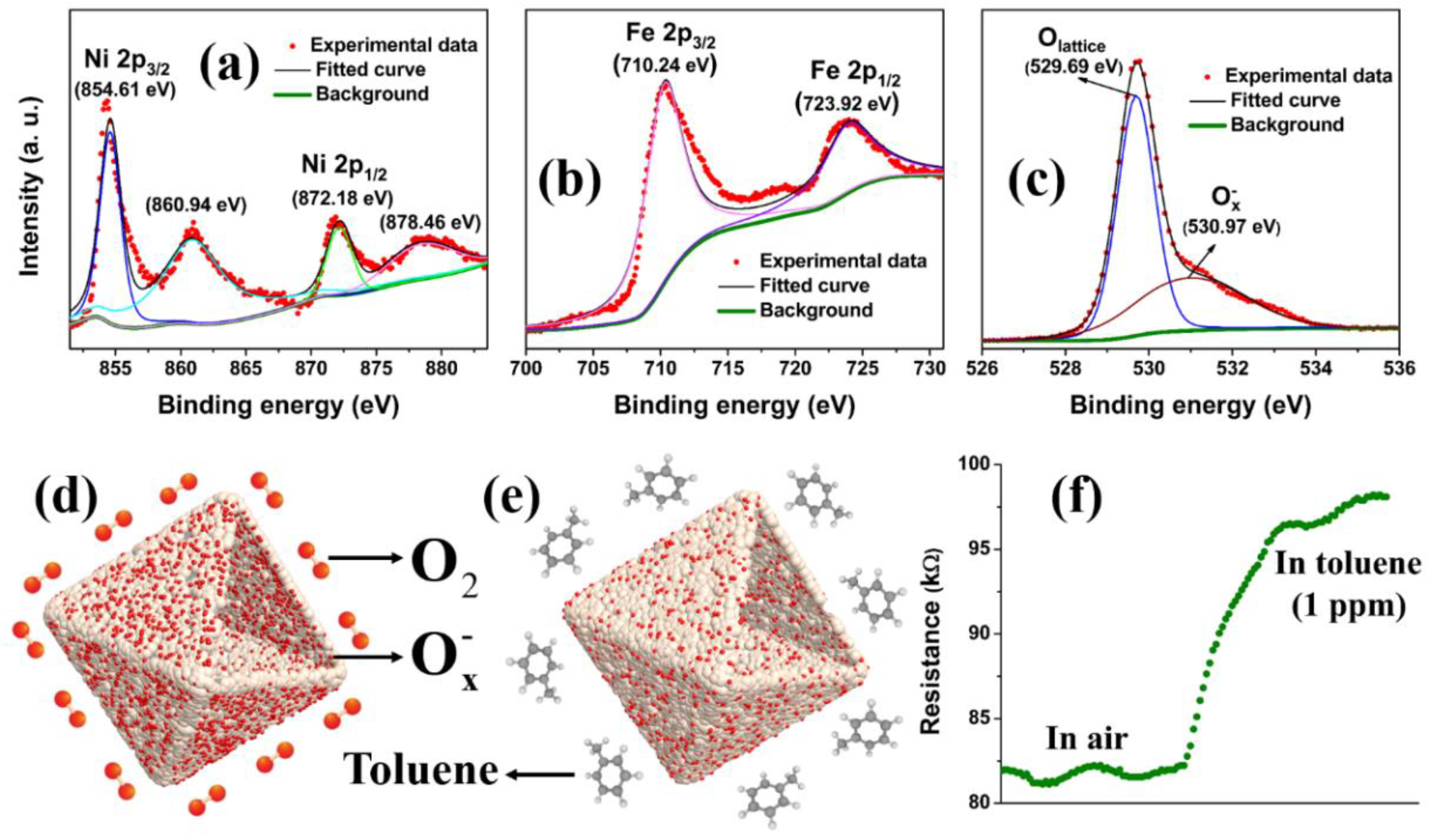
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Resistive-based gas sensors for detection of benzene, toluene and xylene (BTX) gases: A review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4342–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Tomer, V.K.; Vandna, C.; Dahiya, M.S.; Nehra, S.P.; Duhan, S.; Kailasam, K. A low temperature, highly sensitive and fast response toluene gas sensor based on In(III)-SnO2 loaded cubic mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3564–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Bortnyak, R.A.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Naotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Choi, S.J.; Yang, D.J.; Bae, J.; Park, J.; Kim, I. Highly sensitive and selective hydrogen sulfide and toluene sensors using Pd functionalized WO3 nanofibers for potential diagnosis of halitosis and lung cancer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, J.M.; Hooper, K.; Rich, C.H. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of toluene: A review. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 94, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, M.; Takagi, M.; Walterfang, M.; Lubman, D.I. Toluene misuse andlong-term harms: A systematic review of the neuropsychological andneuroimaging literature. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2008, 32, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.M.; Naik, G.K.; Lee, H.J.; Song, H.G.; Lee, C.R.; Lee, I.H.; Yu, Y.T. Au@NiO core-shell nanoparticles as a p-type gas sensor: Novel synthesi, characterization, and their gas sensing properties with sensing mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 268, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zou, C.; Su, Y.J.; Li, M.; Han, Y.T.; Kong, E.S.W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.F. An ultrasensitive NO2 gas sensor based on a hierarchical Cu2O/CuO mesocrystal nanoflower. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17120–17131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ikram, M.; Lv, H.; Chang, J.B.; Li, Z.K.; Ma, L.F.; Rehman, A.U.; Lu, G.; Chen, J.H.; et al. Facile synthesis of highly dispersed Co3O4 nanoparticles on expanded, thin black phosphorus for a ppb-level NO2 gas sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1576–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Lim, K.; Park, S.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, J.H. Hollow spheres of CoCr2O4-Cr2O3 mixed oxides with nanoscale heterojunctions for exclusive detection of indoor xylene. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10767–10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigiani, L.; Maccato, C.; Carraro, G.; Gasparotto, A.; Sada, C.; Comini, E.; Barreca, D. Tailoring vapor-phase fabrication of Mn3O4 nanosystems: From synthesis to gas-sensing applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2962–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.C.; Du, S.F.; Wang, Y.D. Monodisperse ZnFe2O4 nanospheres synthesized by a nonaqueous route for a highly selective low-ppm-level toluene gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virumbrales, M.; Regino, S.P.; Torralvo, M.J.; Veronica, B.G. Mesoporous Silica Matrix as a Tool for Minimizing Dipolar Interactions in NiFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.Z.; Sun, F.F.; Dai, S.T.; Lin, X.; Sun, K.M.; Wang, X.F. Hollow NiFe2O4 microspindles derived from Ni/Fe bimetallic MOFs for highly sensitive acetone sensing at low operating temperatures. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Ma, W.; Jiang, F.; Cao, E.S.; Sun, K.M.; Cheng, L.; Song, X.Z. Prussian blue analogue derived porous NiFe2O4 nanocubes for low concentration acetone sensing at low working temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lou, Z.; Deng, J.N.; Wang, L.L. Structure-driven efficient NiFe2O4 materials for ultra-fast response electronic sensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 225, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, W.L. The effect of microstructure on the gas properties of NiFe2O4 sensors: Nanotube and nanoparticle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, S.A.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, H.; Miura, N. Selective NO2 detection using YSZ-based amperometric sensor attached with NiFe2O4 (+Fe2O3) sensing electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Z.; Meng, Y.L.; Chen, X.; Sun, K.M.; Wang, X.F. Hollow NiFe2O4 hexagonal biyramids for high-performance n-propanol sensing at low temperature. New J. Chem. 2015, 5, 76229–76248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.F.; Jiang, D.L.; Zheng, C.M. The preparation and gas-sensing properties of NiFe2O4 nanocubes and nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 739–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.S.; Kuřitka, I.; Vilčáková, J.; Machovský, M.; Škoda, D.; Urbánek, P.; Masař, M.; Gořalik, M.; Urbánek, M.; Kalina, L.; et al. Polypropylene Nanocomposite Filled with Spinel Ferrite NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles and In-Situ Thermally-Reduced Graphene Oxide for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Application. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, X.D.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, H.B.; Xia, F.; Xiao, J.Z. Effects of CoFe2O4 electrode microstructure on the sensing properties for mixed potential NH3 sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, B.C.; Li, Y.C. Facile synthesis of hollow MnFe2O4 nanoboxes based on galvanic replacement reaction for fast and sensitive VOCs sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlan, C.; Tudorache, F.; Pui, A. Increased sensibility of mixed ferrite humidity sensors by subsequent heat treatment. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2017, 14, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virlan, C.; Tudorache, F.; Pui, A. Tertiary NiCuZn ferrites for improved humidity sensors: A systematic study. Arab. J Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.D.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y.D. Templated synthesis of nanostructured materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2610–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovich, N.D.; Stein, A. Controlling macro- and mesostructures with hierarchical porosity through combined hard and soft templating. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3721–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.L.; Lin, L.Q.; Sun, D.H.; Chen, H.M.; Yang, D.P.; Li, Q.B. Bio-inspired synthesis of metal nanomaterials and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6330–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.H.; Tan, C.L.; Sindoro, M.; Zhang, H. Hybrid micro/nano-structures derived from metal-organic frameworks: Preparation and applications in energy storage and conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2660–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Mahmood, A.; Zou, R.Q.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic frameworks and their derived nanostructures for electrochemical energy storage and conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1837–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Li, Z.H.; Garcia, H. Catalysis and photocatalysis by metal organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8134–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stassen, I.; Burtch, N.; Talin, A.; Falcaro, P.; Allendorf, M.; Ameloot, R. An updated roadmap for the integration of metal-organic frameworks with electronic devices and chemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3185–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.X.; Yang, Y.W. Metal-Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Drug/Cargo Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606134–1606153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.X.; Zhao, G.X.; Chen, C.L.; Chai, Z.F.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X.K. Metal-organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.S.; Bruggen, B.V. Metal-organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, B.B.; Yuan, X.Z.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.B.; Xiong, T.; Zeng, G.M. State-of-the-art advances and challenges of iron-based metal organic frameworks from attractive features, synthesis to multifunctional applications. Small 2018, 15, 1803088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.D.; Cao, R.G.; Jeong, S.; Cho, J. Spindle-like mesoporous α-Fe2O3 anode material prepared from MOF template for high-rate lithium batteries. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4988–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, T. MOF-derived 1D α-Fe2O3/NiFe2O4 heterojunction as efficient sensing materials of acetone vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhng, Y.L.; Jia, C.W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Kong, Q.; Chen, G.; Guan, H.T.; Dong, C.J. Highly Sensitive and Selective Toluene Sensor of Bimetallic Ni/Fe-MOFs Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nanorods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 9450–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, X.C.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.D.; Djerdj, I. Combustion synthesis of porous Pt-functionalized SnO2 sheets for isopropanol gas detection with a significant enhancement in response. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 20089–20095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Jiang, M.; Tao, Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Lu, Y.X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.D. Nonaqueous synthesis of Pd-functionalized SnO2/In2O3 nanocomposites for excellent butane sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Lutterotti, L. Method for the simultaneous determination of anisotropic residual stresses and texture by X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Z.; Jiang, J.X.; Sun, D.M.; Qian, X.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, L.C.; Wang, Z.W.; Chai, X.L.; Gan, L.H.; Liu, M.X. A general strategy to synthesize high-level N-doped porous carbons via Schiff-base chemistry for supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 12334–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, T.T.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, T. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) derived hierarchical Co3O4 structures as efficient sensing materials for acetone detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9765–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Kwak, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H. Co3O4−SnO2 Hollow Heteronanostructures: Facile Control of Gas Selectivity by Compositional Tuning of Sensing Materials via Galvanic Replacement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7877–7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, X.W.; Sun, H.B.; Sun, P.; Liang, X.S.; Liu, F.M.; Hu, X.L.; Lu, G.Y. Nanosheet-Assembled ZnFe2O4 Hollow Microspheres for High-Sensitive Acetone Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15414–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.X.; Li, H.R.; Xie, L.Z.; Wang, F.; Deng, H.; Chang, F.Z.; Sun, Y.Z. Flower-like NiO nanostructures synthesized by electrodeposition method for efficient detection of toluene gas. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 92128–92133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; He, Y.H.; Nagashima, K.; Meng, G.; Dai, T.T.; Tong, B.; Deng, Z.H.; Wang, S.M.; Zhu, N.W.; Yanagida, T.; et al. Discrimination of VOCs molecules via extracting concealed features from a emperature-modulated p-type NiO sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J.D.; Su, X.T. 3D flower- and 2D sheet-like CuO nanostructures: Microwave-assisted synthesis and application in gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Deng, J.N.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, T. Nanoparticles-assembled Co3O4 nanorods p-type nanomaterials: One-pot synthesis and toluene-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.H.; Huang, B.Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Xie, E.Q. Synthesis of porous Co3O4 nanonetworks to detect toluene at low concentration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 19327–19332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T. Facile construction of Co3O4 porous microspheres with enhanced acetone gas sensing performances. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Proc. 2019, 101, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Xu, Y.; Rong, Z.; Cheng, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Huo, L. Highly toluene sensing performance based on monodispersed Cr2O3 porous microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 174, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.P.; Zhang, D.M.; Hu, J.C.; Wang, H.P.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, K.J.; Rong, Q.; Zhou, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; et al. Excellent toluene gas sensing properties of molecular imprinted Ag-LaFeO3 nanostructures synthesized by microwave-assisted process. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 111, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ao, S.S.R.; Li, G.D.; Gao, Q.; Zou, X.X.; Wei, C.D. Enhanced sensing performance to toluene and xylene by construvting NiGa2O4-NiO heterostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Gao, K.; Shen, G.; Xue, P.; Wang, D.; Hu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X. Ordered mesoporous NiFe2O4 with ultrathin framework for low-ppb toluene sensing. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, Y.C.; Lee, J.H. Dual role of multiroom-structured Sn-doped NiO microspheres for ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of xylene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16605–16612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Hu, Q.; Mu, X.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Bai, J.L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.Z.; Shen, Z.X.; Xie, E.Q. A low temperature and highly sensitive ethanol sensor based on Au modified In2O3 nanofibers by coaxial electrosponning. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 10935–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, M.E.; Koplin, T.J.; Simon, U. Metal and metal oxide nanoparticles inchemiresistors: Does the nanoscale matter? Small 2006, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorache, F.; Popa, P.D.; Dobromir, M.; Iacomi, F. Studies on the structure and gas sensing properties of nickel–cobalt ferrite thin films prepared by spin coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 178, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, A.M.; Lisa, G.; Iordan, A.R.; Tudorache, F.; Petrila, I.; Borhan, A.I.; Palamaru, M.N.; Mihailescu, C.; Leontie, L.; Munteanu, C. Ni ferrite highly organized as humidity sensors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 156, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurlo, T.A.; Bârsan, N.; Weimar, U. Basics of oxygen and SnO2 interaction: Work function change and conductivity measurements. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 118, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, R.S.; Lai, X.Y.; Wan, J.W.; Lin, G.; Liu, D. Controlled synthesis and enhanced toluene-sensing properties of mesoporous NixCo1-xFe2O4 nanostructured microspheres with tunable composite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Microstructures | Concentration (ppm) | T (°C) | Response | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiO | Flower-like | 5 | 250 | 2.63 | 0.5 ppm | [48] |
| NiO | Nanoparticle | 200 | 210 | 1.6 | 100 ppm | [49] |
| CuO | Flower | 500 | 260 | 2.5 | 10 ppm | [50] |
| Co3O4 | Nanorod | 200 | 200 | 35 | 10 ppm | [51] |
| Co3O4 | Nanosheet | 100 | 150 | 6.08 | 1 ppm | [52] |
| Co3O4 | Microsphere | 100 | 180 | 2.2 | [53] | |
| Cr2O3 | Microsphere | 100 | 170 | 33.64 | 1 ppm | [54] |
| Ag-LaFeO3 | Nanoparticle | 5 | 215 | 24 | 5 ppm | [55] |
| NiGa2O4-NiO | Nanosphere | 100 | 230 | 12.7 | 0.5 ppm | [56] |
| NiFe2O4 | Ordered mesoporous | 1 | 230 | 77.3 | 2 ppb | [57] |
| NiFe2O4 | Hexagonal biyramid | 200 | 140 | 5.73 | 5 ppm | [20] |
| NiFe2O4 | Nano-octahedron | 100 | 260 | 6.41 | 1 ppm | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Jia, C.; Wang, Q.; Kong, Q.; Chen, G.; Guan, H.; Dong, C. MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
Zhang Y, Jia C, Wang Q, Kong Q, Chen G, Guan H, Dong C. MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(8):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanlin, Chaowei Jia, Qiuyue Wang, Quan Kong, Gang Chen, Hongtao Guan, and Chengjun Dong. 2019. "MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor" Nanomaterials 9, no. 8: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059
APA StyleZhang, Y., Jia, C., Wang, Q., Kong, Q., Chen, G., Guan, H., & Dong, C. (2019). MOFs-Derived Porous NiFe2O4 Nano-Octahedrons with Hollow Interiors for an Excellent Toluene Gas Sensor. Nanomaterials, 9(8), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081059