Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Realistic Doses of Benchmark Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes towards Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source and Characterization of MWCNT
2.2. Cells and Experimental Treatments
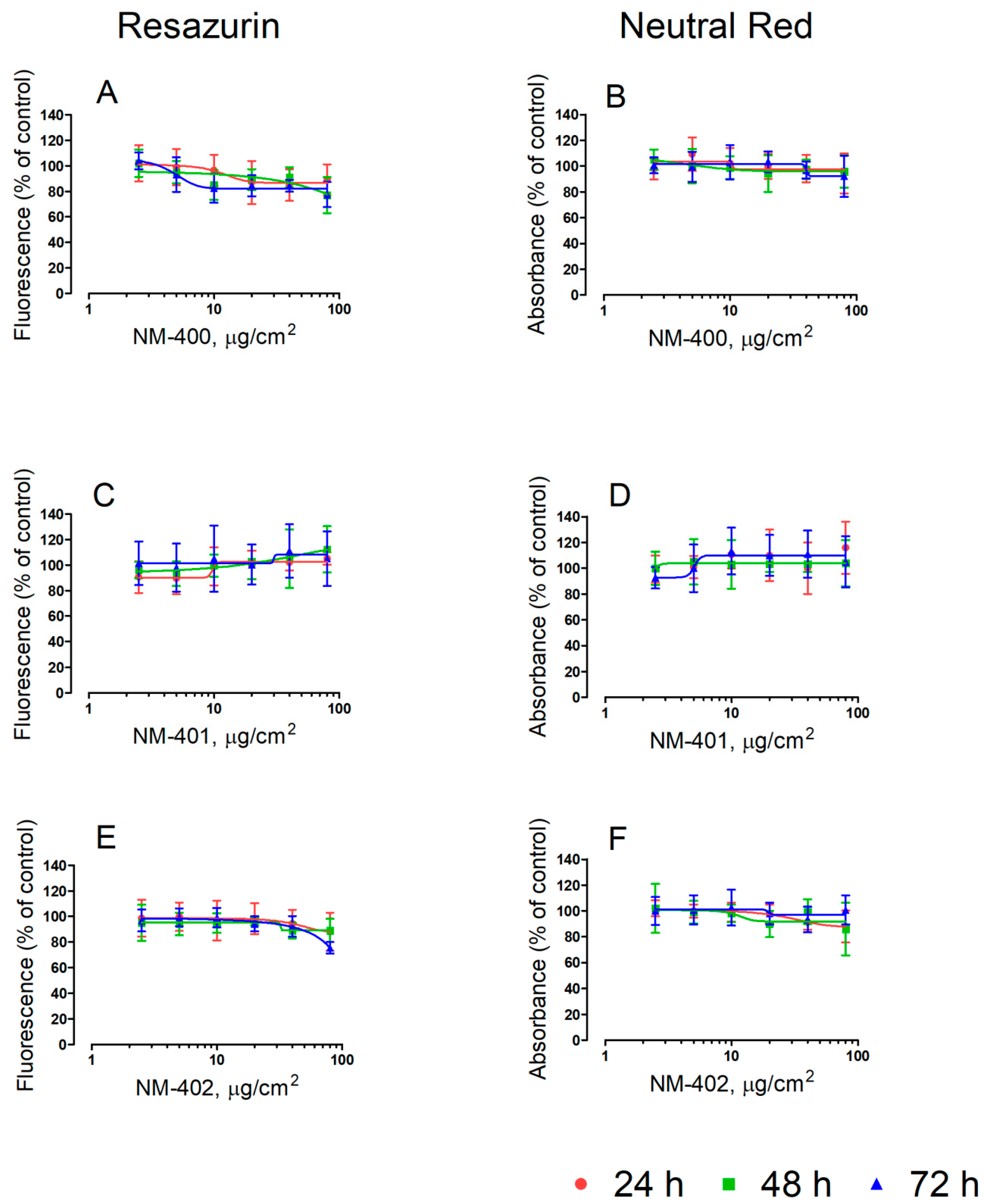
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Nitrite Concentration
2.5. Real Time PCR
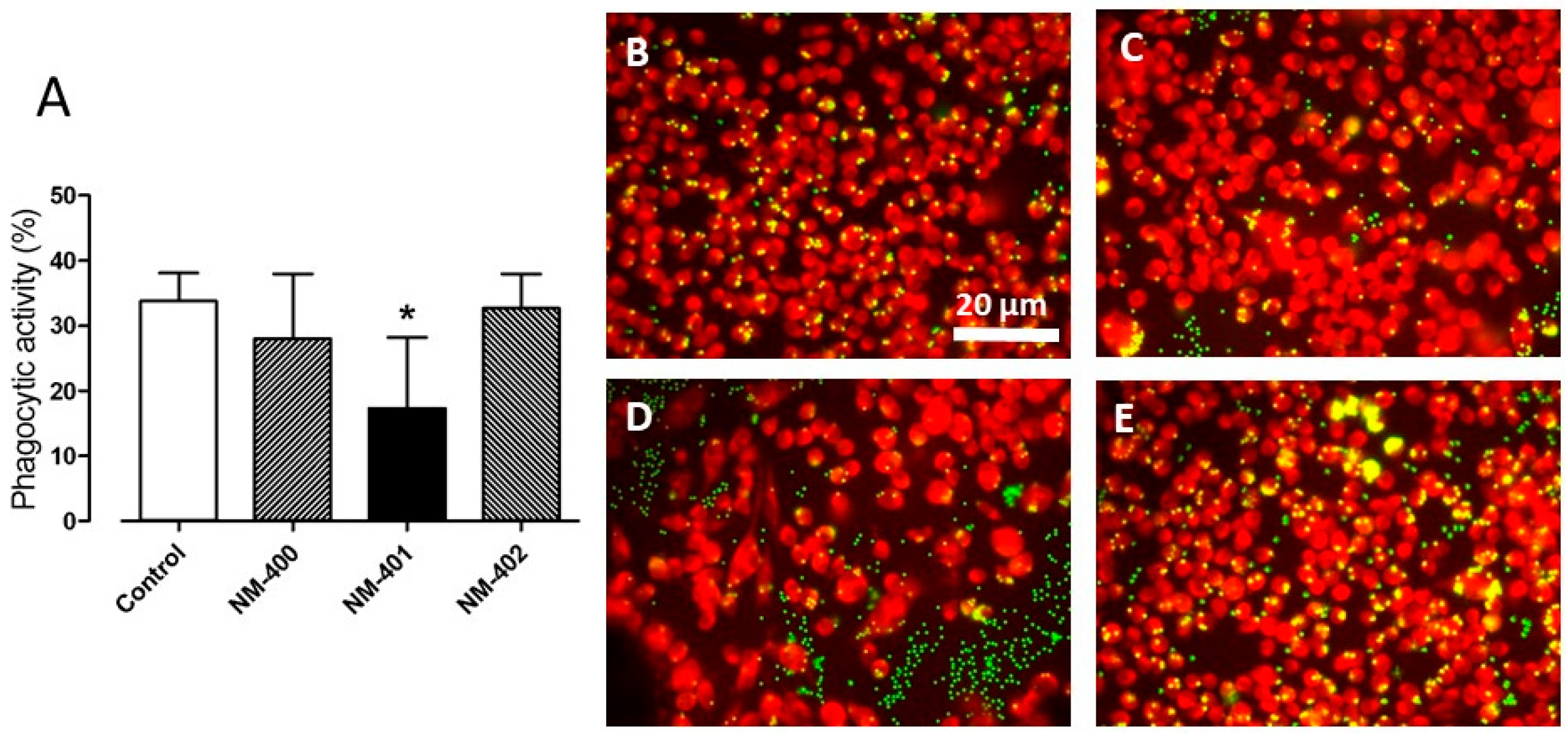
2.6. Phagocytic Activity
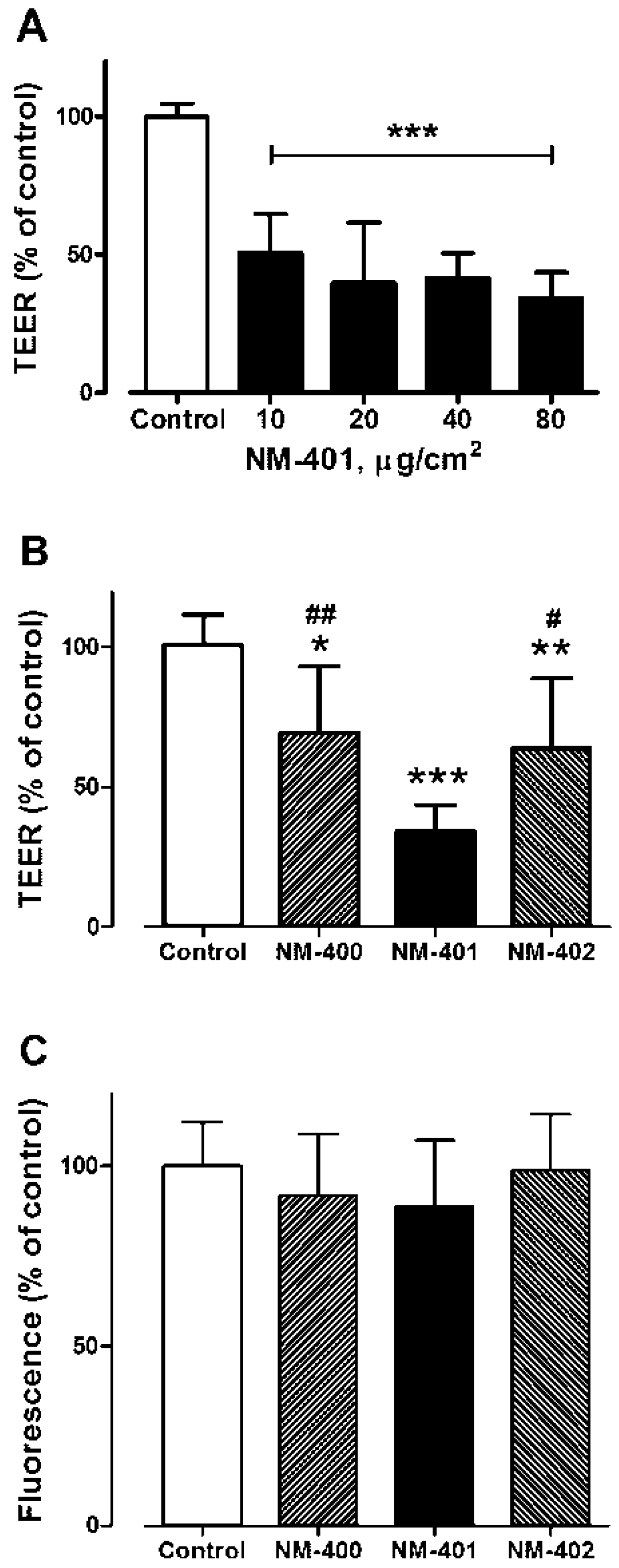
2.7. Trans-Epithelial Electric Resistance
2.8. Statistics
2.9. Reagents
3. Results
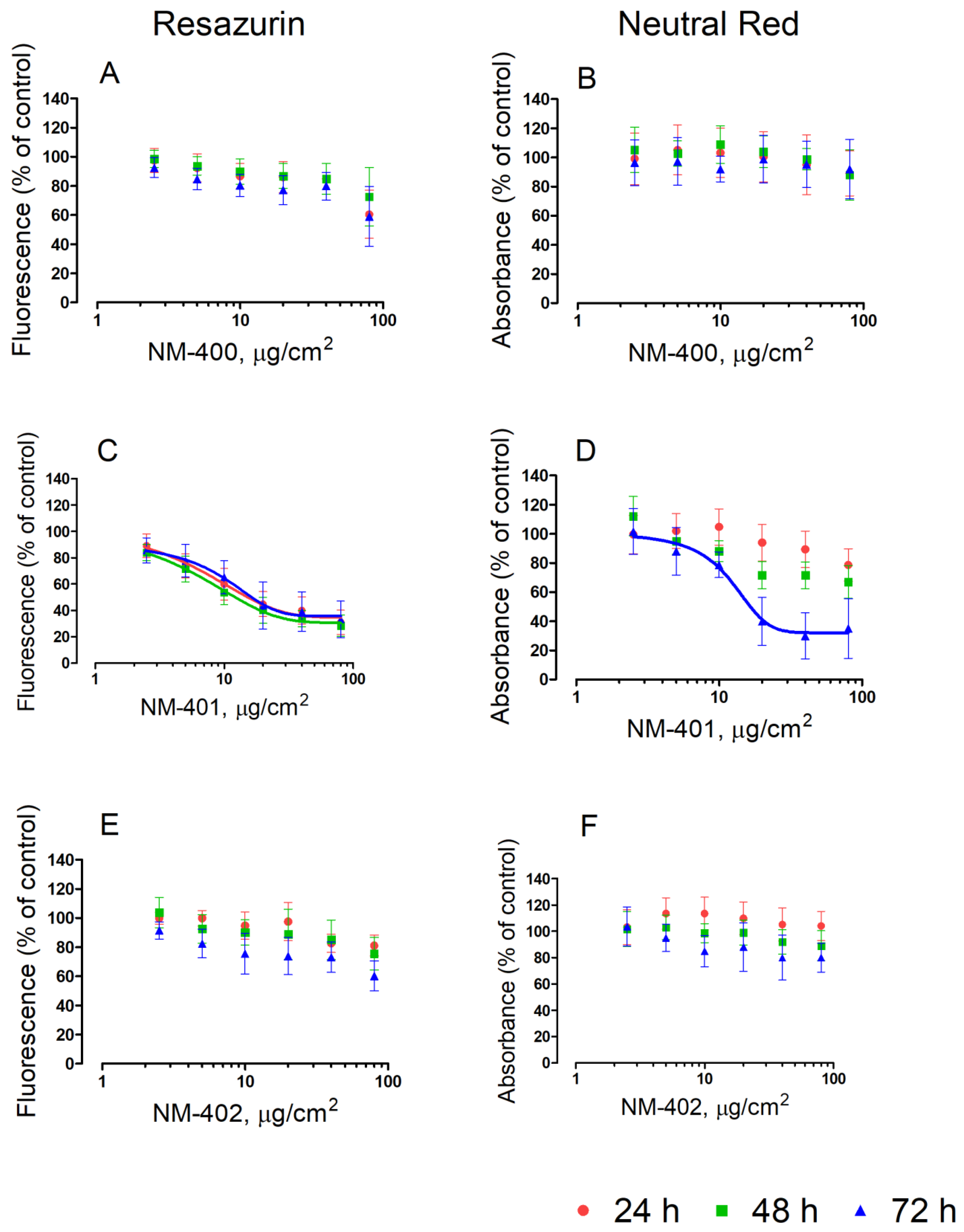
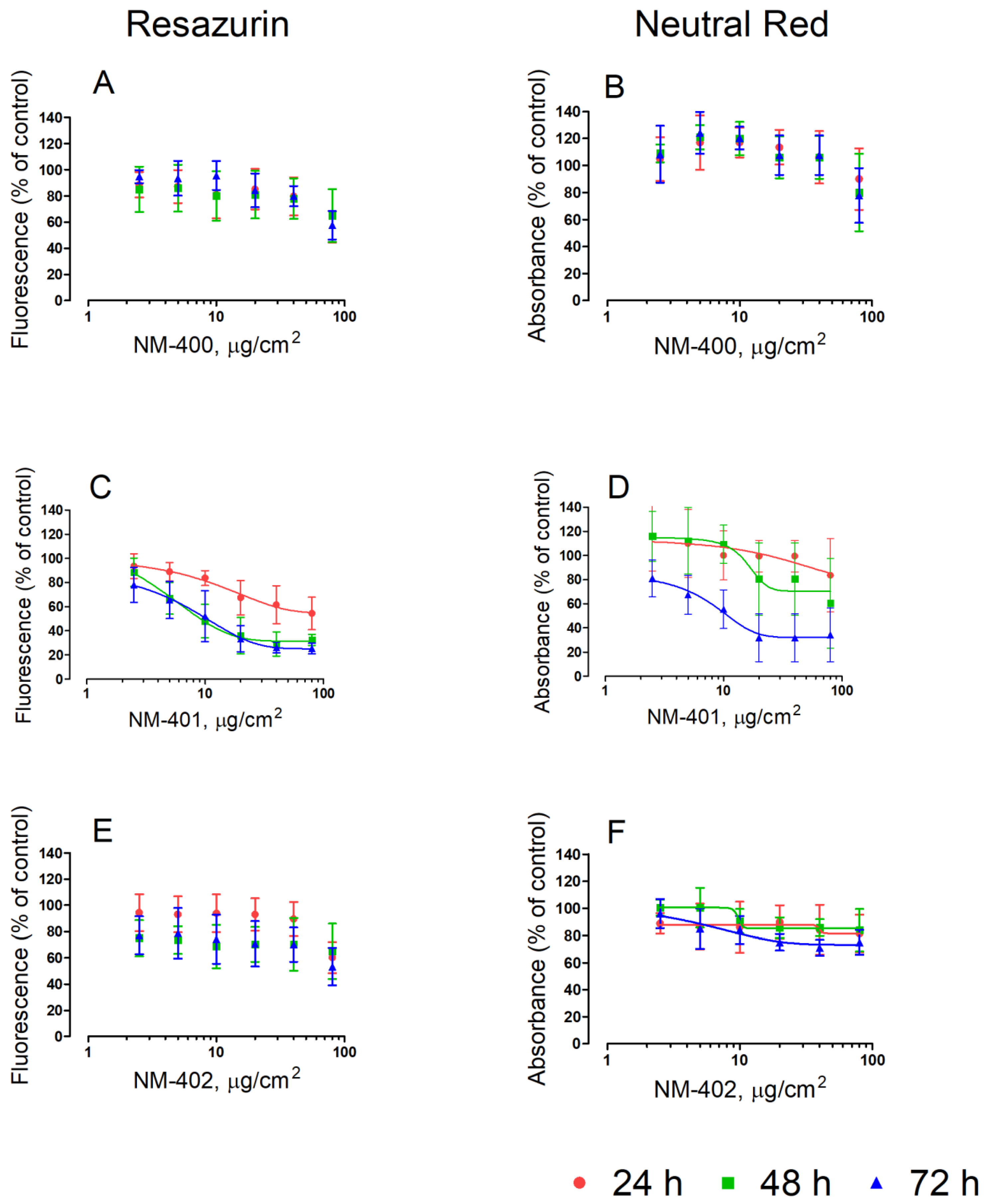
3.1. Viability
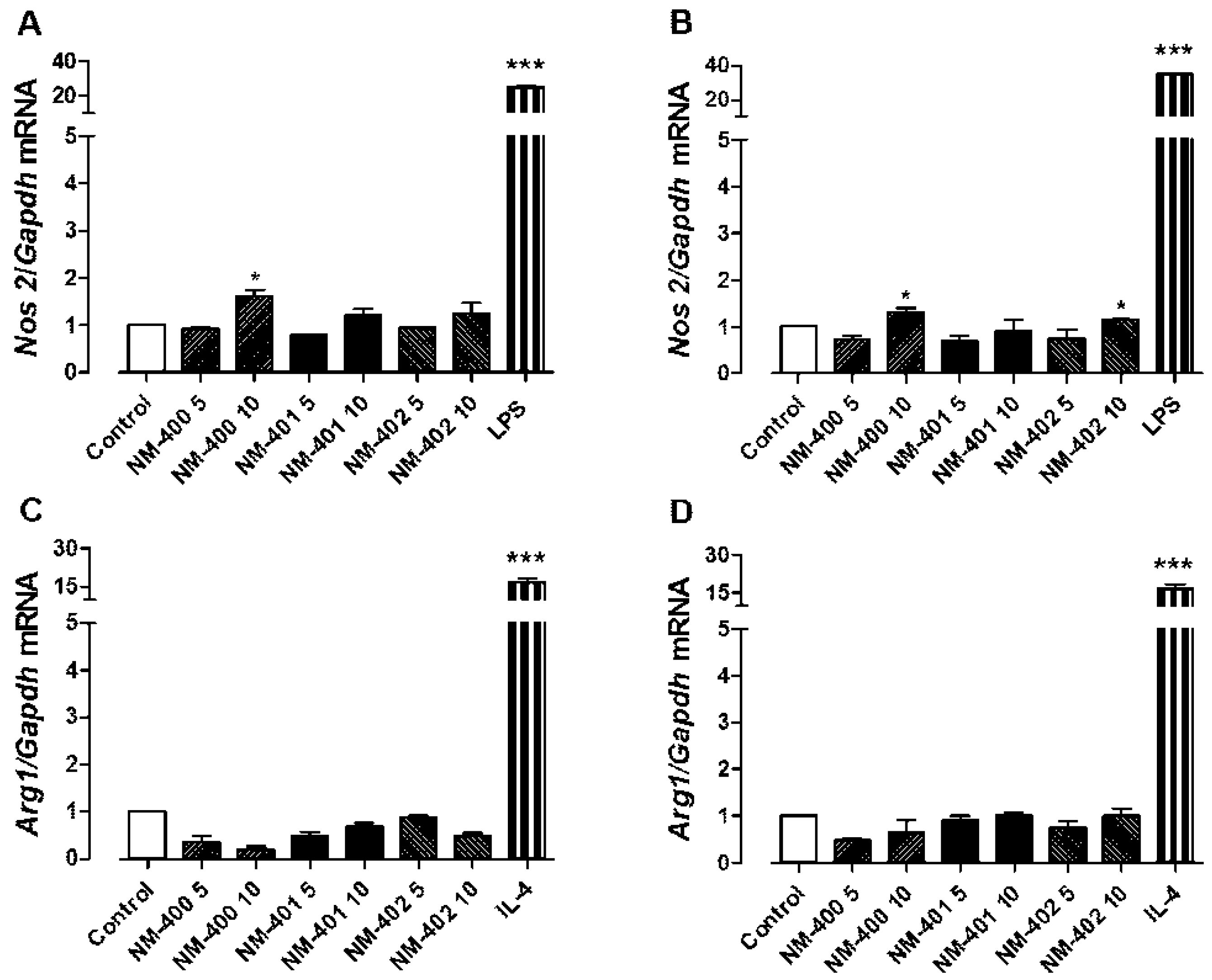
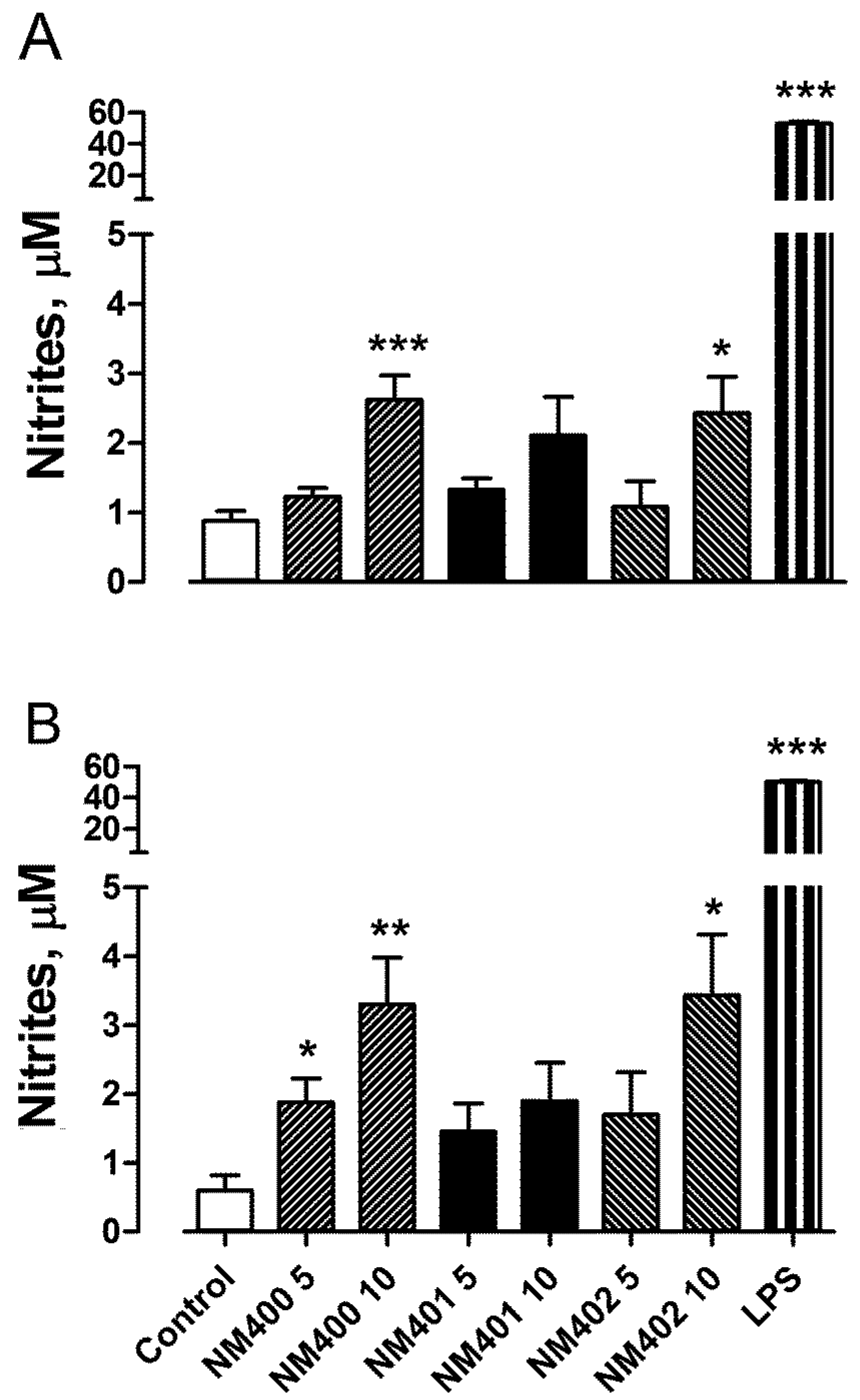
3.2. Macrophage Activation and Phagocytic Activity
3.3. Changes in Trans-Epithelial Electrical Resistance in Airway Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Endo, M. Grow Carbon-Fibers in the Vapor-Phase. Chemtech 1988, 18, 568–576. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, S. Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowack, B.; David, R.M.; Fissan, H.; Morris, H.; Shatkin, J.A.; Stintz, M.; Zepp, R.; Brouwer, D. Potential release scenarios for carbon nanotubes used in composites. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdorster, G.; Castranova, V.; Asgharian, B.; Sayre, P. Inhalation Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) and Carbon Nanofibers (CNF): Methodology and Dosimetry. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2015, 18, 121–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Aitken, R.; Tran, L.; Stone, V.; Duffin, R.; Forrest, G.; Alexander, A. Carbon nanotubes: a review of their properties in relation to pulmonary toxicology and workplace safety. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschberger, K.; Johnston, H.J.; Stone, V.; Aitken, R.J.; Hankin, S.M.; Peters, S.A.; Tran, C.L.; Christensen, F.M. Review of carbon nanotubes toxicity and exposure--appraisal of human health risk assessment based on open literature. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 40, 759–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanone, S.; Andujar, P.; Kermanizadeh, A.; Boczkowski, J. Determinants of carbon nanotube toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 2063–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Health 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortarea, S.; Barosova, H.; Clift, M.J.D.; Wick, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Human Asthmatic Bronchial Cells Are More Susceptible to Subchronic Repeated Exposures of Aerosolized Carbon Nanotubes At Occupationally Relevant Doses Than Healthy Cells. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIOSH. Occupational Exposure to Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers. In Current Intelligence Bulletin 65; 2013. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2013-145/pdfs/2013-145.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Phuyal, S.; Kasem, M.; Rubio, L.; Karlsson, H.L.; Marcos, R.; Skaug, V.; Zienolddiny, S. Effects on human bronchial epithelial cells following low-dose chronic exposure to nanomaterials: A 6-month transformation study. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 44, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, H.K.L.; Hansen, J.S.; Elfving, B.; Lund, S.P.; Kyjovska, Z.O.; Loft, S.; Barfod, K.K.; Jackson, P.; Vogel, U.; Hougaard, K.S. Airway exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes disrupts the female reproductive cycle without affecting pregnancy outcomes in mice. Part Fibre. Toxicol. 2017, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hougaard, K.S.; Jackson, P.; Kyjovska, Z.O.; Birkedal, R.K.; De Temmerman, P.J.; Brunelli, A.; Verleysen, E.; Madsen, A.M.; Saber, A.T.; Pojana, G.; et al. Effects of lung exposure to carbon nanotubes on female fertility and pregnancy. A study in mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 41, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanizadeh, A.; Vranic, S.; Boland, S.; Moreau, K.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Gaiser, B.K.; Andrzejczuk, L.A.; Stone, V. An in vitro assessment of panel of engineered nanomaterials using a human renal cell line: cytotoxicity, pro-inflammatory response, oxidative stress and genotoxicity. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, L.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Aziz, S.A.; Wu, D.; Williams, A.; Yauk, C.L.; White, P.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U.; Halappanavar, S. Multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced genotoxic, inflammatory and pro-fibrotic responses in mice: Investigating the mechanisms of pulmonary carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2017, 823, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louro, H.; Pinhao, M.; Santos, J.; Tavares, A.; Vital, N.; Silva, M.J. Evaluation of the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of benchmark multi-walled carbon nanotubes in relation to their physicochemical properties. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 262, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.; Kling, K.; Jensen, K.A.; Clausen, P.A.; Madsen, A.M.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U. Characterization of genotoxic response to 15 multiwalled carbon nanotubes with variable physicochemical properties including surface functionalizations in the FE1-Muta(TM) mouse lung epithelial cell line. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, S.S.; Knudsen, K.B.; Jackson, P.; Weydahl, I.E.; Saber, A.T.; Wallin, H.; Vogel, U. Multi-walled carbon nanotube-physicochemical properties predict the systemic acute phase response following pulmonary exposure in mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, H.H.; Holt-Casper, D.; Grainger, D.W.; Ghandehari, H. Nanoparticle Uptake: The Phagocyte Problem. Nano Today 2015, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouser, L.; Paudyal, B.; Kaur, A.; Stenbeck, G.; Jones, L.A.; Abozaid, S.M.; Stover, C.M.; Flahaut, E.; Sim, R.B.; Kishore, U. Human Properdin Opsonizes Nanoparticles and Triggers a Potent Pro-inflammatory Response by Macrophages without Involving Complement Activation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, K.; Mast, J.; De Temmerman, P.-J.; Verleysen, E.; Waegeneers, N.; Van Steen, F.; Pizzolon, J.C.; De Temmerman, L.; Van Doren, E.; Jensen, K.A.; et al. Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes, NM-400, NM-401, NM-402, NM-403: Characterisation and Physico-Chemical Properties; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ono-Ogasawara, M.; Myojo, T. A proposal of method for evaluating airborne MWCNT concentration. Ind. Health 2011, 49, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, A.M.; Louro, H.; Antunes, S.; Quarre, S.; Simar, S.; De Temmerman, P.J.; Verleysen, E.; Mast, J.; Jensen, K.A.; Norppa, H.; et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of nanosized titanium dioxide, synthetic amorphous silica and multi-walled carbon nanotubes in human lymphocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repetto, G.; del Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Bussolati, O.; Bianchi, M.G.; Barilli, A.; Balasubramanian, C.; Bellucci, S.; Bergamaschi, E. Non-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes alter the paracellular permeability of human airway epithelial cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 178, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misko, T.P.; Schilling, R.J.; Salvemini, D.; Moore, W.M.; Currie, M.G. A fluorometric assay for the measurement of nitrite in biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 214, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristo, L.; Mc Carthy, S.; Paton, K.; Movia, D.; Prina-Mello, A. Interplay between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated-autophagy in unfunctionalised few-layer graphene-exposed macrophages. 2d Mater. 2018, 5, 045033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.G.; Franchi-Gazzola, R.; Reia, L.; Allegri, M.; Uggeri, J.; Chiu, M.; Sala, R.; Bussolati, O. Valproic acid induces the glutamate transporter excitatory amino acid transporter-3 in human oligodendroglioma cells. Neuroscience 2012, 227, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A. Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 25, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.C.; Morni, W.Z.; Putra, D.F.; Huang, C.L.; Li, C.C.; Hsieh, J.F. Vaccination enhances early immune responses in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei after secondary exposure to Vibrio alginolyticus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, L.B.; Bosquillon, C.; Dailey, L.A.; Delattre, L.; Martin, G.P.; Evrard, B.; Forbes, B. Sparing methylation of beta-cyclodextrin mitigates cytotoxicity and permeability induction in respiratory epithelial cell layers in vitro. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristo, L.; Movia, D.; Bianchi, M.G.; Allegri, M.; Mohamed, B.M.; Bell, A.P.; Moore, C.; Pinelli, S.; Rasmussen, K.; Riego-Sintes, J.; et al. Proinflammatory Effects of Pyrogenic and Precipitated Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles in Innate Immunity Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Bussolati, O.; Barilli, A.; Zanello, P.P.; Bianchi, M.G.; Magrini, A.; Pietroiusti, A.; Bergamaschi, A.; Bergamaschi, E. Airway barrier dysfunction induced by exposure to carbon nanotubes in vitro: which role for fiber length? Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banga, A.; Witzmann, F.A.; Petrache, H.I.; Blazer-Yost, B.L. Functional effects of nanoparticle exposure on Calu-3 airway epithelial cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Gatti, R.; Movia, D.; Bianchi, M.G.; Di Cristo, L.; Fenoglio, I.; Sonvico, F.; Bergamaschi, E.; Prina-Mello, A.; Bussolati, O. Identifying contact-mediated, localized toxic effects of MWCNT aggregates on epithelial monolayers: a single-cell monitoring toxicity assay. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chortarea, S.; Clift, M.J.; Vanhecke, D.; Endes, C.; Wick, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Repeated exposure to carbon nanotube-based aerosols does not affect the functional properties of a 3D human epithelial airway model. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwal, S.; Brown, J.S.; Wang, A.; Houck, K.A.; Dix, D.J.; Kavlock, R.J.; Hubal, E.A. Informing selection of nanomaterial concentrations for ToxCast in vitro testing based on occupational exposure potential. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcal, L.; Torres Andon, F.; Di Cristo, L.; Rotoli, B.M.; Bussolati, O.; Bergamaschi, E.; Mech, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Rasmussen, K.; Riego-Sintes, J.; et al. Comprehensive In Vitro Toxicity Testing of a Panel of Representative Oxide Nanomaterials: First Steps towards an Intelligent Testing Strategy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chidekel, A.; Shaffer, T.H. Cultured human airway epithelial cells (calu-3): a model of human respiratory function, structure, and inflammatory responses. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Torr, E.E.; Mohd Jamili, N.H.; Bosquillon, C.; Sayers, I. Evaluation of differentiated human bronchial epithelial cell culture systems for asthma research. J. Allergy. (Cairo) 2012, 2012, 943982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Ma, Q. Macrophage polarization and activation at the interface of multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegri, M.; Perivoliotis, D.K.; Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Pagliaro, A.; Koklioti, M.A.; Trompeta, A.A.; Bergamaschi, E.; Bussolati, O.; Charitidis, C.A. Toxicity determinants of multi-walled carbon nanotubes: The relationship between functionalization and agglomeration. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyles, M.S.; Young, L.; Brown, D.M.; MacCalman, L.; Cowie, H.; Moisala, A.; Smail, F.; Smith, P.J.; Proudfoot, L.; Windle, A.H.; et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotube induced frustrated phagocytosis, cytotoxicity and pro-inflammatory conditions in macrophages are length dependent and greater than that of asbestos. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1513–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, S.; Grandolfo, D.; Ruenraroengsak, P.; Tetley, T.D. Functional consequences for primary human alveolar macrophages following treatment with long, but not short, multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3115–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, T.; Castranova, V.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; Baron, P.; Deye, G.J.; Li, C.; Jones, W. Effect of fiber length on glass microfiber cytotoxicity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 1998, 54, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeidler-Erdely, P.C.; Calhoun, W.J.; Ameredes, B.T.; Clark, M.P.; Deye, G.J.; Baron, P.; Jones, W.; Blake, T.; Castranova, V. In vitro cytotoxicity of Manville Code 100 glass fibers: effect of fiber length on human alveolar macrophages. Part Fibre. Toxicol. 2006, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Sun, B.; George, S.; Xia, T.; Nel, A.E.; Zink, J.I. Designed synthesis of CeO2 nanorods and nanowires for studying toxicological effects of high aspect ratio nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5366–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenoglio, I.; Aldieri, E.; Gazzano, E.; Cesano, F.; Colonna, M.; Scarano, D.; Mazzucco, G.; Attanasio, A.; Yakoub, Y.; Lison, D.; et al. Thickness of multiwalled carbon nanotubes affects their lung toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.F., Jr.; Wu, Z.; Mitra, S.; Shaw, P.K.; Holian, A. Effect of MWCNT size, carboxylation, and purification on in vitro and in vivo toxicity, inflammation and lung pathology. Part Fibre. Toxicol. 2013, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.J.; Roca, C.P.; Roh, J.Y.; Chatterjee, N.; Jeong, J.S.; Shim, I.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, P.J.; Choi, K.; Giralt, F.; et al. A systems toxicology approach on the mechanism of uptake and toxicity of MWCNT in Caenorhabditis elegans. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 239, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MWCNT | Length (nm) 1 | Thickness (nm) 1 | BET (m2/g) 1 | Main Impurities 1 (ppm) | Redox Potential (O2) | Shape 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NM-400 | 846 ± 446 | 11 ± 3 | 254.00 | Na 1345 ± 151, Al 9951 ± 31, K 97 ± 3, Ca 3 ± 2, V 0, Cr 9 ± 1, Fe 1988 ± 26, Co 693 ± 26, Ni 4 ± 0, Cu 3 ± 0, Zn 2 ± 0, Ba 1 ± 0, Pb 1 ± 0 impurities wt (%) 1.41 | ↑/= O2 | Highly bent (tangled) |
| NM-401 | 4048 ± 2371 | 67 ± 24 | 140.46 | Na 581 ± 32, Mg 0 ± 32, Al 59 ± 4, K 57 ± 9, Ca 2 ± 1, V 1 ± 0, Cr 3 ± 1, Fe 379 ± 71, Ni 2 ± 0, Cu 3 ± 3, Zn 2 ± 1, Ba 1 ± 0 wt (%) of impurities 0.11 | = O2 | Rigid wall (needle-like) |
| NM-402 | 1372 ± 836 | 11 ± 3 | 226.4 | Na 727 ± 120, Al 12955 ± 1530, K 85 ± 7, Ca 2 ± 1, V 1 ± 0, Cr 13 ± 1, Mn 9 ± 1, Fe 16321 ± 664, Co 2 ± 0, Ni 9 ± 1, Cu 4 ± 1, Zn 2 ± 0, Ba 1 ± 0 wt (%) of impurities 3.01 | ↑/= O2 | Highly bent (tangled) |
| Gene | Protein | Forward | Reverse | Melting Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arg1 | Arginase I | 5′-CAG AAG AAT GGA AGA GTC AG-3′ | 5′-GGA GTG TTG ATG TCA GTG TG-3′ | 49 |
| Nos2 | Inducible Nitric oxide synthetase (Nos2) | 5′-GTT CTC AGC CCA ACA ATA CAA GA-3′ | 5′-GTG GAC GGG TCG ATG TCA C-3′ | 59 |
| Gapdh | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 5′-TGT TCC TAC CCC CAA TGT GT-3′ | 5′-GGT CCT CAG TGT AGC CCA AG-3′ | 58 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Cristo, L.; Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Donato, F.; Garzaro, G.; Bussolati, O.; Bergamaschi, E. Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Realistic Doses of Benchmark Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes towards Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070982
Di Cristo L, Bianchi MG, Chiu M, Taurino G, Donato F, Garzaro G, Bussolati O, Bergamaschi E. Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Realistic Doses of Benchmark Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes towards Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(7):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070982
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Cristo, Luisana, Massimiliano G. Bianchi, Martina Chiu, Giuseppe Taurino, Francesca Donato, Giacomo Garzaro, Ovidio Bussolati, and Enrico Bergamaschi. 2019. "Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Realistic Doses of Benchmark Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes towards Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells" Nanomaterials 9, no. 7: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070982
APA StyleDi Cristo, L., Bianchi, M. G., Chiu, M., Taurino, G., Donato, F., Garzaro, G., Bussolati, O., & Bergamaschi, E. (2019). Comparative in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Realistic Doses of Benchmark Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes towards Macrophages and Airway Epithelial Cells. Nanomaterials, 9(7), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9070982





