A Review on Sulfonated Polymer Composite/Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Membranes to Address Methanol Barrier Issue for Methanol Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Composite Membranes
2.1. Sulfonated Composite Membranes
2.2. Sulfonated Fluoride Composite Membranes
2.3. Hydroxyl Sulfonated Composite Membranes
2.4. Sulfonated Chitosan Containing Composite Membranes
3. Sulfonated-Based Modified Membranes
3.1. Sulfonated Organic Membranes
3.2. Sulfonated Inorganic Membranes
3.3. Sulfonated Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Membranes
4. Future Prospective
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEM | Alkaline anion exchange membrane |
| APTES | Aminopropyl Triethoxysilane |
| ATRA | Atom transfer radical addition |
| ADMFCs | Alkaline direct methanol fuel cells |
| Ba | Benzoxazine |
| BisPFPPO-OH | Bis ((p-hydroxy- tetrafluoro) phenyl) phenyl phosphine oxide |
| Bisphenol-AF | Bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) hexafluoropropane |
| BM | Blend membrane |
| BPPO | Bromomethylated poly phenylene oxide |
| BrPEEK | Bromomethylated poly ether ether ketone |
| cSMMs | Charged surface modified macromolecules |
| CS | Chitosan |
| CCSM 110 | Chitosan Sulfate Composite Membranes |
| C30B | Cloisite 30B |
| cSPAES | Cross-linked sulfonated poly arylene ether sulfone |
| DCDPS | Dichlorodiphenyl sulfone |
| DS | Degree of sulfonation |
| DMFCs | Direct methanol fuel cells |
| FSiO2 | Functionalization of silica |
| GA | Glutaraldehyde |
| GPTMS | Glycidoxy propyl trimethoxysilane |
| G-POSS | Glycidyl ether of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes |
| SGO | Sulfonated Graphene oxide |
| g-C3N4 | Graphitic carbon nitride |
| HTPEM | High temperature proton exchange membranes |
| HGMs | Hollow glass microspheres |
| IEC | Ion-exchange capacity |
| ICPTES | Isocyanatopropyl triethoxysilane |
| MEAs | Membrane electrode assemblies |
| MPTES | Mercaptopropyl triethoxysilane |
| MPTMS | Mercaptopropyl- trimethoxysilane |
| MSiSQ | Mesoporous organosilicate |
| MOR | Mordenite |
| NM | Nanocomposites membranes |
| NMP | N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| NPHCs | N-phthaloyl chitosan |
| OCV | Open circuit voltage |
| PEM | Polymer electrolyte membrane |
| PEMFCs | Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells |
| PA | Phosphoric acid |
| PBa | Polybenzoxazine |
| PWA-IL | Phosphotungstate |
| PWA | Phosphotungstic Acid |
| AMPS | Poly 2-Acrylamido-2-Methyl Propanesulfonic Acid |
| ABPBI | Poly 2,5-Benzimidazole |
| AM-POSS | Octa Ammonium Polyhedral Oligosilsesquioxane |
| PES 70 | Poly Ether Sulfone 70 |
| PFPPO-OH | Bis (P-Hydroxy- Tetrafluoro) Phenyl) Phenyl Phosphine Oxide |
| PPEES | Poly Phenylene Ether Ether Sulfone |
| PSSA | Poly Styrene Sulfonic Acid |
| PVA | Poly Vinyl Alcohol |
| PVDF | Poly Vinylidene Fluoride |
| PVDF-HFP | Poly Vinylidene Fluoride-Co-Hexafluoro Propylene |
| PBI | Polybenzimidazole |
| PES | Polyethersulfone |
| PEFC | Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell |
| PSSA | Polystyrene Sulfonic Acid |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PCS | Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan |
| PVB | Polyvinyl Butyral |
| PEMFCs | Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells |
| PEMs | Proton Exchange Membranes |
| PMAV | Poly Methacrylic Acid-2-Acrylamido- 2-Methyl-1-Propanesulfimponic Acid-Vinyltriethoxysilicone |
| QCS | Quaternized Chitosan |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| Semi-IPN | Semi-Interpenetrating Network |
| Si-PWA | Silica Immobilized Phosphotungstic Acid |
| SisPS/A | Silicon-Containing Sulfonated Polystyrene/Acrylate |
| SFBC | Sulfonated Fluorinated Block Copolymer |
| SGO | Sulfonated Graphene oxide |
| SPVDF-co-HFP | Sulfonated Poly Vinylidene Fluoride-Co-Hexafluoro Propylene |
| SPEES | Sulfonated Poly1,4-Phenylene Ether-Ether-Sulfone |
| SPAES | Sulfonated Polyarylene Ether Ketones |
| SPAEKS | Sulfonated Poly Arylene Ether Ketone Sulfone |
| SPEEK | Sulfonated Poly Ether Ether Ketone |
| SPEKES | Sulfonated Poly Ether Ketone Ether Sulfone |
| SPES | Sulfonated Poly Ether Sulfone |
| CBrSPIBIs | Sulfonated Poly Imide- Benzimidazole |
| SPPO | Sulfonated Poly Phenylene Oxide |
| sPAEK | Sulfonated Poly Arylene Ether Ketone |
| SPAni | Sulfonated Polyaniline |
| SPI | Sulfonated Polyimide |
| SPIBI | Sulfonated Polyimides Containing Benzimidazole |
| s-Poly | Sulfonated Polymer |
| SPSU | Sulfonated Polysulfone |
| SSA | Sulfosuccinic Acid |
| SPSF | Sulphonated Polysulphone |
| TBT | Tetrabutyl Titanate |
| TEOS | Tetraethoxysilane |
| VBIm-Br | Vinyl-3-Butylimdazolium- Bromide |
| VPSIm-Cl | Vinyl-Propyl-Triethoxy Silane Imidazolium Chloride |
References
- Kamarudin, S.K.; Achmad, F.; Daud, W.R.W. Overview on the application of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) for portable electronic devices. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 6902–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilbeygi, H.; Ghasemi, M.; Emadzadeh, D.; Ismail, A.F.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Aljlil, S.A.; Jaafer, J.; Martin, D.; Keshani, S. Power generation and wastewater treatment using a novel SPEEK nanocomposite membrane in a dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, B.C.H.; Heinzel, A. Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 2001, 414, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Hickner, M.A.; Einsla, B.; Harrison, W.L.; McGrath, J.E. Synthesis and characterization of partially disulfonated hydroquinone-based poly(arylene ether sulfone)s random copolymers for application as proton exchange membranes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2009, 47, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Hickner, M.A.; Dong, L.; Pivovar, B.S.; McGrath, J.E. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) copolymer proton exchange membranes: Composition and morphology effects on the methanol permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, C.; Jao, T.C.; Pasupathi, S.; Pollet, B.G. Optimisation of electrophoretic deposition parameters for gas diffusion electrodes in high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musse Branco, C.; Sharma, S.; de Camargo Forte, M.M.; Steinberger-Wilckens, R. New approaches towards novel composite and multilayer membranes for intermediate temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 316, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Arico, A.S.; Cretı, P.; Baglio, V.; Antonucci, V. Composite Nafion/Zirconium Phosphate Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell Operation at High Temperature. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2001, 4, A31–A34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamburzev, S.; Appleby, A.J. Recent progress in performance improvement of the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC). J. Power Sources 2007, 107, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikukawa, M.; Sanui, K. Proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes based on hydrocarbon polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1463–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoesmith, J.P.; Collins, R.D.; Oakley, M.J.; Stevenson, D.K. Status of solid polymer fuel cell system development. J. Power Sources 1994, 49, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Lee, Y.M. Synthesis of highly fluorinated poly(arylene ether)s copolymers for proton exchange membrane materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neelakandan, S.; Kanagaraj, P.; Sabarathinam, R.M.; Nagendran, A. Polypyrrole layered SPEES/TPA proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 359, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonert, M.; Jakoby, K.; Schlumbohm, C.; Glusen, A.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. Manufacture of robust catalyst layers for the DMFC. Fuel Cells 2004, 4, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wilkinson, D.P. A review of anode catalysis in the direct methanol fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 155, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpan, C.O.; Cruickshank, C.A.; Matida, E.; Hamdullahpur, F. 1D modeling of a flowing electrolyte-direct methanol fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Tongwen, X.; Dan, W.; Xin, Z. Preparation and characterization of CPPO/BPPO blend membranes for potential application in alkaline direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 577–585. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhuram, J.; Manoharan, R. Investigation of methanol oxidation on unsupported platinum electrodes in strong alkali and strong acid. J. Power Sources 1998, 74, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripkovic, A.V.; Popovic, K.D.; Grgur, B.N.; Blizanac, B.; Ross, P.N.; Markovic, N.M. Methanol electro- oxidation on supported Pt and PtRu catalysts in acid and alkaline solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Bocarsly, A.B. A comparison of physical properties and fuel cell performance of Nafion and zirconium phosphate/Nafion composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 237, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Taama, W.M.; Argyropoulos, P. Performance of the direct methanol fuel cell with radiation-grafted polymer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 171, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, P.; Friedrich, K.A.; Vogt, B.; Stimming, U. Transport properties of ionomer composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 532, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragan, V.M.; Heinzel, A. Estimation of the membrane methanol diffusion coefficient from open circuit voltage measurements in a direct methanol fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2002, 104, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Kaufman, A. Open circuit voltage and methanol crossover in DMFCs. J. Power Sources 2002, 110, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Taama, W.; Cruickshank, J. Performance and modelling of a direct methanol solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 1997, 65, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurauand, B.; Smotkin, E.S. Methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells: A link between power and energy density. J. Power Sources 2002, 112, 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Basri, S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Daud, W.R.W.; Yaakub, Z. Nanocatalyst for direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 35, 7957–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neburchilov, V.; Martin, J.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, J.J. A review of polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 169, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerres, J.A. Development of ionomer membranes for fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-C.; Lin, C.-K.; Kuo, J.-F.; Chen, C.-Y. Preparation and properties of cross- linked sulphonated poly(arylene ether sulphone) blends for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4072–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Robertson, G.; Kim, D.; Guiver, M.; Hu, W.; Jiang, Z. Aromatic poly(ether ketone)s with pendant sulfonic acid phenyl groups prepared by a mild sulfonation method for proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 1934–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Kunz, H.R.; Fenton, J.M. Composite silica/Nafion® membranes prepared by tetraethylorthosilicate sol–gel reaction and solution casting for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 272, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Kim, Y.T.; Fenton, J.M.; Russell Kunz, H.; Rhee, H.W. Chemically-modified Nafion®/poly (vinylidene fluoride) blend ionomers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2003, 117, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.G.; Wang, X.; Hsing, I.M. Composite Nafion/polyvinyl alcohol membranes for the direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 210, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.G.; Hsing, I.M. Nafion Membrane Coated with Sulfonated Poly(vinyl alcohol) Nafion Film for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Electrochem. Solid State 2002, 5, A185–A187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Ha, H.Y.; Hong, S.A.; Oh, I.H. Characteristics of the Nafion ionomer-impregnated composite membrane for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2002, 109, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Study on the preparation and properties of pvdf-composite nafion membranes. Acta Polym. Sin. 2002, 4, 540–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.C.; Ouyang, M.; Fenton, J.M.; Kunz, H.R.; Koberstein, J.T. Study of blend membranes consisting of NafionR and vinylidene fluoride–hexafluoropropylene copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagur-Grodzinki, J. Polymeric materials for fuel cells: Concise review of recent studies. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Oh, S.Y.; Kang, Y.S.; Jung, B. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated polyimide membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 220, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluca, N.W.; Elabd, Y.A. Polymer electrolyte membranes for the direct methanol fuel cell: A review. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2201–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Lee, H.C.; Wang, B.Y.; Lue, S.J.; Lu, C.Y.; Tsai, L.D.; Fang, J.; Chao, C.Y. Sulfonated poly(styrene-block-(ethylene-ran-butylene)-block-styrene (SSEBS)-zirconium phosphate (ZrP) composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazi, R.; Amiji, M. Chitosan-based gastrointestinal delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Park, J.S.; Kim, C.S. Preparation and characterization of protonconducting sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/phosphatoantimonic acid composite membranes. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 4019–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzel, A.; Barragan, V.M. A review of the state-of-the-art of the methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 1999, 84, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyeon, D.H.; Chun, B.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.T. Cross-linked sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/silica hybrid membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2013, 51, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Roy, A.; Lane, O.; Dunn, S.; McGrath, J.E. Hydrophilicehydrophobic multiblock copolymers based on poly(arylene ether sulfone) via low temperature coupling reactions for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Polymer 2008, 49, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Li, W.; Manthiram, A. Poly(arylene ether sulfone)s containing pendant sulfonic acid groups as membrane materials for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 330, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badami, A.S.; Lane, O.; Lee, H.S.; Roy, A.; McGrath, J.E. Fundamental investigations of the effect of the linkage group on the behavior of hydrophilic-hydrophobic poly(arylene ether sulfone) multiblock copolymers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 333, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.T.; Patel, R.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.R. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ether sulfone) grafted poly(styrene sulfonic acid) for proton conducting membranes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakandan, S.; Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Muthumeenal, A. Enhancing proton conduction of sulfonated poly (phenylene etherether sulfone) membrane by charged surface modifying macromolecules for H2/O2 fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2015, 78, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Dong, F.; Yin, X. Highly conductive proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (phthalazinone ether sulfone) an cerium sulfophenyl phosphate. React. Funct. Polym. 2012, 72, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisu, C.; Dong, H.K.; Hyung, K.K.; Chongkyu, S.; Sung, C.K. Polymer blend membranes of sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 384–392. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Hua, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Okamoto, K. Preparation and properties of cross-linked sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone)/sulfonated polyimide blend membranes for fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedicini, R.; Saccà, A.; Carbone, A.; Gatto, I.; Patti, A.; Passalacqua, E. Study on sulphonated polysulphone/polyurethane blend membranes for fuel cell applications. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 579, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Xiang, J.; Li, P.; Sue, H.J. High performance proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells based on a SPEEK/polybenzoxazine cross-linked structure. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47284–47293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, H. A superhydrophobic bromomethylated poly(phenyleneoxide) as a multi- functional polymer filler in SPEEK membrane towards neat methanol operation of direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Guiver, M.D.; Lee, Y.M. Sulfonated hydrocarbon membranes for medium-temperature and low-humidity proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1443–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruichun, J.; Timothy, F.; Shelly, B.; Craig, G. Perfluorocyclobutane and poly(vinylidene fluoride) blend membranes for fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 110, 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Gnana kumar, G.; Kim, P.; Kim, A.; Nahm, K.S.; Nimma Elizabeth, R. Structural, thermal and ion transport studies of different particle size nano composite fillers incorporated PVdF-co-HFP hybrid membranes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulay, Y.; Inan, H.D.; Elif, E.; Unveren, E.E. Sulfonated PEEK and fluorinated polymer based blends for fuel cell applications: Investigation of the effect of type and molecular weight of the fluorinated polymers on the membrane’s properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12038–12053. [Google Scholar]
- Deuk, J.K.; Hye, J.L.; Sang, Y.N. Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) membranes blended with hydrophobic polymers for direct methanol fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 39, 17524–17532. [Google Scholar]
- Unveren, E.E.; Inan, T.Y.; Çelebi, S.S. Partially sulfonated poly(1,4-phenylene ether-ether-sulfone) and poly(vinylidene fluoride) blend membranes for fuel cells. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingshuk, D.; Suparna, D.; Patit, P.K. Low methanol permeable and highly selective membranes composed of pure and/or partially sulfonated PVdF-co-HFP and polyaniline. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Merve, G.S.; Emre, B.; Tülay, Y.I.; Nilhan, K.A.; Atilla, G. Synthesis and fuel cell characterization of blend membranes from phenyl phosphine oxide containing flou- rinated novel polymers. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 465–479. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.; Smita, M.; Sanjay, N.K. Polymer electrolyte membranes from Cloisite30Bbased solid proton conductor and sulfonated polyether ether ketone/polyvinylidene fluoride-cohexafluoro propylene blend s for direct methanol fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61178–61186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dutta, K.; Das, S.; Kundu, P.P. Membrane prepared by incorporation of cross-linked sulfonated polystyrene in the blend of PVdF-co-HFP/Nafion: A preliminary evaluation for application in DMFC. Appl. Energy 2014, 123, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Meng, X.; Wu, J.; Huo, J.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Q. Microstructure and Properties of Novel SPEEK/PVDF-g-PSSA blends for Proton Exchange Membrane with Improved Compatibility. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69621–69628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Dutta, K.; Hazra, S.; Kundu, P.P. Partially Sulfonated Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Induced Enhancements of Properties and DMFC Performance of Nafion Electrolyte Membrane. Fuel Cells 2015, 15, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Soam, S.; Kundu, P.P. Reduction of methanol crossover and improved electrical efficiency in direct methanol fuel cell by the formation of a thin layer on Nafion 117 membrane: Effect of dip-coating of a blend of sulphonated PVdF-co-HFP and PBI. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Beydaghi, H.; Salarizadeh, P.; Shabanikia, A.; Amoli, H.S. Sulfonated poly(etheretherketone) and sulfonated polyvinylidene fluoride-co- hexafluoro- propylene based blend proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 39500–39510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
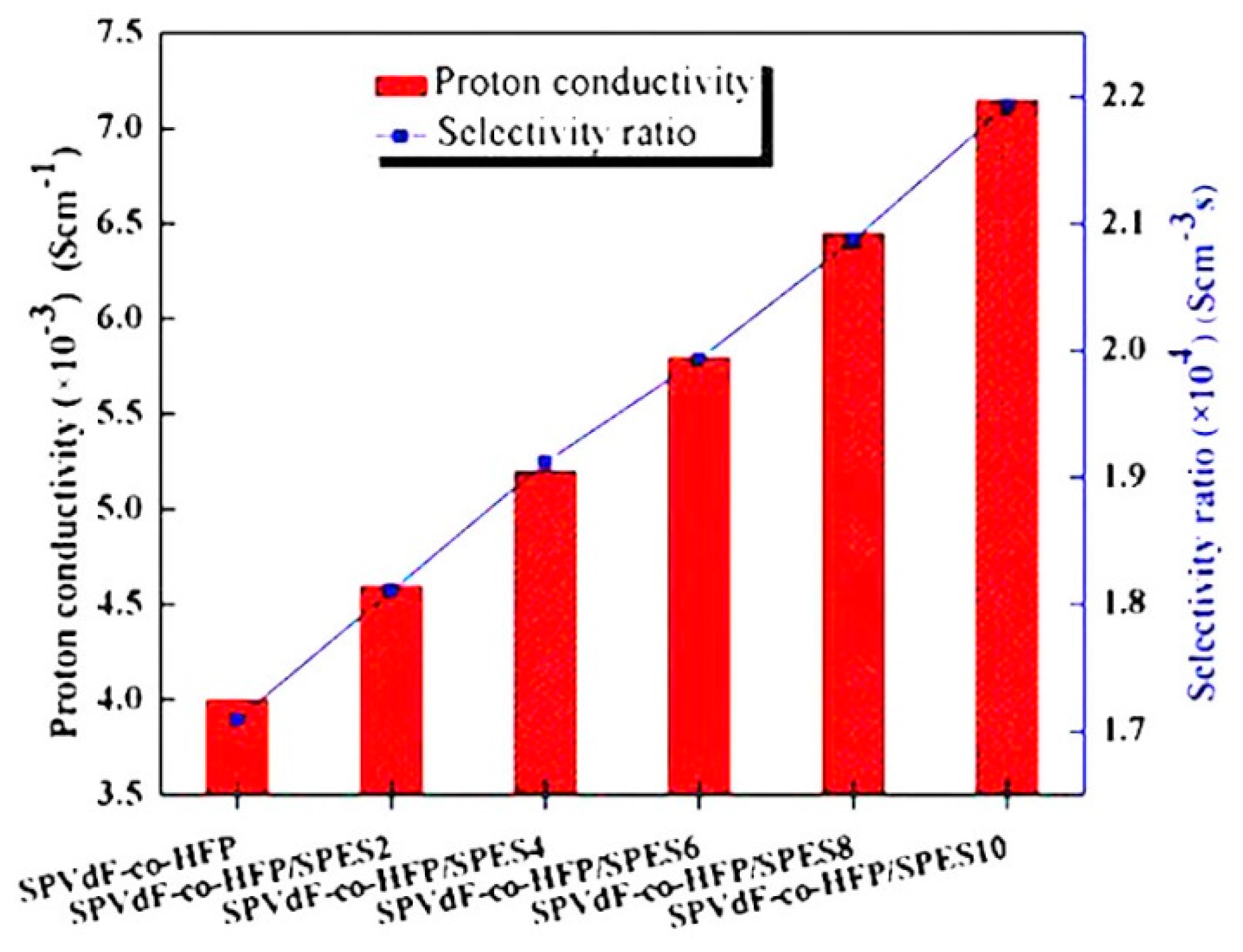
- Uma, D.; Muthumeenal, A.; Sabarathinam, R.M.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication and electrochemical properties of SPVdF-co-HFP/SPES blend proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 258–265. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, J.S.; Yoo, D.J. Proton-conducting phosphotungstic acid/sulfonated fluorinated block copolymer composite membrane for polymer electrolyte fuel cells with reduced hydrogen permeability. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2779–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gong, C.; Qi, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Intermolecular ionic cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membranes containing diazafluorene for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, A.M.; Javanbakht, M.; Hooshyari, K.; Enhessari, M. New proton conducting nanocomposite membranes based on poly vinylalcohol/poly vinyl pyrrolidone/BaZrO3 for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 2015, 269, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dai, C.; Chao, C.; Chang, S. Novel proton exchange membrane based on cross-linked PVA for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 249, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, S.; Compan, V. Polymer blends of SPEEK for DMFC application at intermediate temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5121–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, S. Nafion/poly(vinyl alcohol) nano-fiber composite and Nafion/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T. Preliminary study of SPEEK/PVA blend membranes for DMFC applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 6772–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
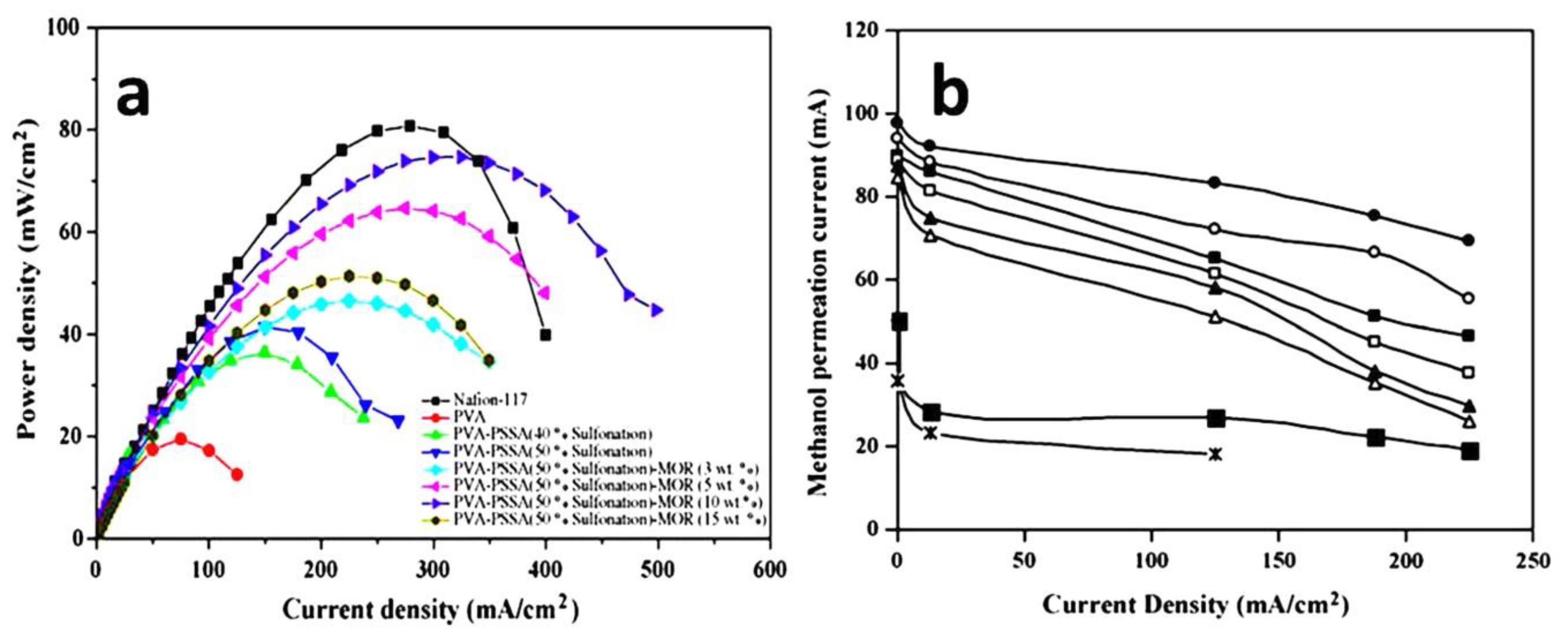
- Bhat, S.D.; Sahu, A.K.; George, C.; Pitchumani, S.; Sridhar, P.; Chandrakumar, N.; Singh, K.K.; Krishna, N.; Shukla, A.K. Mordenite-incorporated PVA–PSSA membranes as electrolytes for DMFCs. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Amirinejad, S.; Amirinejad, M. Phosphotungstic acid doped poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(ether sulfone) blend composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 380, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, N.; Chiu, H. Preparation and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate blended membrane for alkaline solid polymer electrolytes membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 457, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollá, S.; Compañ, V. Nanocomposite SPEEK-based membranes for direct methanol fuel cells at intermediate temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydaghi, H.; Javanbakht, M.; Bagheri, A.; Salarizadeh, P.; Zahmatkesh, H.G.; Kashefi, S.; Kowsari, E. Novel nanocomposite membranes based on blended sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/poly(vinyl alcohol) containing sulfonated graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanosheets for DMFC applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74054–74064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Creber, K.A.M.; Peppley, B.; Tam Bui, V. Chitosan-based electrolyte composite membranes: II mechanical properties and ionic conductivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumeenal, A.; Neelakandan, S.; Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A. Synthesis and properties of novel proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated polyethersulfone and N-phthaloyl chitosan blends for DMFC applications. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, S.; Bhat, S.D.; Sahu, A.K.; Sridhar, P.; Pitchumani, S.; Shukla, A.K. Chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol-sulfonated polyethersulfone mixed-matrix membranes as methanol-barrier electrolytes for DMFCs. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, e73–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Chiu, H.C. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan blended membrane for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 419–420, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Guo, Z.; Cui, Z. Alternatively chitosan sulfate blending membrane as methanol-blocking polymer electrolyte membrane for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, Y.; Hossain, M.A.; Jang, H.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, S.; Jin, L.; Kim, W. Synthesis and properties of grafting sulfonated polymer containing isatin by super acid-catalyzed polyhydroxyalkylation reaction for PEMFC. Renew. Energy 2015, 79, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R.; Hofmann, M.A.; Ambler, C.M.; Lvov, S.N.; Zhou, X.Y.; Chalkova, E. Phenylphosphonic acid functionalized poly[aryloxyphosphazenes] as proton-conducting membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 201, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Roziere, J. Recent advances in the functionalization of polybenzimidazole and polyetherketone for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Norddin, M.N.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Mustafa, A.; Tabe Mohammadi, A. Characterization and performance of proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cell: Blending of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) with charged surface modifying macromolecule. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Norddin, M.N.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Tabe, S. The effect blending sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) with various charged surface modifying macromolecules on proton exchange membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.N.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hwang, I.; Jang, J.H.; Cho, E.A.; Kim, S.-K.; Henkensmeier, D.; Hong, S.-A.; et al. Sulfonated poly(ether sulfone)/sulfonated polybenzimidazole blend membrane for fuel cell applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, C. SPEEK/sulfonated cyclodextrin blend membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5666–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithunsaa, M.; Tashiro, K.; Nunes, S.P.; Chirachanchai, S. Poly(acrylic acid-co-4-vinylimidazole)/Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) composite membranes: A role of polymer chain with proton acceptor and donor for enhancing proton transfer in anhydrous system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 10384–10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Cai, Y.B.; Xu, S. Phosphoric acid-doped cross-linked sulfonated poly(imide-benzimidazole) for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 501, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Guzmán, C.; Carbone, A.; Saccà, A.; Gatto, I.; Pedicini, R.; Passalacqua, E.; Nava, R.; Ornelas, R.; Ledesma-Garcia, J.; et al. Composite membranes based on micro and mesostructured silica: A comparison of physicochemical and transport properties. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5394–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacca, A.; Carbone, A.; Gatto, I.; Pedicini, R.; Freni, A.; Patti, A.; Passalacqua, E. Composites Nafion-titania membranes for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell (PEFC) applications at low relative humidity levels: Chemical physical properties and electrochemical performance. Polym. Test. 2016, 56, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Zavala, A.; Gurrola, M.P.; Arriaga, L.G.; Jennifer, B.A.; Alvarez-Contreras, L.; Carbone, A.; Sacca, A.; Fabio Matera, V.; Pedicini, R.; Alvarez, A.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of composite membranes modified with Halloysite nanotubes and phosphotungstic acid for electrochemical hydrogen pumps. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yeh, T.; Su, Y.; Wang, P.; Hsueh, K.; Tseng, F. High-performance and low-leakage phosphoric acid fuel cell with synergic composite membrane stacking of micro glass microfiber and nano PTFE. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changkhamchom, S.; Sirivat, A. Polymer Electrolyte Composite Membrane Based on Molecular Sieve 13X Mixed with Sulfonated Poly(ether ketone ether sulfone)/ Poly (phenylene ether ether sulfone) blended Membrane for Use in Direct Methanol Fuel Cell. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2017, 36, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, X. Organic-inorganic composite membrane based on sulfonated poly (arylene ether ketone sulfone) with excellent long-term stability for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu-Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, R. Alkaline hybrid composite membrane for direct methanol fuel cells application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 759, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Shabanikia, A.; Javanbakht, M.; Amoli, H.S.; Hooshyari, K.; Enhessari, M. Polybenzimidazole/strontium cerate nanocomposites with enhanced proton conductivity for proton exchange membrane fuel cells operating at high temperature. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 154, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bonis, C.; Cozzi, D.; Mecheri, B.; D’Epifanio, A.; Rainer, A.; de Porcellinis, D.; Licoccia, S. Effect of filler surface functionalization on the performance of Nafion/Titanium oxide composite membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 147, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.; Mir, F.Q.; Shukla, A. Performance of PVDF supported silica immobilized phosphotungstic acid membrane (Si-PWA/PVDF) in direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 17306–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.; Shukla, A. PVDF supported silica immobilized phosphotungstic acid membrane for DMFC application. Solid State Ionics 2014, 262, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Cui, X.; Sun, C.; Dou, S.; Liu, W. Cross-linked organic/inorganic proton exchange membranes with multilayer structure. Solid State Ionics 2012, 227, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Hasran, U.A.; Daud, W.R.W. A novel hybrid Nafion-PBI-ZP membrane for direct methanol fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14668–14677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kumar, M.; Alothman, Z.A. Preparation and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid anion-exchange membranes for electrodialysis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, T.; Fu, Y. PVA–silica anion-exchange hybrid membranes prepared through a copolymer crosslinking agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
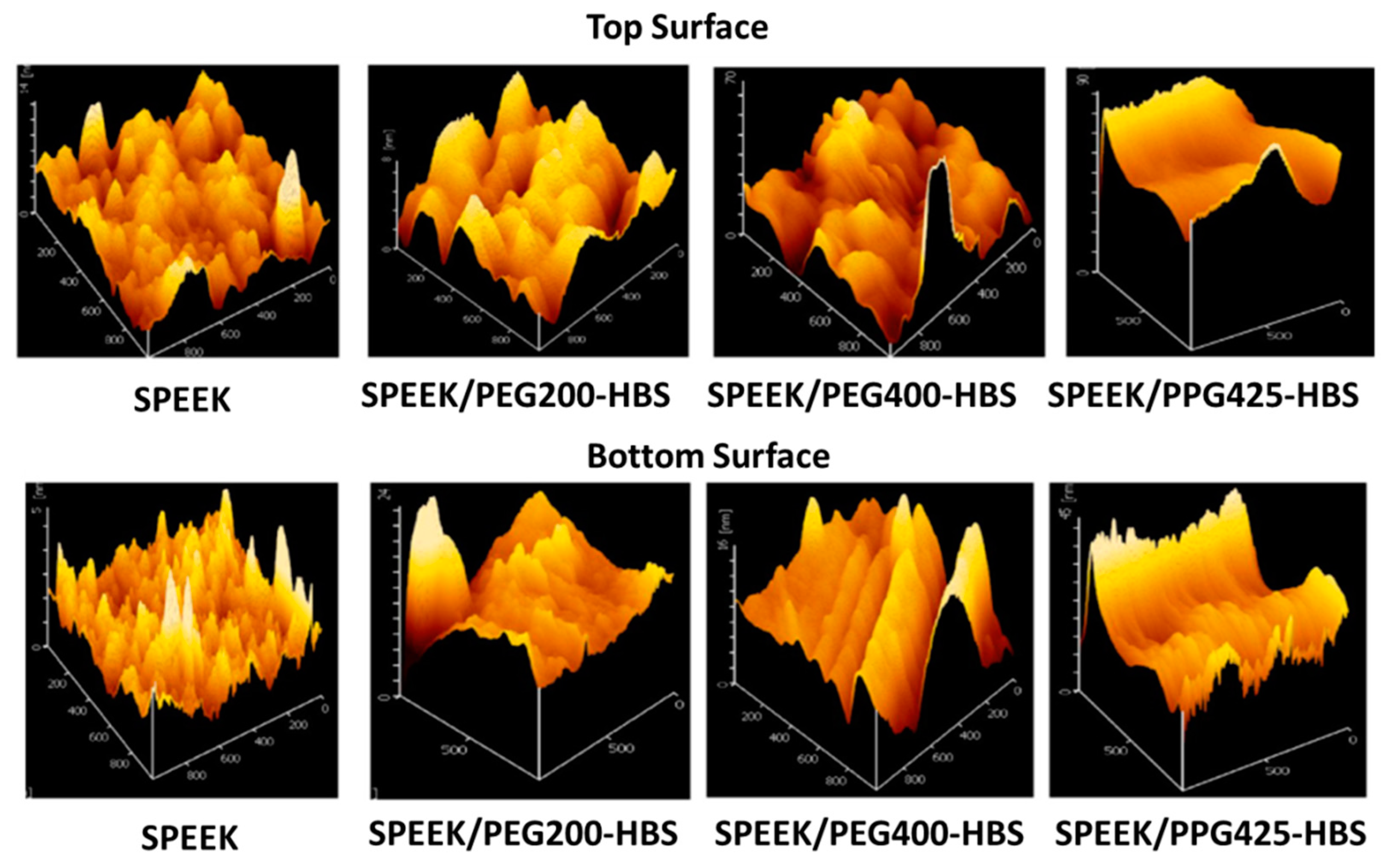
- Kumari, M.; Sodaye, H.S.; Bindal, R.C. Cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)-poly ethylene glycol/silica organic–inorganic nanocomposite membrane for fuel cell application. J. Power Sources 2018, 398, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; JinYoo, D. Artificially designed, low humidifying organic–inorganic (SFBC-50/FSiO2) composite membrane for electrolyte applications of fuel cells. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 130, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, H.Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Ni, H.; Wang, Z. Effect of “bridge” on the performance of organic-inorganic cross-linked hybrid proton exchange membranes via KH550. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ni, N.; Lu, F.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S.; Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, F.; Li, X. Novel octopus shaped organic-inorganic composite membranes for PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16160–16166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.-J.; Lai, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L. Nanohybrids of graphene oxide chemically-bonded with Nafion: Preparation and application for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Lin, B.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, N.; Chu, F.; Hickner, M.A.; Wang, C.; Zhu, L.; Ding, J. Imidazolium-based organic–inorganic hybrid anion exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 508, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, M.; He, G.; Li, Z.; Cao, K.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets/sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) nanocomposite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fu, Y.; Geng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lü, C. A facile route to enhance the properties of polymer electrolyte-based organic–inorganic hybrid proton exchange membranes. Solid State Ionics 2015, 283, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, J.; Duran, A.; Aparicio, M. Sulfonic acid-functionalized hybrid organic-inorganic proton exchange membranes synthesized by sol-gel using 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS). J. Power Sources 2015, 297, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, M.; Yamaura, S.; Zhang, W.; Sakamoto, W.; Yogo, T. Proton-conductive inorganic-organic hybrid membranes synthesized from a trimethoxysilylmethylstyrene–fluorophenylvinyl acid copolymer. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 488, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapainainar, P.; Theampetch, A.; Kongkachuichay, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Holmes, S.M.; Prapainainar, C. Effect of solution casting temperature on properties of nafion composite membrane with surface modified mordenite for direct methanol fuel cell. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 271, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, K.; Oh, I.; Ju, H.; Kim, J. Low methanol permeable cross-linked sulfonated poly(phenylene oxide) membranes with hollow glass microspheres for direct methanol fuel cells. Polymer 2015, 56, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, F.; Cui, Y.; Li, X.; Na, H. Dual cross-linked organic-inorganic hybrid polymer electrolyte membranes based on quaternized poly(ether ether ketone) and (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane. J. Power Sources 2015, 275, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Cui, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; Dou, S. Fabrication and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)-based polymer electrolyte membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 17857–17864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, H.; Chang, Z. Organic-inorganic hybrid proton exchange membrane based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes and sulfonated polyimides containing benzimidazole. J. Power Sources 2014, 263, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Cao, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Z. Preparation and performance of different amino acids functionalized titania-embedded sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) hybrid membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, R.; Yin, F. Proton conductivity and fuel cell performance of organic-inorganic hybrid membrane based on poly(methyl methacrylate)/silica. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 7913–7923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G. A novel cross-linking organic–inorganic hybrid proton exchange membrane based on sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) with 4-amino-phenyl pendant group for fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kima, A.R.; Park, C.J.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated poly ether sulfone/heteropoly acid composite membranes as electrolytes for the improved power generation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Compos. Part B 2018, 155, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Nahm, K.S.; Yoo, D.J. Ternary hybrid (SPEEK/SPVdF-HFP/GO) based membrane electrolyte for the applications of fuel cells: Profile of improved mechanical strength, thermal stability and proton conductivity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108851–108863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Kumar, G.G.; Yoond, J.; Yoo, D.J. Toward improved mechanical strength, oxidative stability and proton conductivity of an aligned quadratic hybrid (SPEEK/FPAPB/Fe3O4-FGO) membrane for application in high temperature and low humidity fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39034–39048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

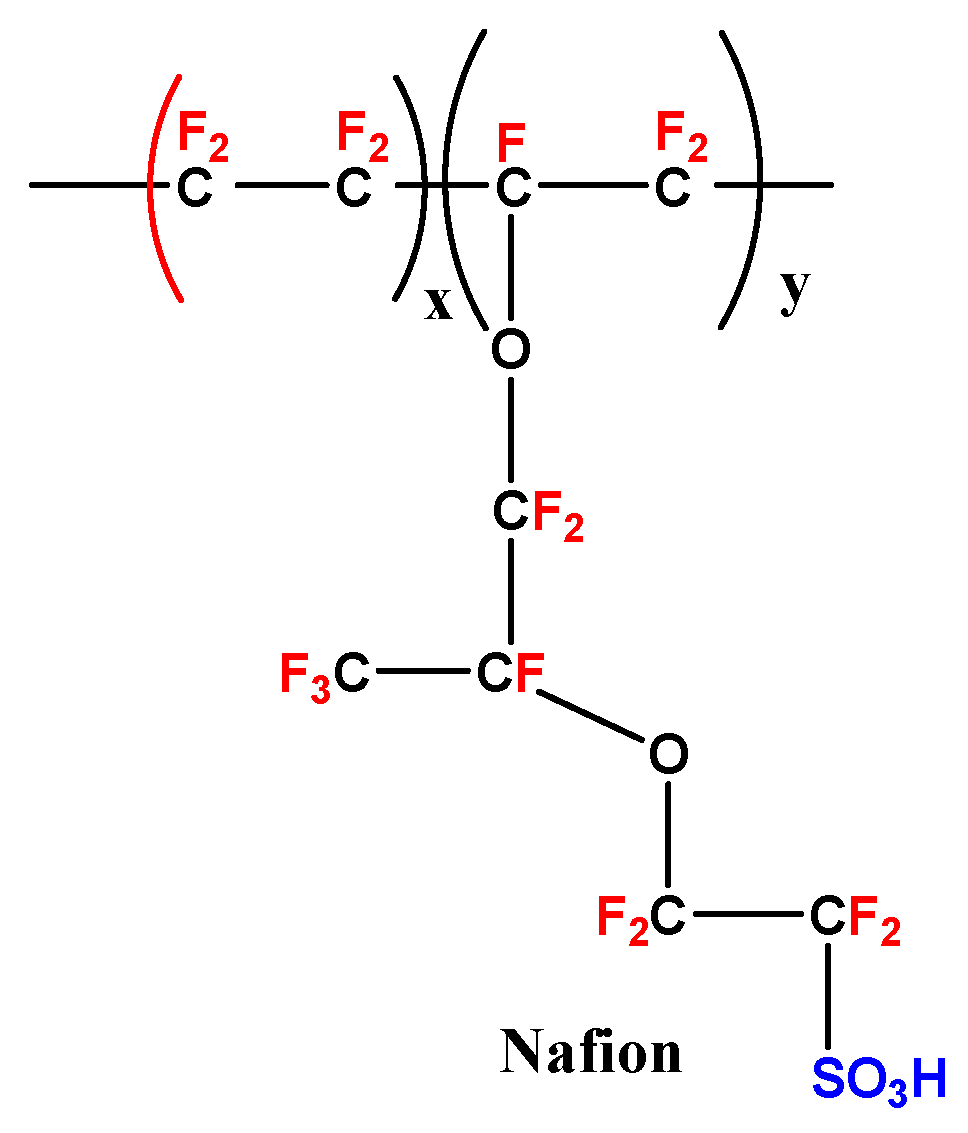

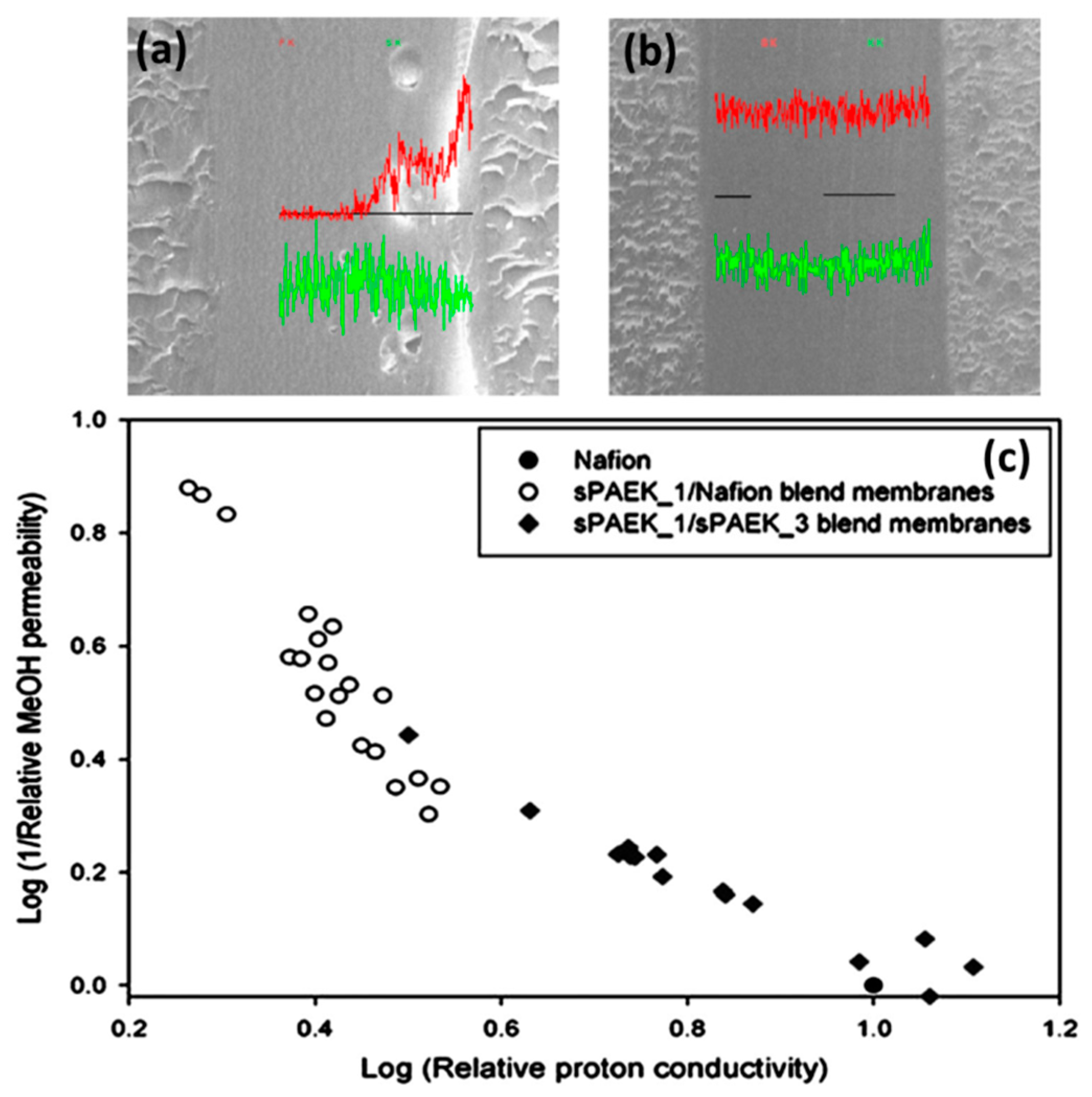
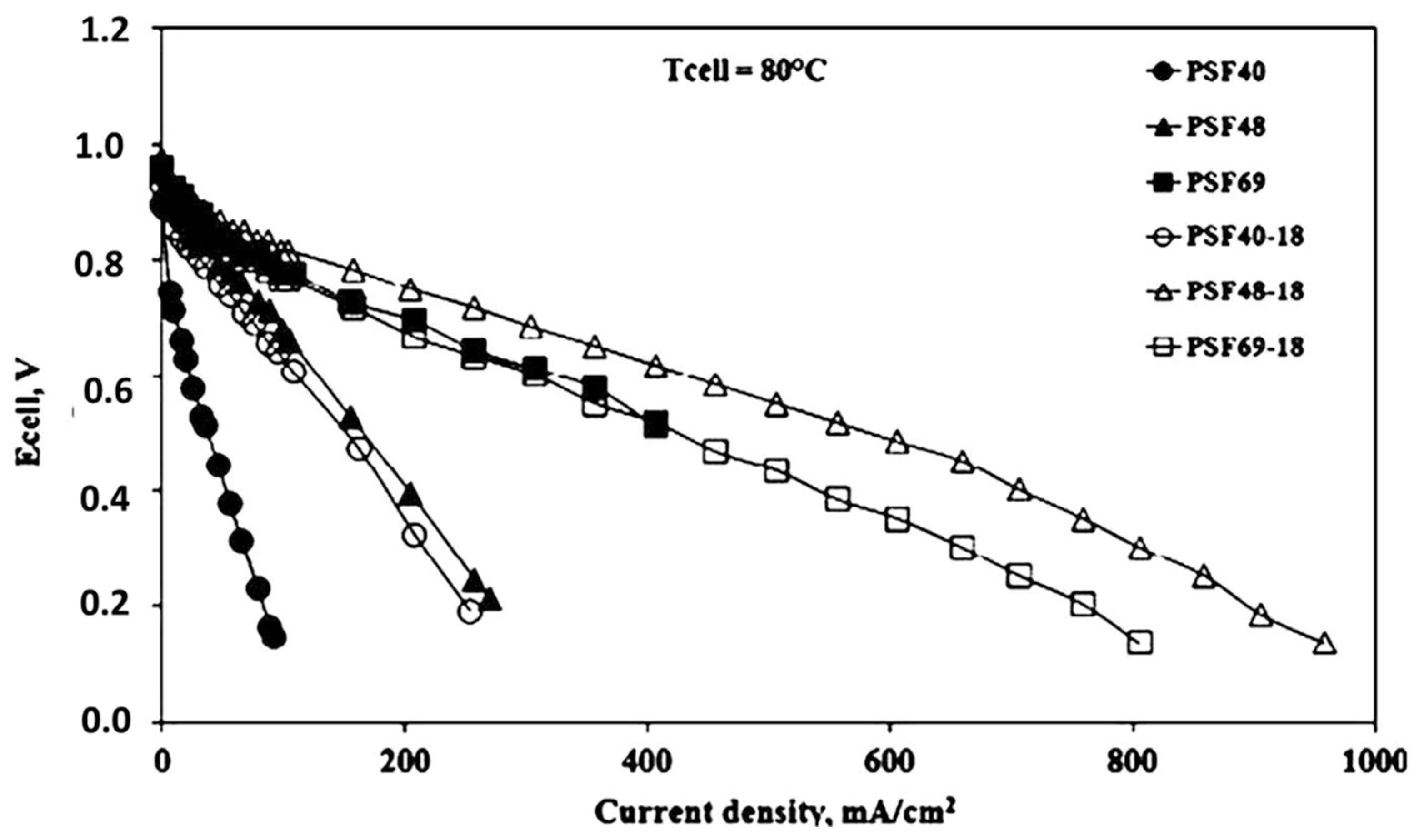
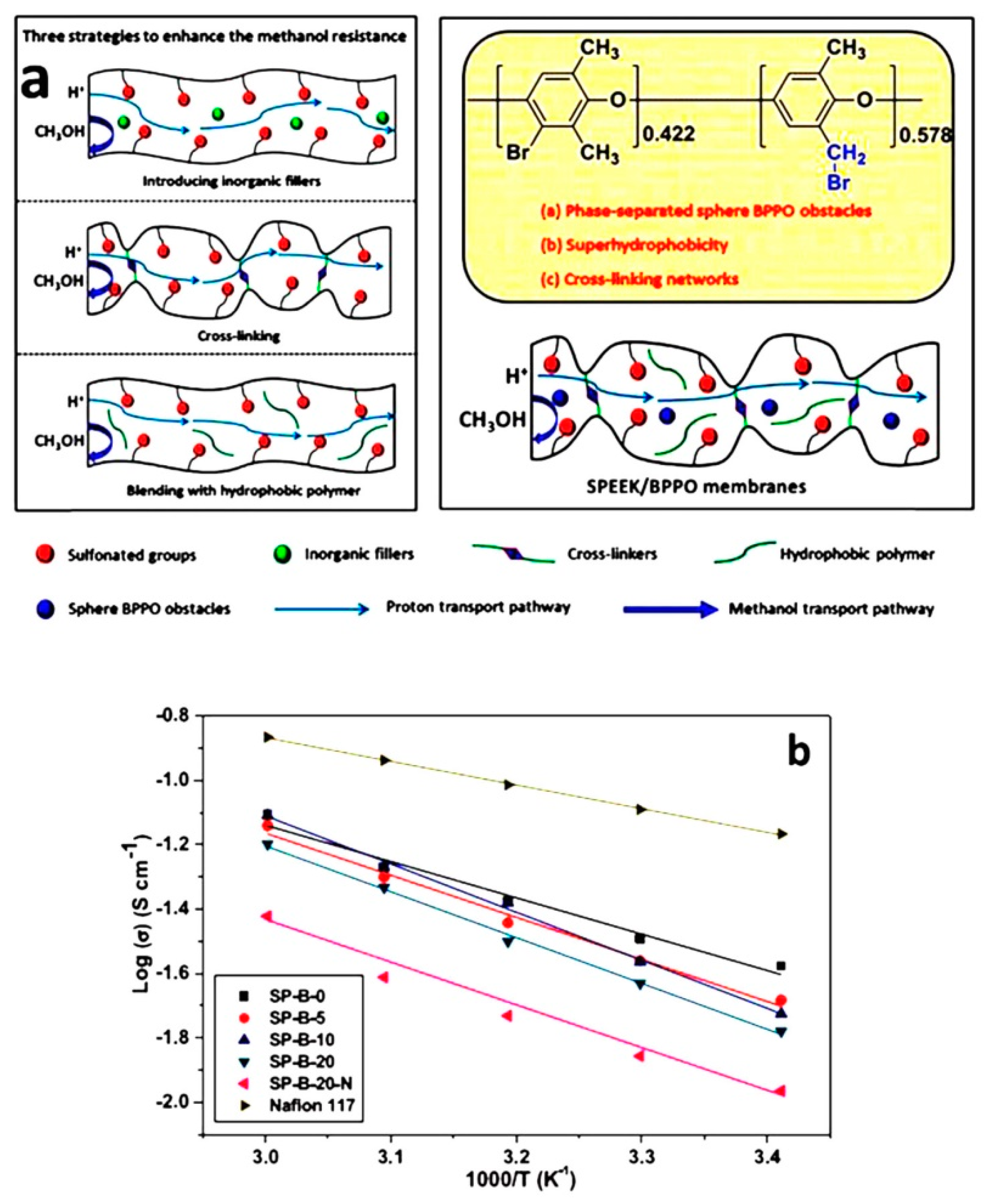
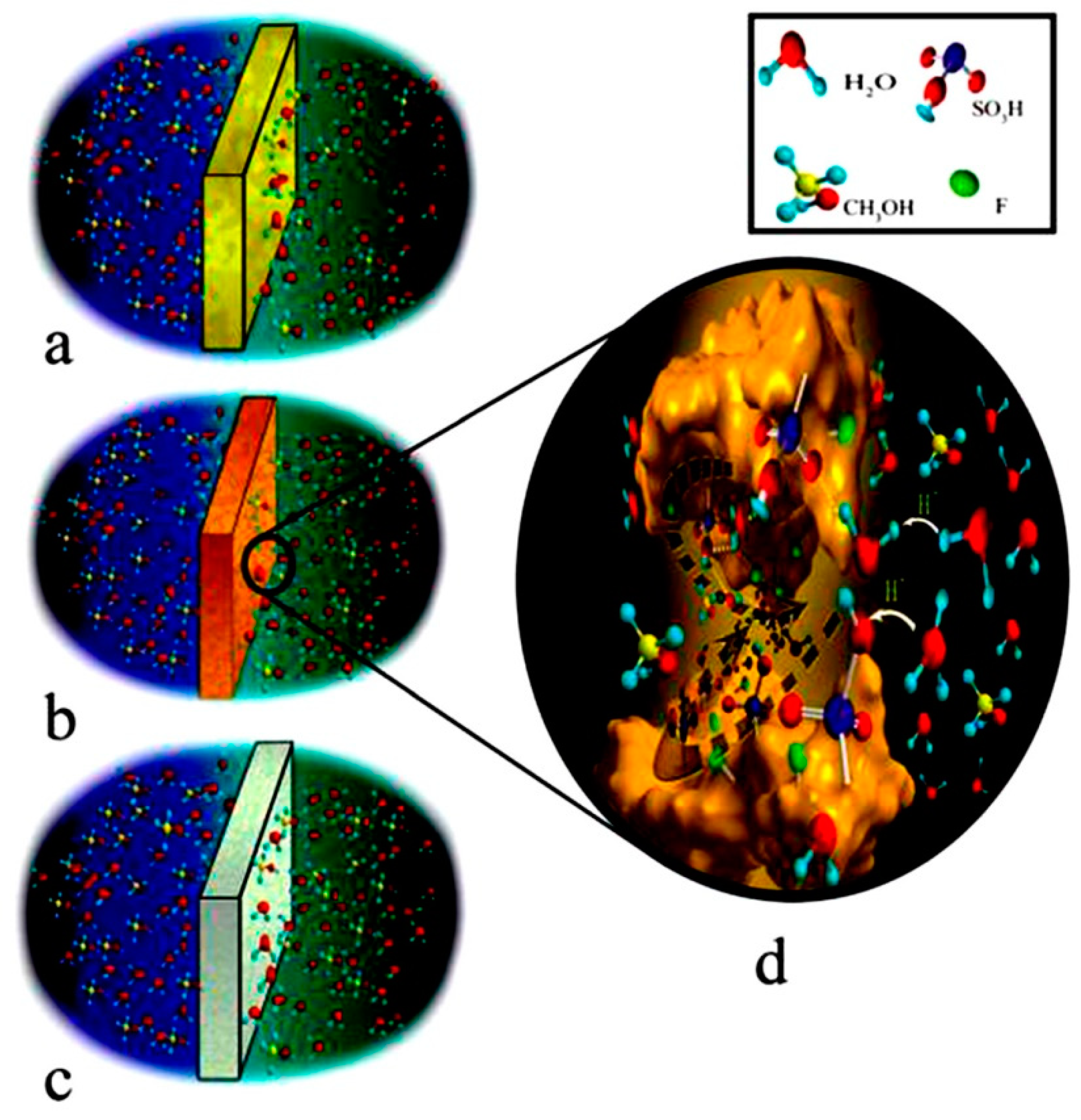

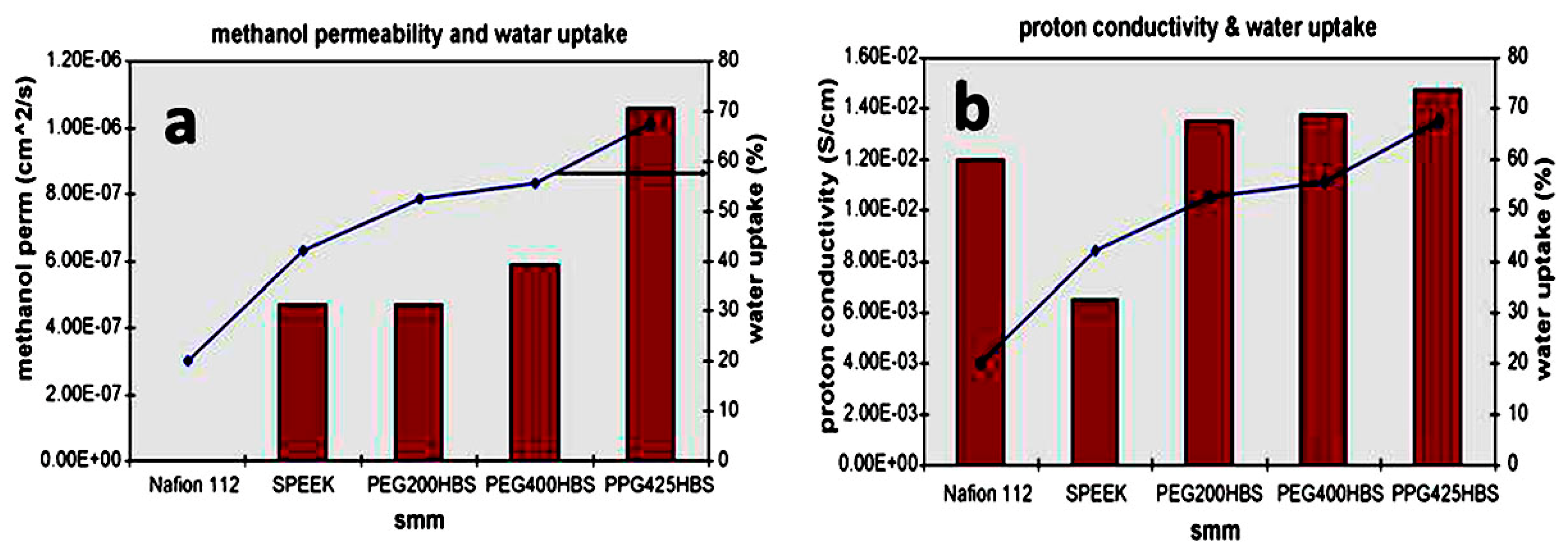
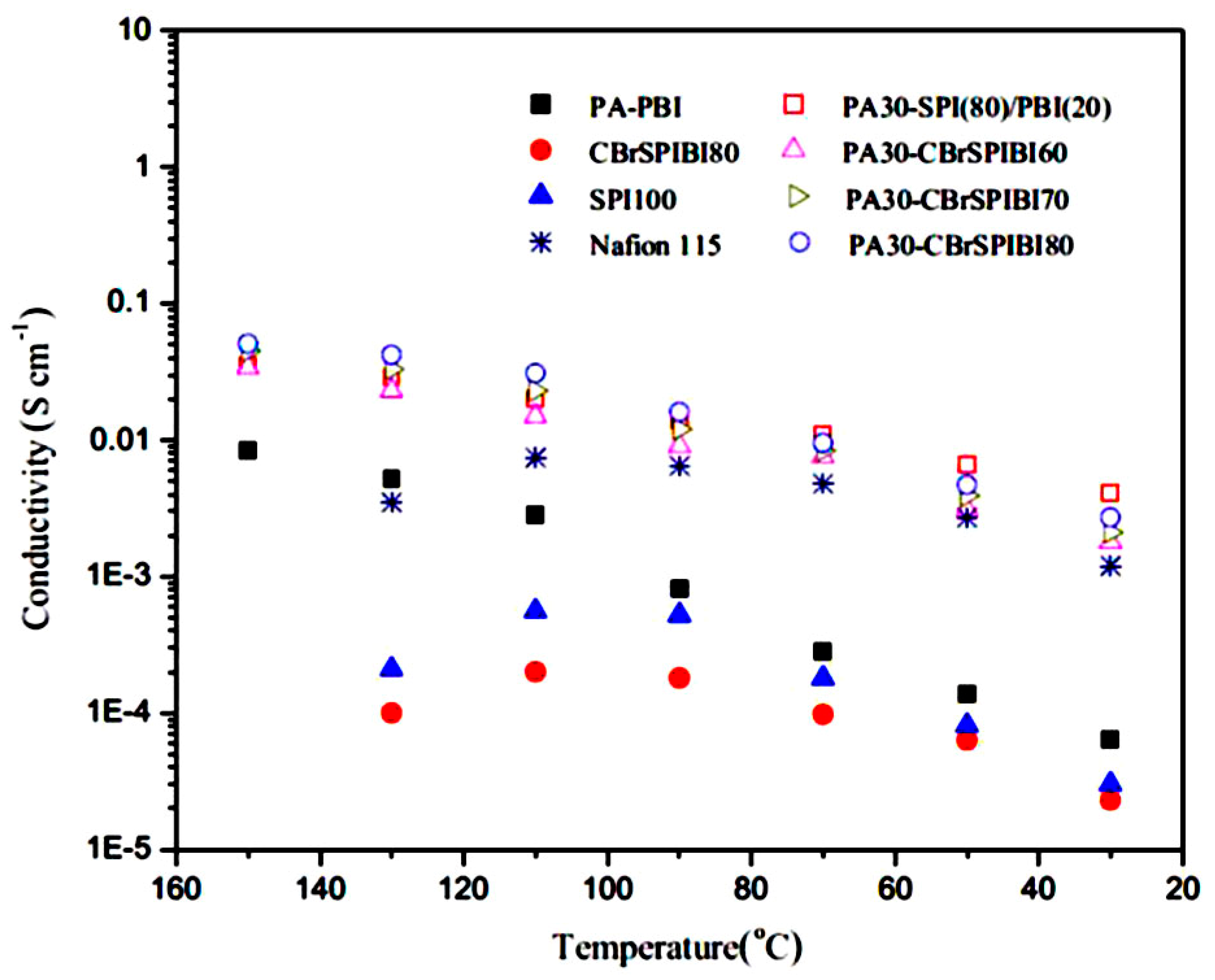
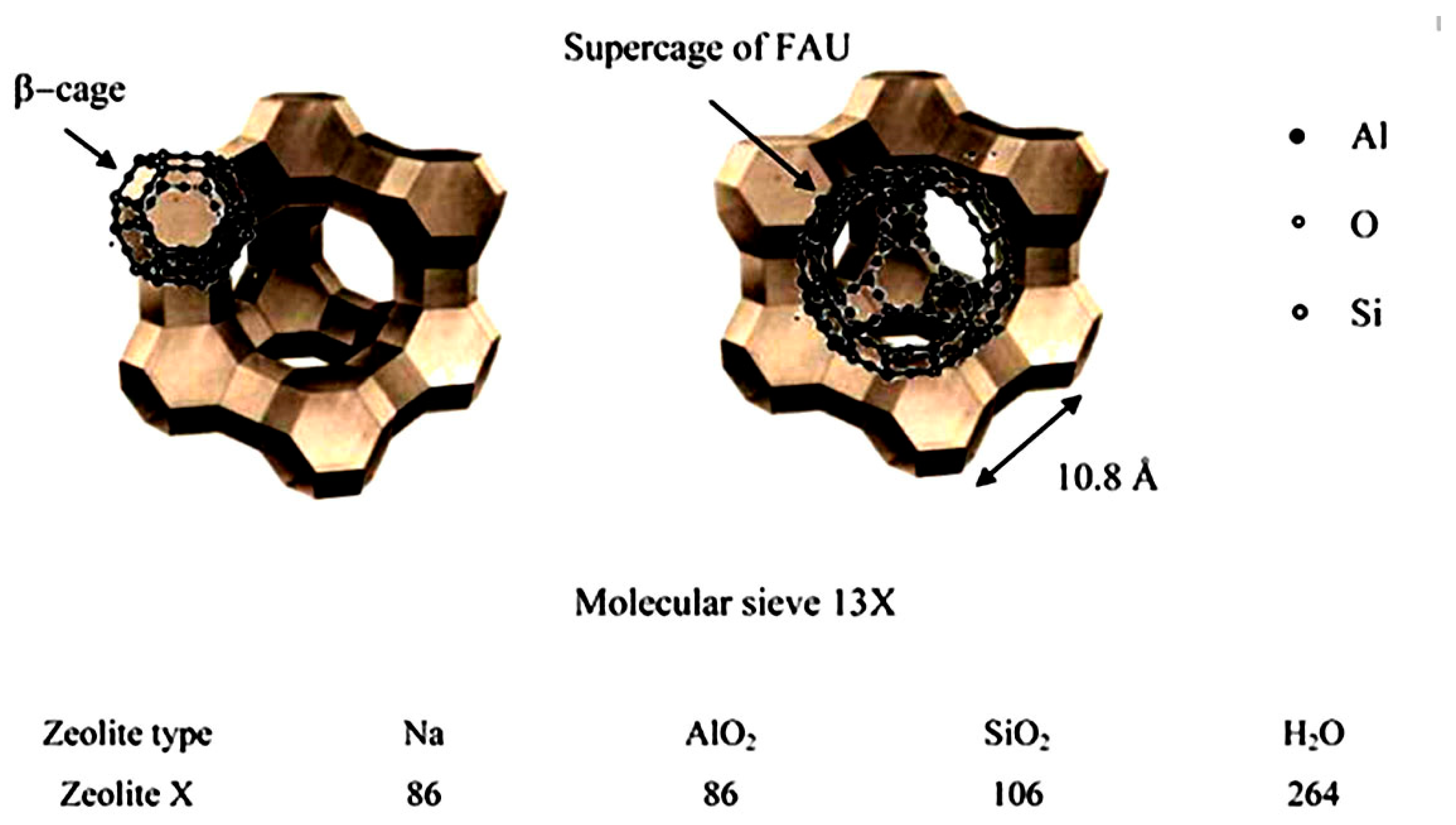



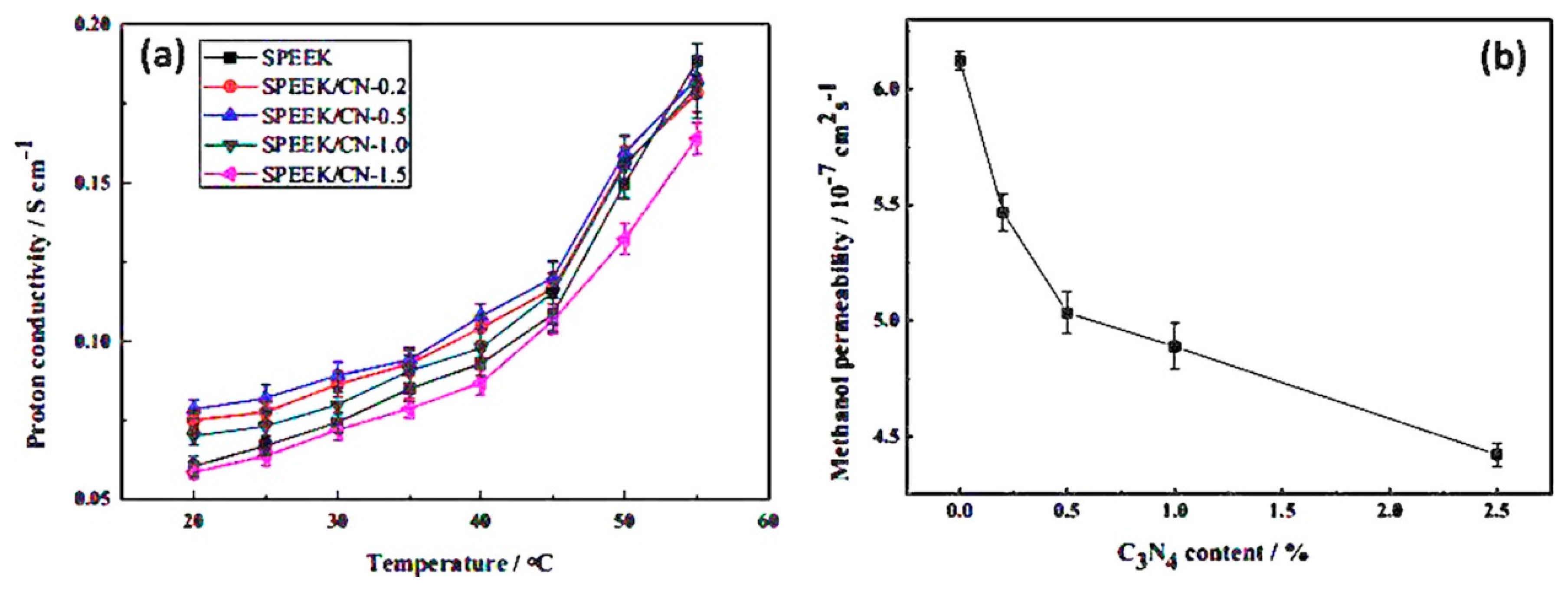
| Author | Blend Membrane Composition | Methanol Permeability (cm2 s−1) 10−6 | Proton Conductivity (S cm−1) | Membrane Selectivity (Ss cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi et al. | cSPAES70-5/SPI(5/5) | - | 11.1 ** | - |
| Zhao et al. | SPEEK/PBa-15% | 0.126 (at 30 °C) & 5.53 (at 80 °C) | 4.25 × 10−3 (at 30 °C) & 2.46 × 10−2 (at 80 °C) | 3.12 × 104 (at 30 °C) & 4.45 × 103 (at 80 °C) |
| Inan et al. | SPEEK70/PVDF(Mw¼275.000) | 0.313 ** | - | - |
| Unveren et al. | SPEES72/PVDF180 (10 wt %) | 2.4 ** | 144.0 * | 6.0 × 107 * |
| Dutta et al. | PAni/PVdF-co-HFP/Pani | 0.0000981 ** | - | 2.38 × 10−6 |
| PAni/SPVdF-co-HFP/PAni | 0.0172 ** | - | 2.45 × 105 | |
| SPAni/SPVdF-co-HFP/SPAni | 0.0529 ** | - | 9.39 × 104 | |
| Seden et al. | SPEEK70/Copolymer 1a | 0.082 ** | 84.4 | - |
| SPEEK70/Copolymer 1b | 0.0013 ** | 30.5 | - | |
| Prasad et al. | SPEEK BNCM D-2 | 0.135 ** | 1.31 & 2.14 × 10−3 | 9.63 × 104 |
| Kumar et al. | S-20 | 1.76 | 3.16 × 10−2 * | 1.80 × 104 |
| Mondal et al. | M2 (70/30 S-PVdF-co-HFP/PBI coated) | 0.492 * | 1.51 × 10−2 ** | 3.0695.3 * |
| Bagheri et al. | MSSP20 | 0.211 | 32.71 | 15.51 × 104 |
| Devi et al. | SPVdF-co-HFP/SPES blends | 3.26 * | 7.2 ** | 2.193 * |
| Molla and Compan | SPEEK-35%PVA | 4.70 ** | 1.1 × 10−2 (at 120 °C) ** | - |
| Muthumeenal et al. | SPES/NPHCs (1) | 0.0171 * | 9.2 × 10−3 (at 30 °C) * & 12.1 × 10−3 (at 80 °C) | 5.3 × 104 * |
| Meenakshi et al. | CS-PVA-SPES (25 wt %) | - | - | 2.41 × 10−4 * |
| Norddin et al. | SPEEK/cSMM | 0.275 ** | 6.4 × 10−3 * | - |
| Changkhamchom et al. | (15% v/v) Molecular sieve13X/S-PEKES/PPEES (5:1) | 0.0487 | 1.44 × 10−2 | 2.95 × 105 |
| Ahmad et al. | Nafion-PBI 1%-ZP 1% | 0.233927 ** | 0.02022 ** | 86,437.06 * |
| Kim et al. | FSiO2-12 | - | 100 ** | - |
| Han et al. | C-SPAEKS/K-SiO2-8 | 0.667 (at 60 °C) | 0.110 (at 120 °C) * | - |
| Peng et al. | NM/GO-0.10 | - | 40.8 (at 20 °C) 82.3 (at 95 °C) | - |
| Feng et al. | Membrane-5 | - | 4.10 × 10−2 (at 30 °C) 9.05 × 10−2 (at 90 °C) | - |
| He et al. | SPI-40-MsiSQ | 0.018 ** | 0.566 (at 80 °C) * | 12.8 × 106 * |
| Ahn et al. | SPPO-HGM (9 wt %)/C-SPPO | 0.267 | 0.0278 | 110,317.46 * |
| Zhang et al. | PA-QPEEK-10%APTES | - | 61.7 (at 200 °C) | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhanapal, D.; Xiao, M.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. A Review on Sulfonated Polymer Composite/Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Membranes to Address Methanol Barrier Issue for Methanol Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050668
Dhanapal D, Xiao M, Wang S, Meng Y. A Review on Sulfonated Polymer Composite/Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Membranes to Address Methanol Barrier Issue for Methanol Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(5):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050668
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhanapal, Duraibabu, Min Xiao, Shuanjin Wang, and Yuezhong Meng. 2019. "A Review on Sulfonated Polymer Composite/Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Membranes to Address Methanol Barrier Issue for Methanol Fuel Cells" Nanomaterials 9, no. 5: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050668
APA StyleDhanapal, D., Xiao, M., Wang, S., & Meng, Y. (2019). A Review on Sulfonated Polymer Composite/Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Membranes to Address Methanol Barrier Issue for Methanol Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials, 9(5), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9050668






