Controlling the Morphologies of Silver Aggregates by Laser-Induced Synthesis for Optimal SERS Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
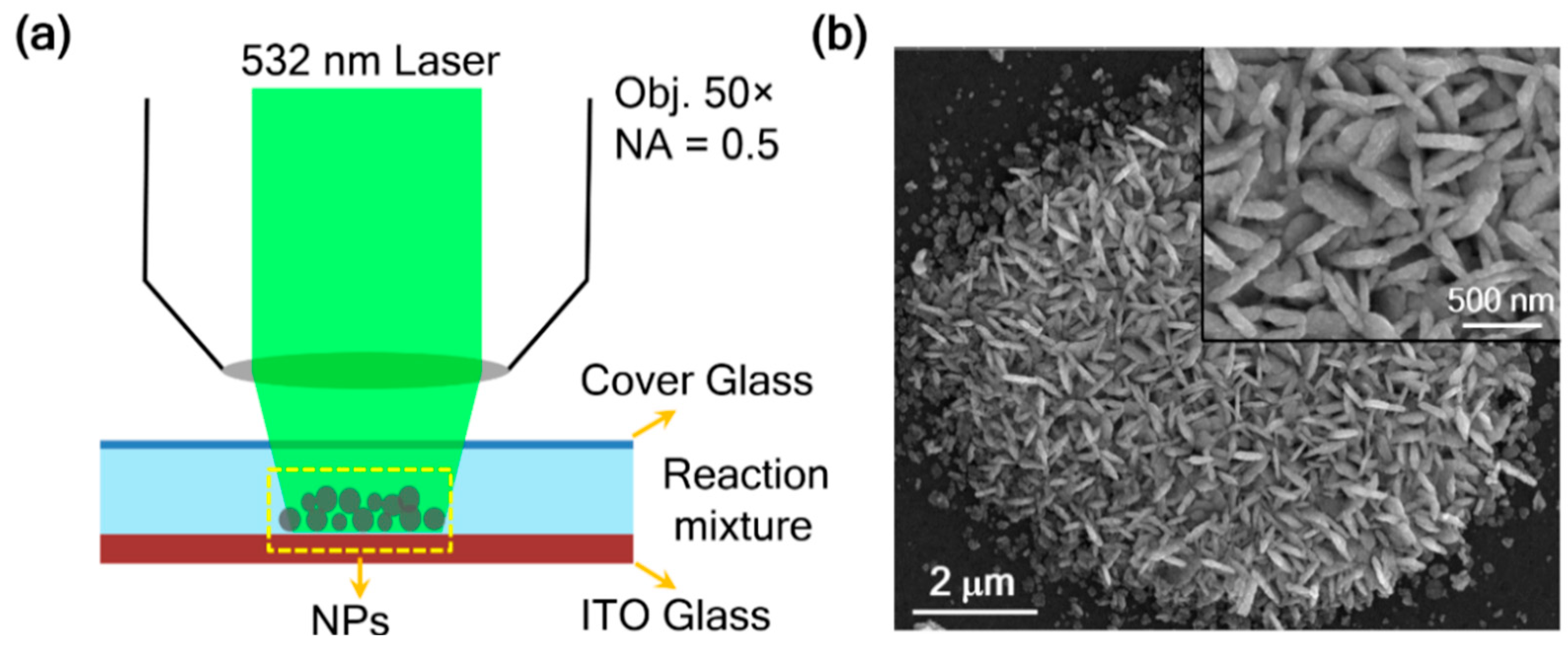
2.1. In Situ Synthesis of Silver Aggregates
2.2. SERS Measurements
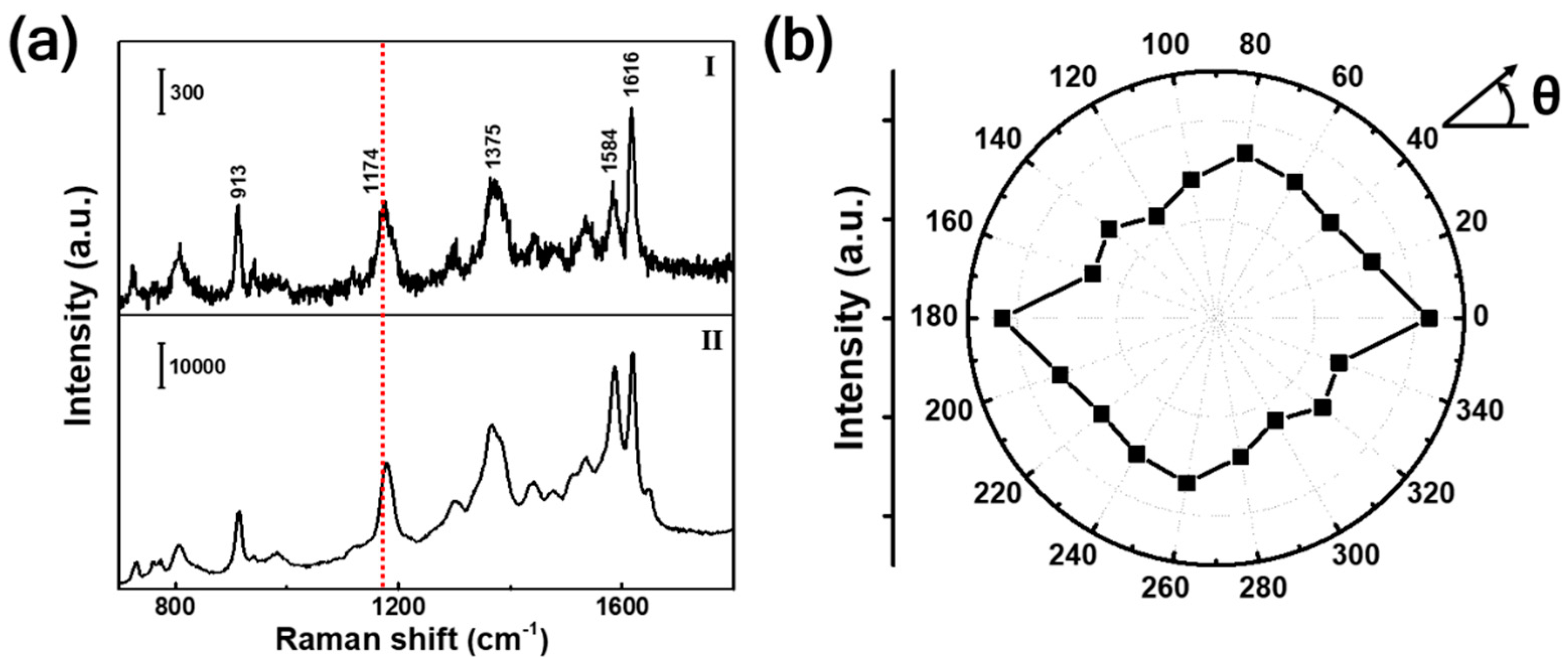
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakonen, A.; Andersson, P.O.; Schmidt, M.S.; Rindzevicius, T.; Käll, M. Explosive and chemical threat detection by surface-enhanced Raman scattering: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, R.; Liu, G.-K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Ding, S.-Y.; Li, J.-F.; Wu, D.-Y.; Tian, Z.-Q. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Bottlenecks and future directions. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.-K.; Jeon, K.-S.; Kim, H.M.; Nam, J.-M.; Suh, Y.D. Nanogap-engineerable Raman-active nanodumbbells for single-molecule detection. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Bjerneld, E.J.; Käll, M.; Börjesson, L. Spectroscopy of single hemoglobin molecules by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, N.; Ji, D.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Z.; Jornet, J.M.; Thompson, A.C.; Collins, R.L.; et al. Superabsorbing metasurfaces with hybrid Ag–Au nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy sensing of drugs and chemicals. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1800045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, L.W.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Petkovic, K.; Liang, Y.; Si, K.J.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, W. Bifunctional plasmonic-magnetic particles for an enhanced microfluidic SERS immunoassay. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 7822–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottat, M.; Lidgi-Guigui, N.; Tijunelyte, I.; Barbillon, G.; Hamouda, F.; Gogol, P.; Aassime, A.; Lourtioz, J.-M.; Bartenlian, B.; Chapelle, M.L.D.L. Soft UV nanoimprint lithography-designed highly sensitive substrates for SERS detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Qi, G.; Xu, S.; Xu, W. Construction of highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanosensor aimed for the testing of glucose in urine. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 53800–53803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, T.; You, R.; Wu, Y.; Shen, H.; Feng, S.; Su, J. Fabrication and characterization of a highly-sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanosensor for detecting glucose in urine. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Li, M.; Jurevic, R.; Cushing, S.K.; Liu, Y.; Wu, N. A gold nanohole array based surface-enhanced Raman scattering biosensor for detection of silver (I) and mercury (II) in human saliva. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11005–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Yang, M.; Lai, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhan, J. A colorimetric and surface-enhanced Raman scattering dual-signal sensor for Hg2+ based on bismuthiol II-capped gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 723, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, Z.; Si, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Deng, H.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, C. Ultrasensitive SERS substrate integrated with uniform subnanometer scale “hot spots” created by a graphene spacer for the detection of mercury ions. Small 2017, 13, 1603347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, F.; Gong, L.; Fang, P.; Chen, J.; Tong, Y. A simple and highly sensitive thymine sensor for mercury ion detection based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and the mechanism study. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y.; et al. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, N.; Tong, L.; Zhang, J. In situ quantitative graphene-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Ma, B.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Hybrid single nanoreactor for in situ sers monitoring of plasmon-driven and small Au nanoparticles catalyzed reactions. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11394–11397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xu, H. In-situ plasmon-driven chemical reactions revealed by high vacuum tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Jing, Q.; Du, Y.; Zhang, B.; Meng, X.; Sun, M.; Schanze, K.S.; Gao, H.; Xu, P. An in situ SERS study of substrate-dependent surface plasmon induced aromatic nitration. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5285–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Gao, W.; Han, Z.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; He, E.; Zheng, H. Ag-Au alloy nanoparticles: Synthesis and in situ monitoring SERS of plasmonic catalysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Aizpurua, J.; Käll, M.; Apell, P. Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, J.M.; Henry, A.-I.; Wustholz, K.L.; Natan, M.J.; Freeman, R.G.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Schatz, G.C. Gold nanoparticle dimer plasmonics: Finite element method calculations of the electromagnetic enhancement to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y. Mesoscopic and microscopic strategies for engineering plasmon-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1701097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-Y.; You, E.-M.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Moskovits, M. Electromagnetic theories of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4042–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Lin, X.-F.; Yang, Z.-L.; Liu, G.-K.; Aroca, R.F.; Mao, B.-W.; Tian, Z.-Q. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering in the ultraviolet spectral region: UV-SERS on rhodium and ruthenium electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9598–9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Duan, S.; Xu, X.; Ren, B.; Lin, S.-H.; Tian, Z.-Q. Chemical enhancement effects in SERS spectra: A quantum chemical study of pyridine interacting with copper, silver, gold and platinum metals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 4195–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, N.; Greeneltch, N.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Schatz, G.C. A look at the origin and magnitude of the chemical contribution to the enhancement mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): Theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halas, N.J.; Lal, S.; Chang, W.-S.; Link, S.; Nordlander, P. Plasmons in strongly coupled metallic nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3913–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Meng, L.-Y.; Shan, H.-Y.; Li, J.-F.; Qian, L.; Williams, C.T.; Yang, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-Q. How to light special hot spots in multiparticle–film configurations. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Chen, S.; Radjenovic, P.; Bodappa, N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Z.-L.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Li, J.-F. Probing the location of 3D hot spots in gold nanoparticle films using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 5316–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering based in situ hybridization strategy for telomere length assessment. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2950–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, K.; Cui, Y. Mixing assisted “hot spots” occupying SERS strategy for highly sensitive in situ study. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4535–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H. Highly surface-roughened “flower-like” silver nanoparticles for extremely sensitive substrates of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4614–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Meng, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z. Three-dimensional and time-ordered surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot-spot matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, T.; Sander, T.; Chen, L.; Klar, P.J. Centimeter-scale-homogeneous SERS substrates with seven-order global enhancement through thermally controlled plasmonic nanostructures. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5099–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ye, H. Sharp convex gold grooves for fluorescence enhancement in micro/nano fluidic biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 8839–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbillon, G. Fabrication and SERS performances of metal/Si and metal/ZnO nanosensors: A review. Coatings 2019, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Deng, M.; Rao, G.; Yan, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiao, Y.; Deng, A.; Yan, C.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; et al. High-performance SERS substrate based on hierarchical 3D Cu nanocrystals with efficient morphology control. Small 2018, 14, 1802477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Xu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, R.; Yao, J. Self-assembled large-scale monolayer of Au nanoparticles at the air/water interface used as a SERS substrate. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4530–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Schade, N.B.; Sun, L.; Fan, J.A.; Bae, D.R.; Mariscal, M.M.; Lee, G.; Capasso, F.; Sacanna, S.; Manoharan, V.N.; et al. Ultrasmooth, highly spherical monocrystalline gold particles for precision plasmonics. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11064–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Zhao, B.; Li, B.; Ozaki, Y. Mercaptoacetic acid-capped silver nanoparticles colloid: Formation, morphology, and SERS activity. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-M.; Yang, Y.; Qin, D. Hollow nanocubes made of Ag–Au alloys for SERS detection with sensitivity of 10−8 M for melamine. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9934–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozuch, J.; Petrusch, N.; Gkogkou, D.; Gernert, U.; Weidinger, I.M. Calculating average surface enhancement factors of randomly nanostructured electrodes by a combination of SERS and impedance spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21220–21225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, A.; Sinsermsuksakul, P.; Yang, P. Polyhedral silver nanocrystals with distinct scattering signatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4597–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Tian, X.-D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.-F. Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy through the interface-assisted self-assembly of three-dimensional silver nanorod substrates. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7275–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, S.; Zhang, H.; Xie, F.; Gong, L.; Wei, Z.; Jin, H.; Chen, J. Highly sensitive detection of glucose: A quantitative approach employing nanorods assembled plasmonic substrate. Talanta 2017, 165, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, S.-G. Highly sensitive and on-site NO2 SERS sensors operated under ambient conditions. Analyst 2018, 143, 3006–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wei, H.; Hao, F.; Nordlander, P.; Xu, H. Remote-excitation surface-enhanced Raman scattering using propagating Ag nanowire plasmons. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dai, X.; Stogin, B.B.; Wong, T.-S. Ultrasensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection in common fluids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Luo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chu, P.K.; Li, J.; Yu, X.-F. Efficient enrichment and self-assembly of hybrid nanoparticles into removable and magnetic SERS substrates for sensitive detection of environmental pollutants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7472–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerneld, E.J.; Murty, K.; Prikulis, J.; Käll, M. Laser-induced growth of Ag nanoparticles from aqueous solutions. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2002, 3, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerneld, E.J.; Svedberg, F.; Käll, M. Laser-induced growth and deposition of noble-metal nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, N.; Lendl, B. On-column silver substrate synthesis and surface-enhanced Raman detection in capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, K.; Szabó, L.; Leopold, L.F.; Chiş, V.; Leopold, N. In situ laser-induced photochemical silver substrate synthesis and sequential SERS detection in a flow cell. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.-B.; Ma, Z.-C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Niu, L.-G.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zheng, W.-H.; Zhao, B.; Xu, Y.; et al. Localized flexible integration of high-efficiency surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) monitors into microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3347–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, S.; Mao, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, C.; Cohick, Z.; Huang, P.-H.; Huang, T.J. In situ fabrication of 3D Ag@ZnO nanostructures for microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman scattering systems. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12175–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Han, B.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Chen, Q.-D.; Sun, H.-B. Femtosecond laser direct writing of plasmonic Ag/Pd alloy nanostructures enables flexible integration of robust SERS substrates. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Z. In situ two-step photoreduced SERS materials for on-chip single-molecule spectroscopy with high reproducibility. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.P.; Bignell, L.J.; Romeo, T.C.; Razal, J.M.; Shepherd, R.L.; Chen, J.; Minett, A.I.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. The citrate-mediated shape evolution of transforming photomorphic silver nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7807–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, M.; Scardaci, V.; D’Urso, L.; Puglisi, O.; Fazio, E.; Compagnini, G. Plasmon sensing and enhancement of laser prepared silver colloidal nanoplates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elechiguerra, J.L.; Reyes-Gasga, J.; Yacaman, M.J. The role of twinning in shape evolution of anisotropic noble metal nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 3906–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañamares, M.V.; Chenal, C.; Birke, R.L.; Lombardi, J.R. DFT, SERS, and single-molecule SERS of crystal violet. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 20295–20300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Chen, T. 3D hierarchical Ag nanostructures formed on poly (acrylic acid) brushes grafted graphene oxide as promising SERS substrates. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Dai, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhang, X.; Fu, L.; Jiang, C. Ultrasensitive SERS performance in 3D “sunflower-like” nanoarrays decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3114–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryche, J.-F.; Bélier, B.; Bartenlian, B.; Barbillon, G. Low-cost SERS substrates composed of hybrid nanoskittles for a highly sensitive sensing of chemical molecules. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, B.J.; Chen, Y.; Mclellan, J.M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Z.; Ginger, D.; Xia, Y. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanobars and nanorice. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Käll, M. Polarization-dependent surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of isolated silver nanoaggregates. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2003, 4, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pong, B.-K.; Elim, H.I.; Chong, J.-X.; Ji, W.; Trout, B.L.; Lee, J.-Y. New insights on the nanoparticle growth mechanism in the citrate reduction of gold (III) salt: Formation of the Au nanowire intermediate and its nonlinear optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6281–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xiao, X.; Yang, C. Surfactantless photochemical deposition of gold nanoparticles on an optical fiber core for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4623–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Halas, N.J. Mesoscopic Au “meatball” particles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Du, S.; Lebedkin, S.; Li, Z.; Kruk, R.; Kappes, M.; Hahn, H. Gold mesostructures with tailored surface topography and their self-assembly arrays for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 5006–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Z.; You, H.; Tian, C.; Li, Z.; Fang, J. Gold mesoparticles with precisely controlled surface topographies for single-particle surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 5567–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Li, Z. Controlling the Morphologies of Silver Aggregates by Laser-Induced Synthesis for Optimal SERS Detection. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111529
Yang L, Yang J, Li Y, Li P, Chen X, Li Z. Controlling the Morphologies of Silver Aggregates by Laser-Induced Synthesis for Optimal SERS Detection. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(11):1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111529
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Longkun, Jingran Yang, Yuanyuan Li, Pan Li, Xiaojuan Chen, and Zhipeng Li. 2019. "Controlling the Morphologies of Silver Aggregates by Laser-Induced Synthesis for Optimal SERS Detection" Nanomaterials 9, no. 11: 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111529
APA StyleYang, L., Yang, J., Li, Y., Li, P., Chen, X., & Li, Z. (2019). Controlling the Morphologies of Silver Aggregates by Laser-Induced Synthesis for Optimal SERS Detection. Nanomaterials, 9(11), 1529. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111529



