Tunable Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heat Transformation Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
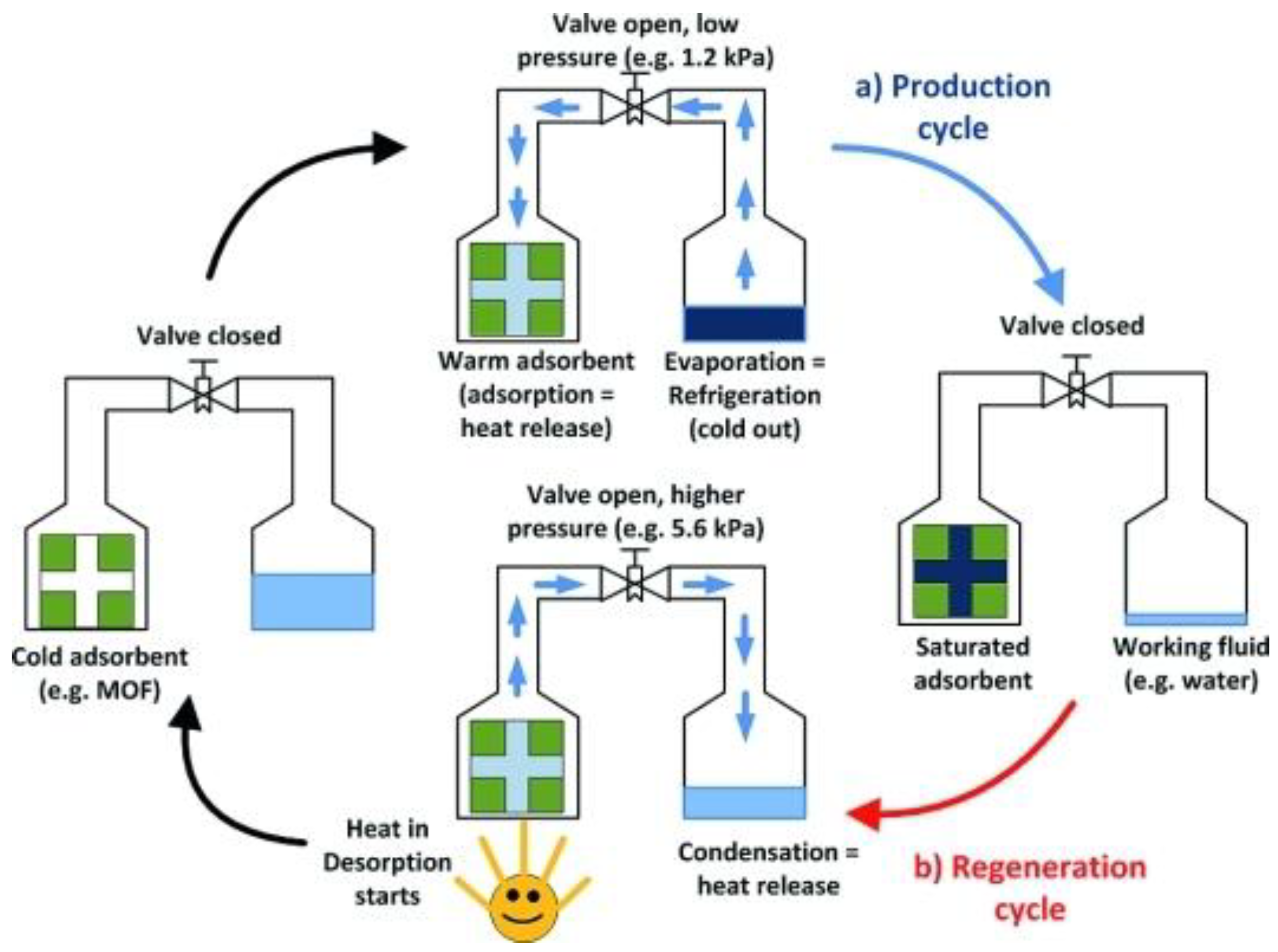
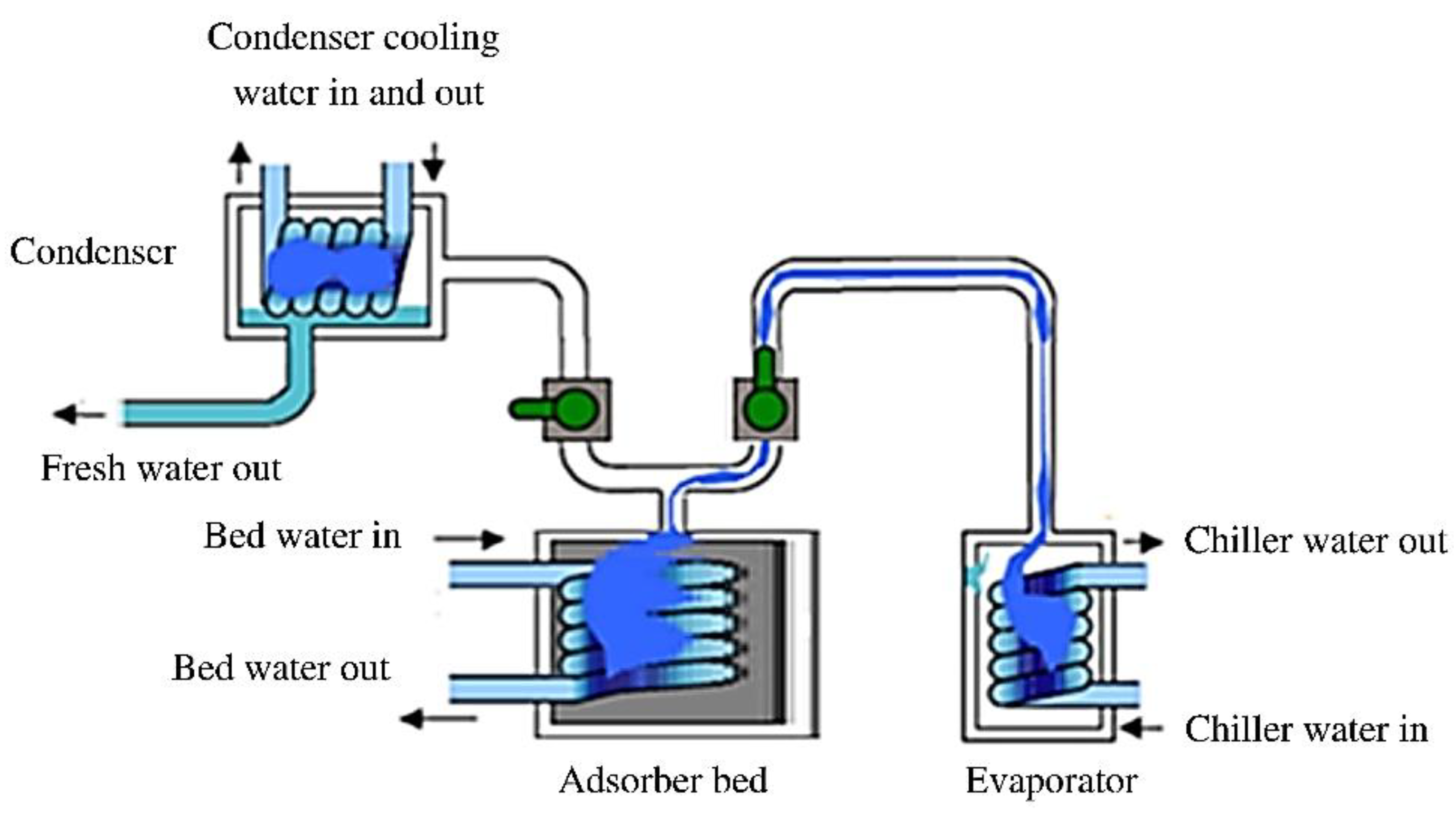
2. Heat Transformation Systems
3. Metal–Organic Frameworks as Adsorbent Materials
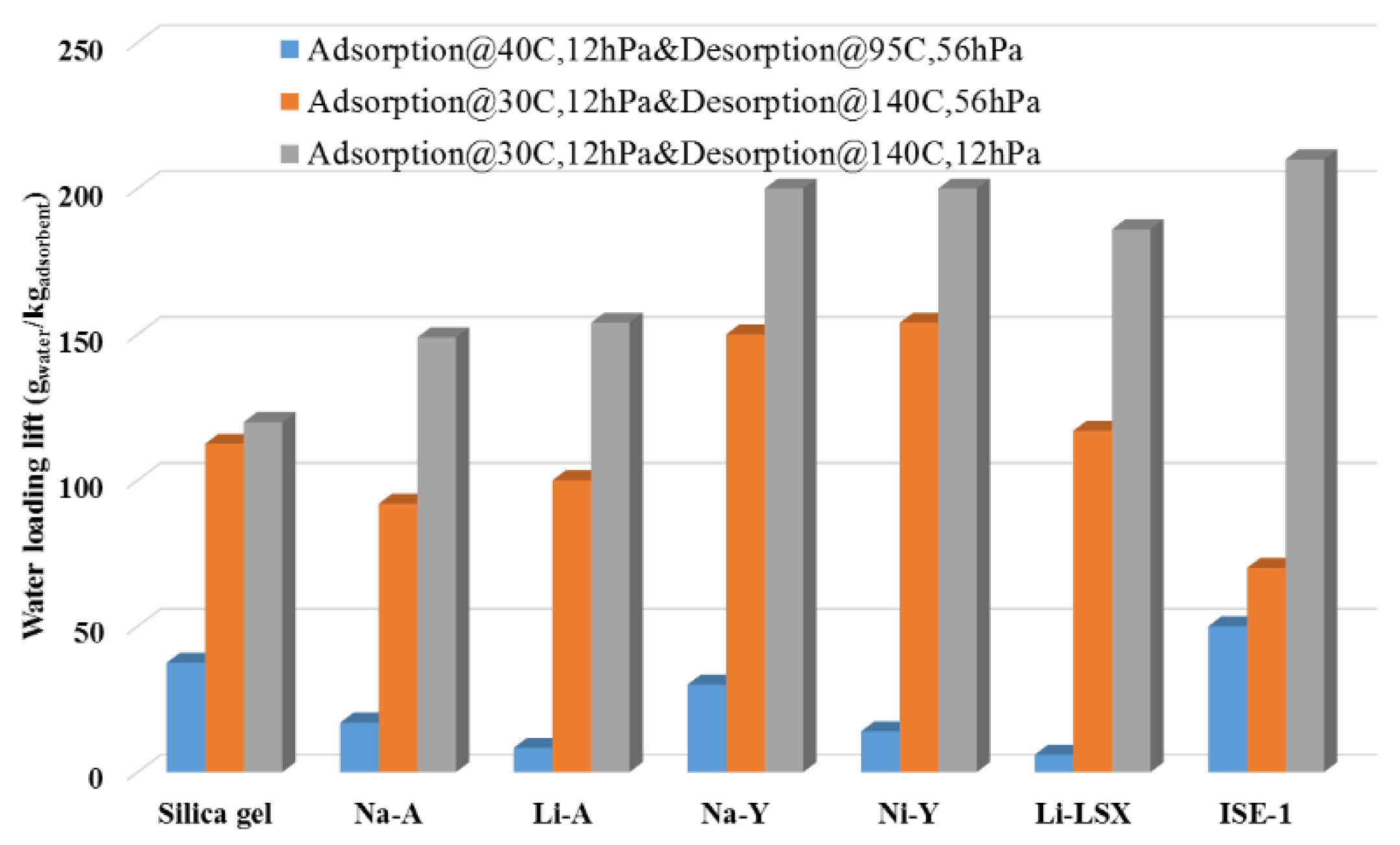
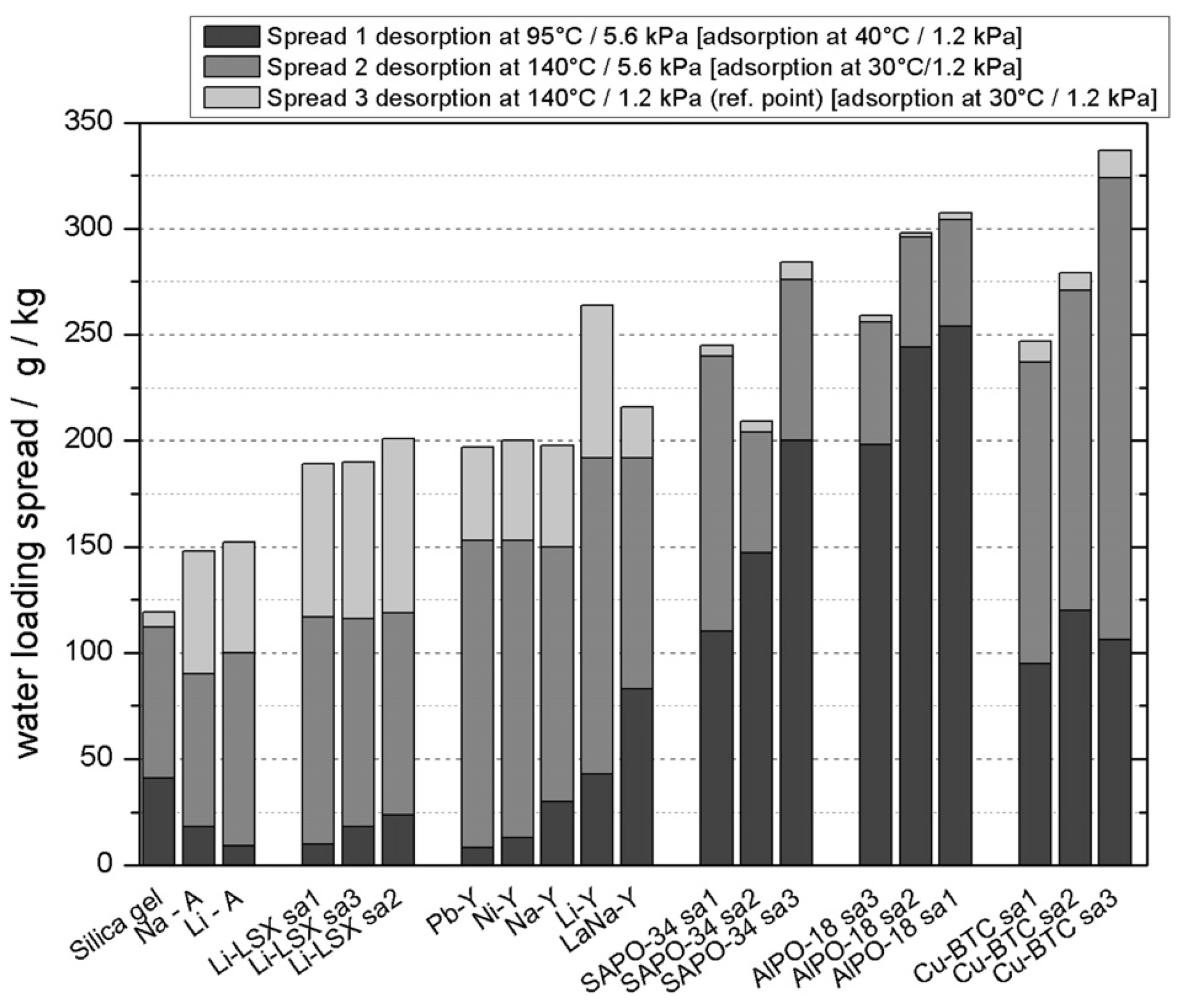
3.1. Thermodynamic Boundaries of MOF Adsorbents
3.2. Copper-Metal-Based MOFs
3.3. Chromium (Cr)-Based MOFs
3.4. Nickel (Ni)-Based MOFs
3.5. Aluminum (Al)-Based MOFs
3.6. Iron (Fe)-Based MOFs
4. Modification/Functionalization of MOFs Based on Water Adsorption
4.1. Functionalized MOFs Bearing a Ligand Functional Group
4.2. Functionalized MOFs with Composite Materials
5. Outlook
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isaac, M.; Van Vuuren, D.P. Modeling global residential sector energy demand for heating and air conditioning in the context of climate change. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alefeld, G.; Radermacher, R. Heat Conversion Systems; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, F.; Henninger, S.; Stach, H.; Jänchen, J.; Henning, H. Novel adsorbents for solar cooling applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference Solar Air Conditioning, Bad Staffelstein, Germany, 6–7 October 2005; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Henning, H.-M. Solar assisted air conditioning of buildings–an overview. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1734–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Mobedi, M.; Ülkü, S. A review on adsorption heat pump: Problems and solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2381–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Chua, H.; Chung, C.; Loke, C.; Kashiwagi, T.; Akisawa, A.; Saha, B. Experimental investigation of the silica gel–water adsorption isotherm characteristics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhou, W.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Methane storage in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5657–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, K.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Pillai, R.S.; Cadiau, A.; Bhatt, P.M.; Assen, A.H.; Maurin, G.; Eddaoudi, M. Gas/vapour separation using ultra-microporous metal–organic frameworks: Insights into the structure/separation relationship. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3402–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogge, S.M.J.; Bavykina, A.; Hajek, J.; Garcia, H.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Vimont, A.; Clet, G.; Bazin, P.; Kapteijn, F.; et al. Metal–organic and covalent organic frameworks as single-site catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3134–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, S.; Lismont, M.; Escudero, A.; Rungtaweevoranit, B.; Parak, W.J. Positioning metal-organic framework nanoparticles within the context of drug delivery—A comparison with mesoporous silica nanoparticles and dendrimers. Biomater 2017, 123, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, R.; Lächelt, U.; Gruber, T.; Rühle, B.; Wuttke, S. Multifunctional Efficiency: Extending the Concept of Atom Economy to Functional Nanomaterials. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lismont, M.; Dreesen, L.; Wuttke, S. Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles in Photodynamic Therapy: Current Status and Perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L. Metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaemchuen, S.; Kabir, N.A.; Zhou, K.; Verpoort, F. Metal–organic frameworks for upgrading biogas via CO 2 adsorption to biogas green energy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9304–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chughtai, A.H.; Ahmad, N.; Younus, H.A.; Laypkov, A.; Verpoort, F. Metal–organic frameworks: Versatile heterogeneous catalysts for efficient catalytic organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6804–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendon, C.H.; Rieth, A.J.; Korzyński, M.D.; Dincă, M. Grand Challenges and Future Opportunities for Metal–Organic Frameworks. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henninger, S.K.; Jeremias, F.; Kummer, H.; Janiak, C. MOFs for use in adsorption heat pump processes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 2625–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younos, T.; Tulou, K.E. Overview of desalination techniques. J. Contemp. Phys. 2005, 132, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, P.G.; Dakkama, H.; Mahmoud, S.M.; AL-Dadah, R.K. Experimental investigation of adsorption water desalination/cooling system using CPO-27Ni MOF. Desalination 2017, 404, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ng, K.C. Experimental investigation of an adsorption desalination plant using low-temperature waste heat. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.C.; Xiao-Lin, W.; Gao, L.; Chakraborty, A.; Saha, B.B.; Koyama, S.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Apparatus and Method for Desalination. US patent 8535486B2, 17 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thu, K.; Ng, K.C.; Saha, B.B.; Chakraborty, A.; Koyama, S. Operational strategy of adsorption desalination systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2009, 52, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, S.; Schmidt, F.; Henning, H.-M. Water adsorption characteristics of novel materials for heat transformation applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, V.; Frazzica, A. Characterisation and comparative analysis of zeotype water adsorbents for heat transformation applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 180, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Liu, Y.; Howe, J.D.; Sholl, D.S. Competitive Binding of Ethylene, Water, and Carbon Monoxide in Metal–Organic Framework Materials with Open Cu Sites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8960–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlier, M.; Munz, G.; Henninger, S.K. Relation of water adsorption capacities of zeolites with their structural properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 264, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristov, Y.I. Novel materials for adsorptive heat pumping and storage: Screening and nanotailoring of sorption properties. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2007, 40, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Gándara, F.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Jiang, J.; Queen, W.L.; Hudson, M.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Water Adsorption in Porous Metal–Organic Frameworks and Related Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivet, J.; Bonnefoy, J.; Daniel, C.; Legrand, A.; Coasne, B.; Farrusseng, D. Structure–property relationships of water adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water stability and adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaemchuen, S.; Wang, J.C.; Gilani, A.G.; Verpoort, F. Metal-organic frameworks applied for water purification. Resour. Efficient Technol. 2018, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.M.; Vaidhyanathan, R.; Iremonger, S.S.; Shimizu, G.K. Enhancing water stability of metal–organic frameworks via phosphonate monoester linkers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14338–14340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivet, J.; Fateeva, A.; Guo, Y.; Coasne, B.; Farrusseng, D. Water adsorption in MOFs: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5594–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasuja, H.; Burtch, N.C.; Huang, Y.-G.; Cai, Y.; Walton, K.S. Kinetic water stability of an isostructural family of zinc-based pillared metal–organic frameworks. Langmuir 2013, 29, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Pei, X.; Zhang, S.; Feng, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B. Water Purification: Adsorption over Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chin. J. Chem. 2016, 34, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, J.; Feng, R.; Hu, T.-L.; Bu, X.-H. Governing metal–organic frameworks towards high stability. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8501–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towsif Abtab, S.M.; Alezi, D.; Bhatt, P.M.; Shkurenko, A.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Aggarwal, H.; Weseliński, Ł.J.; Alsadun, N.; Samin, U.; Hedhili, M.N.; et al. Reticular Chemistry in Action: A Hydrolytically Stable MOF Capturing Twice Its Weight in Adsorbed Water. CHEM 2018, 4, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, H.; van der Veen, M.A.; Gil, B.; Marszalek, B.; Verbiest, T.; De Vos, D.; Stock, N. Structures, sorption characteristics, and nonlinear optical properties of a new series of highly stable aluminum MOFs. Chem. Mater. 2012, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, H.; Marszalek, B.; Wack, J.; Senker, J.; Gil, B.; Stock, N. A new Al-MOF based on a unique column-shaped inorganic building unit exhibiting strongly hydrophilic sorption behaviour. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9486–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küsgens, P.; Rose, M.; Senkovska, I.; Fröde, H.; Henschel, A.; Siegle, S.; Kaskel, S. Characterization of metal-organic frameworks by water adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 120, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, G.; Matsuda, R.; Kitagawa, S. Highly porous and stable coordination polymers as water sorption materials. Chem. Lett. 2010, 39, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, F.; Khutia, A.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. MIL-100(Al, Fe) as water adsorbents for heat transformation purposes-a promising application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10148–10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickenheisser, M.; Jeremias, F.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. Grafting of hydrophilic ethylene glycols or ethylenediamine on coordinatively unsaturated metal sites in MIL-100(Cr) for improved water adsorption characteristics. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2013, 407, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenmann, J.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. Water Adsorption Characteristics of MIL-101 for Heat-Transformation Applications of MOFs. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, G.; Matsuda, R.; Sato, H.; Hori, A.; Takata, M.; Kitagawa, S. Effect of functional groups in MIL-101 on water sorption behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 157, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutia, A.; Rammelberg, H.U.; Schmidt, T.; Henninger, S.; Janiak, C. Water Sorption Cycle Measurements on Functionalized MIL-101Cr for Heat Transformation Application. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, F.; Lozan, V.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. Programming MOFs for water sorption: Amino-functionalized MIL-125 and UiO-66 for heat transformation and heat storage applications. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 15967–15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, A.; Yamada, T.; Kitagawa, H. Wide control of proton conductivity in porous coordination polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2034–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, C.R.; Corrales-Sanchez, T.; Narayan, T.C.; Dincă, M. Postsynthetic tuning of hydrophilicity in pyrazolate MOFs to modulate water adsorption properties. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Benin, A.I.; Jakubczak, P.; Willis, R.R.; LeVan, M.D. CO2/H2O Adsorption Equilibrium and Rates on Metal−Organic Frameworks: HKUST-1 and Ni/DOBDC. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14301–14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenecker, P.M.; Carson, C.G.; Jasuja, H.; Flemming, C.J.; Walton, K.S. Effect of water adsorption on retention of structure and surface area of metal–organic frameworks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6513–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cmarik, G.E.; Kim, M.; Cohen, S.M.; Walton, K.S. Tuning the Adsorption Properties of UiO-66 via Ligand Functionalization. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15606–15613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henninger, S.K.; Habib, H.A.; Janiak, C. MOFs as adsorbents for low temperature heating and cooling applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2776–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, B.B.; El-Sharkawy, I.I.; Miyazaki, T.; Koyama, S.; Henninger, S.K.; Herbst, A.; Janiak, C. Ethanol adsorption onto metal organic framework: Theory and experiments. Energy 2015, 79, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, F.; Frohlich, D.; Janiak, C.; Henninger, S.K. Advancement of sorption-based heat transformation by a metal coating of highly-stable, hydrophilic aluminium fumarate MOF. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 24073–24082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeeva, L.G.; Solovyeva, M.V.; Aristov, Y.I. NH2-MIL-125 as a promising material for adsorptive heat transformation and storage. Energy 2016, 100, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristov, Y.I.; Tokarev, M.M.; Sharonov, V.E. Universal relation between the boundary temperatures of a basic cycle of sorption heat machines. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 2907–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristov, Y.I. Challenging offers of material science for adsorption heat transformation: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, S.S.-Y.; Lo, S.M.-F.; Charmant, J.P.; Orpen, A.G.; Williams, I.D. A chemically functionalizable nanoporous material [Cu3(TMA)2(H2O)3]n. Science 1999, 283, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowsell, J.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Effects of functionalization, catenation, and variation of the metal oxide and organic linking units on the low-pressure hydrogen adsorption properties of metal—organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichte, K.; Kratzke, T.; Kaskel, S. Improved synthesis, thermal stability and catalytic properties of the metal-organic framework compound Cu3(BTC)2. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 73, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestipino, C.; Regli, L.; Vitillo, J.; Bonino, F.; Damin, A.; Lamberti, C.; Zecchina, A.; Solari, P.; Kongshaug, K.; Bordiga, S. Local structure of framework Cu (II) in HKUST-1 metallorganic framework: Spectroscopic characterization upon activation and interaction with adsorbates. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaura, R.; Fujimoto, K.; Noro, S.I.; Kondo, M.; Kitagawa, S. A Pillared-Layer Coordination Polymer Network Displaying Hysteretic Sorption:[Cu2(pzdc)2(dpyg)]n (pzdc=Pyrazine-2, 3-dicarboxylate; dpyg=1, 2-Di (4-pyridyl) glycol). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 114, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn, P.L.; Bourrelly, S.; Serre, C.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Hamon, L.; De Weireld, G.; Chang, J.-S.; Hong, D.-Y.; Kyu Hwang, Y.; et al. High Uptakes of CO2 and CH4 in Mesoporous Metal—Organic Frameworks MIL-100 and MIL-101. Langmuir 2008, 24, 7245–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, P.; Bikkina, C.; Gumma, S. Gas adsorption properties of the chromium-based metal organic framework MIL-J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6616–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, E.; Raya, A.-D.; Mahmoud, S.; Anderson, P.A.; Elsayed, A.; Youssef, P.G. CPO-27 (Ni), aluminium fumarate and MIL-101 (Cr) MOF materials for adsorption water desalination. Desalination 2017, 406, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieth, A.J.; Dincă, M. Tricking Inert Metals into Water-Absorbing MOFs. Joule 2018, 2, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.; Al-Dadah, R.; Mahmoud, S.; Shi, B.; Youessef, P.; Elshaer, A.; Kaialy, W. Characterisation of CPO-27Ni Metal Organic Framework Material for Water Adsorption. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Thermal Energy management Network (SUSTEM), Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 7–8 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Elsayed, E.; Raya, A.-D.; Mahmoud, S.; Elsayed, A.; Anderson, P.A. Aluminium fumarate and CPO-27 (Ni) MOFs: Characterization and thermodynamic analysis for adsorption heat pump applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 99, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.; Guillou, N.; Martineau, C.; Bueken, B.; Van de Voorde, B.; Le Guillouzer, C.; Fabry, P.; Nouar, F.; Taulelle, F.; De Vos, D. The structure of the aluminum fumarate metal–organic framework AAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3664–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loiseau, T.; Serre, C.; Huguenard, C.; Fink, G.; Taulelle, F.; Henry, M.; Bataille, T.; Ferey, G. A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (mil-53) upon hydration. Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lange, M.; Zeng, T.; Vlugt, T.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Manufacture of dense CAU-10-H coatings for application in adsorption driven heat pumps: Optimization and characterization. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2015, 17, 5911–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, D.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. Multicycle water vapour stability of microporous breathing MOF aluminium isophthalate CAU-10-H. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15300–15304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, D.; Pantatosaki, E.; Kolokathis, P.D.; Markey, K.; Reinsch, H.; Baumgartner, M.; van der Veen, M.A.; De Vos, D.E.; Stock, N.; Papadopoulos, G.K. Water adsorption behaviour of CAU-10-H: A thorough investigation of its structure–property relationships. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11859–11869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, L.; Serre, C.; Devic, T.; Loiseau, T.; Millange, F.; Férey, G.; Weireld, G.D. Comparative study of hydrogen sulfide adsorption in the MIL-53 (Al, Cr, Fe), MIL-47 (V), MIL-100 (Cr), and MIL-101 (Cr) metal− organic frameworks at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8775–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férey, G. Hybrid porous solids: Past, present, future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 191–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, P.; Surblé, S.; Serre, C.; Hong, D.-Y.; Seo, Y.-K.; Chang, J.-S.; Greneche, J.-M.; Margiolaki, I.; Férey, G. Synthesis and catalytic properties of MIL-100 (Fe), an iron (III) carboxylate with large pores. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasuja, H.; Zang, J.; Sholl, D.S.; Walton, K.S. Rational tuning of water vapor and CO2 adsorption in highly stable Zr-based MOFs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 23526–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-N.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.-Y.; Cho, H.-Y.; Ahn, W.-S. Adsorption/catalytic properties of MIL-125 and NH2-MIL-Catal. Today 2013, 204, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Liou, K.-H.; Kang, D.-Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Lin, L.-C. Investigation of the Water Adsorption Properties and Structural Stability of MIL-100 (Fe) with Different Anions. Langmuir 2018, 34, 4180–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-I.; Yoon, T.-U.; Kim, M.-B.; Lee, S.-J.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, H.-N.; Lee, U.-H.; Bae, Y.-S. Metal–organic frameworks with high working capacities and cyclic hydrothermal stabilities for fresh water production. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersum, A.D.; Soubeyrand-Lenoir, E.; Yang, Q.; Moulin, B.; Guillerm, V.; Yahia, M.B.; Bourrelly, S.; Vimont, A.; Miller, S.; Vagner, C. An Evaluation of UiO-66 for Gas-Based Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 3270–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, Y.; Kubo, M.; Katsumi, Y.; Meguro, T.; Komeya, K. Assessment of adsorption-desorption characteristics of adsorbents for adsorptive desiccant cooling system. Asian J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, F. Adsorption heat powered heat pumps. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 61, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Calabrese, L.; Freni, A.; Proverbio, E.; Restuccia, G. Zeolites direct synthesis on heat exchangers for adsorption heat pumps. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón-Tovar, L.; Pérez-Carvajal, J.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Composite Salt in Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks for Adsorption Heat Transformation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, N.; Cao, X. Inorganic composite sorbents for water vapor sorption: A research progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaznev, I.; Ponomarenko, I.; Kirik, S.; Aristov, Y. Composites CaCl2/SBA-15 for adsorptive transformation of low temperature heat: Pore size effect. Int. J. Refrig. 2011, 34, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bandosz, T.J. Enhanced Adsorption of Ammonia on Metal-Organic Framework/Graphite Oxide Composites: Analysis of Surface Interactions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, C.; Xiao, J.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics of water vapor on novel adsorbents MIL-101 (Cr)@ GO with super-high capacity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 84, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Burress, J.; Bandosz, T.J. The synthesis and characterization of copper-based metal–organic framework/graphite oxide composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Improved Ethanol Adsorption Capacity and Coefficient of Performance for Adsorption Chillers of Cu-BTC@ GO Composite Prepared by Rapid Room Temperature Synthesis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 11767–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, E.; Wang, H.; Anderson, P.A.; Al-Dadah, R.; Mahmoud, S.; Navarro, H.; Ding, Y.; Bowen, J. Development of MIL-101 (Cr)/GrO composites for adsorption heat pump applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 244, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, N.K.; Abramson, A.R. Thermal conductivity of graphene and graphene oxide nanoplatelets. In Proceedings of the 13th InterSociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 May–1 June 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Mousavi, B.; Luo, Z.; Phatanasri, S.; Chaemchuen, S.; Verpoort, F. Characterization and properties of Zn/Co zeolitic imidazolate frameworks vs. ZIF-8 and ZIF-J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhu, A.X.; Lin, R.B.; Qi, X.L.; Chen, X.M. Pore Surface Tailored SOD-Type Metal-Organic Zeolites. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1268–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birsa Čelič, T.; Mazaj, M.; Guillou, N.; Elkaïm, E.; El Roz, M.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Mali, G.; Rangus, M.; Čendakdak, T.; Kaučič, V.; et al. Study of hydrothermal stability and water sorption characteristics of 3-dimensional Zn-based trimesate. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 14608–14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlıer, M.; Tantekin-Ersolmaz, B.; Erdem-Şenatalar, A. A novel approach to enhance heat and mass transfer in adsorption heat pumps using the zeolite–water pair. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Herrmann, R.; Mittelbach, W.; Schwieger, W. Zeolite/aluminum composite adsorbents for application in adsorption refrigeration. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 33, 1233–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, L.; Freni, A.; Proverbio, E.; Restuccia, G.; Russo, F. Zeolite coated copper foams for heat pumping applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 91, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geus, E.R.; van Bekkum, H.; Bakker, W.J.; Moulijn, J.A. High-temperature stainless steel supported zeolite (MFI) membranes: Preparation, module construction, and permeation experiments. Microporous Mater. 1993, 1, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Freni, A.; Proverbio, E. Silicone composite foams for adsorption heat pump applications. Sustain. Mater.Technol. 2017, 12, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Bonaccorsi, L.; Freni, A.; Proverbio, E. Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolite filled macrocellular foams for adsorption heat pump applications: A preliminary study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 124, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminot, J.; Choisier, A.; Chalfen, J.; Nicolas, S.; Reymoney, J. Heat transfer intensification in fixed bed adsorbers. Heat Recover. Syst. CHP 1993, 13, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

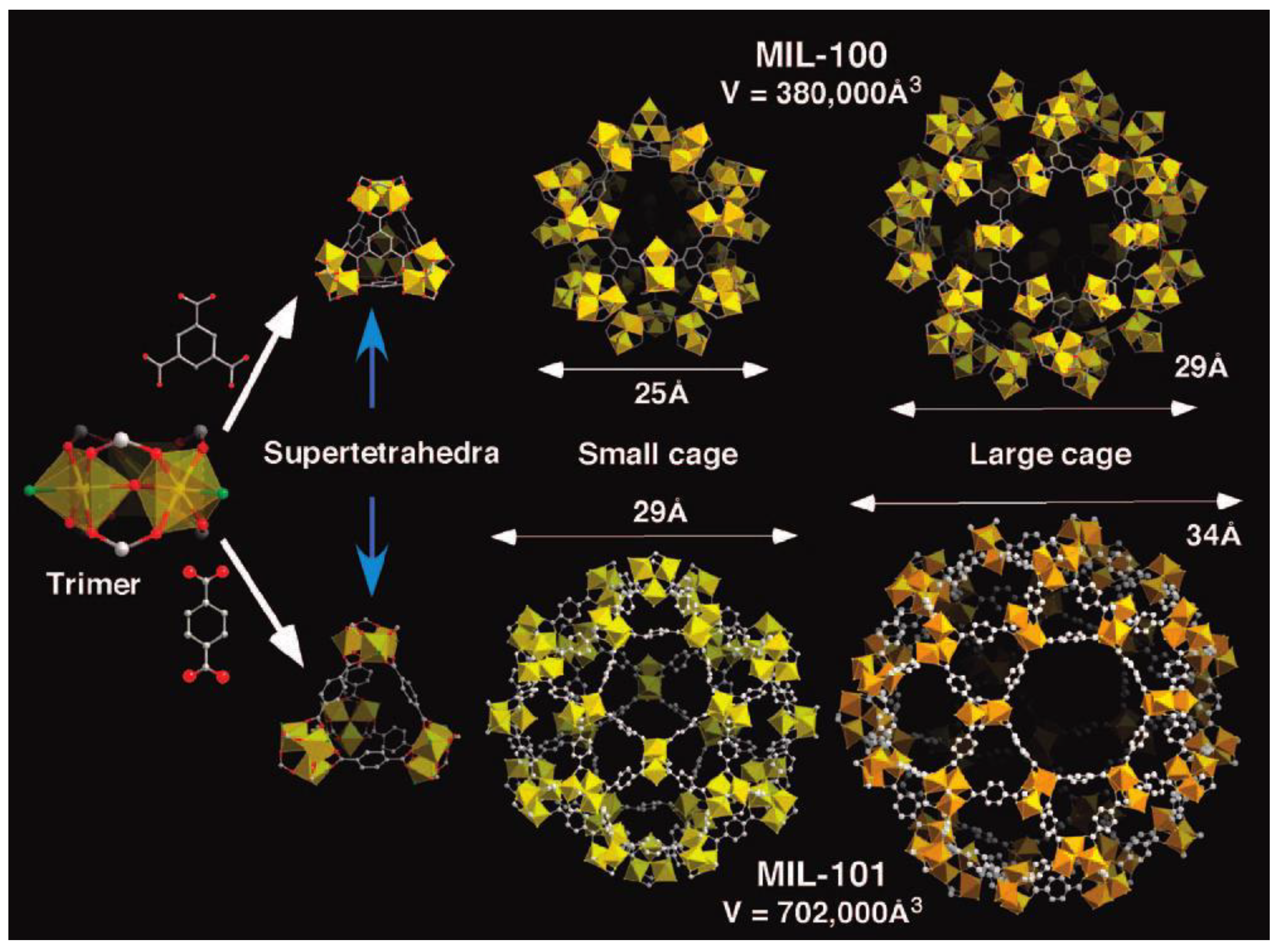

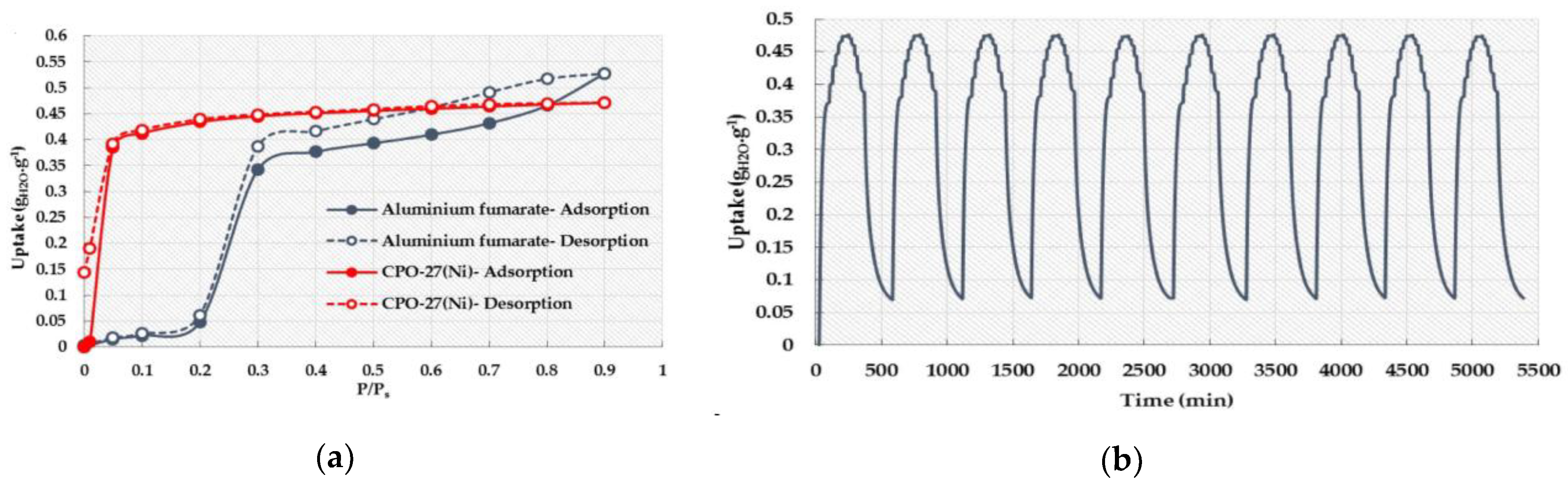
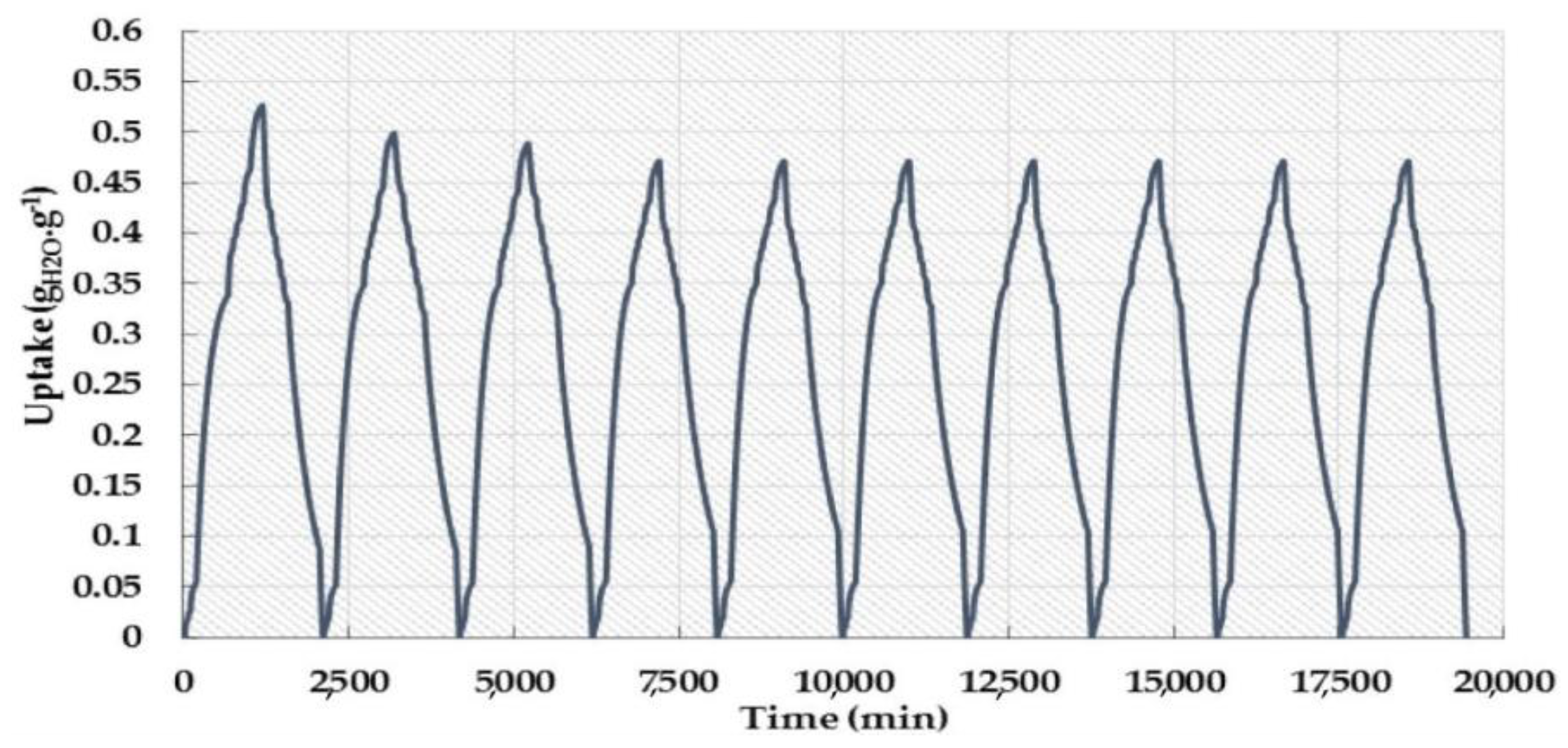
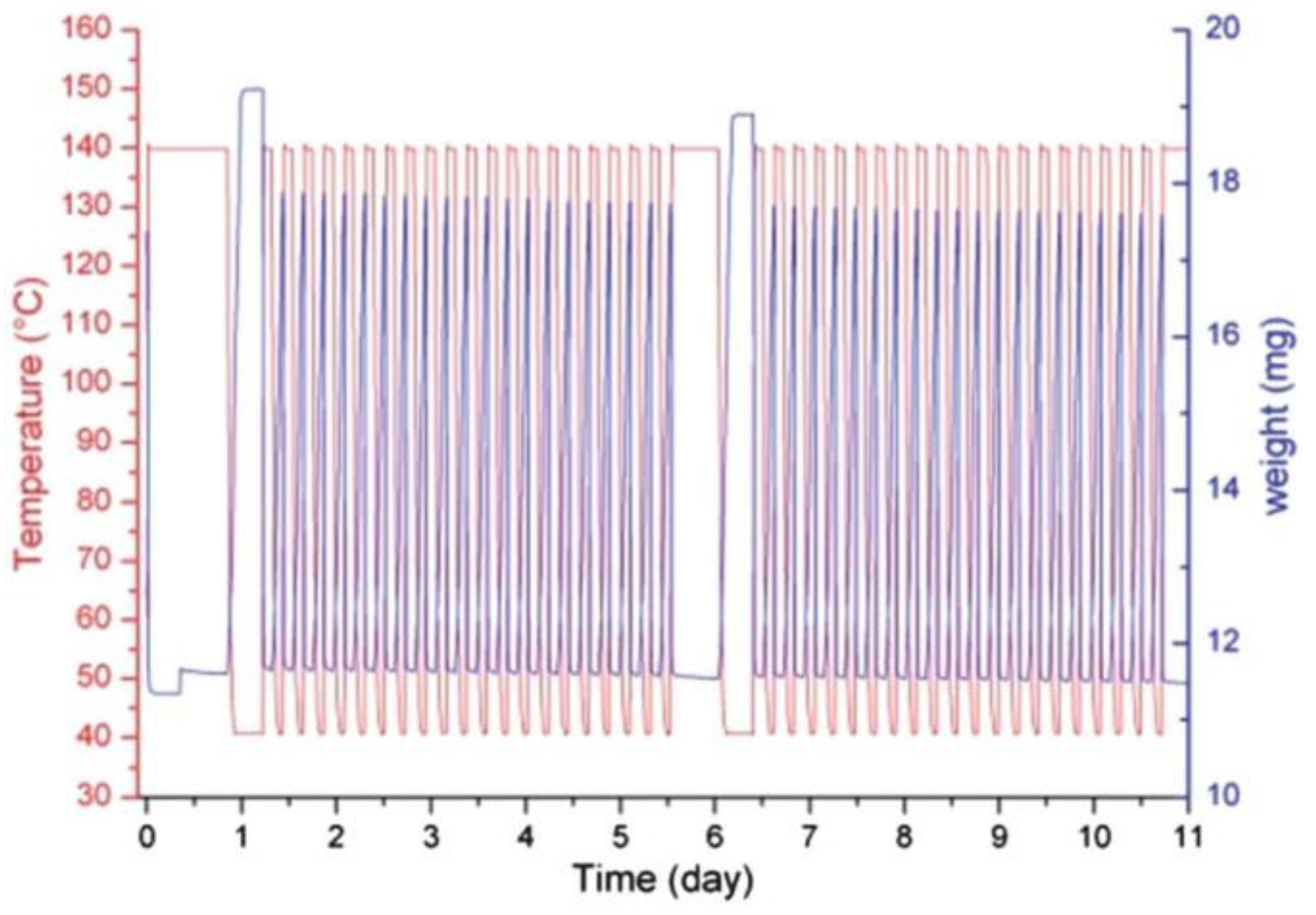
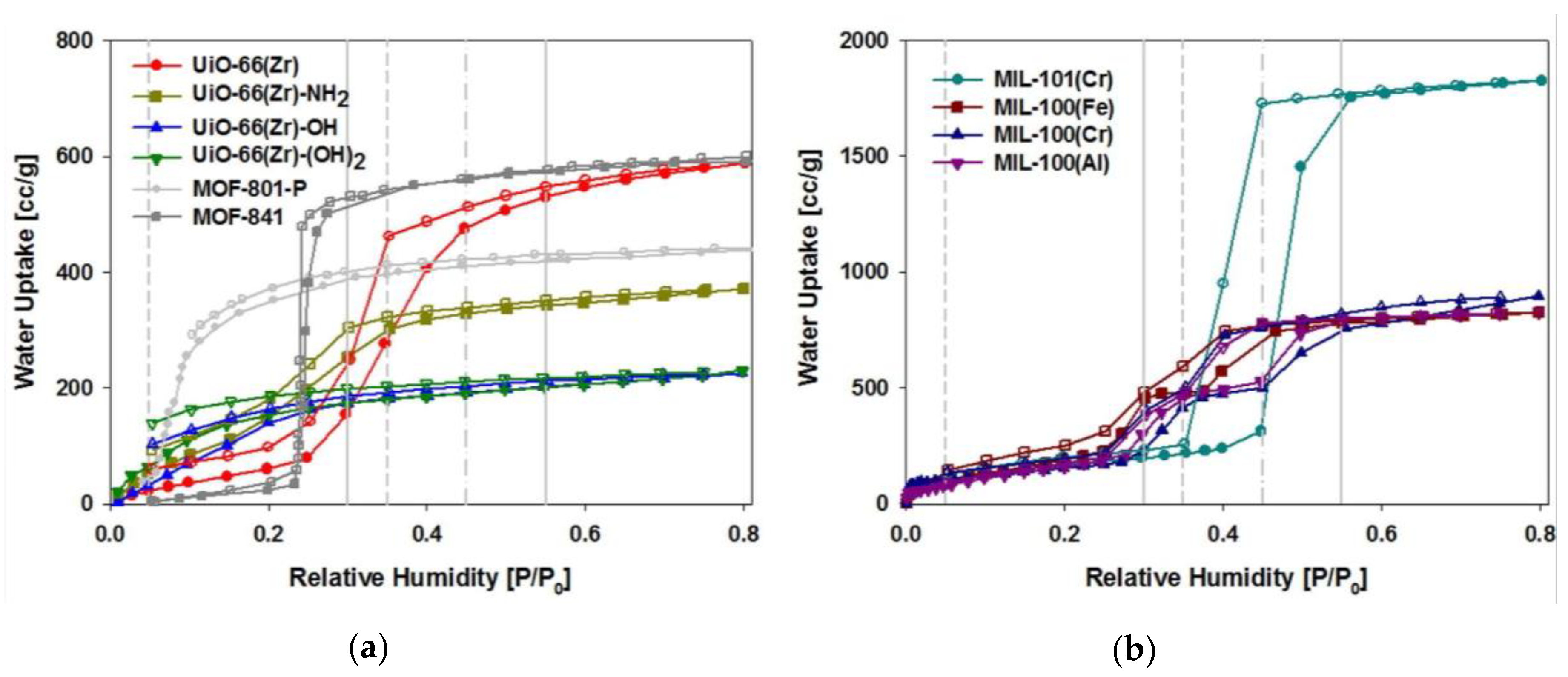
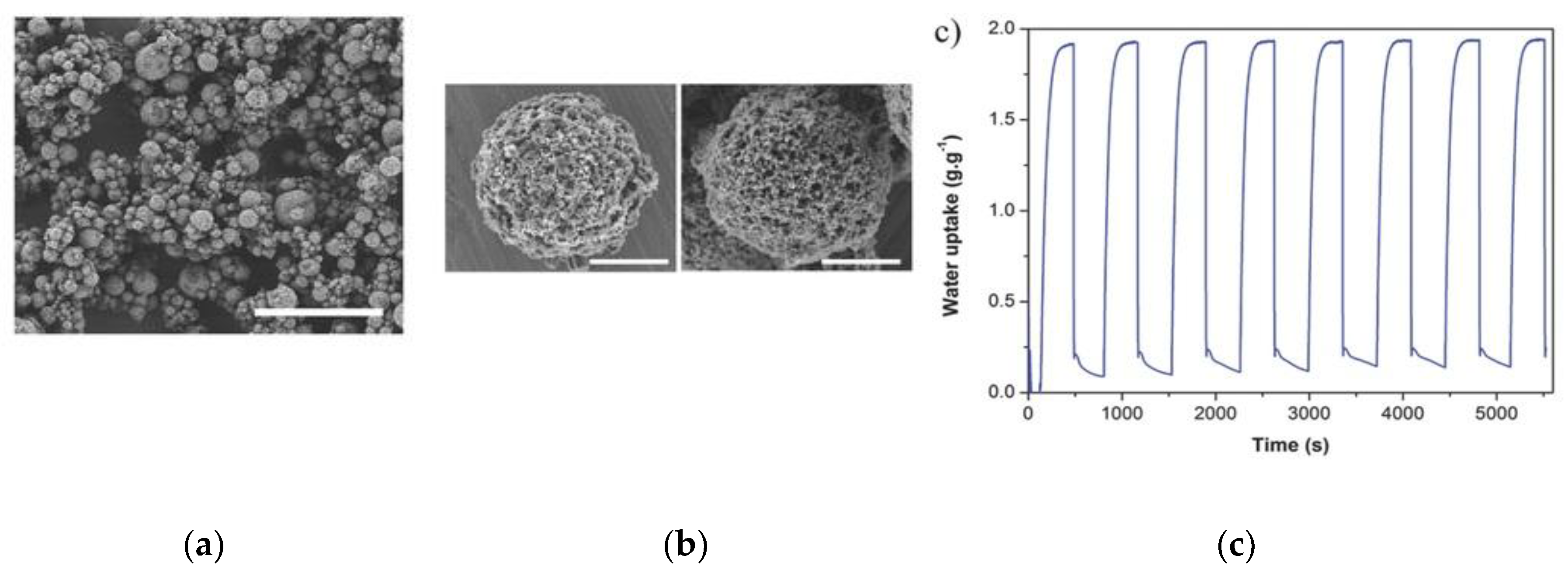
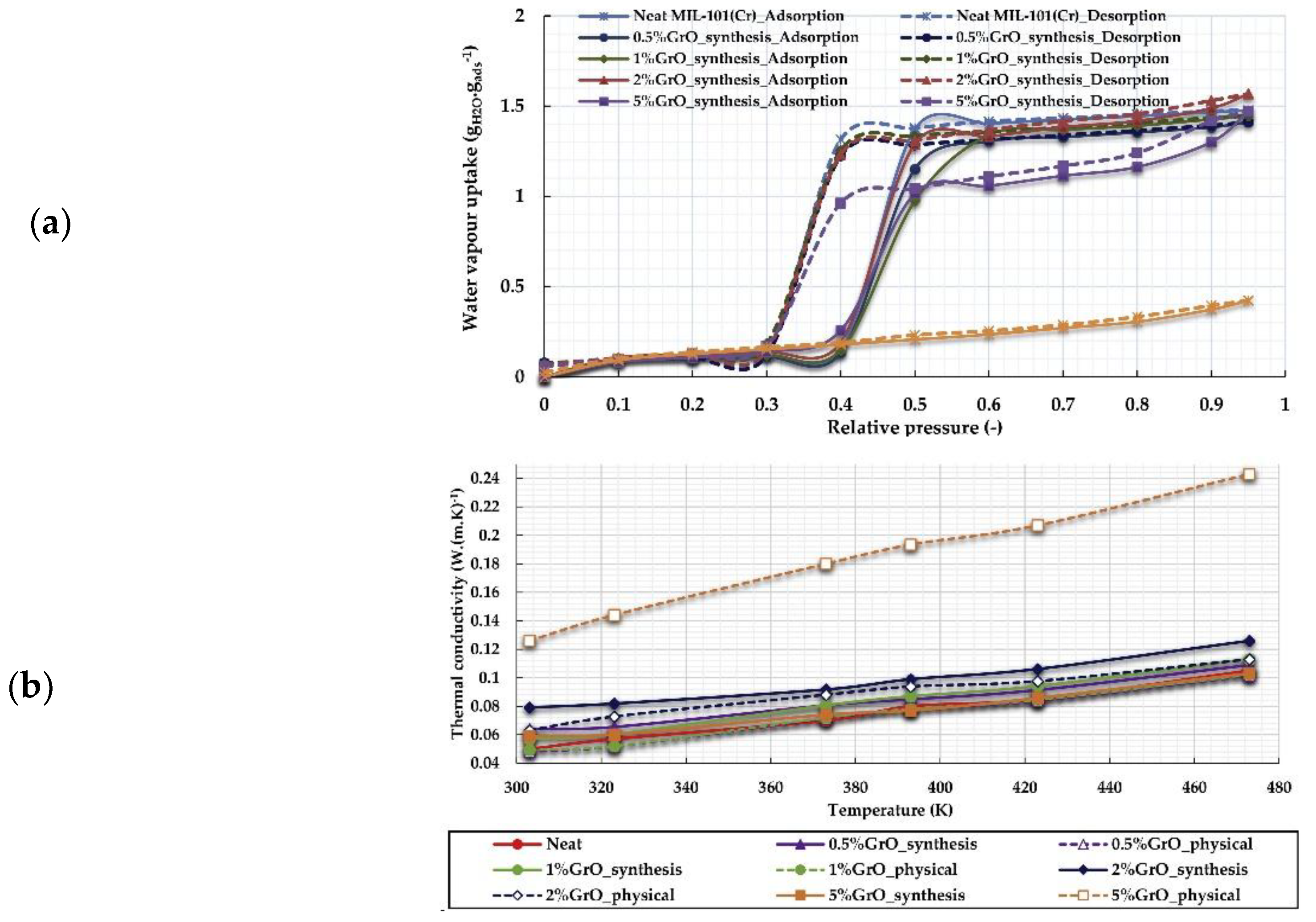
| MOFs | Metals | Linkers | Surface area (m2·g–1) | Pore diameter (nm) | Pore volume (cm3·g–1) | Uptake* (cm3·g–1) | references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAU-10 | Al | 1,3-H2BDC | 635 | 0.7 | 0.25 | 0.31 | [39] |
| CAU-10-H | Al | 1,3-H2BDC | 635 | n.d. | 0.5 | 0.382 | [39] |
| CAU-10-NH2 | Al | 5-H2BDC-NH2 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.19 | [39] |
| CAU-10-NO2 | Al | 5-H2BDC-NO2 | 440 | n.d. | 0.18 | 0.15 | [39] |
| CAU-10-OCH3 | Al | 5-methoxyiso-phthalic acid | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.07 | [39] |
| CAU-10-OH | Al | 5- H2BDC-OH | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.27 | [39] |
| CAU-6 | Al | BDC- NH2 | 620 | n.d. | 0.25 | 0.485 | [40] |
| DUT-4 | Al | H2NDC | 1360 | n.d. | 0.79 | 0.28 | [41] |
| DUT-67 | Zr | H2TDC | 1560 | 1.66/0.88 | 0.60 | 0.625 | [29] |
| MIL-100 | Cr | H3BTC | 1517 | 2.5/2.9 | n.d. | 0.41 | [42] |
| MIL-100 | Fe | H2BDC | 1549 | n.d. | 0.82 | 0.81 | [41] |
| 1917 | 2.5/2.9 | 1.0 | 0.77 | [43] | |||
| MIL-100 | Al | H3BTC | 1814 | 2.5/2.9 | 1.14 | 0.50 | [43] |
| MIL-100 | Cr | H3BTC | 1330 | 2.5/2.9 | 0.77 | 0.40 | [44] |
| 2059 | 2.9/3.4 | 1.103 | 1.01 | [45] | |||
| 3017 | n.d. | 1.61 | 1.28 | [41] | |||
| 3124 | 2.9/3.4 | 1.58 | 1.40 | [46] | |||
| MIL-100-DEG | Cr | H3BTC | 580 | 1.2/1.5/1.9 | 0.50 | 0.33 | [44] |
| MIL-100-EG | Cr | H3BTC | 710 | 1.2/1.5/1.9 | 0.47 | 0.43 | [44] |
| MIL-101-NH2 | Cr | H2BDC | 2509 | <2.9/3.4 | 1.27 | 0.90 | [46] |
| 2690 | <2.9/3.4 | 1.60 | 1.06 | [47] | |||
| MIL-101-NO2 | Cr | H2BDC | 2146 | <2.9/3.4 | 1.19 | 1.08 | [46] |
| 1245 | <2.9/3.4 | 0.7 | 0.44 | [47] | |||
| MIL-101-pNH2 | Cr | H2BDC | 2495 | <2.9/3.4 | 1.44 | 1.05 | [47] |
| MIL-101-pNO2 | Cr | H2BDC | 2195 | <2.9/3.4 | 1.11 | 0.6 | [47] |
| MIL-101-soc | Cr | H4TCPT | 4549 | n.d. | 2.1 | 1.95 | [38] |
| MIL-125 | Ti | H2BDC | 1160 | 0.6/1.1 | 0.47 | 0.36 | [30] |
| MIL-125-NH2 | Ti | H2BDC-NH2 | 830 | 0.6/1.1 | 0.35 | 0.36 | [30] |
| 1220 | 0.6/1.26 | 0.55 | 0.37 | [48] | |||
| MIL-53 | Al | H2BDC | 1040 | 0.7-1.3 | 0.51 | 0.09 | [30] |
| n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.09 | [49] | |||
| MIL-53-NH2 | Al | H2BDC-NH2 | 940 | 0.7-1.3 | 0.37 | 0.05 | [30] |
| n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.09 | [49] | |||
| MIL-53-OH | Al | H2BDC-OH | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.40 | [49] |
| MIL-53 | Ga | H2BDC | 1230 | 0.8-2 | 0.47 | 0.05 | [30] |
| MIL-53-NH2 | Ga | H2BDC-NH2 | 210 | 0.8-2 | n.d. | 0.02 | [30] |
| MIL-53-(COOH)2 | Fe | H2BDC-(COOH)2 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.16 | [49] |
| MIL-68 | In | H2BDC | 1100 | 0.6/1.6 | 0.42 | 0.32 | [30] |
| MIL-68-NH2 | In | H2BDC-NH2 | 850 | 0.6/1.6 | 0.302 | 0.32 | [30] |
| MOF(NDI-SEt) | Zn | Pyrazole ligands | 888 | n.d. | 1.6 | 0.25 | [50] |
| MOF(NDI-SO2Et) | Zn | Pyrazole ligands | 764 | n.d. | <1.6 | 0.25 | [50] |
| MOF(NDI-SOEt) | Zn | Pyrazole ligands | 927 | n.d. | <1.6 | 0.30 | [50] |
| MOF-199 | Cu | H3BTC | 1340 | n.d. | 0.72 | 0.55 | [41] |
| 921 | 2.1 | 0.492 | 0.64 | [51] | |||
| 1270 | 0.9,0.6 | 0.62 | 0.49 | [52] | |||
| MOF-74 | Co | DOT | 1130 | 1.11 | 0.49 | 0.63 | [29] |
| MOF-74 | Mg | DOT | 1250 | 1.11 | 0.53 | 0.75 | [29] |
| 1400 | 1.1 | 0.65 | 0.62 | [52] | |||
| MOF-74 | Ni | DOT | 1040 | 1.11 | 0.46 | 0.615 | [29] |
| 639 | 2.3 | 0.362 | 0.48 | [51] | |||
| MOF-801-P | Zr | Fumaric acid | 990 | 0.74,0.56,0.48 | 0.45 | 0.450 | [29] |
| MOF-801-SC | Zr | Fumaric acid | 690 | 0.74,0.56,0.48 | 0.27 | 0.35 | [29] |
| MOF-802 | Zr | PZDC | 1290 | 0.84,0.74 | 0.49 | 0.11 | [29] |
| MOF-804 | Zr | DOT | 1145 | 0.72,0.68 | 0.46 | 0.29 | [29] |
| MOF-805 | Zr | NDC-(OH)2 | 1230 | 0.95,0.86 | 0.48 | 0.415 | [29] |
| MOF-806 | Zr | BPDC-(OH)2 | 2220 | 1.26,1.01 | 0.85 | 0.425 | [29] |
| MOF-808 | Zr | BTC | 2060 | 1.84 | 0.84 | 0.735 | [29] |
| MOF-841 | Zr | H4MTB | 1390 | 0.92 | 0.53 | 0.640 | [29] |
| PIZOF-2 | Zr | PEDB-(OMe)2 | 2080 | 1.76 | 0.88 | 0.850 | [29] |
| SIM-1 | Zn | 4-methyl-5-imidazolecarboxaldehyde | 570 | 0.65 | 0.303 | 0.14 | [30] |
| UiO-66 | Zr | H2BDC | 1290 | 0.84,0.74 | 0.49 | 0.535 | [29] |
| 1032 | 0.75/1.2 | 0.77 | 0.40 | [48] | |||
| 1105 | 0.55 | 0.39 | [53] | ||||
| 1160 | 0.6 | 0.52 | 0.37 | [52] | |||
| UiO-66-1,4-Naphyl | Zr | 1,4-Naphyl | 757 | n.d. | 0.42 | 0.26 | [53] |
| UiO-66-2,5-(OMe)2 | Zr | 2,5-(OMe)2 | 868 | n.d. | 0.38 | 0.42 | [53] |
| UiO-66-NH2 | Zr | H2BDC-NH2 | 1328 | 0.75/1.2 | 0.70 | 0.38 | [48] |
| 1123 | <0.75/1.2 | 0.52 | 0.34 | [53] | |||
| 1040 | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.37 | [52] | |||
| UiO-66-NO2 | Zr | H2BDC-NO2 | 792 | <0.75/1.2 | 0.40 | 0.37 | [53] |
| UiO-67 | Zr | H2BPDC | 2064 | 1.2/1.6 | 0.97 | 0.18 | [48] |
| ZIF-8 | Zn | 2-MIM | 1255 | n.d. | 0.64 | 0.02 | [41] |
| 1530 | 1.1 | 0.485 | 0.01 | [30] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaemchuen, S.; Xiao, X.; Klomkliang, N.; Yusubov, M.S.; Verpoort, F. Tunable Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heat Transformation Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090661
Chaemchuen S, Xiao X, Klomkliang N, Yusubov MS, Verpoort F. Tunable Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heat Transformation Applications. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(9):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090661
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaemchuen, Somboon, Xuan Xiao, Nikom Klomkliang, Mekhman S. Yusubov, and Francis Verpoort. 2018. "Tunable Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heat Transformation Applications" Nanomaterials 8, no. 9: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090661
APA StyleChaemchuen, S., Xiao, X., Klomkliang, N., Yusubov, M. S., & Verpoort, F. (2018). Tunable Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heat Transformation Applications. Nanomaterials, 8(9), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090661






