Enhanced Oxygen Vacancies in a Two-Dimensional MnAl-Layered Double Oxide Prepared via Flash Nanoprecipitation Offers High Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Material Characterization
2.3. Activity Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, W.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, F.; Zhou, A.; Ma, C.; Dai, B. High-efficiency removal of NOx using dielectric barrier discharge nonthermal plasma with water as an outer electrode. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Tang, C.; Dai, B.; Dong, L. Selective catalytic reduction De-NOx catalysts. Prog. Chem. 2016, 28, 1578–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Jiang, B.; Yao, S.; Han, J.; Zhao, S.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T. Mechanism of NH3-SCR reaction for NOx removal from diesel engine exhaust and hydrothermal stability of Cu-Mn/zeolite catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.C.; Yao, J.; Ma, X.; Gao, L.; Guo, M. Removal of SO2 and NOX using microwave swing adsorption over activated carbon carried catalyst. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Ji, W.; Yang, G.; Liu, L.S.; Wu, J.X.; Wang, E.Y.; Gou, X. Comparison of De-NOx performance of Mn/AC and Mn/Bio-char on low-temperature SCR. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 694, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; He, F.; Mei, D.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Hu, H. Thermodynamic calculation for the activity and mechanism of Mn/TiO2 catalyst doped transition metals for SCR at low temperature. Catal. Commun. 2014, 52, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhou, W.; Xie, A.; Wu, F.; Yao, C.; Li, X.; Zuo, S.; Liu, T. Effect of MnO2 polymorphs structure on the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over TiO2-Palygorskite. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, S.; Qiu, L.; Gao, Y.S.; O’Hare, D.; Wang, Q. The synthesis of CuyMnzAl1−zOx mixed oxide as a low-temperature NH3-SCR catalyst with enhanced catalytic performance. Dalton Trans. 2017, 47, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over novel Mn–Zr mixed oxide catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Dan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Dai, B. Enhanced low temperature NO reduction performance via MnOx-Fe2O3/vermiculite monolithic honeycomb catalysts. Catalysts 2018, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Xiao, R.; Xu, H.; Shen, K.; Zhou, C. A comparative study on the Mn/TiO2-M (M. = Sn, Zr or Al) Ox catalysts for NH3-SCR reaction at low temperature. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over iron and manganese oxides supported on titania. Appl. Catal. B. Environ. 2003, 44, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, M.; Chmielarz, L.; Węgrzyn, A.; Góra-Marek, K.; Piwowarska, Z.; Witkowski, S.; Bidzińska, E.; Kuśtrowski, P.; Wach, A.; Majda, D. Hydrotalcite derived (Cu, Mn)-Mg-Al metal oxide systems doped with palladium as catalysts for low-temperature methanol incineration. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Hao, J.; Xu, W.; Li, J. Low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over amorphous MnOx catalysts prepared by three methods. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Fang, P.; Ren, T.; Liu, Y.; Cen, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z. Tuning the property of Mn-Ce composite oxides by titanate nanotubes to improve the activity, selectivity and SO2/H2O tolerance in middle temperature NH3-SCR reaction. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Study on MnOx-FeOy composite oxide catalysts prepared by supercritical antisolvent process for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciulescu, M.; Caravaggio, G.; Dobri, A.; Moir, J.; Burich, R.; Charland, J.P.; Bulsink, P. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Mn-containing catalysts. Appl. Catal. B. Environ. 2012, 123–124, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Dan, J.; Zhang, J.; Cao, P.; Dai, B. Microspherical MnO2-CeO2-Al2O3 mixed oxide for monolithic honeycomb catalyst and application in selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at 50–150 °C. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Tang, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, D.; Dong, L.; Dai, B. Highly selective catalytic reduction of NOx by MnOx–CeO2–Al2O3 catalysts prepared by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. J. Environ. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yu, F.; Altaf, N.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Dai, B.; Wang, Q. Two-dimensional layered double hydroxides for reactions of methanation and methane reforming in C1 chemistry. Materials 2018, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonska, M.; Nocun, M.; Golabek, K.; Palkovits, R. Effect of preparation procedures on catalytic activity and selectivity of copper-based mixed oxides in selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia into nitrogen and water vapour. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonska, M.; Palkovits, R. Nitrogen oxide removal over hydrotalcite-derived mixed metal oxides. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomares, A.E.; Franch, C.; Ribera, A.; Abellan, G. NOx selective catalytic reduction at high temperatures with mixed oxides derived from layered double hydroxides. Catal. Today 2012, 191, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carja, G.; Delahay, G. Mesoporous mixed oxides derived from pillared oxovanadates layered double hydroxides as new catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2004, 47, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, R.; Cousin, R.; Poupin, C.; Aboukais, A.; Siffert, S. Propene oxidation and NO reduction over MgCu-Al(Fe) mixed oxides derived from hydrotalcite-like compounds. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Li, C.M.; Yu, C.; Tran, T.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.Q.; Yu, J.; Xu, G.W. Synthesis, characterization and activity evaluation of Cu-based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for DeNOx reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.H.; Nie, Y.; Yang, R.Y.; Cui, Y.H.; O’Hare, D.; Wang, Q. Highly dispersed CuyAlOx, mixed oxides as superior low-temperature alkali metal and SO2 resistant NH3-SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 538, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, F.; Zhu, M.; Shi, Y.; Dan, J.; Lv, Y.; Guo, X.; Dai, B. Up-scaled flash nano-precipitation production route to develop a MnOx-CeO2-Al2O3 catalyst with enhanced activity and H2O resistant performance for NOx selective catalytic reduction with NH3. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 134, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, M.; Ginart, P.; Gindy, M.E. Generic method of preparing multifunctional fluorescent nanoparticles using flash nanoprecipitation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conterosito, E.; Gianotti, V.; Palin, L. Facile preparation methods of hydrotalcite layered materials and their structural characterization by combined techniques. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 470, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguezreinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. The activity and characterization of CeO2-TiO2 catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Cai, S.; Fang, C.; Huang, L.; Li, H.; Gao, R.; Shi, L. Design of meso-TiO2@MnO(x)-CeO(x)/CNTs with a core-shell structure as DeNO(x) catalysts: Promotion of activity, stability and SO2-tolerance. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9821–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Duan, X.; Xie, Q.; Lai, S.; Xie, T. A highly-efficient oxygen evolution electrode based on defective nickel-iron layered double hydroxide. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Bian, T.; Zhou, C.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Wu, L.Z.; Tung, C.H.; Smith, L.J.; O’Hare, D.; Zhang, T. Defect-rich ultrathin ZnAl-layered double hydroxide nanosheets for efficient photoreduction of CO2 to CO with water. Adv. Mater. 2016, 27, 7824–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Pan, B.; Xie, Y. Ultrathin spinel-structured nanosheets rich in oxygen deficiencies for enhanced electrocatalytic water oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7399–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jia, X.; Chen, G.; Shang, L.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wu, L.Z.; Tung, C.H.; O’Hare, D.; Zhang, T. Ultrafine NiO nanosheets stabilized by TiO2 from monolayer NiTi-LDH precursors: An active water oxidation electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Lyu, M.; Fan, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiao, C.; Wei, S. Low overpotential in vacancy-rich ultrathin CoSe2 nanosheets for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15670–15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wei, Z.; Dong, C.L.; Ma, J.; Shen, S.; Li, Y. Filling the oxygen vacancies in Co3O4 with phosphorus: An ultra-efficient electrocatalyst for the overall water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2563–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiu, C.; Xu, H.; Lin, T.; Lin, Z.; Gong, M.; Chen, Y. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over monolith catalyst of MnOx/CeO2–ZrO2–Al2O3. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Xiang, J.; Su, S.; Wang, P.; Hu, S.; Sun, L. Ag modified Mn–Ce/γ-Al2O3 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low-temperature. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 135, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Tang, C.; Yao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Gao, F.; Dong, L. Effect of metal ions doping (M = Ti4+,Sn4+ ) on the catalytic performance of MnOx/CeO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. A. Gen. 2015, 495, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.C.; Pyo, Y.D.; Jin, Y.J.; Gang, C.K.; Shin, Y.J. NOx reduction and N2O emissions in a diesel engine exhaust using Fe-zeolite and vanadium based SCR catalysts. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 110, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schill, L.; Putluru, S.S.R.; Jensen, A.D.; Fehrmann, R. MnFe/Al2O3 Catalyst synthesized by deposition precipitation for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Lett. 2015, 145, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Park, E.D.; Ji, M.K. Manganese oxide catalysts for NOx reduction with NH3, at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 327, 261–269. [Google Scholar]

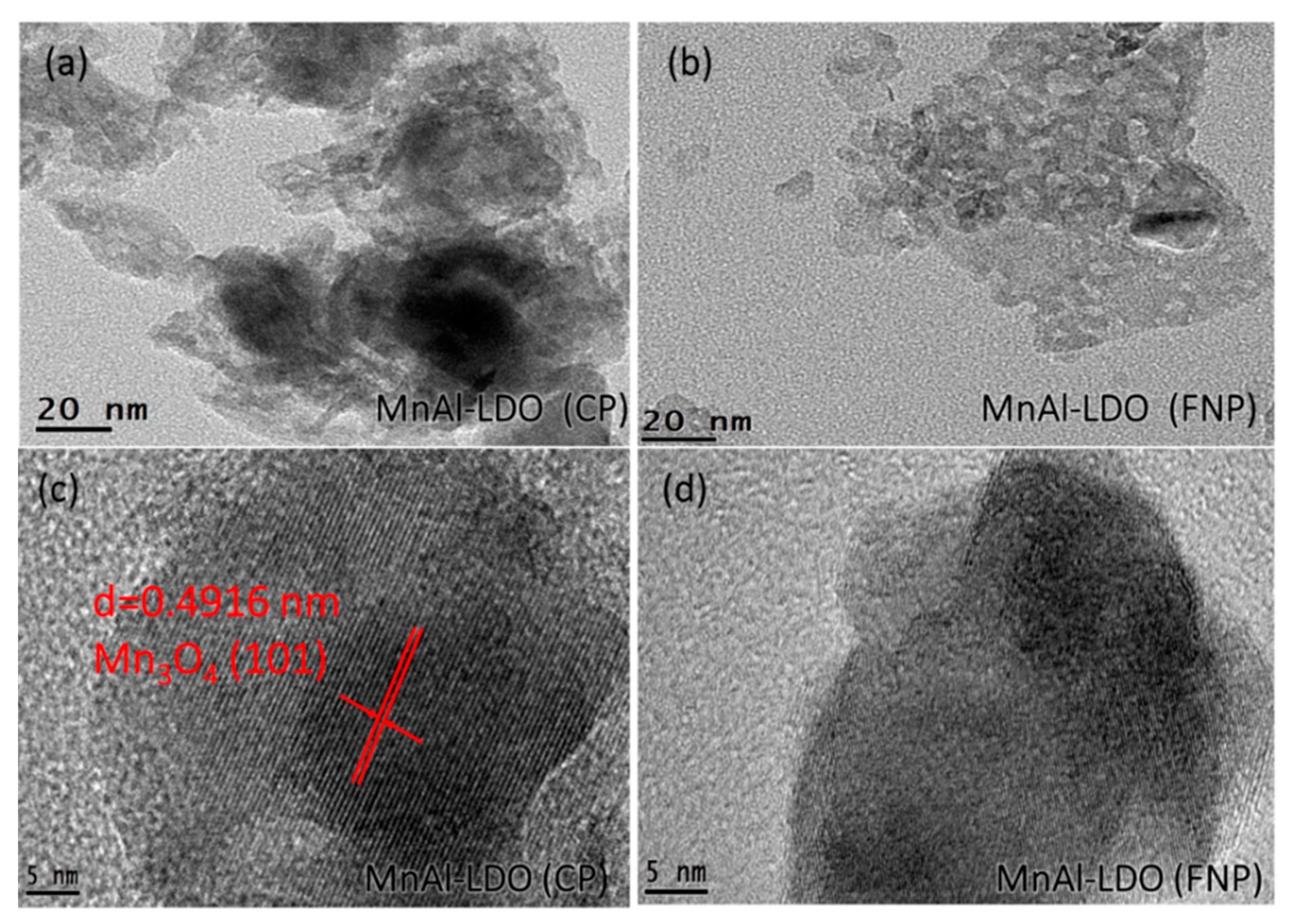
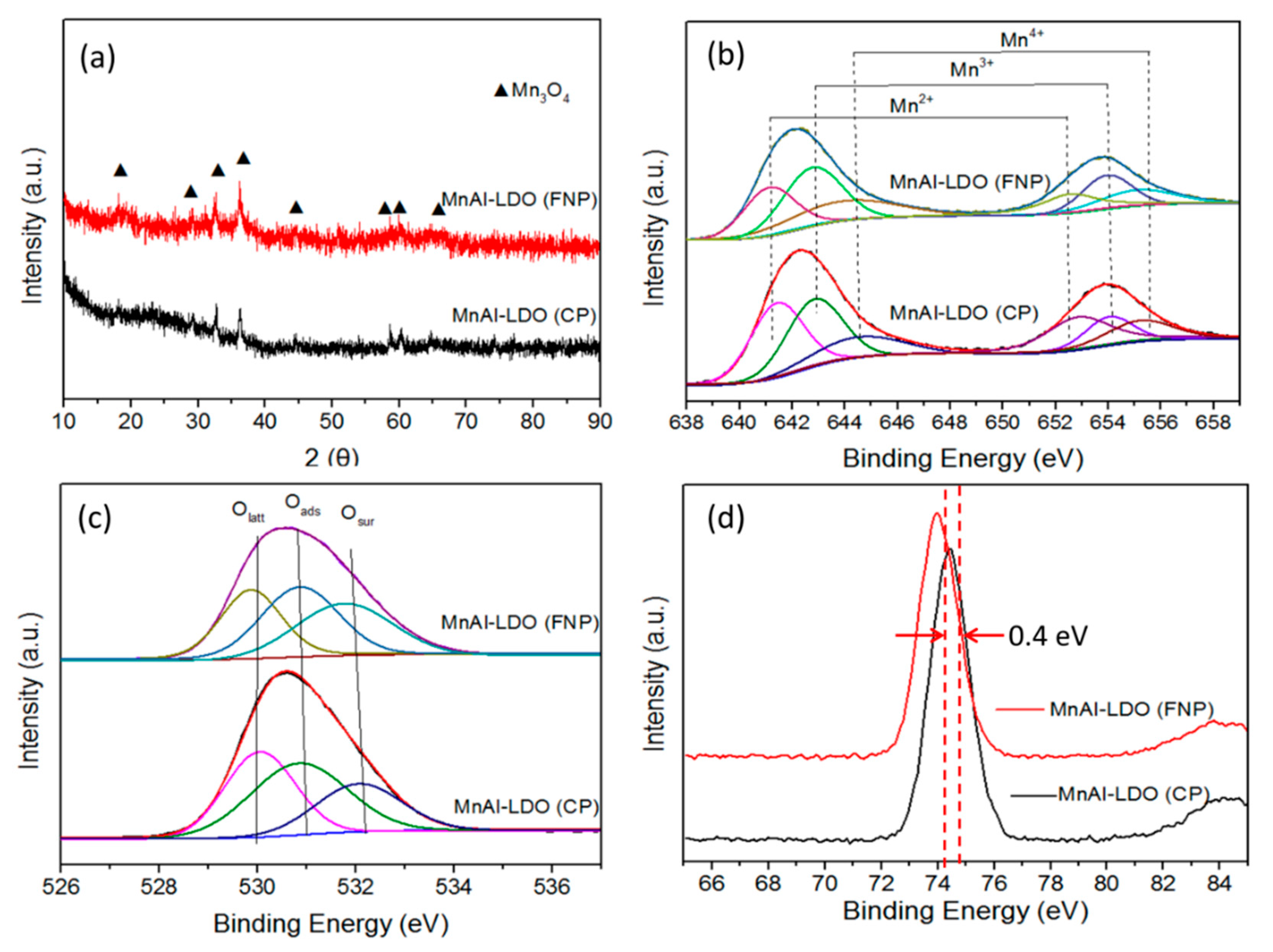
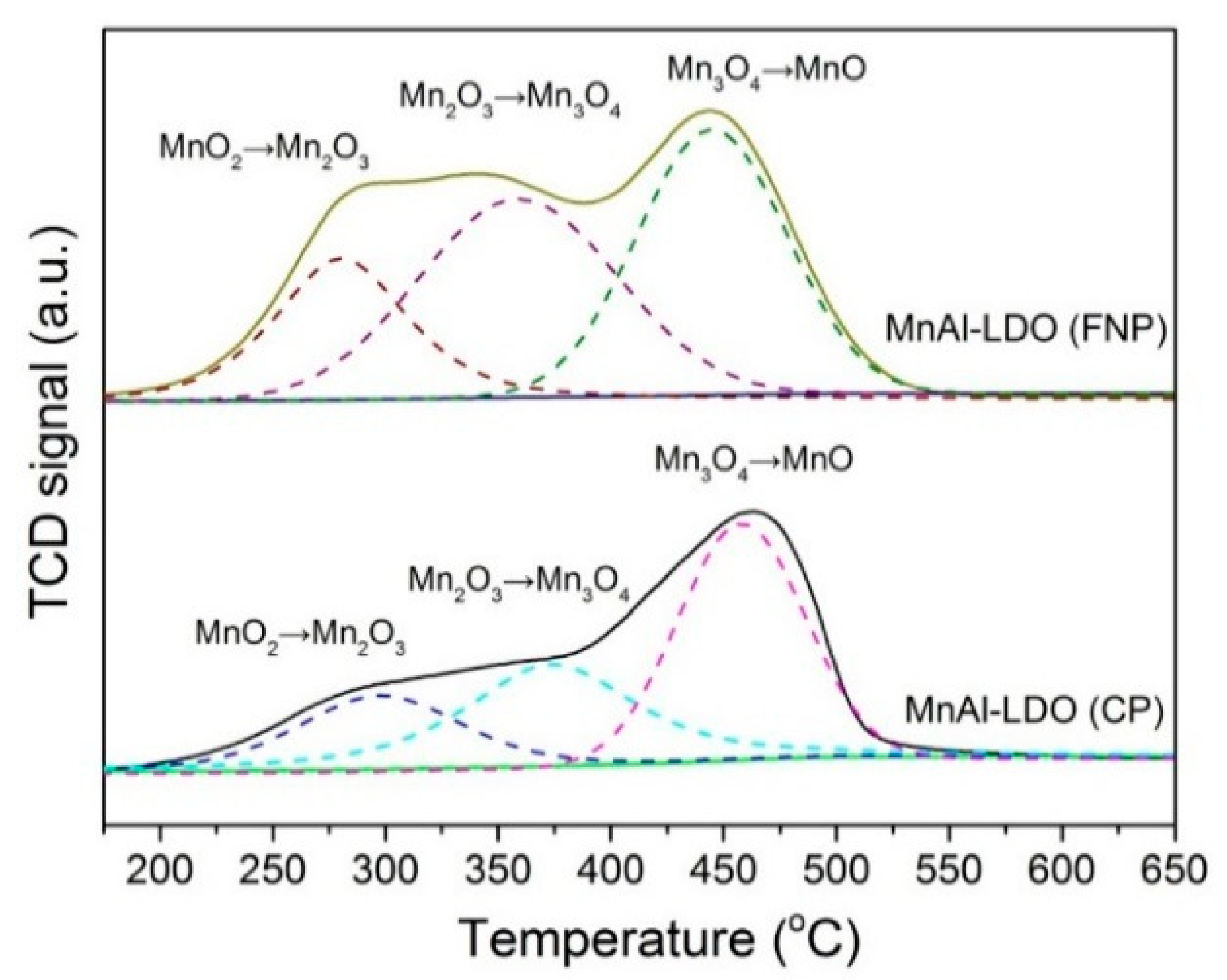

| Samples | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MnAl-LDO (CP) | 169 | 0.37 | 8.77 |
| MnAl-LDO (FNP) | 121 | 0.22 | 7.13 |
| Samples | Surface Atomic Concentration (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mn | O | Mn2+/Mn | Mn3+/Mn | Mn4+/Mn | Olatt | Oads | Osurf | |
| MnAl-LDO (CP) | 22.88 | 9.56 | 57.24 | 34.9 | 41.6 | 23.5 | 30.42 | 35.32 | 34.26 |
| MnAl-LDO (FNP) | 21.66 | 9.28 | 56.35 | 31.8 | 41.4 | 26.8 | 35.44 | 40.57 | 23.99 |
| Mn-Based Catalysts | Synthesis Methods | Temperature (°C) | GHSV (h−1) | NO Content (ppm) | Conversion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn/γ-Al2O3 | Impregnation | 200 | - | 500 | NOx: 67.2% | [14] |
| Cu-Mn/γ-Al2O3 | Impregnation | 200 | - | 500 | NOx: 82.6% | [14] |
| Mn-Fe/VMT | Impregnation | 200 | 30,000 | 500 | NO: 96.5% | [12] |
| Cu2Mn0.5Al0.5Ox | Co-precipitation | 150 | - | 500 | NOx: 91.2% | [10] |
| Mn-Ce-Al (MMO) | Spray drying | 150 | 15,000 | 500 | NOx: 97.4% | [20] |
| Mn–Ce/γ-Al2O3 | Sol-gel | 300 | 30,000 | 700 | NO: 85% | [41] |
| 40 wt %Mn0.75Fe0.25/Al2O3 | Deposition precipitation | 150 | - | 1000 | NO: 71% | [44] |
| MnOx-CeO2-Al2O3 | Flash-nanoprecipitation | 150 | 15,300 | 500 | NOx: 90% | [30] |
| MnAl-LDO (CP) | Co-precipitation | 200 | 60,000 | 500 | NO: 74.68% | This work |
| MnAl-LDO (FNP) | Flash-nanoprecipitation | 200 | 60,000 | 500 | NO: 100% | This work |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Wang, C.; Yu, F.; Shi, Y.; Cao, P.; Dan, J.; Chen, K.; Lv, Y.; Guo, X.; Dai, B. Enhanced Oxygen Vacancies in a Two-Dimensional MnAl-Layered Double Oxide Prepared via Flash Nanoprecipitation Offers High Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080620
Zhao D, Wang C, Yu F, Shi Y, Cao P, Dan J, Chen K, Lv Y, Guo X, Dai B. Enhanced Oxygen Vacancies in a Two-Dimensional MnAl-Layered Double Oxide Prepared via Flash Nanoprecipitation Offers High Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(8):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080620
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dan, Chao Wang, Feng Yu, Yulin Shi, Peng Cao, Jianming Dan, Kai Chen, Yin Lv, Xuhong Guo, and Bin Dai. 2018. "Enhanced Oxygen Vacancies in a Two-Dimensional MnAl-Layered Double Oxide Prepared via Flash Nanoprecipitation Offers High Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3" Nanomaterials 8, no. 8: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080620
APA StyleZhao, D., Wang, C., Yu, F., Shi, Y., Cao, P., Dan, J., Chen, K., Lv, Y., Guo, X., & Dai, B. (2018). Enhanced Oxygen Vacancies in a Two-Dimensional MnAl-Layered Double Oxide Prepared via Flash Nanoprecipitation Offers High Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3. Nanomaterials, 8(8), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080620






