Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating: Simple Auxiliary Control over the Nanoporous Structure of Porous Carbon Monoliths Prepared through the Solvothermal Route
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Preparation of Porous Porous Carbon Monoliths
2.3. Characterization of Porous Carbon Monoliths
3. Results
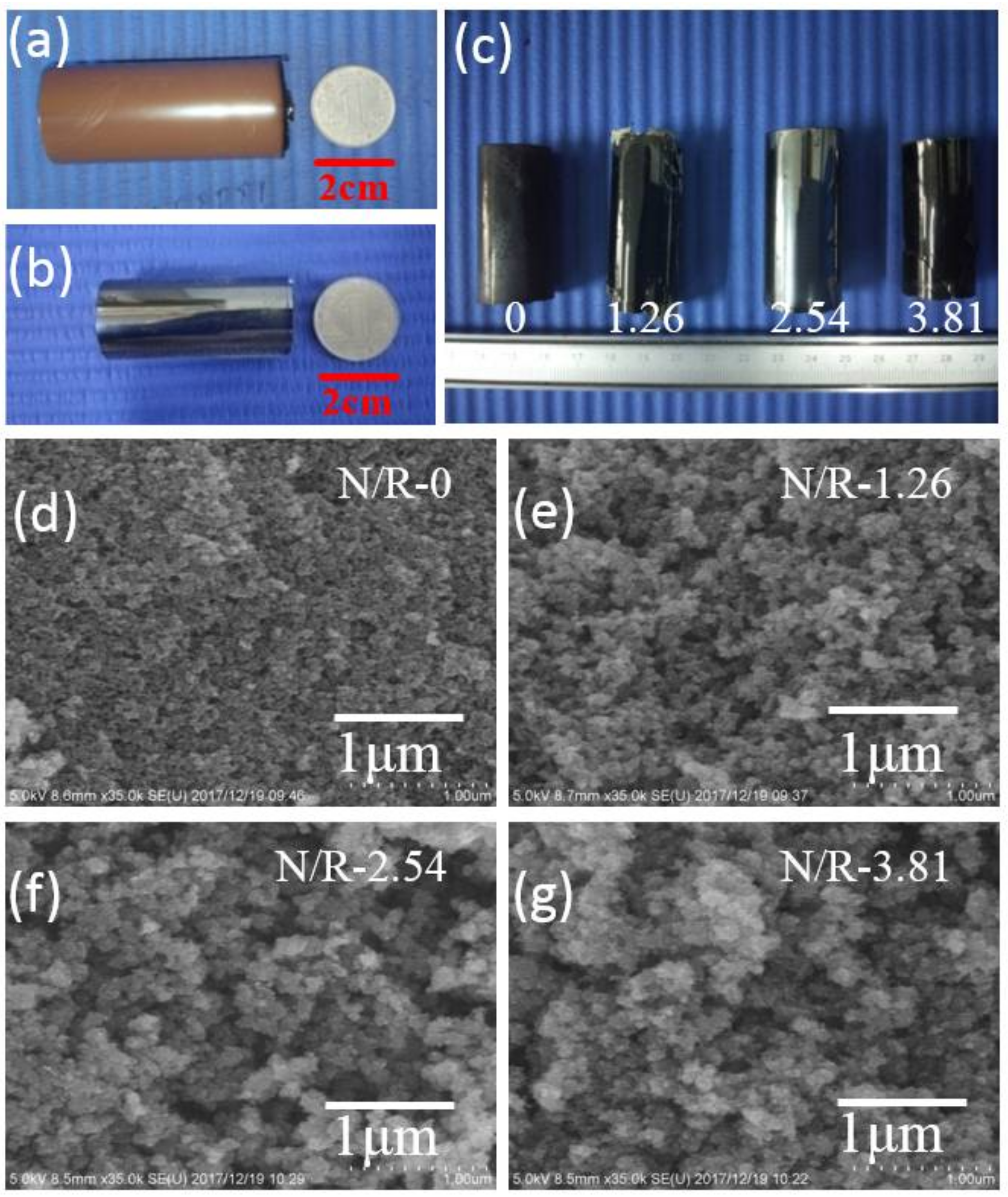
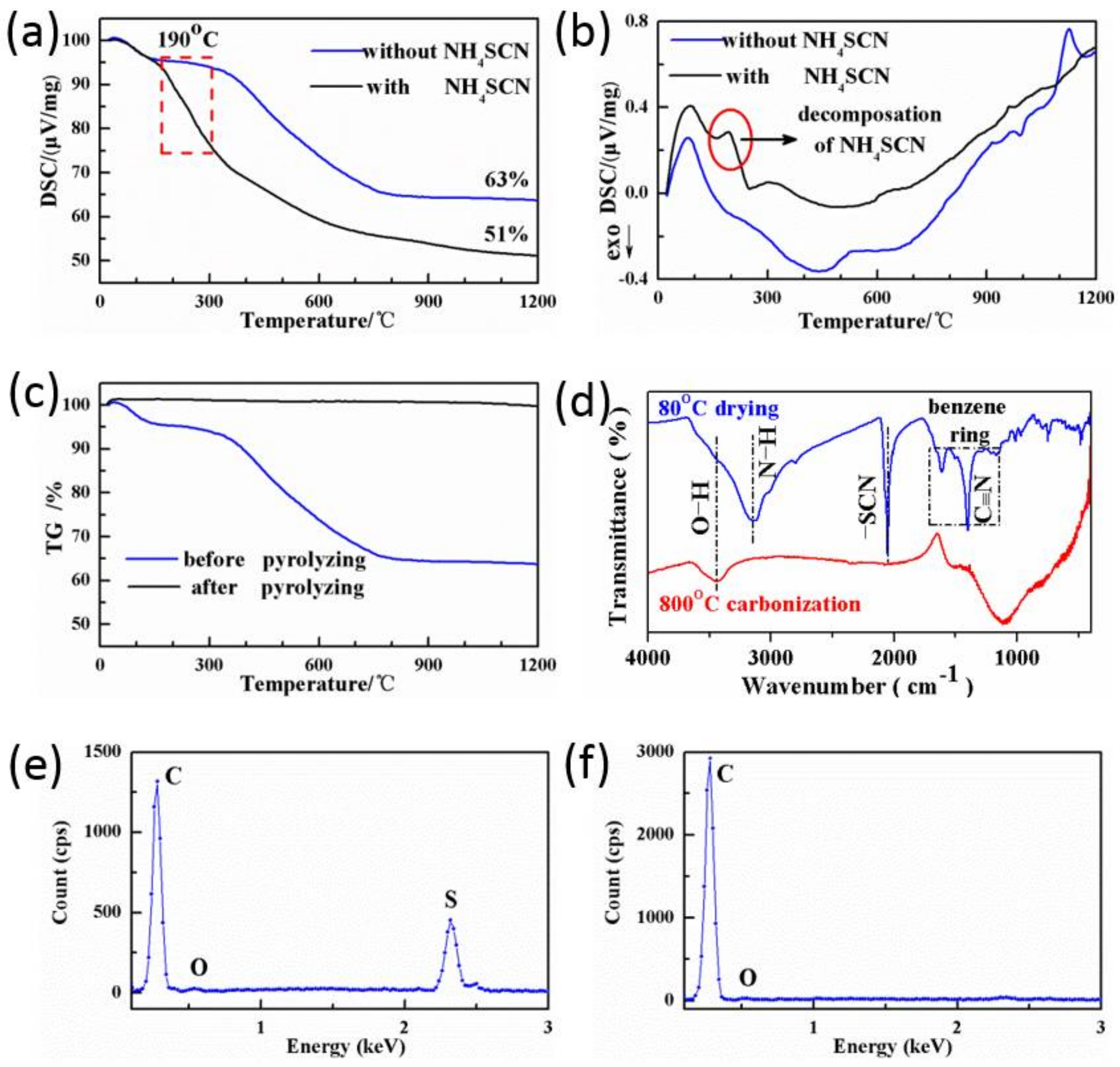
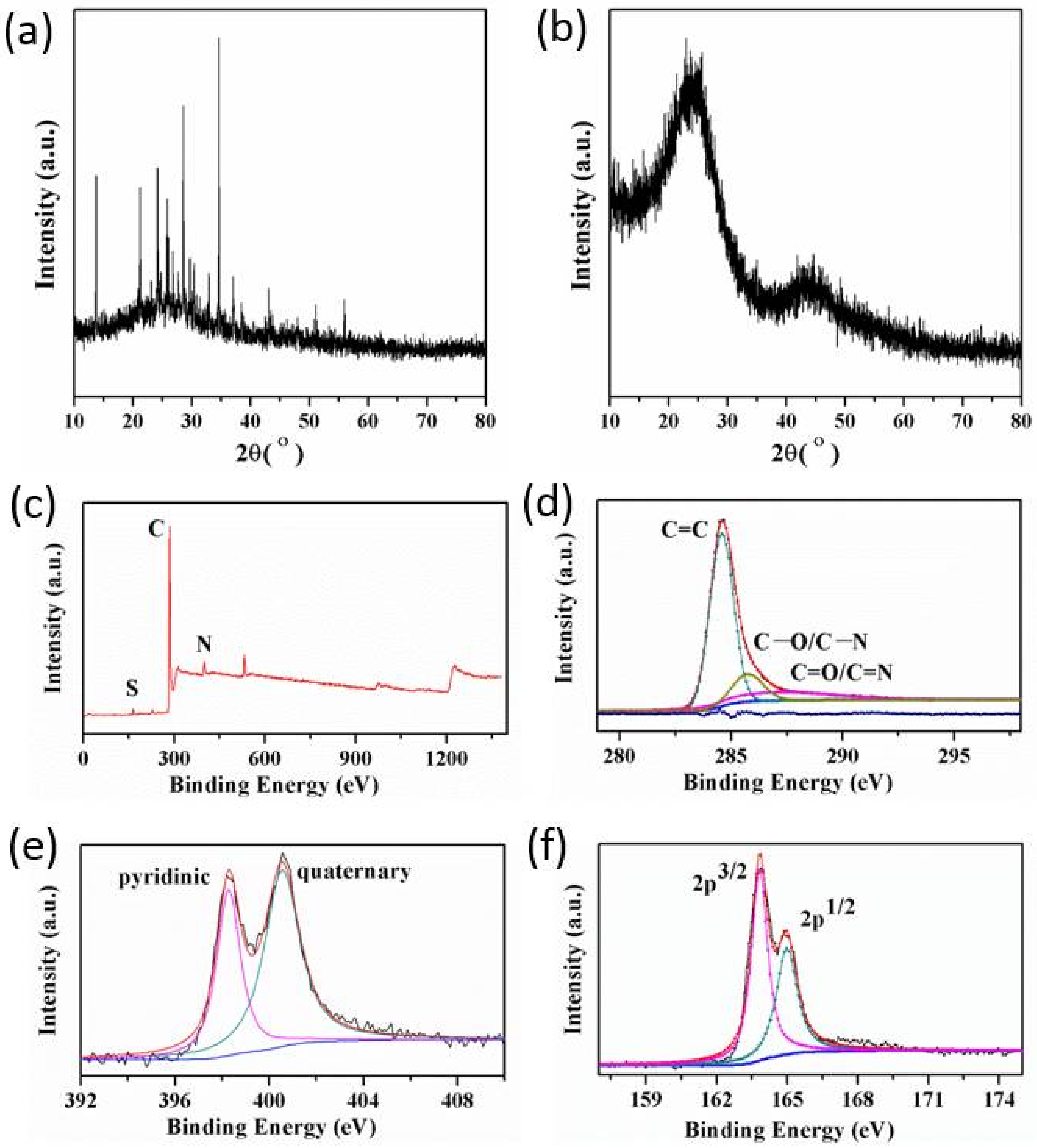
3.1. Proofs of Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating
3.2. Control over the Nanoporous Architecture of Porous Carbon Monoliths
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, K.-J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Xing, K. Synthesis of molybdenum disulfide/carbon aerogel composites for supercapacitors electrode material application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 752, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Yin, R.; Ge, X.; Li, Z.; Yin, L. Ni2P@carbon core-shell nanoparticle-arched 3D interconnected graphene aerogel architectures as anodes for high-performance sodium-ion batteries. Small 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Lu, H.; Fan, W.; Liu, T. In situ growth of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on highly porous graphene/polyimide-based carbon aerogel nanocomposites for effectively selective detection of dopamine. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.J.; Brun, N.; Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Titirici, M.M. Always look on the “light” side of life: Sustainable carbon aerogels. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zou, L.; Song, H.; Morris, G. Ordered mesoporous carbons synthesized by a modified sol–gel process for electrosorptive removal of sodium chloride. Carbon 2009, 47, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L.; Tuan, C.-C.; Li, H.; Sang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wong, C.P.; Liu, H. The hybrid nanostructure of MnCo2O4.5 nanoneedle/carbon aerogel for symmetric supercapacitors with high energy density. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 14401–14412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Hyeon, T. Recent progress in the synthesis of porous carbon materials. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2073–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, L. Co3O4/carbon aerogel hybrids as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries with enhanced electrochemical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8337–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Han, B.H. Preparation of three-dimensional graphene oxide-polyethylenimine porous materials as dye and gas adsorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9172–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, S.; Mondal, K.; Sharma, A. One-step sol–gel synthesis of hierarchically porous, flow-through carbon/silica monoliths. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 12298–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.R.; Feng, Z.P.; Ou, Y.N.; Wu, D.; Fu, R.; Tong, Y.X. Mesoporous MnO2/carbon aerogel composites as promising electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors. Langmuir 2010, 26, 2209–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Feng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C. Ultralow density carbon aerogels with low thermal conductivity up to 2000 °C. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3454–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, C. Shrinkage and pore structure in preparation of carbon aerogels. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Chen, J.L. Magnetic mesoporous Fe/carbon aerogel structures with enhanced arsenic removal efficiency. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 420, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Hao, G.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L. One-pot synthesis of robust superhydrophobic, functionalized graphene/polyurethane sponge for effective continuous oil–water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jia, W. Biomass-derived multifunctional magnetite carbon aerogel nanocomposites for recyclable sequestration of ionizable aromatic organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 245, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Samad, Y.A.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Alhassan, S.M.; Liao, K. Carbon aerogel from winter melon for highly efficient and recyclable oils and organic solvents absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Zheng, B.; Fu, R.; Wu, D. Polyaniline-coated activated carbon aerogel/sulfur composite for high-performance lithium-sulfur battery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Lee, E.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, S.-G.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Jung, J.C. Preparation of activated carbon aerogel and its application to electrode material for electric double layer capacitor in organic electrolyte: Effect of activation temperature. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 32, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; You, L.; Shen, X.; Li, S. An environmentally friendly carbon aerogels derived from waste pomelo peels for the removal of organic pollutants/oils. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 241, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatalo, S.M.; Pileidis, F.; Makila, E.; Sevilla, M.; Repo, E.; Salonen, J.; Sillanpaa, M.; Titirici, M.M. Versatile cellulose-based carbon aerogel for the removal of both cationic and anionic metal contaminants from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25875–25883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Shen, X.; Cui, S.; Fan, M. Facile synthesis of an amine hybrid aerogel with high adsorption efficiency and regenerability for air capture via a solvothermal-assisted Sol-Gel process and supercritical drying. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3436–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Dutta, S.; Wu, K.C.; Kimura, T. Analytical understanding of the materials design with well-described shrinkages on multiscale. Chemistry 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Mulchandani, A.; Yan, Y. Electrochemical synthesis of perfluorinated ion doped conducting polyaniline films consisting of helical fibers and their reversible switching between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Huang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Fan, J. Ordered nanoporous silica with periodic 30−60 nm pores as an effective support for gold nanoparticle catalysts with enhanced lifetime. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9596–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surrey, A.; Bonatto Minella, C.; Fechler, N.; Antonietti, M.; Grafe, H.-J.; Schultz, L.; Rellinghaus, B. Improved hydrogen storage properties of LiBH4 via nanoconfinement in micro- and mesoporous aerogel-like carbon. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 5540–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porada, S.; Schipper, F.; Aslan, M.; Antonietti, M.; Presser, V.; Fellinger, T.P. Capacitive deionization using biomass-based microporous salt-templated heteroatom-doped carbons. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Li, L.; Song, H.; Morris, G. Improving the capacitive deionisation performance by optimising pore structures of the electrodes. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Malfatti, L.; Falcaro, P.; Marongiu, D.; Casula, M.F.; Amenitsch, H.; Innocenzi, P. Self-assembly of shape controlled hierarchical porous thin films: Mesopores and nanoboxes. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4846–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Fu, R.; Zhang, S.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Dresselhaus, G. Preparation of low-density carbon aerogels by ambient pressure drying. Carbon 2004, 42, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, R.W. Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 3221–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Woo, H.J.; Aziz, N.A.; Kufian, M.Z.; Majid, S.R. Synthesis of Al2TiO5 and its effect on the properties of chitosan–NH4SCN polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2013, 19, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshrestha, N.; Gupta, P.N. Structural and electrical characterizations of 50:50 pva:Starch blend complexed with ammonium thiocyanate. Ionics 2016, 22, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-Y.; Huh, S. Hollow s-doped carbon spheres from spherical ct/pedot composite particles and their CO2 sorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 436, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhuo, S. Porous carbon materials with dual N, S-doping and uniform ultra-microporosity for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 209, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, R.; Kim, A.R.; Eo, S.K.; Kang, S.H.; Yoo, D.J. Facile one-step synthesis of cerium oxide-carbon quantum dots/rgo nanohybrid catalyst and its enhanced photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Element Weight (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | S | |
| N/R-2.54 before pyrolyzing | 87.60 | 2.98 | 9.42 |
| N/R-2.54 after pyrolyzing | 93.35 | 6.10 | 0.55 |
| Sample | Element Weight (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | S | |
| N/R-2.54 before pyrolyzing | 74.40 | 15.87 | 9.73 |
| N/R-2.54 after pyrolyzing | 97.54 | 1.51 | 0.95 |
| Samples | Density (g/cm3) | BET Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Micropore Volume (cm3/g) | Micropore Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | External Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/R-0 | 0.21 | 611 | 0.562 | 0.099 | 213 | 398 |
| N/R-1.26 | 0.18 | 761 | 0.551 | 0.142 | 326 | 435 |
| N/R-2.54 | 0.16 | 1131 | 0.667 | 0.316 | 770 | 361 |
| N/R-3.81 | 0.13 | 532 | 0.531 | 0.105 | 125 | 407 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Feng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, R.; Chen, X.; Feng, J. Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating: Simple Auxiliary Control over the Nanoporous Structure of Porous Carbon Monoliths Prepared through the Solvothermal Route. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040255
Zhang Z, Feng J, Jiang Y, Liu P, Zhang Q, Wei R, Chen X, Feng J. Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating: Simple Auxiliary Control over the Nanoporous Structure of Porous Carbon Monoliths Prepared through the Solvothermal Route. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(4):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040255
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhen, Junzong Feng, Yonggang Jiang, Ping Liu, Qiuhua Zhang, Ronghui Wei, Xiang Chen, and Jian Feng. 2018. "Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating: Simple Auxiliary Control over the Nanoporous Structure of Porous Carbon Monoliths Prepared through the Solvothermal Route" Nanomaterials 8, no. 4: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040255
APA StyleZhang, Z., Feng, J., Jiang, Y., Liu, P., Zhang, Q., Wei, R., Chen, X., & Feng, J. (2018). Self-Sacrificial Salt Templating: Simple Auxiliary Control over the Nanoporous Structure of Porous Carbon Monoliths Prepared through the Solvothermal Route. Nanomaterials, 8(4), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040255





