Exploring Reaction Conditions to Improve the Magnetic Response of Cobalt-Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural and Chemical Characterization
2.2. Morphological Characterization
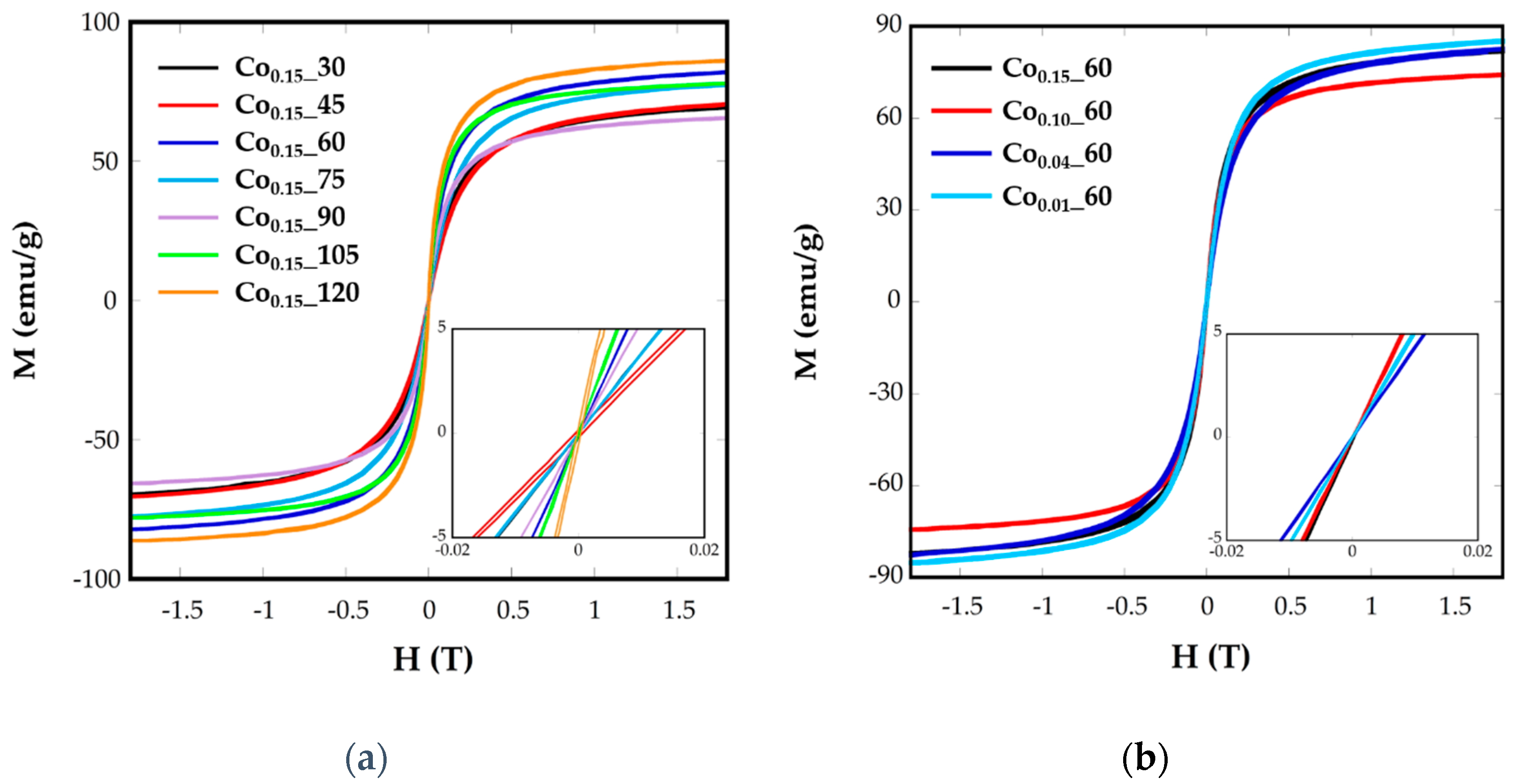
2.3. Magnetic Characterization
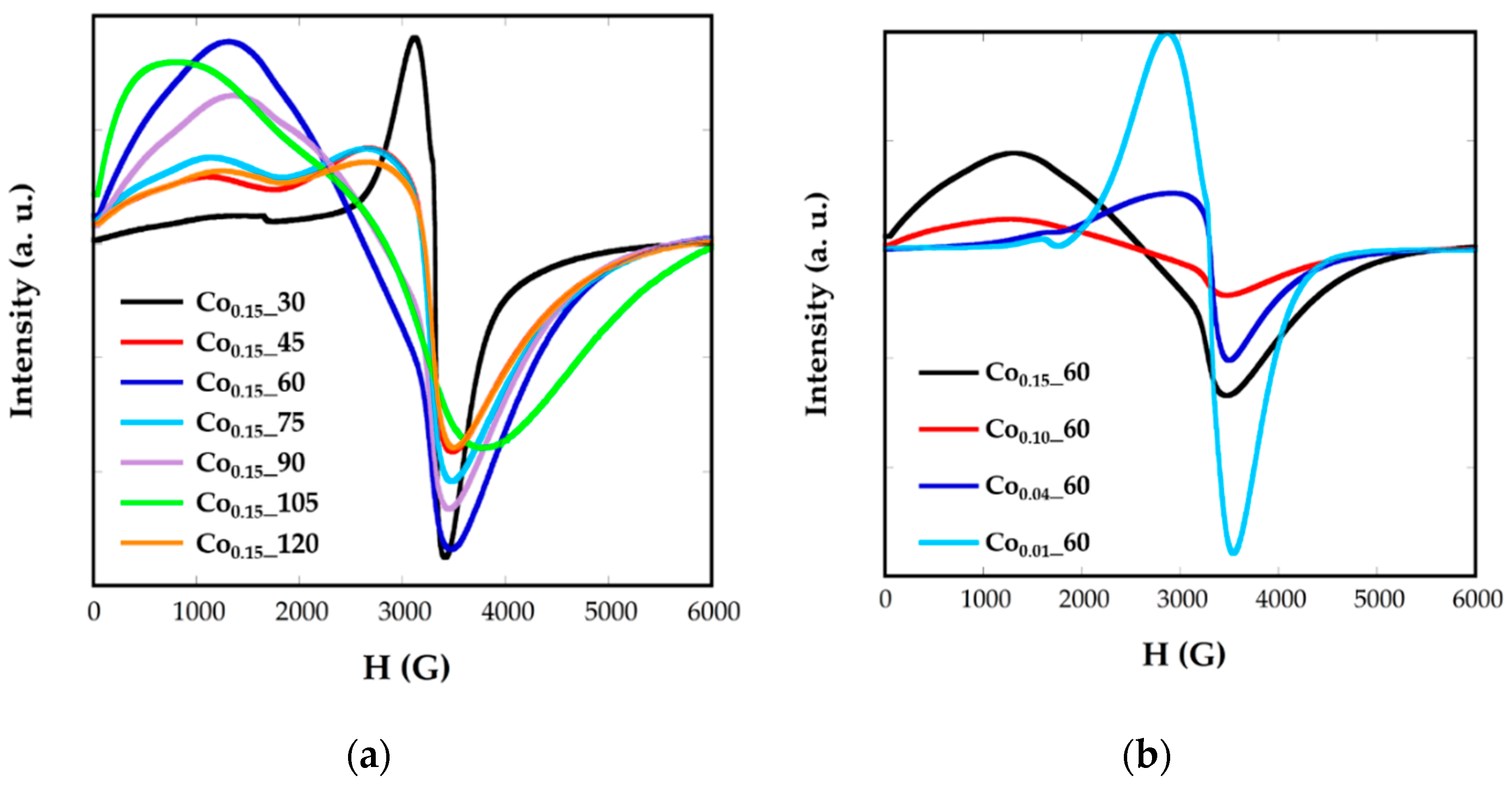
2.4. Electron Magnetic Resonance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Syntheiss of Cobalt-Doped Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikitin, A.; Fedorova, M.; Naumenko, V.; Shchetinin, I.; Abakumov, M.; Erofeev, A.; Gorelkin, P.; Meshkov, G.; Beloglazkina, E.; Ivanenkov, Y.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and MRI application of magnetite water-soluble cubic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 441, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilnawaz, D.; Singh, A.; Mohanty, C.; Sahoo, S.K. Dual drug loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3694–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agotegaray, M.A.; Campelo, A.E.; Zysler, R.D.; Gumilar, F.; Bras, C.; Gandini, A.; Minetti, A.; Massheimer, V.L.; Lassalle, V.L. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug targeting: From design to insights into systemic toxicity. Preclinical evaluation of hematological, vascular and neurobehavioral toxicology. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Magnetic separation techniques in sample preparation for biological analysis: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2014, 101, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriortua, O.K.; Garaio, E.; Herrero de la Parte, B.; Insausti, M.; Lezama, L.; Plazaola, F.; García, J.A.; Aizpurua, J.M.; Sagartzazu, M.; Irazola, M.; et al. Antitumor magnetic hyperthermia induced by RGD-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles, in an experimental model of colorectal liver metastases. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-Rubio, I.; Insausti, M.; Garaio, E.; Gil de Muro, I.; Plazaola, F.; Rojo, T.; Lezama, L. Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared by the seeded-growth route for hyperthermia: Electron magnetic resonance as a key tool to evaluate size distribution in magnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7542–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, S.-H.; Na, W.; Jang, J.-T.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, E.J.; Moon, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Shin, J.S.; Cheon, J. Nanoscale magnetism control via surface and exchange anisotropy for optimized ferrimagnetic hysteresis. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabale, S.; Jadhav, V.; Khot, V.; Zhu, X.; Xin, M.; Chen, H. Superparamagnetic MFe2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn, Mn) nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, induction heating and cell viability studies for cancer hyperthermia applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Gutierrez, V.; Virumbrales, M.; Saez-Puche, R.; Torralvo-Fernandez, M.J. Superparamagnetic behavior of MFe2O4 nanoparticles and MFe2O4/SiO2 composites (M: Co, Ni). J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 20927–20935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafet, Y.; Kittle, C. Antiferromagnetic arrangements in ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1952, 87, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, D.; Casula, M.F.; Falqui, A.; Loche, D.; Mountjoy, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Corrias, A. A structural and magnetic investigation of the inversion degree in ferrite nanocrystals MFe2O4 (M = Mn, Co, Ni). J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.T.; Dung, N.T.; Tung, L.D.; Thanh, C.T.; Quy, O.K.; Chuc, N.V.; Maenosonoe, S.; Thanh, N.T.K. Synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with controlled morphology, monodispersity and composition: The influence of solvent, surfactant, reductant and synthetic conditions. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19596–19610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; de Montferrand, C.; Lalatonne, Y.; Motte, L.; Brioude, A. Effect of cobalt doping concentration on the crystalline structure and magnetic properties of monodisperse CoxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles within nonpolar and aqueous solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4349–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantechi, E.; Campo, G.; Carta, D.; Corrias, A.; de Julián Fernández, C.; Gatteschi, D.; Innocenti, C.; Pineider, F.; Rugi, F.; Sangregorio, C. Exploring the effect of co doping in fine maghemite nanoparticle. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8261–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, A.; Guardia, P.; Brescia, R.; Silvestri, N.; Pugliese, G.; Nitti, S.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. CoxFe3−xO4 Nanocubes for theranostic applications: Effect of cobalt content and particle size. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantechi, E.; Innocenti, C.; Albino, M.; Lottini, E.; Sangregorio, C. Influence of cobalt dopping on the hyperthermin efficiency of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouse, C.A.; Barron, R.A. Reagent control over size, uniformity and composition of Co–Fe–O nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemer, G.; Tirosh, E.; Livneh, T.; Markovich, G. Tuning a coloidan synthesis to control Co2+ doping in ferrite nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14334–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calero-DdelC, V.L.; González, A.M.; Rinaldi, C. A statistical analysis to control the growth of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by the thermodecomposition method. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2010, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A Profile Refinement Method for Nuclear and Magnetic Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent advances in magnetic structure determination by neutron powder diffraction. Physica B 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.; West, A.R. Deviation from Vegard’s law in oxide solid solutions. The systems Li2TiO3–MgO and Li2TiO3–Na2TiO3. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday 1980, 76, 2159–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajroudi, L.; Mlikia, N.; Bessaisb, L.; Madigouc, V.; Villainc, S.; Lerouxc, C. Magnetic, electric and therma properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 59, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattrick, R.A.D.; van der Laan, G.; Henderson, C.M.B.; Kuiper, P.; Dudzik, E.; Vaughan, D.J. Cation site occupancy in spinel ferrites studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism: Developing a method for mineralogist. Eur. J. Mineral. 2002, 14, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, J.M.; Coker, V.S.; Moise, S.; Wincott, P.L.; Vaughan, D.J.; Tuna, F.; Arenholz, E.; van der Laan, G.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; Lloyd, J.R.; et al. Controlled cobalt doping in biogenic magnetite nanoparticles. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyappan, S.; Panneerselvam, G.; Antony, M.P.; Philip, J. High temperature stability of surfactant capped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, V.; Musinu, A.; Ardu, A.; Ennas, G.; Peddis, D.; Niznansky, D.; Sangregorio, C.; Innocenti, C.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Cannas, C. Studying the effect of Zn-substitution on the magnetic and hyperthermic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 10124–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.W.; Falkner, J.C.; Yavuz, C.T.; Colvin, V.L. Synthesis of monodisperse iron oxide nanocrystals by thermal decomposition of iron carboxylate salts. Chem. Commun. 2004, 20, 2306–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Anazi, A.; Abdelraheem, W.H.; Han, C.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sygellou, L.; Arfanis, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Sharma, V.K.; Dionysiou, D.D. Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with controlled composition-peroxymonosulfate mediated degradation of 2-phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 221, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, Y.; Abbas, M.; Noh, H.Y.; Kim, C.G. Morphology-controlled synthesis of highly crystalline Fe3O4 and CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using a facile thermal decomposition method. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 15861–15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ogawa, T.; Hasegawa, D.; Takahashi, M. Synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse magnetite nanocubes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Rice, P.M.; Wang, S.X.; Sun, S. Shape-Controlled Synthesis and Shape-Induced Texture of MnFe2O4 Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11458–11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, E.C.; Wohlfarth, E.P.A. A Mechanism of magnetic hysteresis heterogeneous alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1948, 240, 599–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Castellanos-Rubio, I.; Munshi, R.; Orue, I.; Pelaz, B.; Gries, K.I.; Parak, W.J.; del Pino, P.; Pralle, A. Model driven optimization of magnetic anisotropy of exchange-coupled core-shell ferrite nanoparticles for maximal hysteretic loss. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7380–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.M.; Nunes, W.C.; Socolovsky, L.M.; Knobel, M.; Zanchet, D. Effect of dipolar interaction observed in iron-based nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2005, 72, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruvera, I.J.; Mendoza, P.; Calatayud, M.P.; Goya, G.F.; Sanchez, F.H. Determination of the blocking temperature of magnetic nanoparticles: The good, the bad and the ugly. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 184304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usov, N.A. Numerical simulation of field-cooled and zero field-cooled processes for assembly of superparamagnetic nanoparticles with uniaxial anisotropy. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 023913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.P.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Montero, M.I.; Serna, C.J. Surface and internal spin canting in γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3058–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einsenstein, I.; Aharoni, A. Asymptotic superparamagnetic time constants for cubic anisotropy. II. Negative anisotropy constants. Phys. Rev. B 1977, 16, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonczewski, J.C. Origin of Magnetic Anisotropy in Cobalt-Substituted Magnetite. Phys. Rev. 1958, 110, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenker, H. Magnetic Anisotropy of Cobalt Ferrite and Nickel Cobalt Ferrite. Phys. Rev. 1957, 107, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nlebedim, I.C.; Snyder, J.E.; Moses, A.J.; Jiles, D.C. Anisotropy and Magnetostriction in Non-Stoichiometric Cobalt Ferrite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3084–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
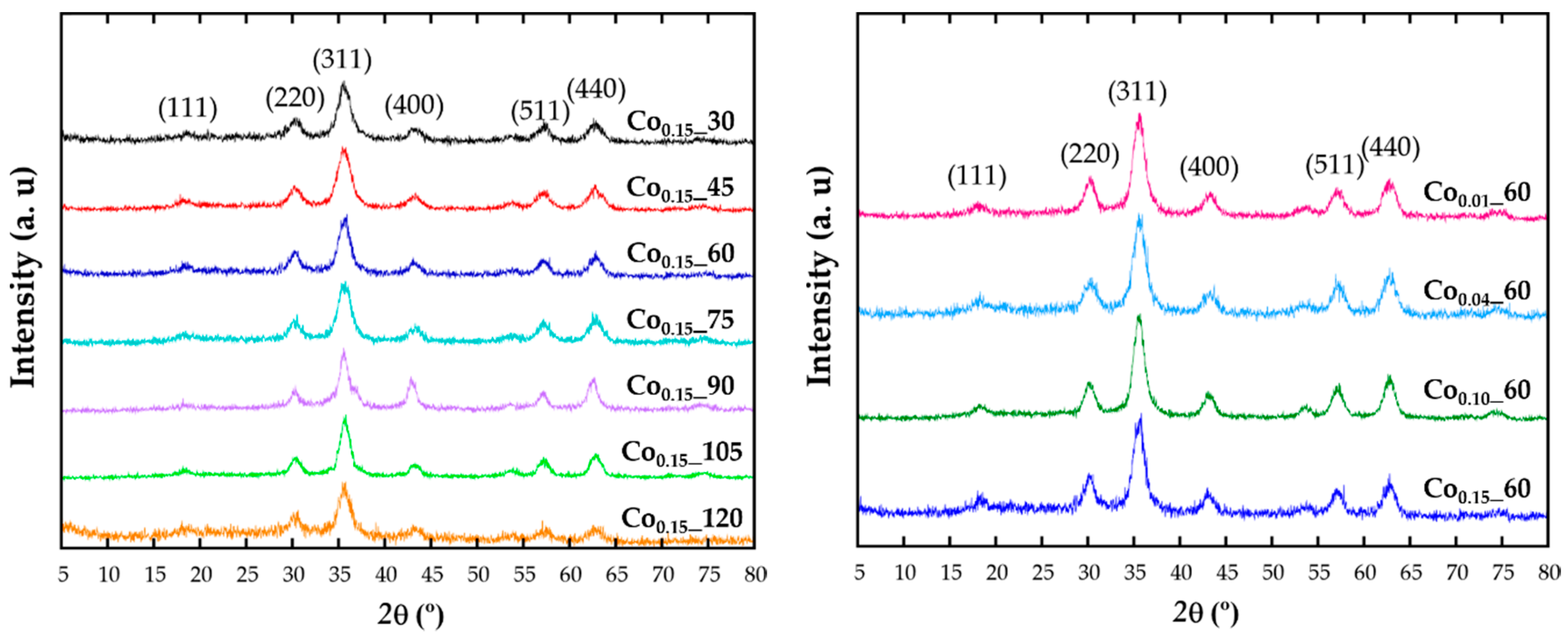
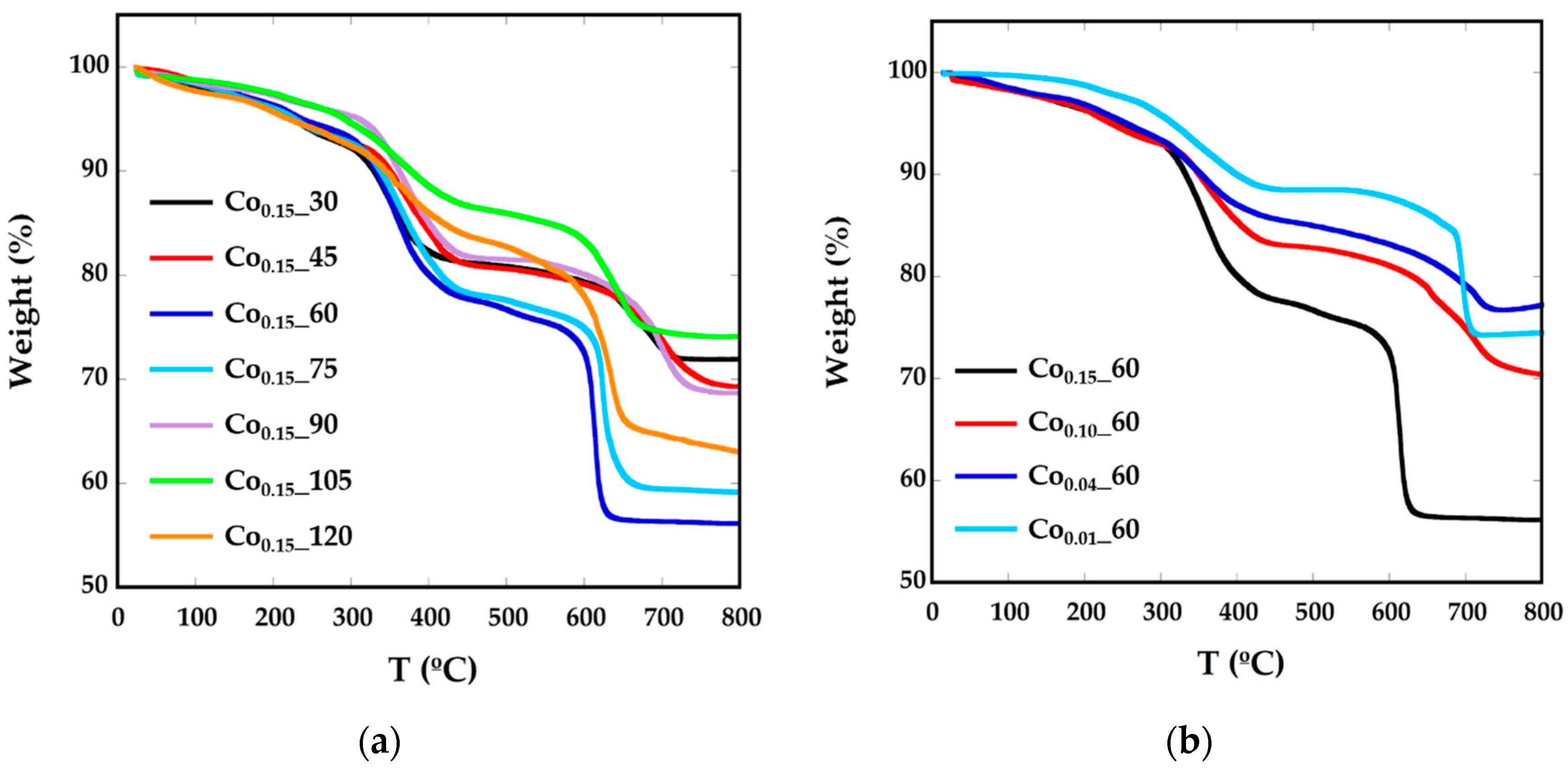
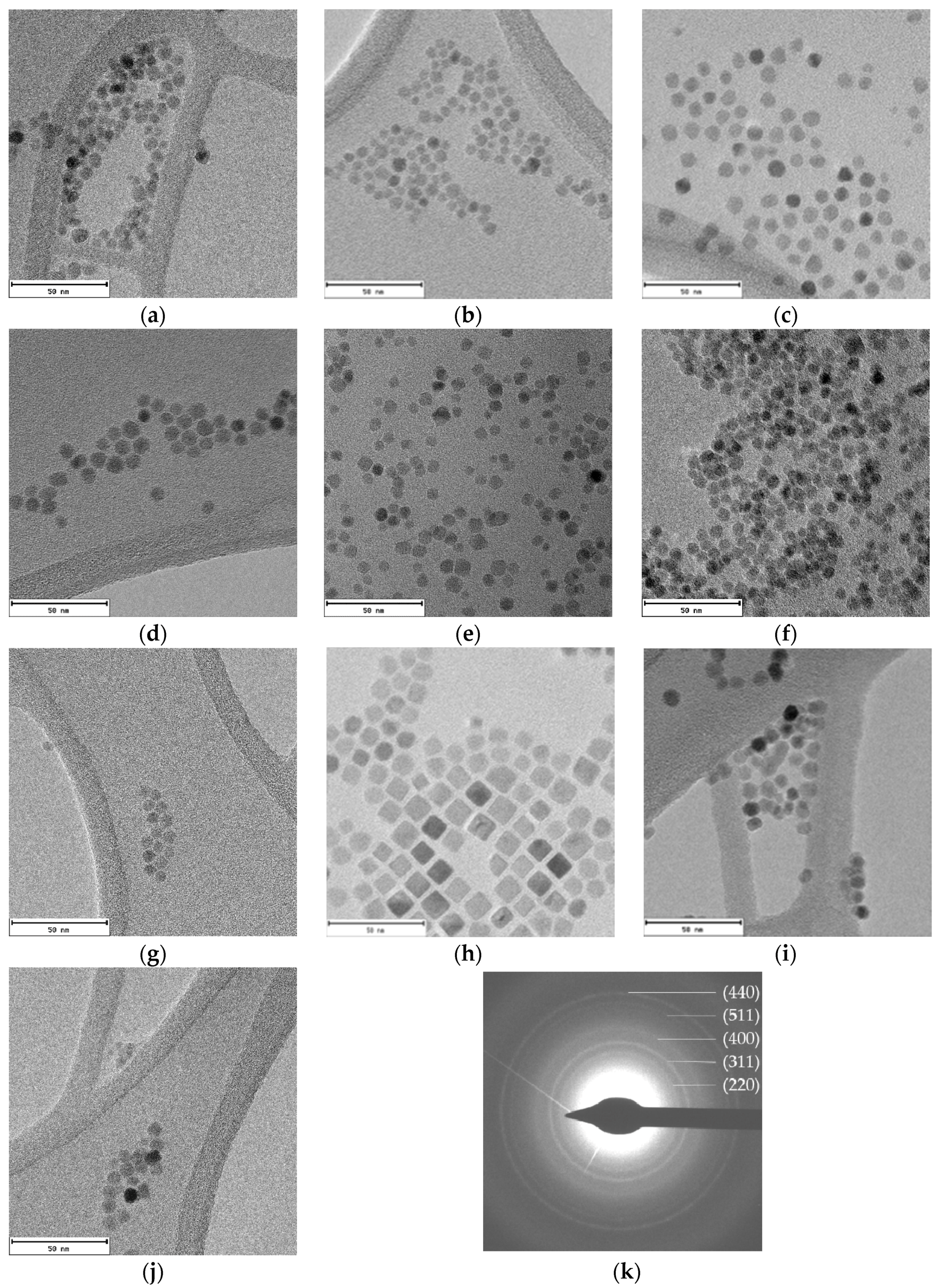
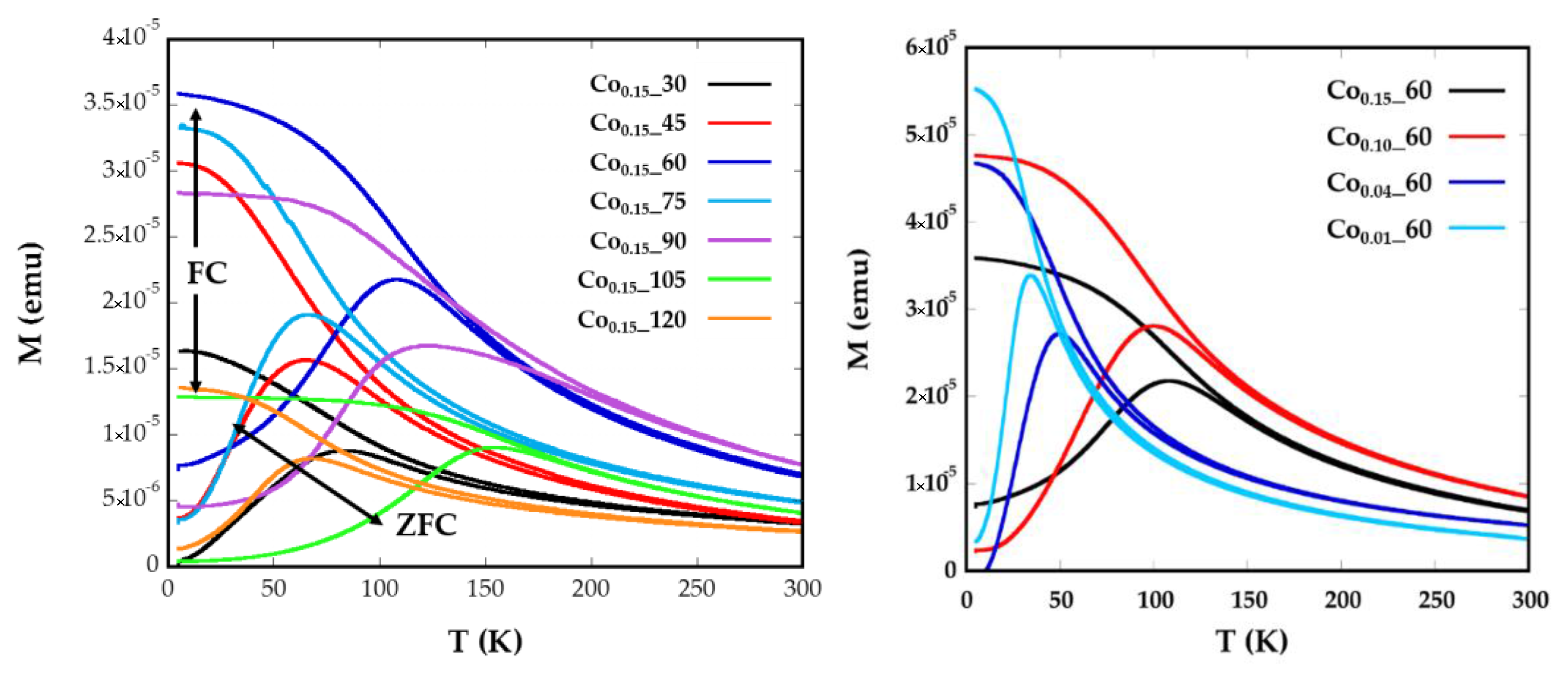

| Sample | a (Å) | ICP | TGA (%) | TEM (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co0.15_30 | 8.3757 (4) | Co0.08Fe2.92O4 | 28.08 | 6 (1) |
| Co0.15_45 | 8.3701 (3) | Co0.08Fe2.92O4 | 30.68 | 6 (1) |
| Co0.15_60 | 8.3780 (3) | Co0.14Fe2.86O4 | 43.82 | 8 (1) |
| Co0.10_60 | 8.3769 (2) | Co0.07Fe2.93O4 | 29.58 | 7 (1) |
| Co0.04_60 | 8.3700 (3) | Co0.03Fe2.97O4 | 23.31 | 7 (1) |
| Co0.01_60 | 8.3730 (2) | Co0.01Fe2.99O4 | 25.77 | 6 (1) |
| Co0.15_75 | 8.3671 (3) | Co0.1Fe2.9O4 | 40.85 | 7 (1) |
| Co0.15_90 | 8.4277(4) | Co0.09Fe2.11O4 | 31.33 | 11 (1) |
| Co0.15_105 | 8.3798 (2) | Co0.11Fe2.89O4 | 25.89 | 8 (1) |
| Co0.15_120 | 8.3671 (5) | Co0.16Fe2.84O4 | 36.981 | 6 (1) |
| Sample | ICP | <Tb> (K) | DZFC/FC (nm) | Keff (0 K) (KJ/m3) | Kc (KJ/m3) | Cox | Hc (5 K) (Oe) | Ms (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co0.15_60 | Co0.14Fe2.86O4 | 75.7 | 7.51 (1) | 138 | 553.2 | 0.05 | 5.300 | 82.15 |
| Co0.1_60 | Co0.07Fe2.93O4 | 66.7 | 7.68 (1) | 102 | 434 | 0.04 | 3650 | 74.25 |
| Co0.04_60 | Co0.03Fe2.97O4 | 34.8 | 7.39(1) | 54.9 | 219.6 | 0.02 | 999 | 82.59 |
| Co0.01_60 | Co0.01Fe2.99O4 | 24.6 | 6.86 (1) | 46.5 | 186.2 | 0.02 | 610 | 85.25 |
| Co0.15_30 | Co0.08Fe2.92O4 | 51.8 | 6.37 (2) | 115.6 | 462.4 | 0.05 | 3.300 | 69.66 |
| Co0.15_45 | Co0.08Fe2.92O4 | 47.8 | 6.14 (1) | 107 | 428 | 0.04 | 3.600 | 70.58 |
| Co0.15_75 | Co0.1Fe2.9O4 | 46.1 | 6.44 (1) | 102.4 | 409.6 | 0.04 | 3.310 | 77.48 |
| Co0.15_90 | Co0.09Fe2.11O4 | 96.5 | 10.7 (2) | 55.1 | 220.6 | 0.02 | 2.262 | 65.63 |
| Co0.15_105 | Co0.11Fe2.89O4 | 110.2 | 7.96 (1) | 208.8 | 835.2 | 0.08 | 6.360 | 77.93 |
| Co0.15_120 | Co0.16Fe2.84O4 | 49.9 | 5.98 (2) | 120.9 | 483.6 | 0.05 | 1.800 | 86.16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galarreta, I.; Insausti, M.; Gil de Muro, I.; Ruiz de Larramendi, I.; Lezama, L. Exploring Reaction Conditions to Improve the Magnetic Response of Cobalt-Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020063
Galarreta I, Insausti M, Gil de Muro I, Ruiz de Larramendi I, Lezama L. Exploring Reaction Conditions to Improve the Magnetic Response of Cobalt-Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(2):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020063
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalarreta, Itziar, Maite Insausti, Izaskun Gil de Muro, Idoia Ruiz de Larramendi, and Luis Lezama. 2018. "Exploring Reaction Conditions to Improve the Magnetic Response of Cobalt-Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 8, no. 2: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020063
APA StyleGalarreta, I., Insausti, M., Gil de Muro, I., Ruiz de Larramendi, I., & Lezama, L. (2018). Exploring Reaction Conditions to Improve the Magnetic Response of Cobalt-Doped Ferrite Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 8(2), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020063





