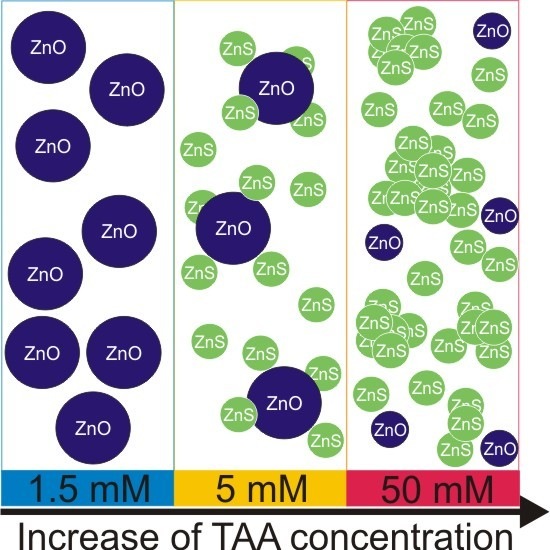
The Critical Role of Thioacetamide Concentration in the Formation of ZnO/ZnS Heterostructures by Sol-Gel Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Powder Extraction
2.3. Characterization
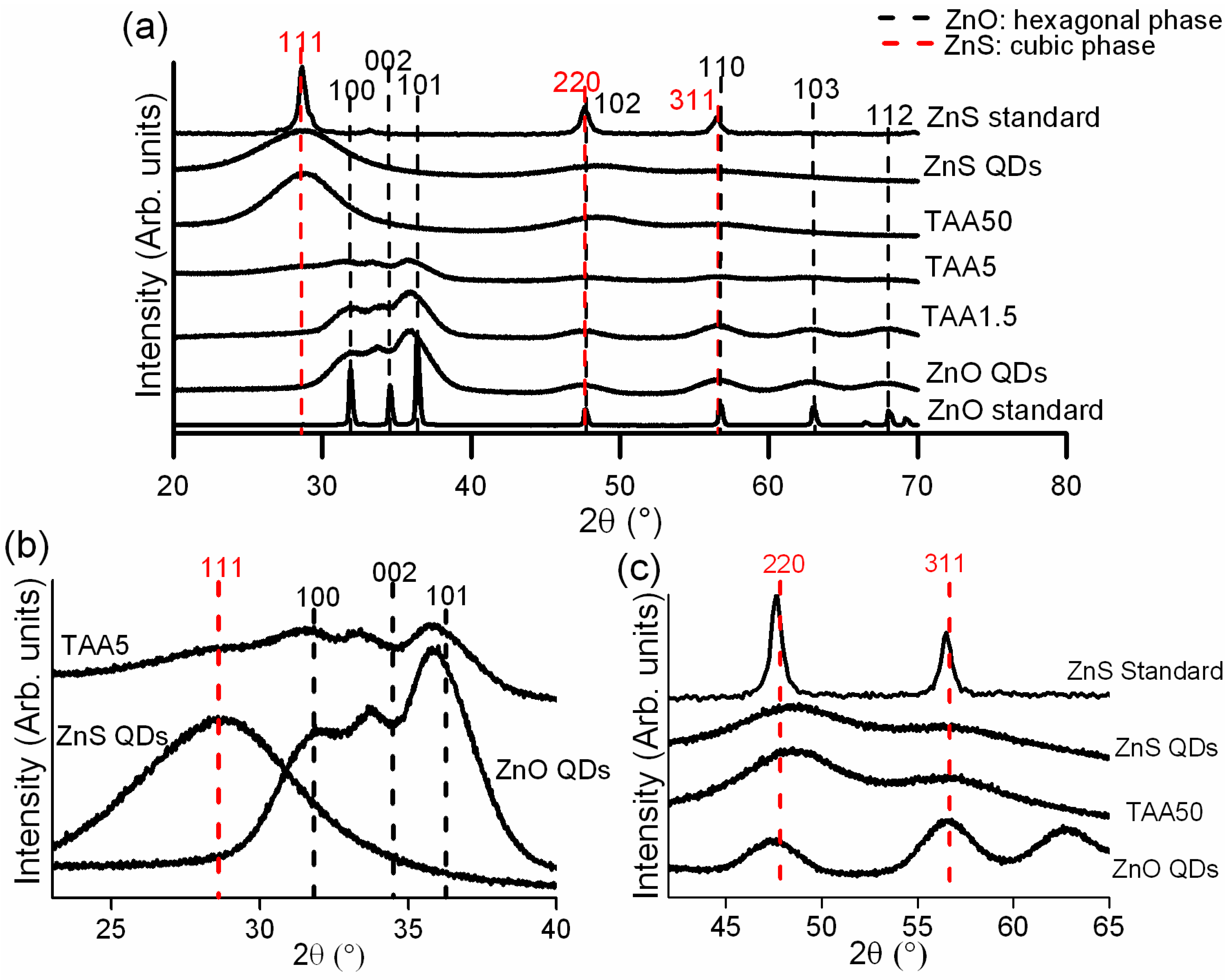
2.3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of powders
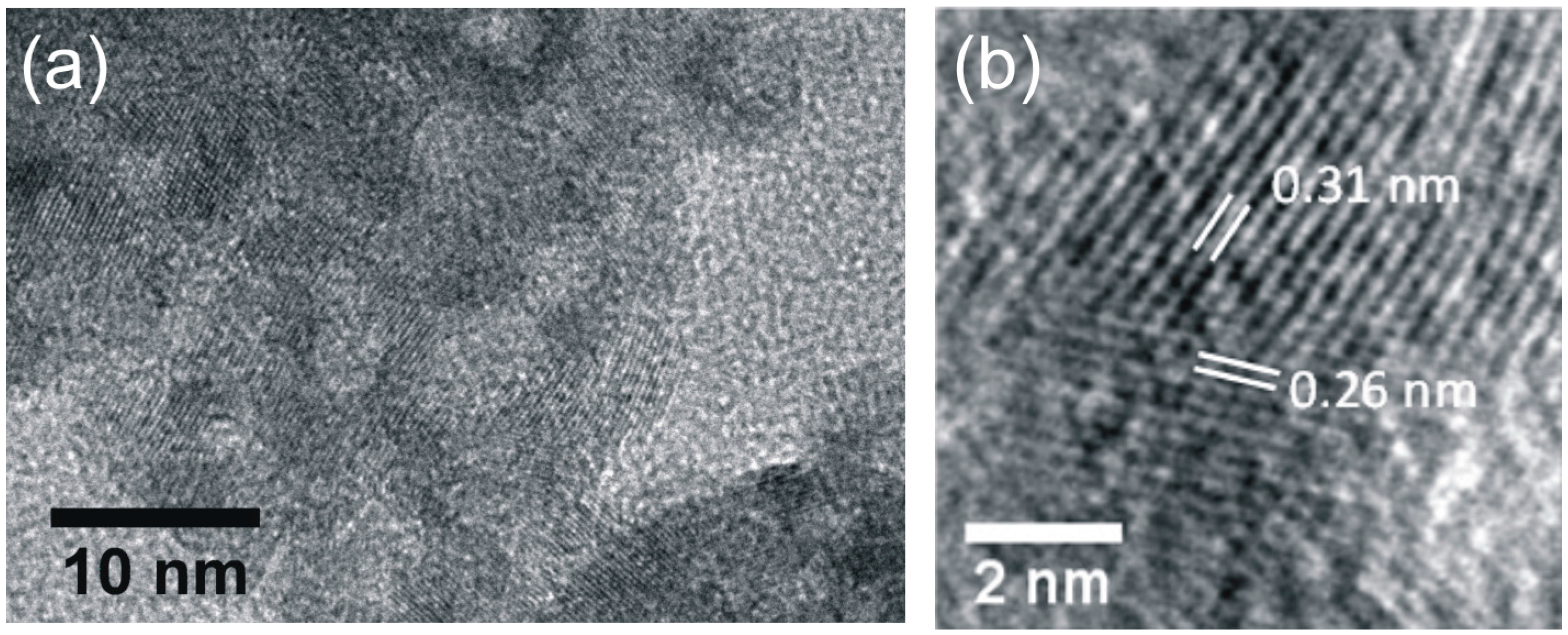
2.3.2. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM)
2.3.3. X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS)
2.3.4. Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS)
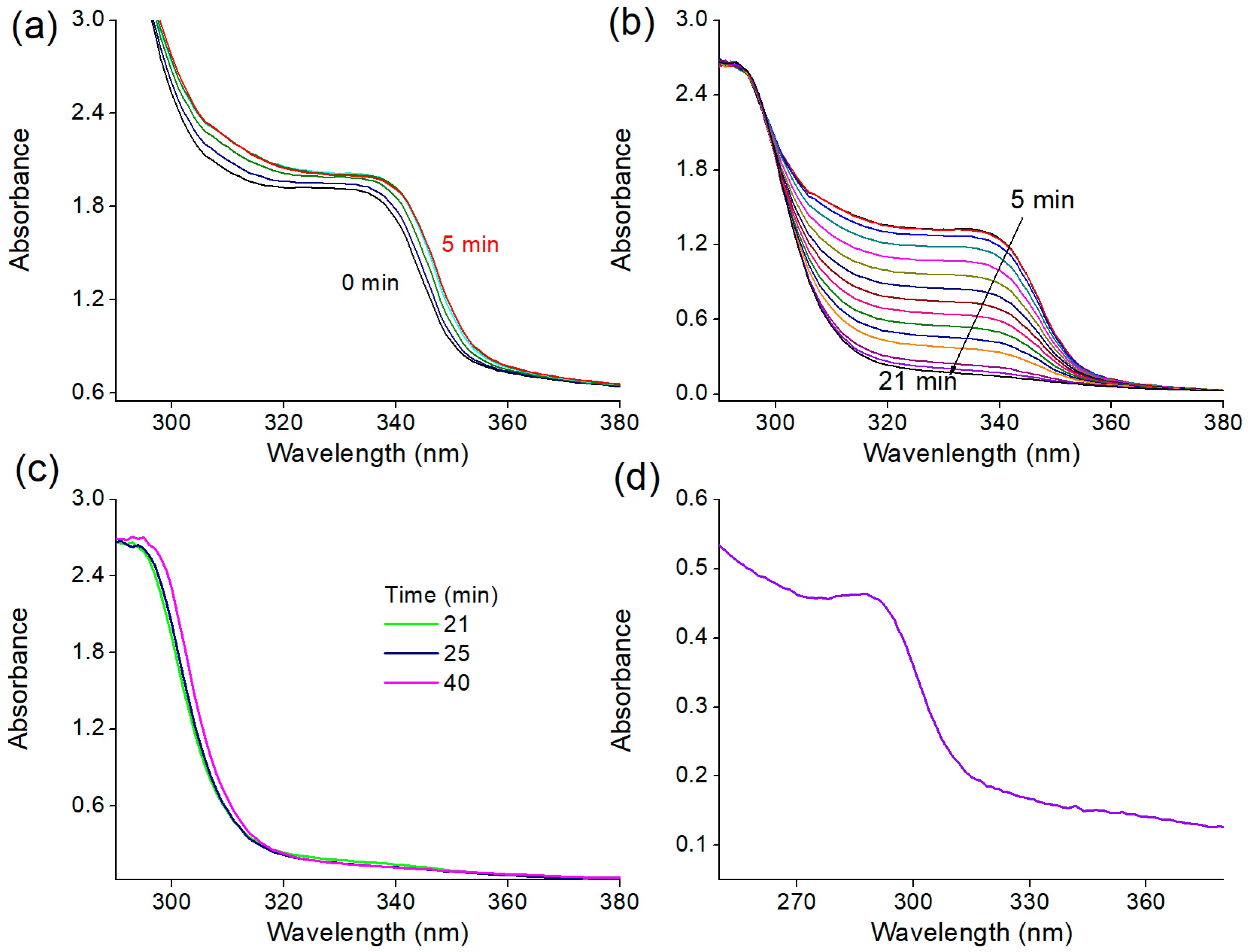
2.3.5. UV-vis Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Features of Powders
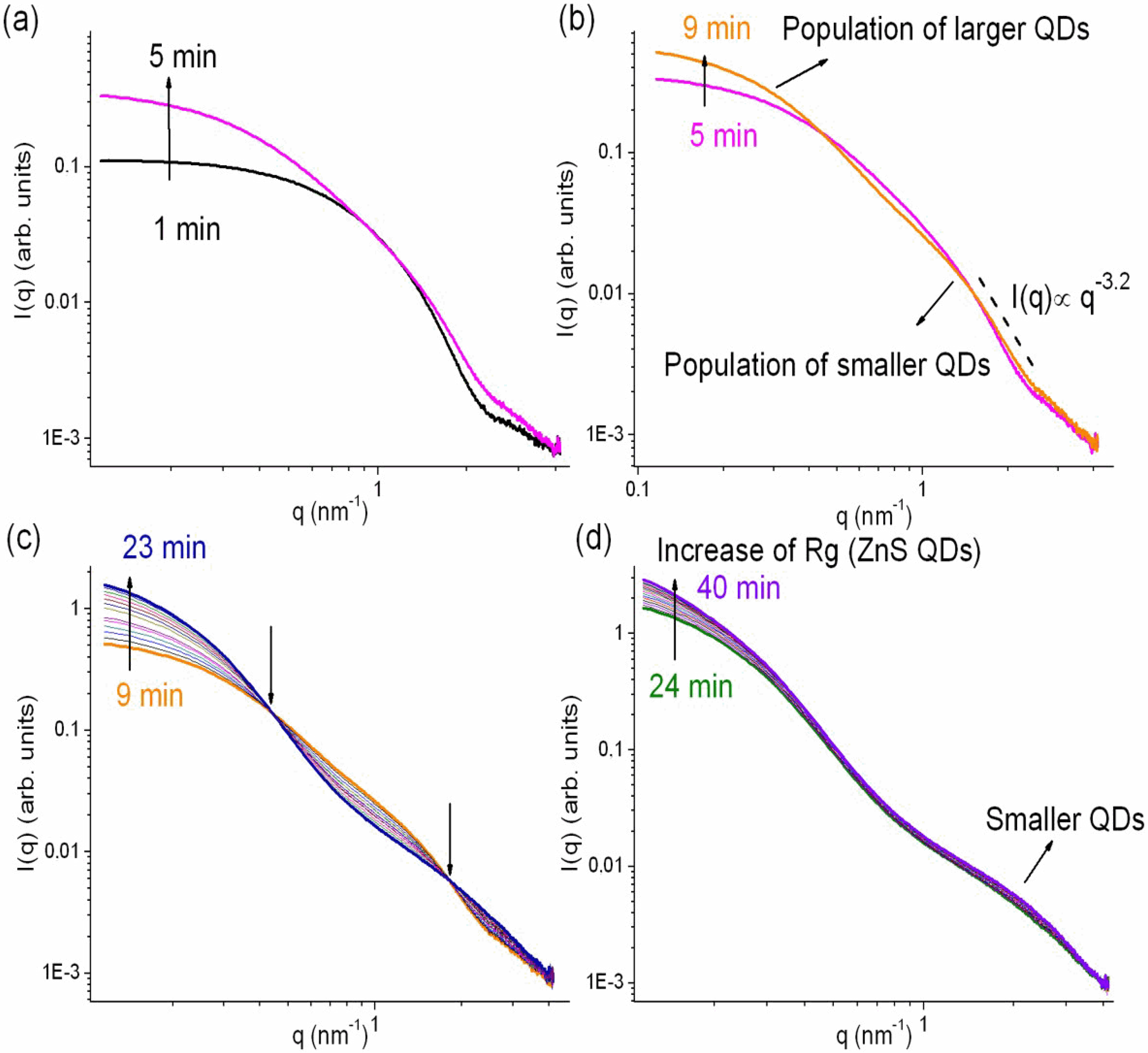
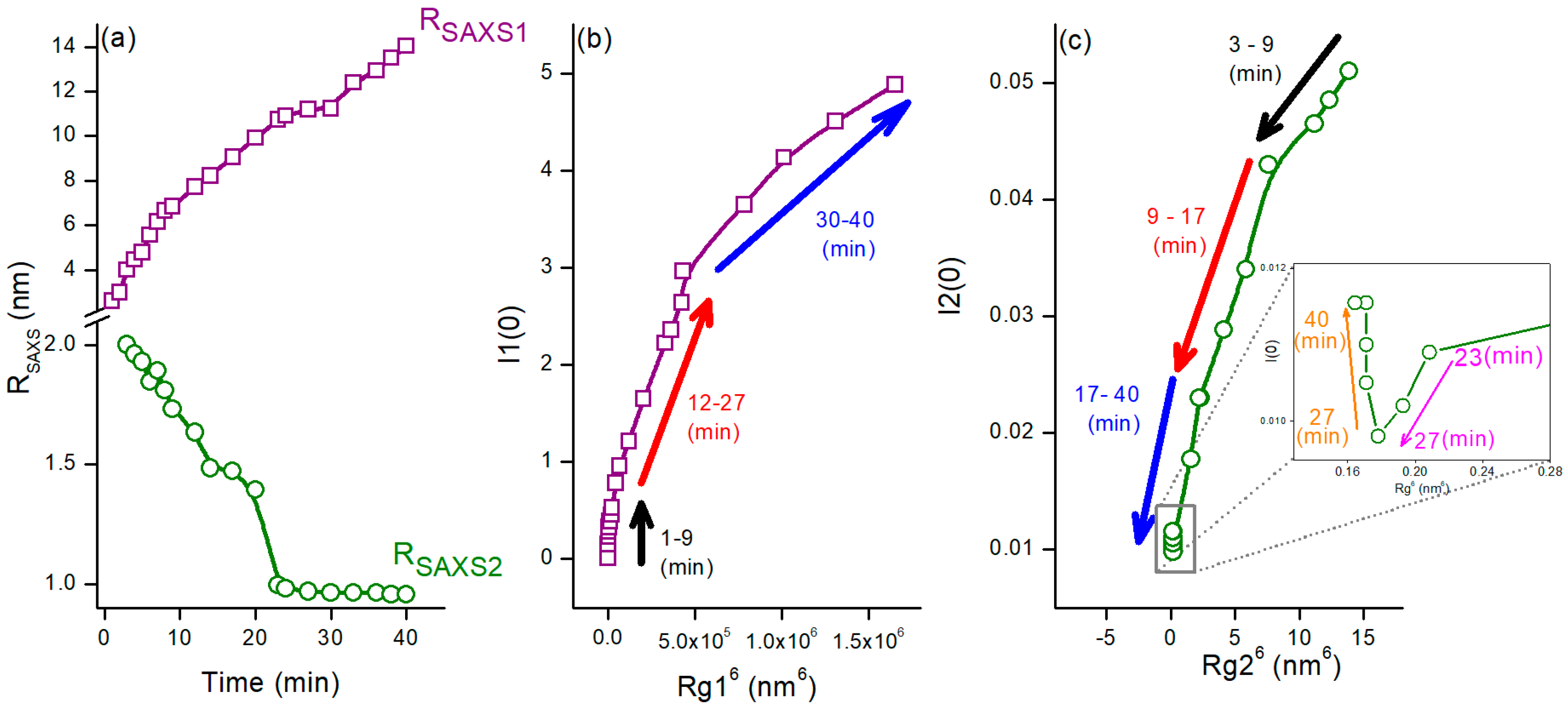
3.2. Time-Resolved Study of the Nanoparticle Synthesis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K.-K.; Shan, C.-X.; He, G.-H.; Wang, R.-Q.; Sun, Z.-P.; Liu, Q.; Dong, L.; Shen, D.-Z. Advanced encryption based on fluorescence quenching of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 7167–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.-H. Synthesis and characterization of ZnS with controlled amount of S vacancies for photocatalytic H2 production under visible light. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, S. ZnO nanorod gas sensor for ethanol detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2012, 162, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kang, C.K.; Kim, K.K.; Park, I.K.; Hwang, D.K.; Park, S.J. UV Electroluminescence Emission from ZnO Light-Emitting Diodes Grown by High-Temperature Radiofrequency Sputtering. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.-M. ZnO Nanoparticles Applied to Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2013, 37, 5329–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, K.; Ihsan, N.; Irie, K.; Mishima, K.; Okuyamam, T.; Mutom, H. Bioimaging application of highly luminescent silica-coated ZnO-nanoparticle quantum dots with biotin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 399, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussodia, R.-O.; Balan, L.; Merlin, C.; Mustin, C.; Schneider, R. Biocompatible and stable ZnO quantum dots generated by functionalization with siloxane-core PAMAM dendrons. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaia, E.B.; Kaminski, R.C.K.; Caetano, B.L.; Briois, V.; Chiavacci, L.A.; Bourgaux, C. Surface modified Mg-doped ZnO QDs for biological imaging. Eur. J. Nanomed. 2015, 7, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lv, P.; Huo, D.; Zhang, C.; Ding, Y.; Xu, P.; Hu, Y. Doxorubicin loaded chitosan-ZnO hybrid nanospheres combining cell imaging and cancer therapy. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60549–60551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chawla, S. Enhanced UV emission in ZnO/ZnS core shell nanoparticles prepared by epitaxial growth in solution. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2013, 9, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhao, S.; Wu, P.; Zhang, K.; Peng, C.; Zheng, S. Synthesis and characterization of new Cd-doped ZnO/ZnS core-shell quantum dots with tunable and highly visible photoluminescence. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, P.; Protière, M.; Li, L. Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanocrystals. Small 2009, 5, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnaeni; Kim, K.H.; Nguyen, D.L.; Lim, H.; Nga, P.T.; Cho, Y.-H. Shell layer dependence of photoblinking in CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Kahen, K.; Hahn, M.A.; Rajeswaran, M.; Maccagnano-Zacher, S.; Silcox, J.; Cragg, G.E.; Efros, A.L.; Krauss, T.D. Non-blinking semiconductor nanocrystals. Nature 2009, 459, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Dev, A.; Chaudhuri, S. Fabrication and luminescent properties of c-axis oriented ZnO-ZnS core-shell and ZnS nanorod arrays by sulfidation of aligned ZnO nanorod arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 5039–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, J.; Jiang, K. ZnO–ZnS heterostructures with enhanced optical and photocatalytic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 2875–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.M.; Shen, W.Z. A Facile Chemical Conversion Synthesis of ZnO/ZnS Core/Shell Nanorods and Diverse Metal Sulfide Nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6415–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Y.; Jia, C.; Wei, M.; Cheng, Y. Chemical Conversion Synthesis of ZnS Shell on ZnO Nanowire Arrays: Morphology Evolution and Its Effect on Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 4, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Liu, B.; Xu, L.; Hu, F.-N.; Zhu, J.-J. Facile Route to Zn-Based II−VI Semiconductor Spheres, Hollow Spheres, and Core/Shell Nanocrystals and Their Optical Properties. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10286–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Pandey, A.C.; Bhargava, R.N. Synthesis and characterisation: Zinc oxide–sulfide nanocomposites. Physica B 2009, 404, 3894–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, W.; Lim, Y.; Seo, W.-S.; Cho, H.; Lee, J. Control of the shell structure of ZnO–ZnS core-shell structure. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 5825–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadollahkhani, A.; Kazeminezhad, I.; Lu, J.; Nur, O.; Hultman, L.; Willander, M. Synthesis, structural characterization and photocatalytic application of ZnO@ZnS core-shell nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36940–36950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookhakian, M.; Amin, Y.M.; Basirun, W.J.; Tajabadi, M.T.; Kamarulzaman, N. Synthesis, structural, and optical properties of type-II ZnO–ZnS core–shell nanostructure. J. Lumin. 2014, 145, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, B.L.; Silva, M.N.; Santilli, C.V.; Briois, V.; Pulcinelli, S.H. Unified ZnO Q-dot growth mechanism from simultaneous UV-Vis and EXAFS monitoring of sol-gel reactions induced by different alkali base. Opt. Mater. 2016, 61, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, B.L.; Briois, V.; Pulcinellim, S.H.; Meneau, F.; Santilli, C.V. Revisiting the ZnO Q-dot Formation Toward an Integrated Growth Model: From Coupled Time Resolved UV−Vis/SAXS/XAS Data to Multivariate Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, B.L.; Santilli, C.V.; Meneau, F.; Briois, V.; Pulcinellim, S.H. In Situ and Simultaneous UV−vis/SAXS and UV−vis/XAFS Time-Resolved Monitoring of ZnO Quantum Dots Formation and Growth. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4404–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, L.; Anderson, M.A. Semiconductor clusters in the sol-gel process: Quantized aggregation, gelation, and crystal growth in concentrated zinc oxide colloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 2826–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenkamp, E.A. Synthesis and Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5566–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlbrecher, J.; Bressler, I. SASfit; Paul Scherrer Institut: Villigen, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, L.E. Electron–electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: The size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4403–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, A.N.; Sokolov, P.S.; Tafeenko, V.A.; Lathe, C.; Zubavichus, Y.V.; Veligzhanin, A.A.; Chukichev, M.V.; Solozhenko, V.L. Nanocrystallinity as a Route to Metastable Phases: Rock Salt ZnO. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.-C.; Hua, C.C.; Lee, T.-C. Low-temperature phase transition of ZnS: The critical role of ZnO. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 194, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.A.; Andres, J.; Li, M.S.; Sambrano, J.R.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E. Zinc blende versus wurtzite ZnS nanoparticles: Control of the phase and optical properties by tetrabutylammonium hydroxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20127–20137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.R. Solid State Chemistry and Its Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992; ISBN 978-1-119-94294-8. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Dai, J.; Hu, J. Control mechanism behind broad fluorescence from violet to orange in ZnO quantum dots. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ji, Y.; Tan, T. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of water-dispersible ZnS quantum dots modified with mercaptoacetic acid. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 570, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briois, V.; Giorgetti, C.; Baudelet, F.; Blanchandin, S.; Tokumoto, M.S.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V. Dynamical Study of ZnO Nanocrystal and Zn-HDS Layered Basic Zinc Acetate Formation from Sol−Gel Route. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 3253–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, A.L.; Bernardi, M.I.B.; Mesquita, A. Local structure and photoluminescence properties of nanostructured Zn1−xMnxS material. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2015, 12, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Chaudhary, S.; Bhasin, K.K.; Gradzielski, M. Evolution of ZnS Nanoparticles via Facile CTAB Aqueous Micellar Solution Route: A Study on Controlling Parameters. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 4, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinier, A.; Fournet, G. Small Angle Scattering of X-rays, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1955; pp. 1–268. [Google Scholar]
- Rabani, J. Sandwich colloids of zinc oxide and zinc sulfide in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 7707–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanhel, L. Colloidal ZnO nanostructures and functional coatings: A survey. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | NZn-O | RZn-O | σ2Zn-O (Å2) | NZn-S | RZn-S | σ2Zn-S (Å2) | Rfactor | LCF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % ZnO | % ZnS | ||||||||
| ZnO Standard | 4 | 1.97 | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.0003 | |||||
| ZnO QDs | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 1.97 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.0014 | |||||
| TAA1.5 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 1.99 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.0003 | 98 | 2 | |||
| TAA5 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 2 | 0.007 ± 0.005 | 2.2 ± 1.0 | 2.34 | 0.007 ± 0.005 | 0.0027 | 37 | 63 |
| TAA50 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 2.02 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 2.34 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 0.0001 | 23 | 77 |
| ZnS Standard | 4 | 2.34 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 0.0004 | |||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berbel Manaia, E.; Kiatkoski Kaminski, R.C.; Caetano, B.L.; Magnani, M.; Meneau, F.; Rochet, A.; Santilli, C.V.; Briois, V.; Bourgaux, C.; Chiavacci, L.A. The Critical Role of Thioacetamide Concentration in the Formation of ZnO/ZnS Heterostructures by Sol-Gel Process. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020055
Berbel Manaia E, Kiatkoski Kaminski RC, Caetano BL, Magnani M, Meneau F, Rochet A, Santilli CV, Briois V, Bourgaux C, Chiavacci LA. The Critical Role of Thioacetamide Concentration in the Formation of ZnO/ZnS Heterostructures by Sol-Gel Process. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerbel Manaia, Eloísa, Renata Cristina Kiatkoski Kaminski, Bruno Leonardo Caetano, Marina Magnani, Florian Meneau, Amélie Rochet, Celso Valentim Santilli, Valérie Briois, Claudie Bourgaux, and Leila Aparecida Chiavacci. 2018. "The Critical Role of Thioacetamide Concentration in the Formation of ZnO/ZnS Heterostructures by Sol-Gel Process" Nanomaterials 8, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020055
APA StyleBerbel Manaia, E., Kiatkoski Kaminski, R. C., Caetano, B. L., Magnani, M., Meneau, F., Rochet, A., Santilli, C. V., Briois, V., Bourgaux, C., & Chiavacci, L. A. (2018). The Critical Role of Thioacetamide Concentration in the Formation of ZnO/ZnS Heterostructures by Sol-Gel Process. Nanomaterials, 8(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020055