Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Chiral and Achiral Separations of Pharmaceuticals, Biologics and Chemicals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MWCNTs for Chiral Separation of Pharmaceuticals
3. SWCNTs for Chiral Separation of Pharmaceuticals
4. SWCNTs and MWCNTs for Chiral Separation in Biological Active Compounds
5. SWCNTs and MWCNTs for Achiral Separation of Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals
6. MWCNTs for Achiral Separation in Biologics
7. SWCNTs for Achiral Separation in Purification
8. Separation of Isomers of CNTs
9. Advantages and Drawbacks
10. Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Xie, J.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, K.; Fan, S. Fabrication of ultralong and electrically uniform single-walled carbon nanotubes on clean substrates. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3137–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eatemadi, A.; Daraee, H.; Karimkhanloo, H.; Kouhi, M.; Zarghami, N.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Abasi, M.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Joo, S.W. Carbon nanotubes: Properties, synthesis, purification, and medical applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocan, L.; Ilie, I.; Tabaran, F.A.; Iancu, C.; Mosteanu, O.; Pop, T.; Zdrehus, C.; Bartos, D.; Mocan, T.; Matea, C. Selective laser ablation of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus with lgG functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh Pasha, M.; Poursalehi, R. Carbon nanotube formation over laser ablated m and M/Pd (M = Fe, Co, Ni) catalysts: The effect of Pd addition. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2016, 24, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, L.; Lawaetz, M.; Bjoern, L.; Vennits, B.; Blemings, A.; Eklof, B. Randomized clinical trial comparing endovenous laser ablation, radiofrequency ablation, foam sclerotherapy and surgical stripping for great saphenous varicose veins. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 98, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoranneviss, M.; Elahi, A.S. Review of carbon nanotubes production by thermal chemical vapor deposition technique. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2016, 629, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.A.; Tali, B.A. Synthesis of carbon nanotubes by catalytic chemical vapour deposition: A review on carbon sources, catalysts and substrates. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 41, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Fina, A. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 914–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajter, R.F.; French, R.H.; Ching, W.; Podgornik, R.; Parsegian, V.A. Chirality-dependent properties of carbon nanotubes: Electronic structure, optical dispersion properties, hamaker coefficients and van der Waals-London dispersion interactions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruland, W.; Schaper, A.; Hou, H.; Greiner, A. Multi-wall carbon nanotubes with uniform chirality: Evidence for scroll structures. Carbon 2003, 41, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, R.; Bertozzi, C.R. Progress and challenges for the bottom-up synthesis of carbon nanotubes with discrete chirality. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 494, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hersam, M.C. Progress towards monodisperse single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-J.; Usrey, M.L.; Strano, M.S. Selective functionalization and free solution electrophoresis of single-walled carbon nanotubes: Separate enrichment of metallic and semiconducting swnt. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, I.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Morante, S.; Gañán, J. Novel supports in chiral stationary phase development for liquid chromatography. Preparation, characterization and application of ordered mesoporous silica particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1363, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Merli, D.; Profumo, A. Analytical application of carbon nanotubes, fullerenes and nanodiamonds in nanomaterials-based chromatographic stationary phases: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 783, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Qiu, H. Progress in stationary phases modified with carbonaceous nanomaterials for high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 65, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Merli, D.; Dondi, D.; Paganini, G.; Profumo, A. Improving selectivity in gas chromatography by using chemically modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes as stationary phase. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Merli, D.; Dondi, D.; Milanese, C.; Galinetto, P.; Bozzetti, C.; Profumo, A. Radiation-induced grafting of carbon nanotubes on hplc silica microspheres: Theoretical and practical aspects. Analyst 2013, 138, 3778–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Maiocchi, M.; Cucca, L.; Merli, D.; Profumo, A. Solid-phase extraction of PFOA and PFOS from surface waters on functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes followed by UPLC-ESI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3657–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Carbon nanotubes applications in separation science: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Ozawa, H.; Fujigaya, T.; Nakashima, N. Evaluation of affinity of molecules for carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2517–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, C.; Lenancker, G.; Guillaume, Y.C. Non-covalent functionalisation of monolithic silica for the development of carbon nanotube hplc stationary phases. Talanta 2012, 99, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujigaya, T.; Yoo, J.; Nakashima, N. A method for the coating of silica spheres with an ultrathin layer of pristine single-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2011, 49, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, S. Layer-by-layer self-assembled multi-walled carbon nanotubes/silica microsphere composites as stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3304–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, C.; Gharbi, T.; Guillaume, Y.C. A novel stationary phase based on amino derivatized nanotubes for hplc separations: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, S.D.; Svec, F.; Fréchet, J.M. Incorporation of carbon nanotubes in porous polymer monolithic capillary columns to enhance the chromatographic separation of small molecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqel, A.; Yusuf, K.; Al-Othman, Z.A.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Alwarthan, A.A. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes incorporation into benzyl methacrylate monolithic columns in capillary liquid chromatography. Analyst 2012, 137, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, D.; Speltini, A.; Dondi, D.; Longhi, D.; Milanese, C.; Profumo, A. Intermolecular interactions of substituted benzenes on multi-walled carbon nanotubes grafted on hplc silica microspheres and interaction study through artificial neural networks. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, H.; Jabbari, M. Development of graphene-carbon nanotube-coated magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient sorbent for hplc determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental water samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, B.; Liao, Y.; Liu, H. Nanoparticle: Is it promising in capillary electrophoresis? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, B.; Liu, K.; Liao, Y.; Liu, H. CE-MS analysis of heroin and its basic impurities using a charged polymer-protected gold nanoparticle-coated capillary. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moliner-Martínez, Y.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Evaluation of carbon nanostructures as chiral selectors for direct enantiomeric separation of ephedrines by ekc. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 2573–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H. Applications of nanomaterials in enantioseparation and related techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 39, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, C.; Aljhani, R.; Gharbi, T.; Guillaume, Y.C. Incorporation of carbon nanotubes in a silica hplc column to enhance the chromatographic separation of peptides: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, C.; Agiovlasileti, D.; Guillaume, Y.C. Peculiarities of a novel bioenzymatic reactor using carbon nanotubes as enzyme activity enhancers: Application to arginase. Talanta 2011, 85, 2703–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y. Preparation, characterization, and analytical applications of a novel polymer stationary phase with embedded or grafted carbon fibers. Talanta 2010, 82, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ai, P.; Duan, A.-H.; Yuan, L.-M. Single-walled carbon nanotubes for improved enantioseparations on a chiral ionic liquid stationary phase in GC. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, N.; Cui, X.; De Beer, T.; Liu, T.; Tang, T.; Sajid, M.; Ouyang, J. The use of silica nanoparticles for gas chromatographic separation. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4552–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, J. Determination of n-alkanes contamination in soil samples by micro gas chromatography functionalized by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2016, 158, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-García, M.; Aguilar-Caballos, M.; Gómez-Hens, A. Nanomaterials as tools in chromatographic methods. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-L.; Lin, Y.-C. The role of methacrylate polymerized as porous-layered and nanoparticle-bound phases for open-tubular capillary electrochromatography: Substitution of a charged monomer for a bulk monomer. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3949–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stege, P.W.; Sombra, L.L.; Messina, G.; Martinez, L.D.; Silva, M.F. Determination of melatonin in wine and plant extracts by capillary electrochromatography with immobilized carboxylic multi-walled carbon nanotubes as stationary phase. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassen, H.; Antony, V.; Ghanem, A.; Yajadda, M.M.A.; Han, Z.J.; Ostrikov, K. Organic/hybrid nanoparticles and single-walled carbon nanotubes: Preparation methods and chiral applications. Chirality 2014, 26, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Hernández-Borges, J. Recent applications of carbon nanotube sorbents in analytical chemistry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1357, 110–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Y.; Liu, H. Applications of nanomaterials in liquid chromatography: Opportunities for separation with high efficiency and selectivity. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Yajadda, M.M.A.; Han, Z.J.; Su, D.; Wang, G.; Ostrikov, K.K.; Ghanem, A. Single-walled carbon nanotube-based polymer monoliths for the enantioselective nano-liquid chromatographic separation of racemic pharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1360, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillaume, Y.C.; André, C. Fast enantioseparation by hplc on a modified carbon nanotube monolithic stationary phase with a pyrenyl aminoglycoside derivative. Talanta 2013, 115, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, N.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Baeyens, W.R.; Delanghe, J.R.; Taes, Y.E.; Xie, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, Y. On the use of dispersed nanoparticles modified with single layer β-cyclodextrin as chiral selecor to enhance enantioseparation of clenbuterol with capillary electrophoresis. Talanta 2006, 69, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, R.; Ciuparu, D.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Horváth, C.; Wilkins, J.A. Incorporation of single-wall carbon nanotubes into an organic polymer monolithic stationary phase for μ-HPLC and capillary electrochromatography. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, J.H.; Bouvrette, P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.-Q.; Sacher, E. Electrophoretic separation of aniline derivatives using fused silica capillaries coated with acid treated single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarigh, G.D.; Shemirani, F. In situ immobilization of a general resolving agent on the magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube for the direct enantioenrichment of DL-mandelic acid. Talanta 2015, 144, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarigh, G.D.; Shemirani, F. Magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite as an adsorbent for preconcentration and determination of lead (II) and manganese (II) in various matrices. Talanta 2013, 115, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. A selective voltammetric method for uric acid detection at β-cyclodextrin modified electrode incorporating carbon nanotubes. Analyst 2002, 127, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyori, R.; Tokunaga, M.; Kitamura, M. Stereoselective organic synthesis via dynamic kinetic resolution. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 68, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner-Martínez, Y.; Cárdenas, S.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M. Recent developments in capillary EKC based on carbon nanoparticles. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, E.B.; Jorio, A.; Samsonidze, G.G.; Capaz, R.B.; Souza Filho, A.G.; Mendes Filho, J.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Review on the symmetry-related properties of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 2006, 431, 261–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, T.D.; Skoulidas, A.I.; Sholl, D.S. Can chiral single walled carbon nanotubes be used as enantiospecific adsorbents? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1858–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, B.; Simonet, B.M.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcarcel, M. Surfactant-coated single-walled carbon nanotubes as a novel pseudostationary phase in capillary EKC. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, K.; Hong, Y. Preparation of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin cross-linked multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their application in enantioseparation of clenbuterol. Chin. J. Chem. 2011, 29, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Bi, H.; Liu, B.; Kong, J. On-chip chiral separation based on bovine serum albumin-conjugated carbon nanotubes as stationary phase in a microchannel. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 3129–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranyi, A.; Péter, A.; Ilisz, I.; Fueloep, F.; Scriba, G.K. Cyclodextrin-mediated enantioseparation of phenylalanine amide derivatives and amino alcohols by capillary electrophoresis—Role of complexation constants and complex mobilities. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Star, A.; Steuerman, D.W.; Heath, J.R.; Stoddart, J.F. Starched carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2508–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knych, H.K.; Mitchell, M.; Steinmetz, S.; McKemie, D. Detection, pharmacokinetics and cardiac effects following administration of clenbuterol to exercised horses. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, H.A.; James, K.J.; Scholzen, S.; Borys, D.J. A descriptive study of adverse events from clenbuterol misuse and abuse for weight loss and bodybuilding. Subst. Abus. 2013, 34, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebedeva, M.V.; Prokhorova, A.F.; Shapovalova, E.N.; Shpigun, O.A. Clarithromycin as a chiral selector for enantioseparation of basic compounds in nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2759–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, M.; Yu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, X. Capillary electrophoretic enantioseparation of basic drugs using a new single-isomer cyclodextrin derivative and theoretical study of the chiral recognition mechanism. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.T.; Kim, D.W.; Showkat, A.M.; Jeong, Y.T.; Lim, K.T. Enhancing adsorption of multi-walled carbon nanotubes for dye removal. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2016, 8, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Valcárcel, M. B-cyclodextrin functionalized carbon quantum dots as sensors for determination of water-soluble C60 fullerenes in water. Analyst 2016, 141, 2682–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J. Preparation and adsorption studies of β-cyclodextrin grafted onto multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujigaya, T.; Nakashima, N. Non-covalent polymer wrapping of carbon nanotubes and the role of wrapped polymers as functional dispersants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 16, 024802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleyman, R.; Hirbod, S.; Adeli, M. Advances in the biomedical application of polymer-functionalized carbon nanotubes. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, B.; Mende, M.; Pötschke, P.; Petzold, G. Dispersability and particle size distribution of cnts in an aqueous surfactant dispersion as a function of ultrasonic treatment time. Carbon 2010, 48, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Zhuang, R.-C.; Mäder, E. Surfactant assisted dispersion of functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous media. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Anas, A.K.; Bakar, S.A.; Ardyani, T.; Zin, W.M.W.; Ibrahim, S.; Sagisaka, M.; Brown, P.; Eastoe, J. Enhanced dispersion of multiwall carbon nanotubes in natural rubber latex nanocomposites by surfactants bearing phenyl groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 455, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.; Rojas, E.; Bergey, D.; Johnson, A.; Yodh, A. High weight fraction surfactant solubilization of single-wall carbon nanotubes in water. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y. Carbon nanotubes as separation carrier in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 4181–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, G.; Silva, R.; Gil, R.A.; Gomez, R.; Fernández, L.P. On-line enantioseparation of chlorpheniramine using β-cyclodextrin and carbon nanotubes after multivariate optimization. Talanta 2013, 105, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Sheng, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Nagatsu, M. Removal of polychlorinated biphenyls from aqueous solutions using β-cyclodextrin grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.K.; Green, M.L.; Griffin, J.L.; Hammer, J.; Lago, R.M.; Tsang, S.C. Purification and opening of carbon nanotubes via bromination. Adv. Mater. 1996, 8, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, N.; Sharifi, A.; Lashgari, E. Selective adsorption of metoprolol enantiomers using 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin cross-linked multiwalled carbon nanotube. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Sun, C.-H.; Jiao, F.-P.; Yu, J.-G.; Jiang, X.-Y. Chiral separation of propranolol enantiomers by oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes/β-cyclodextrin impregnated thin-layer chromatography. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2014, 10, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.G.; Yin, D.H.; Liu, J.F.; Yu, J.G.; Yang, X.N.; Zeng, D.M. Application of a mixture of oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and d-(−)-tartaric acid-impregnated silica gel as stationary phases for thin-layer chromatographic enantioseparation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 602–604, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Yi, Z.; Wu, J. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes mediated thin-layer chromatographic enantioseparation of ofloxacin. Curr. Nanosci. 2013, 9, 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, S.; Nakajima, S.; Ozaki, H.; Takemoto, R.; Itabashi, Y.; Kuksis, A. Enantioseparation of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids by hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin-modified micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 3196–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudaz, S.; Geiser, L.; Souverain, S.; Prat, J.; Veuthey, J.L. Rapid stereoselective separations of amphetamine derivatives with highly sulfated γ-cyclodextrin. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3910–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.X.; Lin, J.M.; Chan, W.H.; Lee, A.W.; Huie, C.W. Separation of enantiomers in microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography using chiral alcohols as cosurfactants. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 3263–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.Q.; Lü, W.J.; Ma, Y.H.; Hu, Q.; Dong, L.J.; Chen, X.G. Chiral separation of β-blockers by meekc using neutral microemulsion: Analysis of separation mechanism and further elucidation of resolution equation. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huie, C.W. Recent applications of microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Terabe, S. Partial separation zone technique for the separation of enantiomers by affinity electrokinetic chromatography with proteins as chiral pseudo-stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 694, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Boccuzzi, K.A.; Ferjani, S.; Rosenblatt, C. Carbon nanotube-induced chirality in an achiral liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 121908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Martens, J.; Bhushan, R. Enantiomerization study of atropine and its semipreparative enantioseparation along with (1RS, 2SR)-(±)-ephedrine on polyacrylamide column using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, S.; Huang, M. Determination of ephedra alkaloids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chromatographia 2001, 54, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avula, B.; Khan, I. Separation and determination of ephedrine enantiomers and synephrine by high performance capillary electrophoresis in dietary supplements. Chromatographia 2004, 59, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, K.M.; Al-Hazmi, A.H.; Alasiri, A.M.; Ali, M.E.-S. A GC-MS method for detection and quantification of cathine, cathinone, methcathinone and ephedrine in oral fluid. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Cao, Y.; Lou, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Chai, Y.; Lu, F. Rapid on-site detection of ephedrine and its analogues used as adulterants in slimming dietary supplements by TLC-SERS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukovic, G.; Balaz, M.; Doak, P.; Berova, N.D.; Zheng, M.; Mclean, R.S.; Brus, L.E. Racemic single-walled carbon nanotubes exhibit circular dichroism when wrapped with DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9004–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Fu, G.-j.; Zhang, Z.-Z. Separation of mandelic acid and its derivatives with new immobilized cellulose chiral stationary phase. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2013, 14, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, E.; Nakamichi, K.; Furui, M.; Mori, T. R-(−)-mandelic acid production from racemic mandelic acids by pseudomonas polycolor with asymmetric degrading activity. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-S.; Kim, J.-M.; Chang, S.-M.; Kim, W.-S. Chiral recognition of mandelic acid by l-phenylalanine-modified sensor using quartz crystal microbalance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2931–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Tong, J. Application of derivatized magnetic materials to the separation and the preconcentration of pollutants in water samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Tian, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, B. A general chiral selector immobilized on silica magnetic microspheres for direct separation of racemates. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8499–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Su, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of teicoplanin-modified hybrid magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their application in chiral separation of racemic compounds. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 399, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Ghanem, A. Enantioselective nano liquid chromatographic separation of racemic pharmaceuticals: A facile one-pot in situ preparation of lipase-based polymer monoliths in capillary format. Chirality 2014, 26, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayadunne, E.; El Rassi, Z. Facile preparation of octadecyl monoliths with incorporated carbon nanotubes and neutral monoliths with coated carbon nanotubes stationary phases for HPLC of small and large molecules by hydrophobic and π-π interactions. Talanta 2014, 129, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Choi, K.; Ahmed, A.Y.B.H.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Chung, D.S. Highly sensitive chiral analysis of amino acids by in-line single drop microextraction and capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 677, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Hernández, L.; Bernal, J.L.; del Nozal, M.J.; Toribio, L. Chiral analysis of aromatic amino acids in food supplements using subcritical fluid chromatography and chirobiotic T2 column. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szökő, É.; Vincze, I.; Tábi, T. Chiral separations for d-amino acid analysis in biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Koga, R.; Oyama, T.; Han, H.; Ueno, K.; Masuyama, K.; Itoh, Y.; Hamase, K. HPLC analysis of naturally occurring free d-amino acids in mammals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 69, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilisz, I.; Péter, A.; Lindner, W. State-of-the-art enantioseparations of natural and unnatural amino acids by high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 81, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. Extra-facile chiral separation of amino acid enantiomers by LC-tofms analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Xing, H.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Bao, Z. Efficient adsorption separation of acetylene and ethylene via supported ionic liquid on metal-organic framework. AlChE J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Ge, L.; Diao, H.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Ionic liquids as the mofs/polymer interfacial binder for efficient membrane separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32041–32049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabby, A.K.; Rizvi, S.S.; Requena, A.M.S.; de los, A.P.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; Lozano, L.; Godínez, C.; Sánchez-Segado, S.; Alguacil, F.; Tomás-Alonso, F. On the use of ionic liquid technology for the selective separation of organic compounds and metal ions. In Handbook of Membrane Separations: Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Biotechnological Applications, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 615–628. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, L.; Han, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Zi, M.; Chang, Y. (R)-N,N,N-trimethyl-2-aminobutanol-bis (trifluoromethane-sulfon) imidate chiral ionic liquid used as chiral selector in HPCE, HPLC, and CGC. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Du, S. Evaluation of ionic liquids-coated carbon nanotubes modified chiral separation system with chondroitin sulfate e as chiral selector in capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1339, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Q. Evaluation of the enantioselectivity of carbon nanoparticles-modified chiral separation systems using dextrin as chiral selector by capillary electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Song, X.; Duan, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J.; Duan, H. Preparation and characterization of a polystyrene/bovine serum albumin nanoparticle-coated capillary for chiral separation using open-tubular capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-T.; Xiang, L.-L.; Wang, J.-L.; Chen, D.-Y. Application of capillary electrophoresis-frontal analysis for comparative evaluation of the binding interaction of captopril with human serum albumin in the absence and presence of hydrochlorothiazide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 115, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O.; Hemasa, A.L.; Freag, M.S. Hybrid protein-inorganic nanoparticles: From tumor-targeted drug delivery to cancer imaging. J. Control. Release 2016, 243, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Taylor, S.; Fu, K.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hanks, T.W.; Rao, A.M.; Sun, Y.-P. Attaching proteins to carbon nanotubes via diimide-activated amidation. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmani, N.; Farhan, M.; Hadi, S.M. DNA binding and its degradation by the neurotransmitter serotonin and its structural analogues melatonin and tryptophan: Putative neurotoxic mechanism. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokturk, O.; Kanbay, A. Tryptophan metabolism and sleep. In Tryptophan Metabolism: Implications for Biological Processes, Health and Disease; Atilla Engin, A.B.E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 239–252. [Google Scholar]
- Oketch-Rabah, H.A.; Roe, A.L.; Gurley, B.J.; Griffiths, J.C.; Giancaspro, G.I. The importance of quality specifications in safety assessments of amino acids: The cases of l-tryptophan and l-citrulline. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2643S–2651S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Tao, Y.; Gu, X.; Yang, B.; Deng, L.; Kong, Y. Potato starch as a highly enantioselective system for temperature-dependent electrochemical recognition of tryptophan isomers. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 64, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yu, L.-S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Li, Y.-X. Separation of amino acid enantiomers using capillary electrophoresis with a new chiral ligand. LCGC N. Am. 2016, 34, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, F.; Song, H.; Yang, W.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, J. Enantioselective separation of tryptophan by MG–Al layered double hydroxides intercalated with tartaric acid derivative. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 75, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Park, K.-M.; Jo, S.-H.; Nam, H.-G.; Mun, S. Determination of chromatographic separation parameters of tryptophan enantiomers on a Chirosil-SCA chiral stationary phase by using the inverse method based on the initial guesses estimated from elution by characteristic point method. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zor, E.; Patir, I.H.; Bingol, H.; Ersoz, M. An electrochemical biosensor based on human serum albumin/graphene oxide/3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane modified ito electrode for the enantioselective discrimination of d-and l-tryptophan. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsube, S.; Sato, K.; Ando, T.; Isogai, E.; Yoneyama, H. Secretion of d-alanine by Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2016, 162, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, X. An innovative approach for separation and purification of natural products using carbon nanotube-alginate gel beads as a novel stationary phase. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10878–10885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, C.; Dondi, D. Tuning retention and selectivity in reversed-phase liquid chromatography by using functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, M.; Funatsu, T. Catecholamine analysis with strong cation exchange column liquid chromatography-peroxyoxalate chemiluminescence reaction detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, A.; Shi, G. Selective extraction and analysis of catecholamines in rat blood microdialysate by polymeric ionic liquid-diphenylboric acid-packed capillary column and fast separation in high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detector. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1409, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkova, H.; Petrak, O.; Skrha, J.; Widimský, J., Jr.; Zelinka, T. Pheochromocytoma and markers of oxidative stress. Physiol. Res. 2013, 62, 331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, L.; Orlowski, R.; Cohen, D. Pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma: Review of perioperative management of blood pressure and update on genetic mutations associated with pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2013, 15, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. Voltammetric separation of dopamine and ascorbic acid with graphite electrodes modified with ultrafine TiO2. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2000, 11, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldart, S.E.; Brown, P.R. Separation of purine and pyrimidine bases by capillary zone electrophoresis with carbonate buffers. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 831, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, S.A.; Palmer, C.P.; Warner, I.M. Peer reviewed: Molecular micelles: Novel pseudostationary phases for ce. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 140A–149A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Simultaneous determination of five bioactive constituents in rhizoma chuanxiong by capillary electrophoresis with a carbon nanotube-polydimethylsiloxane composite electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.M.; Arabieh, M.; Sepehrian, H. Nanoporous graphene oxide membrane and its application in molecular sieving. Carbon Lett 2015, 16, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatemi, S.; Foroutan, M. Review on carbon nanotubes and carbon nanotube bundles for gas/ion separation and water purification studied by molecular dynamics simulation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aral, H.; Çelik, K.S.; Aral, T.; Topal, G. Preparation of a novel ionic hybrid stationary phase by non-covalent functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes with amino-derivatized silica gel for fast hplc separation of aromatic compounds. Talanta 2016, 149, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, J. A micro gas chromatography with separation capability enhanced by polydimethylsiloxane stationary phase functionalized by carbon nanotubes and graphene. Talanta 2016, 154, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, H.; Agah, M. Self-patterned gold-electroplated multicapillary gas separation columns with MPG stationary phases. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 22, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Myers, E.; Tang, H.; Aldridge, S.; McCaig, H.; Whiting, J.; Simonson, R.; Lewis, N.S.; Roukes, M. Nanoelectromechanical resonator arrays for ultrafast, gas-phase chromatographic chemical analysis. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3899–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, V.R.; Stadermann, M.; Bakajin, O.; Synovec, R.E. High-speed, temperature programmable gas chromatography utilizing a microfabricated chip with an improved carbon nanotube stationary phase. Talanta 2009, 77, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-J.; Serrano, G.; Wise, K.D.; Kurabayashi, K.; Zellers, E.T. Evaluation of a microfabricated thermal modulator for comprehensive two-dimensional microscale gas chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5556–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Gu, C.; Gu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Wang, C.; Hu, X. Capillary column coated with graphene oxide as stationary phase for gas chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 757, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Miner, J.N. Patients with gout differ from healthy subjects in renal response to changes in serum uric acid. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 84, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumfart, J.; Weschke, B.; Ringe, H.; Weinhold, N.; Müller, D. Acute renal failure unmasking lesch-nyhan disease in a patient with tuberous sclerosis complex. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, T.T.; Moura, E.L.R.; Oliveira, M.C.D.; Boff, G.; Junqueira, L.F., Jr.; Veiga, J.P.R. Prevalence of high serum uric acid is increased in ambulatory subjects with hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2010, 46, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Lin, M. Voltammetric uric acid sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of polytetraphenylporphyrin, polypyrrole, and graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huang, T.; Hu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Xie, Q. Differential pulse voltammetric simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid on a glassy carbon electrode modified with electroreduced graphene oxide and imidazolium groups. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.R.; Reddy, T.M.; Narayana, P.; Gopal, P.; Reddaiah, K. Electrochemical determination of dopamine and its simultaneous resolution in the presence of uric acid at poly (pyrocatechol violet) modified glassy carbon electrode: A voltammetric study. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2016, 4, 250–256. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. Carbon nanotube-modified electrodes for the simultaneous determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Analyst 2002, 127, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Ouyang, J.; Baeyens, W.R.; Delanghe, J.R.; Shen, X.; Yang, Y. Enhanced separation of purine and pyrimidine bases using carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotubes as additive in capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 3243–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ren, J. Separation of purine and pyrimidine bases by capillary electrophoresis using β-cyclodextrin as an additive. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2004, 34, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Carrión, C.; Armenta, S.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M.; Lendl, B. Determination of pyrimidine and purine bases by reversed-phase capillary liquid chromatography with at-line surface-enhanced raman spectroscopic detection employing a novel sers substrate based on ZnS/CdSe silver-quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9391–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markelj, J.; Zupančič, T.; Pihlar, B. Optimization of high performance liquid chromatography method for simultaneous determination of some purine and pyrimidine bases. Acta. Chim. Slov. 2015, 63, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentoft, C.; Vestergaard, M.; Løvendahl, P.; Kristensen, N.B.; Moorby, J.M.; Jensen, S.K. Simultaneous quantification of purine and pyrimidine bases, nucleosides and their degradation products in bovine blood plasma by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1356, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; McGown, L.B. Sequence-based separation of single-stranded DNA at high salt concentrations in capillary zone electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Müller, C.E. High-sensitivity capillary electrophoresis method for monitoring purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase reactions by a reversed electrode polarity switching mode. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4764–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klampfl, C.W.; Himmelsbach, M.; Buchberger, W.; Klein, H. Determination of purines and pyrimidines in beer samples by capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 454, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.D.; Zhang, C.; Hantao, L.W.; Anderson, J.L. Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: Fundamentals, advances, and perspectives. Anal. Chem. 2013, 86, 262–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.-Y.; Xiao, X.-H.; Luo, X.-J.; Li, G.-K. Application of ionic liquids in the microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenolic compounds from medicinal plants. Talanta 2009, 78, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiang, C.; Yan, H.; Han, Y.; Qiao, F. Graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with an amine-terminated ionic liquid for determination of (Z)-3-(chloromethylene)-6-fluorothiochroman-4-one in urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1474, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wu, X.-S.; Wen, G.-Y.; Qiao, Y. Imidazolium ionic liquid functionalized carbon nanotubes for improved interfacial charge transfer and simultaneous determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers. Molecules 2016, 21, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Yuan, D.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C.; Dai, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Mixed hemimicelle solid-phase extraction based on magnetic carbon nanotubes and ionic liquids for the determination of flavonoids. Carbon 2014, 72, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vera, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Combined use of carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid to improve the determination of antidepressants in urine samples by liquid chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kašička, V.; Prusík, Z.; Sázelová, P.; Koval, D.; Barth, T.; Hlaváček, J.; Ježek, J.; Klasová, L.; Slaninová, J.; Velek, J. Analytical and preparative separations of biologically active peptides by capillary and free-flow electromigration methods. Collect. Czech. Chem. Commun. 2016, 4, 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shaik, M.K.A.R.B.; Venkateshwarlu, K.P. Purification of peptides using surrogate stationary phases on reversed-phase columns. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, C.; Goto, A.; Tsujii, Y.; Ishizuka, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Fukuda, T. Surface interaction of well-defined, concentrated poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) brushes with proteins. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 4795–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nema, T.; Chan, E.C.; Ho, P.C. Applications of monolithic materials for sample preparation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dubin, P. Capillary modification by noncovalent polycation adsorption: Effects of polymer molecular weight and adsorption ionic strength. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3463–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordi, V.; Yao, N.; Wei, J. Method for supporting platinum on single-walled carbon nanotubes for a selective hydrogenation catalyst. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Male, K.B.; Hrapovic, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Luong, J.H. Electrochemical detection of carbohydrates using copper nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 516, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Dai, H. Noncovalent sidewall functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes for protein immobilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 3838–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, J.-F.; Sacher, E.; Meunier, M.; Luong, J. A mediatorless biosensor for putrescine using multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 336, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Komatsu, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Shimawaki, T.; Aonuma, S.; Kimura, T.; Osuka, A. Optically active single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupke, R.; Hennrich, F.; Löhneysen, H.V.; Kappes, M.M. Separation of metallic from semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 2003, 301, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Lastella, S.; Kim, S.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F. Length separation of zwitterion-functionalized single wall carbon nanotubes by GPC. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Yasumitsu, T.; Zhao, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, F.; Bauri, A.K.; Aonuma, S.; Kimura, T.; Komatsu, N. Preferential extraction of left-or right-handed single-walled carbon nanotubes by use of chiral diporphyrin nanotweezers. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L. Towards chirality-pure carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, K.; Burghard, M. Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Small 2005, 1, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.A.; Talío, M.C.; Luconi, M.O.; Fernández, L.P. Evaluation of carbon nanotubes as chiral selectors for continuous-flow enantiomeric separation of carvedilol with fluorescent detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Liao, X.-Y.; Yu, J.-G.; Jiao, F.-P.; Jiang, X.-Y. Chiral carbon nanotubes and carbon nanotube chiral composites: Preparation and applications. Nano 2013, 8, 1330002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisman, L.; Marom, G.; Wagner, H.D. Dispersions of surface-modified carbon nanotubes in water-soluble and water-insoluble polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.; Kaushal, R.; Tripathi, S.; Sharma, A.L.; Kaur, I.; Bharadwaj, L.M. Comparative study of carbon nanotube dispersion using surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Lin, Y.; Taylor, S.; Gaillard, J.; Rao, A.M.; Sun, Y.-P. Sonication-assisted functionalization and solubilization of carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Alemany, L.B.; Margrave, J.L.; Khabashesku, V.N. Sidewall carboxylic acid functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15174–15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Merli, D.; Quartarone, E.; Profumo, A. Separation of alkanes and aromatic compounds by packed column gas chromatography using functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, D.; Speltini, A.; Ravelli, D.; Quartarone, E.; Costa, L.; Profumo, A. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes as the gas chromatographic stationary phase: Role of their functionalization in the analysis of aliphatic alcohols and esters. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7275–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
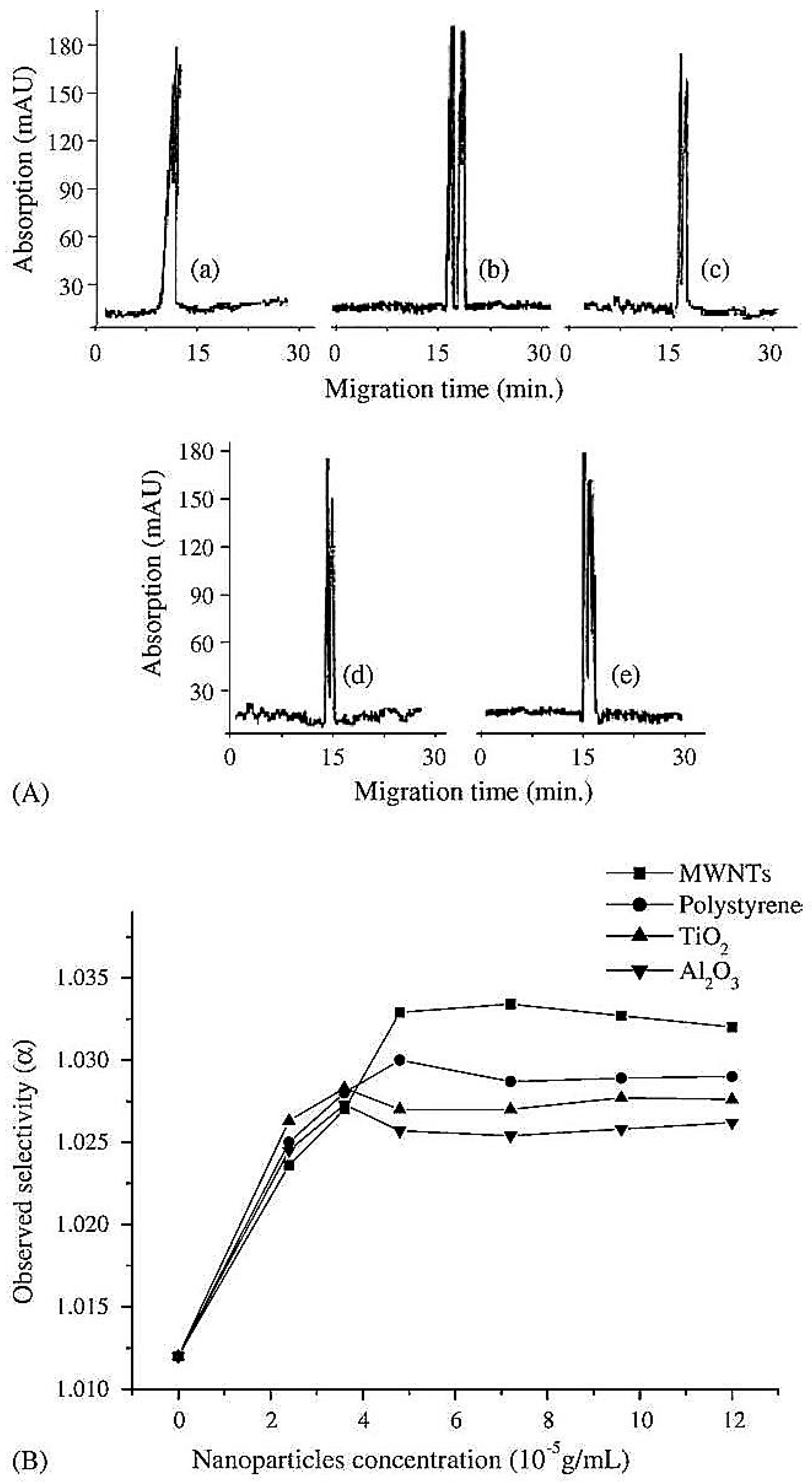
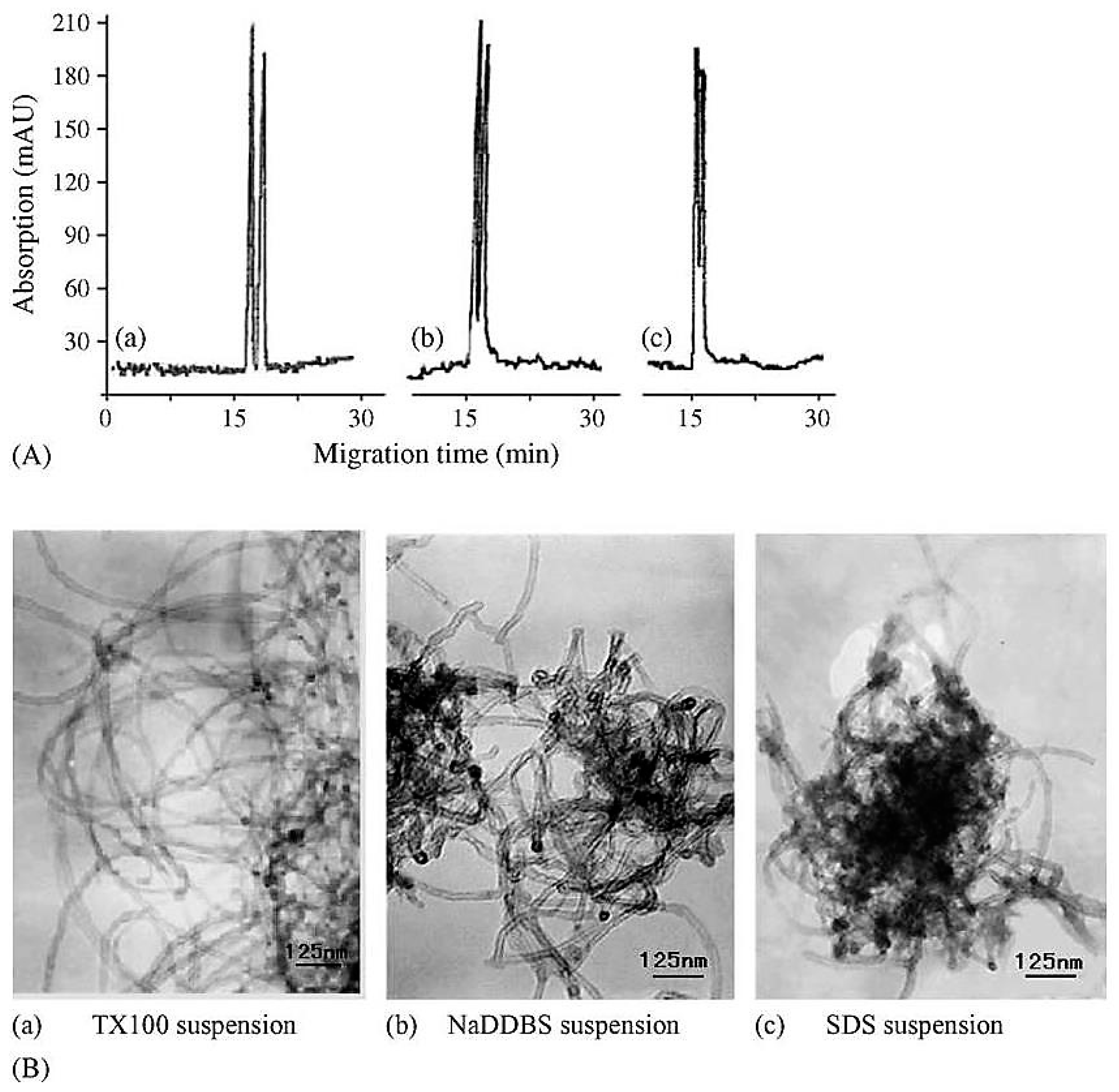
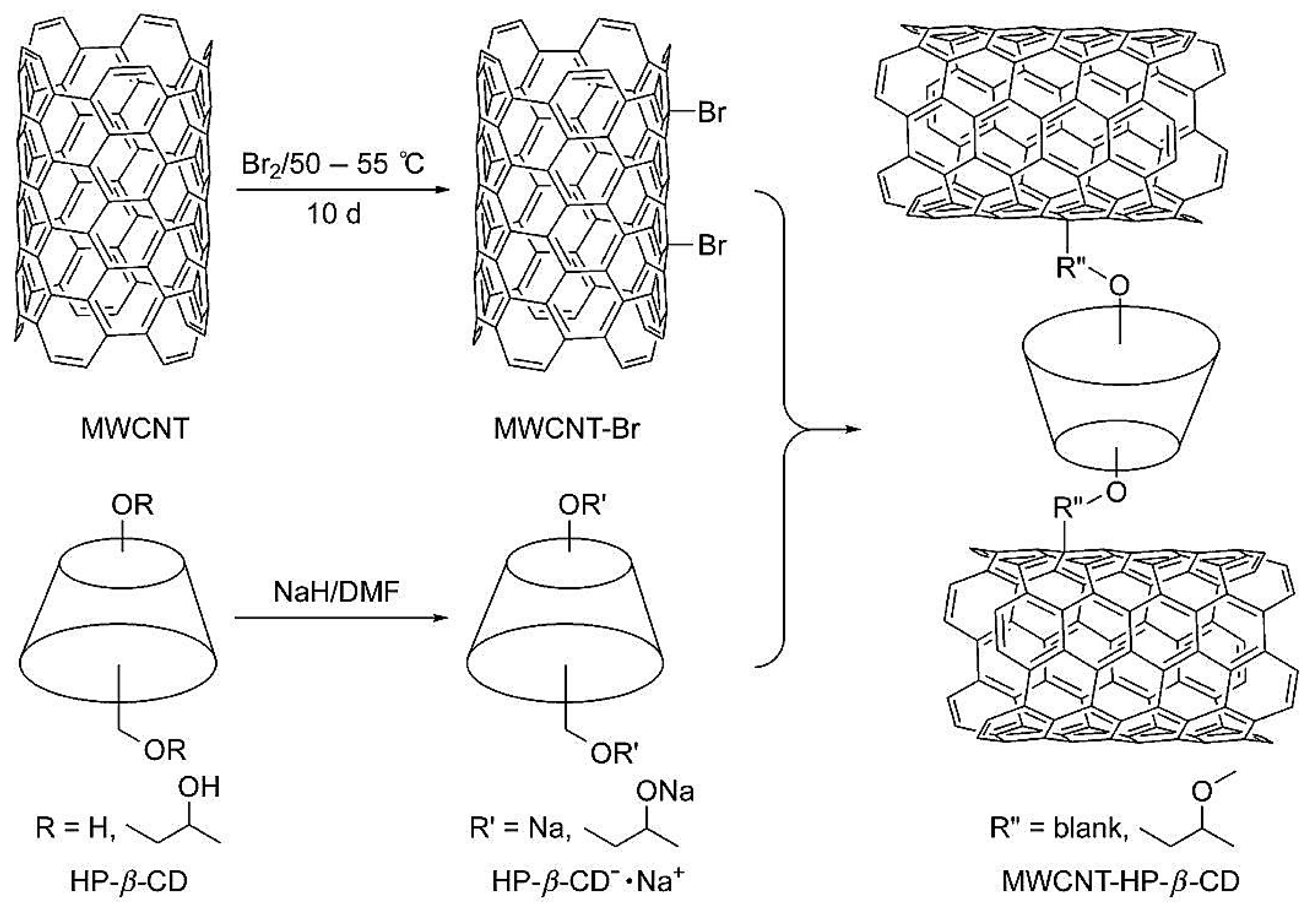
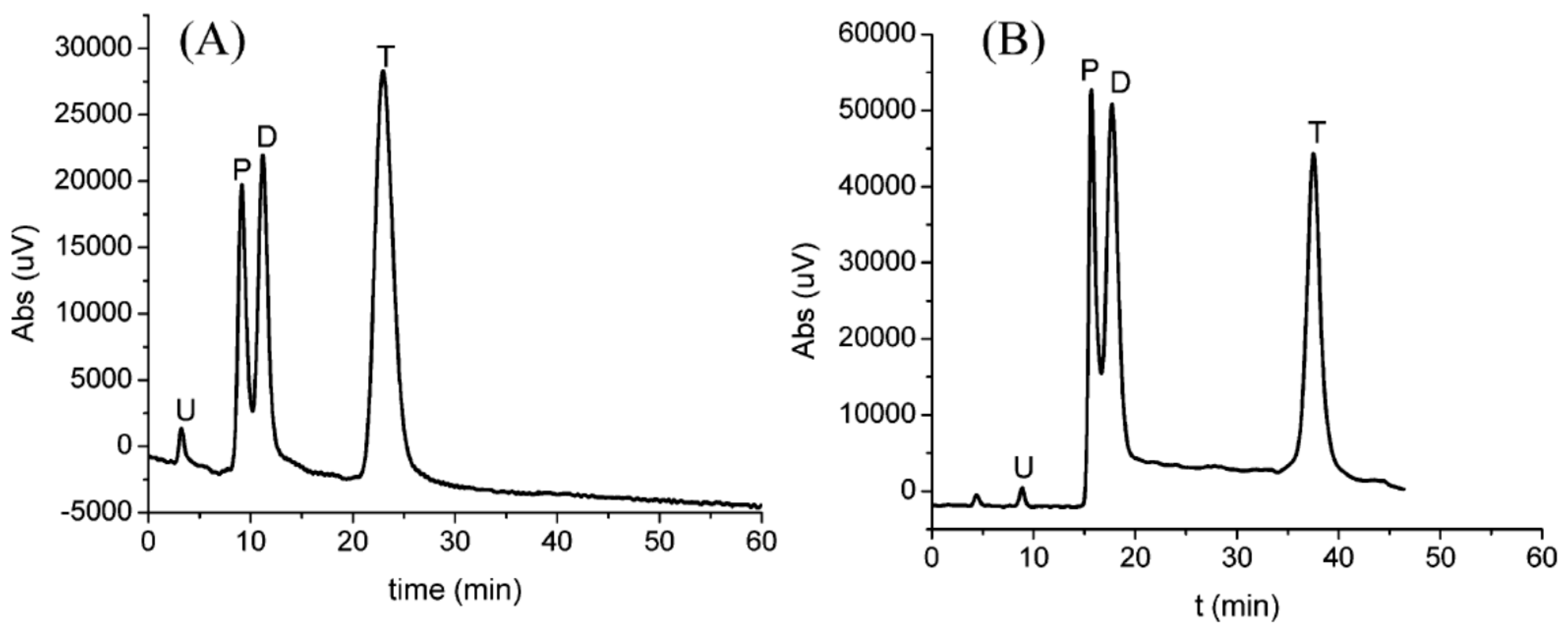
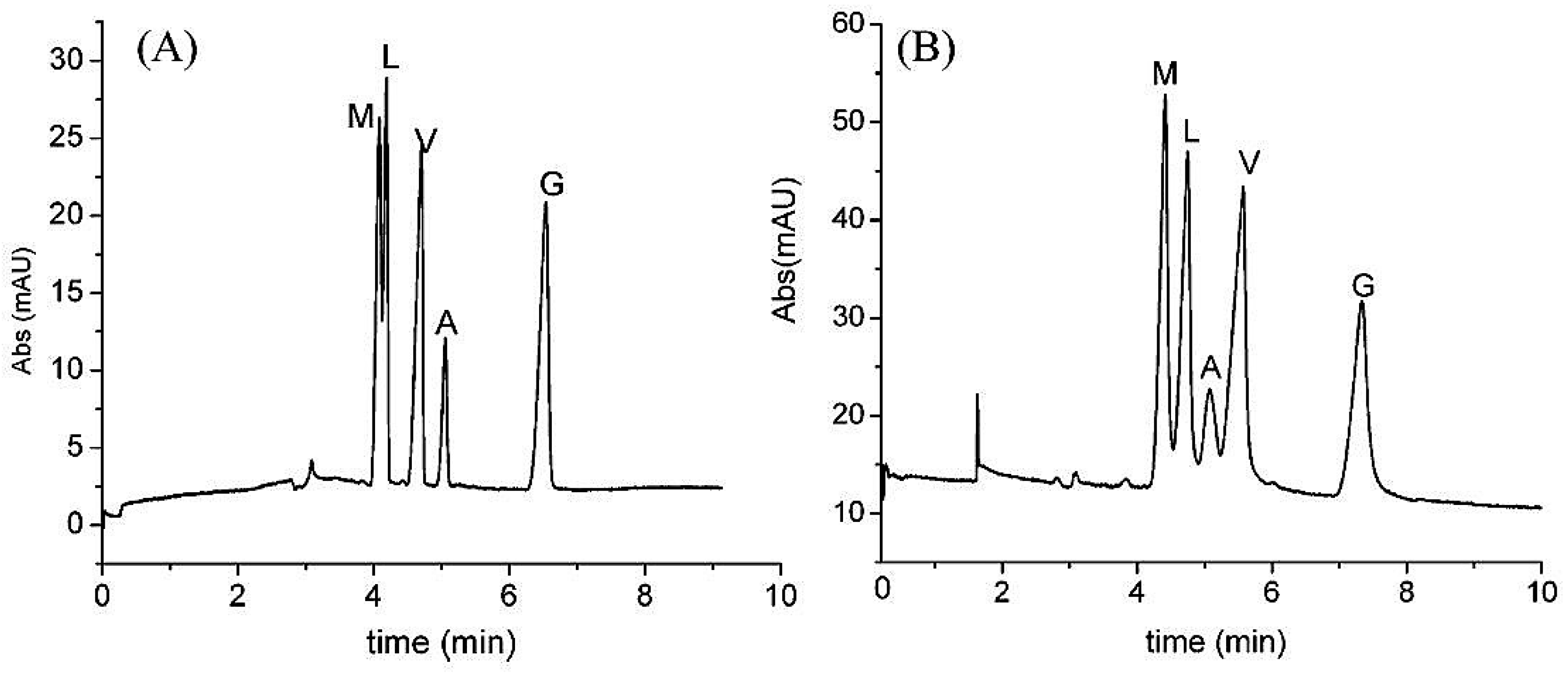
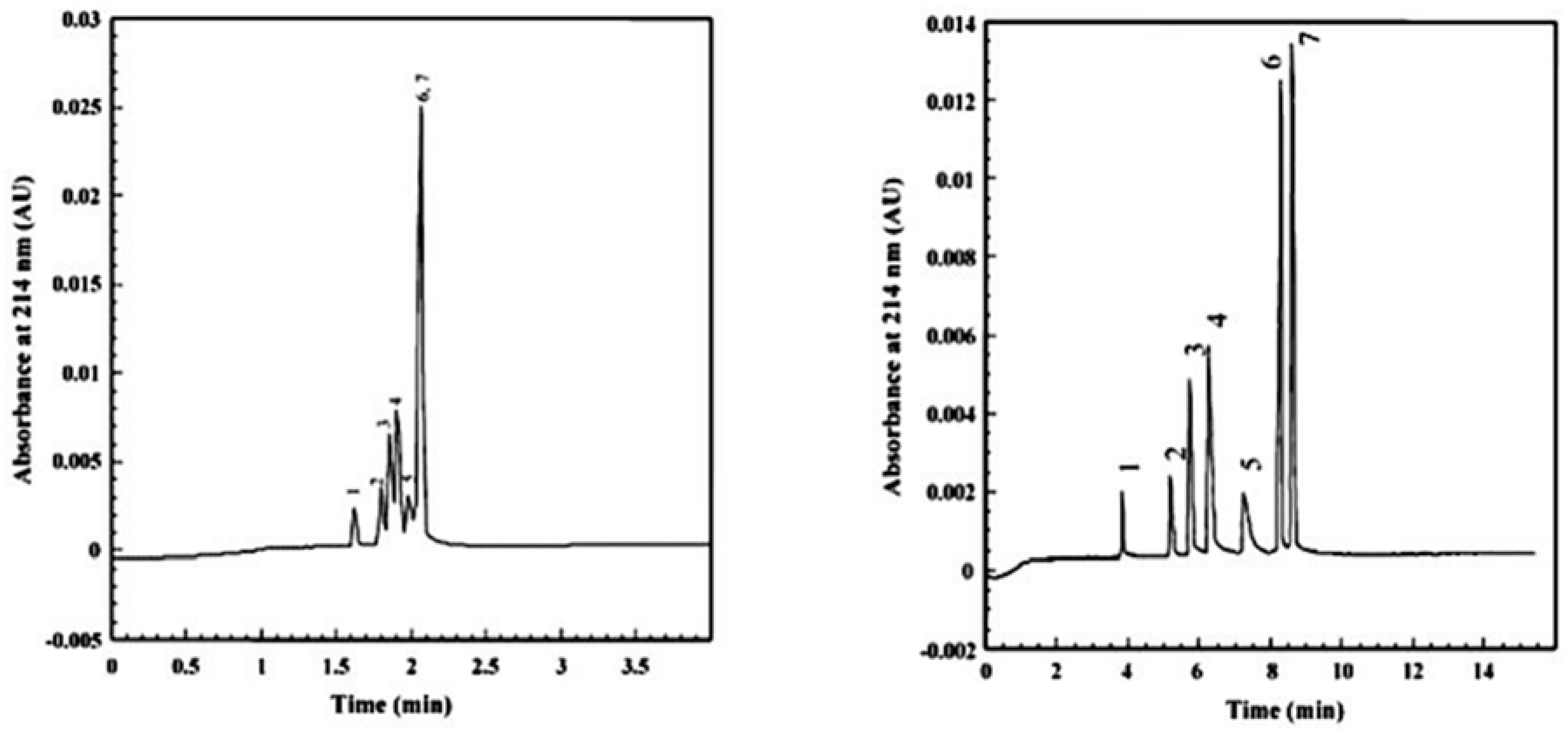
| Template | Format | Analyte | Analysis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-CD-MWCNTs | Pseudo-stationary phase | Clenbuterol | CE | [48] |
| HP-β-CD-MWCNTs | Added in stationary phase | Clenbuterol | TLC | [59] |
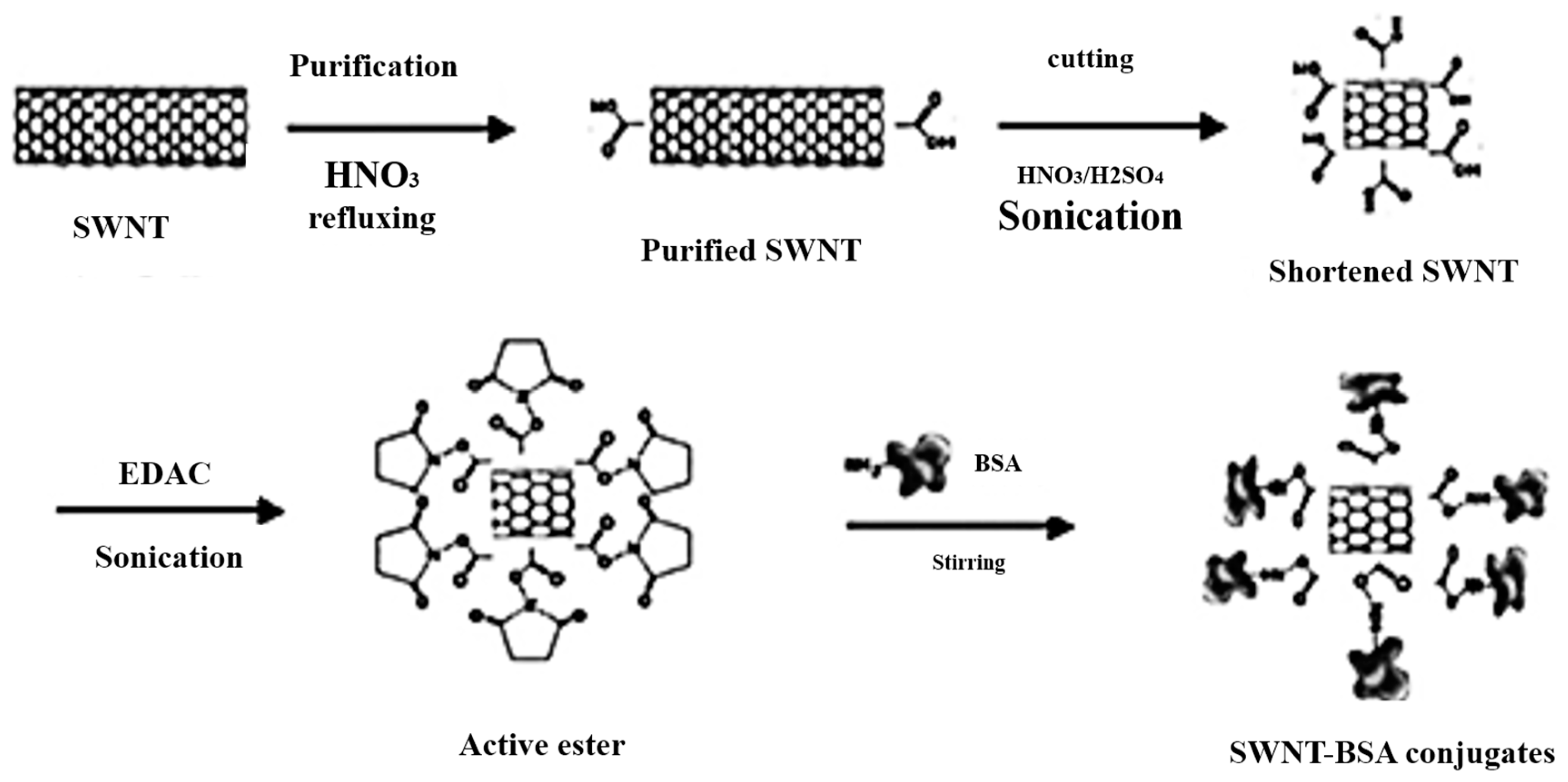
| BSA-SWCNTs | Stationary phase | Tryptophan | MCE | [60] |
| Chiral ion liquid-SWCNTs | Chemical bonding | Amino acids, carvone, (dl) leucine, of (±)-N-phenyl-α-methylbenzylamine | GC | [37] |
| SDS-MWCNTs | Pseudo-stationary phase (partial filling) | Ephedrine and norephedrine | EKC | [32] |
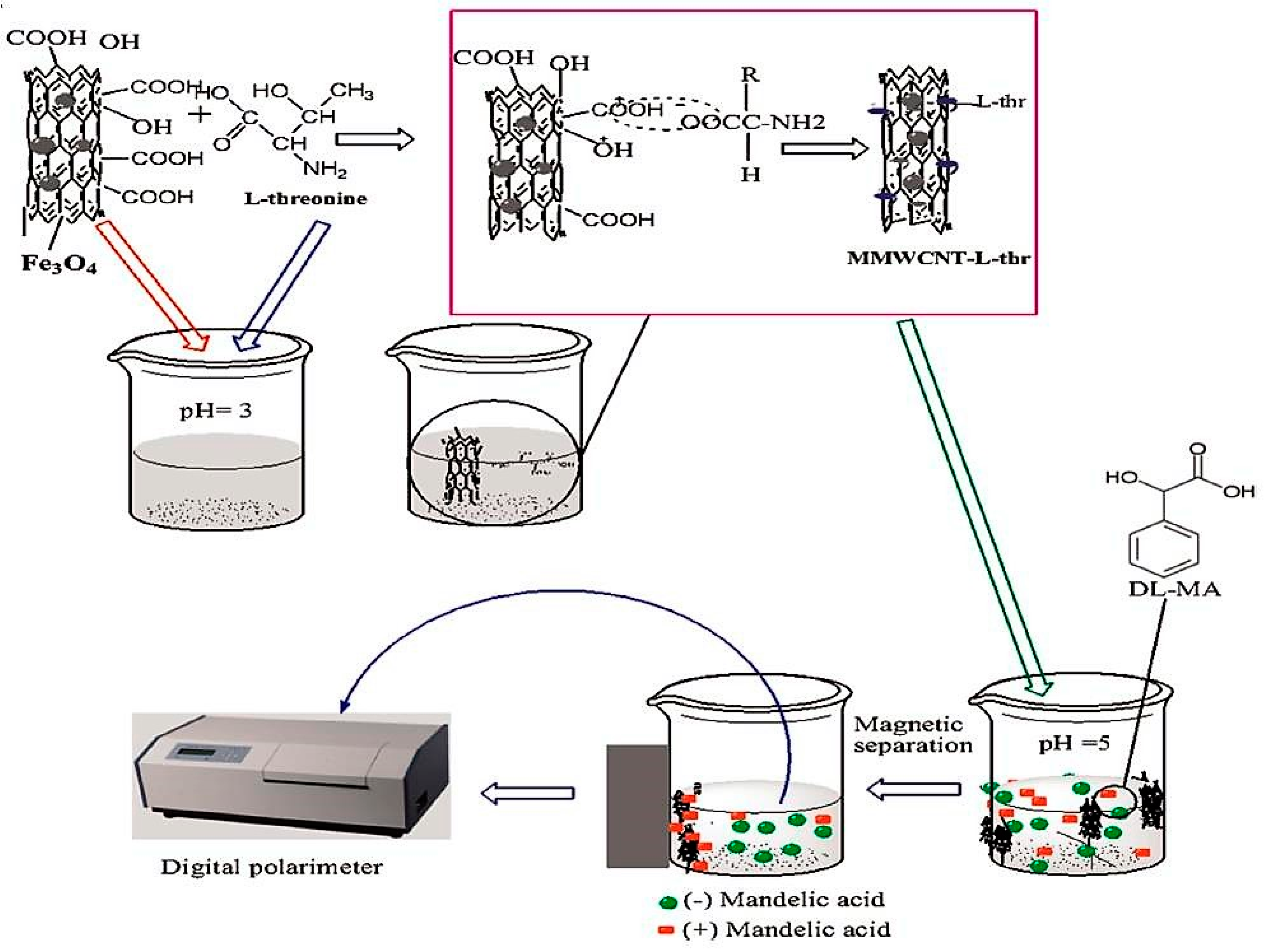
| l-Threonine-MMWCNTS | Modification with chiral selector | (dl) Mandelic acid | Magnetic field | [51] |
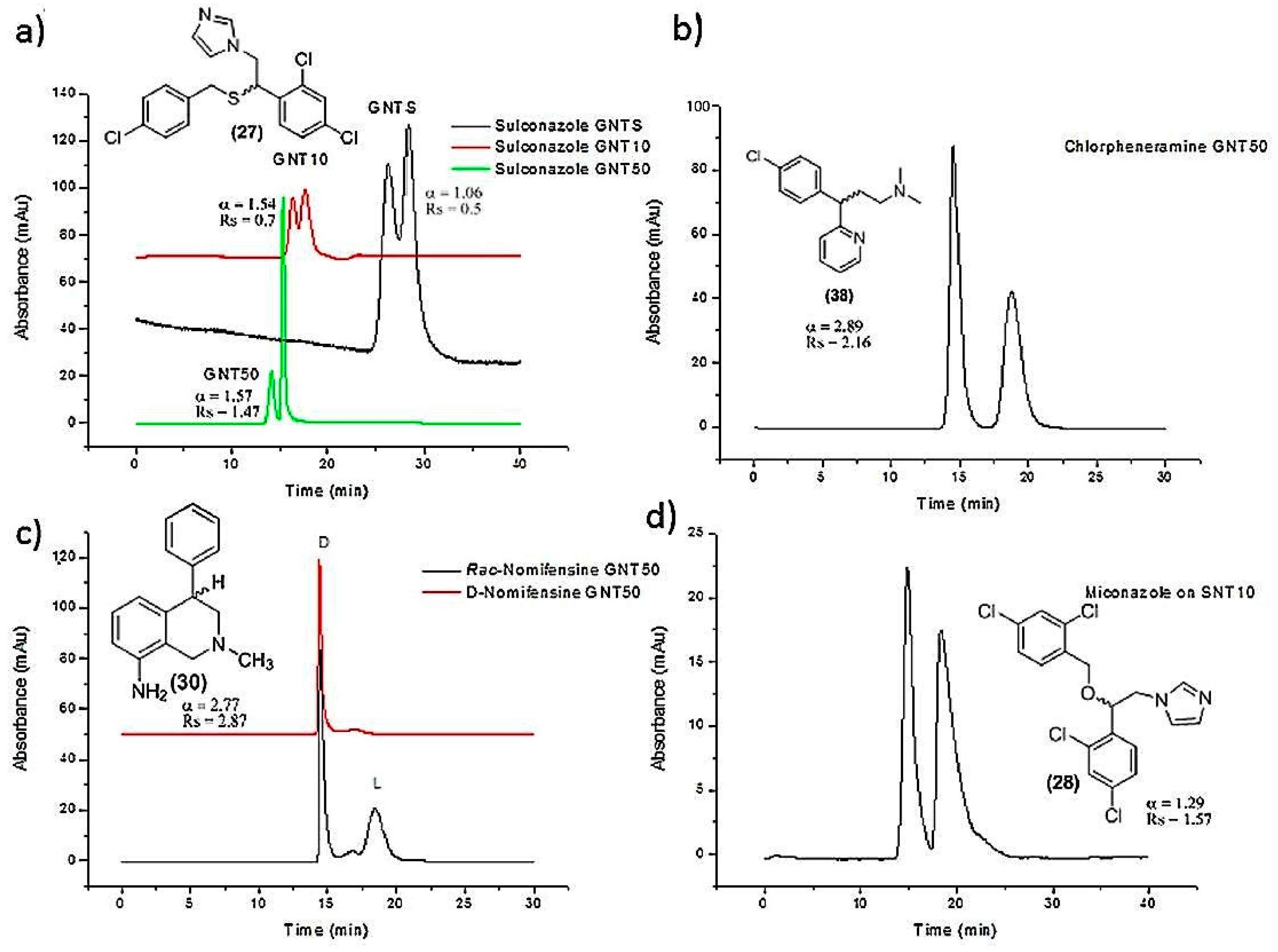
| SWCNTs-polymer based column | Encapsulation in monolithic column | Etozoline, celiprolol, cizolirtine, miconazole, sulconazole, nomifensine, chlorpheniramine | Nano-HPLC | [46] |
| PNA-CNTs | Immobilization on CNTs coated monolithic column | Ten amino acids | HPLC | [47] |
| Template | Format | Analyte | Analysis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWCNT | Added in monolithic polymer based column | Phenol, toluene, uracil and N, N-diethyl-m-toluamide | HPLC | [49] |
| MWCNTs | Modified with electrodes | Uric acid and ascorbic acid or dopamine and ascorbic acid | Voltametric separation via electrodes | [53,136] |
| Carboxylic SWCNTs | Added in run buffer | Theobromine, caffeine or epinephrine and dl-noradrenaline or catechol and hydroquinone | CE | [76] |
| c-MWCNTs | Added in run buffer | Six pyrimidine and purine bases | CZE | [137] |
| SWCNTs-PDDA | SWCNTs encapsulated in fused capillary coated with PDDA | Seven aniline derivatives | CE | [50] |
| MMWCNTs | Magnetization of MWCNTs with iron oxide nanoparticles | Lead and manganese | Magnetic field | [52] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemasa, A.L.; Naumovski, N.; Maher, W.A.; Ghanem, A. Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Chiral and Achiral Separations of Pharmaceuticals, Biologics and Chemicals. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070186
Hemasa AL, Naumovski N, Maher WA, Ghanem A. Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Chiral and Achiral Separations of Pharmaceuticals, Biologics and Chemicals. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(7):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070186
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemasa, Ayman L., Nenad Naumovski, William A. Maher, and Ashraf Ghanem. 2017. "Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Chiral and Achiral Separations of Pharmaceuticals, Biologics and Chemicals" Nanomaterials 7, no. 7: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070186
APA StyleHemasa, A. L., Naumovski, N., Maher, W. A., & Ghanem, A. (2017). Application of Carbon Nanotubes in Chiral and Achiral Separations of Pharmaceuticals, Biologics and Chemicals. Nanomaterials, 7(7), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070186







