Biogenic Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using a Biosurfactant Extracted from Corn and Their Antimicrobial Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
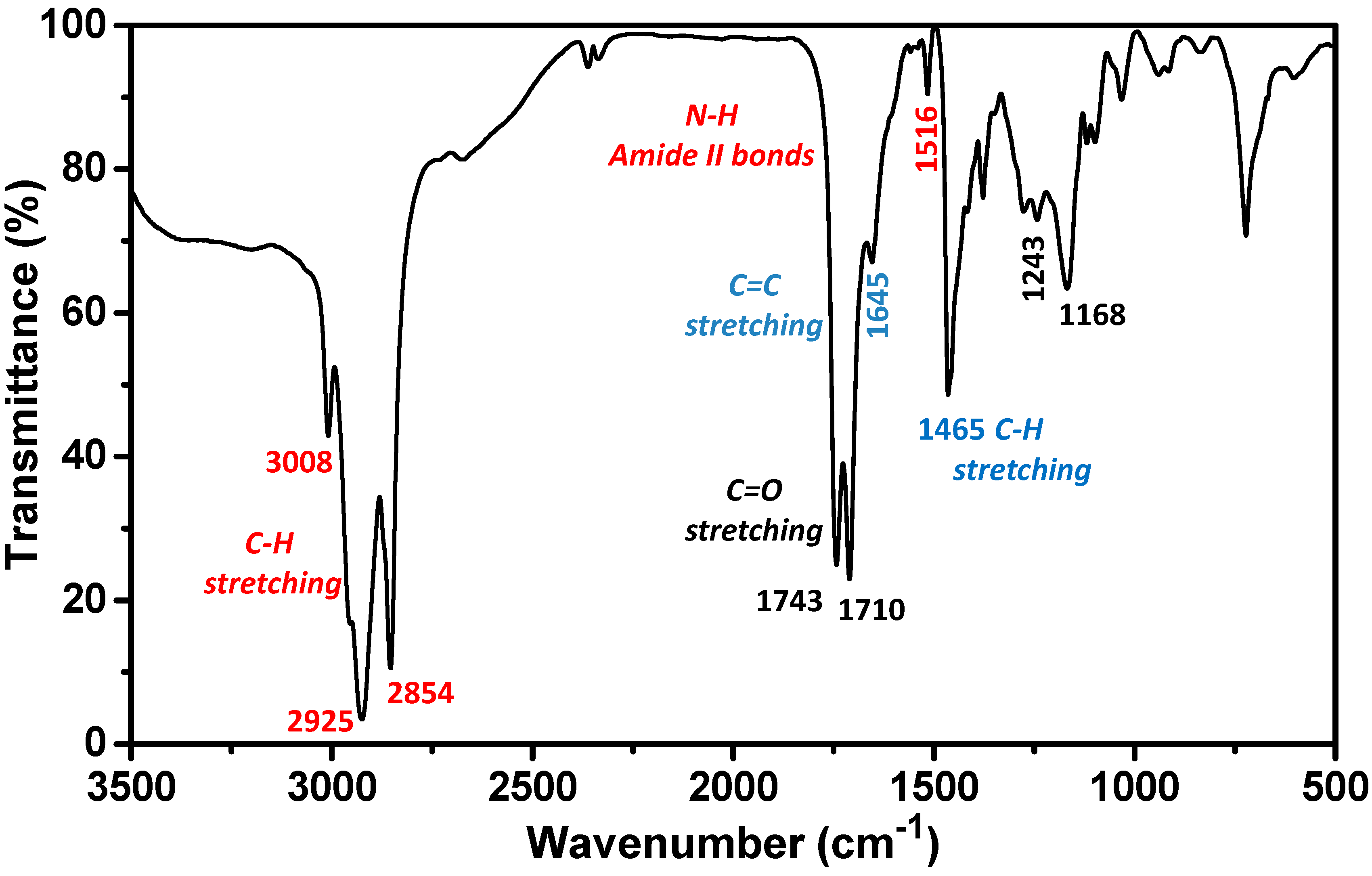
2.1. Biosurfactant Extraction and Characterization
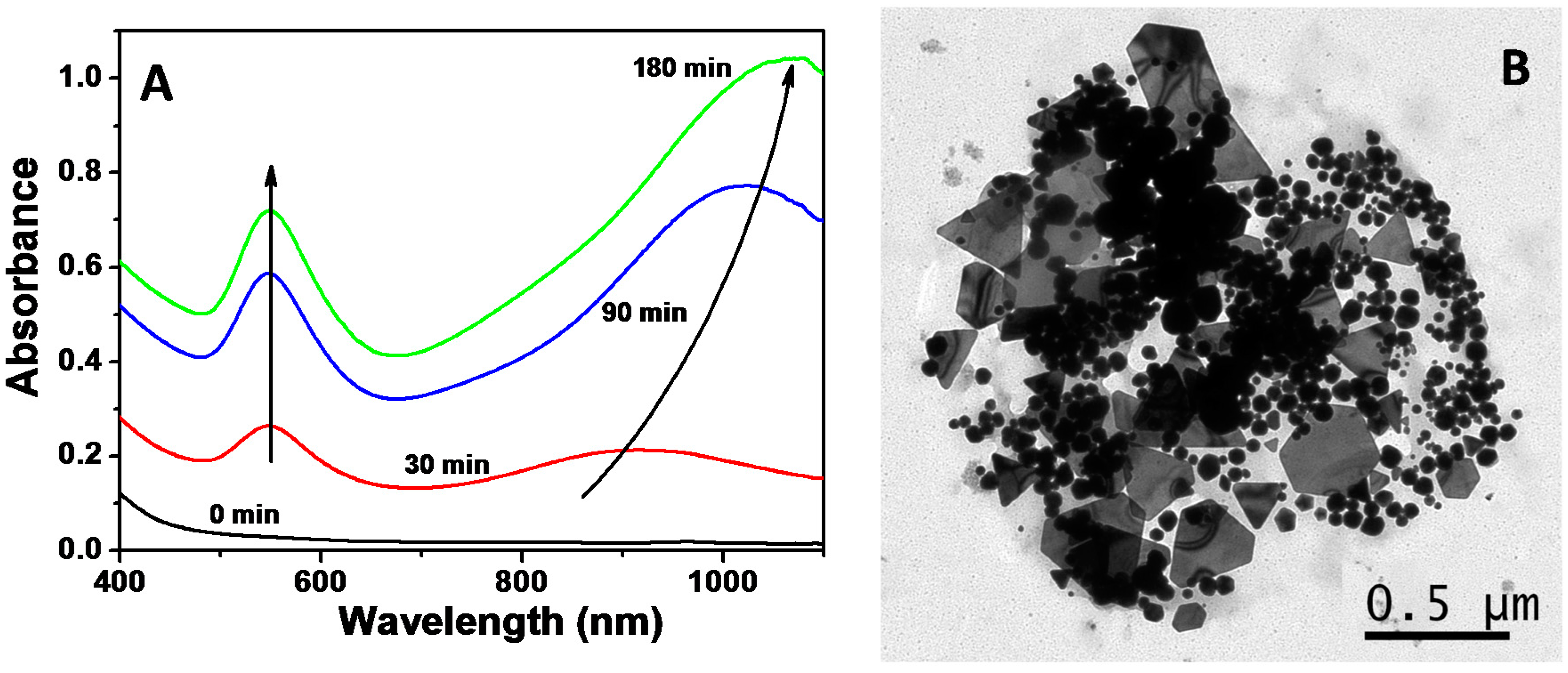
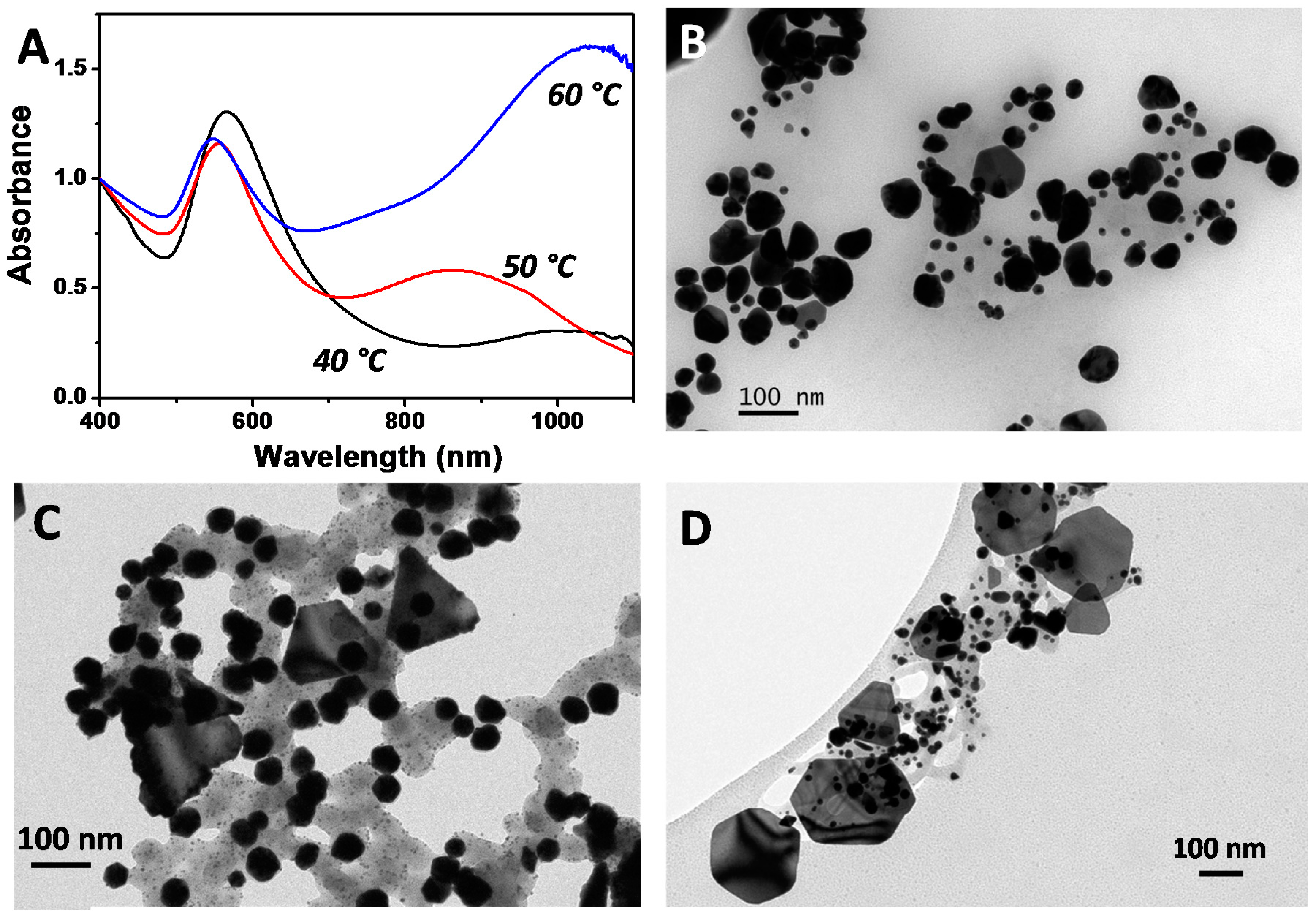
2.2. Synthesis of Au NPs Using the Biosurfactant Extracted from CSL
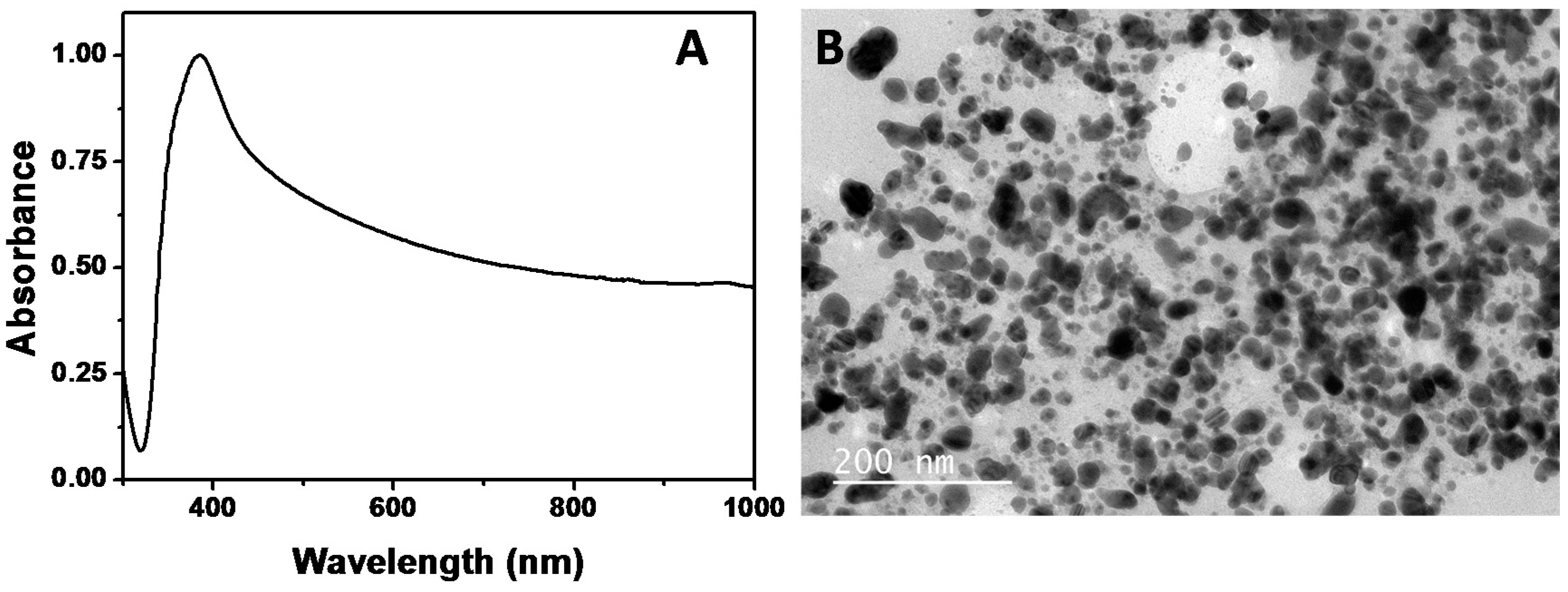
2.3. Synthesis of Ag NPs Using the Biosurfactant Extracted from CSL
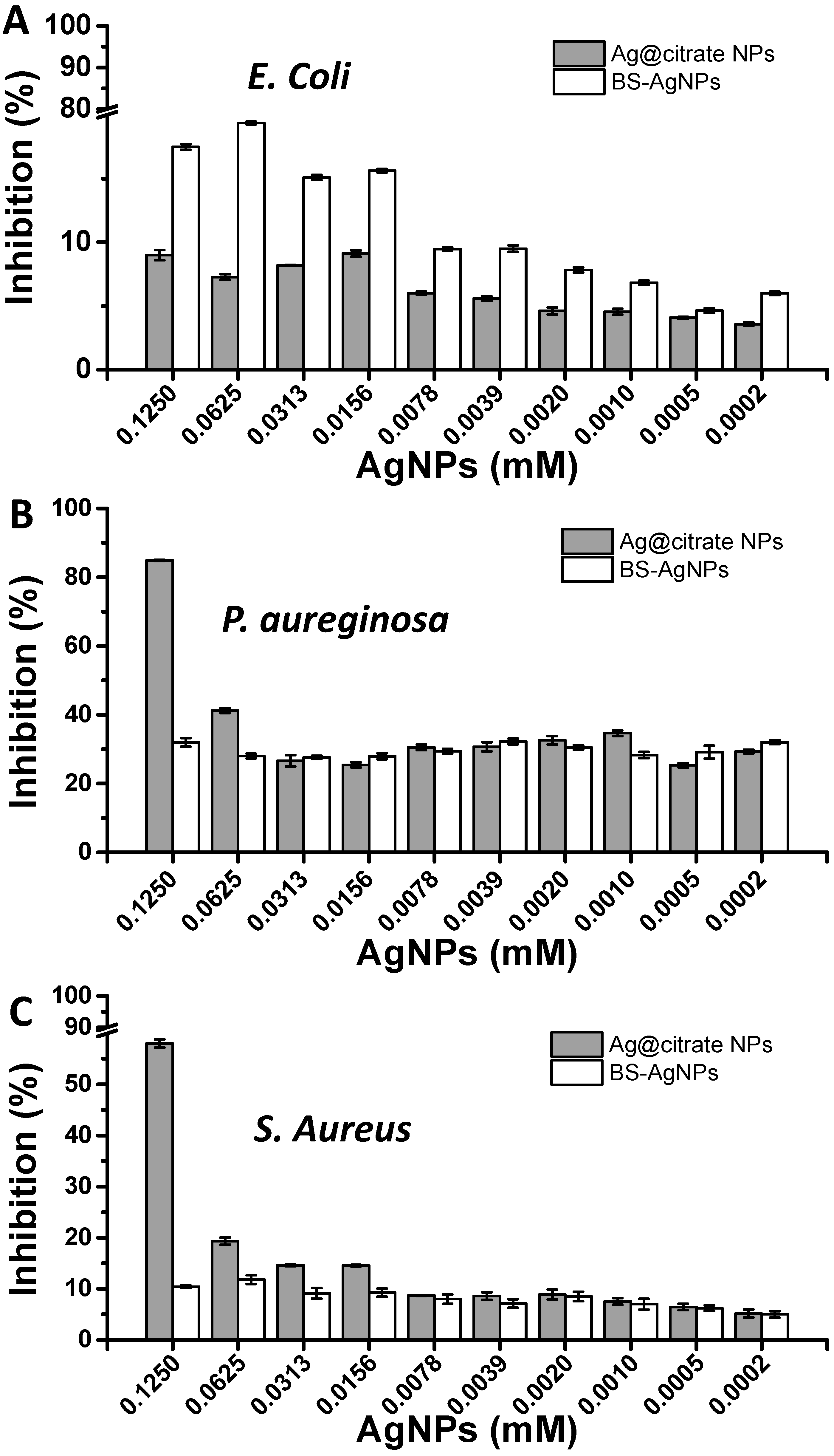
2.4. Antimicrobial Assay of Biosurfactant-Stabilized Ag NPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Characterization Techniques
3.3. Extraction and Characterization of Biosurfactant from CSL
3.4. Synthesis of Au NPs
3.5. Synthesis of Ag NPs
3.6. Antimicrobial Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saha, K.; Agasti, S.S.; Kim, C.; Li, X.; Rotello, V.M. Gold Nanoparticles in Chemical and Biological Sensing. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2739–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Graña, S.; Le Beulze, A.; Treguer-Delapierre, M.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Grana, E.; Cloutet, E.; Hadziioannou, G.; Leng, J.; Salmon, J.-B.; et al. Hierarchical self-assembly of a bulk metamaterial enables isotropic magnetic permeability at optical frequencies. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 85, 3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhao, P.; Astruc, D. Anisotropic Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Applications, and Toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1756–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Graña, S.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Self-Assembly of Au@Ag Nanorods Mediated by Gemini Surfactants for Highly Efficient SERS-Active Supercrystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2013, 1, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jun, B.H.; Kim, T.H.; Joung, J. Direct synthesis and inkjetting of silver nanocrystals toward printed electronics. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schrojenstein Lantman, E.M.; Deckert-Gaudig, T.; Mank, A.J.G.; Deckert, V.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Catalytic processes monitored at the nanoscale with tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, A.D.; Van Duyne, R.P. Single Silver Nanoparticles as Real-Time Optical Sensors with Zeptomole Sensitivity. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Martínez, A.; Auguié, B.; Alonso-Gómez, J.L.; Džolič, Z.; Gómez-Grańa, S.; Žinić, M.; Cid, M.M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Intense optical activity from three-dimensional chiral ordering of plasmonic nanoantennas. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5499–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liz-Marzán, L.M. Tailoring Surface Plasmons through the Morphology and Assembly of Metal Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastús, N.G.; Comenge, J.; Puntes, V. Kinetically Controlled Seeded Growth Synthesis of Citrate-Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Size Focusing versus Ostwald Ripening. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11098–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastús, N.G.; Merkoçi, F.; Piella, J.; Puntes, V. Synthesis of Highly Monodisperse Citrate-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Kinetic Control and Catalytic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ankamwar, B.; Singh, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Biological synthesis of triangular gold nanoprisms. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, B.; Herricks, T.; Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Polyol Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Use of Chloride and Oxygen to Promote the Formation of Single-Crystal, Truncated Cubes and Tetrahedrons. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courrol, L.C.; de Oliveira Silva, F.R.; Gomes, L. A simple method to synthesize silver nanoparticles by photo-reduction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 305, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, S.F.; Assal, M.E.; Khan, M.; Al-Warthan, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Biogenic synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and prospects toward green chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 9709–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płaza, G.A.; Chojniak, J.; Banat, I.M. Biosurfactant mediated biosynthesis of selected metallic nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13720–13737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, I.M.; Satpute, S.K.; Cameotra, S.S.; Patil, R.; Nyayanit, N. V Cost effective technologies and renewable substrates for biosurfactants’ production. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Jean, J.-S.; Fan, C.-W.; Chen, H.-R.; Wang, J.-C.; Nimje, V.R. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles via an Environmentally Benign Route Using a Biosurfactant. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 6693–6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Baker, S.C.; Chen, C.-C.; Jean, J.-S.; Fan, C.-W.; Chen, H.-R.; Wang, J.-C. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using surfactin: A biosurfactant as stabilizing agent. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, S.; Madhu, S.; Singh, S. Extracellular synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles using psychrophilic bacteria. Process Biochem. 2011, 46, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, P.; Berchmans, S. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: An Ecofriendly Approach Using Hansenula anomala. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.S.; Don, M.M. Biosynthesis and structural characterization of Ag nanoparticles from white rot fungi. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchi, S.; Kumar, G.; Lo, A.-Y.; Tseng, C.-M.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chin, T.-S. Exploitation of de-oiled jatropha waste for gold nanoparticles synthesis: A green approach. Arab. J. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecino, X.; Bustos, G.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Salt-free aqueous extraction of a cell-bound biosurfactant: A kinetic study. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2015, 18, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Silva, A.F.; Rufino, R.D.; Luna, J.M.; Souza, J.E.G.; Sarubbo, L.A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a biosurfactant produced in low-cost medium as stabilizing agent. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 17, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.G.; Mamidyala, S.K.; Das, B.; Sridhar, B.; Sarala Devi, G.; Karuna, M.S. Synthesis of biosurfactant-based silver nanoparticles with purified rhamnolipids isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa BS-161R. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecino, X.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Optimization of liquid–liquid extraction of biosurfactants from corn steep liquor. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecino, X.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Study of the Surfactant Properties of Aqueous Stream from the Corn Milling Industry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5451–5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, C.; Gibbs, B. Biosurfactants: Production: Properties: Applications; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 329–371. [Google Scholar]
- Shaligram, N.S.; Singhal, R.S. Singhal Surfactin—A Review on Biosynthesis, Fermentation, Purification and Applications. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Panwar, J.; Yun, Y.-S. Biogenic Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Plant Extracts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharaei-Fathabad, E. Biosurfactants in pharmaceutical industry: A mini-review. Am. J. Drug Discov. Dev. 2011, 1, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.M.; Stamford, T.L. M.; Sarubbo, L.A.; de Luna, J.M.; Rufino, R.D.; Banat, I.M. Microbial biosurfactants as additives for food industries. Biotechnol. Prog. 2013, 29, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdev, D.P.; Cameotra, S.S. Biosurfactants in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Evidence for Seed-Mediated Nucleation in the Chemical Reduction of Gold Salts to Gold Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2001, 137, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Fernández-Barbero, A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Growing Au/Ag Nanoparticles within Microgel Colloids for Improved Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 9462–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, M.S.; Li, W.; Xia, Y. Facile Synthesis of Gold Icosahedra in an Aqueous Solution by Reacting HAuCl4 with N-Vinyl Pyrrolidone. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 13181–13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Graña, S.; Fernández-López, C.; Polavarapu, L.; Salmon, J.-B.; Leng, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Pérez-Juste, J. Gold Nanooctahedra with Tunable Size and Microfluidic-Induced 3D Assembly for Highly Uniform SERS-Active Supercrystals. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8310–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Rodriguez, M.A.; Sanchez-Molina, M.; Lucena-Serrano, A.; Lucena-Serrano, C.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, B.; Algarra, M.; Diaz, A.; Valpuesta, M.; Lopez-Romero, J.M.; Perez-Juste, J.; et al. Synthesis of vinyl-terminated Au nanoprisms and nanooctahedra mediated by 3-butenoic acid: Direct Au@pNIPAM fabrication with improved SERS capabilities. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4557–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.C. Synthesis of Single-Crystalline Gold Nanoplates in Aqueous Solutions through Biomineralization by Serum Albumin Protein. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10226–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, N.; Saha, R.; Pal, S.K. Protein-assisted synthesis route of metal nanoparticles: exploration of key chemistry of the biomolecule. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M.; Marco, F. Biosynthesis of Metal Nanoparticles: Novel Efficient Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, V.; Soumya, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chakra, S.; Bhatt, D.; Sreedhar, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulose, S.P.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P. V; Mun, G.L.K.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, Y.-H.; Lin, K.-S.; Ke, W.-J.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Chiang, C.-L.; Tzou, D.-Y.; Liu, S.-T. The Antimicrobial Properties of Silver NanoparticlesNPs in Bacillus subtilis Are Mediated by Released Ag+ Ions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawani, A.; Ghosh, A.; Chandra, G. Mosquito larvicidal and antimicrobial activity of synthesized nano-crystalline silver particles using leaves and green berry extract of Solanum nigrum L. (Solanaceae: Solanales). Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkilany, A.M.; Nagaria, P.K.; Hexel, C.R.; Shaw, T.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Wyatt, M.D. Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of Gold Nanorods: Molecular Origin of Cytotoxicity and Surface Effects. Small 2009, 5, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Bera, T.; Roy, A.; Singh, G.; Ramachandrarao, P.; Dash, D. Characterization of enhanced antibacterial effects of novel silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Cui, F.Z.; Kim, T.N.; Kim, J.O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatpurwar, V.; Pokharkar, V. Green synthesis of silver NPs using marine polysaccharide: Study of in vitro antibacterial activity. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Vu, K.; Yang, G.; Tawfiq, K.; Chen, G. Escherichia coli growth and transport in the presence of nanosilver under variable growth conditions. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ung, T.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Mulvaney, P. Controlled Method for Silica Coating of Silver Colloids. Influence of Coating on the Rate of Chemical Reactions. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiña, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. Isolation and functional characterization of a biosurfactant produced by Lactobacillus paracasei. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fatty Acid | Formula | Rel. Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 22.0 ± 2.2 |
| Stearic acid | C18H36O2 | 6.4 ± 1.4 |
| Oleic or elaidic acid | C18H34O2 | 22.5 ± 1.8 |
| Linolelaidic acid | C18H32O2 | 45.9 ± 6.4 |
| Palmitic acid | C16H32O2 | 22.0 ± 2.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Graña, S.; Perez-Ameneiro, M.; Vecino, X.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Perez-Juste, J.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Biogenic Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using a Biosurfactant Extracted from Corn and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060139
Gómez-Graña S, Perez-Ameneiro M, Vecino X, Pastoriza-Santos I, Perez-Juste J, Cruz JM, Moldes AB. Biogenic Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using a Biosurfactant Extracted from Corn and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(6):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060139
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Graña, Sergio, María Perez-Ameneiro, Xanel Vecino, Isabel Pastoriza-Santos, Jorge Perez-Juste, José Manuel Cruz, and Ana Belén Moldes. 2017. "Biogenic Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using a Biosurfactant Extracted from Corn and Their Antimicrobial Properties" Nanomaterials 7, no. 6: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060139
APA StyleGómez-Graña, S., Perez-Ameneiro, M., Vecino, X., Pastoriza-Santos, I., Perez-Juste, J., Cruz, J. M., & Moldes, A. B. (2017). Biogenic Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using a Biosurfactant Extracted from Corn and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Nanomaterials, 7(6), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7060139






