Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Interactions Influence Oral Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
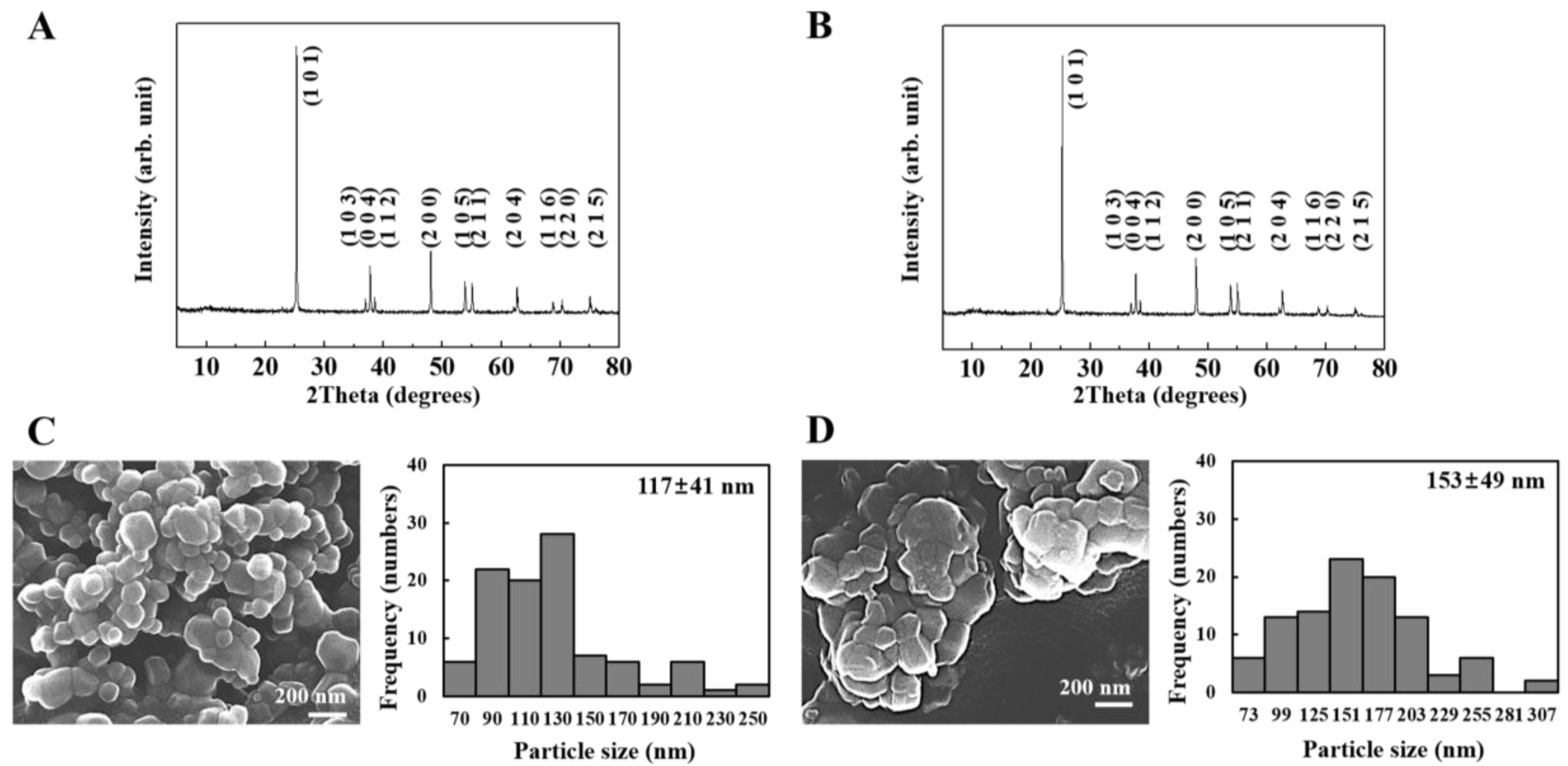
2.1. Characterization
2.2. In Vitro and In Vivo Solubility
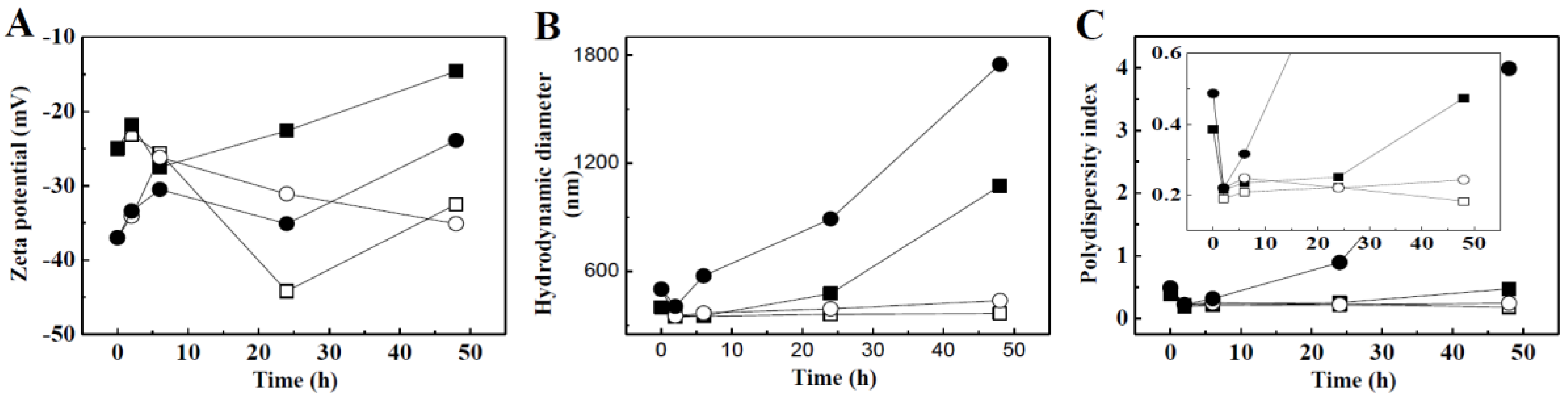
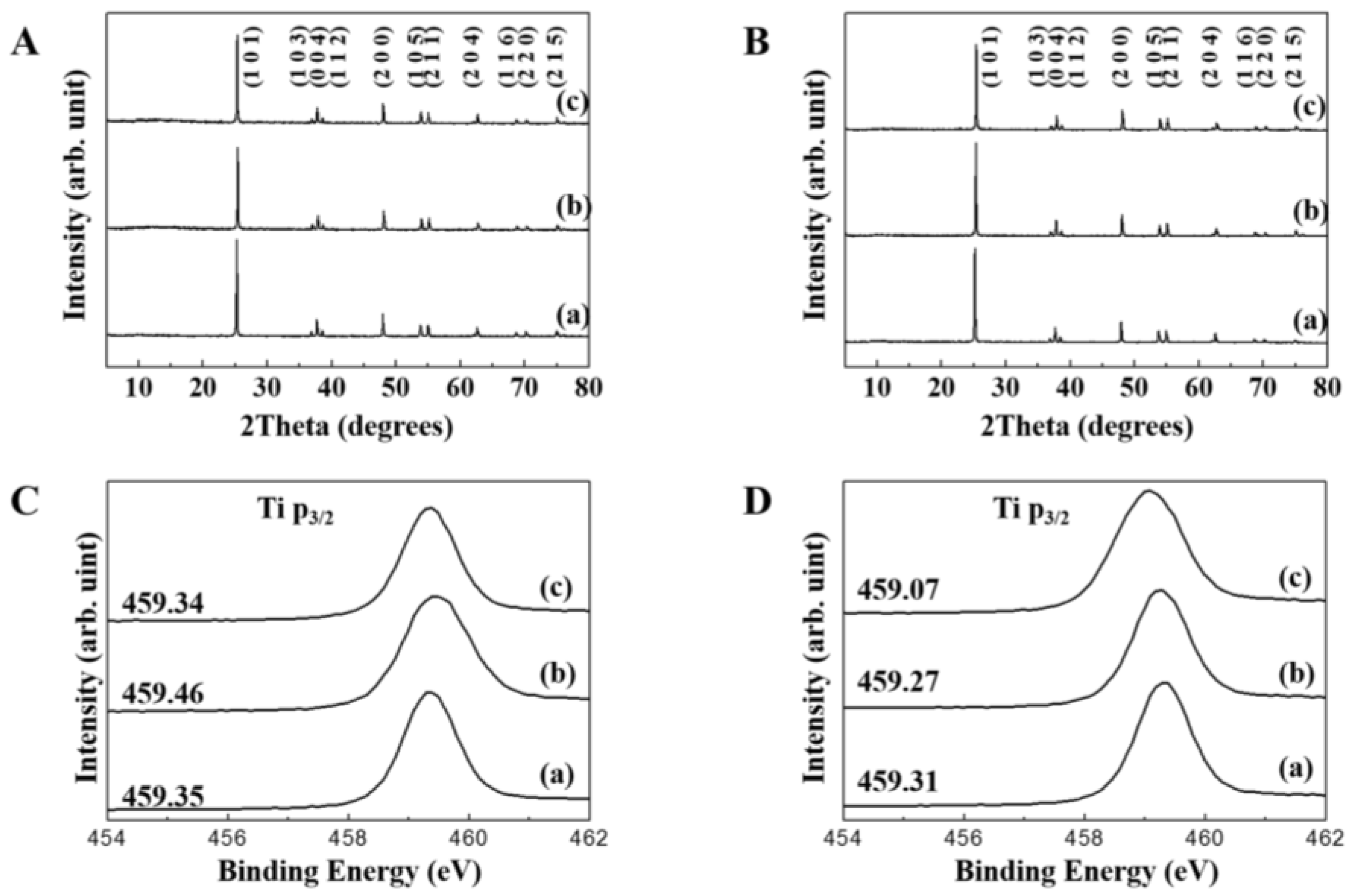
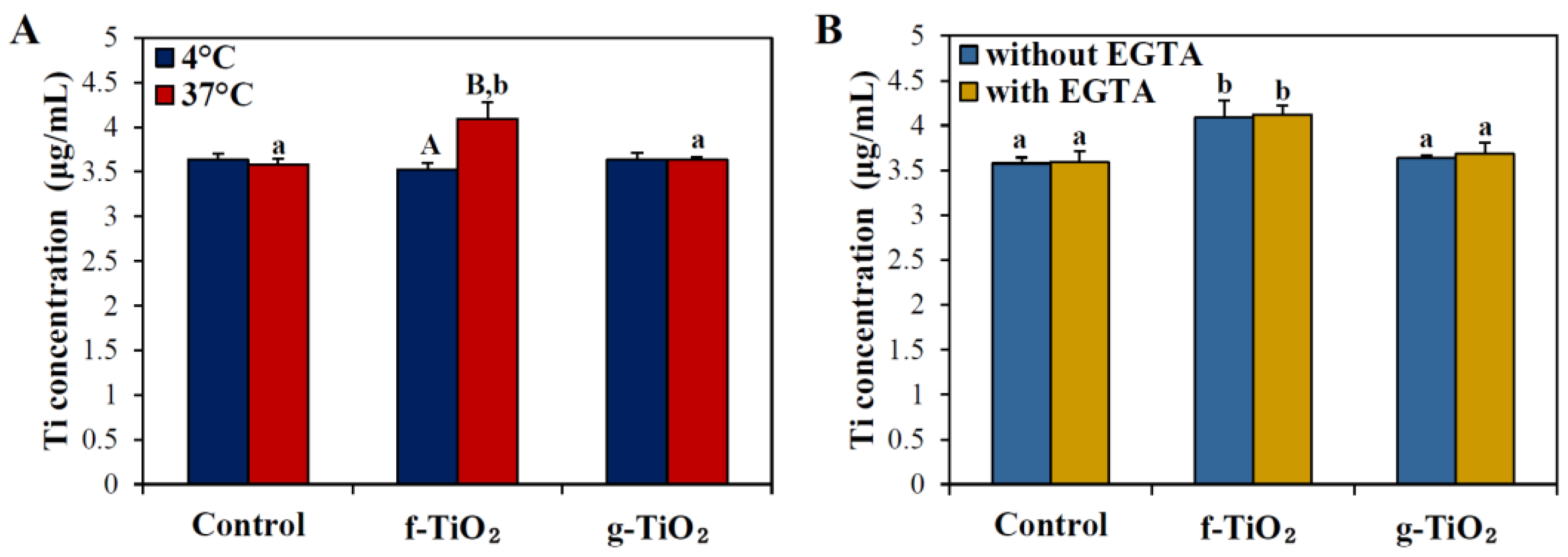
2.3. Physicochemical Properties of TiO2 NPs in the Presence of Biomolecules
2.4. Intestinal Transport Mechanism
2.5. Effects of Biomolecules on Oral Absorption
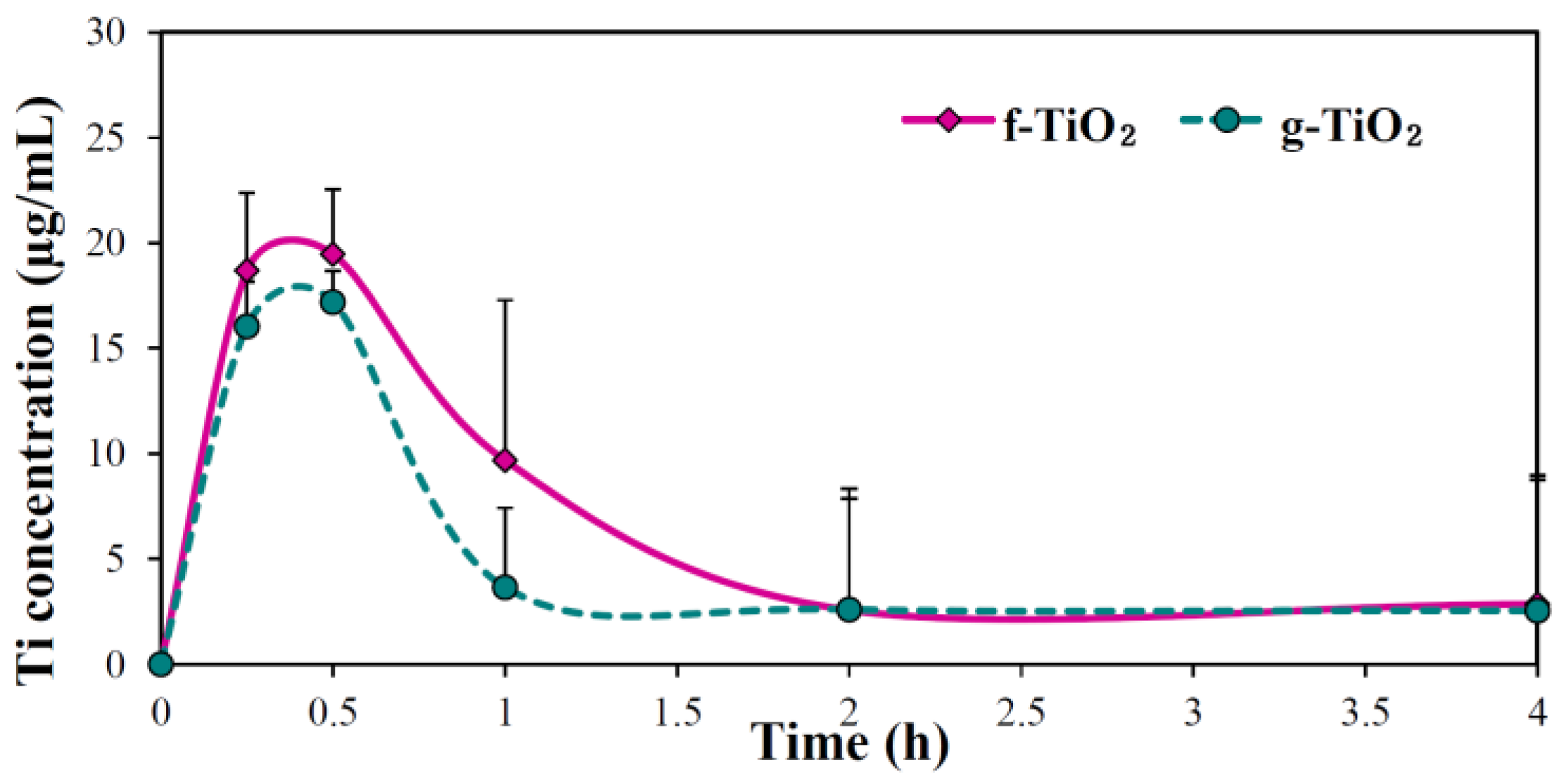
2.6. Effect of TiO2 NP Type on Oral Absorption
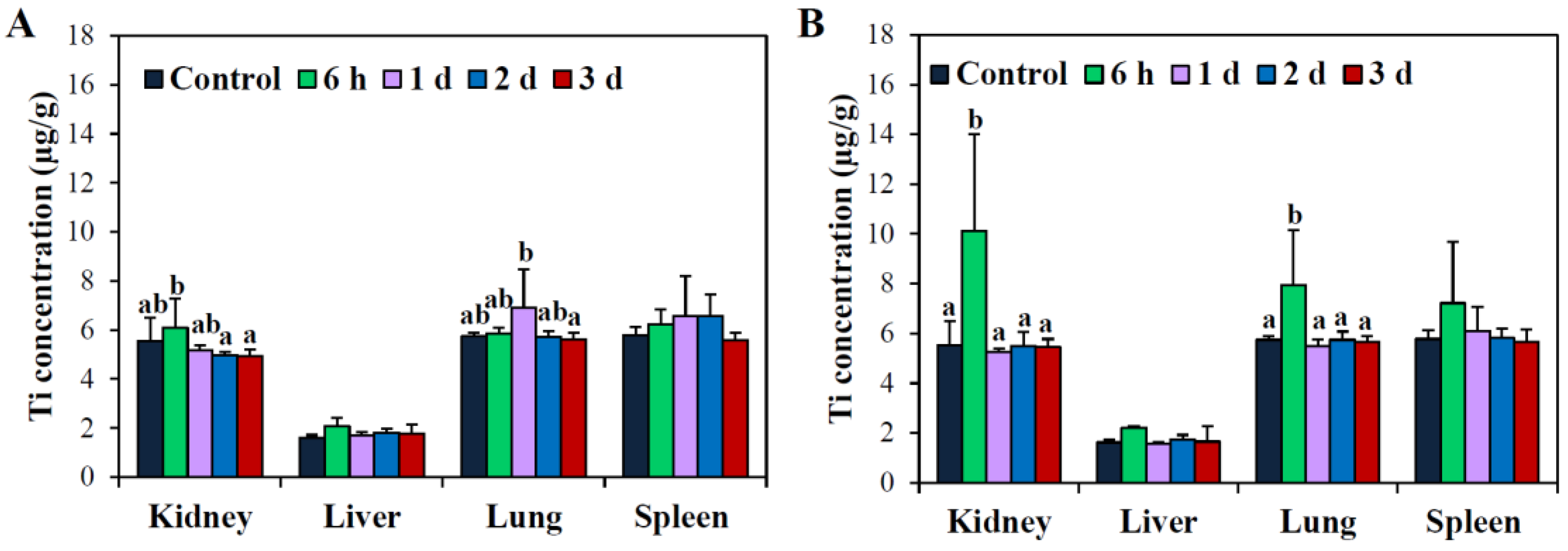
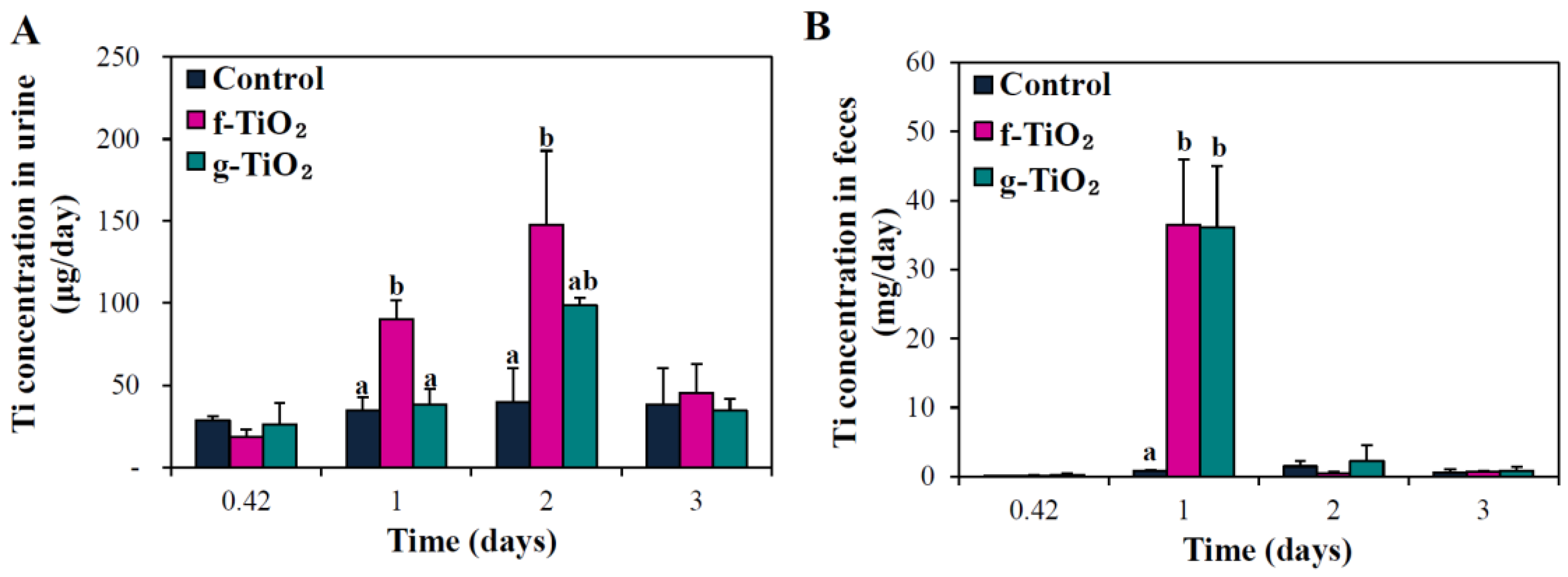
2.7. Tissue Distribution and Excretion Kinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Characterization
4.2. Solubility and ICP-AES Analysis
4.3. Physicochemical Properties of TiO2 NPs in the Presence of Biomolecules
4.4. Intestinal Transport Mechanism
4.5. Animals
4.6. Biokinetic Study
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berger, C.; Song, Z.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Ogbazghi, A.Y.; Feng, R.; Dai, Z.; Marchenkov, A.N.; Conrad, E.H.; First, P.N.; et al. Ultrathin epitaxial graphite: 2D electron gas properties and a route toward graphene-based nanoelectronics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 19912–19916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Teo, J.; Chen, X.; Asakura, H.; Tanaka, T.; Teramura, K.; Yan, N. A series of NiM (M = Ru, Rh, and Pd) bimetallic catalysts for effective lignin hydrogenolysis in water. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, P.L.; Xiang, X.; Heiden, P. Chitosan nanoparticle based delivery systems for sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buso, D.; Pacifico, J.; Martucci, A.; Mulvaney, P. Gold-nanoparticle-doped TiO2 semiconductor thin films: Optical characterization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadale, T.C.; Takale, S.P.; Sonawane, R.S.; Joshi, H.M.; Patil, S.I.; Kale, B.B.; Ogale, S.B. N-doped TiO2 nanoparticle based visible light photocatalyst by modified peroxide sol-gel method. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 14595–14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodurov, I.; Yovcheva, T.; Sainov, S. PMMA films refractive index modulation via TiO2 nanoparticle inclusions and corona poling. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 3045–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Fabricius, L.; Hristovski, K.; von Goetz, N. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.J.B.; van Bemmel, G.; Herrera-Rivera, Z.; Helsper, H.P.F.G.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Weigel, S.; Tromp, P.C.; Oomen, A.G.; Rietveld, A.G.; Bouwmeester, H. Characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food products: Analytical methods to define nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6285–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, A.P.; Kirillin, M.Y.; Priezzhev, A.V.; Lademann, J.; Hast, J.; Myllyla, R. Optical Sensing of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles within Horny Layer of Human Skin and Their Protecting Effect against Solar UV Radiation. In Proceedings of the SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, San Jose, CA, USA, 22 January 2005; pp. 113–122.
- Donaldson, K.; Beswick, P.H.; Gilmour, P.S. Free radical activity associated with the surface of particles: A unifying factor in determining biological activity? Toxicol. Lett. 1996, 88, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, T.; Tokunaga, H.; Ando, M.; Utsumi, H. Quantitative determination of OH radical generation and its cytotoxicity induced by TiO2–UVA treatment. Toxicol. In Vitro 2002, 16, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.-P.; Sun, Y.-P. Photocatalytic killing effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on Ls-174-t human colon carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3191–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNicoll, A.; Kelly, M.; Aksoy, H.; Kramer, E.; Bouwmeester, H.; Chaudhry, Q. A study of the uptake and biodistribution of nano-titanium dioxide using in vitro and in vivo models of oral intake. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B.; Hoke, R.A.; Finlay, C.; Donner, E.M.; Reed, K.L.; Sayes, C.M. Development of a base set of toxicity tests using ultrafine TiO2 particles as a component of nanoparticle risk management. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 171, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warheit, D.B.; Brown, S.C.; Donner, E.M. Acute and subchronic oral toxicity studies in rats with nanoscale and pigment grade titanium dioxide particles. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, A.; Shen, H.; Wu, D.; Qiu, D. Bioactive nanoparticle through postmodification of colloidal silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4935–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Harris, M.T. Surface modification of magnetic nanoparticles capped by oleic acids: Characterization and colloidal stability in polar solvents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooney, R.I.; White, A.; O’Mahony, C.; O’Connell, C.; Kelleher, S.M.; Daniels, S.; McDonagh, C. Investigating the colloidal stability of fluorescent silica nanoparticles under isotonic conditions for biomedical applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Yoshino, T.; Matsunaga, T. Surface modification of magnetic nanoparticles using asparagines-serine polypeptide designed to control interactions with cell surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4952–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, N.; Park, J.-H. Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles mediates their exocytosis in macrophages. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6232–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, I.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Protein-nanoparticle interactions: What does the cell see? Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-X.; Song, Z.M.; Cheng, B.; Xiang, K.; Chen, X.-X.; Liu, J.-H.; Cao, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Evaluation of the toxicity of food additive silica nanoparticles on gastrointestinal cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.M.; Chen, N.; Liu, J.-H.; Tang, H.; Deng, X.; Xi, W.-S.; Han, K.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Biological effect of food additive titanium dioxide nanoparticles on intestine: An in vitro study. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janer, G.; del Molino, E.M.; Fernández-Rosas, E.; Fernández, A.; Vázquez-Campos, S. Cell uptake and oral absorption of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, E.; Barreau, F.; Veronesi, G.; Fayard, B.; Sorieul, S.; Chanéac, C.; Carapito, C.; Rabilloud, T.; Mabondzo, A.; Herlin-Boime, N.; et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle impact and translocation through ex vivo, in vivo and in vitro gut epithelia. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Jia, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; et al. Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Kang, B.-C.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; Che, J.-H.; Seok, S.H. Comparative absorption, distribution, and excretion of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles after repeated oral administration. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, C.H.; Sikora, M.; Tomasik, P.; Li, C.; Garcia, V. Rheology of alumina–nanoparticle suspensions: Effects of lower saccharides and sugar alcohols. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, L.E.; Giacomelli, C.E. Unaffected features of BSA stabilized Ag nanoparticles after storage and reconstitution in biological relevant media. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 132, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, V.J. Emerging roles of engineered nanomaterials in the food industry. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, L.; Khosravi-Darani, K. The applications of nanotechnology in food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2011, 51, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekkers, S.; Krystek, P.; Peters, R.J.B.; Lankveld, D.P.K.; Bokkers, B.G.H.; van Hoeven-Arentzen, P.H.; Bouwmeester, H.; Oomen, A.G. Presence and risks of nanosilica in food products. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-M.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, C.-W.; Kim, T.-I.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeong, J.; Paek, S.-M.; Oh, J.-M. Surface treatment of silica nanoparticles for stable and charge-controlled colloidal silica. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-M.; Choi, M.-H.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeong, J.; Kim, Y.-R.; Kim, M.-K.; Paek, S.-M.; Oh, J.-M. Physicochemical properties of surface charge-modified ZnO nanoparticles with different particle sizes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Combined Compendium of Food Additive Specifications; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. European parliament and council directive 94/36/EC of 30 June 1994 on colours for use in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1994, L237, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanović, B.; Cvetković, V.J.; Mitrović, T.L. Effects of human food grade titanium dioxide nanoparticle dietary exposure on Drosophila melanogaster survival, fecundity, pupation and expression of antioxidant genes. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaor, D.; Michelazzi, M.; Leonelli, C.; Sorrell, C.C. The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimundić, M.; Barbara, D.; Vid Šuštar, J.Z.; Jernej, Z.; Roman, Š.; Darko, M.; Deniz, E.; Henry, H.; Damjana, D.; Veronika, K.-I. Effect of engineered TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on erythrocytes, platelet-rich plasma and giant unilamelar phospholipid vesicles. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miessler, G.L.; Tarr, D.A. Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 165–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.-M.; Kim, H.-M.; Choi, M.-H.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, Y.S.; Paek, S.-M.; Oh, J.-M. Colloidal properties of surface coated colloidal silica nanoparticles in aqueous and physiological solutions. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Song, G.; Hristovski, K.; Kiser, M.A. Occurrence and removal of titanium at full scale wastewater treatment plants: Implications for TiO2 nanomaterials. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paek, H.-J.; Chung, H.-E.; Lee, J.-A.; Kim, M.-K.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Maeng, E.-H.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; et al. Quantitative determination of silica nanoparticles in biological matrices and their pharmacokinetics and toxicokinetics in rats. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Rieux, A.; Fievez, V.; Théate, I.; Mast, J.; Préat, V.; Schneider, Y.-J. An improved in vitro model of human intestinal follicle-associated epithelium to study nanoparticle transport by M cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-K.; Lee, J.-A.; Jo, M.-R.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, H.-M.; Oh, J.-M.; Song, N.W.; Choi, S.-J. Cytotoxicity, uptake behaviors, and oral absorption of food grade calcium carbonate nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1938–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
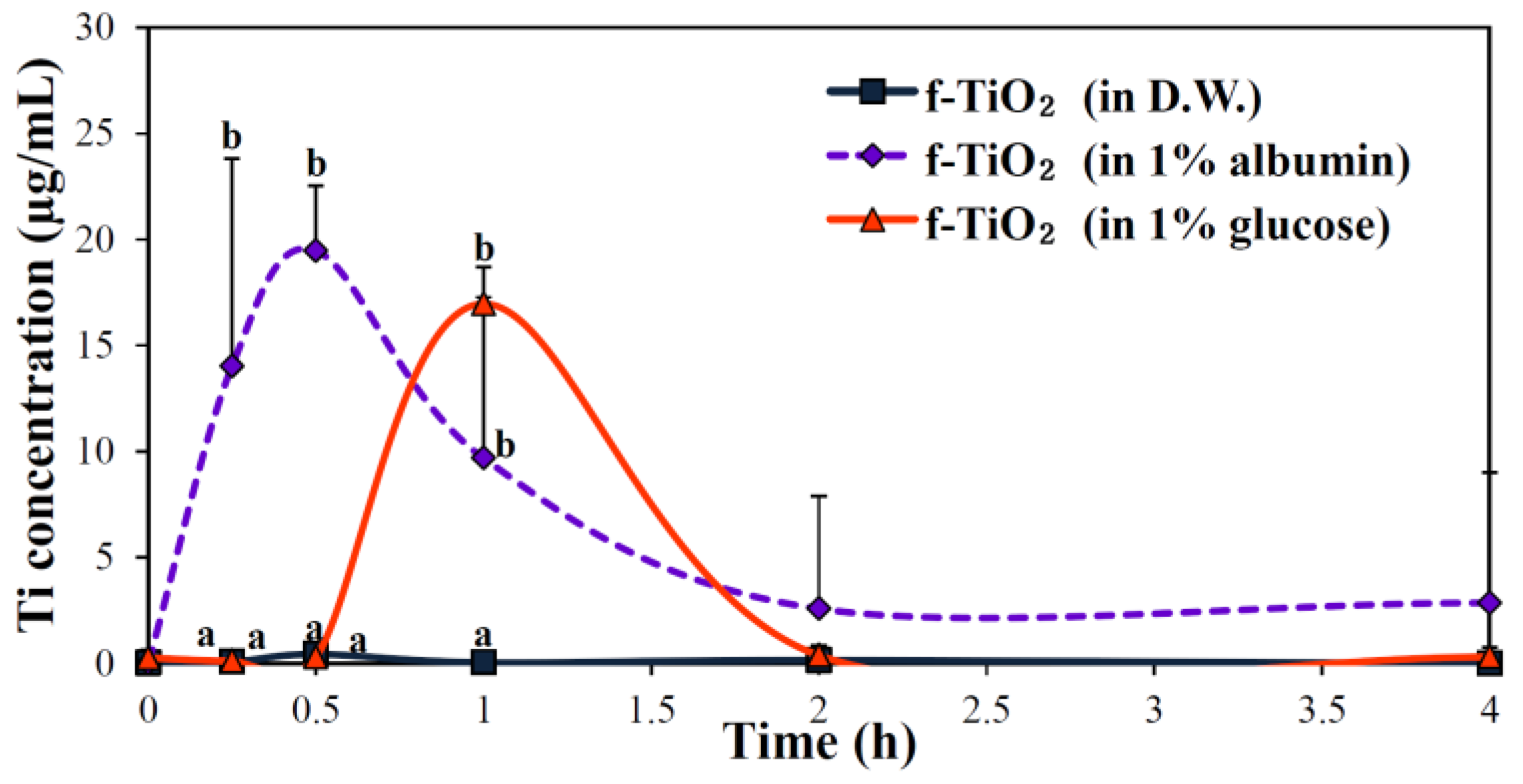
| f-TiO2 (in D.W.) | f-TiO2 (in 1% Albumin) | f-TiO2 (in 1% Glucose) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mg/L) | 0.46 ± 0.09 a | 20.02 ± 1.35 c | 16.96 ± 1.110 b |
| Tmax (h) | 0.5 a | 0.5 a | 1 b |
| AUC (h × mg/L) | 0.54 ± 0.03 a | 30.45 ± 8.34 c | 11.59 ± 1.42 b |
| T1/2 | 0.93 ± 0.18 a | 1.11 ± 0.09 a | 1.36 ± 0.11 b |
| MRT (h) | 1.63 ± 0.30 a | 1.58 ± 0.48 a | 1.70 ± 0.07 a |
| Absorption (%) | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.78 ± 0.21 c | 0.30 ± 0.04 b |
| f-TiO2 | g-TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mg/L) | 20.02 ± 1.35 a | 17.66 ± 0.98 b |
| Tmax (h) | 0.5 a | 0.5 a |
| AUC (h × mg/L) | 30.45 ± 8.34 a | 20.28 ± 6.7 b |
| T1/2 | 1.11 ± 0.09 a | 1.29 ± 0.49 a |
| MRT (h) | 1.58 ± 0.48 a | 1.80 ± 0.71 a |
| Absorption (%) | 0.78 ± 0.21 a | 0.52 ± 0.17 b |
| f-TiO2 | g-TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Excretion via urine (%) | 0.31 ± 0.15 | 0.16 ± 0.02 |
| Excretion via feces (%) | 85.20 ± 18.70 | 86.48 ± 16.96 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, M.-R.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Song, J.H.; Kim, K.-M.; Oh, J.-M.; Choi, S.-J. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Interactions Influence Oral Absorption. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120225
Jo M-R, Yu J, Kim H-J, Song JH, Kim K-M, Oh J-M, Choi S-J. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Interactions Influence Oral Absorption. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(12):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120225
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Mi-Rae, Jin Yu, Hyoung-Jun Kim, Jae Ho Song, Kyoung-Min Kim, Jae-Min Oh, and Soo-Jin Choi. 2016. "Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Interactions Influence Oral Absorption" Nanomaterials 6, no. 12: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120225
APA StyleJo, M.-R., Yu, J., Kim, H.-J., Song, J. H., Kim, K.-M., Oh, J.-M., & Choi, S.-J. (2016). Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Biomolecule Interactions Influence Oral Absorption. Nanomaterials, 6(12), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6120225






