Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
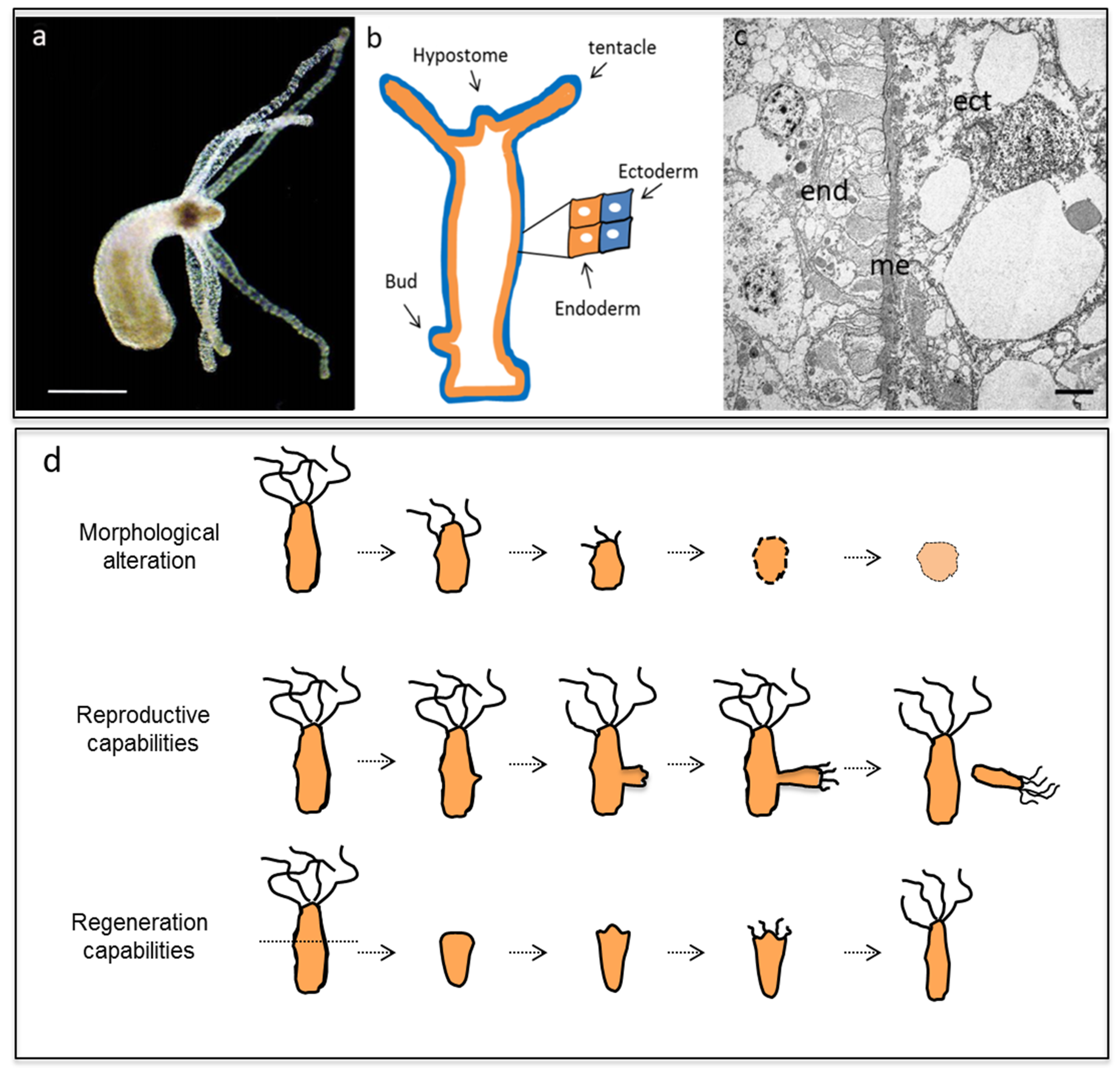
2. Results and Discussion
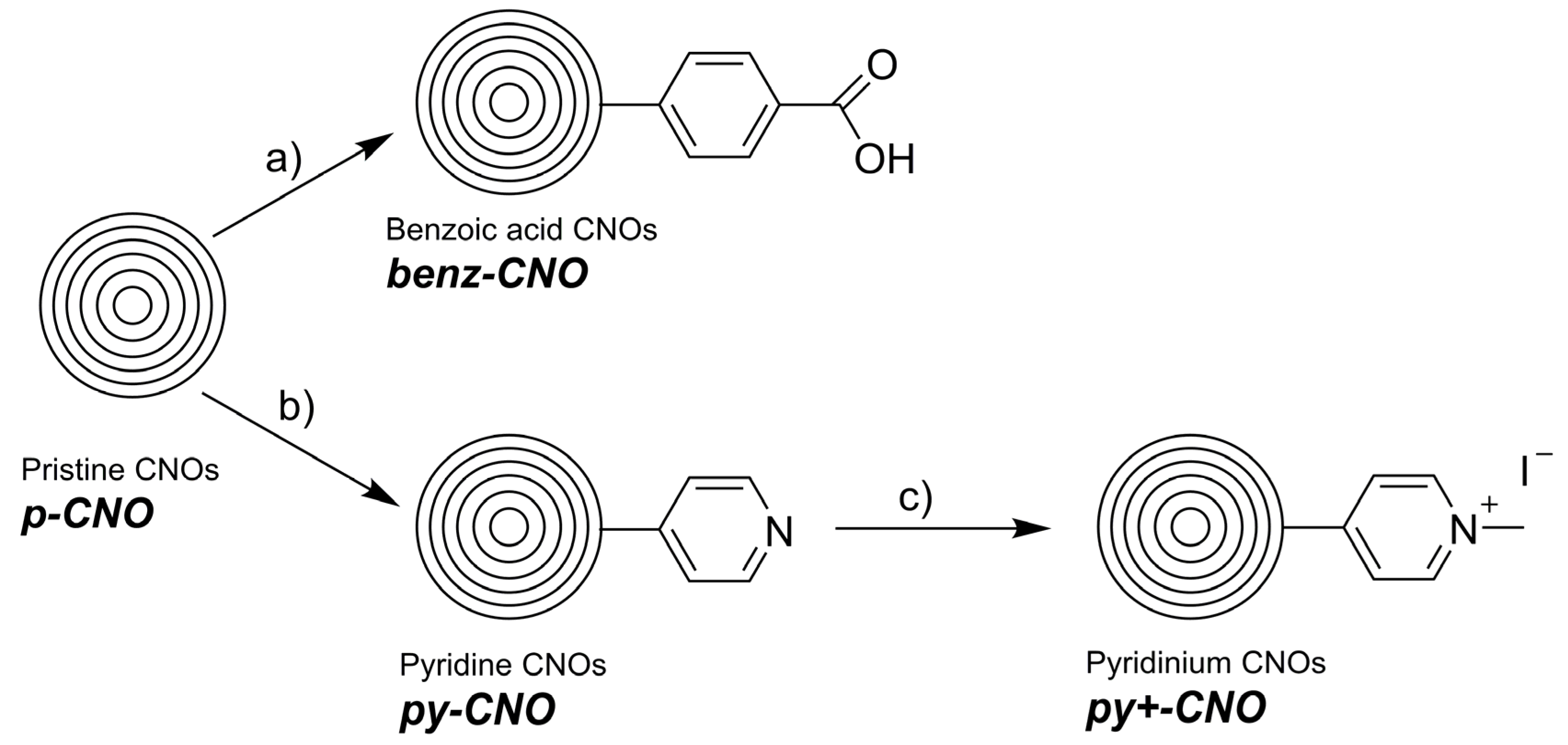

2.1. Hydra Exposure to CNO: Impact on Morphology and Survival Rate
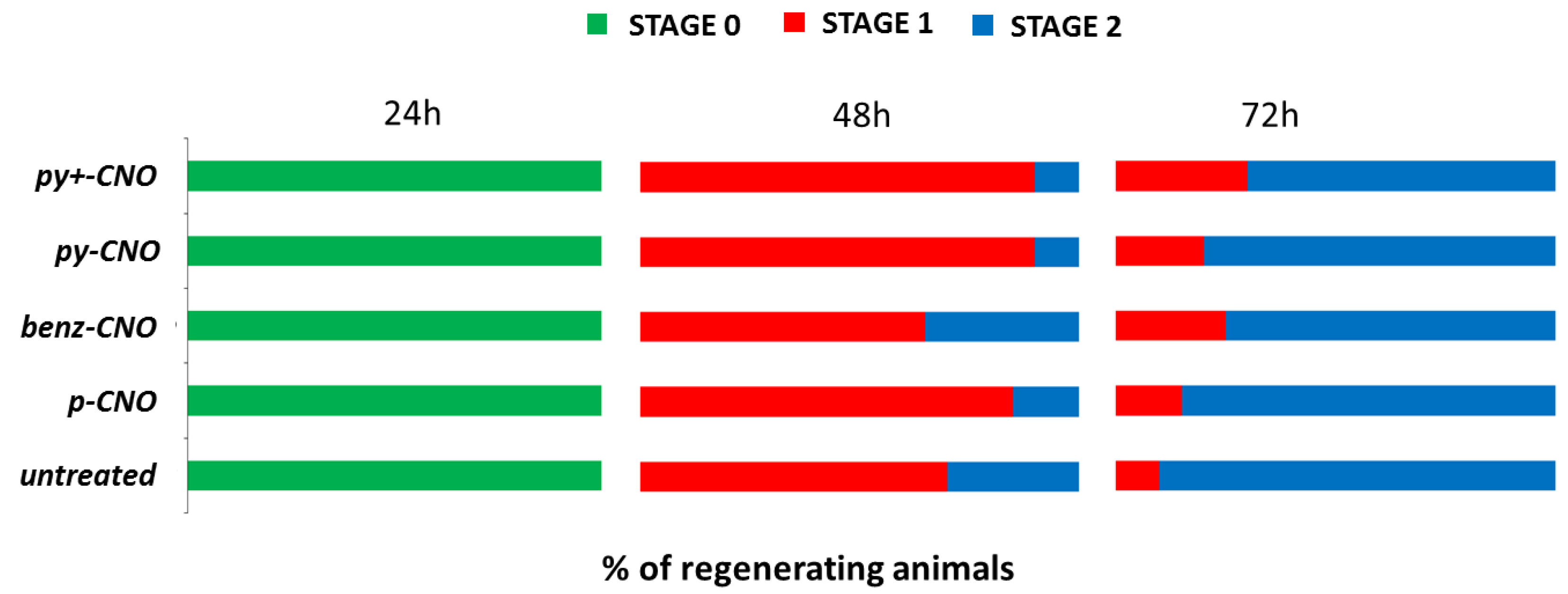
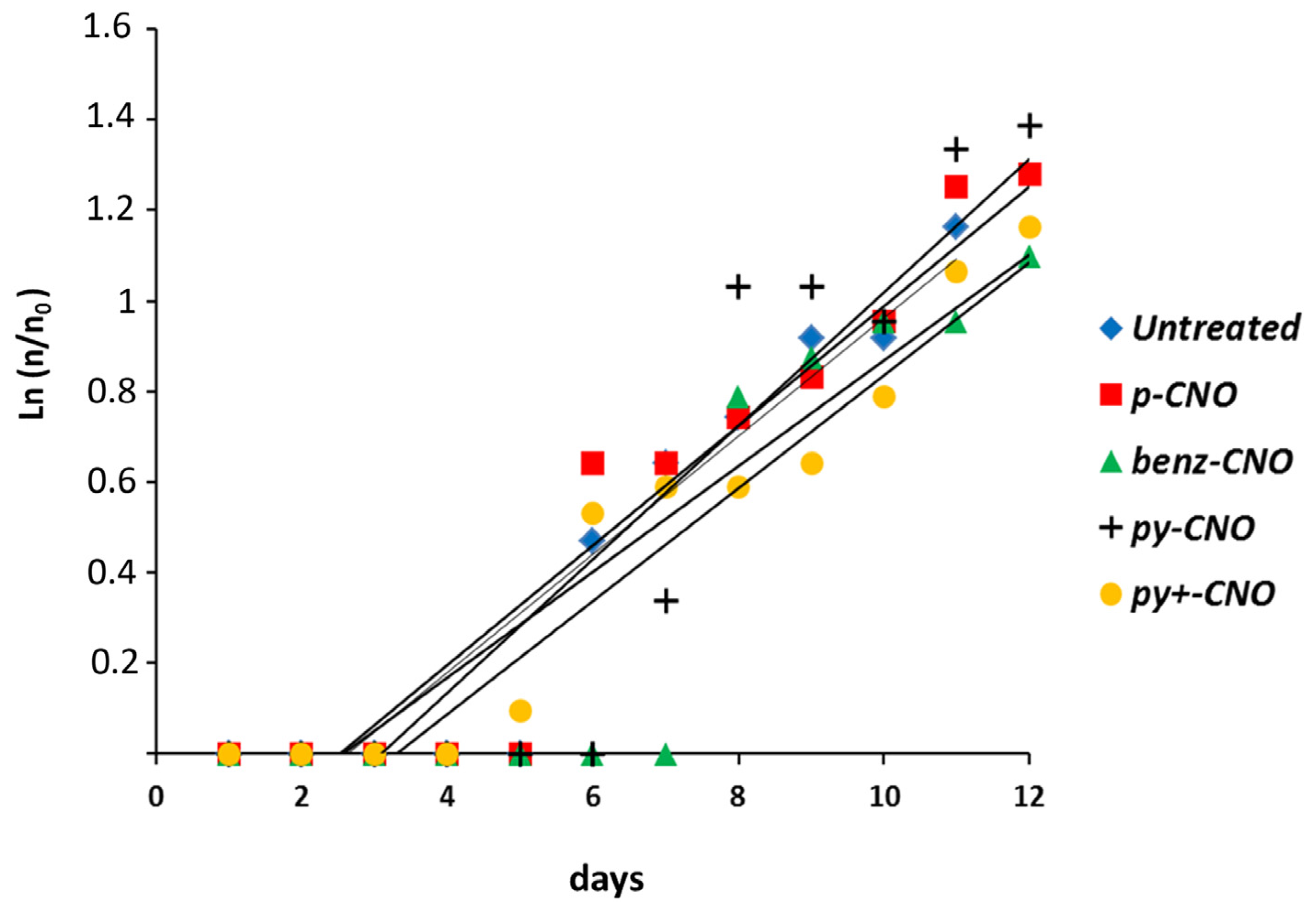
2.2. Hydra Exposure to CNO: Impact on Head Regeneration and Reproductive Capabilities
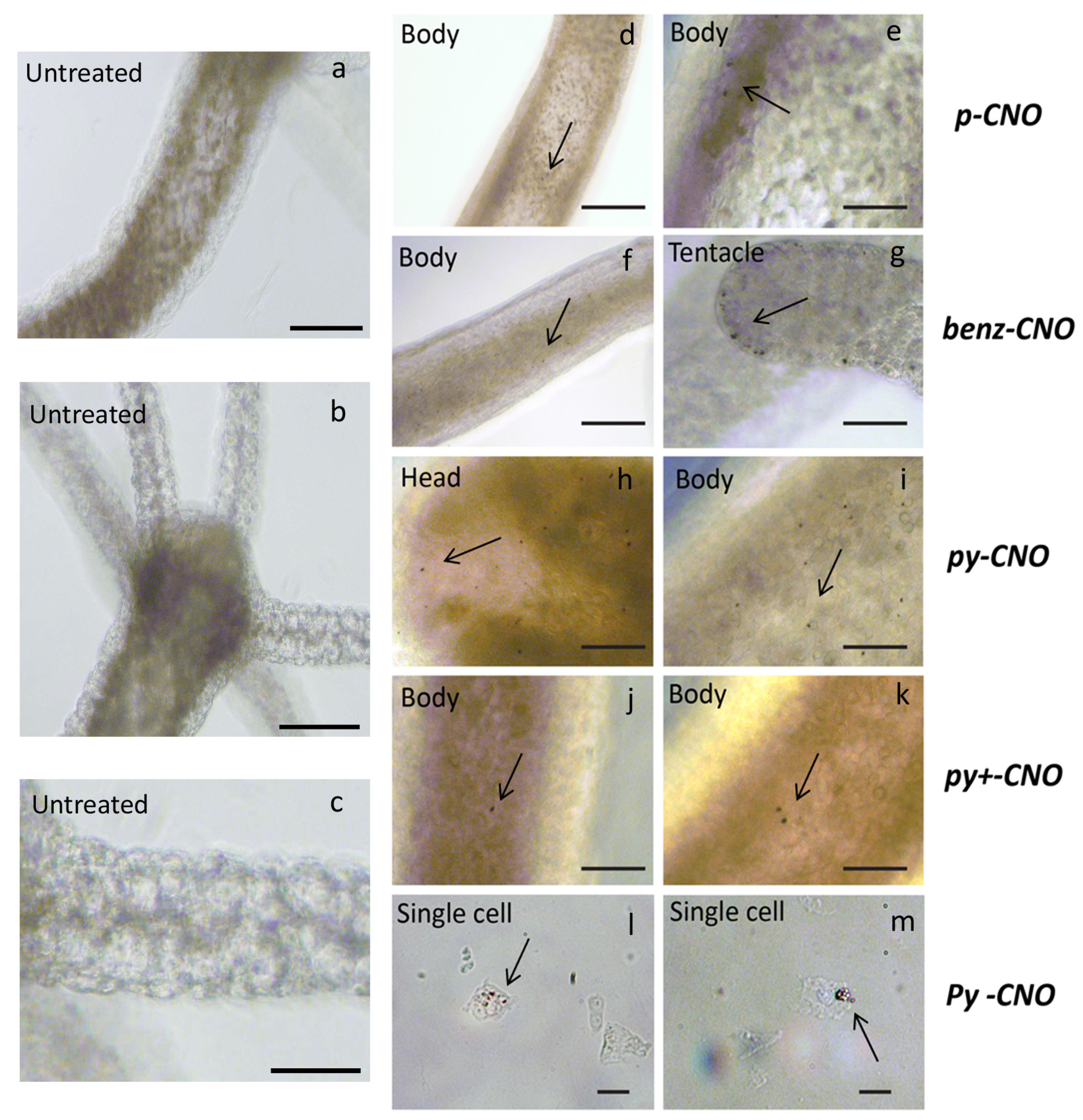
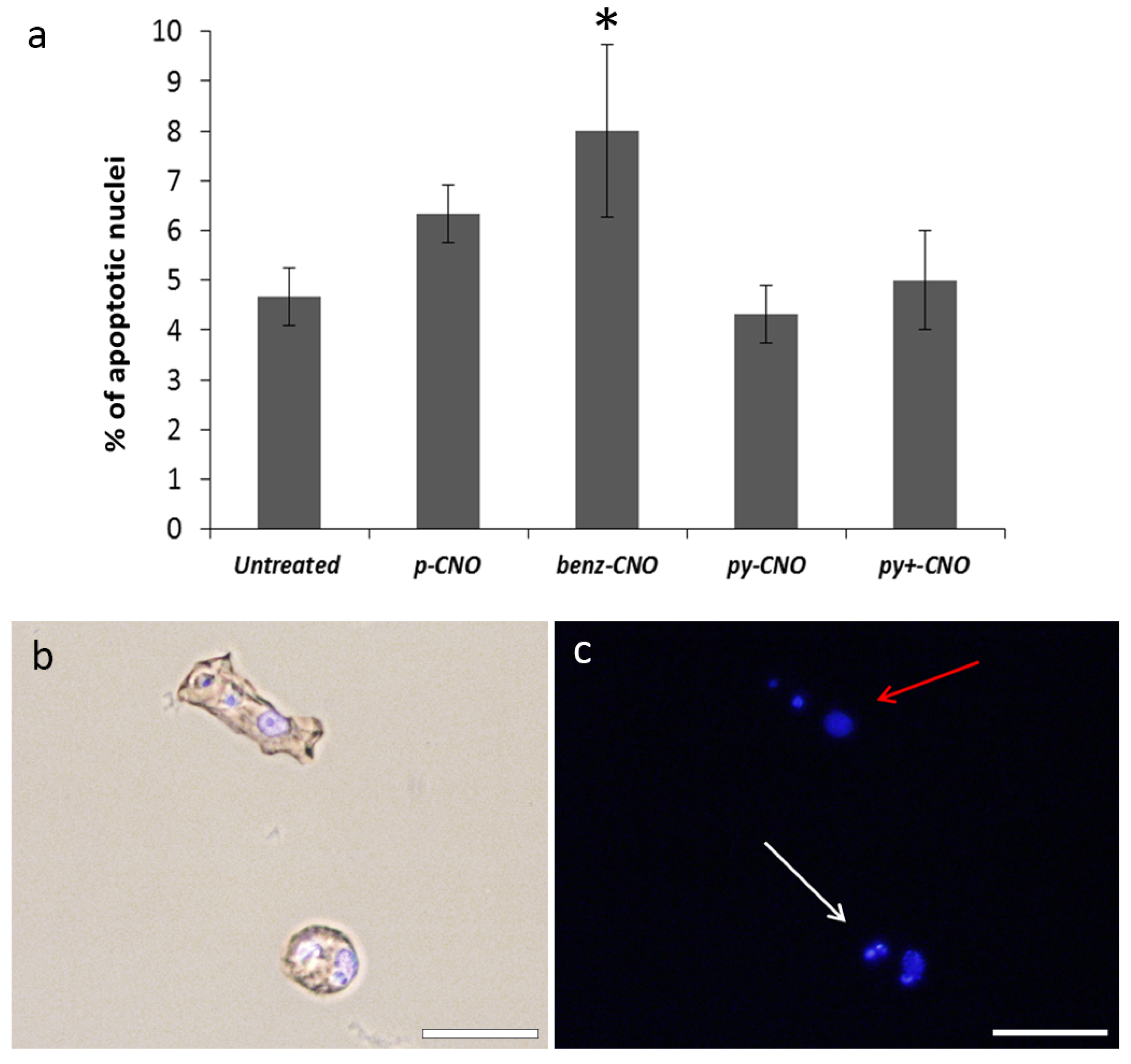
2.3. Hydra Exposure to CNO: Impact on Apoptosis
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Nanomaterial Synthesis
4.1.1. benz-CNO
4.1.2. py-CNO
4.1.3. py+-CNO
4.2. Nanomaterial Characterization
4.2.1. FT-IR Spectroscopy
4.2.2. Raman Spectroscopy
4.2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Zeta-Potential
4.2.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4.3. Biological Methods
4.3.1. Animal Culturing and in vivo Experiments
4.3.2. Hydra Cell and Tissue Analysis
4.3.3. Hydra Growth Rates and Regeneration
4.4. Assessment of Apoptosis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado, J.L.; Herranz, M.Á.; Martín, N. The nano-forms of carbon. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroto, H.W.; Heath, J.R.; O’Brien, S.C.; Curl, R.F.; Smalley, R.E. C60: Buckminsterfullerene. Nature 1985, 318, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, D. Curling and closure of graphitic networks under electron-beam irradiation. Nature 1992, 359, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollmann, W.; Spreadborough, J. Action of graphite as lubricant. Nature 1960, 186, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1993, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Yudasaka, M.; Yamada, R.; Bandow, S.; Suenaga, K.; Kokai, F.; Takahashi, K. Nano-aggregates of single-walled graphitic carbon nano-horns. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 309, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.H.; Zakhidov, A.A.; de Heer, W.A. Carbon nanotubes—The route toward applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbro, C.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Da Ros, T.; Kostarelos, K.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Targeting carbon nanotubes against cancer. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3911–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.-Q.; Qian, W.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wei, F. The road for nanomaterials industry: A review of carbon nanotube production, post-treatment, and bulk applications for composites and energy storage. Small 2013, 9, 1237–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartelmess, J.; Quinn, S.J.; Giordani, S. Carbon nanomaterials: Multi-functional agents for biomedical fluorescence and Raman imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4672–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Qu, X. New horizons for diagnostics and therapeutic applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Bonaccorso, F.; Fal'ko, V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roche, S.; Boggild, P.; Stefano, B.; Koppens, F.H.L.; Palermo, V.; Pugno, N.; et al. Science and technology roadmap for graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4598–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartelmess, J.; Giordani, S. Carbon nano-onions (multi-layer fullerenes): Chemistry and applications. Beilstein. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1980–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesner, M.R.; Lowry, G.V.; Alvarez, P.; Dionysiou, D.; Biswas, P. Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4336–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.N. Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive 2006/121/EC of the European Parliament and of the COUNCIL of 18 December 2006. Available online: http://www.hse.gov.uk/reach/resources/regulationammendments1206.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Yang, M.; Flavin, K.; Kopf, I.; Radics, G.; Hearnden, C.H.A.; McManus, G.J.; Moran, B.; Villalta-Cerdas, A.; Echegoyen, L.A.; Giordani, S.; et al. Functionalization of carbon nanoparticles modulates inflammatory cell recruitment and NLRP3 inflammasome ictivation. Small 2013, 9, 4194–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordani, S.; Bartelmess, J.; Frasconi, M.; Biondi, I.; Cheung, S.; Grossi, M.; Wu, D.; Echegoyen, L.; O’Shea, D.F. NIR fluorescence labelled carbon nano-onions: Synthesis, analysis and cellular imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7459–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; de Luca, E.; Signorelli, A.; Baldrighi, M.; Becce, M.; Brescia, R.; Nardone, V.; Parisini, E.; Echegoyen, L.; Pompa, P.P.; et al. Boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) functionalized carbon nano-onions for high resolution cellular imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13761–13769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, E.; Zhu, S.; Blickley, T.M.; McClellan-Green, P.; Haasch, M.L. Ecotoxicology of carbon-based engineered nanoparticles: Effects of fullerene (C60) on aquatic organisms. Carbon 2006, 44, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usenko, C.Y.; Harper, S.L.; Tanguay, R.L. In vivo evaluation of carbon fullerene toxicity using embryonic zebrafish. Carbon 2007, 45, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S. Acute toxicities of six manufactured nanomaterial suspensions to Daphnia magna. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, R.S.; Garcia, M.L.; da Rocha, A.M.; Flores, J.A.; Pinheiro, M.V.B.; Monserrat, J.M.; Ferreira, J.L.R. Effects of carbon nanomaterials fullerene C60 and fullerol C60(OH)18–22 on gills of fish Cyprinus carpio (Cyprinidae) exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 114, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological interactions of graphene-family nanomaterials: An interdisciplinary review. Chem. Res. Tox. 2012, 25, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, Q. Health and ecosystem risks of graphene. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 3815–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Li, X. Ecotoxicological effects of graphene oxide on the protozoan Euglena gracilis. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Dong, S.; Petersen, E.J.; Gao, S.; Huang, Q.; Mao, L. Biological uptake and depuration of radio-labeled graphene by Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12524–12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, F.; Bucheli, T.D.; Lukhele, L.P.; Magrez, A.; Nowack, B.; Sigg, L.; Knauer, K. Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Ji, J.; Yang, K.; Lin, D.; Wu, F. Systematic and quantitative investigation of the mechanism of carbon nanotubes’ toxicity toward algae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8458–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhiem, S.; Riding, M.J.; Baumgartner, W.; Martin, F.L.; Semple, K.T.; Jones, K.C.; Schäffer, A.; Maes, H.M. Interactions of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with algal cells: Quantification of association, visualization of uptake, and measurement of alterations in the composition of cells. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Toxicity of single walled carbon nanotubes to rainbow trout, (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Respiratory toxicity, organ pathologies, and other physiological effects. Aquat. Tox. 2007, 82, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Flahaut, E.; Cheng, S.H. Effect of carbon nanotubes on developing zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Environ. Toc. Chem. 2007, 26, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, C.P. The responses of Ceriodaphnia dubia toward multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Effect of physical–chemical treatment. Carbon 2011, 49, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.A.; Moua, M.; Chen, J.; Klaper, R.D. Core structure and surface functionalization of carbon nanomaterials alter impacts to daphnid mortality, reproduction, and growth: Acute assays do not predict chronic exposure impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9444–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Férard, J.F.; Eullaffroy, P. Ecotoxicity of selected nano-materials to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Mauter, M.S.; Isaacs, J.A.; Elimelech, M. New perspectives on nanomaterial aquatic ecotoxicity: Production impacts exceed direct exposure impacts for carbon nanotoubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2902–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P.; Jacobsen, N.R.; Baun, A.; Birkedal, R.; Kühnel, D.; Jensen, K.A.; Vogel, U.; Wallin, H. Bioaccumulation and ecotoxicity of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.K.; Chung, Y.S.; Johari, S.A.; Kim, T.G.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, S.W.; Yu, I.J. Acute toxicity comparison of single-walled carbon nanotubes in various freshwater organisms. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 323090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Jafvert, C.T. The role of surface functionalization in the solar light-induced production of reactive oxygen species by single-walled carbon nanotubes in water. Carbon 2011, 49, 5099–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Li, Q. Photochemical transformation of carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Role of reactive oxygen species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14080–14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Q. Ambient water and visible-light irradiation drive changes in graphene morphology, structure, surface chemistry, aggregation, and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3410–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, B.; Itkis, M.E.; Haddon, R.C. Nitric acid purification of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 13838–13842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavin, C.; Kopf, I.; del Canto, E.; Navio, C.; Bittencourt, C.; Giordani, S. Controlled carboxylic acid introduction: A route to highly purified oxidised single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17881–17887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Canto, E.; Flavin, K.; Movia, D.; Navio, C.; Bittencourt, C.; Giordani, S. Critical investigation of defect site functionalization on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Mater. 2010, 23, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movia, D.; Prina-Mello, A.; Bazou, D.; Volkov, Y.; Giordani, S. Screening the cytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes using novel 3D tissue-mimetic models. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9278–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.J.; Henry, T.B.; Zhao, J.; Mac-Cuspie, R.I.; Kirschling, T.L.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Hackley, V.; Xing, B.; White, J.C. Identification and avoidance of potential artifacts and misinterpretations in nanomaterial ecotoxicity measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4226–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Hydra, a model system for environmental studies. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. A comparison of methods for measuring acute toxicity to Hydra vulgaris. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollino, C.A.; Holdway, D.A. Potential of two hydra species as standard toxicity test animals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1999, 43, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galliot, B.; Miljkovic-Licina, M.; de Rosa, R.; Chera, S. Hydra, a niche for cell and developmental plasticity. Semin. Cell Dev. Boil. 2006, 17, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galliot, B.; Ghila, L. Cell plasticity in homeostasis and regeneration. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2010, 77, 837–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karntanut, W.; Pascoe, D. The toxicity of copper, cadmium and zinc to four different Hydra (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Chemosphere 2002, 47, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdway, D.A.; Lok, K.; Semaan, M. The acute and chronic toxicity of cadmium and zinc to two hydra species. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascoe, D.; Karntanut, W.; Muller, C.T. Do pharmaceuticals affect freshwater invertebrates? A study with the cnidarian Hydra vulgaris. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B.; Gagne, F.; Blaise, C. The effects of pharmaceuticals on the regeneration of the cnidarian, Hydra attenuata. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachura, S.; Cambon, J.P.; Blaise, C.; Vasseur, P. 4-nonylphenol-induced toxicity and apoptosis in Hydra attenuata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosone, A.; Tortiglione, C. Methodological approaches for nanotoxicology using cnidarian models. Toxicol. Mech. Metch. 2013, 23, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortiglione, C. An ancient model organism to test in vivo novel functional nanocrystals. In Biomedical Engineering: From Theory to Application; Fazel-Rezai, R., Ed.; InTech-Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 225–252. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosone, A.; Marchesano, V.; Mazzarella, V.; Tortiglione, C. Nanotoxicology using the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis: From developmental toxicity to genotoxicology. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortiglione, C.; Quarta, A.; Malvindi, M.A.; Tino, A.; Pellegrino, T. Fluorescent nanocrystals reveal regulated portals of entry into and between the cells of Hydra. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosone, A.; Mattera, L.; Marchesano, V.; Quarta, A.; Susha, A.S.; Tino, A.; Rogach, A.L.; Tortiglione, C. Mechanisms underlying toxicity induced by CdTe quantum dots determined in an invertebrate model organism. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tino, A.; Ambrosone, A.; Mattera, L.; Marchesano, V.; Susha, A.; Rogach, A.; Tortiglione, C. A new in vivo model system to assess the toxicity of semiconductor nanocrystals. Int. J. Biomater. 2011, 2011, 792854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosone, A.; Scotto di Vettimo, M.R.; Malvindi, M.A.; Roopin, M.; Levy, O.; Marchesano, V.; Pompa, P.P.; Tortiglione, C.; Tino, A. Impact of amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles on a living organism: Morphological, behavioral, and molecular biology implications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesano, V.; Hernandez, Y.; Salvenmoser, W.; Ambrosone, A.; Tino, A.; Hobmayer, B.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Tortiglione, C. Imaging inward and outward trafficking of gold nanoparticles in whole animals. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moros, M.; Ambrosone, A.; Stepien, G.; Fabozzi, F.; Marchesano, V.; Castaldi, A.; Tino, A.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Tortiglione, C. Deciphering intracellular events triggered by mild magnetic hyperthermia in vitro and in vivo. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2167–2183. [Google Scholar]
- Palkar, A.; Melin, F.; Cardona, C.M.; Elliot, B.; Naskar, A.K.; Edie, D.D.; Kumbhar, A.; Echegoyen, L. Reactivity differences between carbon nano onions (CNOs) prepared by different methods. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 2, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flavin, K.; Chaur, M.N.; Echegoyen, L.; Giordani, S. Functionalization of multilayer fullerenes (carbon nano-onions) using diazonium compounds and “click” chemistry. Org. Lett. 2009, 12, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, J.L.; Yang, J.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Bronikowski, M.J.; Smalley, R.E.; Tour, J.M. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes by electrochemical reduction of aryl diazonium salts: A bucky paper electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6536–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Campidelli, S.; Giordani, S.; Bonifazi, D.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Organic functionalisation and characterisation of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2214–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, H.R. The interstitial cell lineage of hydra: A stem cell system that arose early in evolution. J. Cell. Sci. 1996, 109, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilby, O.K. The Hydra regeneration assay. In Proceedings of Workshop Organised by Association Francaise de Teratologie, Royaumont, France, 3 June 1988; pp. 108–124.
- Bottger, A.; Alexandrova, O. Programmed cell death in Hydra. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiron, J.P.; Lamande, J.; Moussa, F.; Trivin, F.; Ceolin, R. Effect of “micronized” C60 fullerene on the microbial growth in vitro. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2000, 58, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, M.; Falih, A.M. Fungal growth on buckminsterfullerene. Microbiology 1997, 143, 2097–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, F.; Chrétien, P.; Pressac, M.; Trivin, F.; Szwarc, H.; Céolin, R. Preliminary study of the influence of cubic C60 on cultured human monocytes: Lack of interleukin-1B secretion. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Struct. 1997, 5, 503–510. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharenko, L.P.; Zakharov, I.K.; Vasiunina, E.A.; Karamysheva, T.V.; Danilenko, A.M.; Nikiforov, A.A. Determination of the genotoxicity of fullerene C60 and fullerol using the method of somatic mosaics on cells of Drosophila melanogaster wingand SOS-chromotest. Genetika 1997, 33, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, T.; Oguri, I.; Yamakoshi, Y.N.; Myata, N. Novel harmful effects of (60) fullerene on mouse embryos in vitro and in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1996, 393, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Oberdorster, E.; Haasch, M.L. Toxicity of an engineered nanoparticle (fullerene, C60) in two aquatic species, Daphnia and fathead minnow. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, S5–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchesano, V.; Ambrosone, A.; Bartelmess, J.; Strisciante, F.; Tino, A.; Echegoyen, L.; Tortiglione, C.; Giordani, S. Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1331-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031331
Marchesano V, Ambrosone A, Bartelmess J, Strisciante F, Tino A, Echegoyen L, Tortiglione C, Giordani S. Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology. Nanomaterials. 2015; 5(3):1331-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031331
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchesano, Valentina, Alfredo Ambrosone, Juergen Bartelmess, Federica Strisciante, Angela Tino, Luis Echegoyen, Claudia Tortiglione, and Silvia Giordani. 2015. "Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology" Nanomaterials 5, no. 3: 1331-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031331
APA StyleMarchesano, V., Ambrosone, A., Bartelmess, J., Strisciante, F., Tino, A., Echegoyen, L., Tortiglione, C., & Giordani, S. (2015). Impact of Carbon Nano-Onions on Hydra vulgaris as a Model Organism for Nanoecotoxicology. Nanomaterials, 5(3), 1331-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031331





