An Investigation of the Cytotoxicity and Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Effect of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata on Human Liver Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
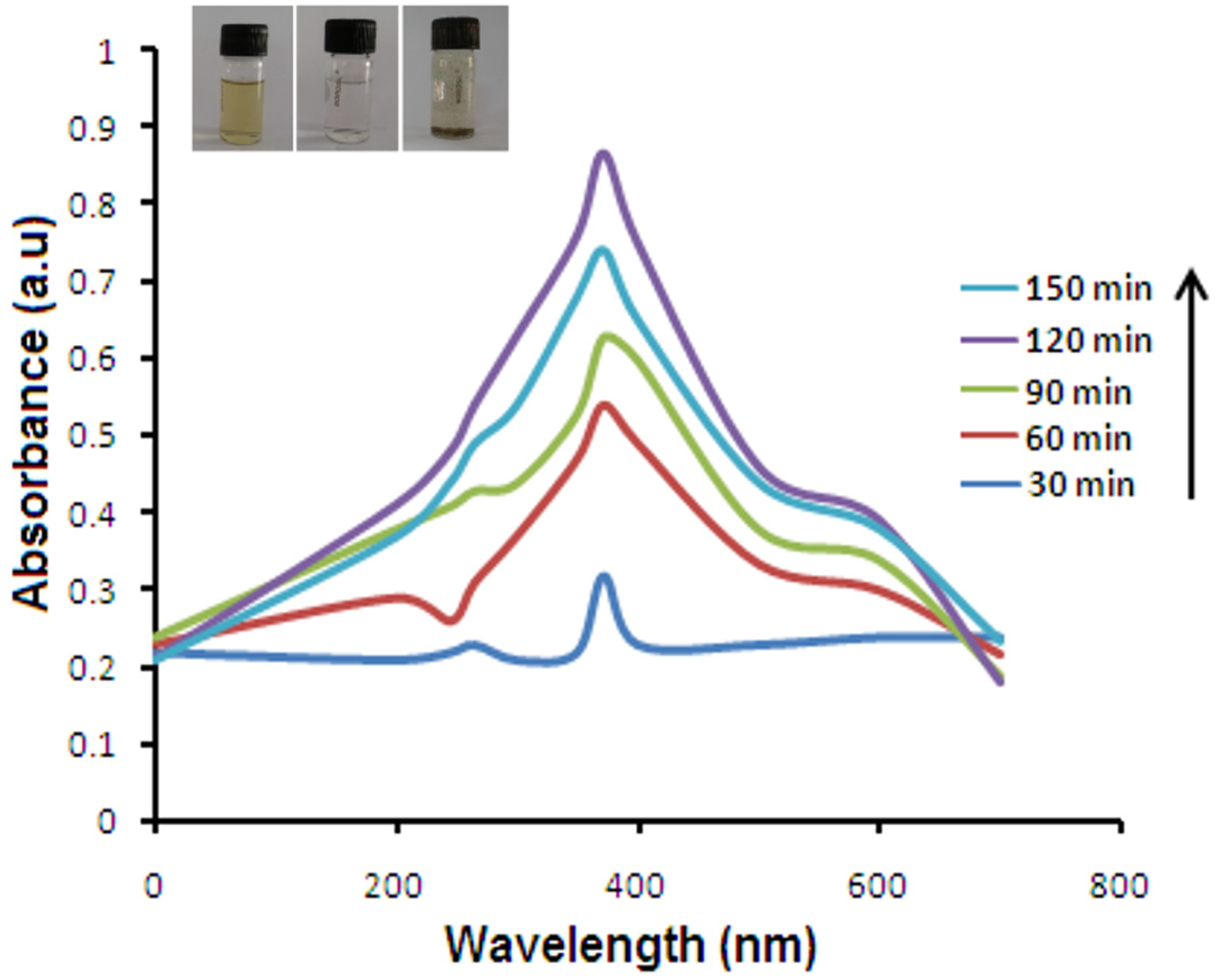
2.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.2. X-ray Powder Diffraction Analysis
2.3. FTIR Spectroscopy

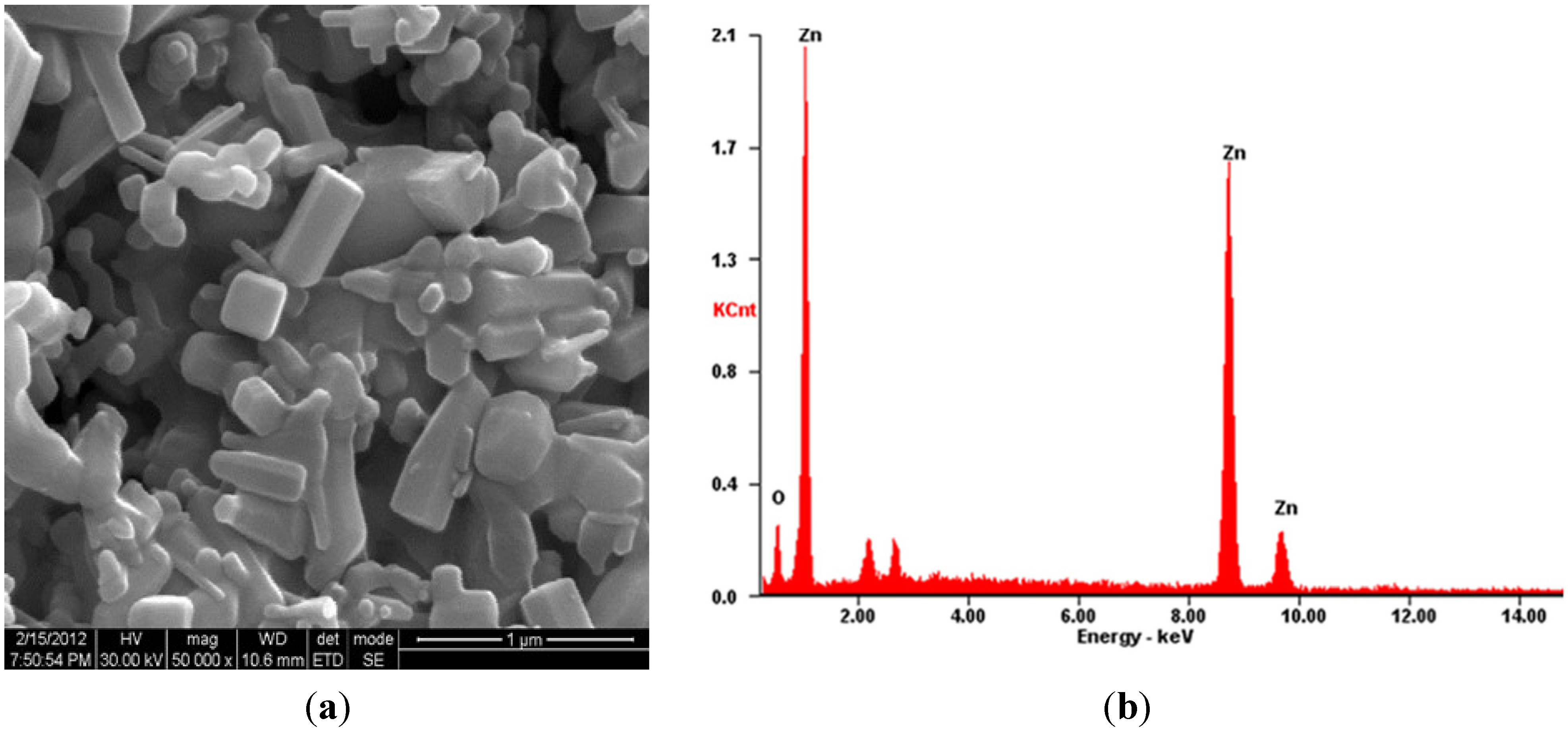
2.4. SEM-EDX Analysis
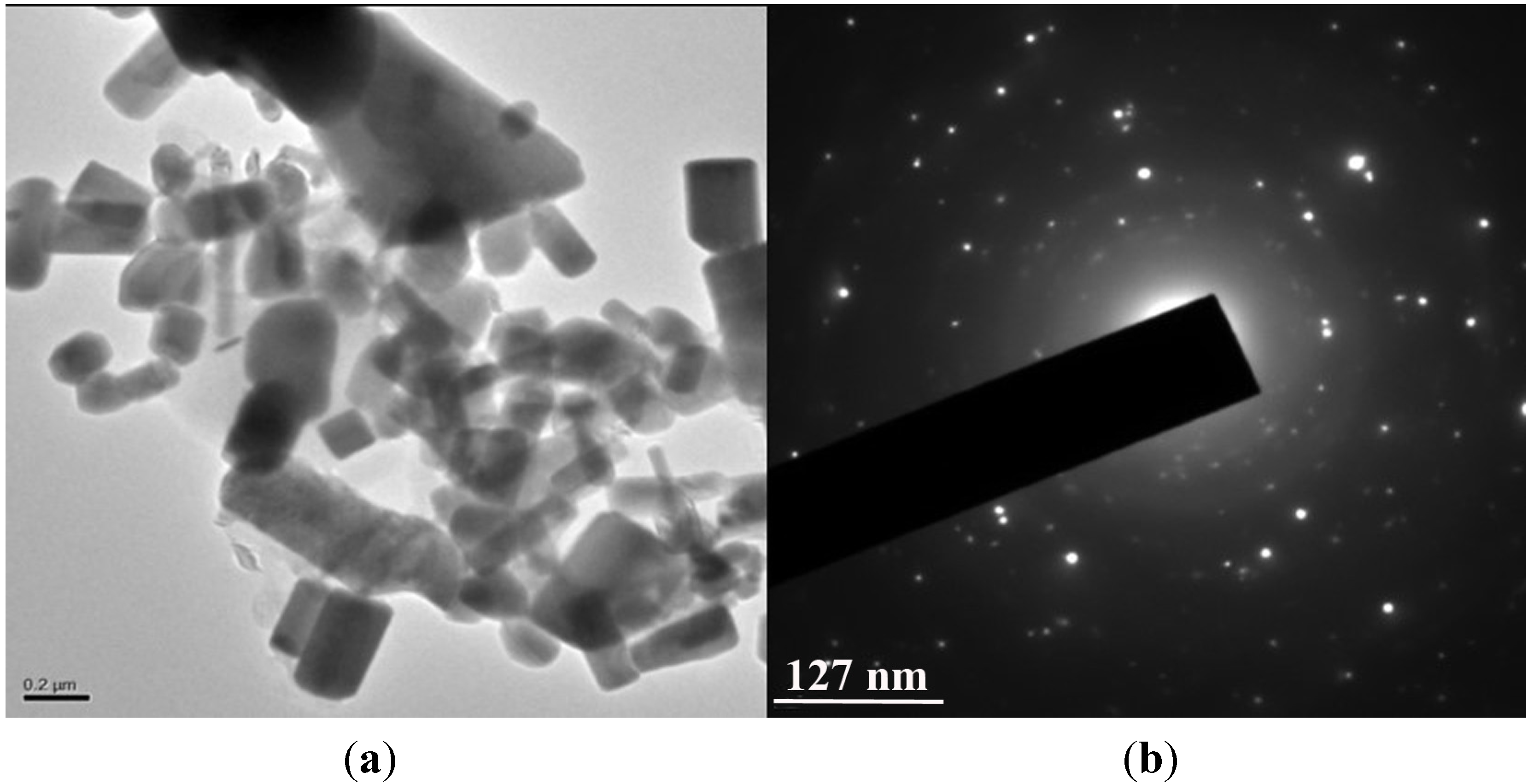
2.5. HRTEM Analysis and SAED Pattern
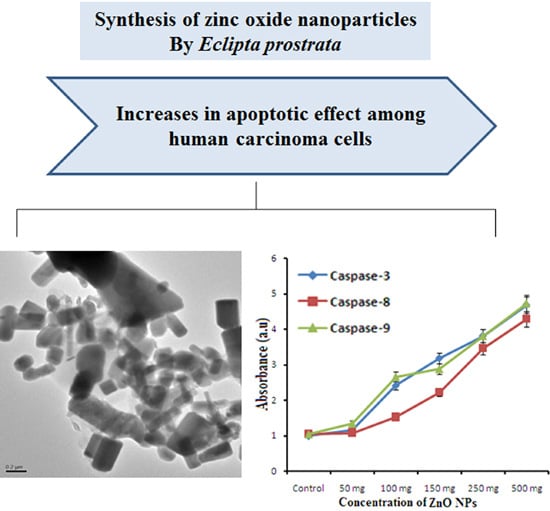
2.6. Anticancer Activity
2.6.1. Cytotoxicity Study of Hep-G2 Cell Line
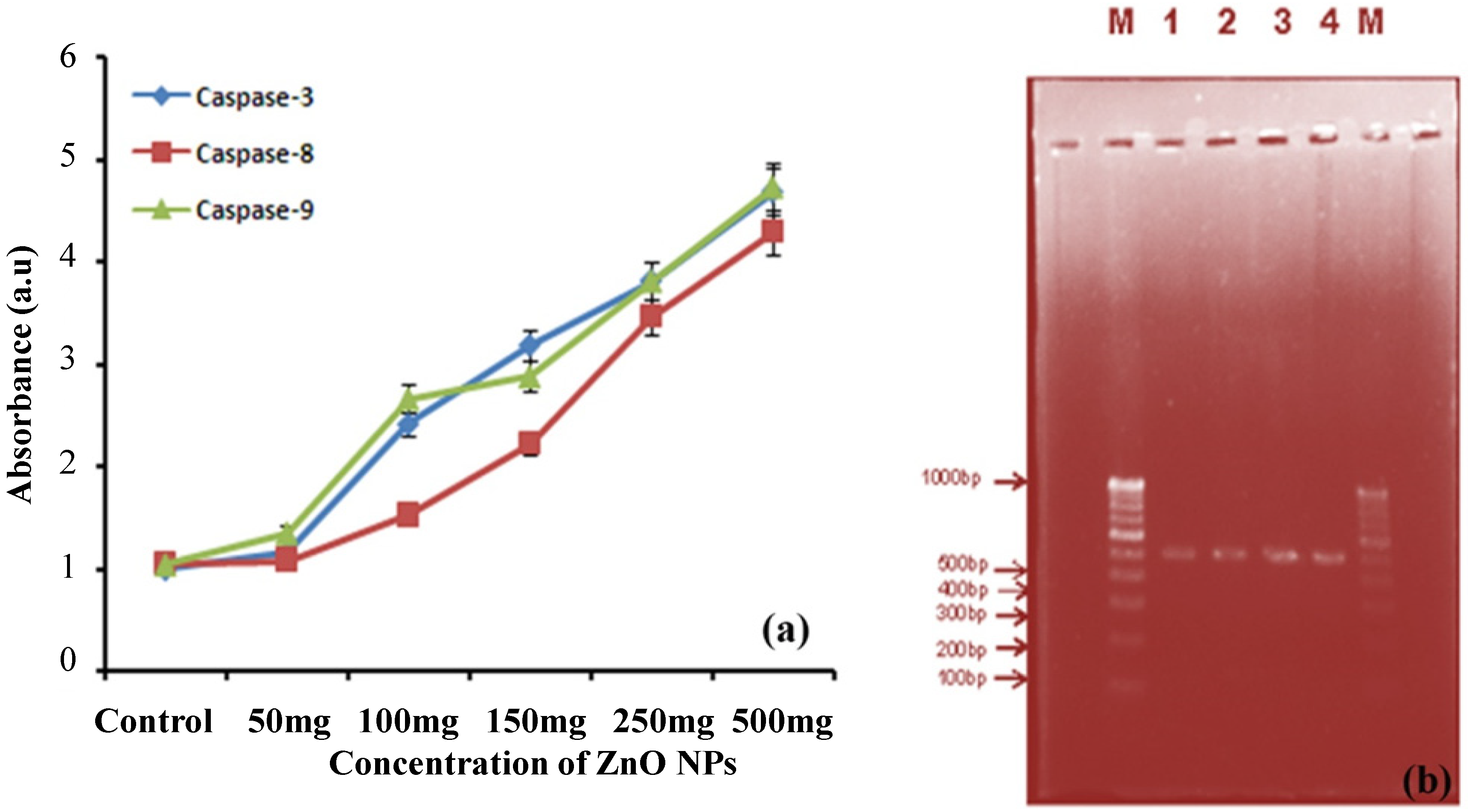
2.6.2. Caspase-3, -8, -9 Assays
2.6.3. DNA Fragmentation Assay
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Collection of E. Prostrata
3.2. Preparation of Plant Extract
3.3. Biosynthesis of ZnO NPs
3.4. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.5. Characterization of ZnO NPs
3.6. Anticancer Activity
3.6.1. Cytotoxicity Study of Hep-G2 Cell Line
3.6.2. Caspase -3, -8, -9 Assay
3.6.3. DNA Fragmentation Assay
3.6.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mamede, A.C.; Tavares, S.D.; Abrantes, A.M.; Trindade, J.; Maia, J.M.; Botelho, M.F. The role of vitamins in cancer: A review. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, D.D.; Macaluso, M.; Cinti, C.; Khalili, K.; Giordano, A. How does a normal human cell become a cancer cell? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 22, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karakosta, A.; Golias, C.H.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Peschos, D.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Genetic models of human cancer as a multistep process: Paradigm models of colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and chronic myelogenous and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 24, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eva, S.; Una, F.; Afshin, S. Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: The story so far. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, R.S.; Sahoo, S.K. Cancer nanotechnology: Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 842–850. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, V.; Bharde, A.; Ramanathan, R.; Bhargava, S.K. Inorganic materials using “unusual” microorganisms. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 179, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskam, G. Metal oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and application. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 37, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchnick, M.A.; Fairhurst, D.; Pinnell, S.R. Microfine zinc oxide (Z-cote) as a photostable UVA/UVB sunblock agent. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 40, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, G.M.; Mohammed, W.H.; Marzoog, T.R.; Al-Amiery, A.A.A.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B. Green synthesis, antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles using Eucalyptus chapmaniana leaves extract. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibkia, K.; Omidi, Y.; Siahi, M.R.; Javadzadeh, A.R.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Barar, J.; Maleki, N.; Mohammadi, G.; Nokhodchi, A. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced uveitis by methylprednisolone acetate nanosuspension in rabbits. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 23, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidya, C.S.; Hiremath, M.N.; Chandraprabha, M.A.L.; Antonyraj, I.; Gopal, V.; Jai, A.; Bansal, K. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Calotropis gigantean. In Proceedings of National Conference on Women in Science and Engineering, Dharwad, India, 6 April 2013.
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract, structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasangeetha, D.; Thambavani, S.D. One pot synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles via chemical and green method. Res. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.X. Advances in studies on chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Eclipta prostrata. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 44, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, V.G.; Kannabiran, K. Anticancer-cytotoxic activity of saponins isolated from the leaves of Gymnema sylvestre and Eclipta prostrata on Hela cells. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2009, 3, 227–229. [Google Scholar]
- Tewtrakul, S.; Subhadhirasakul, S.; Tansakul, P.; Cheenpracha, S.; Karalai, C. Antiinflammatory constituents from Eclipta prostrata using RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajiv, P.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Bio-fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus L. and its size-dependent antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Spect. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 112, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, J.; Ghosh, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Acharya, K. Biosynthesis and safety evaluation of ZnO nanoparticles. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Santhoshkumar, T. Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, G.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Green synthesis of Zinc oxide nanoparticles by Aloe barbadensis miller leaf extract, structure and optical properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Shukla, V.K.; Yadav, R.S.; Sharma, P.K.; Singh, P.K.; Pandey, A.C. Biological approach of zinc oxide nanoparticles formation and its characterization. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2011, 2, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Singh, P.; Pandey, A.K.; Dhawan, A. Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutat. Res. 2012, 745, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and ROS-triggered mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human liver cells (HepG2). Apoptosis 2012, 17, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawati, M.I.; Tay, C.Y.; Leong, D.T. Mechanistic investigation of the biological effects of SiO2, TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles on intestinal cells. Small 2015, 11, 1655–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawati, M.I.; Tay, C.Y.; Leong, D.T. Effect of zinc oxide nanomaterials-induced oxidative stress on the p53 pathway. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10133–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.L.; Tay, C.Y.; Setyawati, M.I.; Leong, D.T. Biomimicry 3D gastrointestinal spheroid platform for the assessment of toxicity and inflammatory effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Small 2015, 11, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, S.; Pokhrel, S.; Xia, T.; Gilbert, B.; Ji, Z.; Schowalter, M.; Rosenauer, A.; Damoiseaux, R.; Bradley, K.A.; Mädler, L. Use of a rapid cytotoxicity screening approach to engineer a safer zinc oxide nanoparticle through iron doping. ACS Nano 2009, 4, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanni, M.; Tay, C.Y.; Setyawati, M.I.; Xie, J.; Ong, C.N. Toxicity profiling of water contextual zinc oxide, silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human oral and gastrointestinal cell systems. Environ. Toxicol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.T.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, A.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Cytotoxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles: Importance of microenvironment. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 8638–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanni, M.; Yue, J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.; Ong, C.N.; Leong, D.T. Pro-inflammatory responses of RAW264.7 macrophages when treated with ultralow concentrations of silver, titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 297, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W.; Khoom, S.P.K.; Heng, B.C.; Setyawati, M.I.; Tan, E.C.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, S.; Fang, W.; Leong, D.T.; Loo, J.S.C. The role of the tumor suppressor p53 pathway in the cellular DNA damage response to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8218–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurnherr, T.B.; Xiao, L.; Diener, L.; Arslan, O.; Hirsch, C.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Grieder, K.; Wampfler, B.; Mathur, S.; Wick, P.; et al. In vitro mechanistic study towards a better understanding of ZnO nanoparticle toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, M.I.; Kanth, S.B.; Kalishwaralal, K.; Gurunathan, S. Antitumor activity of silver nanoparticles in Dalton’s lymphoma ascites tumor model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, M.; Saquib, Q.; Azam, A.; Naqvi, S.A.H. Zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Int. J. Nanopart. 2009, 2, 402–415. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, Z.M.; Harhaji-Trajkovic, L.M.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Kepic, D.P.; Arsikin, K.M.; Jovanovic, S.P.; Pantovic, A.C.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Trajkovic, V.S. In vitro comparison of the photothermal anticancer activity of graphene nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulkumar, K.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Vanaja, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Malarkod, C.; Pandian, K.; Annadurai, G. Piper nigrum leaf and stem assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial activity against agricultural plant pathogens. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minjas, J.N.; Sarda, R.K. Laboratory observations on the toxicity of Swartzia madagascariensis (Leguminosae) extract to mosquito larvae. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 80, 460–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Siegel, P.M.; Shu, W.; Drobnjak, M.; Kakonen, S.M.; Massague, T.A. A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. J Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, C.; Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Evaluation of caspase activity in apoptotic cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 265, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyavani, K.; Ramanathan, T.; Gurudeeban, S. Plant mediated synthesis of biomedical silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Citrullus colocynthis. Res. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, C.L.; Hoffman, D.R. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of hymenoptera venom and venom sac extracts. Toxicon 1983, 21, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, I.-M.; Rahuman, A.A.; Marimuthu, S.; Kirthi, A.V.; Anbarasan, K.; Rajakumar, G. An Investigation of the Cytotoxicity and Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Effect of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata on Human Liver Carcinoma Cells. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1317-1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031317
Chung I-M, Rahuman AA, Marimuthu S, Kirthi AV, Anbarasan K, Rajakumar G. An Investigation of the Cytotoxicity and Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Effect of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata on Human Liver Carcinoma Cells. Nanomaterials. 2015; 5(3):1317-1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031317
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Ill-Min, Abdul Abdul Rahuman, Sampath Marimuthu, Arivarasan Vishnu Kirthi, Karunanithi Anbarasan, and Govindasamy Rajakumar. 2015. "An Investigation of the Cytotoxicity and Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Effect of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata on Human Liver Carcinoma Cells" Nanomaterials 5, no. 3: 1317-1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031317
APA StyleChung, I.-M., Rahuman, A. A., Marimuthu, S., Kirthi, A. V., Anbarasan, K., & Rajakumar, G. (2015). An Investigation of the Cytotoxicity and Caspase-Mediated Apoptotic Effect of Green Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Eclipta prostrata on Human Liver Carcinoma Cells. Nanomaterials, 5(3), 1317-1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano5031317