Abstract
Conjugation of multiple nanomaterials has become the focus of recent materials development. This new material class is commonly known as nanohybrids or “horizon nanomaterials”. Conjugation of metal/metal oxides with carbonaceous nanomaterials and overcoating or doping of one metal with another have been pursued to enhance material performance and/or incorporate multifunctionality into nano-enabled devices and processes. Nanohybrids are already at use in commercialized energy, electronics and medical products, which warrant immediate attention for their safety evaluation. These conjugated ensembles likely present a new set of physicochemical properties that are unique to their individual component attributes, hence increasing uncertainty in their risk evaluation. Established toxicological testing strategies and enumerated underlying mechanisms will thus need to be re-evaluated for the assessment of these horizon materials. This review will present a critical discussion on the altered physicochemical properties of nanohybrids and analyze the validity of existing nanotoxicology data against these unique properties. The article will also propose strategies to evaluate the conjugate materials’ safety to help undertake future toxicological research on the nanohybrid material class.
1. Introduction
Richard Feynman’s “plenty of room at the bottom” vision inspired the synthesis and manipulation of nano-scale materials to achieve unique physical, chemical and electronic properties for a wide range of applications [1]. As commercial materials demanded higher performance and needed to display multiple functions simultaneously, materials research had to shift its focus from singular nanomaterials (NMs) to hierarchical ensembles [2,3,4]. Such nano-scale conjugates are commonly termed nanohybrids (NHs), which bring together atypical combinations of metals, metalloids and carbon-only nanostructures with unique soft and hard external coatings [2,5,6,7]. The pursuance of such ensembles has expanded the scope of applications [8,9] and resulted in a very large set of new materials with unknown environmental and health risks. Therefore, it is critical to develop an effective strategy for assessing the safety of this large and ever expanding set of NH materials.
The primary motivation of NH synthesis was to create composite materials that exhibit the enhancement of the component properties. For example, in the field of nuclear medicine, chelated radioisotopes of different metals are used despite their kinetic instability and release of toxic metals within the body [10]. Incorporation of such metals within fullerenes, known as endohedral metallofullerenes (EMFs) [5], makes the ensembles highly stable and provides an excellent alternative to the current options [5,10]. Such NHs are applied in a wide range of applications, including biomedical products and devices (e.g., nuclear medicine, drug delivery, cancer therapy [11,12]), electronic applications (e.g., nanoelectronics [13], super-semiconductors [14,15] and optoelectronics [16]), renewable energy (e.g., solar cell technologies [17,18,19], electrochemical fuel cells [3,20,21], catalysts [3,7,22]) and environmental remediation [23,24,25]. The effectiveness of conjugation thus realized continues to broaden the scope of ensemble applications, manifesting unique physical, chemical and biological properties. Such a wide application scope increases the likelihood of exposure and associated risks, as aquatic systems have a high potential for acting as a ‘sink’ for environmental contaminants. This increased production of NHs and the potential for exposure raises an obvious question: do the established nanotoxicological theories and testing strategies for aquatic systems hold true for these ensembles with emergent properties?
The field of nanotoxicology emerged from the study of particulates [26,27,28]. Historically, deleterious effects from exposure to ultrafine particles, e.g., PM10, PM2.5, as well as from mineral fibers, such as asbestos, raised safety concerns and resulted in comprehensive evaluation of their effects on environmental and human health. Particulate toxicology evolved through classical toxicity investigations utilizing both in vivo and in vitro techniques. Inhalation, instillation and oral exposure with endpoints of mortality, metabolic changes, biodistribution within the species body, reproductive and other physiological behavioral changes were evaluated during in vivo studies [29,30,31,32,33]; while cellular level studies concentrated on uptake, cell viability, DNA structural damage, immunogenicity and apoptosis [34,35]. Such detailed investigations were feasible due to a limited set of variables on the particulate side, which was severely compromised after the advent of nanotechnology. New particles with unique sizes, shapes, chemical identities and a variety of surface functionalization brought forward new challenges in evaluating the particulate-based toxicological effects of a widening set of nano-scale materials. The toxicological community has focused on revealing the mechanisms of toxicity and identifying key physicochemical properties, e.g., size, shape, surface chemistry and dissolution, that contribute to the observed toxic responses [36,37,38,39], thus narrowing down the scope of work. As the materials field moves from singular NMs to conjugated NHs, similar challenges reappear; i.e., what properties should the toxicological community now be concerned about? Will the NHs elucidate properties that can be described as a summative product of the individual components, or will novel emergent properties surface due to such conjugation? These questions center on recent literature presenting evidence of the altered and novel properties of such NHs.
Most NHs are composed of NMs with unique chemical origin or physical properties. When conjugated, the resultant properties of the ensembles are expected to be different. It is also likely that during hybridization, one or more of the components’ properties will become dominant, which can be a function of the mode of conjugation or the synthesis procedure. Such changes may be manifested in their resultant size [40], shape [41,42], crystalline structure [41,42], surface chemistry [43], dissolution properties [44], sorption characteristics [45], band-gap energetics [46], oxidation resistance [40], etc. Furthermore, the emergence of unique and novel properties are also likely; e.g., unique physical and mechanical behavior, enhanced reactivity and localized changes in chemical or electronic properties can emerge, which have not been highly considered as governing parameters for toxicity determination. Bimetallic core-shell NHs have been generated possessing simple spherical [47] to cubic [41], rod-like [41], plate-like [42], triangular [48] or triangular-bipyramidal [41] structures. Complex polyhedral [49], bipyramidal [50] and dumbbell [51] configurations have also resulted from hybridization. Hierarchical three-dimensional (3-D) exotic nano-structures are also obtained when exohedral conjugation occurs between zero-D fullerene, 1-D carbon nanotube and/or 2-D graphene plates [52,53].
Similarly, mechanical properties, such as stiffness, have also shown to be altered due to fullerene insertion in nanopeapods [53,54]. Moreover, bandgap modulation and variation in electronic attributes due to the insertion of fullerene onto carbon nanotubes are also observed [46]. Similarly, reactivity has been altered due to conjugation; titanium dioxide hybridized with platinum to form binary electrocatalyst has been shown to induce a strong metal support interaction (SMSI) phenomenon [55,56], resulting in altered sorption properties. The emergence of such novel properties or alterations to the known physicochemical characteristics of individual nanoparticles will most certainly affect NHs’ environmental interactions [43,57], compared to what has been observed with component materials [26,34,58,59]. However, as NH synthesis infers infinite combinations of individual NMs to obtain a large set of NHs, there is a critical need to formulate effective research strategies for assessing the environmental health and safety of this ever-expanding material class.
This paper describes the most common NHs being produced, identifies a few of their emergent properties and presents their potential implications for nanotoxicity in aquatic systems. We have focused this review on aquatic ecosystems, as with increasing use, NMs, including NHs, are likely to find their way into such environments, where they may impact relevant species. The article will introduce NH properties as per material classification and highlight key toxicity end-points for aquatic organisms and microbes, with a specific focus on metals/metal oxides and carbonaceous materials. Considerations for toxicity evaluation of NHs are described in light of the identified properties.
2. Classification, Applications and Characterization of Nanohybrids
NHs can be classified on the basis of their parent materials, i.e., whether the component materials are organic/inorganic or metallic/carbonaceous. For the scope of this review, NHs are mainly categorized into four classes: carbon-carbon NHs (CCNH), carbon-metal NHs (CMNH), metal-metal NHs (MMNH) and organo-metal-carbon NHs (OMCNH). Such classification is useful to identify key properties of the NHs, relevant to their safety, however, not necessarily the only basis for classifying these nano-ensembles. CCNHs are synthesized by conjugating multiple carbonaceous NMs with different geometry; i.e., carbon nanotubes (single-walled or multiwalled), fullerenes or graphene [52,60]. When such carbon-based NMs are combined with their metallic counterparts, the conjugates can be classified under the CMNH category [61,62,63]. Such metal and metal oxide NMs include gold [64], silver [65,66], titania [67,68], zinc oxide [69,70], alumina [71] and iron oxides [72]. Two or more metal-based NMs may also be hybridized, either by chemical attachment or by overcoating, to prepare MMNHs [73]. Moreover, synthetic macromolecules (e.g., drug molecules, proteins, dyes and other long chain polymers), enzymes and proteins are utilized to generate carbon- or metal-based NHs that can be classified under the OMCNH category. Conjugation and/or overcoating processes to generate NHs offer unique properties tailored toward a wide range of applications. Table 1 presents a summary of such applications that include: processes and devices for electronic and energy industries, biomedical applications, environmental remediation, catalytic processes, construction materials, lubrication, heat transfer and others.

Table 1.
Types and current applications of nanohybrid materials.
| Broad Application Areas | Specific Applications | NH Class | Specific Types | Citation | Environmental Exposure Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics and energy | Field effect transistors | CCNH | Fullerene-CNT peapods | [46,74,75] | Leachate; surface water |
| Graphene-CNT hybrid | [76] | ||||
| CMNH | Graphene-ZnO hybrid | [77] | |||
| Graphene nanosheet/metal nitride hybrid | [78] | ||||
| OMCNH | Graphene-organic molecule hybrid | [79,80] | |||
| Poly(3-hexylthiophene)-fullerene hybrid | [81] | ||||
| Energy storage/supercapacitors | CCNH | Graphene oxide-CNT peapods | [82] | ||
| CMNH | MnO2/CNT hybrid | [83] | |||
| CNT/RuO2 hybrid | [84] | ||||
| Graphene-Mn3O4 | [85] | ||||
| Lithium ion batteries/storage | CCNH | Fullerene-CNT peapods | [86] | ||
| Graphene-CNT hybrid | [87,88,89] | ||||
| Carbon nano-onions | [90] | ||||
| CMNH | Graphene-TiO2 hybrid | [91] | |||
| MMNH | ZnO-Au hybrid | [92] | |||
| Transparent conductive films | CCNH | CNT-graphene exohedral hybrid | [76,93,94] | ||
| Fullerene/CNT/graphene-oxide hybrid | [95] | ||||
| CMNH | SWNT-Au | [96] | |||
| MMNH OMCNH | Ag/TiO2 nanowire | [97] | |||
| Graphene-Ag nanowire | [98] | ||||
| Photovoltaics | CCNH | Graphene-fullerene hybrid | [99,100,101,102] | ||
| Optical limiting devices | CMNH | CNT-fullerene | [103] | ||
| ZnO-graphene quantum dots | [104] | ||||
| Graphene/TiO2 | [105] | ||||
| MMNH | Ag/TiO2 nanowire | [106] | |||
| OMCNH | Fullerene/CNT with porphyrins/phthalocyanines | [107] | |||
| dihydronaphthyl-fullerene | [108] | ||||
| CCNH CMNH | Graphene-fullerene hybrid | [109] | |||
| Fullerene-CNT | [110] | ||||
| MWNT-ZnO NH | [111] | ||||
| MMNH | Au@TiO2, Au@ZrO2, Ag@TiO2, and Ag@ZrO2 core-shell NHs | [112] | |||
| Fuel Cell | OMCNH | Oligothiophene-graphene, porphyrin-graphene | [13,113] | ||
| MMNH | Pt-Pd | [114] | |||
| CCNH | Graphene-CNT exohedral hybrid | [115] | |||
| CMNH | CNT/TiO2-Pt | [116] | |||
| Pt-reduced graphene oxide | [21] | ||||
| MMNH | Pd-Cu | [117] | |||
| Biomedical | Bioimaging and cancer therapy | CMNH | Quantum dot-Fe3O4-CNT | [118] | Atmosphere |
| MMNH | Au-Fe shell-core | [119,120] | |||
| MRI agents | CMNH | Gadofullerene | [121,122,123] | ||
| Drug delivery | CCNH | Fullerene-CNT | [124] | ||
| CMNH | Quantum dot-Fe3O4-CNT | [118] | |||
| MMNH | Au-Fe3O4 | [125] | |||
| OMCNH | Pluronic F-127/graphene | [126] | |||
| Parclitaxel-Au | [127] | ||||
| Environmental monitoring and remediation | Chemical sensing | CCNH | Carbon nanotube-graphene nanosheet hybrid | [128] | Leachate |
| CMNH | Pt-graphene | [129] | |||
| MWNT-zerovalent iron | [130] | ||||
| Graphene-iron | [131] | ||||
| Graphene-ZnO | [132] | ||||
| MMNH | Au-Ag | [133] | |||
| Pt/TiO2 nanotube | [134] | ||||
| OMCNH | Hematoporphyrin-ZnO | [135] | |||
| Biosensors | CCNH | Reduced graphene oxide-MWNT | [136] | ||
| Gas sensors | CCNH | Graphene-CNT hybrid | [137] | ||
| Contaminant degradation | CMNH | CNT-TiO2 | [138] | ||
| ZnO-reduced graphene oxide | [139] | ||||
| Pathogen detection | MMNH | Fe3O4-Au-Fe3O4 nanodumbbelland Fe3O4-AuNR nanonecklace | [140] | ||
| Au-Ag | [141] | ||||
| Antimicrobial | CMNH | CdSe-Au | [142] | ||
| Graphene-ZnO | [132] | ||||
| Ag-graphene oxide | [143] | ||||
| Heavy metal removal | CCNH | Carbon nano-onions | [144] | ||
| Bio-imaging | CCNH | Carbon nano-onions | [145] | ||
| Catalysis | Catalyst support/catalyst | OMCNH | CNT-enzyme | [146] | Atmosphere; leachate |
| CCNH | N-doped CNT-graphene peapods | [147] | |||
| CMNH | CNT/Pd | [148] | |||
| Graphene-Au | [149] | ||||
| MMNH | Au-Pd core-shell structure | [150] | |||
| Construction industry | Nano-reinforcement in composites | Pt/Pd-Fe/TiO2 | [114] | leachate | |
| CCNH | CNT-Graphene nanoplatelet hybrid | [151] | |||
| Structural health monitoring | CCNH | CNT-graphene nanoplatelet hybrid | [152] | ||
| Miscellaneous | Antimicrobial coating/paint | CCNH | Carbon nano-onions | [153] | Leachate |
| Temperature sensor | CCNH | Azafullerene-CNT peapods | [154] | - | |
| Heat transfer | CCNH | Graphene wrapped MWNT | [155] | - |
Abbreviations: CCNH, carbon-carbon nanohybrid (NH); CMNH, carbon-metal NH; OMCNH, organo-metal-carbon NH; MMNH, metal-metal NH; CNT, carbon nanotubes; SWNT, single walled carbon nanotubes; MWNT, multi walled carbon nanotubes.
Such a widespread application of NHs necessitates a careful evaluation of their toxicity to aquatic organisms. Systematic evaluation of NM toxicity requires detailed physicochemical characterization. Most characterization techniques utilized for singular NMs are also applicable to NHs [156]. Key physicochemical parameters that are relevant to toxicity include: particle size distribution, morphology, surface potential, wettability, concentration, the presence of functional groups, adsorption properties, band gap energetics, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and metal dissolution. These parameters are characterized using electron microscopy, e.g., transmission, scanning and scanning tunneling electron microscopy; several spectroscopic techniques, UV-Visible, atomic absorption, Raman, Fourier transformed infrared, X-ray photoelectron, and energy dispersive spectroscopy; interfacial characterization tools, e.g., electrophoretic mobility and dynamic and static light scattering; thermo-gravimetric analysis and inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy for metal dissolution. However, hybridization will likely alter some of these inherent properties or present emergent novel properties that are not typically manifested by singular NMs. Thus, it is to be ensured that classical characterization techniques utilized for singular NM characterization are appropriately adjusted to measure altered and emergent properties presented by these conjugated NHs.
3. Key Properties Relevant to Toxicity
The near-atomic size factor of NMs enhances their interaction with biological species, organs, tissues and cells and has manifested unique toxicological responses [26,157]. Moreover, due to their large surface area to volume ratio, NMs provide reactive surfaces influencing particle-particle and cell-particle interactions [26,27]. Unique toxicological responses from NMs have been correlated to their geometry, chemical composition, chemical stability, and surface chemistry [26,27]. In addition to these common determinants, the release of dissolved ionic species from metallic NMs are also known to impart biological stress [158]. This section identifies potential alterations to well-known NM physicochemical attributes and the manifestation of novel emergent properties resulting from hybridization that will likely influence the toxicological outcomes of NHs.
3.1. Alteration of Well-Known NM Properties Relevant to Toxicity
3.1.1. Bandgap Energetics, Photocatalytic Activity and ROS Generation Potential
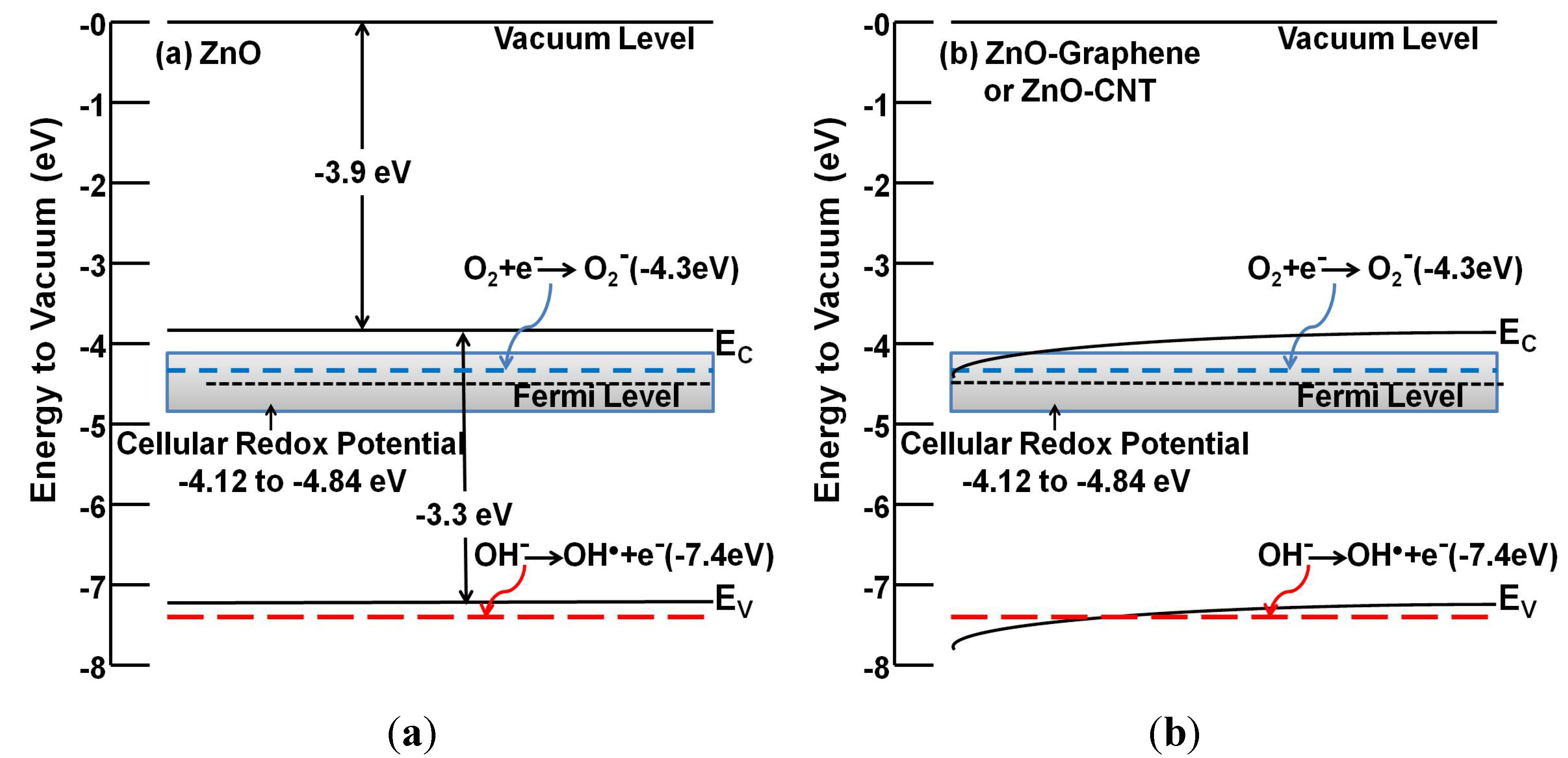
Cellular toxicity resulting from exposure to carbonaceous and metallic NMs is known to be mediated by oxygen-containing radicals, such as peroxides and singlet-oxygen, collectively known as reactive oxygen species or ROS [159]. ROS generation depends on the photo- and catalytic-activity of NMs dictated by their electronic properties [160]. A ROS-mediated toxicity paradigm of metal oxide NMs hypothesizes that a surface’s ability to generate oxidative stress is directly correlated to the energetic positioning of its conduction band (Ec) with respect to cellular redox potential [161,162]. When the Ec overlaps with the cellular redox potential, the nanomaterials quench the reducing capacity of antioxidants present in the cell, such as glutathione. NM hybridization significantly alters the electronic properties through band bending (Figure 1) and, thus, can display altered cellular toxicity.
One of the key reasons to design and develop NHs is to tune the bandgap for achieving the desired electronic and photoactive properties for applications in solid-state electronics [46] or pollutant degradation [63]. However, differences in the mode and extent of hybridization and the materials utilized can contribute to the differences in band-structure alterations, which can subsequently cause uncertainty in the shift of conduction band (Ec) positioning. Such an Ec shift can cause overlap with the cellular redox potential and can mediate ROS generation ability. Figure 1 shows the bandgap energy diagram of (a) ZnO NM and (b) ZnO-graphene or ZnO-CNT NH. Ec for ZnO is positioned at −3.9 eV (Figure 1a), which resides outside the cellular redox potential range of −4.12 eV to –4.84 eV [161]. When conjugated with carbonaceous nanomaterials, e.g., CNTs or graphene, the excellent charge transfer and separation characteristics of carbonaceous nanomaterial causes band-bending of ZnO toward the CNT/graphene work function (−4.3 to −5.0 eV), as shown in Figure 1b [163,164]. Such band-edge movement causes the overlap of the Ec position with the cellular redox potential, thus likely causing increased photocatalytic activity, ROS generation and cytotoxicity from ZnO-graphene NHs [132,165]. Therefore, systematic evaluation of the altered band structure can hold the key to precise understanding of the ROS generation potential and the corresponding nanotoxicity.
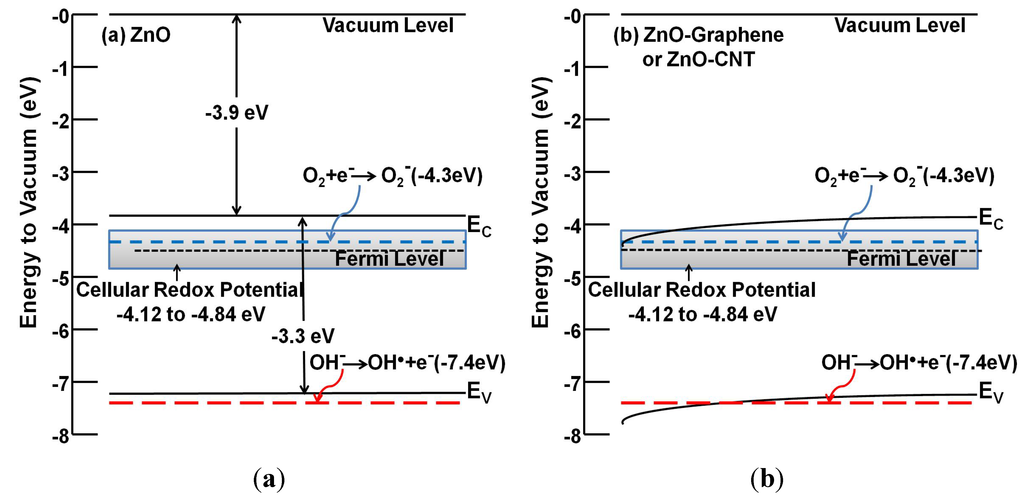
Figure 1.
Bandgap energetics diagram of (a) ZnO and (b) ZnO-graphene or ZnO-CNT NH. The diagrams also show the relative energetic positions of the cellular redox potential (−4.12 to −4.84 eV) and relevant oxygen species (superoxides and hydroxy radicals).
Figure 1.
Bandgap energetics diagram of (a) ZnO and (b) ZnO-graphene or ZnO-CNT NH. The diagrams also show the relative energetic positions of the cellular redox potential (−4.12 to −4.84 eV) and relevant oxygen species (superoxides and hydroxy radicals).
3.1.2. Dissolution Characteristics
Metal dissolution from metallic (e.g., Ag) and metal oxide (e.g., ZnO) NMs is also well-known to affect toxicity towards microbes [166], aquatic invertebrates and vertebrates [167] and higher trophic level species [168]. Hybridization of metal NMs can alter dissolution properties and, thus, can impact toxicological consequences. For example, dissolution of highly reactive Ag is reduced if protected by a thin layer of relatively inert gold (Au), irrespective of the Ag:Au ratio in the NH [44]. On the contrary, rapid dissolution of Ag is observed under physiological conditions if it surrounds an Au core [169]. Similarly, conjugation of carbonaceous NMs with metallic ones may change their dissolution chemistry, as observed in the case of Ag dissolution, where the rate of Ag+ ion production is decreased (leading to long-term antimicrobial actions) when conjugated with graphene nanosheets using polymeric linkers [170]. Thus, variability in dissolution properties introduced via the hybridization of NMs will likely influence nanotoxicological responses in aquatic organisms.
3.1.3. Surface Chemistry
NMs’ surface functionality and chemistry control their environmental toxicity on the basis of their sorption or reactivity with the cell-membrane proteins, lipids or polysaccharides [171,172]. When NMs are hybridized, the surface characteristics become altered due to the incorporation of functional moieties, solvent effects, surface coating, bonding characteristics and linking molecules that conjugate multiple nanomaterials [156] and will likely influence NH-cell interaction. For example, nanopeapods that encapsulate fullerenes within SWNT cylindrical structures may prevent the direct interaction of fullerenes with cells or aquatic species, whereas exohedral fullerene-CNT NHs or nanobuds will likely present both CNT and fullerene surfaces to biological species, modulating toxicological responses in a more profound way [52,156]. The chemistry and nature of bonding between fullerenes and CNTs will also play a significant role in the toxicity of the NHs. Seamless conjugation of fullerene-CNT by covalent bonding produces less soluble hybrids (i.e., nanobuds) than those conjugated via organic linkers, creating non-covalent bonds between CNT and fullerenes [156]. This difference in solvent affinity will have implications in hydrophobic interactions during NH-cell interactions. Additionally, organic-carbonaceous hybrids, such as MWNT-porphyrin conjugates, introduce toxic moieties that can increase antimicrobial effects (when compared to pristine MWNT), via ROS-mediated cell damage under visible irradiation [173]. Thus, the presence of multiple reactive surfaces with changes in bond structure between multiple NMs, as well as the presence of unique inorganic/organic moieties will influence NH toxicity.
3.2. Emergence of Novel Toxicological Properties for NHs
3.2.1. Dimensionality and Surface Morphology
NM shape and size have been established as key physicochemical parameters for their toxicological responses enabled by their underlying surface area and morphological effects [36,174,175,176]. However, these properties are dependent on the dimensionality of the material; i.e., whether it is zero-dimensional (fullerenes or spherical metals), one-dimensional (CNTs or metal nanorods) or two-dimensional (graphene or plate-like metal NPs). For example, CNTs’ needle-like appearance can induce increased toxicity compared to the globular or planar structures of fullerenes or graphene, respectively [174,175]. However, when these NMs are conjugated, altered dimensionality is the most obvious consequence, dictated by the types of parent material and the mode of conjugation. For example, when fullerenes or graphene are incorporated endohedrally within the hollow structure of a CNT, e.g., nano-peapods, the one-dimensional CNTs will likely mask the zero or two-dimensionality of the fullerenes [177] or graphene [147]. Furthermore, exohedral or outer surface conjugation of carbon-based nanostructures can result in unique three-dimensional structures, as observed in the case of nanobuds [52,178], other hierarchical configurations (e.g., grapevine-like fullerene-CNT NHs [103], or multilayered CNT-graphene NH [89] structures). The role of dimensionality here can be realized as the presentation of the altered geometry of the NHs to cells and tissues. For example, CNTs’ well-known asbestos-like [179] or fullerenes’ ROS-dependent toxicity [180] might be further reinforced by membrane disruption dynamics, due to the edge roughness of graphene [181] when conjugated as a single NH unit. Similarly, metal NMs when decorated on 2-D graphene or 1-D CNT surfaces can lead to less agglomeration, resulting in increased available reactive surface area and, thus, can alter cellular interactions. Moreover, polydispersity and different shapes of metal NMs (from cubic or spherical to dumbbell shaped or flowerlike structures) conjugated on the CNT/graphene surfaces will generate a wide-array of diverse surface morphologies, possibly modulating the cytotoxicity of these unique NHs. Thus, dimensionality can serve as one of the emergent parameters, causing unpredictability in biological responses from NH exposures.
3.2.2. Mechanical Properties
Hybridization of NMs, particularly CNTs with other structures, affects their mechanical properties; i.e., mechanical stiffness, bendability/curling ability, etc. CNTs are known to have excellent compressive, tensile and flexural strength [182]. Encapsulation of fullerenes has been shown to increase the bending strength of SWNTs [183], resulting in stiffer tubules [54]. On the contrary, the elastic moduli of graphene nanosheets are predicted to decrease, due to fullerene conjugation on the planar surfaces when estimated via molecular dynamics simulations [184]. On the other hand, graphene exhibits enhanced mechanical properties when decorated with AgNPs, displaying increased tensile strength and a Young’s modulus by 82% and 136%, respectively [185]. Such evidence indicates that NH mechanical properties will likely be different than their parent materials; such emergent behavior may lead to novel physical interactions, as well as unique particle-particle interactions during exposure to biological organisms.
3.2.3. Synergistic Properties
One of the key underlying reasons for conjugation or hybridization is to acquire synergy between multiple functionalities of NMs; i.e., the conjugation of two or more NMs manifests enhanced- or multi-functionality, which otherwise may not be attainable. Therefore, removing one component from the NH will compromise the synergy between multiple properties. For example, unique hierarchical structures, like Ag-supported-graphene-wrapped-ZnO (Ag-graphene-ZnO NH), can display synergistic functionality. Photoactive ZnO produces charges (i.e., electron-hole pairs) under illumination, while highly conductive graphene helps to increase the degree of charge separation and prevent recombination and Ag acts as an electron sink, improving the photodynamic degradation of pollutants [186]. While synergism in NHs may be beneficial for applications, its contribution towards toxicity and cellular interaction should not be ignored. For example, combinatory biocidal and photocatalytic activity in the dark and illuminated conditions is observed in Ag-TiO2 core-shell formulations [187]. In this case, TiO2 not only protects the AgNPs from fast dissolution (long-term antimicrobial actions), but also serves as an AgNP carrier to bacterial entities. Moreover, Ag+ dissolution accompanied by the evolution of ROS from photoactive TiO2 presents synergism in combined bactericidal performance [188]. Such properties that work in sync are unique to this horizon NH material class and necessitate a fundamental understanding of their effects on aquatic species.
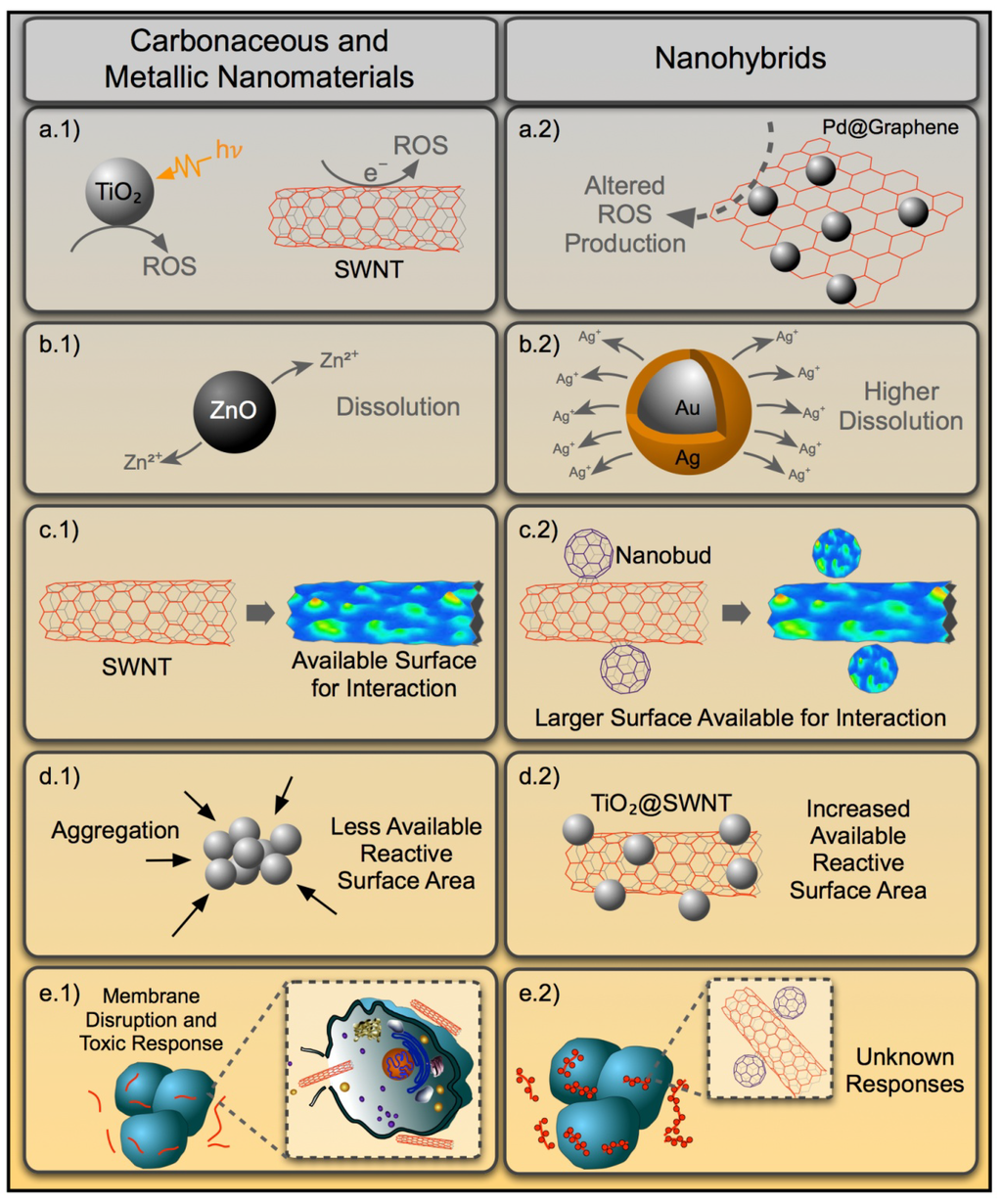
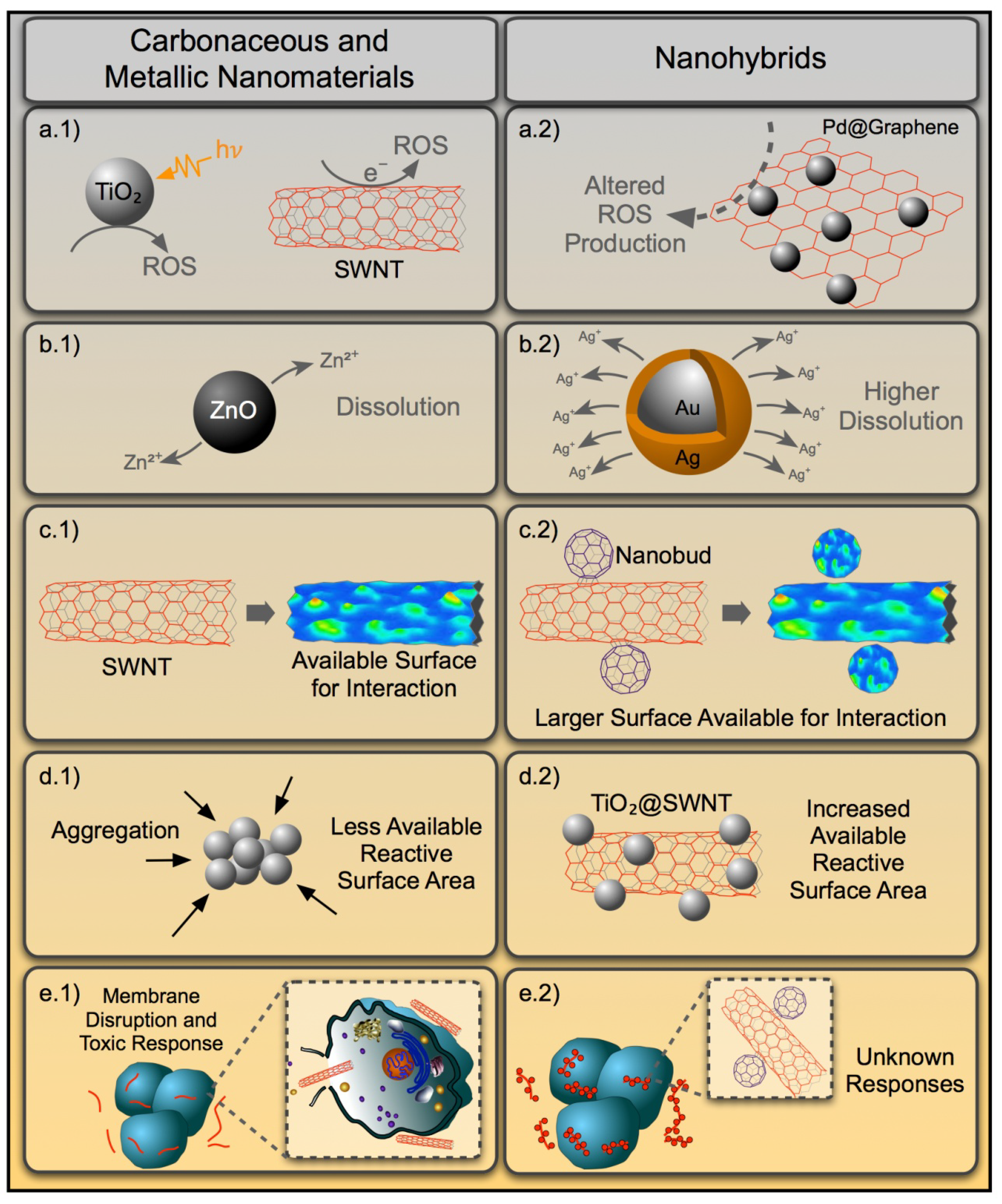
Figure 2.
Diagram showing the relevant properties of carbonaceous and metal NMs that are associated with toxicity (right panels, a.1–e.1). How these properties might be altered for nanohybrid materials is displayed in the corresponding left panels (a.2–e.2).
Figure 2.
Diagram showing the relevant properties of carbonaceous and metal NMs that are associated with toxicity (right panels, a.1–e.1). How these properties might be altered for nanohybrid materials is displayed in the corresponding left panels (a.2–e.2).
4. Toxicological Implications for NHs Based on Current Biological Effects and Mechanisms of Action
4.1. Aquatic Nanoparticle Toxicity Testing Strategies
Compared to assessments on mammalian models, fewer studies have investigated the impact of NHs on the health of aquatic organisms to try and understand the toxicity and modes of action of singular NMs. It is only prudent to assess the potential implications from NHs by evaluating component material impacts. It is to be noted, however, that due to the sheer diversity in NM types and associated variables (metal content, purity, size, shape, surface chemistry) and combinations, the toxicity data can be quite challenging to consolidate and interpret for a given NH [189]. Two types of singular NMs that have been a prominent focus of study in aquatic toxicology are metal- and carbon-based NMs. For metals, most studies have focused on TiO2 [190], Ag [191], ZnO [31] and CuO [192] nanoparticles, with a smaller subset examining quantum dots [193], Al [194], Ni [195], Ce [196], Fe [197] and Au [198] particles. The carbonaceous materials primarily investigated include multiple types of carbon nanotubes (i.e., SWNTs vs. MWNTs) [199], graphene [200] and fullerenes [201]. Possible toxicological implications for hybridization of carbonaceous and metallic NMs to make different NHs have been summarized in Figure 2. Detailed description of such properties' alteration has been provided in the previous section. In this section, we review what has been learned with regard to the biological effects and mechanisms of action (MOA) in aquatic species exposed to these select types of singular NMs. We additionally discuss the application of such knowledge to NH toxicity testing in light of the potential for NHs to possess new emergent properties.
In the field of aquatic toxicology, traditional animal models of study found throughout the literature include pelagic invertebrates (Daphnia sp.), benthic invertebrates (Hyalella azteca), large (i.e., Rainbow trout) and small (i.e., fathead minnow, P. promelas) fishes and a number of algae species [202]. Researchers have also utilized models that allow for the testing of specific endpoints (such as development in zebrafish, Daniorerio [203]) or species-specific effects on marine algae and invertebrates [204], plants [205], emergent insects [206], filter feeding organisms [207] and snails [208], among others. As each nanoparticle has its own set of unique properties, as discussed above, the selection of an appropriate test organism and exposure route can maximize our understanding of the potential effects. This can pose quite a challenge, as we have a poor understanding of which NMs and in what concentrations they will be found in the aquatic environment.
4.2. Biological Mechanisms of Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Toxicity
While information about the acute and chronic overt toxicity of metal nanoparticles is important for understanding the risk these materials pose, elucidation of the underlying mechanisms of toxicity may help us mitigate these risks more effectively. Studies on these mechanisms have proposed a diverse array of potential targets. The most widely probed mechanism is oxidative stress as a result of the production ROS, as discussed earlier. While internal ROS production is a natural phenomenon in biological tissues, excessive ROS (from external sources) can cause oxidative damage and cell apoptosis. Exposure to TiO2, Ag, Zn and Al nanoparticles have all been shown to increase ROS by direct measurement in tissues of exposed organisms [203,209,210,211]. The measurement of lipid peroxidation (LPO) can also serve as an indicator of oxidative stress, as ROS can damage the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. Examples of metal nanoparticles increasing LPO include numerous fish species exposed to ZnO and TiO2 [212,213,214].
Plants and animals have natural defense systems to mitigate the effects of oxidative stress. Numerous antioxidants are produced to scavenge ROS and prevent potential damage, including super oxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase, catalase (CAT) and glutathione (GSH). Increased levels of these antioxidants have been used as biomarkers of oxidative stress in numerous studies, including tilapia exposed to Ag nanoparticles [215], carp exposed to ZnO [214], marine invertebrates exposed to CuO [204] and Daphnia magna exposed to TiO2 [216]. Measurement of the phase II enzyme responsible for the metabolism of GSH, glutathione s-transferase (GST), has also been used as a downstream indicator of oxidative stress [204,212]. Metallothionein, a protein involved in binding free metal and decreasing oxidative stress, has also been shown to be upregulated during metal nanoparticle exposure [217,218]. In addition to acting as biomarkers of exposure, disruption of natural antioxidant levels has also been proposed as a mechanism of toxicity. For example, Daphnia magna exposed to Cu nanoparticles exhibited an initial increase in antioxidants to combat oxidative stress, but over time, antioxidant production decreased, potentially due to extensive damage [219]. This phenomenon was also seen in the livers of fish exposed to TiO2 [212].
The measurement of oxidative stress biomarkers provides strong evidence of metal nanoparticle exposure, but the measurement of downstream effects can provide biomarkers of the effect for these materials. Studies have shown that TiO2, Ni and Ag nanoparticles caused membrane breakage, leading to decreased membrane integrity [195,209,220]. Differential production of Na/K ATPase during nanoparticle exposure may also be indicative of the loss of cell homeostasis [213,221,222]. Irritation of the gills of zebrafish by Ag and Cu nanoparticles led to increased gill filament width, which could cause respiratory distress [192,223]. Though a large majority of mechanistic studies have focused on the mechanisms of toxicity in animals, a few researchers have examined toxic mechanisms in plants and phytoplankton. In addition to some of the biomarkers of exposure described above, depletion of chlorophyll content and decreased photosystem II activity are commonly measured biomarkers of the effect as a result of exposure to Ag, Cu, Zn and Cu nanoparticles [224,225,226].
It is important to note that many of the properties of metal-based NMs that cause oxidative damage to aquatic species make these materials valuable for manufacturers as antimicrobial agents [227]. However, these properties may have unintended consequences in bacterial communities found in our wastewater treatment plants and aquatic ecosystems [228]. ROS production in particular has been shown to cause general oxidative stress in a number of bacterial species, as well as lipid and protein oxidation, DNA/RNA damage and the interruption of cell signaling pathways [229].
Perhaps the most difficult aspect of examining the aquatic toxicity of metal nanoparticles is assessing the contributions of dissolved metals from the particles, and the particles themselves have on toxicity. Many studies have attributed the toxicity of metal nanoparticles to the dissolved fraction [38,191], while others hypothesize that particles and dissolved ions may have individual and potentially different, toxic mechanisms [192,230]. The mechanical separation of intact particles from dissolved ions allows for researchers to examine the individual contribution of each metal species on toxicity [231]. For example, Griffit et al. [192] exposed zebrafish to Cu nanoparticles, as well as ionic copper. The dissolved fraction of copper was not enough to explain the toxicity of the copper nanoparticles, and gene expression profiles between the two exposure scenarios showed differential modes of action, suggesting that nano-copper toxicity involves more than just dissolved copper toxicity.
Though intact nanoparticles and their dissolved ions may have individual contributions to toxicity, it is also possible for metal nanoparticles to act as catalysts for the increased toxicity of different metals. Wang et al. 2011 [232] showed that the combination of arsenic (As) with TiO2 particles caused higher toxicity than equivalent individual exposures, with a similar response seen in the presence of Al particles [222]. Researchers have shown that metals can bind to TiO2, which may facilitate increased internalization and, therefore, increased toxicity [221,233].
While direct interactions of metal nanoparticles and their dissolved ions with biochemical targets present numerous toxic mechanisms, physical interactions with organisms may indirectly cause toxicity. For example, TiO2 has been implicated in decreasing growth and reproduction in Daphnia magna, due to changing gut morphology and clogging the gut, which may, in turn, decrease nutrient uptake [234,235]. Ag nanoparticles also decreased food intake and digestion in snails, suggesting digestive damage [236]. Direct binding of TiO2, Ag and Ce nanoparticles to Daphnia magna carapace has also been hypothesized to interfere with normal molting activity [196,237]. Exposure to metal oxide nanoparticles has also been shown to decrease hatching success in zebrafish embryos [230,238]. One possible explanation is that dissolved ions from the particles freely diffuse through the embryonic chorion and chelate the enzyme responsible for breaking down the chorion (zebrafish hatching enzyme, ZHE1), rendering it inactive. As a result, larval fish cannot hatch and eventually die [239,240].
All of the above mechanisms may also be influenced by the presence or absent of numerous abiotic factors that likely influence the toxicity of metal NMs in aquatic systems, which include salinity, pH, temperature and the presence of divalent ions [202]. However, one factor that may have the greatest influence on NM toxicity is the presence of dissolved organic matter (DOM). This factor becomes key during NM transformation in the environment. For metal NMs, DOM in aquatic systems has been shown to influence both size and toxicity. In general, DOM helps to stabilize particles, effectively decreasing particle size and aggregation [241,242,243], and as a result, toxicity is typically reduced in the presence of DOM. This has been demonstrated for the metal NMs, Ag and TiO2 [241,242,244,245].
The influence of natural light on particle toxicity also cannot be ignored if toxicity tests are to represent environmentally realistic exposures, a property especially important for assessing metal toxicity. Select metal nanoparticles have been shown to have increased and decreased toxicity in the presence of UV light. TiO2 exhibits strong photoreactivity by the formation of reactive oxygen species in the presence of ultraviolet light [246]. While this property may be favorable for applications, such as anti-microbial coatings, the photocatalysis of TiO2 has been shown to increase toxicity in aquatic organisms [242,243,247]. UV light has also been shown to influence particle size and resulting toxicity, though results have been contradictory. Poda et al. [241] showed that UV lights caused the oxidation of PVP coatings on silver nanoparticles, which, in turn, caused a decreased particle size and increased dissolution, while Shi et al. [248] showed that sunlight caused an increased particle size and particulate deposition. In both cases, the addition of UV light decreases the toxicity of Ag particles, though the hypothesized mechanisms differed.
4.3. Biological Mechanisms of Carbon Nanoparticle Toxicity
Current research centered on the toxicity of carbon NMs in aquatic organisms has been minimal compared to mammalian systems, where there has been a heavy emphasis on carbon nanotubes and their pulmonary exposures and effects [249]. The primary carbon NMs that have been studied in aquatic organisms include SWNTs, MWNTs, fullerenes and graphene. The toxic effects of these materials have been evaluated in a number of species, including microbes, invertebrates (daphnia, snails, mussels) and a number of fishes. Similar to metal NMs, the primary biological MOA that has been most commonly evaluated for these materials is oxidative stress, which is typically assessed in concert with mortality, survival, growth and reproduction. However, this mechanism has not been met without controversy, as some reports have emerged that suggest organisms can manage oxidative stress and that other more subtle MOAs should be considered. It has also been proposed that the chemicals used to suspend carbon NMs (i.e., surfactants) may be a significant contributing factor to oxidative-mediated mechanisms [250]. A few studies have additionally investigated impacts on cell membrane integrity and immune parameters, such as the modulation of the expression of genes, IL-1β and INFα, in trout macrophage primary cells exposed to carbon nanotubes [251].
Understanding whether NMs are absorbed and distributed in biological systems is critical in defining toxicity and setting regulatory standards (i.e., limits of exposure). In general, this has been difficult to assess for carbonaceous nanoparticles, as we have limited availability of adequate analytical detection methods (reviewed by Edgington et al. [252]), which have made such assessments difficult. Due to the difficultly in tracking, detection and quantification of carbon NMs in aquatic organisms, most reports have relied on radiolabeled materials. Of the few studies performed to date, most agree that carbon nanomaterials are not readily absorbed into organisms through a dietary route. For example, separate studies collectively show that CNTs enter the gut of invertebrates (copepods, Daphnia), where they either accumulate or are eliminated with no evidence that they are absorbed across the gut epithelium [253,254,255,256]. More recent work by our group has utilized near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) imaging and quantitative methods to show similar results in fathead minnows exposed to SWNT by gavage [255].
Investigations of carbon nanoparticle toxicity have focused on a number of properties inherent to the particles, including shape and surface functionalization. Much of our understanding of shape effects comes from studies performed in mammalian systems, which show that the fibrous tube-like shape of CNT makes it easy for them to penetrate cell membranes. However, the majority of studies performed in aquatic organisms do not support that carbon nanomaterials are taken up into tissues. Only a few studies have performed comparisons of graphene and/or graphite and CNT in efforts to investigate shape effects on biological effects. For example, Kang et al. [257] tested the ability of CNT, nC60 and graphite to cause toxicity to multiple bacterial strains in wastewater effluent and driver water extracts. Results of this work reveal that graphite and C60 were less toxic, as measured by cell inactivation, compared to the SWNT. While a number of parameters likely contribute to this observation, the diverse shape of the particles should be considered as a contributing factor. Conversely, other studies have shown that graphene nanosheets with sharp edges cause considerable damage to bacterial cell membranes [258], implying that shape has an important influence on toxicity for some species.
One property that makes carbon nanomaterials of the same type (i.e., CNT) potentially distinct from a toxicological point of view is their surface chemistry. This property has been more widely studied compared to the influence of shape in aquatic models. Variations in surface chemistry can be tightly controlled during particle synthesis and include such variations as the addition of neutral, positive or negative functional groups. The impacts of such diverse surface modifications of CNT were shown in studies on Daphnia, where carboxylation of SWNTs increased toxicity, while functionalization with amine groups or poly-ethylene glycol (PEG) decreased toxicity. In the same study, the exposure of Daphnia to unfunctionalized fullerenes was associated with decreased reproduction and growth, which improved when the fullerenes were hydroxylated [259]. Interestingly, in a follow-up study, this same group showed that the toxicity profiles for aminated SWNT were not consistent in multigenerational effects. In fact, these SWNTs decreased survival or reproduction in F1 and F2 generation Daphnids [260].
Despite the lack of observed acute toxicity, absorption and systemic distribution, carbon NMs may pose more subtle health effects. Current theories of study include the ‘Trojan horse hypothesis’, which suggests that due to their sorptive nature, carbon NMs can interact with other more well-known chemical contaminants, which can then be transported into organisms through multiple means. While this hypothesis is being widely investigated in the drug delivery arena, few studies have been conducted that are relevant to aquatic systems. Conversely, the interaction of carbon NMs with such contaminants may limit their bioavailability, resulting in decreased toxicity. While a number of studies support the ability of CNTs, fullerenes and graphene to sorb well-known toxic chemicals, such as polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and xenoestrogens [261], only a few studies have probed the associated toxicity. In a study by Parks et al. [262], the sorption of SWNTs with PCBs was shown to decrease bioaccumulation and toxicity to benthic organisms. Similar results were observed in zebrafish hepatocytes co-exposed to fullerenes (C60) and metalloid arsenic (As(III)), where the overall As toxicity, as measured by oxidative stress, was diminished by the presence of C60 [263]. Furthermore, due to their sorptive nature, carbon NMs may produce a state of ‘nutrient depletion’ as an indirect mechanism of toxicity [264,265,266], as they sequester growth factors and other molecules necessary for good nutrition. It has been observed in mammalian studies that due to the sorptive nature of CNT, they are able to interact with proteins, growth factors and other molecules; however, this hypothesis has not been examined in aquatic models.
Similar to metals, the presence of DOM has been shown to influence both environmental fate and transport, as well as the toxicity of carbonaceous nanomaterials. A number of studies report that altering the pH varies the surface charge of carbon nanotube, which alters the way DOM coats the particles [267,268]. In essence, this ultimately changes particle stability in aqueous environments, typically resulting in increased aggregate size. Interestingly, DOM-suspended MWNT did indeed show increased aggregates; however, this modification of the MWNT did not result in an altered toxicity profile compared to non-DOM MWNT suspensions [267]. Conversely, studies performed on Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos show that while the toxic effects of Aqu/nC60 and raw MWNT were not altered with the addition of DOM, the adverse effects associated with exposure to nC60 (prepared in toluene) and acid-treated MWNTs were reduced [269]. A reduction in microbial toxicity has also been observed in microbes exposed to nC60 in the presence of DOM [270].
5. Application of Biological Effects of Constituent NMs to Understanding NH Toxicity
In assessing the health impacts of NMs, there has been a movement to understand the key properties of nanoparticles and the environmental influences that drive adverse health outcomes. As described above in the previous sections, studies have been heavily focused on the influence of DOM, dissolution (for metals), surface chemistry, shape and their relationship to oxidative stress, adsorption and gross endpoints, such as mortality and reproduction. While these studies provide important toxicological data for single NMs, this information may not be entirely applicable to predicting and understanding the potential toxicity of NHs. Hybridization of NMs will likely influence the toxicological responses of aquatic organisms. A focus of current testing strategies thus far has centered on correlating key attributes of NMs to select biological end-points. Thus, it is expected that the alteration of such toxicologically relevant properties or the introduction of novel emergent ones will significantly influence the potential health and ecosystem impacts of NHs. Oxidative stress imparted toward microbes or aquatic organisms is highly dependent on generated ROS and their specific types; i.e., superoxides, hydroxyl radicals or singlet oxygen. Thus, it follows that hybridization-induced changes in band-gap energetics that influence ROS generation will likely have an impact on toxic effects that include signal transduction, DNA damage, lipid peroxidation, enzyme dysfunction, mitochondrial oxidative disorder and apoptosis. In fact, changes in ROS production and subsequent toxicity implications of Fe NP for overcoated structures, i.e., for Fe/Ni, Fe/Pt, Fe/Pd and Fe/Cu, have already been reported in the literature [271]. As materials science communities continue to control band gap energetics through the production of NHs, particularly the conjugation of multiple metal/metal oxides or with carbonaceous surfaces, it will be important to assess altered ROS production by such novel materials and their impacts on aquatic species.
Similarly, dissolution products of NMs, e.g., from ZnO, CuO or Ag, can damage cell membranes via reaction with transport proteins, produce chelating compounds with essential intracellular proteins or alter cellular metal ion concentrations, resulting in organelle damage. These cellular consequences are highly dependent on the dissolved metal speciation and ion concentration. When hybridized, metal dissolution rates will likely become altered, either due to over-coating with a different metal of varying solubility or due to the increased surface area of metal NMs as a result of their controlled distribution over a secondary surface. A recent study showed the comparative toxicity of Au-Ag hybrids towards Daphnia magna in the presence of synthetic surface waters (SSF) and presented LC50 values for two Au-Ag combinations [44]. The displayed toxic effects from these NHs lay in between the manifested effects from singular AgNPs and AuNPs. Similar responses are likely to occur from overcoated NHs, as well as from exohedrally or endohedrally distributed metal/metal oxide-carbonaceous NHs. However, significant uncertainty remains regarding how these overcoated and conjugated NHs will manifest dissolution properties that can be linked with toxic responses.
Biological responses associated with exposure to NMs may also be influenced by shape and size. Conjugation will inherently introduce new dimensional changes, bringing forward NMs with altered size/shape, surface area and reactivity [272,273]. This emergent dimensionality attribute will likely influence NH toxicity by altering interactions with cellular membranes, which may alter the mechanisms of particle uptake, either by diffusion or energy-requiring processes. Furthermore, placing one NM of a certain density onto a second one may also change the mechanical stiffness of the NHs. An abundance of literature already reports the influence of stiffness/rigidity on the cytotoxicity for singular NMs [274,275,276]. In addition, adverse biological effects of other ‘stiff’ particles, which are not easily cleared, such as crocidolite asbestos fibers, are well documented. Such altered mechanical property may lead to significant changes in NM clearance from biological tissues and organisms. Both changes in dimensionality and stiffness may thus lead to changes in the way these NHs interact with biological molecules, which is an MOA being highly studied for carbon-based nanoparticles.
6. Conclusions
Materials science has moved on from singular NM synthesis and functionalization to hierarchical ensembles of more complex NHs. Multifunctionality is almost a necessity for many current and future applications. Thus, NHs will be the future of nano-scale materials that synergize multiple functions. It is likely that hybridization will lead to the alteration of existing properties or the emergence of properties not yet characterized that need to be considered in assessing toxicity in aquatic systems. As we are still beginning to define such properties of NHs, we should consider how toxicity might be altered as a result. As a research community, we should strive to develop standard protocols for accurate measurements of these properties, perform systematic studies to assess variations of such properties and bridge our understanding of these properties to underlying cellular mechanisms of action. Since the production of such an ever-expanding set of NHs with new compositions and emergent properties is imminent, the evaluation of their biological behavior is necessitated.
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors: biological effects and toxicity: T.S., J.H.B.; NH description and analysis of properties and figures: N.B.S., A.R.M.N.A., N.A., J.P.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Feynman, R.P. There’s plenty of room at the bottom. Eng. Sci. 1960, 23, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Cai, W.W.; Kodjie, S.L.; Tenneti, K.K. Nanohybrid shish-kebabs: Periodically functionalized carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muszynski, R.; Seger, B.; Kamat, P.V. Decorating graphene sheets with gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5263–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowski, K.; Njuguna, J.; Janowski, B.; Pielichowski, J. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes (poss)-containing nanohybrid polymers. In Supramolecular Polymers/Polymeric Betains/Oligomers; Donnio, B., Guillon, D., Harada, A., Hashidzume, A., Jaeger, W., Janowski, B., Kudaibergenov, S., Laschewsky, A., Njuguna, J., Pielichowski, J., et al., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2006; Volume 201, pp. 225–296. [Google Scholar]
- Akasaka, T.; Nagase, S. Endofullerenes: A New Family of Carbon Clusters; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Carril, M.; Fernández, I.; Rodríguez, J.; García, I.; Penadés, S. Gold-coated iron oxide glyconanoparticles for MRI, CT, and US multimodal imaging. Particle Particle Syst. Charact. 2013, 31, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.J.; Dong, S.J.; Wang, E. Gold/platinum hybrid nanoparticles supported on multiwalled carbon nanotube/silica coaxial nanocables: Preparation and application as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetidis, S. Flexible organic electronic devices: Materials, process and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Adv. Funct. Solid State Mater. 2008, 152, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M.; Nicole, L. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: From laboratory to market. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 696–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.A.; Yang, S.; Dunsch, L. Endohedral fullerenes. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5989–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Malhotra, M.; Shao, W.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Abbasi, S. Polymeric nanohybrids and functionalized carbon nanotubes as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S.; Tian, F.R.; Stoeger, T.; Kreyling, W.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Grazu, V.; Borm, P.; Estrada, G.; Ntziachristos, V.; Razansky, D. Multifunctional nanocarriers for diagnostics, drug delivery and targeted treatment across blood-brain barrier: Perspectives on tracking and neuroimaging. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Du, F.; Ren, D.M.; Chen, Y.S.; Zheng, J.Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Tian, J.G. Covalently porphyrin-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes: A novel photoactive and optical limiting donor-acceptor nanohybrid. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 3021–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Zhang, J.Z. Optical properties and applications of hybrid semiconductor nanomaterials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 3015–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, M.; Wright, A.E.; Hammer, N.I. Semiconductor nanocrystals hybridized with functional ligands: New composite materials with tunable properties. Materials 2010, 3, 614–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watcharotone, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Piner, R.; Jung, I.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Evmenenko, G.; Wu, S.E.; Chen, S.F.; Liu, C.P.; et al. Graphene-silica composite thin films as transparent conductors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1888–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.F.; Zhao, H.G.; Wu, N.Q.; El Khakani, M.A.; Ma, D.L. Tuning the charge-transfer property of PbS-quantum dot/TiO2-nanobelt nanohybrids via quantum confinement. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bashir, S.M. Photophysical properties of fluorescent pmma/SiO2 nanohybrids for solar energy applications. J. Lumines. 2012, 132, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Drost, C.; Sgobba, V.; Gerhards, C.; Leubner, S.; Calderon, R.M.K.; Ruland, A.; Guldi, D.M. Innovative inorganic-organic nanohybrid materials: Coupling quantum dots to carbon nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2010, 49, 6425–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Silicate-based polymer-nanocomposite membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 842–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-H.; Jeon, Y.; Ok, J.; Park, J.; Yoon, S.-H.; Choy, J.-H.; Shul, Y.-G. Pt nanoparticle-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 5669–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.L.; Gao, G.; Huang, P.; Wang, X.S.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Guo, S.W.; Cui, D.X. Preparation of Pt Ag alloy nanoisland/graphene hybrid composites and its high stability and catalytic activity in methanol electro-oxidation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Park, M.; Shinkai, S. Fabrication of silica nanotubes by using self-assembled gels and their applications in environmental and biological fields. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4286–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Aranda, P.; Darder, M.; Rytwo, G. Hybrid materials based on clays for environmental and biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9306–9321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.Z.; Li, X.L.; Xu, B.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Gao, B.F.; Fan, X.R. Improved photocatalytic activity of anatase TiO2-pillared HTaWO6 for degradation of methylene blue. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2012, 155, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Brant, J.; Hotze, M.; Sempf, J.; Oberley, T.; Sioutas, C.; Yeh, J.I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdorster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G.; Stone, V.; Donaldson, K. Toxicology of nanoparticles: A historical perspective. Nanotoxicology 2007, 1, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B.; Sayes, C.M.; Reed, K.L. Nanoscale and fine zinc oxide particles: Can in vitro assays accurately forecast lung hazards following inhalation exposures? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7939–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovern, S.B.; Strickler, J.R.; Klaper, R. Behavioral and physiological changes in Daphnia magna when exposed to nanoparticle suspensions (titanium dioxide, nano-C-60, and C(60)HxC(70)Hx). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiench, K.; Wohlleben, W.; Hisgen, V.; Radke, K.; Salinas, E.; Zok, S.; Landsiedel, R. Acute and chronic effects of nano- and non-nano-scale TiO2 and ZnO particles on mobility and reproduction of the freshwater invertebrate Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.; Jia, G.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; et al. Acute toxicity and biodistribution of different sized titanium dioxide particles in mice after oral administration. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, F.; Lao, F.; Li, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ge, C.; Zhou, G.; Li, B.; et al. Time-dependent translocation and potential impairment on central nervous system by intranasally instilled TiO2 nanoparticles. Toxicology 2008, 254, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S.A.; Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Thompson, J.W.; Lin, Y.-S.; Haynes, C.L. Assessing nanoparticle toxicity. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. Palo Alto Calif. 2012, 5, 181–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Dykman, L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1647–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Hu, Z. Size dependent and reactive oxygen species related nanosilver toxicity to nitrifying bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Badawy, A.M.; Silva, R.G.; Morris, B.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Surface charge-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, N.M.; Rogers, N.J.; Apte, S.C.; Batley, G.E.; Gadd, G.E.; Casey, P.S. Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): The importance of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Palma, S.; Fisher, N.S.; Wong, S.S. Effect of morphology of ZnO nanostructures on their toxicity to marine algae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 102, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-J.; Idrobo, J.-C.; Olamit, J.; Liu, K.; Browning, N.D.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Growth mechanisms and oxidation resistance of gold-coated iron nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Miyamae, N.; Lim, S.; Kimura, K.; Zhang, X.; Hikino, S.; Nishio, M. Crystal structures and growth mechanisms of Au@Ag core-shell nanoparticles prepared by the microwave-polyol method. Cryst. Growth Design 2006, 6, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Matsuo, R.; Jiang, P.; Miyamae, N.; Ueyama, D.; Nishio, M.; Hikino, S.; Kumagae, H.; Kamarudin, K.S.N.; Tang, X.-L. Shape-dependent evolution of Au@Ag core-shell nanocrystals by PVP-assisted N,N-dimethylformamide reduction. Cryst. Growth Design 2008, 8, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Sharma, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Enhanced antibacterial activity of bimetallic gold-silver core-shell nanoparticles at low silver concentration. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 5120–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Albee, B.; Alemayehu, M.; Diaz, R.; Ingham, L.; Kamal, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Bishnoi, S.W. Comparative toxicity study of Ag, Au, and Ag-Au bimetallic nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. Analyt. Bioanalyt. Chem. 2010, 398, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Yang, J.-W. Self-assembled flower-like TiO2 on exfoliated graphite oxide for heavy metal removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Ohno, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Sugai, T.; Suenaga, K.; Kishimoto, S.; Mizutani, T.; Inoue, T.; Taniguchi, R.; Fukui, N.; et al. Transport properties of C-78, C-90 and Dy@C-82 fullerenes-nanopeapods by field effect transistors. Physica E 2004, 21, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Tsuji, M.; Matsunaga, M.; Yamaguchi, D. Shape changes in Au-Ag bimetallic systems involving polygonal Au nanocrystals to spherical Au/Ag alloy and excentered Au core Ag/Au alloy shell particles under oil-bath heating. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 2984–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Chaudhary, M.; Ahmad, A.; Bhargava, S.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of triangular Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bulletin 2007, 42, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Carbó-Argibay, E.; Glaria, A.; Rodríguez-González, B.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Rapid epitaxial growth of Ag on Au nanoparticles: From Au nanorods to core-shell Au@Ag octahedrons. Chem. A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 5558–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tsuji, M.; Lim, S.; Miyamae, N.; Nishio, M.; Hikino, S.; Umezu, M. Synthesis and growth mechanism of pentagonal bipyramid-shaped gold-rich Au/Ag alloy nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6372–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Yang, Z.; Chang, H.-T. Synthesis of dumbbell-shaped Au-Ag core-shell nanorods by seed-mediated growth under alkaline conditions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6089–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasibulin, A.G.; Pikhitsa, P.V.; Jiang, H.; Brown, D.P.; Krasheninnikov, A.V.; Anisimov, A.S.; Queipo, P.; Moisala, A.; Gonzalez, D.; Lientschnig, G.; et al. A novel hybrid carbon material. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.G.; Casillas, G.; Sun, Z.Z.; Yan, Z.; Ruan, G.D.; Peng, Z.W.; Raji, A.R.O.; Kittrell, C. A seamless three-dimensional carbon nanotube graphene hybrid material. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, A.; Ghassemi, M.; Mirnouri Langroudi, S.M.; Rezaei Nejad, H.; Hamedi, M.H. Effect of defect and C60s density variation on tensile and compressive properties of peapod. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2010, 50, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauster, S.J.; Fung, S.C.; Baker, R.T.K.; Horsley, J.A. Strong interactions in supported-metal catalysts. Science 1981, 211, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Akalework, N.G.; Pan, C.-J.; Su, W.-N.; Rick, J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lee, J.-F.; Lin, J.-M.; Tsai, L.-D.; Hwang, B.-J. Ultrathin TiO2-coated MWCNTs with excellent conductivity and SMSI nature as Pt catalyst support for oxygen reduction reaction in PEMFCs. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20977–20985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valodkar, M.; Modi, S.; Pal, A.; Thakore, S. Synthesis and anti-bacterial activity of Cu, Ag and Cu-Ag alloy nanoparticles: A green approach. Mater. Res. Bulletin 2011, 46, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Maedler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle-cell interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.W.; Monthioux, M.; Luzzi, D.E. Encapsulated C-60 in carbon nanotubes. Nature 1998, 396, 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, G.M.A.; Guldi, D.M.; Zambon, E.; Pasquato, L.; Tagmatarchis, N.; Prato, M. Dispersable carbon nanotube/gold nanohybrids: Evidence for strong electronic interactions. Small 2005, 1, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoufis, T.; Tomou, A.; Gournis, D.; Douvalis, A.P.; Panagiotopoulos, I.; Kooi, B.; Georgakilas, V.; Arfaoui, I.; Bakas, T. Novel nanohybrids derived from the attachment of fept nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 5942–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.Y.; Han, G.Y.; Chang, Y.Z.; Dong, J.H. The synthesis and properties of ZnO-graphene nano hybrid for photodegradation of organic pollutant in water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Mai, Z.B.; Kang, X.H.; Dai, Z.; Zou, X.Y. Clay-chitosan-gold nanoparticle nanohybrid: Preparation and application for assembly and direct electrochemistry of myoglobin. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 4732–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, V. Time resolved emission studies of Ag-adenine-templated Cds (Ag/Cds) nanohybrids. Nanotechnology 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, S.; Yu, K.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, F.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, J. Crystal engineering and SERS properties of Ag-Fe3O4 nanohybrids: From heterodimer to core-shell nanostructures. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 17930–17937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elim, H.I.; Cai, B.; Kurata, Y.; Sugihara, O.; Kaino, T.; Adschiri, T.; Chu, A.-L.; Kambe, N. Refractive index control and rayleigh scattering properties of transparent TiO2 nanohybrid polymer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10143–10148. [Google Scholar]
- Ohno, T.; Tagawa, S.; Itoh, H.; Suzuki, H.; Matsuda, T. Size effect of TiO-SiO2 nano-hybrid particle. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassinopoulos, A.; Das, R.N.; Anastasiadis, S.H.; Giannelis, E.P.; Anglos, D. Random lasing action from ZnO-silica nanohybrids. J. Opt. 2010, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Goudar, V.S.; Padmalekha, K.G.; Bhat, S.V.; Indi, S.S.; Vasan, H.N. ZnO/Ag nanohybrid: Synthesis, characterization, synergistic antibacterial activity and its mechanism. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acierno, D.; Filippone, G.; Romeo, G.; Russo, P. Dynamics of stress bearing particle networks in poly(propylene)/alumina nanohybrids. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Gunawan, P.; Xu, R. Self-assembled Fe3O4-layered double hydroxide colloidal nanohybrids with excellent performance for treatment of organic dyes in water. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ren, B.; Yao, J.-L.; Gu, R.-A.; Tian, Z.-Q. Synthesis of agcoreaushell bimetallic nanoparticles for immunoassay based on surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4002–4006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Hatakeyama, R. Photoresponse of Fullerene and Azafullerene Peapod Field Effect Transistors. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO 2009), Genoa, Italy, 26–30 July 2009; pp. 86–89.
- Li, Y.F.; Kaneko, T.; Hatakeyama, R. Electrical transport properties of fullerene peapods interacting with light. Nanotechnology 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, A.A.; Chandra, B.; Kasry, A.; Maarouf, A.; Martyna, G.J.; Tulevski, G.S. Carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid transparent conductor and field effect transistor. U.S. Patent 20130130037 A1, 23 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Kwon, S.Y.; Myung, S.; Jung, M.W.; Kim, S.J.; Min, B.K.; Kang, M.-A.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.; An, K.-S. High-mobility ambipolar ZnO-graphene hybrid thin film transistors. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mao, S.; Lu, G. Graphene-based field-effect transistor biosensors. U.S. Patent 20120214172 A1, 23 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, T.-J.; Akinwande, D.; Dodabalapur, A. Hybrid graphene/organic semiconductor field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hines, D.R.; Jung, B.J.; Bronsgeest, M.S.; Tunnell, A.; Ballarotto, V.; Katz, H.E.; Fuhrer, M.S.; Williams, E.D.; Cumings, J. Polymeric semiconductor/graphene hybrid field-effect transistors. Organ. Electron. 2011, 12, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeomi, M.; Vipul, S.; Shinya, O.; Shuichi, N.; Wataru, T.; Shuzi, H.; Keiichi, K. Ambipolar transport in bilayer organic field-effect transistor based on poly(3-hexylthiophene) and fullerene derivatives. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Wu, X.F.; Xie, L.Y.; Yang, K.; Jiang, P.K. Graphene oxide-encapsulated carbon nanotube hybrids for high dielectric performance nanocomposites with enhanced energy storage density. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3847–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Pinero, E.; Khomenko, V.; Frackowiak, E.; Beguin, F. Performance of manganese oxide/cnts composites as electrode materials for electrochemical capacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A229–A235. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, C. Inkjet printing of single-walled carbon nanotube/RuO2 nanowire supercapacitors on cloth fabrics and flexible substrates. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Mao, S.; Wen, Z.H. One-Pot Fabrication of Crumpled Graphene-Based Nanohybrids for Supercapacitors; UWM Research Foundation: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, S.; Iwai, Y.; Hirose, M. Electrochemical lithium ion storage property of C60 encapsulated single-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Res. Bulletin 2009, 44, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y. Graphene derivative-carbon nanotube composite material and preparation methods thereof. U.S. Patent 20130252499 A1, 26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Yeoh, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, G. Chemical-free synthesis of graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid materials for reversible lithium storage in lithium-ion batteries. Carbon 2012, 50, 4557–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y. Carbon nanotubes grown in situ on graphene nanosheets as superior anodes for li-ion batteries. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4323–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.D.; Yao, B.; Bai, Y.J. Preparation of carbon nano-onions and their application as anode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 8923–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, J.S.; Luan, D.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Madhavi, S.; Lou, X.W. Graphene-supported anatase TiO2 nanosheets for fast lithium storage. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5780–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Shi, Y.Y.; Nisar, A.; Sun, H.Y.; Shen, W.C.; Wei, M.; Zhu, J. Synthesis of hierarchical flower-like ZnO nanostructures and their functionalization by Au nanoparticles for improved photocatalytic and high performance li-ion battery anodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7723–7729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.-K.; Lee, D.W.; Choi, H.J.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, B.-S. Transparent, flexible conducting hybrid multilayer thin films of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with graphene nanosheets. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3861–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, V.C.; Chen, L.M.; Allen, M.J.; Wassei, J.K.; Nelson, K.; Kaner, R.B.; Yang, Y. Low-temperature solution processing of graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid materials for high-performance transparent conductors. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, V.C.; Huang, J.H.; Tevis, I.; Kim, F.; Kim, J.; Chu, C.W.; Stupp, S.I.; Huang, J.X. Surfactant-free water-processable photoconductive all-carbon composite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4940–4947. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, B.S.; Jung, D.H.; Oh, S.K.; Han, C.S.; Jung, H.T. Single-walled carbon nanotube gold nanohybrids: Application in highly effective transparent and conductive films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 8377–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholmanov, I.N.; Stoller, M.D.; Edgeworth, J.; Lee, W.H.; Li, H.; Lee, J.; Barnhart, C.; Potts, J.R.; Piner, R.; Akinwande, D.; et al. Nanostructured hybrid transparent conductive films with antibacterial properties. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5157–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, Q.; Huang, L. Transparent, flexible conducting graphene hybrid films with a subpercolating network of silver nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, S.; Li, M.; Xie, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, N.; Yang, S. Noncovalent functionalization of graphene attaching [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) and application as electron extraction layer of polymer solar cells. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4070–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, P.; Fu, M. Influence of polymer/fullerene-graphene structure on organic polymer solar devices. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2012, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Heo, M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Shin, H.S. Reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-wrapped fullerene (C-60) wires. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8365–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Park, K.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L.M. Fullerene-grafted graphene for efficient bulk heterojunction polymer photovoltaic devices. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, H.R.; Fan, L.Z.; Yang, S.H. Synthesis and characterization of a grapevine nanostructure consisting of single-walled carbon nanotubes with covalently attached 60 fullerene balls. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 5981–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.I.; Kwon, B.W.; Park, D.H.; Seo, W.S.; Yi, Y.; Angadi, B.; Lee, C.L.; Choi, W.K. Emissive ZnO-graphene quantum dots for white-light-emitting diodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-I.; Moon, G.-H.; Monllor-Satoca, D.; Park, Y.; Choi, W. Solar photoconversion using graphene/TiO2 composites: Nanographene shell on TiO2 core versus TiO2 nanoparticles on graphene sheet. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Fu, W.; Yang, H.; Sui, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yin, G.; Li, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zou, G. One-step synthesis of coaxial Ag/TiO2 nanowire arrays on transparent conducting substrates: Enhanced electron collection in dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1324–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, F.; Chitta, R.; Sandanayaka, A.S.D.; Subbaiyan, N.K.; D’Souza, L.; Araki, Y.; Ito, O. Supramolecular carbon nanotube-fullerene donor-acceptor hybrids for photoinduced electron transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15865–15871. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.-L.; Feng, J.; Sun, L.-C.; Wang, S.; Xie, S.-L.; Xie, S.-Y.; Huang, R.-B.; Zheng, L.-S. Functionalized dihydronaphthyl-C60 derivatives as acceptors for efficient polymer solar cells with tunable photovoltaic properties. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2012, 104, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Tian, J.G. Porphyrin and fullerene covalently functionalized graphene hybrid materials with large nonlinear optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 9681–9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackiewicz, N.; Bark, T.; Cao, B.; Delaire, J.A.; Riehl, D.; Ling, W.L.; Foillard, S.; Doris, E. Fullerene-functionalized carbon nanotubes as improved optical limiting devices. Carbon 2011, 49, 3998–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Elim, H.I.; Foo, Y.L.; Yu, T.; Liu, Y.J.; Ji, W.; Lee, J.Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Wee, A.T.S.; Thong, J.T.L.; et al. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes beaded with ZnO nanoparticles for ultrafast nonlinear optical switching. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, R.T.; Nair, A.S.; Singh, N.; Aslam, M.; Nagendra, C.L.; Philip, R.; Vijayamohanan, K.; Pradeep, T. Freely dispersible Au@TiO2, Au@ZrO2, Ag@TiO2, and Ag@ZrO2 core-shell nanoparticles: One-step synthesis, characterization, spectroscopy, and optical limiting properties. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3439–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wan, X.; Tian, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y. Synthesis, characterization and optical limiting property of covalently oligothiophene-functionalized graphene material. Carbon 2009, 47, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.M.; Madras, G. Low temperature co oxidation and water gas shift reaction over Pt/Pd substituted in Fe/TiO2 catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 18798–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, N.; Jafri, R.I.; Rajalakshmi, N.; Ramaprabhu, S. Graphene-multi walled carbon nanotube hybrid electrocatalyst support material for direct methanol fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 7284–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigdon, W.A.; Sightler, J.J.; Larrabee, D.; McPherson, E.; Huang, X. Titania and carbon nanotube composite catalyst supports for durable electrocatalyst performance. ECS Trans. 2013, 50, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Huang, Y.X.; Liu, X.W.; Sheng, G.P.; Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q. Three-dimensional bimetallic Pd-Cu nanodendrites with superior electrochemical performance for oxygen reduction reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 89, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-L.; He, Y.-J.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, J.-H. Quantum dots conjugated with Fe3O4-filled carbon nanotubes for cancer-targeted imaging and magnetically guided drug delivery. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16469–16476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, A.L.; James, B.; Jesse, A.; Konstantin, S. Hybrid plasmonic magnetic nanoparticles as molecular specific agents for MRI/optical imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Shelton, M.; Singh, A.K.; Senapati, D.; Khan, S.A.; Ray, P.C. Multifunctional plasmonic shell-magnetic core nanoparticles for targeted diagnostics, isolation, and photothermal destruction of tumor cells. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolskar, R.D. Gadofullerene MRI contrast agents. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laus, S.; Sitharaman, B.; Tóth, É.; Bolskar, R.D.; Helm, L.; Asokan, S.; Wong, M.S.; Wilson, L.J.; Merbach, A.E. Destroying gadofullerene aggregates by salt addition in aqueous solution of Gd@C60(OH)x and Gd@C60[C(COOH2)]10. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9368–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, E.; Bolskar, R.D.; Borel, A.; Gonzalez, G.; Helm, L.; Merbach, A.E.; Sitharaman, B.; Wilson, L.J. Water-soluble gadofullerenes: Toward high-relaxivity, Ph-responsive MRI contrast agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.; Peterlik, H.; Pfeiffer, R.; Bernardi, J.; Kuzmany, H. Fullerene release from the inside of carbon nanotubes: A possible route toward drug delivery. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 445, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, N.F.; Xu, L.G.; Wang, L.B.; Li, Z.K.; Ma, W.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Xu, C.L.; Kotov, N.A. Multifunctional magnetoplasmonic nanoparticle assemblies for cancer therapy and diagnostics (theranostics). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 228–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.Q.; Yu, J.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.; Dong, H.Q. Engineering of a novel pluronic F127/graphene nanohybrid for Ph responsive drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.D.; Khanal, B.P.; Zubarev, E.R. Paclitaxel-functionalized gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11653–11661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Xi, Q.; Yang, W. A high performance electrochemical sensor for acetaminophen based on single-walled carbon nanotube-graphene nanosheet hybrid films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wen, D.; Zhai, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Platinum nanoparticle ensemble-on-graphene hybrid nanosheet: One-pot, rapid synthesis, and used as new electrode material for electrochemical sensing. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Fan, P.; Quan, X. Intensified internal electrolysis for degradation of methylene blue as model compound induced by a novel hybrid material: Multi-walled carbon nanotubes immobilized on zero-valent iron plates (Fe0-CNTs). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, H.; Chandra, V.; Jung, S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, K.S.; Bin Kim, S. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal using iron nanoparticle decorated graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3583–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, T.; Gopalan, A.I.; Lee, K.-P.; Park, S.-Y. Glucose sensing, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of graphene-ZnO nanoparticle hybrids. Carbon 2012, 50, 2994–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M.; Wang, X.X.; Cui, M.L.; Lin, L.P.; Jiang, S.L.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, L.H. A promising non-aggregation colorimetric sensor of AuNRs-Ag+ for determination of dopamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.A.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yang, X.L.; Li, C.Z. Electrocatalytic activity of Pt doped TiO2 nanotubes catalysts for glucose determination. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 500, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Makhal, A.; Bora, T.; Lakhsman, K.; Singha, A.; Dutta, J.; Pal, S.K. Hematoporphyrin-ZnO nanohybrids: Twin applications in efficient visible-light photocatalysis and dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2012, 4, 7027–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, V.; Devadas, B.; Chen, S.M. Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-multiwalled carbon nanotubes hybrid material modified electrode for glucose biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Jiang, J. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with self-assembled cylindrical graphene-carbon nanotube hybrid. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 192, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue on multiwalled carbon nanotubes-TiO2. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 398, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Pan, L.K.; Liu, X.J.; Lu, T.; Zhu, G.; Sun, Z. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by ZnO-reduced graphene oxide composite synthesized via microwave-assisted reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 10086–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Irudayaraj, J. Multifunctional magnetic-optical nanoparticle probes for simultaneous detection, separation, and thermal ablation of multiple pathogens. Small 2010, 6, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Du, C.; Fu, Y. Localized surface plasmon resonance-based hybrid Au-Ag nanoparticles for detection of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costi, R.; Saunders, A.E.; Elmalem, E.; Salant, A.; Banin, U. Visible light-induced charge retention and photocatalysis with hybrid CdSe-Au nanodumbbells. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.R.; Sarma, R.K.; Saikia, R.; Kale, V.S.; Shelke, M.V.; Sengupta, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide sheets and its antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 2011, 83, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, M.B.; Su, C.; Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Characterization of carbon nano-onions for heavy metal ion remediation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, S.K.; Ghosh, M.; Roy, M.; Begum, A.; Sarkar, S. Carbon nano-onions as nontoxic and high-fluorescence bioimaging agent in food chain-an in vivo study from unicellular E. coli to multicellular C. elegans. Mater. Exp. 2012, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Preethichandra, D.M.G.; Ekanayake, E.M.I.M. Nano-biosensor development for biomedical and environmental measurements. In New Developments and Applications in Sensing Technology; Mukhopadhyay, S., Lay-Ekuakille, A., Fuchs, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germary, 2011; Volume 83, pp. 279–292. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, R.; Cui, T.; Jun, M.-S.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, A.; Su, D.S.; Zhang, Z.; Yoon, S.-H.; Miyawaki, J.; Mochida, I.; et al. Open-ended, n-doped carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid nanostructures as high-performance catalyst support. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 999–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Karousis, N.; Tsotsou, G.-E.; Evangelista, F.; Rudolf, P.; Ragoussis, N.; Tagmatarchis, N. Carbon nanotubes decorated with palladium nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 13463–13469. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Qi, J.; Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F. Gold nanoparticles-graphene hybrids as active catalysts for suzuki reaction. Mater. Res. Bulletin 2010, 45, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B. One-pot, seedless synthesis of flowerlike Au-Pd bimetallic nanoparticles with core-shell-like structure via sodium citrate coreduction of metal ions. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 7036–7042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.K.; Dichiara, A.; Bai, J.B. Carbon nanotube-graphene nanoplatelet hybrids as high-performance multifunctional reinforcements in epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 74, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.H.; Park, H.W.; Park, Y.B. Piezoresistive behavior and multi-directional strain sensing ability of carbon nanotube-graphene nanoplatelet hybrid sheets. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly-Pottuz, L.; Vacher, B.; Ohmae, N.; Martin, J.M.; Epicier, T. Anti-wear and friction reducing mechanisms of carbon nano-onions as lubricant additives. Tribol. Lett. 2008, 30, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Hatakeyama, R. C59N peapods sensing the temperature. Sensors 2013, 13, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, S.S.J.; Ramaprabhu, S. Graphene wrapped multiwalled carbon nanotubes dispersed nanofluids for heat transfer applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizuete, M.; Barrejon, M.; Gomez-Escalonilla, M.J.; Langa, F. Endohedral and exohedral hybrids involving fullerenes and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4370–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Bonzongo, J.C.; Barber, D.S. Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, Y.-W.; An, Y.-J. Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus aureus. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergio, M.; Behzadi, H.; Otto, A.; Spoel, D. Fullerenes toxicity and electronic properties. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Z.; Xia, T.; Meng, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Liu, R.; Pokhrel, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.-P.; et al. Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4349–4368. [Google Scholar]
- Burello, E.; Worth, A.P. A theoretical framework for predicting the oxidative stress potential of oxide nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.T.; Sugavaneshwar, R.P.; Nanda, K.K. Carbon nanotube-ZnO nanowire hybrid architectures as multifunctional devices. AIP Adv. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.O.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Han, T.H.; Kim, B.H.; Park, M.; No, K.; Kim, S.O. Vertical ZnO nanowires/graphene hybrids for transparent and flexible field emission. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3432–3437. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.J.; Liu, J.C.; Liu, L.; Sun, D.D. Enhancing stability and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles by surface modification of graphene oxide. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 3896–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, B.A.; Afrooz, A.R.M.N.; Bae, S.; Aich, N.; Katz, L.; Saleh, N.B.; Kirisits, M.J. Effects of chloride and ionic strength on physical morphology, dissolution, and bacterial toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 761–769. [Google Scholar]
- Shoults-Wilson, W.A.; Reinsch, B.C.; Tsyusko, O.V.; Bertsch, P.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Unrine, J.M. Role of particle size and soil type in toxicity of silver nanoparticles to earthworms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-P.; Fang, T.; Xiong, D.-W.; Zhu, W.-T.; Sima, X.-F. Comparative toxicity of nano-ZnO and bulk ZnO suspensions to zebrafish and the effects of sedimentation, OH production and particle dissolution in distilled water. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Ji, Y.L.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.Q.; Wu, X.C.; Xu, H.Y. Using gold nanorods core/silver shell nanostructures as model material to probe biodistribution and toxic effects of silver nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Lin, M.S.; Tan, S.Z.; Mai, W.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Liang, Z.W.; Lin, Z.D.; Zhang, X.J. The use of polyethyleneimine-modified reduced graphene oxide as a substrate for silver nanoparticles to produce a material with lower cytotoxicity and long-term antibacterial activity. Carbon 2012, 50, 3407–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Saha, K.; Kim, C.; Rotello, V.M. The role of surface functionality in determining nanoparticle cytotoxicity. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschling, T.L.; Golas, P.L.; Unrine, J.M.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Gregory, K.B.; Lowry, G.V.; Tilton, R.D. Microbial bioavailability of covalently bound polymer coatings on model engineered nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5253–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, I.; Mondal, D.; Martin, J.; Kane, R.S. Photoactivated antimicrobial activity of carbon nanotube-porphyrin conjugates. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17369–17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, H.F.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Pei, R.J.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Guo, X.B. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fulleren. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Hu, P.P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.Z.; Luo, L.F.; Huang, C.Z. Toxicity of graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotubes against human cells and zebrafish. Sci. China Chem. 2012, 55, 2209–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeublin, N.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Maurer, E.I.; Park, K.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Afrooz, A.R.M.N.; Vaia, R.A.; Saleh, N.B.; Hussain, S.M. Does shape matter? Bioeffects of gold nanomaterials in a human skin cell model. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3248–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.W.; Luzzi, D.E. Formation mechanism of fullerene peapods and coaxial tubes: A path to large scale synthesis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2000, 321, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zeng, X.C. Periodic graphene nanobuds. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, C.A.; Duffin, R.; Kinloch, I.; Maynard, A.; Wallace, W.A.H.; Seaton, A.; Stone, V.; Brown, S.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, D.Y.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Fullerene water suspension (nC60) exerts antibacterial effects via ROS-independent protein oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8127–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, H.; von dem Bussche, A.; Creighton, M.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B.; Gao, H. Graphene microsheets enter cells through spontaneous membrane penetration at edge asperities and corner sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar]
- Salvetat, J.-P.; Bonard, J.-M.; Thomson, N.; Kulik, A.; Forro, L.; Benoit, W.; Zuppiroli, L. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. A 1999, 69, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Pan, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, Q. The effects of encapsulating C60 fullerenes on the bending flexibility of carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2007, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.P.; Xu, L.Q.; Fan, Z.Y.; Wei, N.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Z.G. Mechanical properties of graphene nanobuds: A molecular dynamics study. Curr. Nanosci. 2012, 8, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Hu, N.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Chai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Paper-like graphene-Ag composite films with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W. Dramatically enhanced photocatalytic properties of Ag-modified graphene-ZnO quasi-shell-core heterojunction composite material. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 24118–24125. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, W.J.; Cheng, C.C.; Hsieh, J.H. Rattle-structured Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite capsules with bactericide and photocatalysis activities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Noriega-Trevino, M.E.; Nino-Martinez, N.; Marambio-Jones, C.; Wang, J.; Damoiseaux, R.; Ruiz, F.; Hoek, E.M.V. Synergistic bactericidal activity of Ag-TiO2 nanoparticles in both light and dark conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8989–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Gunsolus, I.L.; Murphy, C.J.; Haynes, C.L. Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3036–3049. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.; Bradley, T.; Moore, J.T.; Kuykindall, T.; Minella, L. Acute and chronic toxicity of nano-scale TiO2 particles to freshwater fish, cladocerans, and green algae, and effects of organic and inorganic substrate on TiO2 toxicity. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.W. Acute toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticle suspensions against Daphnia magna: The importance of their dissolved fraction varying with preparation methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Weil, R.; Hyndman, K.A.; Denslow, N.D.; Powers, K.; Taylor, D.; Barber, D.S. Exposure to copper nanoparticles causes gill injury and acute lethality in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8178–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouldin, J.L.; Ingle, T.M.; Sengupta, A.; Alexander, R.; Hannigan, R.E.; Buchanan, R.A. Aqueous toxicity and food chain transfer of quantum dotsTM in freshwater algae and Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strigul, N.; Vaccari, L.; Galdun, C.; Wazne, M.; Liu, X.; Christodoulatos, C.; Jasinkiewicz, K. Acute toxicity of boron, titanium dioxide, and aluminum nanoparticles to Daphnia magna and Vibrio fischeri. Desalination 2009, 248, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Shao, K.; Feng, W.; Lin, Z.; Liang, C.; Sun, Y. Biotoxicity of nickel oxide nanoparticles and bio-remediation by microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, B.K.; Biswas, A.; Rosenkranz, P.; Jepson, M.A.; Lead, J.R.; Stone, V.; Tyler, C.R.; Fernandes, T.F. Effects of silver and cerium dioxide micro- and nano-sized particles on Daphnia magna. J. Environm. Monit. 2011, 13, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tian, S.; Cai, Z. Toxicity assessment of iron oxide nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo Garcia-Cambero, J.; Nunez Garcia, M.; Diaz Lopez, G.; Lopez Herranz, A.; Cuevas, L.; Perez-Pastrana, E.; Sendra Cuadal, J.; Ramis Castelltort, M.; Castano Calvo, A. Converging hazard assessment of gold nanoparticles to aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.J.; Zhang, L.; Mattison, N.T.; O’Carroll, D.M.; Whelton, A.J.; Uddin, N.; Nguyen, T.; Huang, Q.; Henry, T.B.; Holbrook, R.D.; et al. Potential release pathways, environmental fate, and ecological risks of carbon nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9837–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretti, C.; Oliva, M.; Pietro, R.D.; Monni, G.; Cevasco, G.; Chiellini, F.; Pomelli, C.; Chiappe, C. Ecotoxicity of pristine graphene to marine organisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.M.; Dinis, A.M.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Peixoto, F.; Videira, R.A.; Jurado, A.S. Studies on the toxicity of an aqueous suspension of C60 nanoparticles using a bacterium (gen. Bacillus) and an aquatic plant (Lemna gibba) as in vitro model systems. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Cornelis, G.; Fernandes, T.; Tsyusko, O.; Decho, A.; Sabo-Attwood, T.; Metcalfe, C.; Steevens, J.A.; Klaine, S.J.; Koelmans, A.A.; et al. Ecotoxicity test methods for engineered nanomaterials: Practical experiences and recommendations from the bench. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarsky, A.; Dupuis, L.; Taylor, J.; Eisa-Beygi, S.; Strek, L.; Trudeau, V.L.; Moon, T.W. Assessment of nanosilver toxicity during zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, P.-E.; Tankoua, O.F.; Pan, J.-F.; Berhanu, D.; Herrenknecht, C.; Poirier, L.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Amiard, J.-C.; Berard, J.-B.; Risso, C.; et al. Behavioural and biochemical responses of two marine invertebrates scrobicularia plana and hediste diversicolor to copper oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.B.; Klaine, S.J. Abiotic and biotic factors that influence the bioavailability of gold nanoparticles to aquatic macrophytes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10223–10230. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-W.; Kim, S.-M.; Choi, J. Genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assays using the freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna and the larva of the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius to screen the ecological risks of nanoparticle exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 28, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagne, F.; Turcotte, P.; Auclair, J.; Gagnon, C. The effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the metallome in freshwater mussels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 158, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernot, R.J.; Brandenburg, M. Freshwater snail vital rates affected by non-lethal concentrations of silver nanoparticles. Hydrobiologia 2013, 714, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Kammer, F.V.D.; Weilhartner, A.; Ottofuelling, S.; Hofmann, T. Nanostructured TiO2: Transport behavior and effects on aquatic microbial communities under environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8098–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, T.P.; Hwang, H.-M. Effect of humic acids and sunlight on the cytotoxicity of engineered zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles to a river bacterial assemblage. J. Environ. Sci. China 2013, 25, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakrashi, S.; Dalai, S.; Humayun, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. Ceriodaphnia dubia as a potential bio-indicator for assessing acute aluminum oxide nanoparticle toxicity in fresh water environment. PLoS One 2013, 8, e74003. [Google Scholar]
- Diniz, M.S.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Lourenco, J.; Castro, L.; Peres, I.; Mendonca, E.; Picado, A. Liver alterations in two freshwater fish species (Carassius auratus and Danio rerio) following exposure to different TiO2 nanoparticle concentrations. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Federici, G.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D. Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Gill injury, oxidative stress, and other physiological effects. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Chen, L. Oxidative stress responses in different organs of carp (Cyprinus carpio) with exposure to ZnO nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 80, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, R.; Rahuman, A.A. Histopathological studies and oxidative stress of synthesized silver nanoparticles in mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). J. Environ. Sci. China 2012, 24, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shi, Z.; Yang, X.; Cui, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Guo, L. Bioaccumulation and biomarker responses of cubic and octahedral Cu2O micro/nanocrystals in Daphnia magna. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5981–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, P.-E.; Richard, M.; Caupos, F.; Vergnoux, A.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Luna-Acosta, A.; Akcha, F.; Amiard, J.-C.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Guibbolini, M.; et al. A mesocosm study of fate and effects of CuO nanoparticles on endobenthic species (Scrobicularia plana, Hediste diversicolor). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.C.; Chan, K.M. Effects of Cu2O nanoparticle and CuCl2 on zebrafish larvae and a liver cell-line. Aquatic Toxicol. 2011, 105, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Cui, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Guo, L. Differential oxidative stress of octahedral and cubic Cu2O micro/nanocrystals to Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10255–10262. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, J.; Christian, P.; Urrea, J.A.G.; Roos, N.; Hassellov, M.; Tollefsen, K.E.; Thomas, K.V. Effects of silver and gold nanoparticles on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 96, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.H.; Cui, M.M.; Shi, Z.W.; Tan, C.; Yang, X.P. Enhanced oxidative stress and physiological damage in Daphnia magna by copper in the presence of nano-TiO2. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Forthaus, B.E.; Wang, J. Synergistic toxic effect of nano-Al2O3 and As(V) on Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3003–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Hyndman, K.; Denslow, N.D.; Barber, D.S. Comparison of molecular and histological changes in zebrafish gills exposed to metallic nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 107, 404–415. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, A.; Singh, A.P.; Chaudhary, B.R.; Singh, S.K.; Dash, D. Effect of silver nanoparticles on growth of eukaryotic green algae. Nano Micro Lett. 2012, 4, 158–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of growth and biochemical indicators of Salvinia natans exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc accumulation in plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, F.; Samadani, M.; Dewez, D. Effect of soluble copper released from copper oxide nanoparticles solubilisation on growth and photosynthetic processes of Lemna gibba L. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambio-Jones, C.; Hoek, E.M.V. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, P.A.; Jamting, A.K.; Escher, B.I.; Herrmann, J. A review of the detection, fate and effects of engineered nanomaterials in wastewater treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Moos, N.; Slaveykova, V.I. Oxidative stress induced by inorganic nanoparticles in bacteria and aquatic microalgae—State of the art and knowledge gaps. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 605–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, W.; He, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, Z. Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to zebrafish embryo: A physicochemical study of toxicity mechanism. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Hull, M.S.; Bednar, A.J.; Goss, J.D.; Gunter, J.C.; Bouldin, J.L.; Vikesland, P.J.; Steevens, J.A. Fractionating nanosilver: Importance for determining toxicity to aquatic test organisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9571–9577. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Irons, D.R.; Wang, J. Synergistic toxic effect of nano-TiO2 and As(V) on Ceriodaphnia dubia. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Von der Kammer, F.; Hofmann, T.; Baalousha, M.; Ottofuelling, S.; Baun, A. Algal testing of titanium dioxide nanoparticles-testing considerations, inhibitory effects and modification of cadmium bioavailability. Toxicology 2010, 269, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.; Rivetti, C.; Rosenkranz, P.; Maria Navas, J.; Barata, C. Effects of nanoparticles of TiO2 on food depletion and life-history responses of Daphnia magna. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130, 174–183. [Google Scholar]
- Fouqueray, M.; Dufils, B.; Vollat, B.; Chaurand, P.; Botta, C.; Abacci, K.; Labille, J.; Rose, J.; Garric, J. Effects of aged TiO2 nanomaterial from sunscreen on Daphnia magna exposed by dietary route. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croteau, M.-N.; Dybowska, A.D.; Luoma, S.N.; Valsami-Jones, E. A novel approach reveals that zinc oxide nanoparticles are bioavailable and toxic after dietary exposures. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrunz, A.; Duester, L.; Prasse, C.; Seitz, F.; Rosenfeldt, R.; Schilde, C.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R. Biological surface coating and molting inhibition as mechanisms of TiO2 nanoparticle toxicity in Daphnia magna. PLoS One 2011, 6, e20112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. The impact of ZnO nanoparticle aggregates on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Nanotechnology 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Ear, J.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Yamada, K.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Zebrafish high-throughput screening to study the impact of dissolvable metal oxide nanoparticles on the hatching enzyme, ZHE1. Small 2013, 9, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, T.; Meng, H.; Ji, Z.; Liu, R.; George, S.; Xiong, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. High content screening in zebrafish speeds up hazard ranking of transition metal oxide nanoparticles. ACS nano 2011, 5, 7284–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poda, A.R.; Kennedy, A.J.; Cuddy, M.F.; Bednar, A.J. Investigations of UV photolysis of PVP-capped silver nanoparticles in the presence and absence of dissolved organic carbon. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Chu Thi Thanh, B.; Kelly, J.J.; Gaillard, J.-F.; Gray, K.A. Cytotoxicity of commercial nano-TiO2 to Escherichia coli assessed by high-throughput screening: Effects of environmental factors. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.P.; Bar-Ilan, O.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W.; Hamers, R.J.; Pedersen, J.A. Influence of humic acid on titanium dioxide nanoparticle toxicity to developing zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4718–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, A.J.; Chappell, M.A.; Bednar, A.J.; Ryan, A.C.; Laird, J.G.; Stanley, J.K.; Steevens, J.A. Impact of organic carbon on the stability and toxicity of fresh and stored silver nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10772–10780. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Ji, J.; Long, Z.; Yang, K.; Wu, F. The influence of dissolved and surface-bound humic acid on the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles to Chlorella sp. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4477–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Rao, T.N.; Tryk, D.A. Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2000, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Brennan, A.; Diamond, S.A. Phototoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles under solar radiation to two aquatic species: Daphnia magna and Japanese medaka. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-P.; Ma, C.-Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yu, C.-P. Effect of light on toxicity of nanosilver to Tetrahymena pyriformis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkowski, J.; Lanone, S. Respiratory toxicities of nanomaterials—A focus on carbon nanotubes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, D.; Fox, J.E.; Akerman, J.M.; Sloman, K.A.; Henry, T.B.; Handy, R.D. Minimal effects of waterborne exposure to single-walled carbon nanotubes on behaviour and physiology of juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 146, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaper, R.; Arndt, D.; Setyowati, K.; Chen, J.; Goetz, F. Functionalization impacts the effects of carbon nanotubes on the immune system of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgington, A.J.; Petersen, E.J.; Herzing, A.A.; Podila, R.; Rao, A.; Klaine, S.J. Microscopic investigation of single-wall carbon nanotube uptake by Daphnia magna. Nanotoxicology 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.J.; Akkanen, J.; Kukkonen, J.V.; Weber, W.J., Jr. Biological uptake and depuration of carbon nanotubes by Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2969–2975. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, A.N.; Portis, L.M.; Schierz, P.A.; Washburn, K.M.; Perron, M.M.; Burgess, R.M.; Ho, K.T.; Chandler, G.T.; Ferguson, P.L. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes to benthic organisms at the base of the marine food chain. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2013, 32, 1270–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisesi, J.H., Jr.; Merten, J.; Liu, K.; Parks, A.N.; Afrooz, A.R.; Glenn, J.B.; Klaine, S.J.; Kane, A.S.; Saleh, N.B.; Ferguson, P.L.; et al. Tracking and quantification of single-walled carbon nanotubes in fish using near infrared fluorescence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgington, A.J.; Roberts, A.P.; Taylor, L.M.; Alloy, M.M.; Reppert, J.; Rao, A.M.; Mao, J.; Klaine, S.J. The influence of natural organic matter on the toxicity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2010, 29, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Mauter, M.S.; Elimelech, M. Microbial cytotoxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials: Implications for river water and wastewater effluent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.A.; Moua, M.; Chen, J.; Klaper, R.D. Core structure and surface functionalization of carbon nanomaterials alter impacts to daphnid mortality, reproduction, and growth: Acute assays do not predict chronic exposure impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9444–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.A.; Chen, J.; Moua, M.; Klaper, R.D. Multigeneration impacts on Daphnia magna of carbon nanomaterials with differing core structures and functionalizations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2014, 33, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Saleh, T.A. Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene—An overview. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 2828–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, A.N.; Chandler, G.T.; Portis, L.M.; Sullivan, J.C.; Perron, M.M.; Cantwell, M.G.; Burgess, R.M.; Ho, K.T.; Ferguson, P.L. Effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes on the bioavailability of PCBs in field-contaminated sediments. Nanotoxicology 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo Costa, C.L.; Chaves, I.S.; Ventura-Lima, J.; Ferreira, J.L.; Ferraz, L.; de Carvalho, L.M.; Monserrat, J.M. In vitro evaluation of co-exposure of arsenium and an organic nanomaterial (fullerene, C(60)) in zebrafish hepatocytes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 155, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.J.; Henry, T.B.; Zhao, J.; Maccuspie, R.I.; Kirschling, T.L.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Hackley, V.; Xing, B.; White, J.C. Identification and avoidance of potential artifacts and misinterpretations in nanomaterial ecotoxicity measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4226–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Von Dem Bussche, A.; Buechner, M.; Yan, A.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Adsorption of essential micronutrients by carbon nanotubes and the implications for nanotoxicity testing. Small 2008, 4, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, M.A.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Huang, J.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Graphene-induced adsorptive and optical artifacts during in vitro toxicology assays. Small 2013, 9, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloy, M.M.; Roberts, A.P. Effects of suspended multi-walled carbon nanotubes on daphnid growth and reproduction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rattanaudompol, U.S.; Li, H.; Bouchard, D. Effects of humic and fulvic acids on aggregation of aqu/nC60 nanoparticles. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Jang, M.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Xing, B.; Tanguay, R.L.; Lee, B.G.; Kim, S.D. Embryonic toxicity changes of organic nanomaterials in the presence of natural organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lyon, D.Y.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J. Effect of soil sorption and aquatic natural organic matter on the antibacterial activity of a fullerene water suspension. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. SETAC 2008, 27, 1888–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Le Thanh, T.; Chang, Y.-S. Comparative toxicity of bimetallic Fe nanoparticles toward Escherichia coli: Mechanism and environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Nano 2014, 1, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.P.; Xia, Q.; Hwang, H.-M.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: Generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, K.J.; Reynolds, S.H.; Kashon, M.L.; Lowry, D.T.; Dong, C.; Hubbs, A.F.; Young, S.-H.; Salisbury, J.L.; Porter, D.W.; Benkovic, S.A. Genotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes at occupationally relevant doses. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.R.; Kisin, E.R.; Tkach, A.V.; Yanamala, N.; Mercer, R.; Young, S.-H.; Fadeel, B.; Kagan, V.E.; Shvedova, A.A. Factoring-in agglomeration of carbon nanotubes and nanofibers for better prediction of their toxicity versus asbestos. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Okazaki, Y.; Chew, S.H.; Misawa, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Ishihara, T.; Yamashita, K.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Yasui, H. Diameter and rigidity of multiwalled carbon nanotubes are critical factors in mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1330–E1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
