Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Cesium Tungsten Bronze Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of CsxWO3 Using Benzyl Alcohol as Solvent
2.3. Preparation of CsxWO3 Using Anhydrous Ethanol as Solvent
2.4. Fabrication Process for CsxWO3 Coated Glass
2.5. Characterization
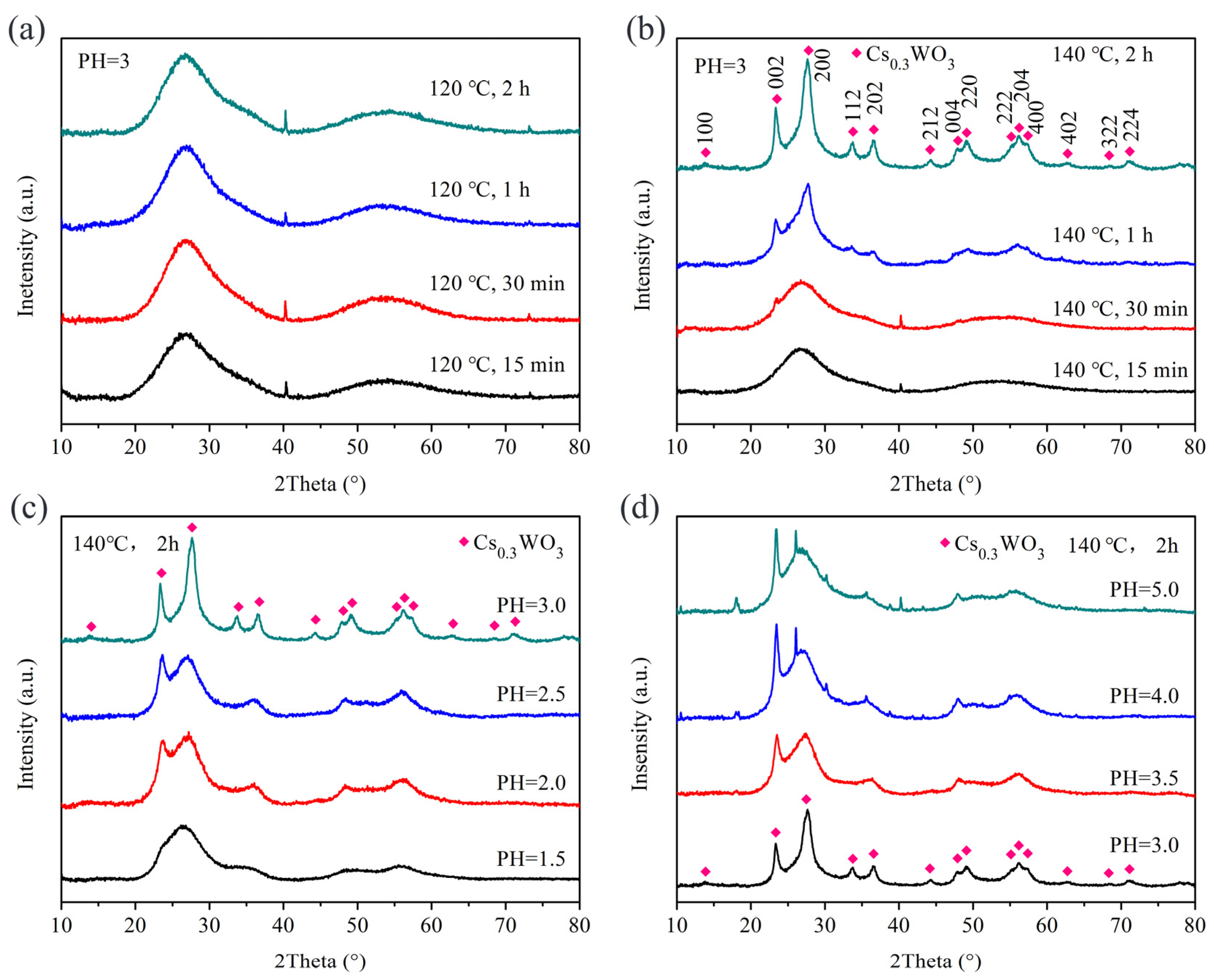
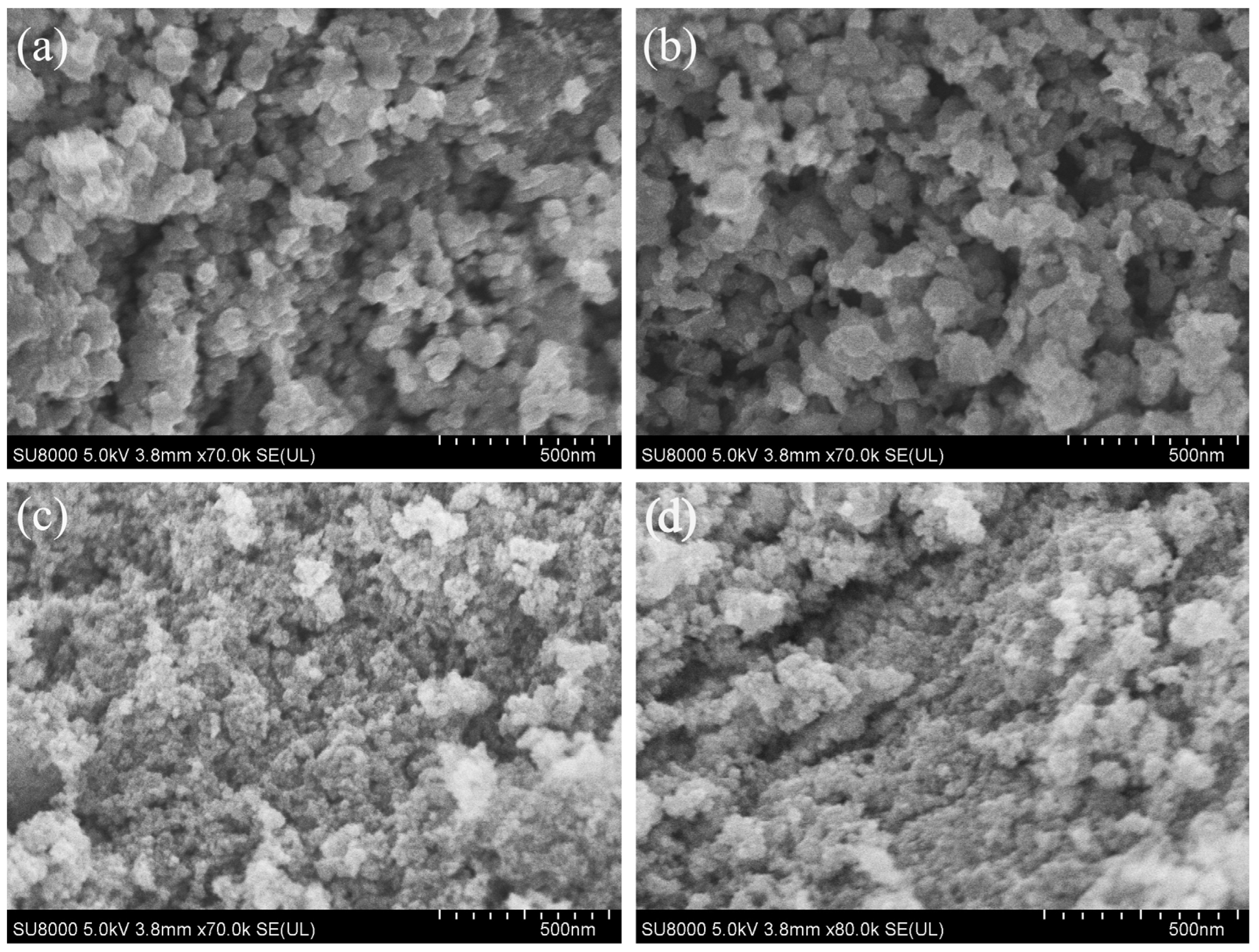
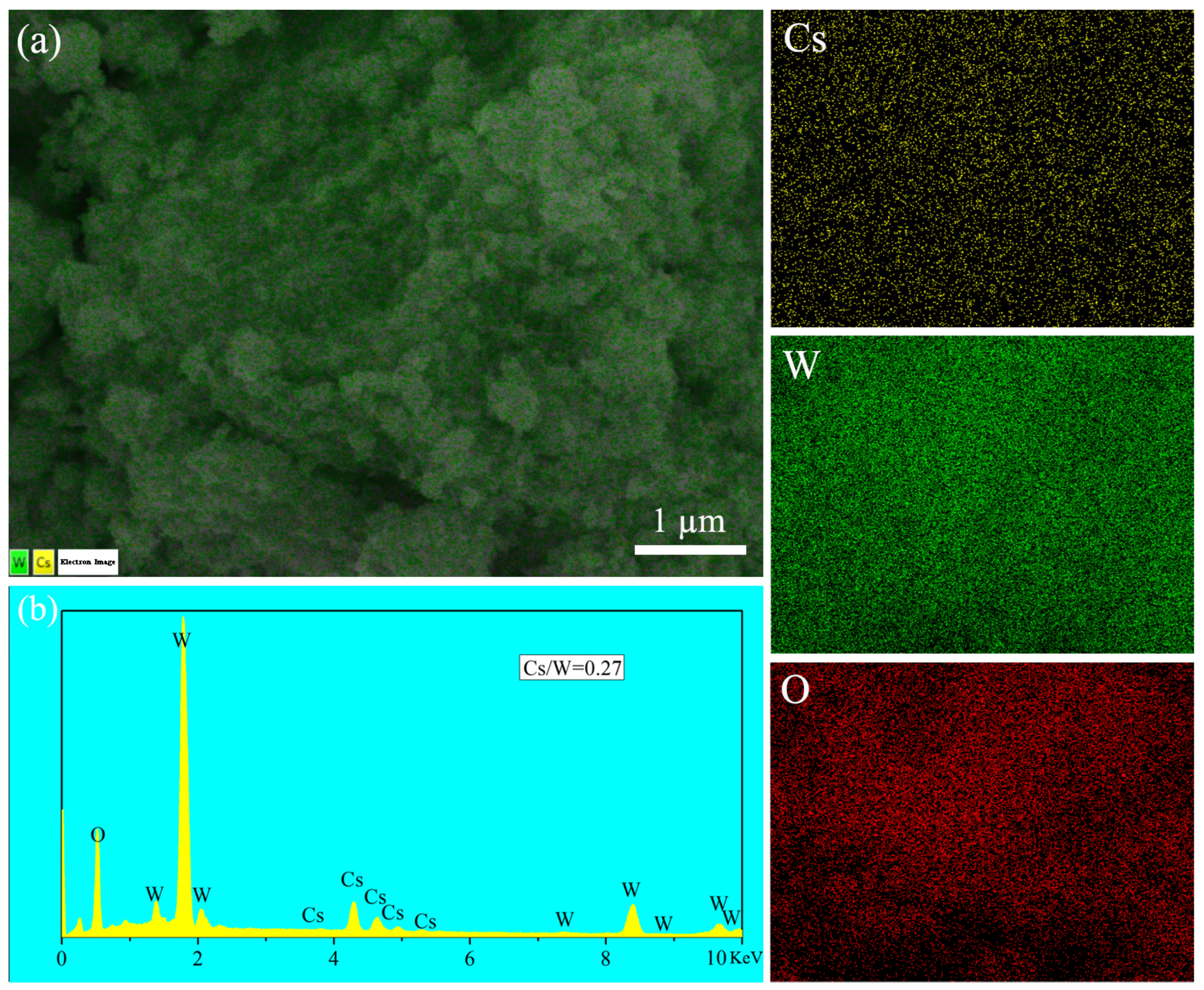
3. Results and Discussion
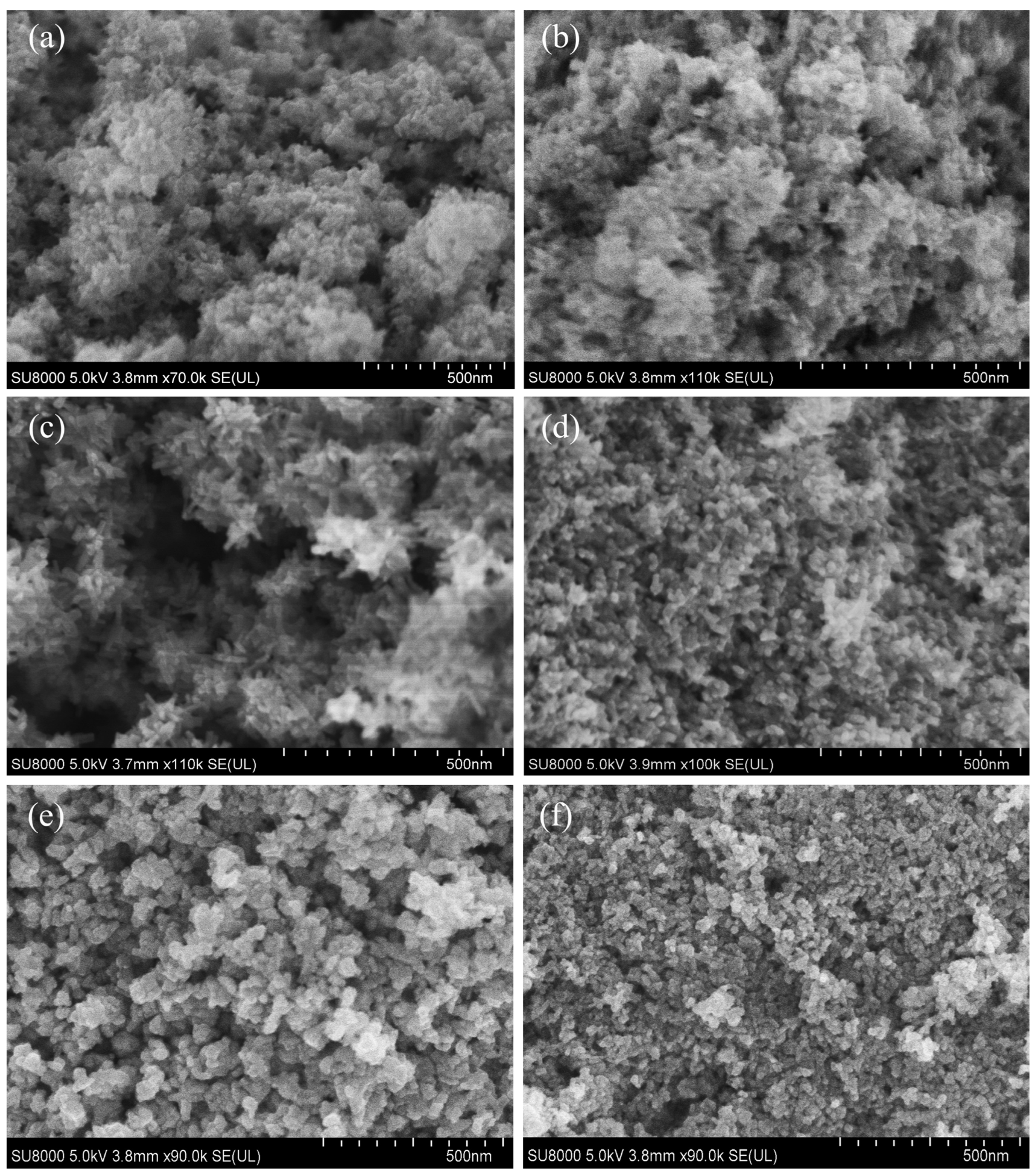
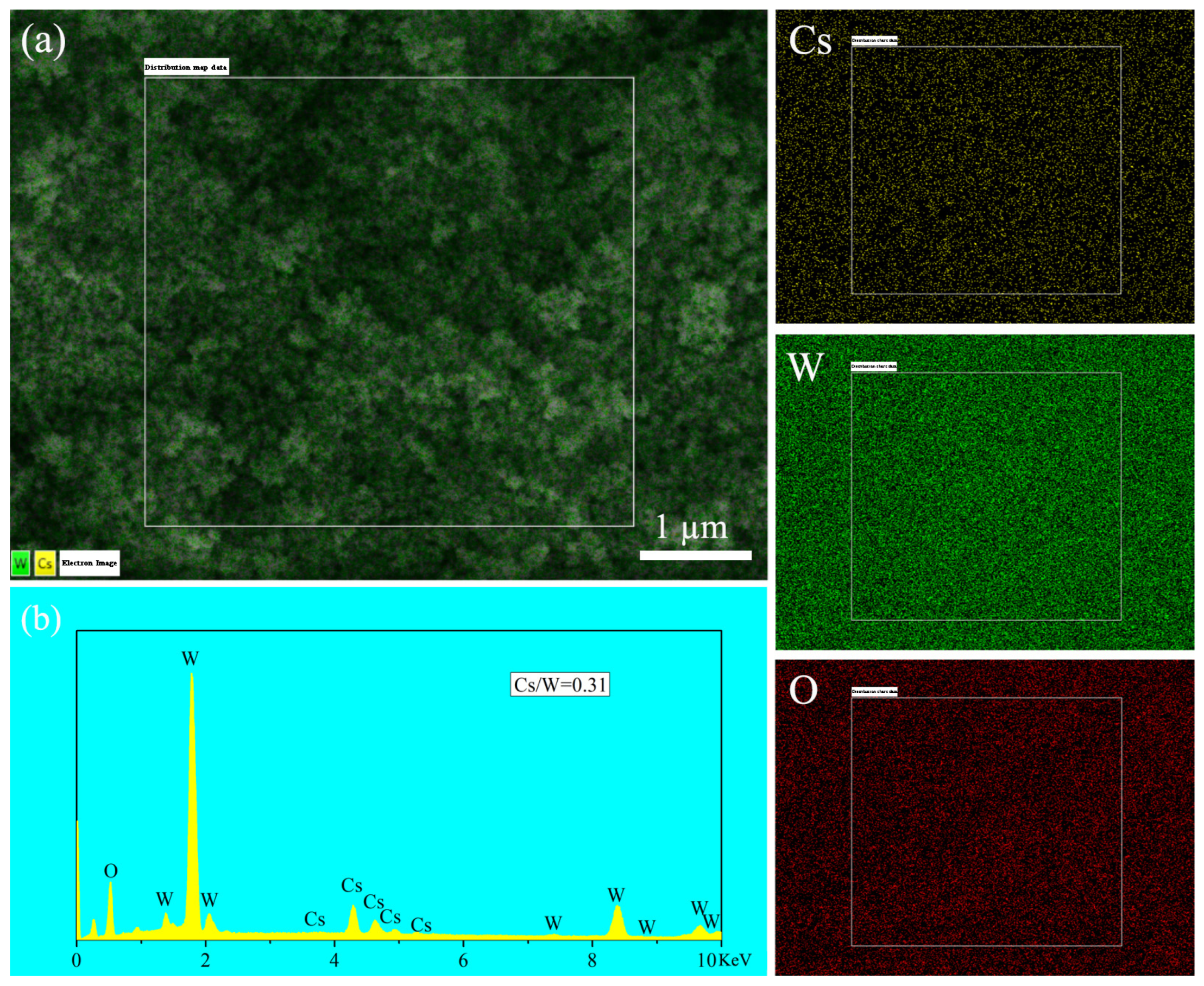
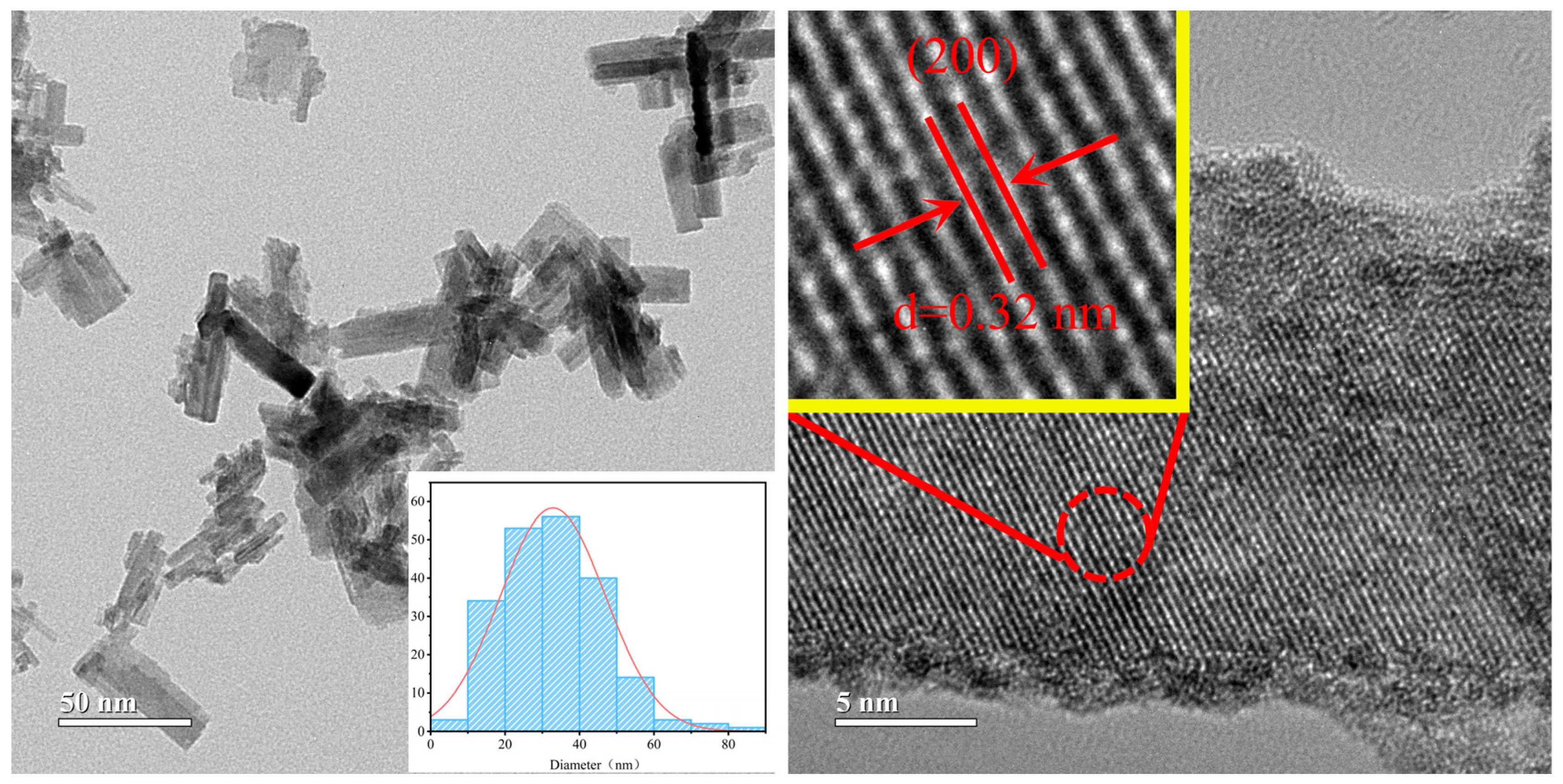
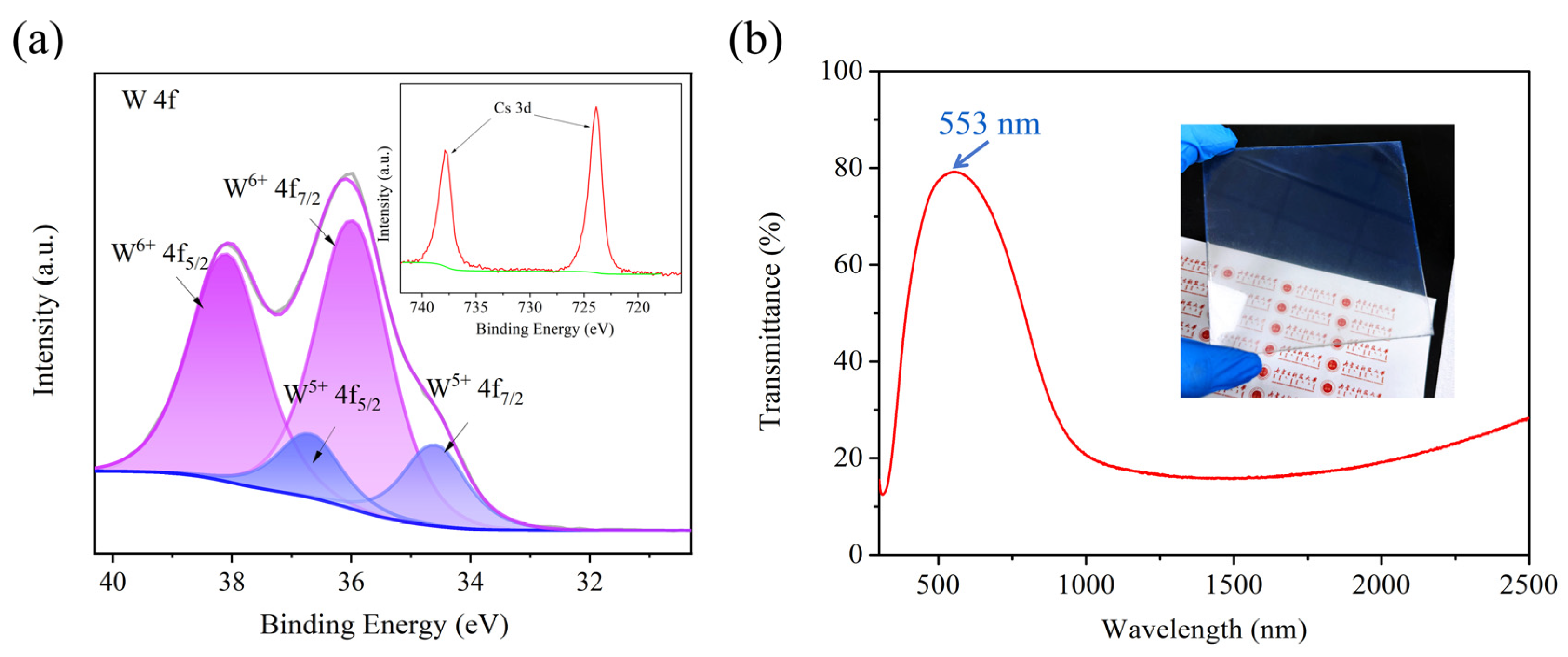
3.1. Using Benzyl Alcohol as Solvent
3.2. Using Anhydrous Ethanol as Solvent
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, W.-T.; Xiao, M.-Q.; Huang, L.; Qiu, Q.-Q.; Li, H.; Qi, X.-P.; Zeng, J.-M. Ant nest-like WO3 films for improving electrochromic and energy-storage dual-functional performance by the surface modification of N-doped carbon. Tungsten 2024, 7, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafin, Y.N.; Abduvalov, A.; Kaikanov, M.; Poulopoulos, S.G.; Atabaev, T.S. A review on WO3 photocatalysis used for wastewater treatment and pesticide degradation. Heliyon 2025, 11, e40788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Liu, T.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. One-step ball-milling synthesis of cesium tungsten bronze nanoparticles and near-infrared shielding performance. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 21393–21401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-T.; Yang, H.-Z.; Lai, L.-X.; Rachmawati, D. Study on photoelectric conversion properties for near-infrared absorbing materials. ChemNanoMat 2023, 9, e202200536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheref, Y.; Lochon, F.; Daugas, L.; Cleret de Langavant, C.; Larquet, E.; Baron, A.; Gacoin, T.; Kim, J. Dual-band LSPR of tungsten bronze nanocrystals tunable over NIR and SWIR ranges. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 9795–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, N.; Abraham, M.; Parvathy, P.A.; Das, S.; Sahoo, S.K. Flexible and thermoresponsive AEMR-pNIPAM/Cs0.33WO3 composite hydrogel film with NIR shielding potential for smart windows and smart curtains. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Fan, H.; Dai, Y.; Kong, J.; Ge, L. Insight into the solar utilization of a novel Z-scheme Cs0.33WO3/CdS heterostructure for UV-Vis-NIR driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Zhang, B.; Feng, S.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, A.; Ren, H.; Liu, W. Cs0.33WO3/(t-m)-BiVO4 double Z-type heterojunction photothermal synergistic enhanced full-spectrum degradation of antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Guo, C.; Zheng, N.; Sun, T.; Liu, S. CsxWO3 Nanorods coated with polyelectrolyte multilayers as a multifunctional nanomaterial for bimodal imaging-guided photothermal/photodynamic cancer treatment. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-M.; Motora, K.G.; Kuo, D.-H.; Lai, C.-C.; Huang, B.R.; Saravanan, A. Cesium tungsten bronze nanostructures and their highly enhanced hydrogen gas sensing properties at room temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 25752–25762. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, N.; Huang, J.-Y.; He, S.; Hanggai, W.; Chao, L.-M. Applications of optical control materials based on localized surface plasmon resonance effect in smart windows. Tungsten 2024, 6, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Adachi, K. Near infrared absorption of tungsten oxide nanoparticle dispersions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 4059–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, H.J.; Lee, S.; Choi, K.H.; Shin, G. Facile fabrication of high-efficiency near-infrared absorption film with tungsten bronze nanoparticle dense layer. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Chen, D.-H. Preparation and near-infrared photothermal conversion property of cesium tungsten oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, S.; Luo, H.; Yao, H.; Huang, X.; Jin, P. The preparation of a high performance near-infrared shielding CsxWO3/SiO2 composite resin coating and research on its optical stability under ultraviolet illumination. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-X.; Ando, Y.; Dong, X.-L.; Shi, F.; Yin, S.; Adachi, K.; Chonan, T.; Tanaka, A.; Sato, T. Microstructure and electrical–optical properties of cesium tungsten oxides synthesized by solvothermal reaction followed by ammonia annealing. J. Solid State Chem. 2010, 183, 2456–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Cao, C.; Gao, Y.; Luo, H. Synthesis of CsxWO3 nanoparticles and their NIR shielding properties. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13469–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yin, S.; Zhang, P.; Yan, M.; Adachi, K.; Chonan, T.; Sato, T. Novel synthesis of homogenous CsxWO3 nanorods with excellent NIR shielding properties by a water controlled-release solvothermal process. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8227–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, H.; Kang, L.; Zhao, Z. Effects of Mo-doping on microstructure and near-infrared shielding performance of hydrothermally prepared tungsten bronzes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y. Influence of size and shape on optical properties of cesium tungsten bronze: An experimental and theoretical approach. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 6436–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yin, S.; Dong, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Sato, T. Microwave-assisted synthesis of CsxWO3 nanoparticle and its near-infrared absorbing properties. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2013, 10, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Sun, C.; Peng, L.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y. Passive energy-saving buildings realized by the combination of transparent heat-shielding glass and energy storage cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbühler, K. What is a green solvent? A comprehensive framework for the environmental assessment of solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Ta, N.; Cao, F.; He, S.; He, J.; Chao, L. Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Cesium Tungsten Bronze Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080627
Huang J, Ta N, Cao F, He S, He J, Chao L. Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Cesium Tungsten Bronze Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(8):627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080627
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jingyi, Na Ta, Fengze Cao, Shuai He, Jianli He, and Luomeng Chao. 2025. "Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Cesium Tungsten Bronze Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 15, no. 8: 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080627
APA StyleHuang, J., Ta, N., Cao, F., He, S., He, J., & Chao, L. (2025). Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis of Cesium Tungsten Bronze Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 15(8), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15080627







