Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.3. Wastewater Characterization
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Water Quality Parameters
2.6. Enumeration of Aerobic Plate Count (APC)
2.7. Silver and Zinc Concentrations
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2. Wastewater Characterization
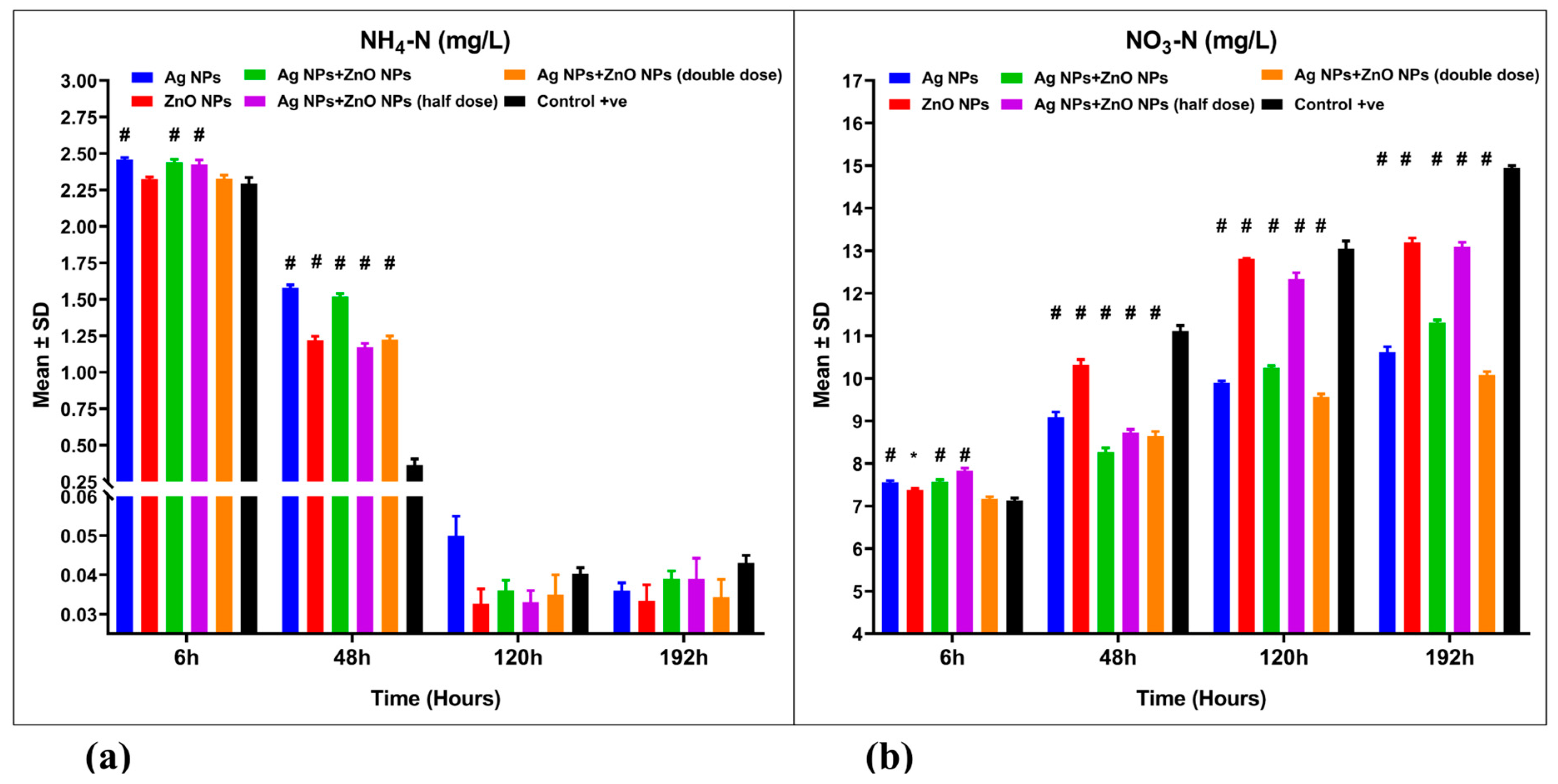
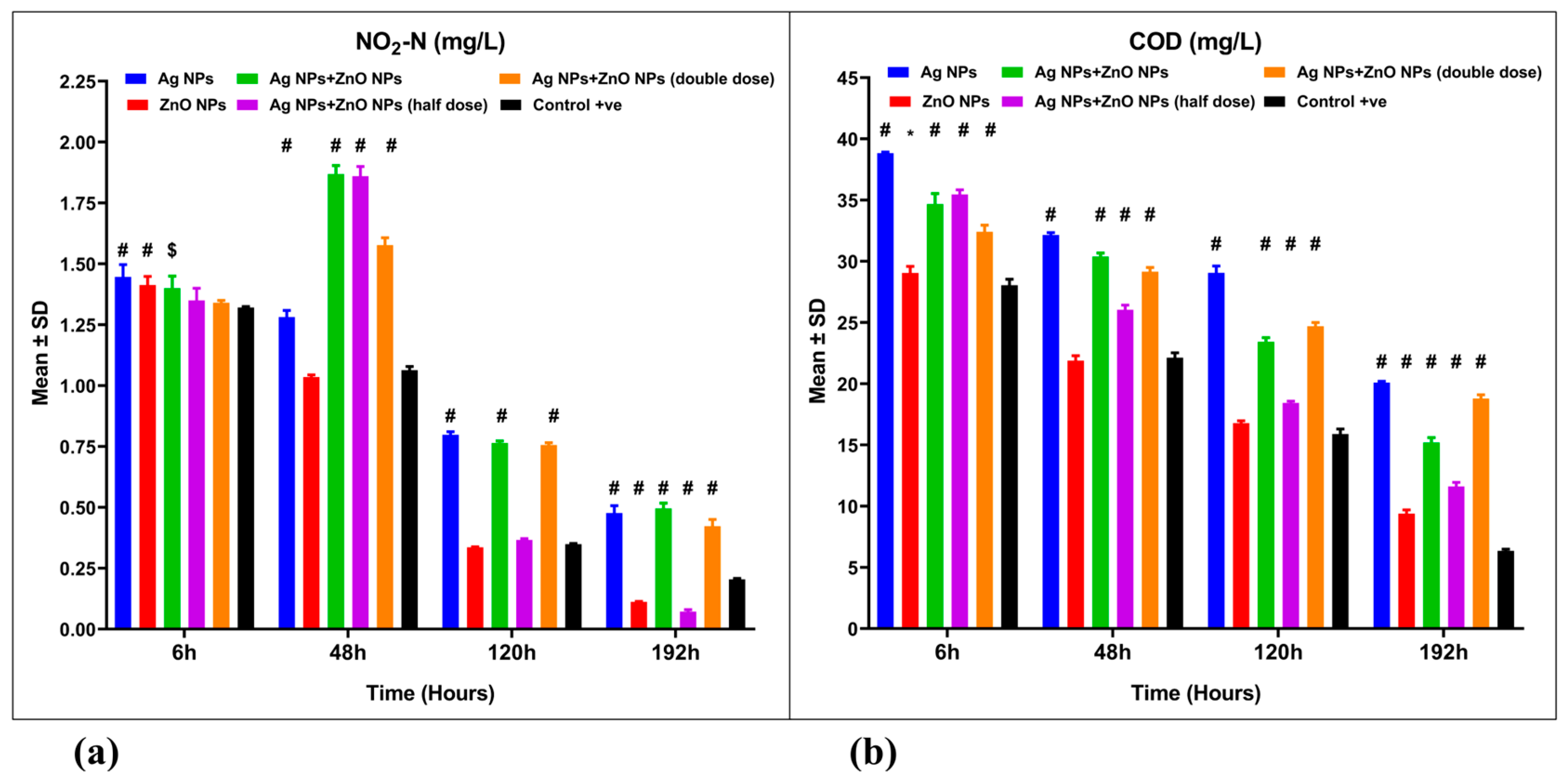
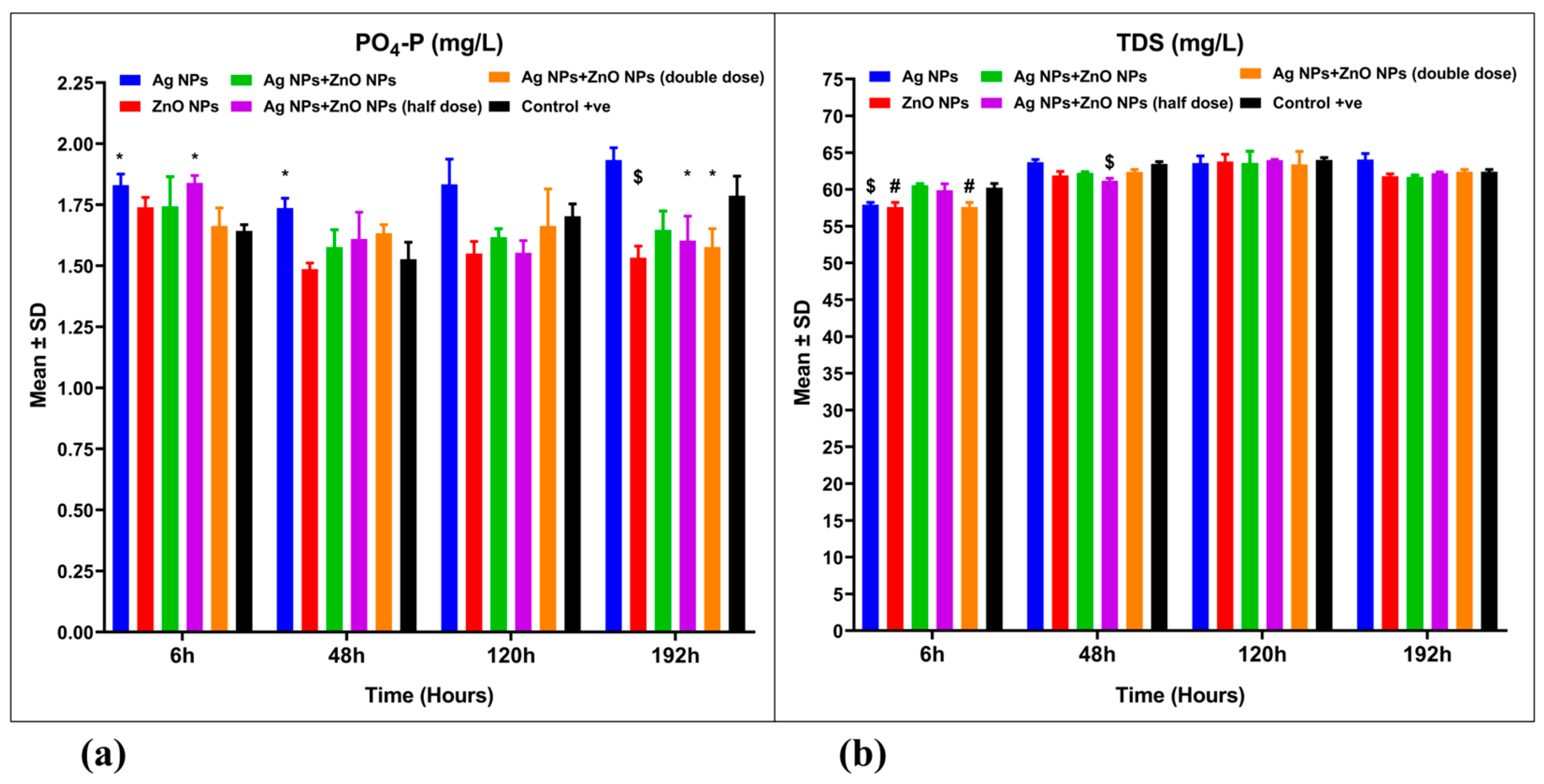
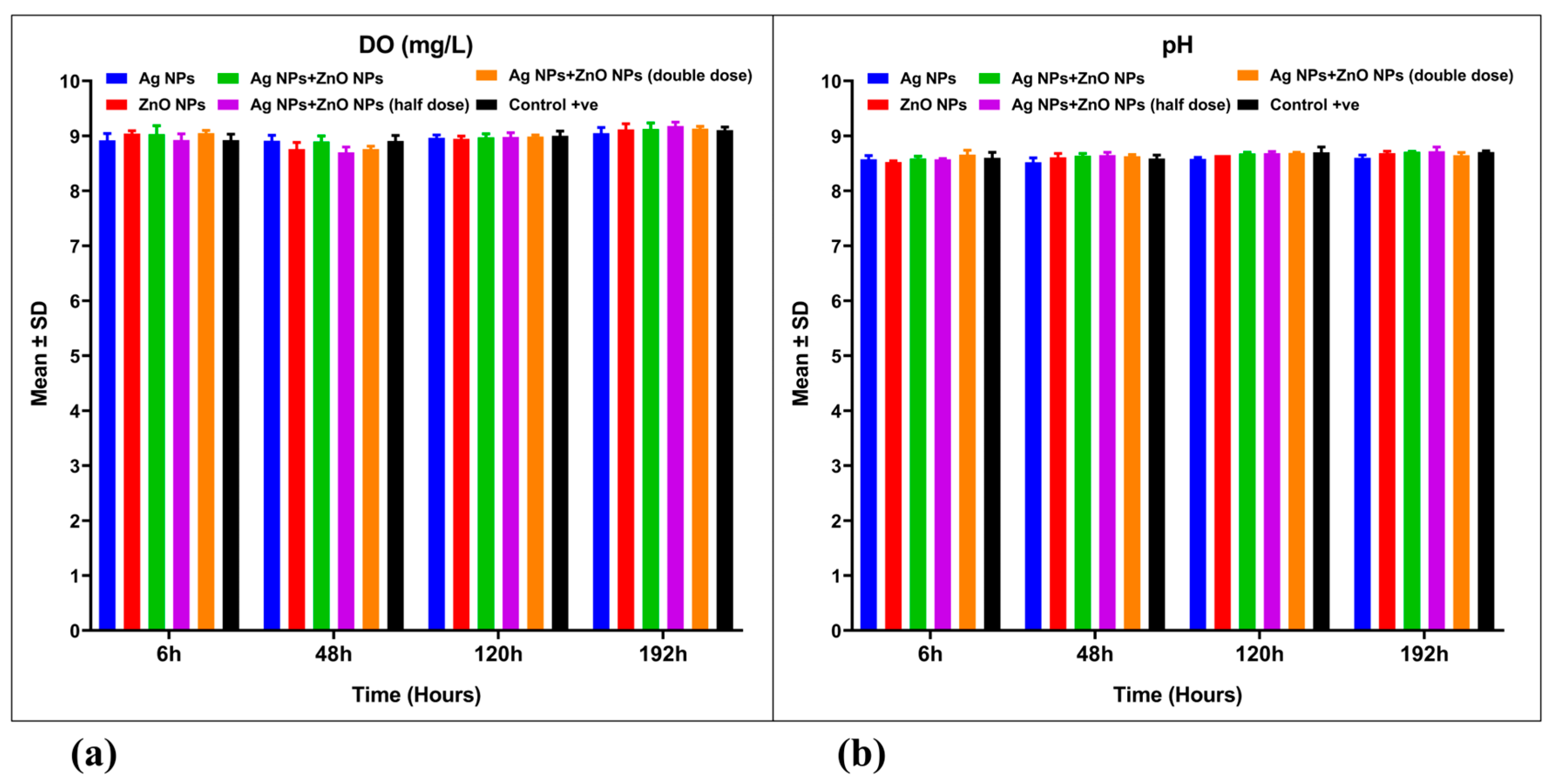
3.3. Water Quality Parameters
3.4. Aerobic Plate Count (APC)
3.5. Silver and Zinc Concentrations
4. Discussion
- NH4+ + CO2 + 1.5 O2 + Nitrosomonas → NO2− + H2O + H+ (first step)
- NO2− + 0.5 O2 + Nitrobacter → NO3− (second step)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Izah, S.C.; Richard, G.; Stanley, H.O.; Sawyer, W.E.; Ogwu, M.C.; Uwaeme, O.R. Integrating the one health approach and statistical analysis for sustainable aquatic ecosystem management and trace metal contamination mitigation. ES Food Agrofor. 2023, 14, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, K.; Garnier, J.; Nielsen, L.R.; Buttigieg, S.; Meneghi, D.D.; Holmberg, M.; Kock, R. Roadmap to a One Health agenda 2030. CABI Rev. 2017, 2017, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Bateman, I.J.; Hinchliffe, S.J.; Bass, D.L.; Hartnell, R.; Santos, E.M.; Tyler, C.R. Sustainable aquaculture through the One Health lens. Nat. Food. 2020, 1, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Porchas, M.; Martinez-Cordova, L.R. World aquaculture: Environmental impacts and troubleshooting alternatives. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 389623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.K.; Yi, Y. Minimizing environmental impacts of freshwater aquaculture and reuse of pond effluents and mud. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, W.; Qu, X.; Xin, W.; Guo, C.; Chen, Y. Effects of aquaculture on lakes in the Central Yangtze River Basin, China, I. water quality. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2018, 80, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauda, A.B.; Ajadi, A.; Tola-Fabunmi, A.S.; Akinwole, A.O. Waste production in aquaculture: Sources, components and managements in different culture systems. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Massaut, L. Risks associated with the use of chemicals in pond aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 1999, 20, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Zeng, C. Toxic effects of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate to decapod crustaceans: A review on factors influencing their toxicity, physiological consequences, and coping mechanisms. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, R.; Baldisserotto, B. Nitrogen and phosphorus waste in fish farming. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2008, 34, 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.Y.; Lowry, G.V.; Jolivet, J.P.; Wiesner, M.R. Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental, health and safety perspective. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Durrani, T. The role of some important metal oxide nanoparticles for wastewater and antibacterial applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Ecotox. 2021, 3, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Ahamad, L.; Chaudhary, A.; Kumar, G.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, S. Nanoparticle-mediated bioremediation as a powerful weapon in the removal of environmental pollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, A.S.; Bano, S.; Khan, N.; Sultana, S.; Rehman, Z.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, M.Z. Nanoremediation technologies for sustainable remediation of contaminated environments: Recent advances and challenges. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y. The effects of silver nanoparticles on intact wastewater biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venis, R.A.; Basu, O.D. Silver and zinc oxide nanoparticle disinfection in water treatment applications: Synergy and water quality influences. H2Open J. 2021, 4, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosselhy, D.A.; El-Aziz, M.A.; Hanna, M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Husien, M.M.; Feng, Q. Comparative synthesis and antimicrobial action of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Mahdy, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Recent progress in applications of nanoparticles in fish medicine: A review. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimapilis, E.A.S.; Hsu, C.S.; Mendoza, R.M.O.; Lu, M.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2018, 28, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, L.; Lin, D. Toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles to Escherichia coli: Mechanism and the influence of medium components. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.T.; Hossain, M.S.; Shariffuddin, J.H. Green synthesis and photocatalytic insights: A review of zinc oxide nanoparticles in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 26, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puay, N.Q.; Qiu, G.; Ting, Y.P. Effect of Zinc oxide nanoparticles on biological wastewater treatment in a sequencing batch reactor. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 88, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, J.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, M.; Thakur, R.R.; Chand, S.; Rout, P.R.; Shahid, M.K. Advances in Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites for Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Water 2024, 16, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Z. Impact of metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles on wastewater treatment and anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Xing, B. Environmental processes and toxicity of metallic nanoparticles in aquatic systems as affected by natural organic matter. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, F.; Sonderer, T.; Scholz, R.W.; Nowack, B. Modeled environmental concentrations of engineered nanomaterials (TiO2, ZnO, Ag, CNT, fullerenes) for different regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9216–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibiya, A.; Jeyavani, J.; Santhanam, P.; Preetham, E.; Freitas, R.; Vaseeharan, B. Comparative evaluation on the toxic effect of silver (Ag) and zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles on different trophic levels in aquatic ecosystems: A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2022, 42, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.S.; Mo, K.; Kim, M. A case study on the relationship between conductivity and dissolved solids to evaluate the potential for reuse of reclaimed industrial wastewater. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 16, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1985; Volume 2254. [Google Scholar]
- Lipps, W.C.; Baxter, T.E.; Braun-Howland, E.B.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 6222:1999; Water Quality—Enumeration of Culturable Micro-Organisms—Colony Count by Inoculation in a Nutrient Agar culture Medium. ISO—International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Olejnik, S.; Algina, J. Generalized eta and omega squared statistics: Measures of effect size for some common research designs. Psychol. Methods 2003, 8, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics, 6th ed.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2024; ISBN 9781529668704. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, A.B.; Shaheen, M.A.; Abbas, A.; Zaman, Y.; Bratty, M.A.; Najmi, A.; Hanbashi, A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; ur Rehman, Z.; et al. Thermodynamic and kinetic insights into azo dyes photocatalytic degradation on biogenically synthesized ZnO nanoparticles and their antibacterial potential. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Shaban, M.; Siddique, A.B.; Zulfiqar, A.; Lali, N.S.; Naeem-ul-Hassan, M.; Irfan, M.I.; Sher, M.; ur Rehman, M.F.; Hanbashi, A.; et al. Greenly synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles: An efficient, cost-effective catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid and with improved antioxidant and phyto-toxic properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Amin, H.M. Silver nanoparticles modified electrodes for electroanalysis: An updated review and a perspective. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijanzadeh, A.R.; Vakili, M.R.; Khordad, R. A study of the surface plasmon absorption band for nanoparticles. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 7, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, M.I.; El-Mahdy, M.M.; Theiner, S.; El-Matbouli, M.; Saleh, M. In vitro assessment of the antimicrobial activity of silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles against fish pathogens. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scown, T.M.; Santos, E.M.; Johnston, B.D.; Gaiser, B.; Baalousha, M.; Mitov, S.; Tyler, C.R. Effects of aqueous exposure to silver nanoparticles of different sizes in rainbow trout. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 115, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwiche, C.C. The nitrogen cycle. Sci. Am. 1970, 223, 136–147. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24925899 (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Stein, L.Y.; Nicol, G.W. Nitrification. In eLS; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiu, Z.; Alvarez, P.J. Impacts of silver nanoparticles on cellular and transcriptional activity of nitrogen-cycling bacteria. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, M.G.; Stein, L. Research on Nitrification and Related Processes, Part B; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 496. [Google Scholar]
- Marcilhac, C.; Sialve, B.; Pourcher, A.M.; Ziebal, C.; Bernet, N.; Béline, F. Digestate color and light intensity affect nutrient removal and competition phenomena in a microalgal-bacterial ecosystem. Water Res. 2014, 64, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, H.; Toolabian, K.; Thompson, I.; Qiu, G. Biotoxicity evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles on bacterial performance of activated sludge at COD, nitrogen, and phosphorus reduction. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, K.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Removal of silver nanoparticles in simulated wastewater treatment processes and its impact on COD and NH4 reduction. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.K.; Hu, Z.Q. Nitrification inhibition by silver nanoparticles. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radniecki, T.S.; Stankus, D.P.; Neigh, A.; Nason, J.A.; Semprini, L. Influence of liberated silver from silver nanoparticles on nitrification inhibition of Nitrosomonas europaea. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidri, I.; Shahid, M.; Hussain, S.; Shahzad, T.; Mahmood, F.; Hassan, M.U.; Al-Khayri, J.M.; Aldaej, M.I.; Sattar, M.N.; Rezk, A.A.; et al. Efficacy of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles in treating wastewater for sustainable wheat cultivation. Plants 2023, 12, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Zuo, J. Response of anammox granules to ZnO nanoparticles at ambient temperature. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 13, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Yu, N.; Han, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; She, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; et al. Effect of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on microbial diversity and removal performance of sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levard, C.; Hotze, E.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Brown, G.E., Jr. Environmental transformations of silver nanoparticles: Impact on stability and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6900–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, Y.; Gu, J.D.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.; Lin, J.G. Influence of critical factors on nitrogen removal contribution by anammox and denitrification in an anammox-inoculated wastewater treatment system. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.B.; Singh, B.; Zhu, Y.G. 2019. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in agricultural soils-synthesis and prospective. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, A.; Salamanca, A. Nitrate toxicity to aquatic animals: A review with new data for freshwater invertebrates. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrokh, S.; Hosseinkhani, B.; Emtiazi, G. The impact of silver nanoparticles on bacterial aerobic nitrate reduction process. J. Bioprocess. Biotech. 2014, 4, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, V.; Lu, Y.; Darwin, A.J. Periplasmic nitrate reductase (NapABC enzyme) supports anaerobic respiration by Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Effects of ZnO nanoparticles on wastewater biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, H. Alumina nanoparticles-induced effects on wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removal after short-term and long-term exposure. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, H.; Rafiee, M.; Yazdanbakhsh, A.R.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Guanglei, Q. A comparative study on the toxicity of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) on aerobic granular sludge and flocculent activated sludge: Reactor performance, microbial behavior, and mechanism of toxicity. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Enhanced biological nitrogen removal under low dissolved oxygen in an anaerobic-anoxic-oxic system: Kinetics, stoichiometry and microbial community. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.D.; Noguera, D.R. Evaluating the effect of dissolved oxygen on ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in activated sludge. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Xenopoulos, M.A.; Williams, C.J.; Hoque, M.E.; Metcalfe, C.D. Effects of silver nanoparticles on bacterial activity in natural waters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazouli, M.A.; Eslamifar, M.; Javan, F. Water disinfection using silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Nano Res. 2021, 69, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, G.; Kubo, A.L.; Vija, H.; Kahru, A.; Bondar, D.; Karpichev, Y.; Bondarenko, O. Synergistic antibacterial effect of copper and silver nanoparticles and their mechanism of action. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The Potential of Silver Nanoparticles for Antiviral and Antibacterial Applications: A Mechanism of Action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Du, M.R.; Liu, K.K.; Zhou, R.; Ma, R.N.; Jiao, Z.; Shan, C.X. Hydrophilic ZnO nanoparticles@ calcium alginate composite for water purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13305–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Jain, M.; Pandey, A.; Pant, K.K.; Ziora, Z.M.; Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Shetti, N.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Leveraging the potential of silver nanoparticles-based materials towards sustainable water treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Dybowska, A.; Berhanu, D.; Luoma, S.N.; Valsami-Jones, E. The complexity of nanoparticle dissolution and its importance in nanotoxicological studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 438, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musee, N.; Zvimba, J.N.; Schaefer, L.M.; Nota, N.; Sikhwivhilu, L.M.; Thwala, M. Fate and behavior of ZnO- and Ag-engineered nanoparticles and a bacterial viability assessment in a simulated wastewater treatment plant. J Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2014, 49, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Adeleye, A.S.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Keller, A.A. Heteroaggregation of nanoparticles with bio-coloids and geocolloids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 226, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Lenihan, H.S.; Cherr, G.; Cardinale, B.J.; Miller, R.; Ji, Z. Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.M.E.; Luxton, T.P.; Silva, R.G.; Scheckel, K.G.; Suidan, M.T.; Tolaymat, T.M. Impact of environmental conditions (pH, ionic strength, and electrolyte type) on the surface charge and aggregation of silver nanoparticles suspensions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanopart Res. 2009, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, G.; kumar Chinnaiyan, S.; Sugumaran, A.; Narayanasamy, D. Sustainable bioactivity enhancement of ZnO–Ag nanoparticles in antimicrobial, antibiofilm, lung cancer, and photocatalytic applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 26663–26682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennifer, M.; Maciej, W. Nanoparticle Technology as a Double-Edged Sword: Cytotoxic, Genotoxic and Epigenetic Effects on Living Cells. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 4, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.Y.; Gottschalk, F.; Hungerbühler, K.; Nowack, B. Comprehensive probabilistic modelling of environmental emissions of engineered nanomaterials. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, G.; Bracale, M.; Vannini, C. Phytotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Aquatic Plants, Algae, and Microorganisms. In Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae and Microorganisms: Concepts and Controversies 2; Tripathi, D.K., Ahmad, P., Sharma, S., Chauhan, D.K., Dubey, N.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
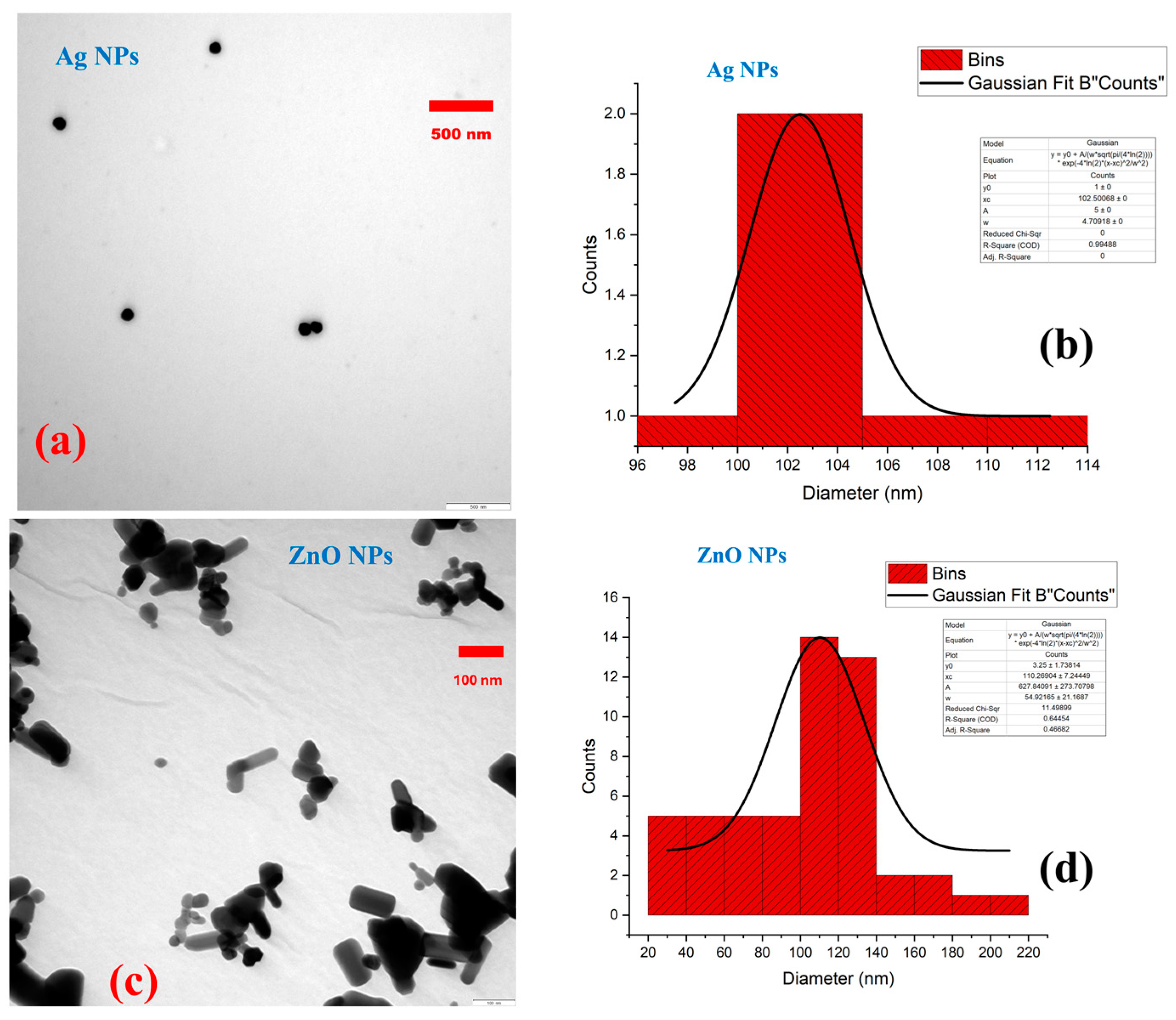
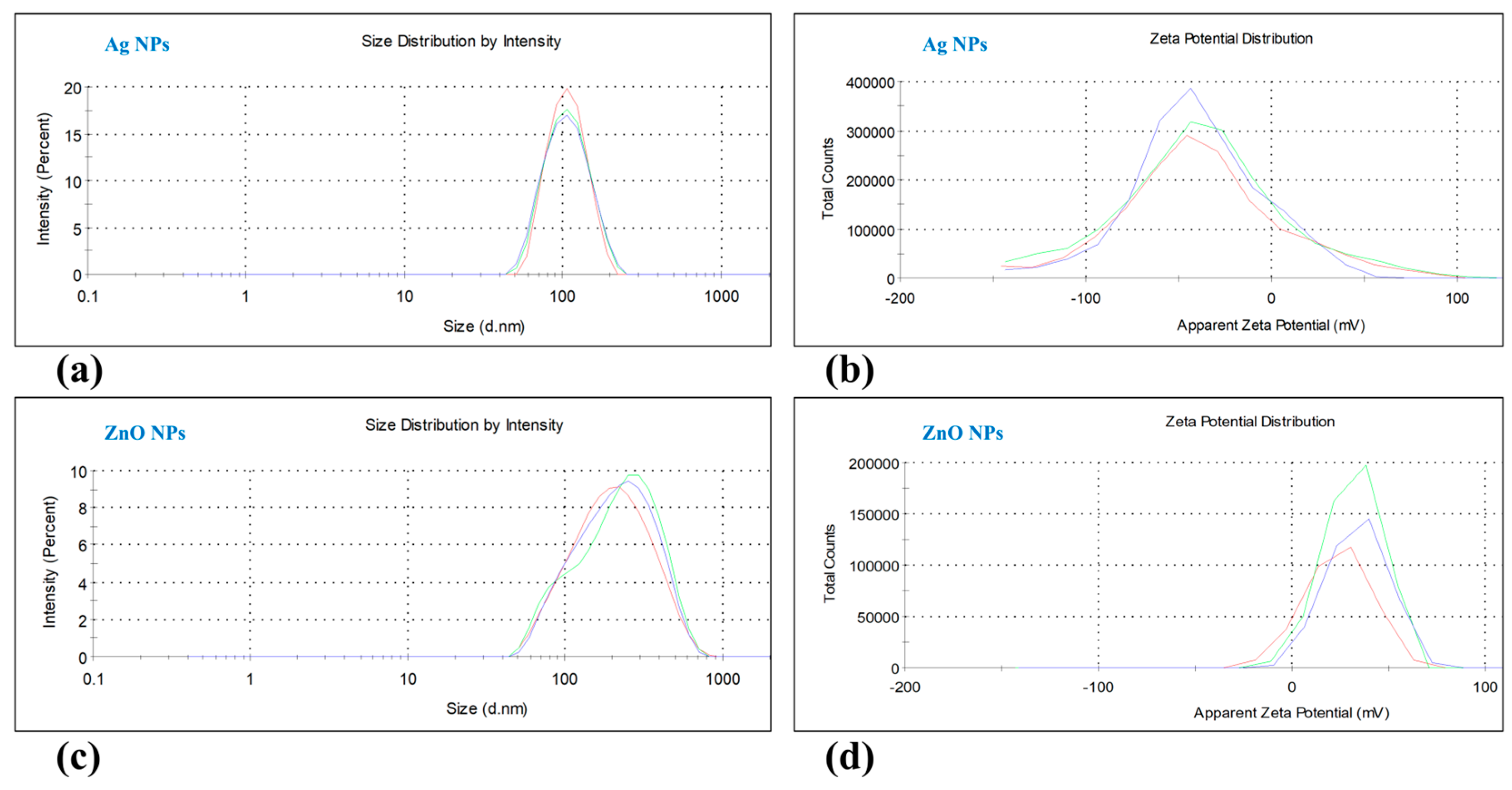



| Parameters | Measurement |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 18 °C |
| pH | 8.54 |
| Conductivity | 94.1 μs/cm * |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | 60.22 mg/L |
| Ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N) | 2.34 mg/L |
| Nitrite nitrogen (NO2-N) | 1.32 mg/L |
| Nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) | 6.99 mg/L |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | 30.15 mg/L |
| Total phosphorus (PO4-P) | 1.66 mg/L |
| Silver (Ag) | 0.007 mg/L |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.14 mg/L |
| Aerobic plate count (APC) | 5.562 Log10 CFU/mL |
| Source of Variation | df | SS | MS | F | p | Effect Size (ω2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 0.8988 | 0.1798 | 481.2 | 0.001 | 0.0127 |
| Time | 3 | 67.46 | 22.49 | 60,192 | 0.001 | 0.958 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 2.008 | 0.1339 | 358.4 | 0.001 | 0.0285 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.0179 | 0.00037 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 70.39 | |||||
| Nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 68.66 | 13.73 | 1586 | 0.001 | 0.1944 |
| Time | 3 | 243.9 | 81.29 | 9390 | 0.001 | 0.6912 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 39.84 | 2.656 | 306.8 | 0.001 | 0.1126 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.4155 | 0.008657 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 352.8 | |||||
| Nitrite nitrogen (NO2-N, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 1.623 | 0.1262 | 476.8 | 0.001 | 0.029 |
| Time | 3 | 18.08 | 6.028 | 8854 | 0.001 | 0.836 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 1.893 | 0.3246 | 185.4 | 0.001 | 0.225 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.03268 | 0.000681 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 21.63 | |||||
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 1237 | 247.4 | 1610 | 0.001 | 0.2427 |
| Time | 3 | 3717 | 1239 | 8062 | 0.001 | 0.7297 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 132.7 | 8.844 | 57.55 | 0.001 | 0.0256 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 7.376 | 0.1537 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 5093 | |||||
| Total phosphorus (PO4-P, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 0.4492 | 0.08985 | 17.00 | 0.001 | 0.354 |
| Time | 3 | 0.2045 | 0.06818 | 12.90 | 0.001 | 0.158 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 0.2813 | 0.01876 | 3.549 | 0.001 | 0.169 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.2537 | 0.005285 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 1.189 | |||||
| Total dissolved solids (TDS, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 14.28 | 2.855 | 5.897 | 0.001 | 0.039 |
| Time | 3 | 225.0 | 75.02 | 154.9 | 0.001 | 0.736 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 40.98 | 2.732 | 5.643 | 0.001 | 0.111 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 23.24 | 0.4842 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 303.5 | |||||
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO, mg/L) | Treatment | 5 | 0.0275 | 0.0055 | 0.6824 | 0.682 | 0.009 |
| Time | 3 | 0.7909 | 0.2636 | 32.68 | 0.001 | 0.542 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 0.1998 | 0.0133 | 1.651 | 0.095 | 0.055 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.3872 | 0.0081 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 1.405 | |||||
| pH | Treatment | 5 | 0.07633 | 0.01527 | 5.359 | 0.001 | 0.166 |
| Time | 3 | 0.1067 | 0.03558 | 12.49 | 0.001 | 0.263 | |
| Interaction | 15 | 0.05056 | 0.003370 | 1.183 | 0.316 | 0.021 | |
| Residual (Error) | 48 | 0.1367 | 0.002849 | ||||
| Total | 71 | 0.3704 |
| Water Parameters | Ag NPs (0.05 mg/L) | ZnO NPs (1 mg/L) | Ag NPs (0.05 mg/L) + ZnO NPs (1 mg/L) | Ag NPs (0.025 mg/L) + ZnO NPs (0.5 mg/L) | Ag NPs (0.1 mg/L) + ZnO NPs (2 mg/L) | Control + ve (Untreated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 98.46% | 98.58% | 98.33% | 98.33% | 98.53% | 98.16% |
| NO2-N (mg/L) | 63.89% | 91.52% | 65.42% | 94.52% | 67.98% | 84.52% |
| COD (mg/L) | 33.33% | 68.82% | 49.59% | 61.49% | 37.65% | 78.94% |
| PO4-P (mg/L) | −16.47% | 7.68% | 0.80% | 3.41% | 5.02% | −7.63% |
| Source of Variation | df | SS | MS | F | p | Effect Size (ω2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 5 | 6.999 | 1.400 | 35.46 | 0.001 | 0.151 |
| Time | 11 | 15.59 | 1.417 | 35.90 | 0.001 | 0.337 |
| Interaction | 55 | 16.70 | 0.3036 | 7.689 | 0.001 | 0.323 |
| Residual (Error) | 144 | 5.685 | 0.03948 | |||
| Total | 215 | 44.97 |
| Source of Variation | df | SS | MS | F | p | Effect Size (ω2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silver Concentration (Ag, mg/L) | Treatment | 4 | 0.00567 | 0.00142 | 986.5 | 0.001 | 0.507 |
| Time | 2 | 0.00307 | 0.00154 | 1069 | 0.001 | 0.275 | |
| Interaction | 8 | 0.00240 | 0.0003 | 208.9 | 0.001 | 0.214 | |
| Residual (Error) | 30 | 0.00004 | 0.0000014 | ||||
| Total | 44 | 0.01118 | |||||
| Zinc Concentration (Zn, mg/L) | Treatment | 4 | 7.822 | 1.955 | 3392 | 0.001 | 0.7687 |
| Time | 2 | 1.431 | 0.7157 | 1242 | 0.001 | 0.1406 | |
| Interaction | 8 | 0.9038 | 0.1130 | 196.0 | 0.001 | 0.0884 | |
| Residual (Error) | 30 | 0.01729 | 0.00058 | ||||
| Total | 44 | 10.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou-Okada, M.; El-Matbouli, M.; Saleh, M. Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070559
Abou-Okada M, El-Matbouli M, Saleh M. Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(7):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070559
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou-Okada, Mahmoud, Mansour El-Matbouli, and Mona Saleh. 2025. "Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment" Nanomaterials 15, no. 7: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070559
APA StyleAbou-Okada, M., El-Matbouli, M., & Saleh, M. (2025). Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Effective Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Nanomaterials, 15(7), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070559









