Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
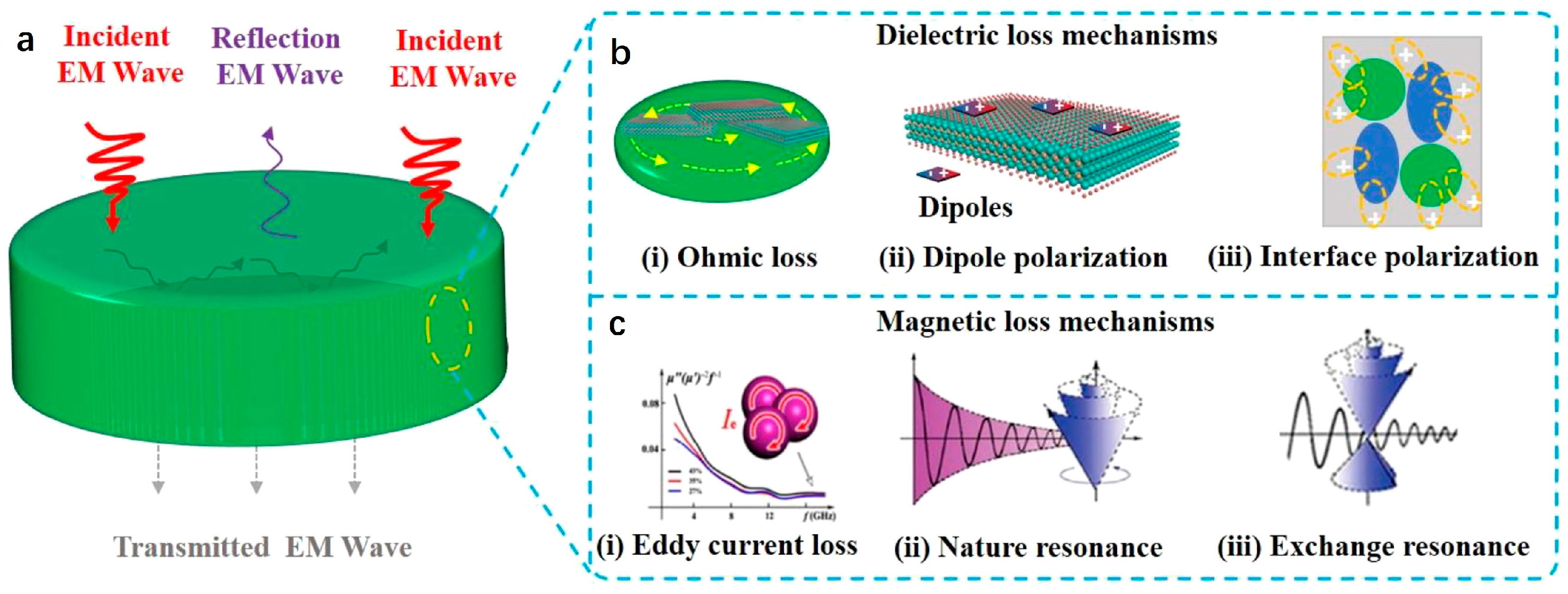
2. MA Absorption Mechanisms
2.1. Impedance Matching
2.2. Attenuation Characteristics
2.2.1. Dielectric Loss
2.2.2. Magnetic Loss
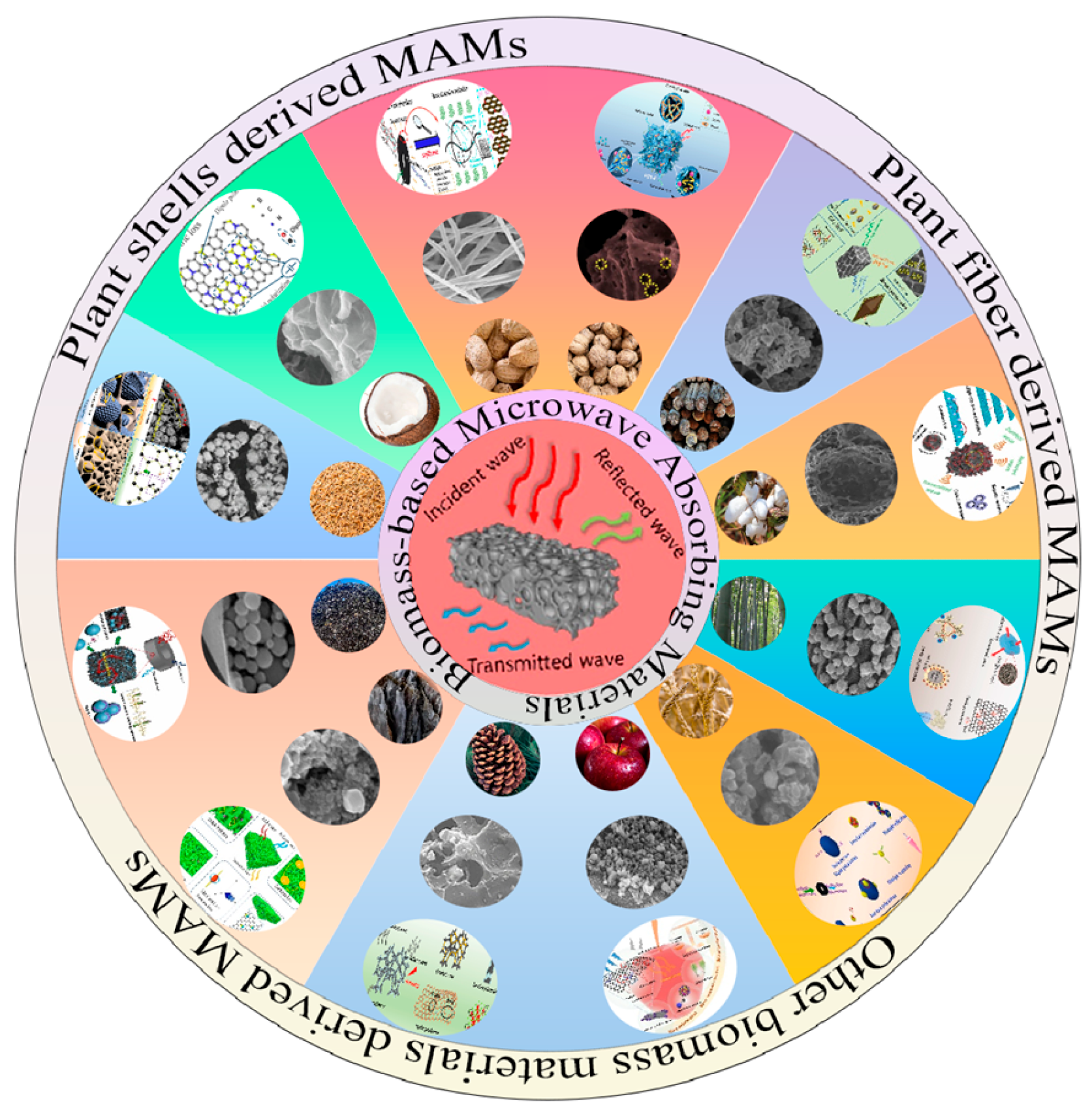
3. Biomass-Derived Microwave Absorption Materials
3.1. Plant Shells-Derived MAMs
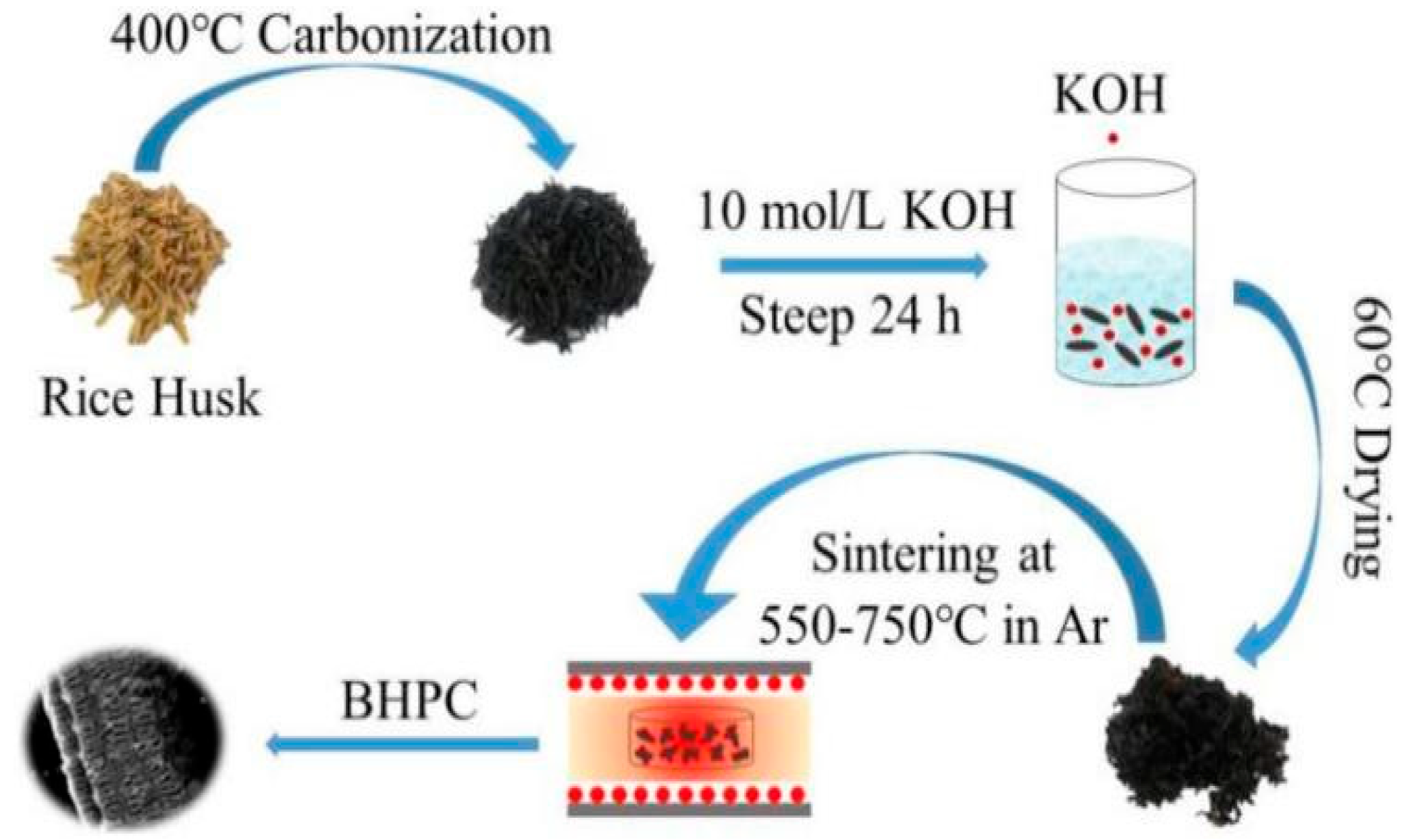
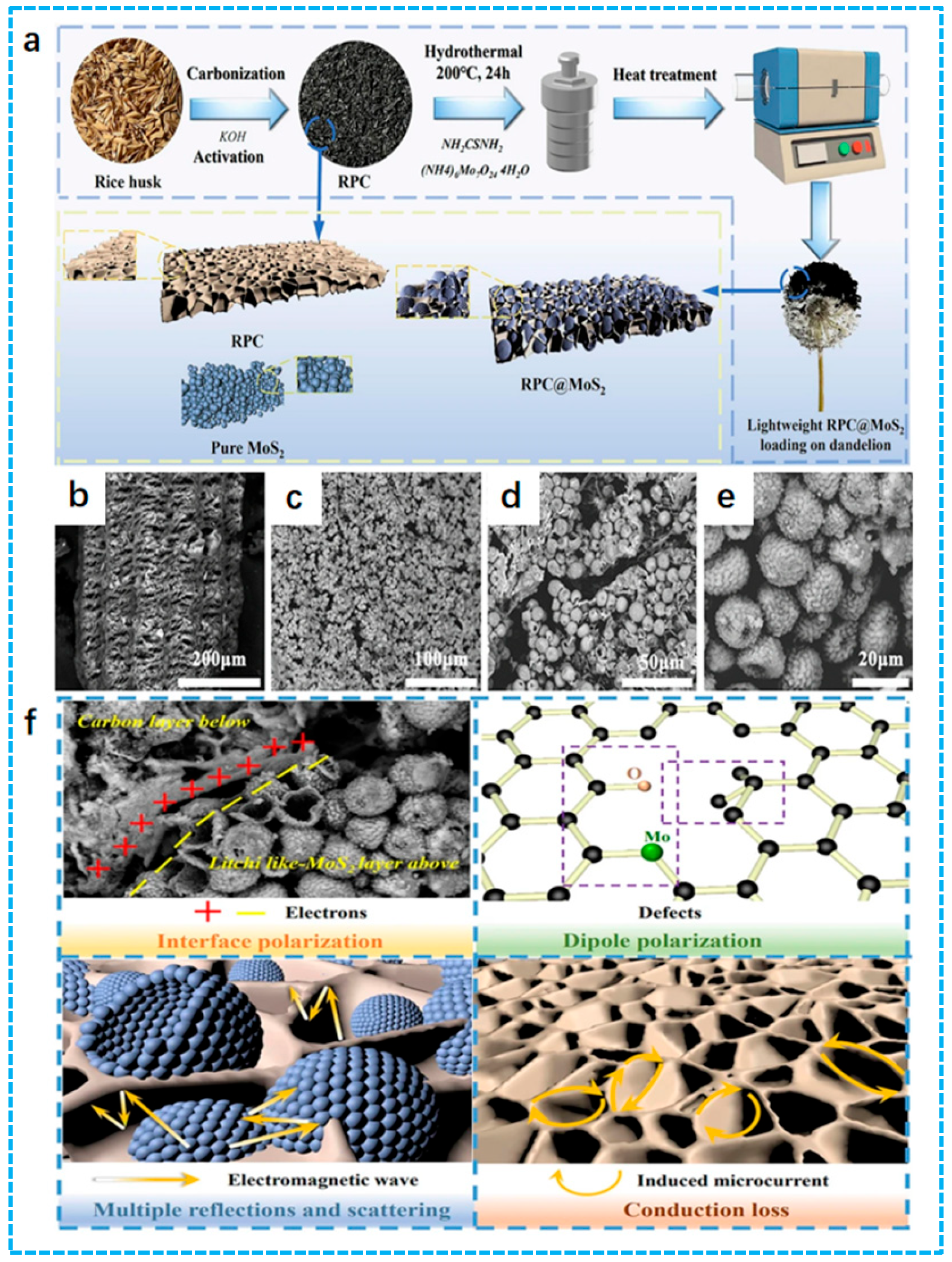
3.1.1. Rice Husk as Precursor
3.1.2. Coconut Shell as Precursor
3.1.3. Other Biomass Shells as Precursors
3.2. Plant Fiber as Precursor
3.2.1. Wood Fiber as Precursor
3.2.2. Cotton Fiber as Precursor
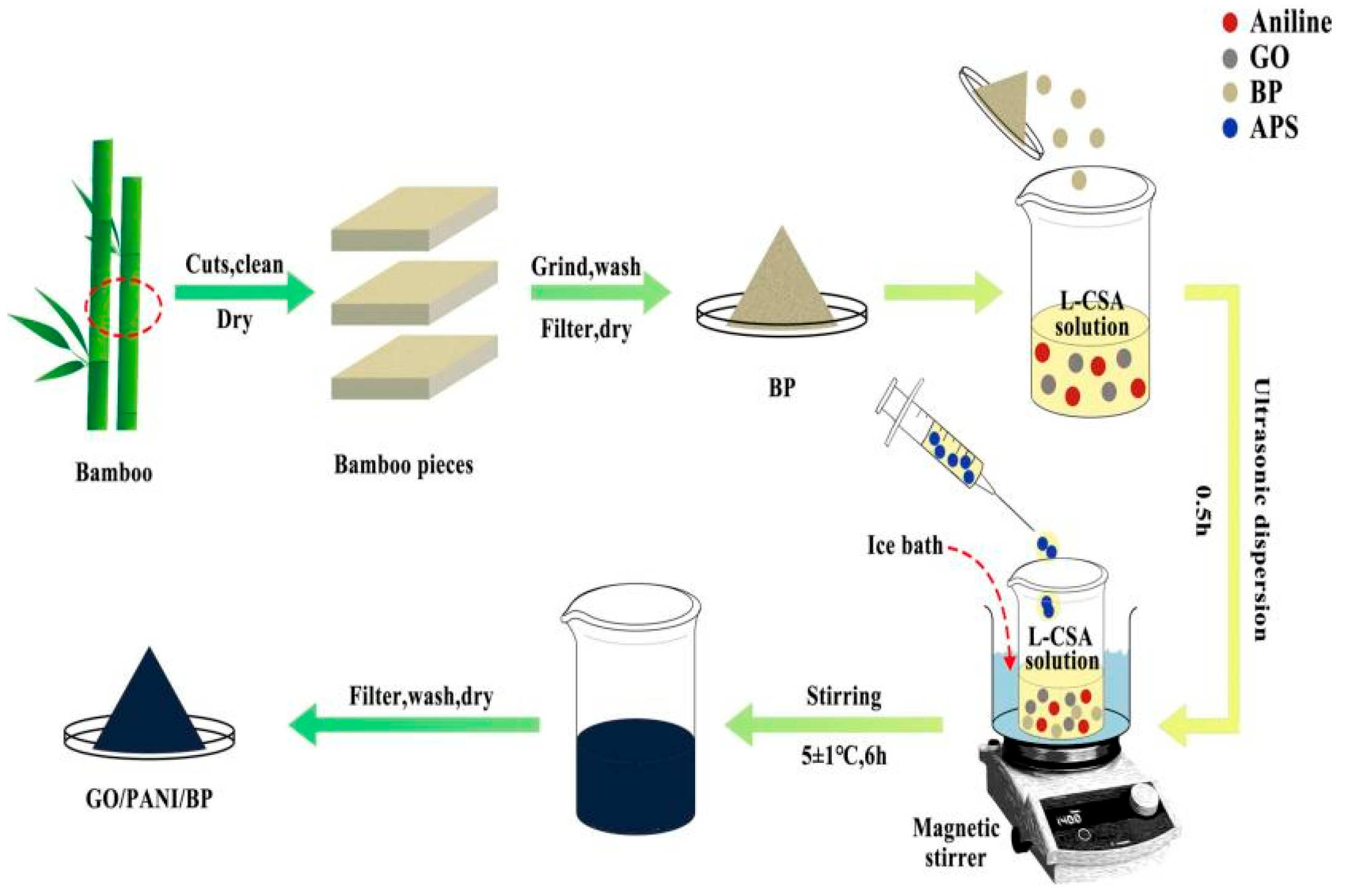
3.2.3. Bamboo Fiber as Precursor
3.3. Other Biomass Materials as Precursors
4. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, J.; Yan, L.; Song, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, A.; Du, H.; Liu, J. Thermally insulated C/SiC/SiBCN composite ceramic aerogel with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Y. Fabrication of cage-like Ni/C@Co/NC composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 3914–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Dong, C.; Yang, D.; Lei, D.; Bao, J.; Song, Q.; Liu, J. Ingeniously construction of industrial carbon fiber/nickel-iron layered double hydroxide heterostructure composite for high-efficient microwave absorption in aircraft. Compos. Commun. 2024, 51, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. Mesoporous MXene nanosheets/CNF composite aerogels for electromagnetic wave absorption and multifunctional response. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 502, 157770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, J.; Shi, Y.; Zou, X.; Tahir, H.E.; Holmes, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y. A dual-mode sensor for colorimetric and fluorescent detection of nitrite in hams based on carbon dots-neutral red system. Meat Sci. 2019, 147, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Du, C.; Sun, C.; Cao, J.; Ji, S.; Sun, H. Development of a Crop Spectral Reflectance Sensor. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic fields assisted blanching—Effect on the dielectric and physicochemical properties of cabbage. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Wang, B.; Zeng, S.; Mu, R.; Li, G.; Li, B.; Lv, W. Research progress and application of ultrasonic- and microwave-assisted food processing technology. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3707–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.A.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C. Efficient removal of lignin from vegetable wastes by ultrasonic and microwave-assisted treatment with ternary deep eutectic solvent. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 149, 112357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhu, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Ling, P. Investigation of an Experimental Laser Sensor-Guided Spray Control System for Greenhouse Variable-Rate Applications. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jia, W.; Li, Y.; Ou, M. Method for Estimating Canopy Thickness Using Ultrasonic Sensor Technology. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Dai, C. Quantitative Analysis of Cadmium Content in Tomato Leaves Based on Hyperspectral Image and Feature Selection. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandwal, A.; Liu, L.; Deen, M.J.; Jasrotia, R.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Nie, Z. Electromagnetic Wave Sensors for Noninvasive Blood Glucose Monitoring: Review and Recent Developments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongpradubchai, S.; Makul, N.; Rattanadecho, P. Novel Microwave-Assisted Drying Technique for Thai Medicinal Herbs Utilizing an Asymmetrical Double-Feed Microwave/Vacuum System. Eng. Sci. 2024, 32, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Rattanadecho, P.; Jiamjiroch, K. Microwave Imaging for Breast Cancer Detection—A Comprehensive review. Eng. Sci. 2024, 30, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Qaiser, N.; Hwang, B. Mechanically pressed polymer-matrix composites with 3D structured filler networks for electromagnetic interference shielding application. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2024, 22, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pathak, S.; Singh, A.; Verma, R.; Khanduri, H.; Jain, K.; Tawale, J.; Wang, L.; Pant, R.P. Augmented magnetic nanoparticle assimilation in rGO sheets for tailored static and dynamic magnetic properties in surface functionalized Co0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 nanoferrite-rGO hybrid structures. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 18036–18047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ohlan, A.; Kumar, P.; Verma, V. Improved Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Response of Polyaniline Containing Magnetic Nano-ferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 33, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, C.L. 5 G wireless telecommunications expansion: Public health and environmental implications. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Li, H.; Wang, M.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, L.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in construction strategies and multifunctional properties of flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 171, 112630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. Recent research progress of carbon-based and their composites for electromagnetic waves absorption. Text. Res. J. 2022, 93, 1889–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, W.; Ren, X.; Zhu, M. Progress and Challenges of Ferrite Matrix Microwave Absorption Materials. Materials 2024, 17, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z. Fabrication of core-shell structure NiFe2O4@SiO2 decorated nitrogen-doped graphene composite aerogels towards excellent electromagnetic absorption in the Ku band. Carbon 2023, 210, 118047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tao, W.; Liao, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; He, H.; Wang, X. Cellulose nanofiber/MXene/FeCo composites with gradient structure for highly absorbed electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, T.; Meng, A.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. Efficient electromagnetic wave absorption performances dominated by exchanged resonance of lightweight PC/Fe3O4@PDA hybrid nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Z.; Zou, J.; Gu, Z.; Wu, G. MOF-derived NiFe2S4/Porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 610, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Yin, P. Metal-organic framework-derived carbon nanotubes for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, W. Two-Dimensional Metal Organic Framework derived Nitrogen-doped Graphene-like Carbon Nanomesh toward Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 643, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Wu, N.; Sui, Z.; Ban, Q.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Ultralight aerogel sphere composed of nanocellulose-derived carbon nanofiber and graphene for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 7931–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, S.T.A.; Singh, C.; Godara, S.K. Functionalization and synthesis of biomass and its composites as renewable, lightweight and eco-efficient microwave-absorbing materials: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Q.; Qiu, F.; Peng, Y.; Tang, S. Fabrication of functional biomass carbon aerogels derived from sisal fibers for application in selenium extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 111, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gong, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, C. Biomass-derived porous carbon materials: Synthesis, designing, and applications for supercapacitors. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 3864–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, H.; Cai, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, C.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L. Valorization of Biomass-Derived Polymers to Functional Biochar Materials for Supercapacitor Applications via Pyrolysis: Advances and Perspectives. Polymers 2023, 15, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lee, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; He, S.; Han, J.; Ahn, J.; Cheong, J.Y.; Jiang, S.; Kim, I.-D. Inspired by Wood: Thick Electrodes for Supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 8866–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y. Salt-assisted synthesis of advanced carbon-based materials for energy-related applications. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 10263–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Wang, Y.; Lou, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, W. Vanadium oxide/carbonized chestnut needle composites as cathode materials for advanced aqueous zinc-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2024, 77, 109859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, J.; Ma, N.; Ma, X.; Gao, M. Bacterial cellulose hydrogel for sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jayan, H.; Gao, S.; Zhou, R.; Yosri, N.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Recent and emerging trends of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-based sensors for detecting food contaminants: A critical and comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, F.; Han, N. Biomass-derived carbon material as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 168, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-H.; Huang, H.; Haq, M.U.; Zhang, L.; Feng, J.-J.; Wang, A.-J. Lignin-derived iron carbide/Mn, N, S-codoped carbon nanotubes as a high-efficiency catalyst for synergistically enhanced oxygen reduction reaction and rechargeable zinc-air battery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 647, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Hong, R.; Cao, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.; Cheng, J. Green synthesis of porous bamboo-based activated carbon with high VOCs adsorption performance via steam activation method. J. Porous Mater. 2024, 31, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H. Hierarchical porous carbon materials produced from heavy bio-oil for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Pang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, G.; Dong, C.; Wang, L.; Gong, C. Biomass derived porous carbon (BPC) and their composites as lightweight and efficient microwave absorption materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 207, 108562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhi, D.D.; Guo, Z.H.; Li, J.-Z.; Chen, Y.; Meng, F.-B. 3D porous biomass-derived carbon materials: Biomass sources, controllable transformation and microwave absorption application. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 647–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peymanfar, R.; Mirkhan, A. Biomass-derived materials: Promising, affordable, capable, simple, and lightweight microwave ab-sorbing structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liang, B.; Shi, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, T.; Gu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Melhi, S.; Alshammari, A.S.; et al. Recent progress of carbon-based magnetic fibers for electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 2024, 229, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liang, B.; Gao, H.; Zhao, R.; Dong, Q.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Gu, J.; et al. Research progress on spherical carbon-based electromagnetic wave absorbing composites. Carbon 2024, 227, 119244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Colorado, H.; Li, H.; et al. Biomass-based electromagnetic wave absorption materials with unique structures: A critical review. ES Food Agrofor. 2023, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, M.; Ren, X. Magnetic/electric synergy Co@CN/CNTs absorber toward high efficiency electromagnetic waves absorption. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 28394–28402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassin, J.-M.; Lou, X.; Pagnoulle, C.; Saib, A.; Bednarz, L.; Huynen, I.; Jérôme, R.; Detrembleur, C. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanocomposites with Exceptional Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11186–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, L.; Liao, Q.; Kang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Toward the application of high frequency electromagnetic wave absorption by carbon nanostructures. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Kong, J. Research progress and future perspectives on electromagnetic wave absorption of fibrous materials. iScience 2023, 26, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Pan, X.-F.; Guan, Z.-j.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Wang, K.-J.; Jiang, J.-T. Flower-like hierarchical Fe3O4-based heterostructured microspheres enabling superior electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 642, 158633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xiong, X.; Du, Y.; Lv, X.; Wu, Z.; Luo, K.; Qian, Y.; Che, R. Dual-coupling networks engineering of self-assembled ferromagnetic microspheres with enhanced interfacial polarization and magnetic interaction for microwave absorption. InfoMat 2024, 35, e12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Meng, X. Like-hydrangea Fe3O4@MoS2 composites towards high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 26670–26679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Han, F.; Ye, X.; Meng, X. Hierarchical 0D/2D NiFe2O4/Ti3C2Tx MXene composites for boosting microwave absorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 289, 116224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Xianfeng, M. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of ZIF-67 derived Co@C/MoS2 nanocomposites. Chi-Nese J. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 40, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, J.-L.; Chang, Y.-K.; Liu, S.; Li, P.-H.; Cui, P.-H.; Hu, Q.-K.; Wang, L.-B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.-K.; Xia, Q.-X. Solid solution strategy modulated defects engineering of (Cr1-xVx)2AlC MAX phase toward superior electromagnetic wave absorption. Rare Metals 2024, 43, 3205–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M. Functional–Structural Integrated Aramid Nanofiber-based Honeycomb Materials with Ultrahigh Strength and Multi-Functionalities. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1122–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, H.; Cao, X.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, B.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. Graphite wrapped FeNi3/Co with carbon nanotubes anchored on MgO@carbon fiber rein-forcements via continuous fabrication for high-efficiency microwave attenuation. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1640–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tu, H.; Wang, S.; Meng, X. 3D high-temperature resistance BaTiO3/EG hybrids with enhanced EMWs absorption capacity. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 45754–45762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Shenb, B.; Wang, Z. SiC-Fe3O4 dielectric–magnetic hybrid nanowires: Controllable fabrication, characterization and electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16397–16402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; He, W.; Quan, G.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Lei, L.; Du, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; et al. Sterculia lychnophora seed-derived porous carbon@CoFe2O4 composites with efficient microwave absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 155027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L. Toward the application of electromagnetic wave absorption by two-dimension materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 25562–25576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.-F.; Xu, L.; Jia, L.-C.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yan, D.-X. Recent progress on carbon-based microwave absorption materials for multifunctional applications: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 283, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ruan, K.; Wang, G.; Gu, J. Advances and mechanisms in polymer composites toward thermal conduction and electromagnetic wave absorption. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1195–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Saleem, M.; Tian, Z.; Ren, P. Current progress on the modification of carbon nanotubes and their application in electromagnetic wave absorption. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 14419–14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-M.; Cao, W.-Q.; Shi, H.-L.; Fang, X.-Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, Z.-L.; Jin, H.-B.; Wang, W.-Z.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M.-S. Multi-wall carbon nanotubes decorated with ZnO nanocrystals: Mild solution-process synthesis and highly efficient microwave absorption properties at elevated temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10540–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Cao, M.-S.; Hou, Z.-L.; Song, W.-L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, M.-M.; Jin, H.-B.; Fang, X.-Y.; Wang, W.-Z.; Yuan, J. Temperature dependent microwave attenuation behavior for carbon-nanotube/silica composites. Carbon 2013, 65, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Du, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Han, X. Pea-like Fe/Fe3C Nanoparticles Embedded in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes with Tunable Dielectric/Magnetic Loss and Efficient Electromagnetic Absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 4268–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, P.; Han, J. Designable synthesis of core-shell SiCw@C heterostructures with thickness-dependent electromagnetic wave absorption between the whole X-band and Ku-band. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Kong, J. Ultraflexible, highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, and self-healable triboelectric nanogenerator based on Ti3C2Tx MXene for self-powered wearable electronics. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Liang, X.; Ji, G.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, G. Dielectric polarization in electromagnetic wave absorption: Review and perspective. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, Z.; Pan, H.; Wu, R. Electromagnetic absorption materials: Current progress and new frontiers. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 127, 100946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ro, J.C.; Suh, S.-J. Fe/Co ratio dependent excellent microwave absorption of FeCo alloys with a wide bandwidth in the high-frequency region. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 145, 111513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Wen, G.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Advances in Carbon Microsphere-Based Nanomaterials for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Langmuir 2024, 40, 18857–18881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Hui, S.; Xiao, T.D.; Ge, S.; Hines, W.A.; Budnick, J.I.; Taylor, G.W. Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4404–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-S.; Kim, S.-T.; Yoon, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-S. Magnetic, dielectric, and microwave absorbing properties of iron particles dispersed in rubber matrix in gigahertz frequencies. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10F905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Qiao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Feng, J.; Xue, D. Microwave absorption properties of the Ni nanowires composite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 235005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, M. Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: Cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Yu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Multi-dimensional ordered mesoporous carbon/silica@Ni composite with hierarchical nanostructure for strong and broadband microwave absorption. Carbon 2021, 176, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Guan, Y.; Liu, B. Preparation of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/zinc ferrite@nitrogen-doped carbon composite for broadband and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2025, 214, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Hu, P.; Li, X.; Hong, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, J. NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, R.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Qian, M.; Chen, B. Recent progress in biomass-derived carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave ab-sorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zuo, M.; Cai, J.; Zhai, X.; Zhou, C.; Shi, J.; et al. Comparative study on physicochemical, nutritional and cooking properties of different pigmented dehusked rice varieties influenced by superheated steam treatment. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 117, 103934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wu, N.; Pan, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Scalable manufacturing of light, multifunctional cellulose nanofiber aerogel sphere with tunable microstructure for microwave absorption. Carbon 2023, 203, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
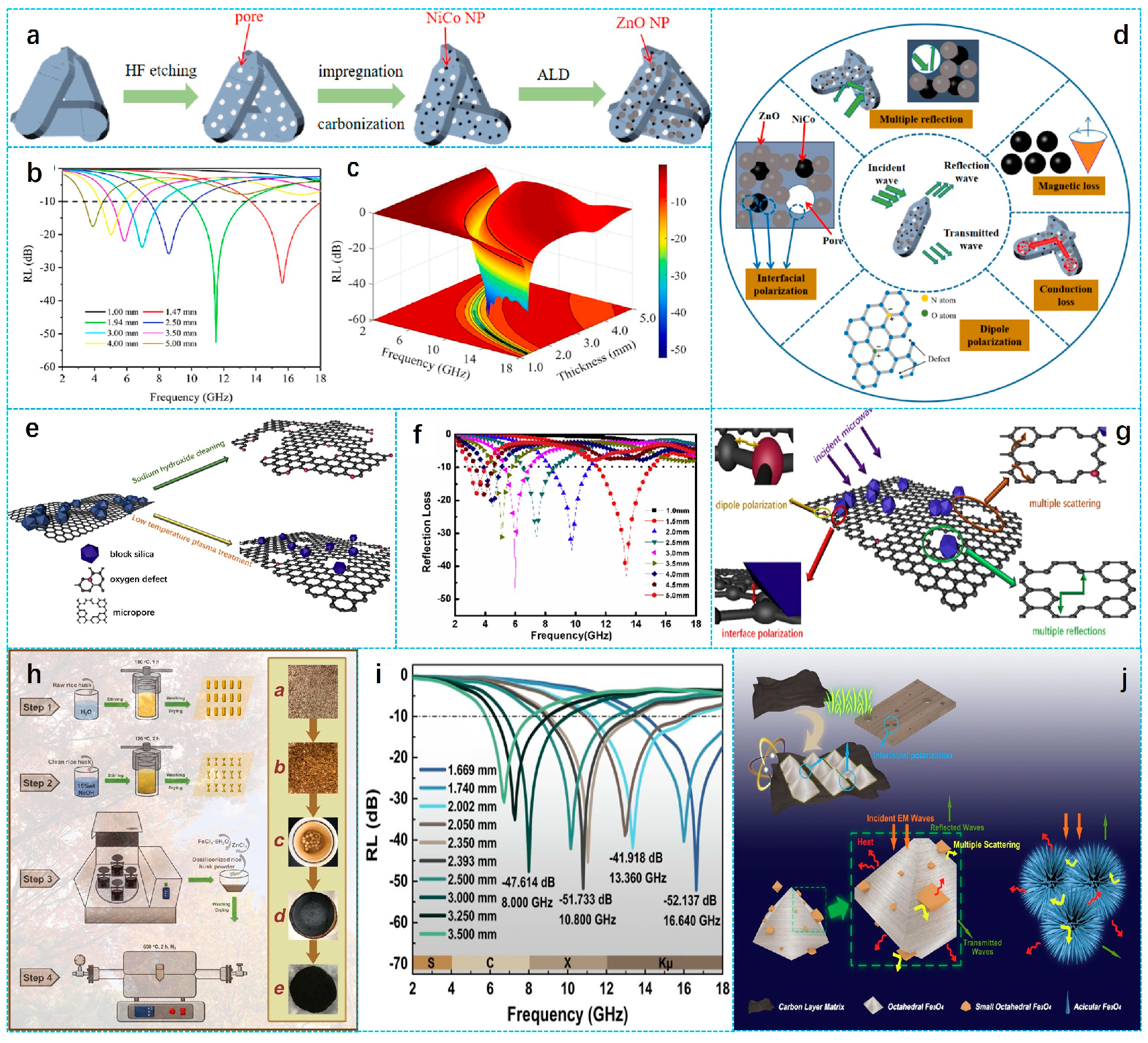
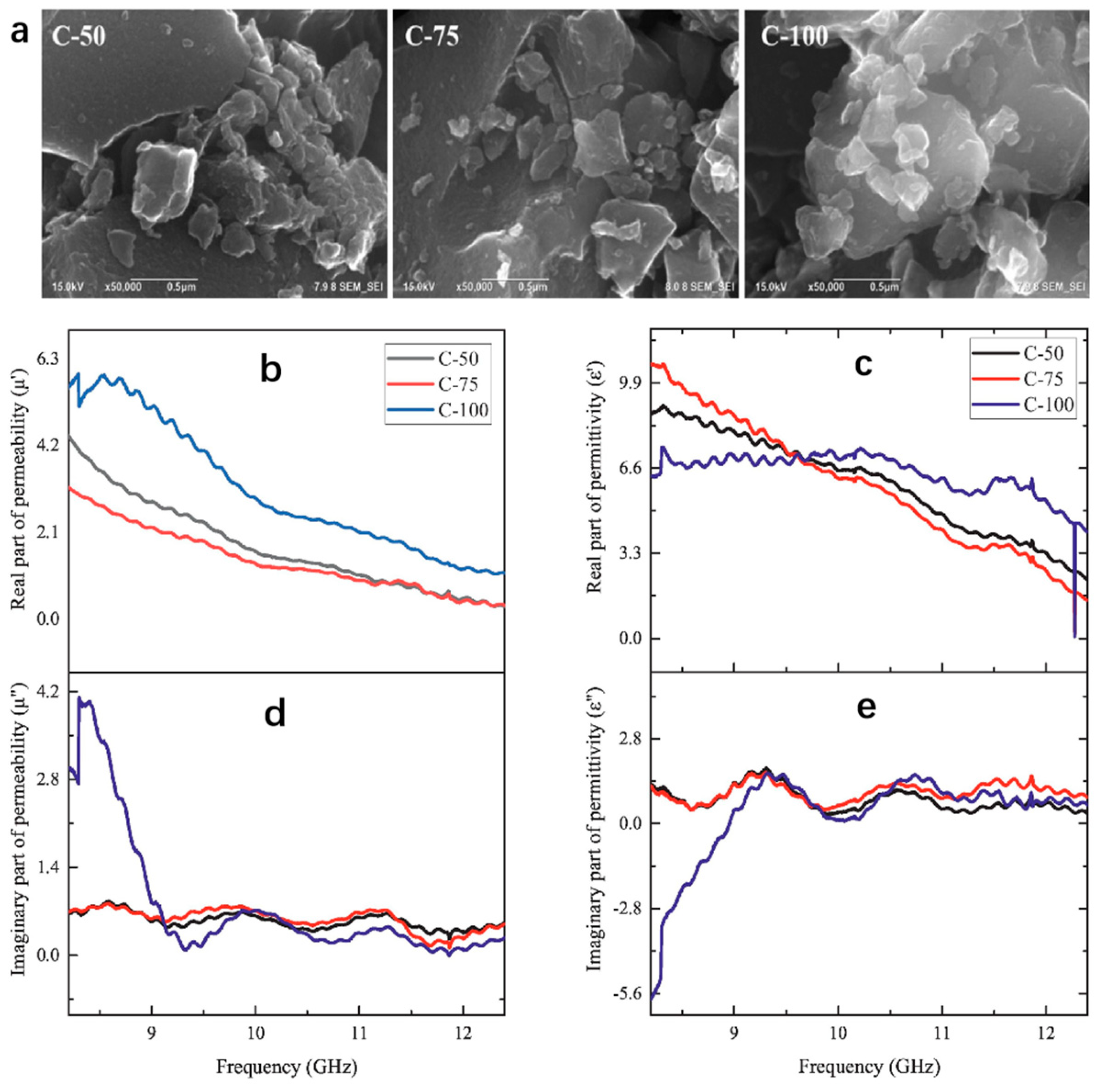
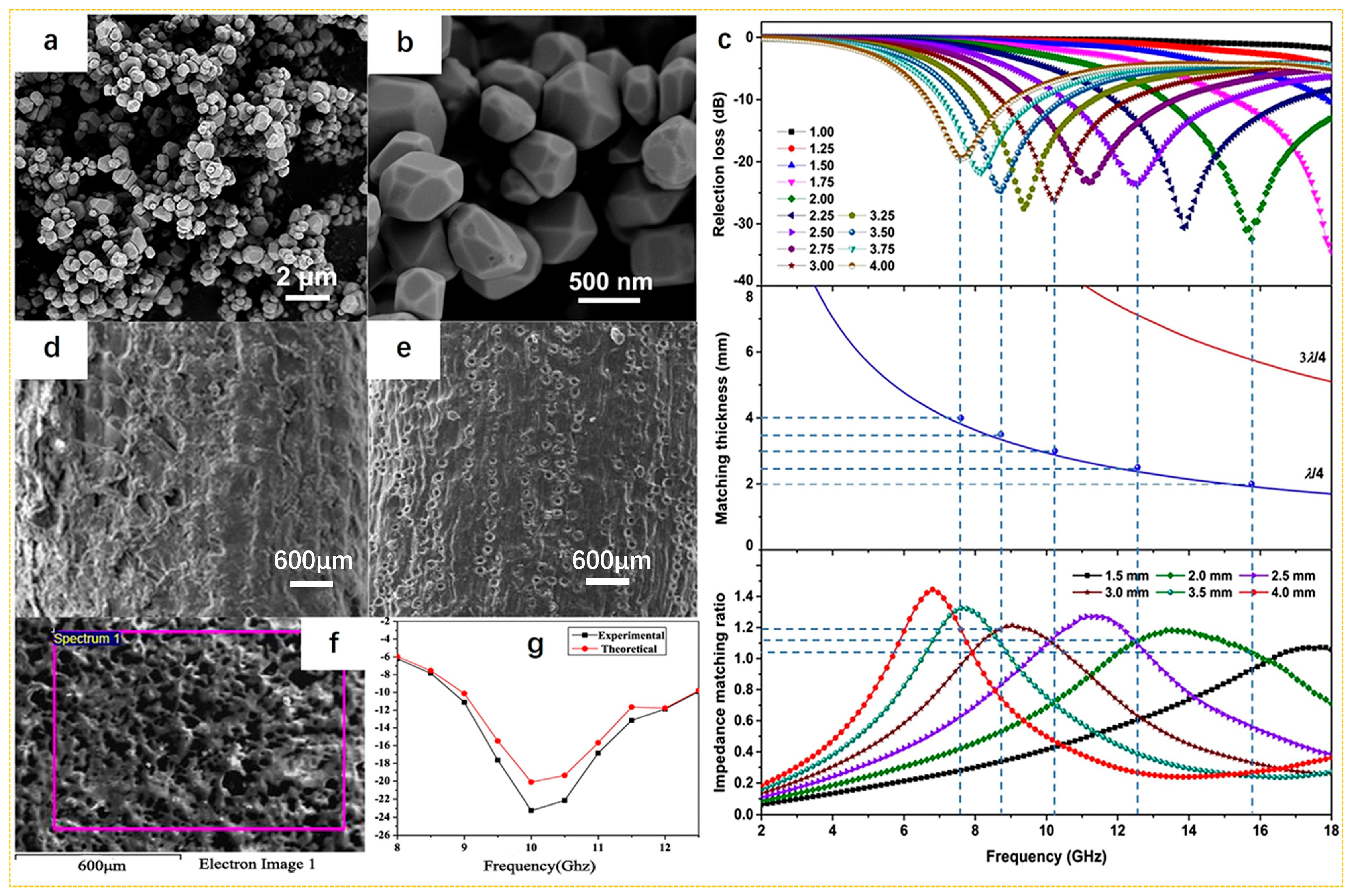
- Wu, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yao, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Rice husk derived hierarchical porous carbon with lightweight and efficient microwave absorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 275, 125246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, X.; Meng, Z.; Yao, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y. Nickel/porous carbon derived from rice husk with high microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 925, 166732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xiang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K. Facile synthesis of NiCo2 nanoparticles grown on rice husk waste-derived porous carbon for high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 9780–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Wu, S.; Su, X.; Wang, T.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, H.; Meng, A.; Zhang, M. Rice husk derived porous carbon embedded with Co3Fe7 nanoparticles towards microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Zhou, H. Construction of lychee-like MoS2 microspheres on rice husk-derived porous carbon for enhanced dielectric loss and efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Tong, S.; Zhang, K.; Xiang, J. Controllable surface functionalization of rice husk-derived porous carbon by atomic layer deposition for highly-efficient microwave absorption. Vacuum 2024, 224, 113199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.; Liu, Q.; Kong, X. Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent. Carbon 2020, 161, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Fang, B.; Wu, W.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Z. Acicular or octahedral Fe3O4/rice husk-based activated carbon composites through graphitization synthesis as superior electromagnetic wave absorbers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 151, 106635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Dash, A.K.; Nath, G. Dielectric characterization analysis of natural fiber based hybrid composite for microwave ab-sorption in X-band frequency. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-H.; Xie, Y.-L.; Chen, Y. Innovative multi-functional foamed concrete made from rice husk ash: Thermal insulation and electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 16112–16128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
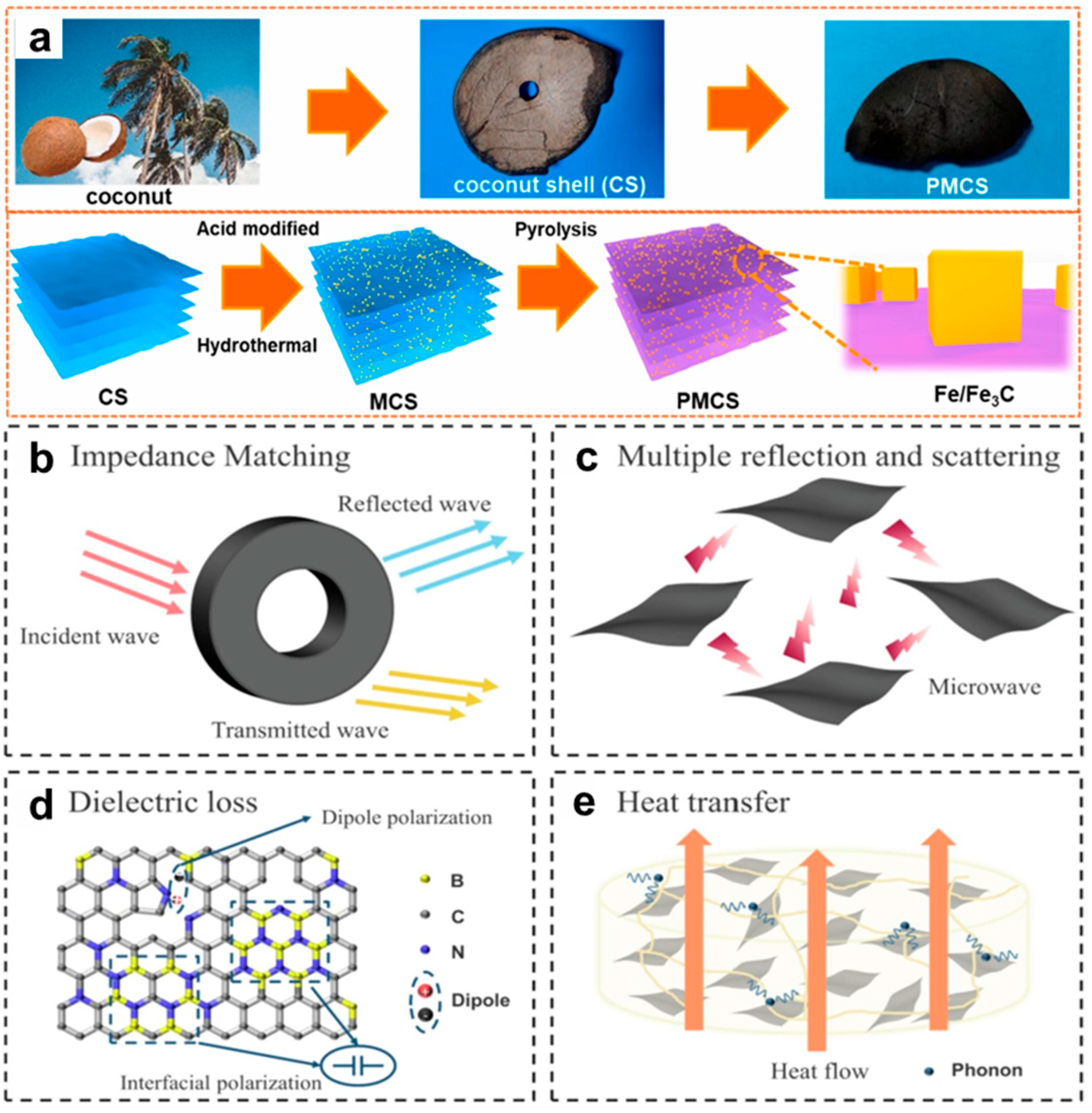
- Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gan, L.; He, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, P.; Qiu, F. Preparation and application of Mg–Al composite oxide/coconut shell carbon fiber for effective removal of phosphorus from domestic sewage. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 126, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Bao, C.; Wang, Q.; Dong, C.; Guan, H. Tuning the microwave absorption capacity of TiP2O7 by composited with biomass carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 515, 145974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.P.; Nath, G.; Mishra, P. Ultrasonically synthesized dielectric microwave absorbing material from coconut coir dust. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Z.-H.; Zhu, J.-L.; Gao, J.-F.; Dai, K.; Huang, H.-D.; Li, Z.-M. Facile heteroatom doping of biomass-derived carbon aerogels with hierarchically porous architecture and hybrid conductive network: Towards high electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness and high ab-sorption coefficient. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, R.; Jeyalakshmi, T.; Mohan, S.S.; Saravanan, M.; Goparaju, A.; Murthy, P.B. Coco peat—An alternative artificial soil ingredient for the earthworm toxicity testing. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2014, 6, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Iqbal, M.N.; Malek, M.F.; Lee, Y.S.; Zahid, L.; Mezan, M.S. A Study of the Anechoic Performance of Rice Husk-Based, Geometrically Tapered, Hollow Absorbers. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2014, 2014, 498767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, H.; Xu, L.; Teng, Y.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, L.; et al. Microwave-absorbed porous carbon was prepared from agricultural coconut shell waste by a simple one-step high temperature charring. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 307, 117509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, J.Y.; Soleimani, H.; Yahya, N.; Sanusi, Y.K.; Kozlowski, G.; Öchsner, A.; Adebayo, L.L.; Wahaab, F.A.; Sikiru, S.; Balogun, B.B. Electromagnetic wave absorption of coconut fiber-derived porous activated carbon. Bol. Soc. Esp. Cerám. Vidrio 2022, 61, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widanarto, W.; Budianti, S.I.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Kurniawan, C.; Handoko, E.; Alaydrus, M. Improved microwave absorption traits of coconut shells-derived activated carbon. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 126, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanath, Y.; Ashamanjari, K.; Mahesh, K.; Mylarappa, M.; Ramu, M.; Prashantha, S.; Nagaswarupa, H.; Raghavendra, N.; Siddeswara, D. Development and characterization of titanium phosphates (Tip2O7) and lithium titanium phosphate (Litip2o7) and their thermal and electric properties. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 5, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Ning, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, W.; Li, Y. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of coconut shell-derived nanocomposite. Carbon 2022, 196, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Shi, S.; Wan, G.; Zhou, M.; Deng, Z.; Teng, S.; Wang, G. BCN nanosheets derived from coconut shells with outstanding microwave absorption and thermal conductive properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Yu, X.; Ji, Q.; Chen, L.; Yagoub, A.E.-G.; Olugbenga, F.; Zhou, C. Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing cellulose nanocrystals from peanut shells using a deep eutectic solvent containing lignin-derived phenol. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 195, 116415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, J.; Chen, L.; Ren, M.; Zhou, C. Utilization of walnut shell by deep eutectic solvents: Enzymatic digestion of cellulose and preparation of lignin nanoparticles. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 192, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Gu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B. A biomass derived porous carbon for broadband and lightweight microwave absorption. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, T. Almond C/FexOy composite material based on biomass porous carbon structure with high-efficiency microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 13166–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Z.; Qiu, X.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Q. Walnut shell-derived nanoporous carbon@Fe3O4 composites for outstanding microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ma, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Li, A.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, C. Biomass derived PANI/BPC composite with enhanced polarization loss for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 176, 112805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wang, X.; Chai, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, R.-C. Fabricating lignin-based carbon nanofibers as versatile supercapacitors from food wastes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassan, A.; Li, J.; Abdalla, I.; Xu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Ant-Nest-Inspired Biomimetic Composite for Self-Cleaning, Heat-Insulating, and Highly Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, early view, 2407458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Ding, S.; Ling, H.; Wang, T.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Meng, A.; Li, Q. Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performances of Fe3O4@C decorated walnut shell-derived porous carbon. Carbon 2020, 167, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Di, X.; Chen, J.; She, L.; Pan, H.; Zhao, B.; Che, R. Multi-dimensional C@NiCo-LDHs@Ni aerogel: Structural and componential engineering towards efficient microwave absorption, anti-corrosion and thermal-insulation. Carbon 2022, 191, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Tong, Y.; Liu, C.; Sun, H.; Hu, Q.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X.; Feng, Y. In-situ generated Ni/Ni3Si to enhance electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Ni/PDCs/biomass ceramic composites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 663. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jia, C.; Cai, P.; Chen, G.; Dong, C.; Guan, H. Biomass carbon derived from pine nut shells decorated with NiO nanoflakes for enhanced microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 9126–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Cui, Z.; Tang, Y.; Hu, X. Distinct property of biochar from pyrolysis of poplar wood, bark, and leaves of the same origin. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 202, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Hu, X. Sequential activation of willow wood with ZnCl2 and H3PO4 drastically impacts pore structure of activated carbon. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 221, 119387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xiong, Y.; Dang, B.; Ye, Z.; Jin, C.; Sun, Q.; Yu, X. In-situ anchoring of Fe3O4/ZIF-67 dodecahedrons in highly compressible wood aerogel with excellent microwave absorption properties. Mater. Des. 2019, 182, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Huang, Y.; Deng, C.; Jiao, Y.; Wu, W.; Seidi, F.; Xiao, H. Hierarchically porous biochar derived from orthometric integration of wooden and bacterial celluloses for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 218, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Xing, R.; Huang, R.; Kong, J.; Su, R. Biomass-derived fire-retardant porous carbon towards efficient electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding. Carbon 2024, 227, 119268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Hu, G.; Zhang, B.; Pan, S. Ni/Porous Carbon-Based Composite Derived from Poplar Wood with Ultrabroad Band Microwave Absorption Performance. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazhayal, L.; Wilson, P.; Prabhakaran, K. Waste to wealth: Lightweight, mechanically strong and conductive carbon aerogels from waste tissue paper for electromagnetic shielding and CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; He, M.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, S.; Zhong, X.; Fan, L.; Huang, T.; Liao, Q.; Wang, Y. Three-dimensional hierarchical architecture of the TiO2/Ti3C2Tx/RGO ternary composite aerogel for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8212–8222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Yan, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; Kong, L. Ultralight, compressible, and anisotropic MXene@Wood nanocomposite aerogel with excellent electromagnetic wave shielding and absorbing properties at different directions. Carbon 2021, 182, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Qi, J.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, H.; Gao, K.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Shang, Z.; et al. Promoting Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance by Integrating MoS2@Gd2O3/MXene Multiple Hetero-Interfaces in Wood-Derived Carbon Aerogels. Small 2024, 20, 2306915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Arumugam, S.S.; Sabarinathan, D.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Metal organic framework based fluorescence sensor for detection of antibiotics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 1002–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ni, C.; Yan, S.; Yu, L.; Li, X. “Tree blossom” Ni/NC/C composites as high-efficiency microwave absorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, G.; Hua, W.; Liu, K.; Cheng, F.; Xie, X. Bimetallic MOF@wood-derived hierarchical porous carbon composites for efficient microwave absorption. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 141, 110688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Gao, C.; Song, C.; Liu, Z.; Fatehi, P.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Wood-derived porous carbon foams filled with Ti3C2TxMXene/CoFe-MOF for electromagnetic shielding with flame retardant, heat insulation and excellent cycle stability. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 133, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wen, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Niu, J.; Yang, S.; Yuan, W.; Yu, M.; Yang, G.; Ding, S. In-situ growth of carbon nanotubes for the modification of wood-derived biomass porous carbon to achieve efficient Low/Mid-Frequency electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 676, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wang, G.; Zou, L.; Zhuo, Y.; Liang, F.; Pei, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, K.; Chen, J. Multi-scale design of MWCNT/glass fiber/balsa wood composite multilayer stealth structure with wide broadband absorption and excellent mechanical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cui, J.; He, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, W.; Lv, H. Transparent electromagnetic absorption film derived from the biomass derivate. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 185, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Amal, T.C. Deciphering the complex cotton genome for improving fiber traits and abiotic stress resilience in sustainable agriculture. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 6937–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ran, F.; Fan, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, Z.; Lv, T.; Liu, Y. Microstructural engineering of flexible and broadband microwave absorption films with hierarchical superstructures derived from bimetallic metal-organic framework. Carbon 2021, 178, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Kuang, Z. Cotton fiber-derived carbon decorated with MoS2 for high electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 326, 129844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, E.; Xiang, Z.; Yu, L.; Xiong, J.; Pan, F.; Lu, W. Fe@NPC@CF nanocomposites derived from Fe-MOFs/biomass cotton for lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Liang, L.; Ning, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Che, R.; et al. Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal-organic-framework. Carbon 2020, 161, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Ji, R.; Yu, Y.; Huang, B.; Tong, G.; Wu, W. Modulating multiple interfaces, defects, and dual-scale interlinked frameworks of cotton-derived spiral CF@Ni@CNT fibers for boosted thermal conduction and microwave absorption. Carbon 2024, 228, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Di, X.; Wang, N.; Cheng, R.; Yang, L. Heterostructure design of carbon fiber@graphene@layered double hydroxides synergistic microstructure for lightweight and flexible microwave absorption. Carbon 2022, 197, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Gong, C. Biomass-derived heterogeneous RGO/Ni/C composite with hollow structure for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 31, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
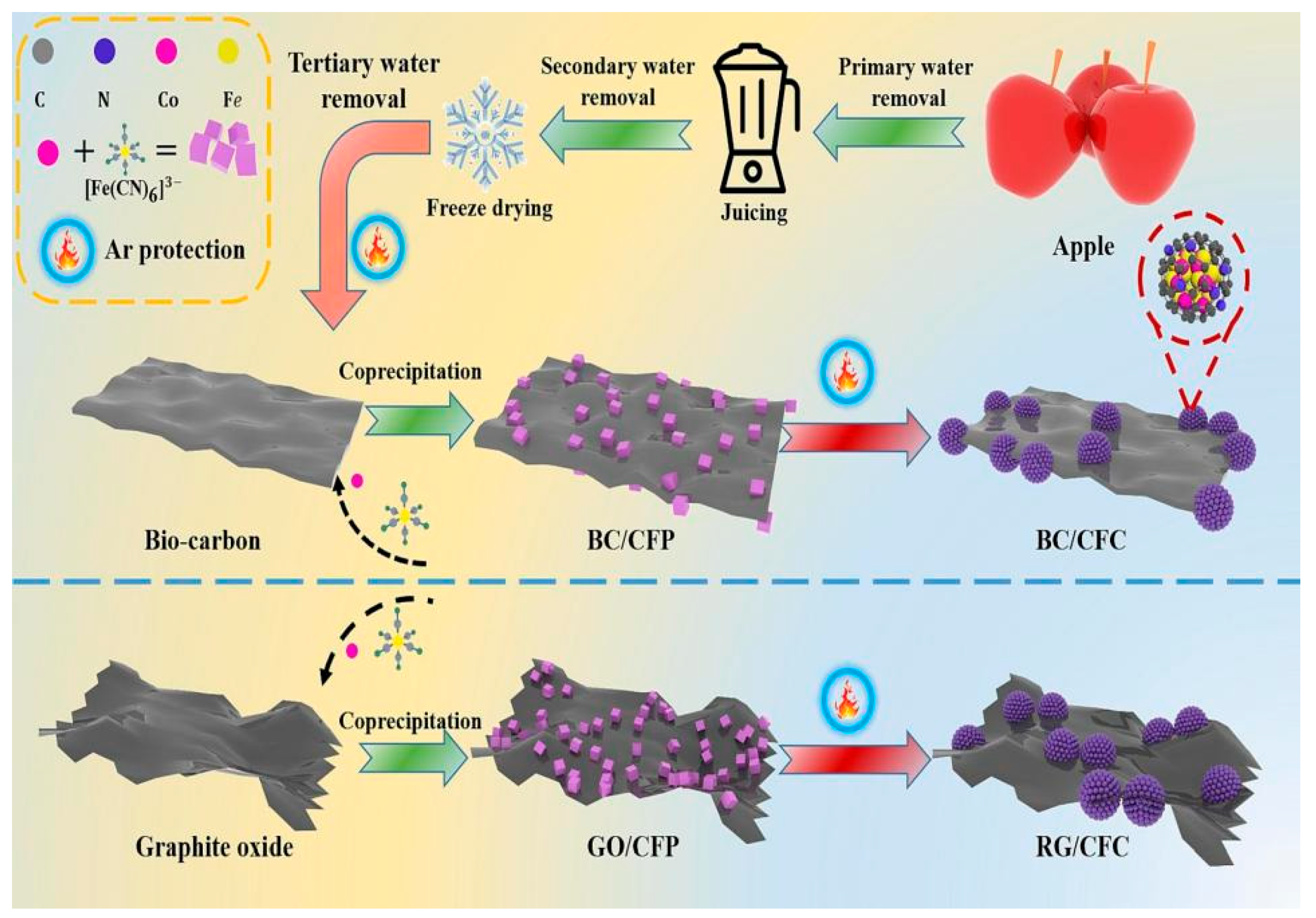
- Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Su, X.; Huo, S.; Qu, Z. Efficient Fe3O4@porous carbon microwave absorber constructed from cotton cellulose nanofibers hydrogel. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 997, 174956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Dai, J.; Tang, Y. Facile preparation of cotton-derived carbon fibers loaded with hollow Fe3O4 and CoFe NPs for significant low-frequency electromagnetic absorption. Powder Technol. 2021, 380, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guo, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. A Sustainable and Low-Cost Route to Design NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles/Biomass-Based Carbon Fibers with Broadband Microwave Absorption. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Xu, R.; Peng, H.; Chen, X.; Kang, Y. Lightweight TiO2@C/Carbon Fiber Aerogels Prepared from Ti3C2Tx/Cotton for High-Efficiency Microwave Absorption. Langmuir 2022, 38, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Q.; Peng, X.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Layered double hydroxide functionalized biomass carbon fiber for highly efficient and recyclable fluoride adsorption. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Ye, L.; Li, X.; Yan, B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Magnetic core-shell structure in-situ encapsulated in bamboo-derived carbon skeleton for efficient microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 888, 161510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Lou, Z.; Xu, L.; Lv, H. Pore-regulation in 2D biochar-based flakes towards wideband microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Lv, B. Facile preparation of CoFe alloy/carbonized bamboo fibers for broadband microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 970, 172545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, L.; Zong, M.; Liu, P.; Li, T. Magnetic porous CoNi@C derived from bamboo fiber combined with metal-organic-framework for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 595, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Long, H.; Liu, H.; Guo, Y.; Bai, T.; Bin Xu, B.; Amin, M.A.; Qiu, H.; Helal, M.H.; Liu, C.; et al. Regulating microstructure and composition by carbonizing in-situ grown metal-organic frameworks on cotton fabrics for boosting electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 7290–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Meng, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, P.; Xia, L.; Zhong, B.; Wang, H.; Wen, G. A facile precursor pyrolysis route to bio-carbon/ferrite porous architecture with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption in S-band. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 153269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cui, C.; Yan, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, S.; Tang, H.; Guo, R. Lightweight carbon fiber aerogel@hollow carbon/Co3O4 microsphere for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption in X and Ku bands. Carbon 2024, 230, 119617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Hong, J.; Wang, C.C.; Su, M.; Zhou, S.-F. CoZnO/C@BCN nanocomposites derived from bimetallic hybrid ZIFs for enhanced electro-magnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 17737–17747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Gong, Y.; Zou, X. A Novel Gas Sensor for Detecting Pork Freshness Based on PANI/AgNWs/Silk. Foods 2022, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, J.; Gao, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Construction of layer-by-layer sandwiched graphene/polyaniline nanorods/carbon nanotubes heterostructures for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 272, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Preparation and performance of a bamboo-based electromagnetic wave absorber by interfacial polymerization of graphene oxide/polyaniline. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Shang, K. Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of beaded silicon carbide/silica nanowires. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 48, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, G. 3D porous Ni@BPC composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 926, 166923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dong, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Lei, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Hu, Y. Electromagnetic wave absorbing biomass kelp derived porous carbon anchored by Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 146, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; Pereira, A.; Guo, Z.; Min, Y. Rose-Derived Porous Carbon and In-Situ Fabrication of Cobalt/Nickel Nanoparticles Composites as High-Performance Electromagnetic Wave Absorber. Eng. Sci. 2024, 30, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Jia, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Wu, G. Synthesis of 3D cerium oxide/porous carbon for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Fan, G.; Tang, Y.; Hao, C.; Ma, L.; Song, P. Green carbonization of waste coffee grounds into porous C/Fe hybrids for broadband and high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 170, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Ning, T.; Yan, J.; Dai, K.; Zhai, C.; Yun, J. Graphene-like structure of bio-carbon with CoFe Prussian blue derivative composites for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 652, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, P. Emerging technologies of employing algae and microorganisms to promote the return-to-field of crop straws: A mini-review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1152778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Dai, J.; Tang, Y. Recycling of waste straw in sorghum for preparation of biochar/(Fe,Ni) hybrid aimed at significant electromagnetic absorbing of low-frequency band. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14212–14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, T.; Ling, H.; Meng, A.; Li, S.; Zhang, M. Monodispersed Co@C nanoparticles anchored on reclaimed carbon black toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Bai, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Fan, B.; Yan, Z.; Guo, X. In-situ grown NiCo bimetal anchored on porous straw-derived biochar composites with boosted microwave absorption properties. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2023, 30, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, R. Preparation and wave-absorbing properties of low-cost Fe3O4/corn straw core composite material. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
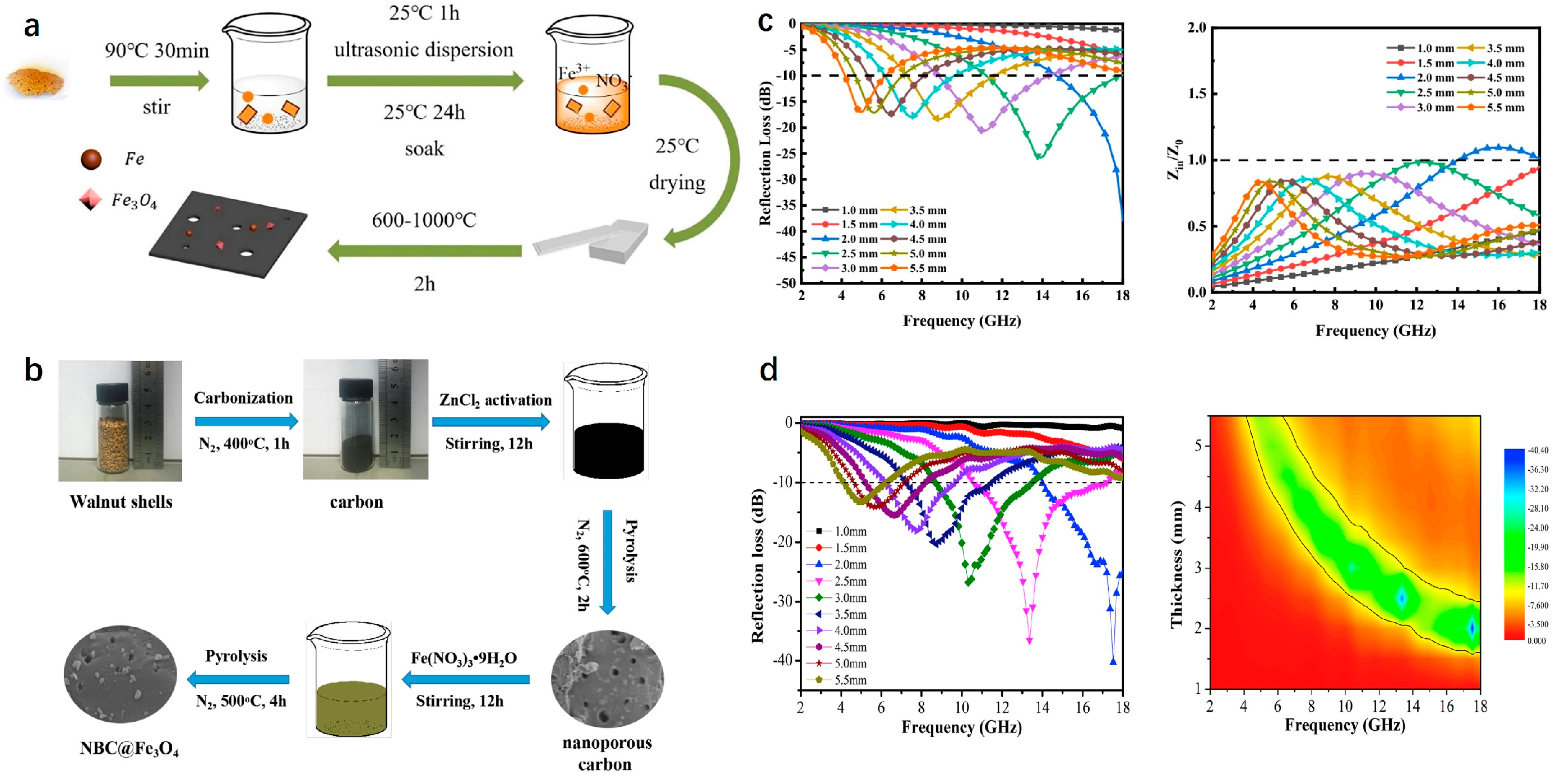

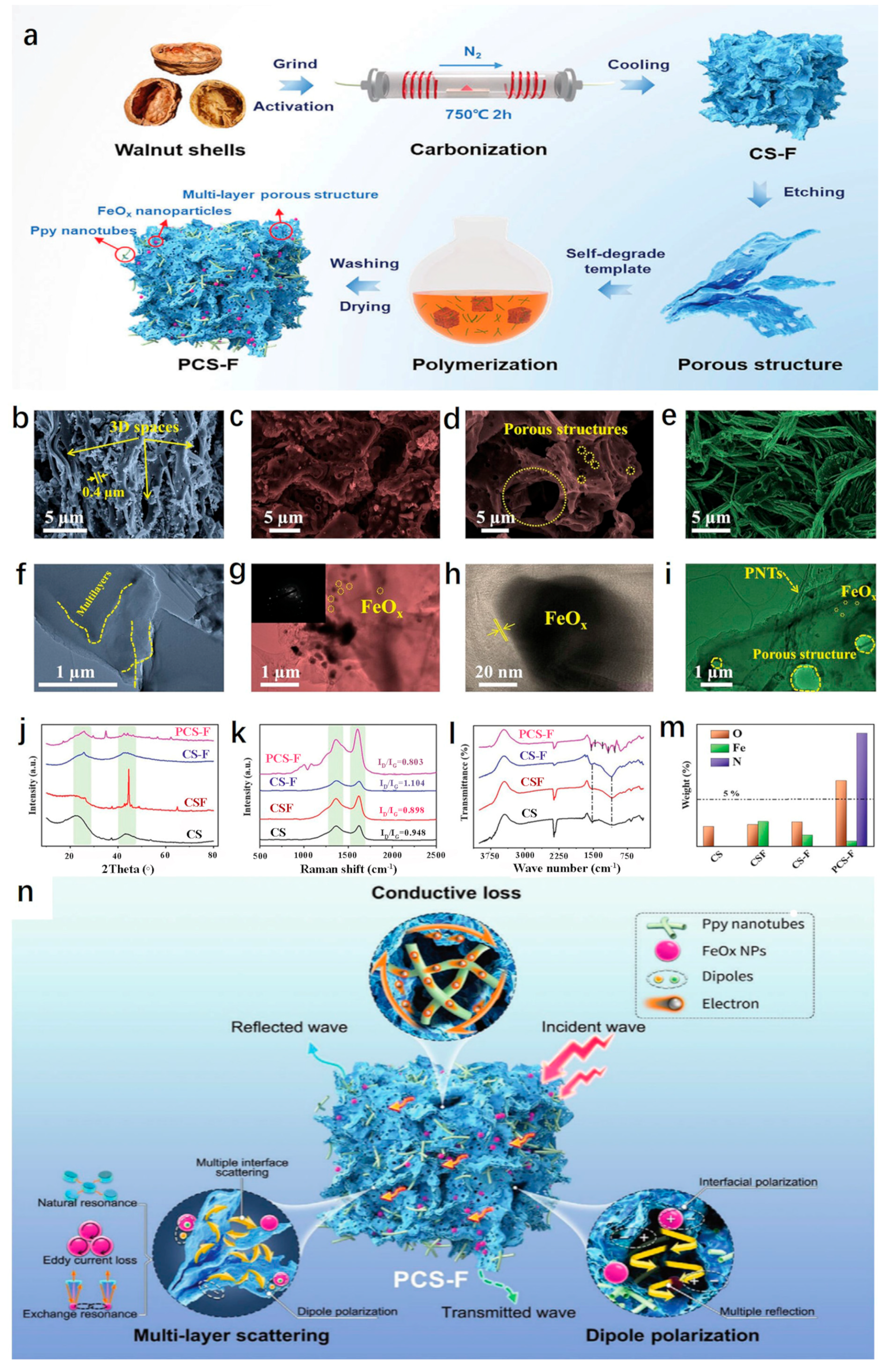

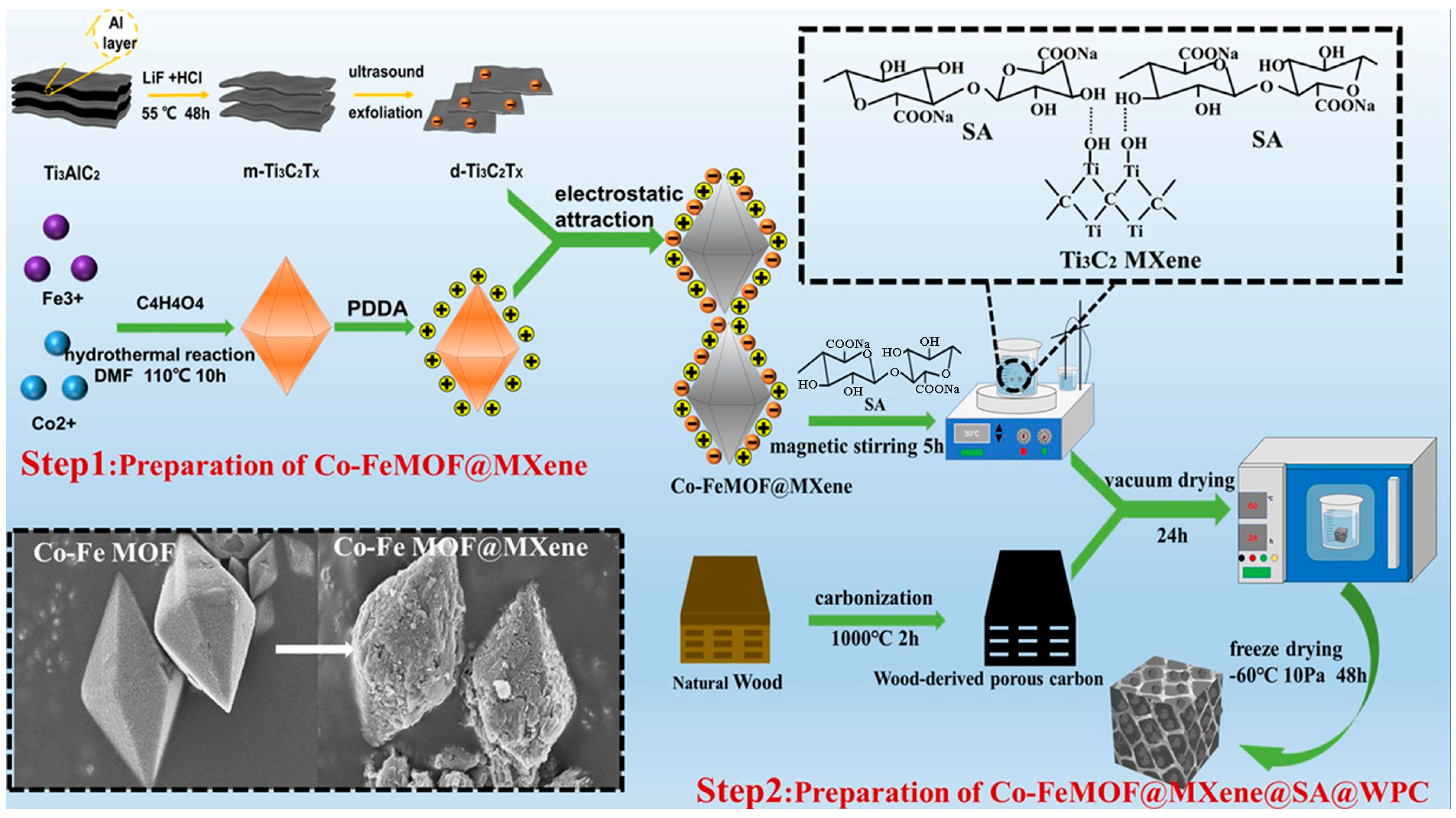

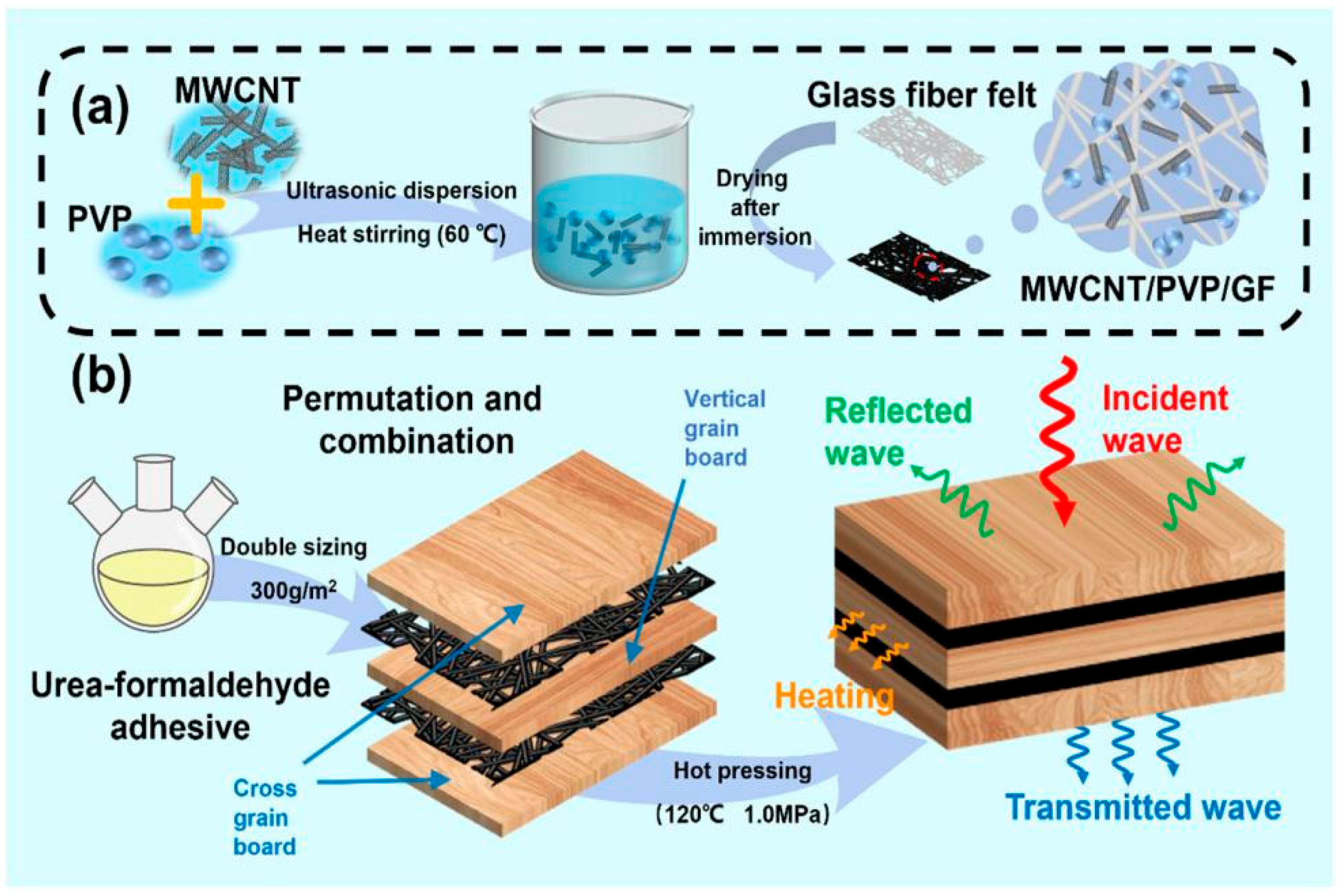
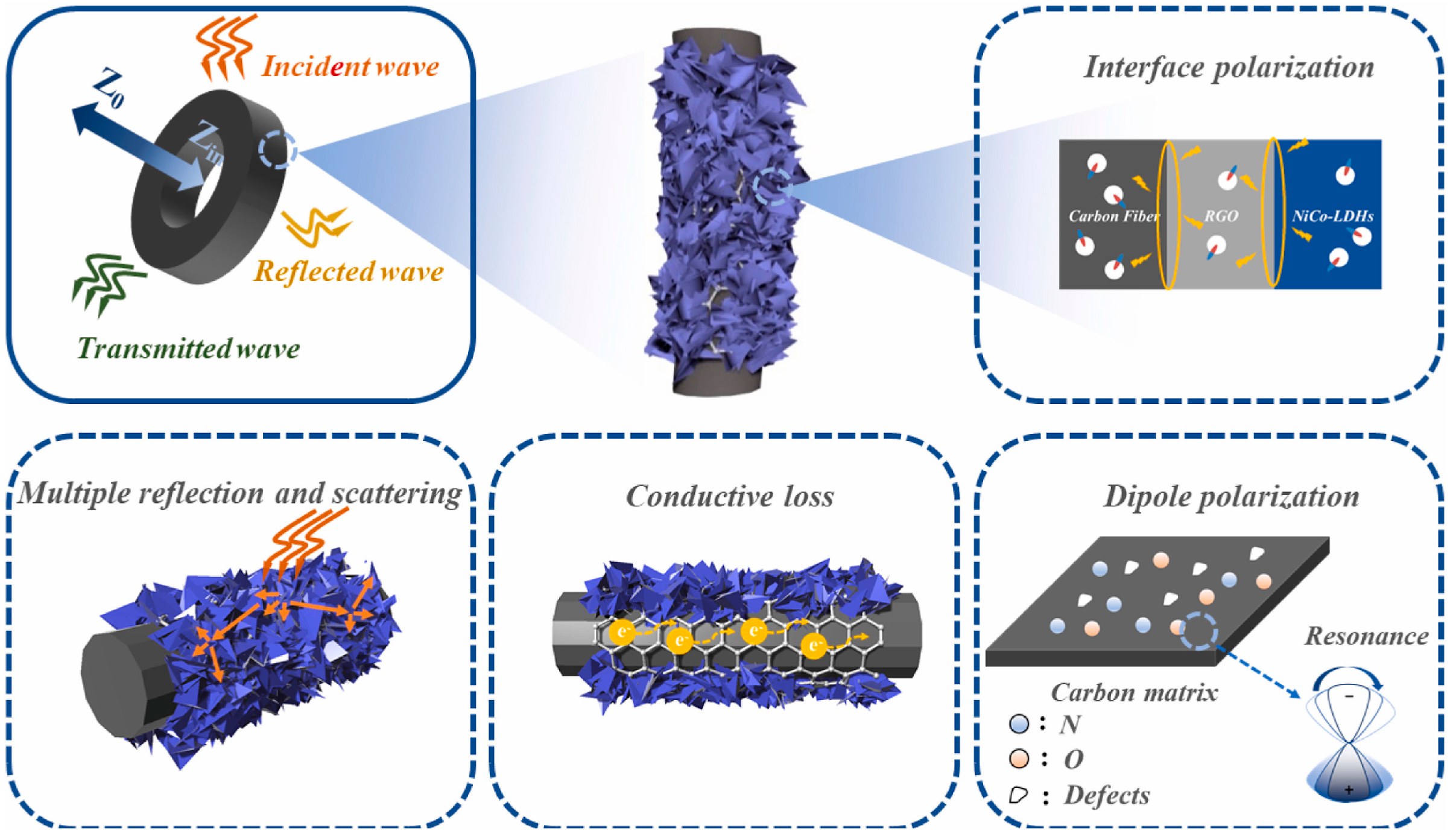
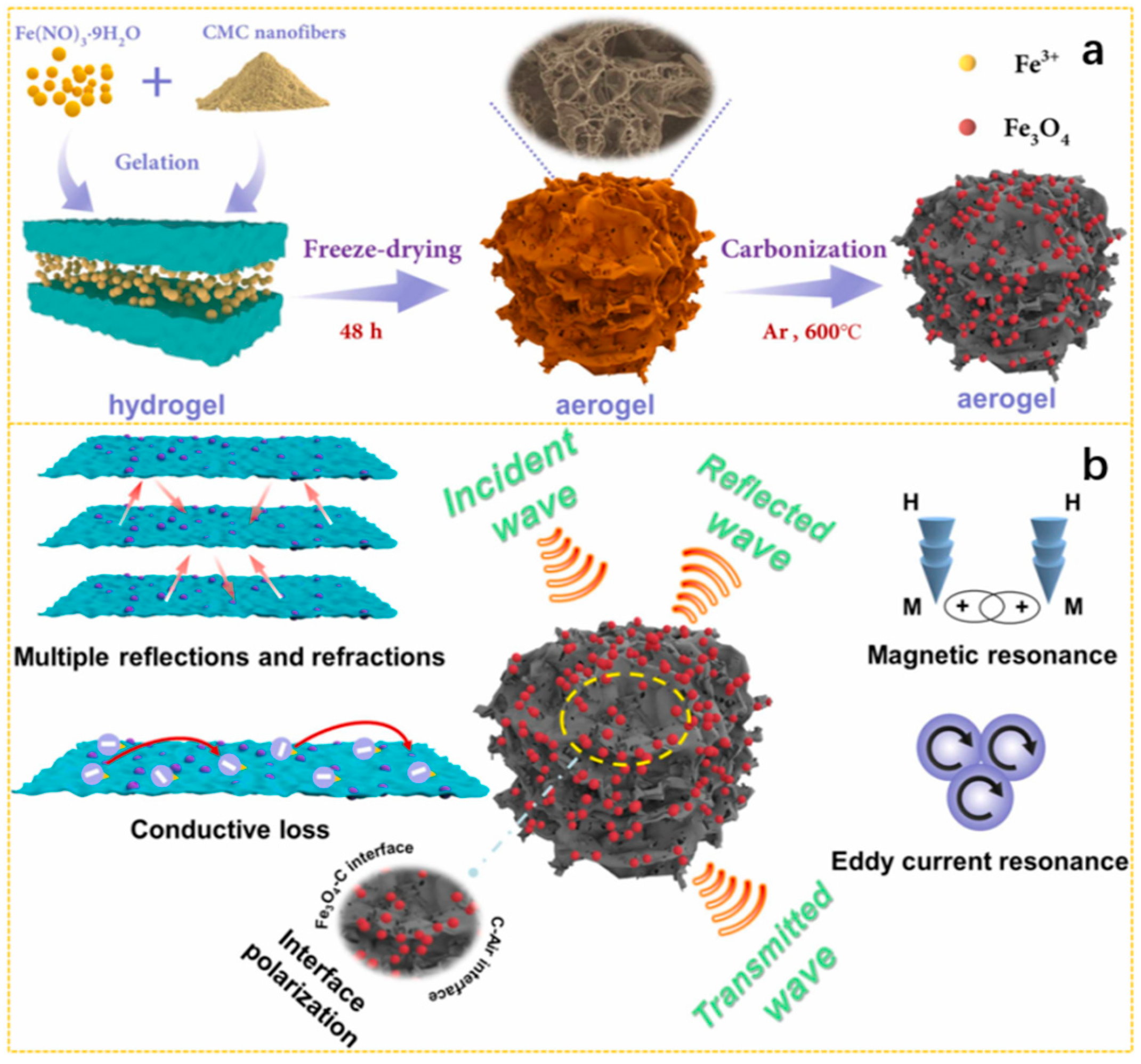
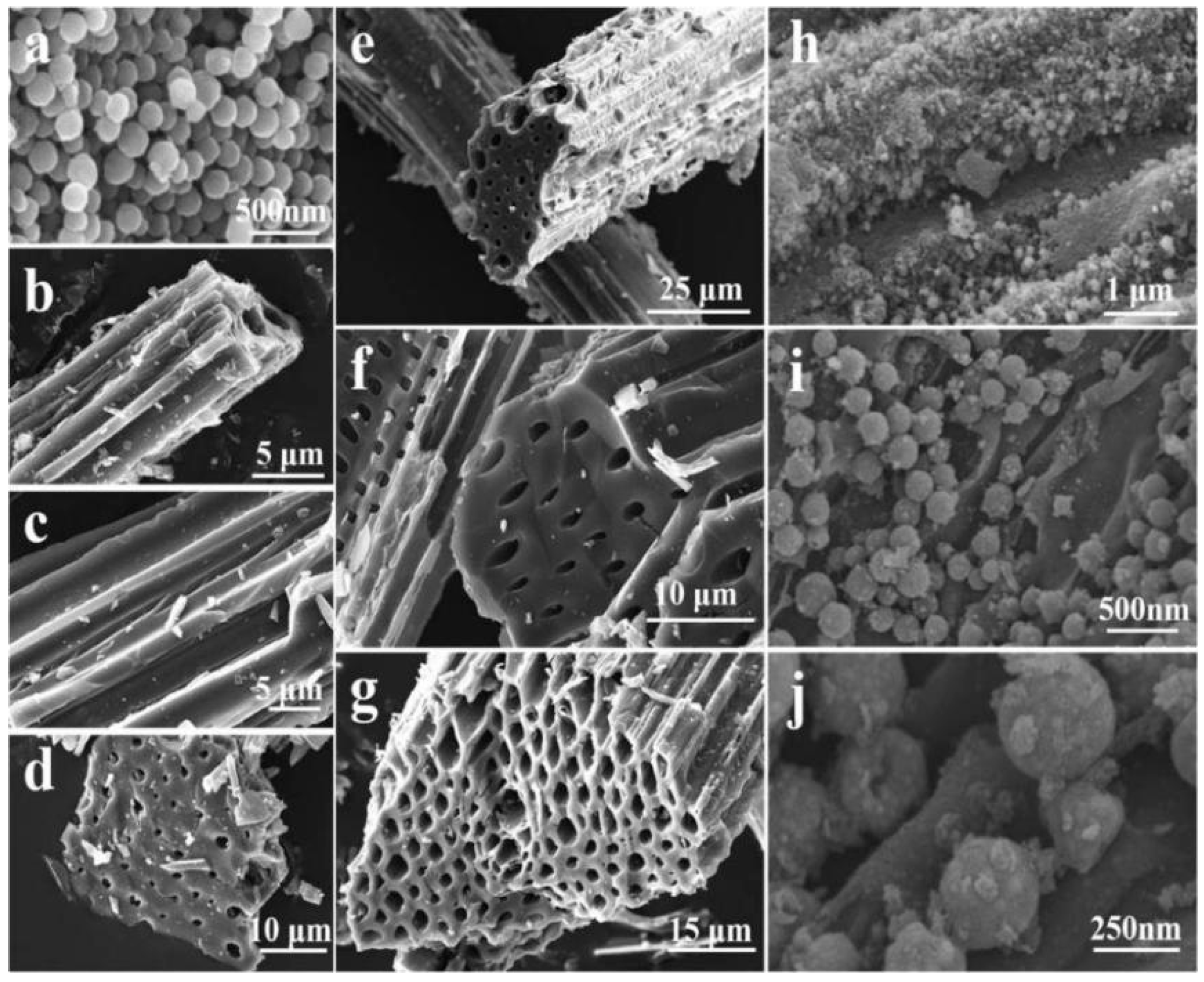
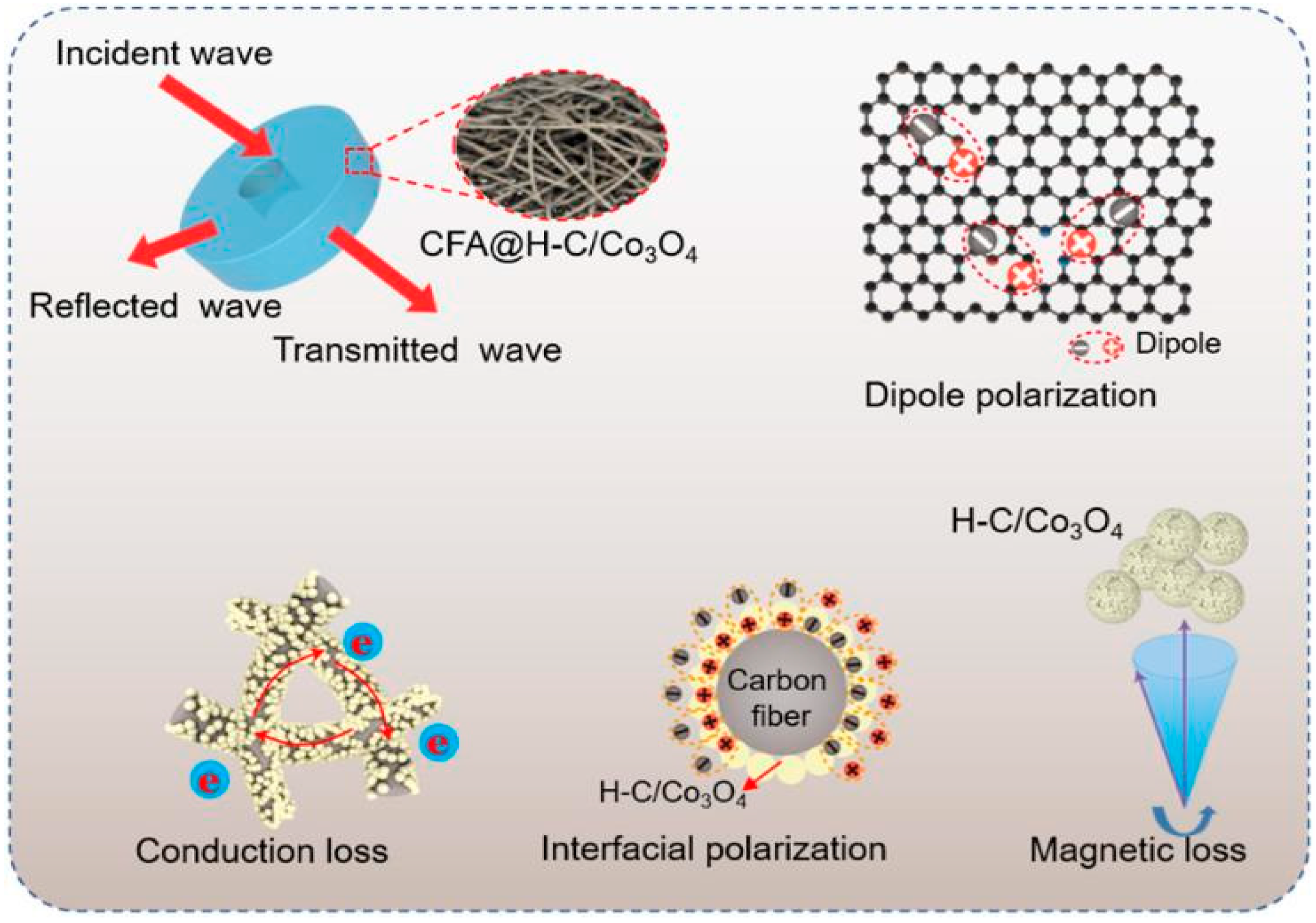

| Biomass Material Category | Biomass Feedstock | Material Components | RLmin (dB) | EAB (GHz) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant shells | Rice husk | Ni/porous carbon(PC) | −58.50 | 3.51 | [88] |
| NiCo2/C | −55.62 | 3.60 | [89] | ||
| FeCo/C | −68.11 | 3.76 | [90] | ||
| ZnO/NiCo/C | −52.50 | 4.48 | [92] | ||
| Fe3O4/C | −52.14 | 13.00 | [94] | ||
| Coconut shell | TiP2O7/C | −32.40 | 6.00 | [98] | |
| Coconut shell/epoxy resin | −23.50 | - | [99] | ||
| Fe/Fe3C | −48.87 | 7.94 | [107] | ||
| Biomass-derived Borocarbonitride/natural rubber | −54.24 | 4.16 | [108] | ||
| Almond wood shell | C/FexOy | −37.90 | 7.04 | [112] | |
| Walnut shell | PNT-Carbonized walnut shell-FeCl3 Activated material | −67.60 | 5.40 | [116] | |
| Fe3O4@C/C | −56.61 | 5.68 | [117] | ||
| Peanut shell | PANI/biomass porous carbon(BPC) | −40.89 | 4.24 | [114] | |
| Ni/polymer-derived ceramic/biomass ceramic | −66.38 | 3.54 | [119] | ||
| Pine nut shell | C@NiCo-LDHs@Ni aerogel | −57.40 | 6.40 | [118] | |
| Plant fiber | Wood fiber | Wood-based porous carbon (WPC)/Ni | −60.40 | 7.30 | [126] |
| MoS2@Gd2O3/Mxene | −57.50 | 4.35 | [130] | ||
| CoFe-MOF@Ti3C2TxMXene@SA@WPC | −57.00 | 5.80 | [134] | ||
| Fir@Co@CNT | −52.00 | 4.20 | [135] | ||
| NiCo2S4/C | −64.74 | 5.26 | [83] | ||
| Cotton fiber | Fe@nanoporous carbon@carbon fiber (Fe@NPC@CF) | −46.20 | 5.20 | [141] | |
| Co@CNT@C | −53.50 | 8.02 | [142] | ||
| CF/restore oxidation graphene (RGO)/NiCo | −60.90 | 6.10 | [144] | ||
| RGO/Ni/C | −39.30 | 4.60 | [145] | ||
| Fe3O4@PC | −54.69 | 7.72 | [146] | ||
| TiO2@C/CF aerogels | −43.18 | 4.36 | [149] | ||
| Bamboo fiber | CoNi/carbonized bamboo fiber | −75.19 | 4.56 | [154] | |
| PC/Fe | −43.20 | 4.72 | [156] | ||
| Carbon fiber aerogel@C/Co3O4 | −43.50 | 7.84 | [157] | ||
| Graphene oxide/PANI/bamboo powder | −44.00 | 5.36 | [161] | ||
| Other biomass materials | Laver | Ni@BPC | −35.73 | 6.37 | [163] |
| Kelp | Kelp porous carbon/Fe3O4 | −75.02 | 4.83 | [164] | |
| Rose | Rose-derived carbon materials/Co (RC/Co) | −47.89 | 4.08 | [165] | |
| Pine cone | CeO2/PC | −56.04 | 5.28 | [166] | |
| Coffee grounds | PC/Fe | −52.68 | 6.40 | [167] | |
| Apple | Biocarbon/CoFe@C | −72.57 | 5.25 | [168] | |
| Straw | Carbon black/Co@C | −53.99 | 6.00 | [171] | |
| NiCo/straw-derived carbon | −27.00 | 4.40 | [172] | ||
| FeCl3/straw-derived carbon | −30.03 | 4.17 | [173] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Zhen, M.; Meng, F.; Meng, X.; Zhu, M. Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070553
Ren X, Zhen M, Meng F, Meng X, Zhu M. Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(7):553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070553
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xujing, Meirong Zhen, Fuliang Meng, Xianfeng Meng, and Maiyong Zhu. 2025. "Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials" Nanomaterials 15, no. 7: 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070553
APA StyleRen, X., Zhen, M., Meng, F., Meng, X., & Zhu, M. (2025). Progress, Challenges and Prospects of Biomass-Derived Lightweight Carbon-Based Microwave-Absorbing Materials. Nanomaterials, 15(7), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15070553







