Quantitative Criteria for Solvent Selection in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Balancing Exfoliation and Stabilization Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Methods
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
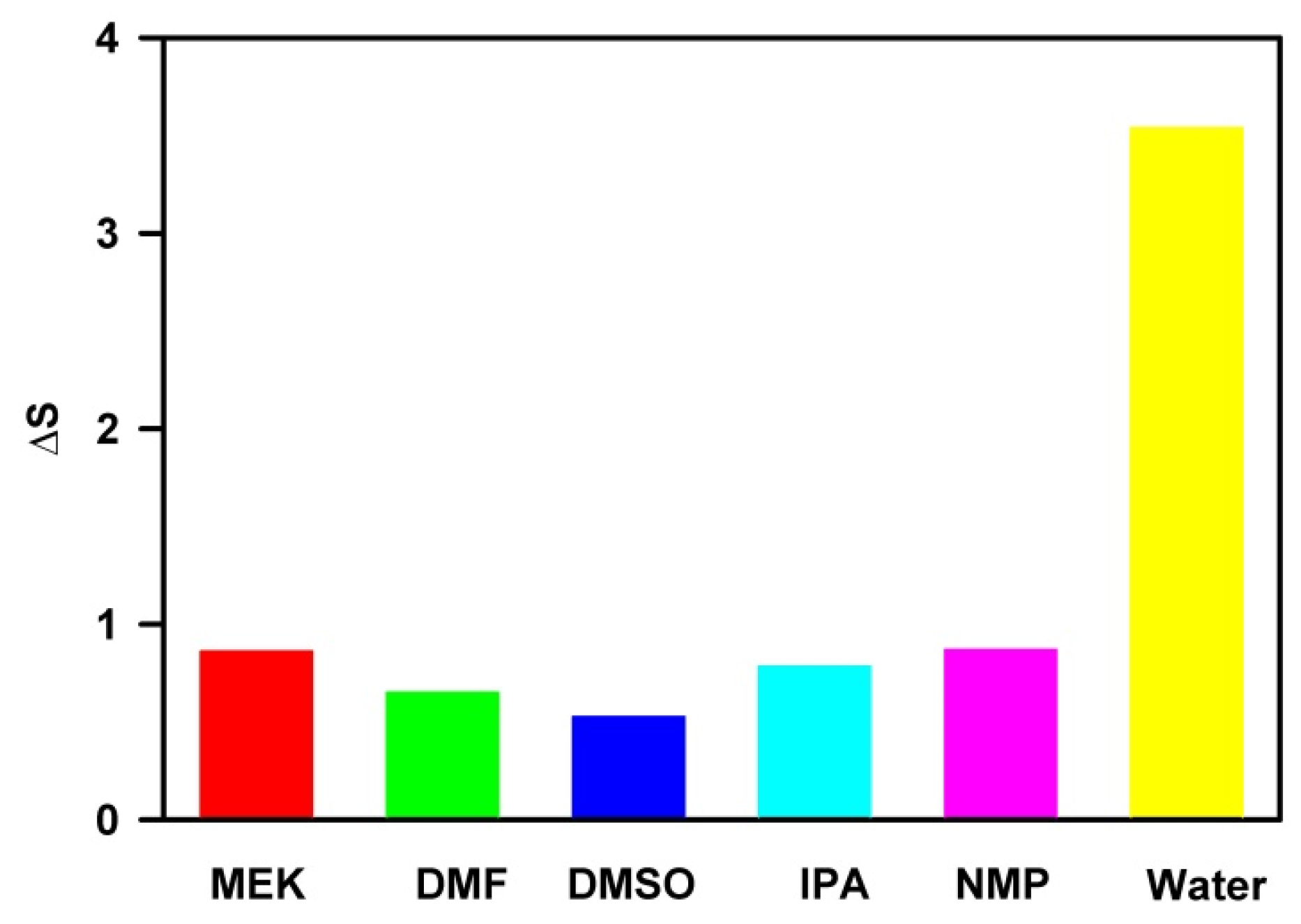
3.1. Structure and Property of Solvent
3.2. Binding of Solvent on Mg(OH)2 Surface
3.3. Insertion of Solvent in Mg(OH)2 Bilayers
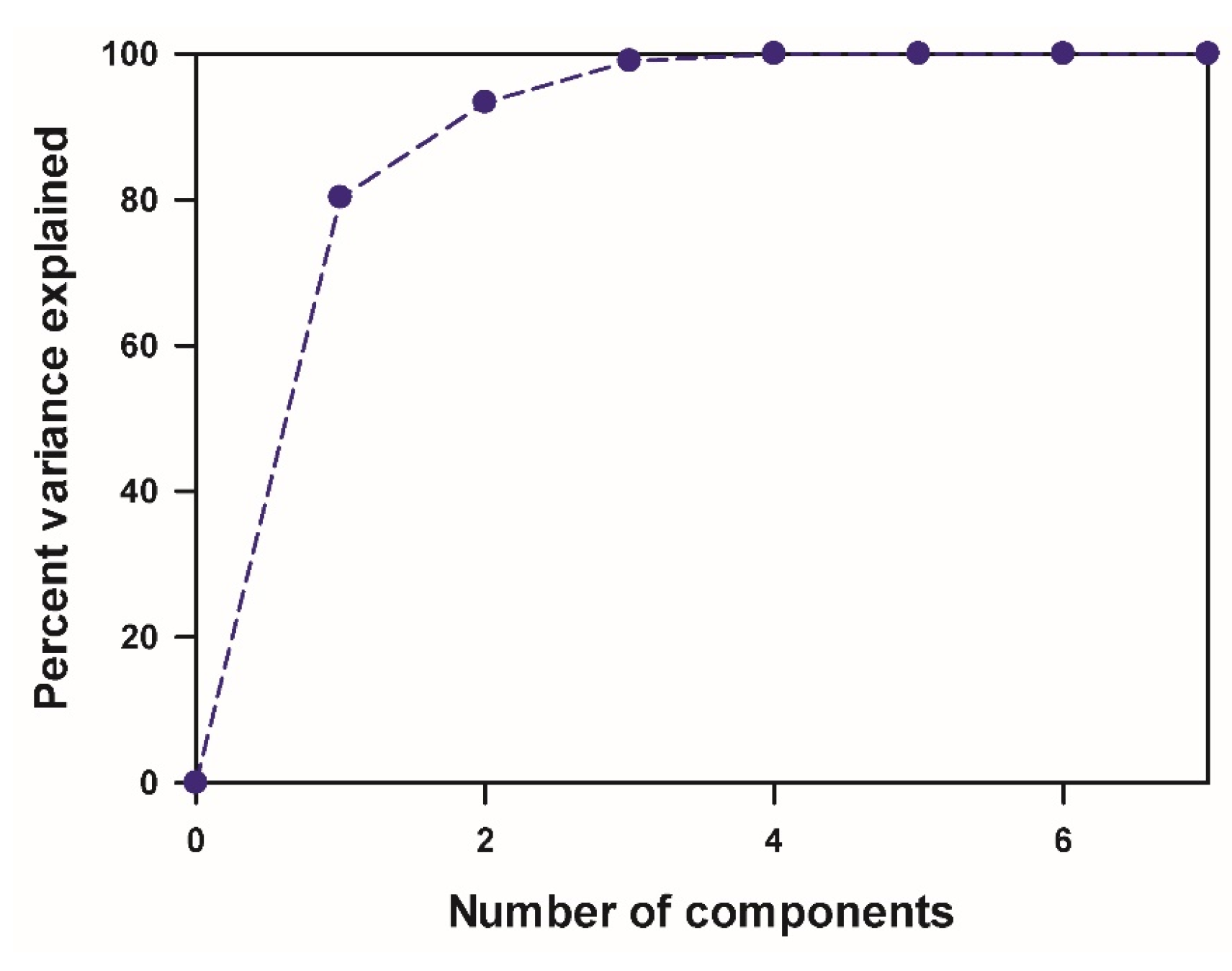
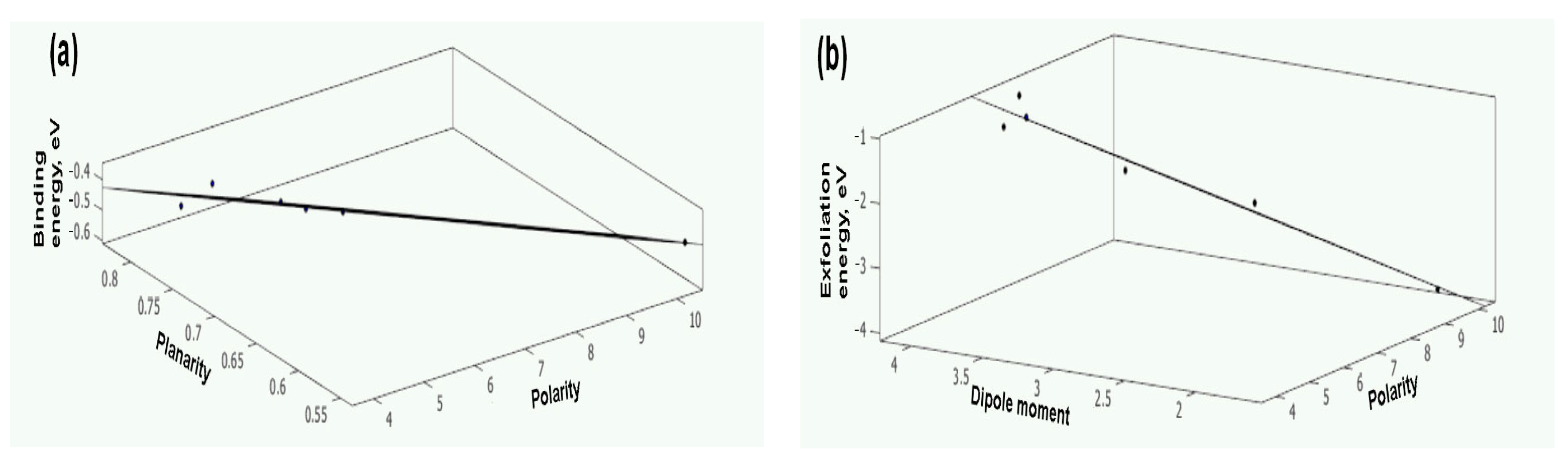
3.4. Quantitative Structure–Property Relationship (QSPR) Analysis
3.5. Biaxial Straining Theory
3.6. Experimental Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPE | liquid-phase exfoliation |
| 2D | two-dimensional |
| CVD | chemical vapor deposition |
| PVD | physical vapor deposition |
| MEK | 2-butanone |
| DMF | dimethylformamide |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| IPA | isopropyl alcohol |
| NMP | N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| o-DCB | ortho-dichlorobenzene |
| HSP | Hansen solubility parameters |
| DFT | density functional theory |
| VASP | Vienna ab initio simulation package |
| PBE | Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof |
| GGA | generalized gradient approximation |
| PAW | projector augmented wave |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| EDS | energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| QSPR | quantitative structure–property relationship |
References
- Murali, A.; Lokhande, G.; Deo, K.A.; Brokesh, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. Emerging 2D nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 276–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreen, S.; Tahir, M.B.; Hussain, A.; Nawaz, T.; Rehman, J.U.; Dahshan, A.; Alzaid, M.; Alrobei, H. Emerging 2D-nanostructured materials for electrochemical and sensing application—A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 1371–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Asaduzzaman Chowdhury, M.; Shahid, A.; Alam, R.; Rahim, A. Synthesis of emerging two-dimensional (2D) materials—Advances, challenges and prospects. FlatChem 2021, 30, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N. Two-dimensional nanomaterials: A critical review of recent progress, properties, applications, and future directions. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 165, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Coleman, J.N. Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Nonlayered Non-Van-Der-Waals Crystals into Nanoplatelets. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Cao, H.Z.; Xue, Y.Q.; Li, B.; Cai, W.H. Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Graphene: An Overview on Exfoliation Media, Techniques, and Challenges. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telkhozhayeva, M.; Teblum, E.; Konar, R.; Girshevitz, O.; Perelshtein, I.; Aviv, H.; Tischler, Y.R.; Nessim, G.D. Higher ultrasonic frequency liquid phase exfoliation leads to larger and monolayer to few-layer flakes of 2D layered materials. Langmuir 2021, 37, 4504–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, Y.; Nicolosi, V.; Lotya, M.; Blighe, F.M.; Sun, Z.Y.; De, S.; McGovern, I.T.; Holland, B.; Byrne, M.; Gun’ko, Y.K.; et al. High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.X.; Yan, Z.; Song, X.F.; Zeng, H.B. 2D materials via liquid exfoliation: A review on fabrication and applications. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1994–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Young, R.J.; Backes, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhukov, A.A.; Tillotson, E.; Conlan, A.P.; Ding, F.; Haigh, S.J.; et al. Mechanisms of liquid-phase exfoliation for the production of graphene. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10976–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, Y.; Lotya, M.; Rickard, D.; Bergin, S.D.; Coleman, J.N. Measurement of multicomponent solubility parameters for graphene facilitates solvent discovery. Langmuir 2010, 26, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.; Nemala, S.S.; De Bellis, G.; Capasso, A. Green solvents for the liquid phase exfoliation production of graphene: The promising case of cyrene. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, K.; Huang, H.N.; Li, W.T.; Ho, Y.H.; Chiang, W.H. Toward Understanding the efficient exfoliation of layered materials by water-assisted cosolvent liquid-phase exfoliation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7586–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreshtt, V.; Pádua, A.A.H.; Blankschtein, D. Liquid-phase exfoliation of phosphorene: Design rules from molecular dynamics simulations. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 8255–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslu, A.; Wu, K.; Sahin, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; Cai, H.; Aoki, T.; Horzum, S.; Kang, J.; Peeters, F.M.; et al. Unusual dimensionality effects and surface charge density in 2D Mg(OH)2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, B.; Hansen, L.B.; Norskov, J.K. Improved adsorption energetics within density-functional theory using revised Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof functionals. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 7413–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmuller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA; Dassault Systèmes. Material Studio, Version 8.0; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014.
- Eisenhaber, F.; Argos, P. Improved strategy in analytic surface calculation for molecular systems: Handling of singularities and computational efficiency. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, M.L. Solvent-accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science 1983, 221, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Senevirathna, H.L.; Weerasinghe, P.V.T.; Wu, P. Engineering electronic structure and band alignment of 2D Mg(OH)2 via anion doping for photocatalytic applications. Materials 2021, 14, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, P.X.; Song, S.H.; Yuan, Q.H.; Yang, P.; Ren, X.Z. Simulation of magnesium hydroxide surface and interface. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 612, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.D. (Ed.) Surface Tension of Pure Liquids and Binary Liquid Mixtures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bonin, K.D.; Kresin, V.V. Electric-Dipole Polarizabilities of Atoms, Molecules, and Clusters; World Scientific Publishing: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.N.; Wu, P. Energetic and configurational mechanisms to facilitate mica nanosheets synthesis by organo-ammonium cation intercalation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 224, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, G.A. An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Thenuwara, H.N.; Senevirathna, H.L. Entropy-driven liquid-phase exfoliation of non-Van-Der-Waals crystals into nanoplatelets. FlatChem 2023, 41, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.T.; Wu, P.; Anariba, F. Modeling stress-strain nonlinear mechanics via entropy changes on surface wetting using the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Results Eng. 2022, 13, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasinghe, P.V.T.; Wu, S.; Lee, W.P.C.; Zhu, Q.; Lin, M.; Wu, P. Mica nanosheets synthesized via liquid Ga embrittlement: Demonstrating enhanced CO2 capture. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.C.; Wu, S.; Anariba, F.; Wu, P. Breaking new ground in mica exfoliation: Harnessing biaxial straining principles through H2 and N2 intercalation for enhanced layer separation. Mater. Today Adv. 2023, 19, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Weerasinghe, P.V.T.; Wu, P. Fostering mica exfoliation through biaxial straining strategy with monovalent cation substitution. FlatChem 2023, 42, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
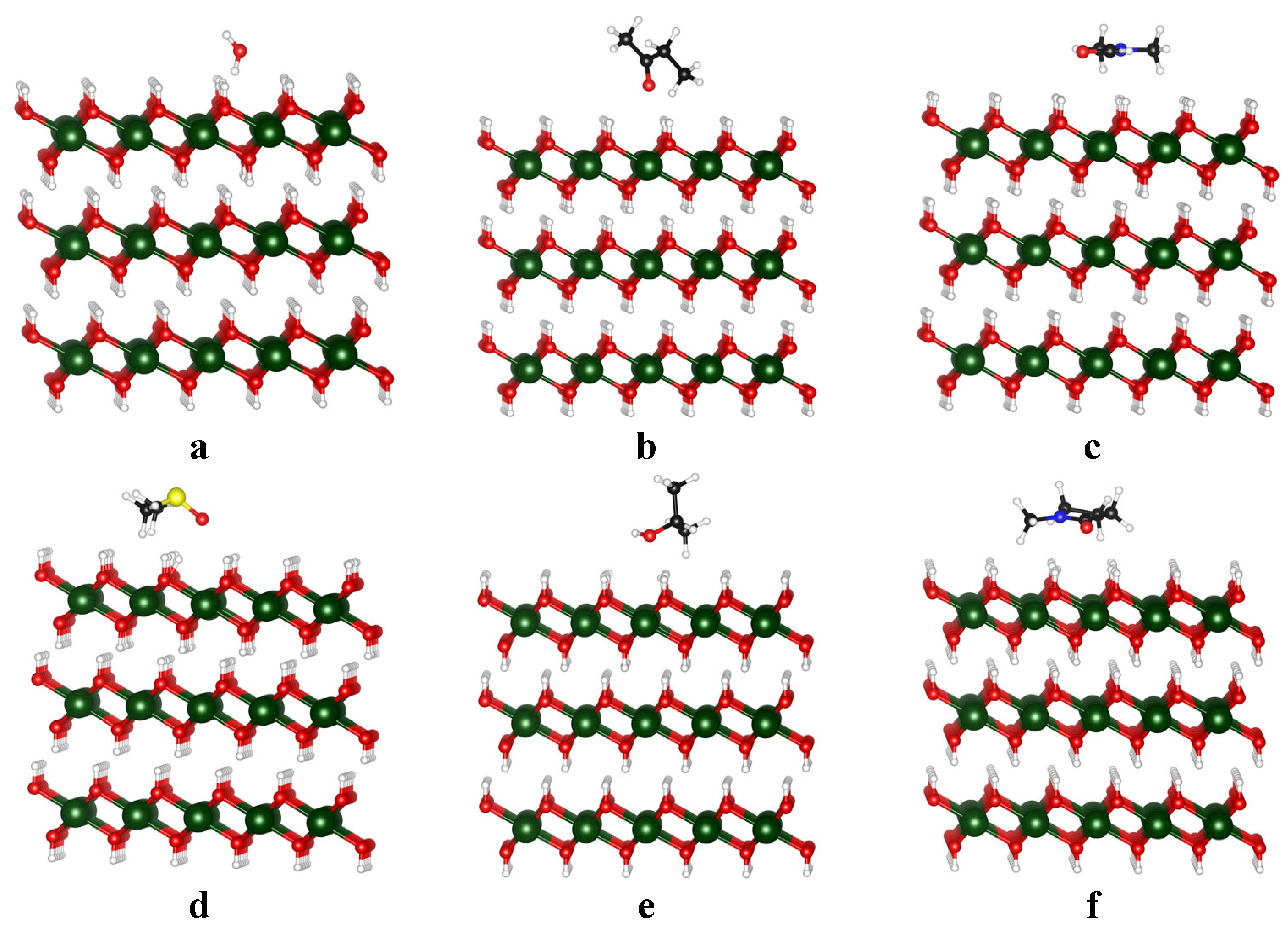
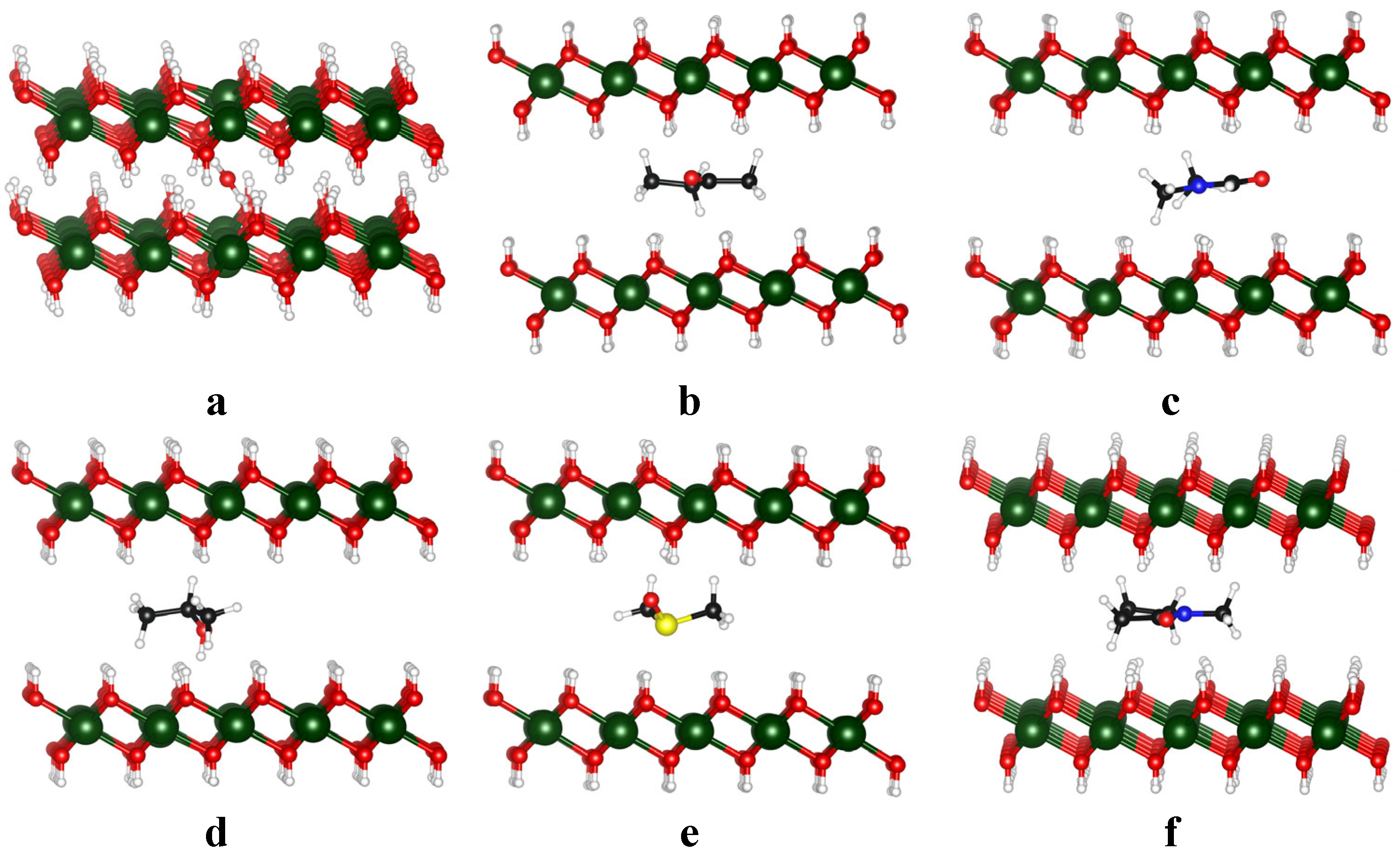

| Name | Formula | Structure * | γ, mN/m [28] | Polarity [29] | Dipole Moment, D [29] | Planarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water | H2O |  | 72.80 | 10.2 | 1.87 | 0.54 |
| MEK | CH3C(O)CH2CH3 | 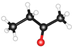 | 24.60 | 4.7 | 2.76 | 0.77 |
| DMF | (CH3)2NC(O)H | 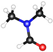 | 37.10 | 6.4 | 3.86 | 0.76 |
| DMSO | (CH3)2SO |  | 43.53 | 7.2 | 4.10 | 0.77 |
| IPA | CH3CHOHCH3 | 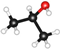 | 23.00 | 3.9 | 1.66 | 0.76 |
| NMP | CH3N(CH2CH2CH2)C(O) | 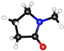 | 40.79 | 6.7 | 4.09 | 0.81 |
| Solvent | , eV | , eV | , Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| − * | −5.55 | 2.50 | |
| H2O | −0.44 | −3.98 | 2.77 |
| MEK | −0.36 | −1.22 | 6.03 |
| DMF | −0.52 | −1.17 | 6.08 |
| DMSO | −0.58 | −1.10 | 6.26 |
| IPA | −0.37 | −1.15 | 6.13 |
| NMP | −0.60 | −1.47 | 6.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, S.; Lee, W.P.C.; Thenuwara, H.N.; Wu, P. Quantitative Criteria for Solvent Selection in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Balancing Exfoliation and Stabilization Efficiency. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050370
Wu S, Lee WPC, Thenuwara HN, Wu P. Quantitative Criteria for Solvent Selection in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Balancing Exfoliation and Stabilization Efficiency. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(5):370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050370
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Shunnian, W. P. Cathie Lee, Hashan N. Thenuwara, and Ping Wu. 2025. "Quantitative Criteria for Solvent Selection in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Balancing Exfoliation and Stabilization Efficiency" Nanomaterials 15, no. 5: 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050370
APA StyleWu, S., Lee, W. P. C., Thenuwara, H. N., & Wu, P. (2025). Quantitative Criteria for Solvent Selection in Liquid-Phase Exfoliation: Balancing Exfoliation and Stabilization Efficiency. Nanomaterials, 15(5), 370. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050370







