The Preparation of Robust Gully-like Surface of Stainless Steel Fiber-Bonded TFPA–TTA–COF with Nano Pores for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Chromatographic Condition
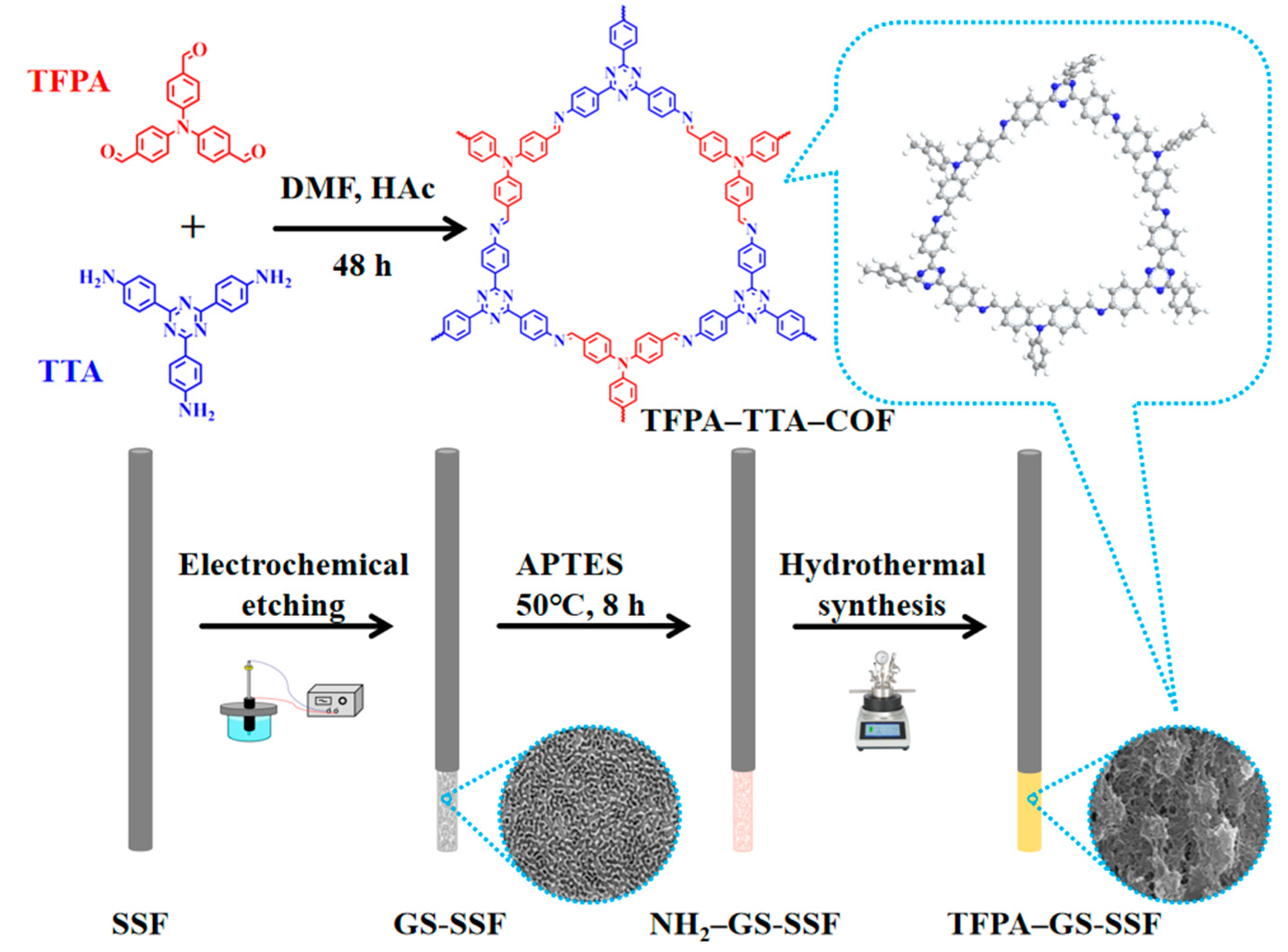
2.4. The Fabrication of the COF
2.5. The Fabrication of the Etched SSF
2.6. The Fabrication of the TFPA–TTA–COF Coated on GS-SSF
2.7. SPME Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
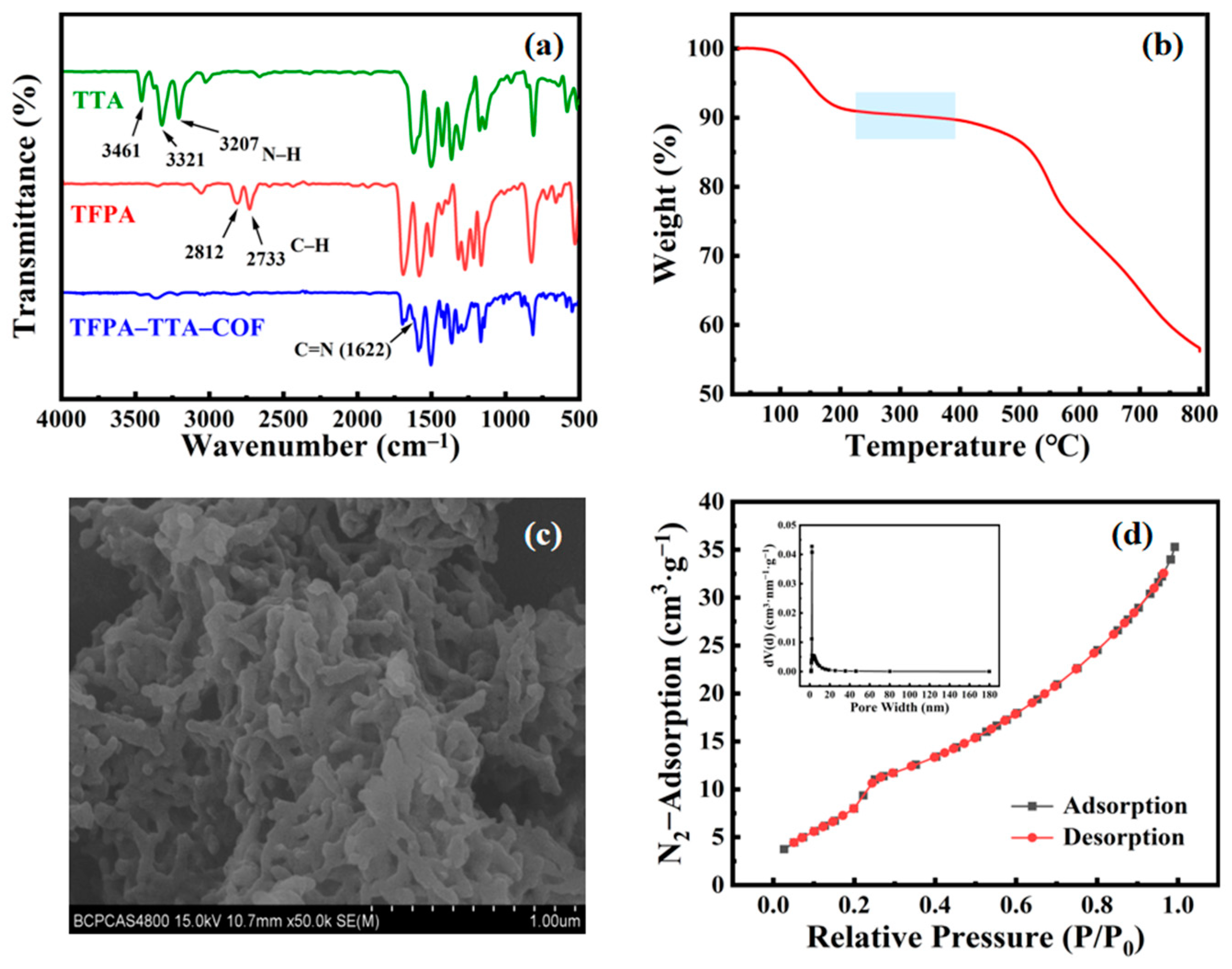
3.1. The Characterization of the TFPA–TTA–COF
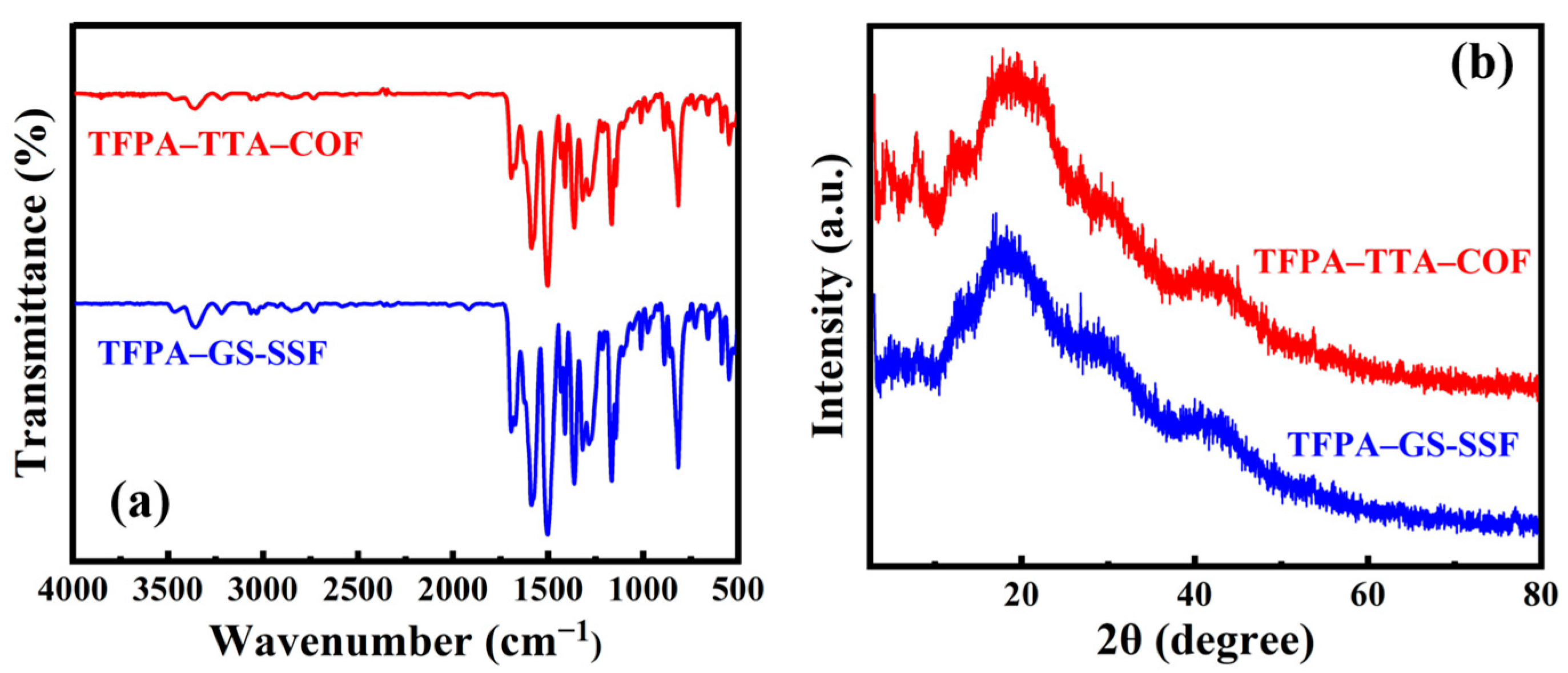
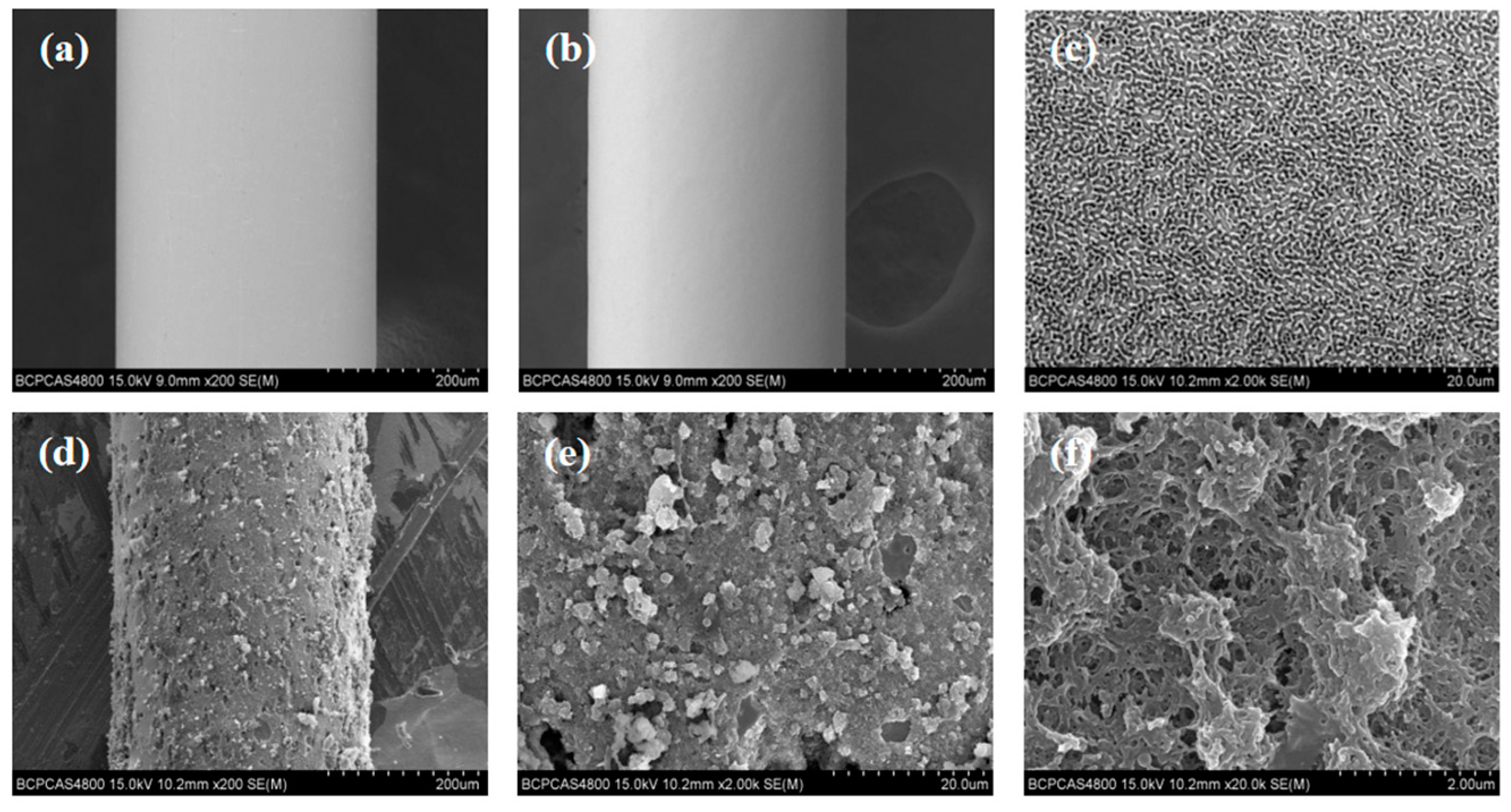
3.2. The Characterization of the SPME Fibers
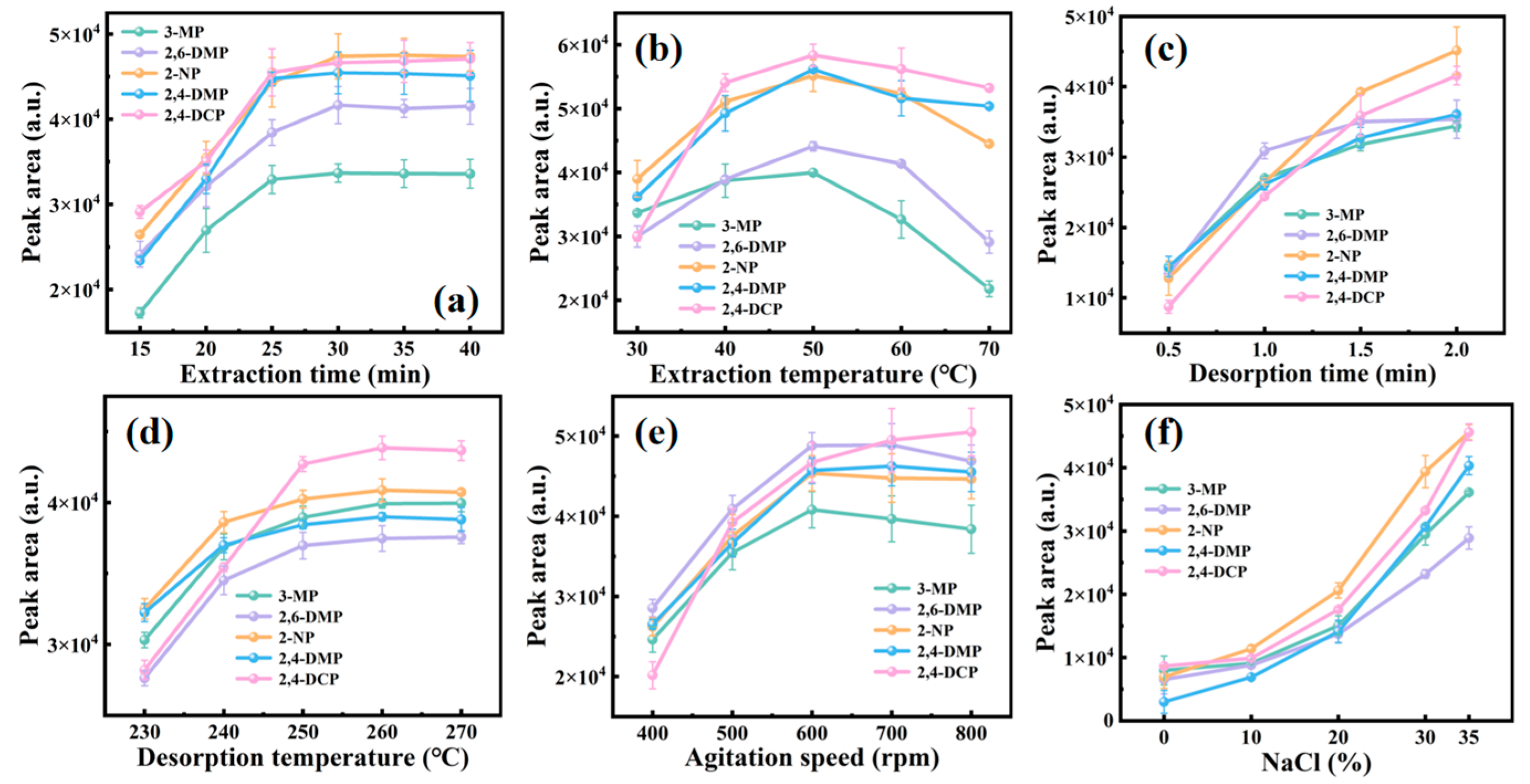
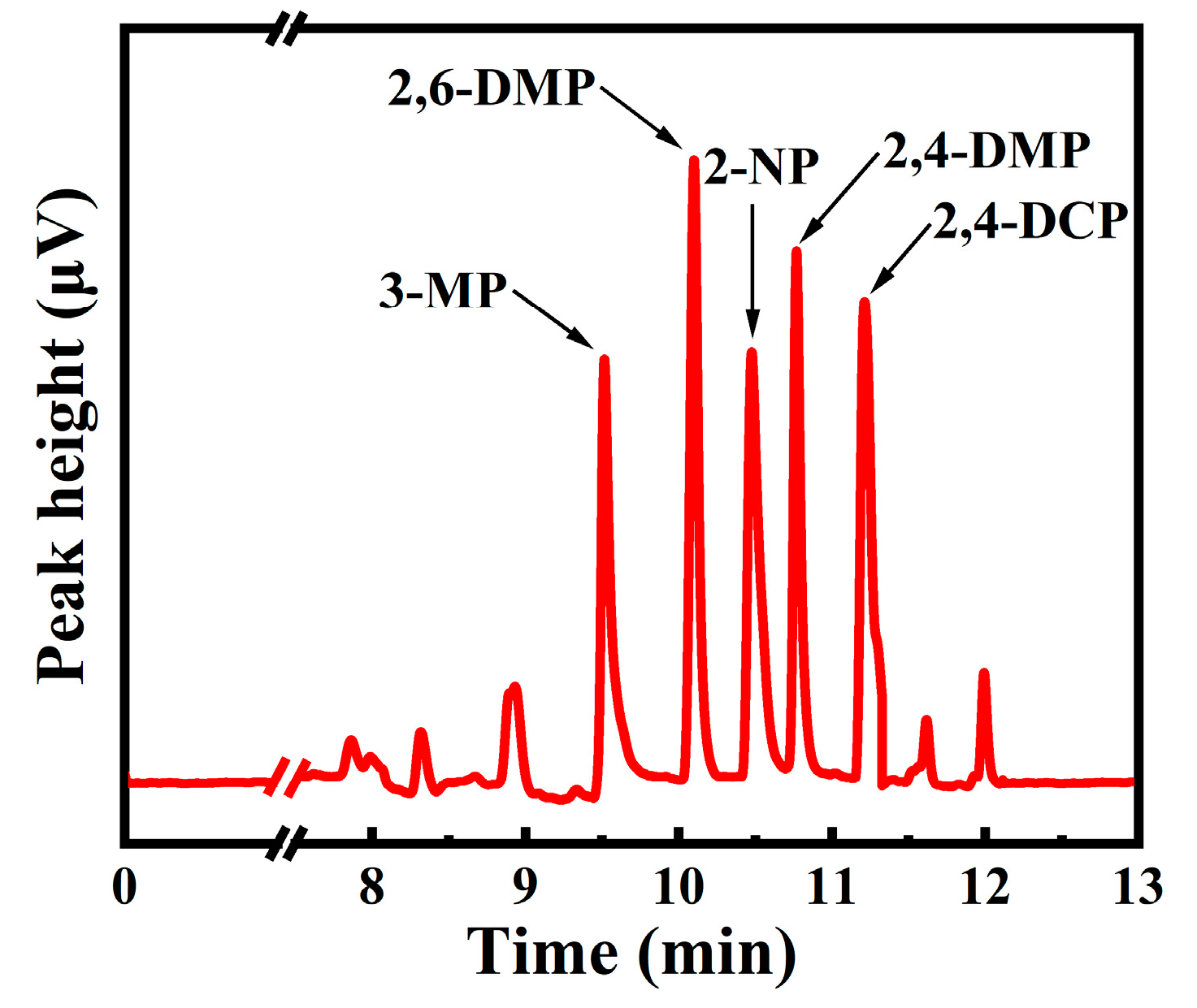
3.3. The Optimization of the Extraction and Desorption Conditions
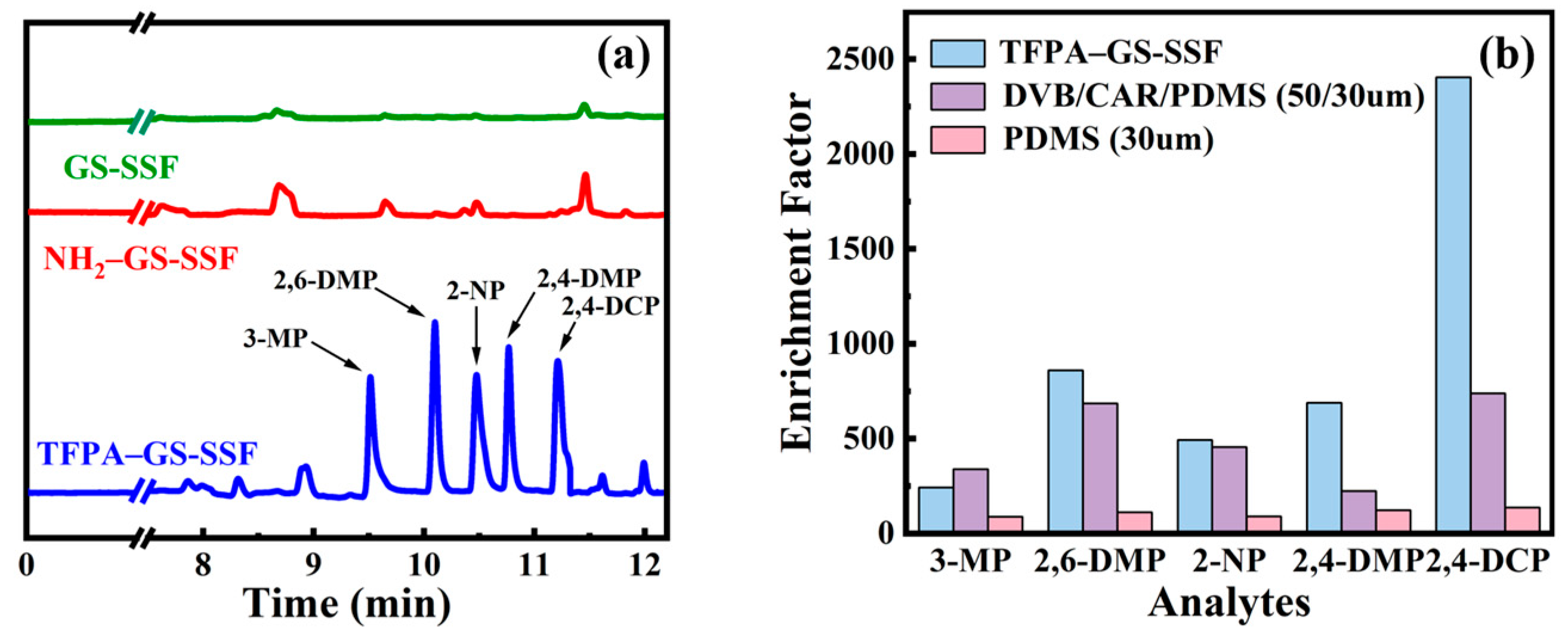
3.4. The Durability and Selectivity of the Prepared SPME Fiber
3.5. The Comparison of the Different SPME Fibers
3.6. The Analytical Figures of Merit
3.7. The Analysis of the PCs in Environmental Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COFs | Covalent organic frameworks |
| PCs | Phenolic compounds |
| SSF | Stainless steel fiber |
| GS-SSF | Gully-like surface of stainless steel fiber |
| SPME | Solid-phase microextraction |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| TTA | 4,4′,4″-(1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triyl) triphenylamine |
| TFPA | Tris(4-formylphenyl) amine |
| APTES | 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane |
| 3-MP | M-cresol |
| 2,6-DMP | 2,6-dimethylphenol |
| 2-NP | O-nitrophenol |
| 2,4-DMP | 2,4-dimethylphenol |
| 2,4-DCP | 2,4-dichlorophenol |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| FID | Flame ionization detector |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| LODs | Limits of detection |
| RSDs | Relative standard deviations |
| EFs | Enrichment factors |
References
- Beya, M.M.; Netzel, M.E.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Smyth, H.; Hoffman, L.C. Plant-Based Phenolic Molecules as Natural Preservatives in Comminuted Meats: A Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P. Phenolic-Rich Plant Extracts With Antimicrobial Activity: An Alternative to Food Preservatives and Biocides? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 753518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Gotoh, H. Feature Selection for the Interpretation of Antioxidant Mechanisms in Plant Phenolics. Molecules 2023, 28, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, C.; Shen, C.; Sun, S.; Meng, X.-Z.; Wang, S.; Li, F. Evaluation of Key Intermediates in Azo Dye Degradation by Advanced Oxidation Processes: Comparing Anilines and Phenols. ACS ES&T Water 2024, 4, 4872–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hou, X.; Yu, C.; Pan, X.; Ma, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, C.; Xin, Y.; Yan, Q. Integration of Wastewater Treatment Units and Optimization of Waste Residue Pyrolysis Conditions in the Brominated Phenol Flame Retardant Industry. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 115, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ni, N.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Simultaneous Phenol Removal and Resource Recovery from Phenolic Wastewater by Electrocatalytic Hydrogenation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4356–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernats, M.; Juhna, T. Removal of Phenols-like Substances in Pharmaceutical Wastewater with Fungal Bioreactors by Adding Trametes Versicolor. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Nie, M.; Diwu, Z.; Wang, L.; Nie, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, B. Simultaneous Biodegradation of Phenolics and Petroleum Hydrocarbons from Semi-Coking Wastewater: Construction of Bacterial Consortium and Their Metabolic Division of Labor. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulsunoglu-Konuskan, Z.; Kilic-Akyilmaz, M. Microbial Bioconversion of Phenolic Compounds in Agro-Industrial Wastes: A Review of Mechanisms and Effective Factors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6901–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndwabu, S.; Malungana, M.; Mahlambi, P. Phenolic Compounds—Occurrence in Water, Sediment and Sludge, and Ecological Risk Evaluation. Clean-Soil Air Water 2023, 51, 2200404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid Phase Microextraction with Thermal Desorption Using Fused Silica Optical Fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Ihsanullah, I. Novel Materials for Dispersive (Micro) Solid-Phase Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Samples: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthana, S.; Illanad, G.; Saket, S.; Ghosh, C. Recent Advances in Solid Phase Microextraction with Various Geometries in Environmental Analysis. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 27608–27621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Rosado, T.; Barroso, M.; Gallardo, E. Solid Phase-Based Microextraction Techniques in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chromiec, A.; Wietecha-Posłuszny, R. Micro-Solid Phase Extraction with in-Lab-Packed Columns for Cost-Efficient Drug Extraction from Urine Samples. Monatsh. Chem. 2024, 155, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspromonte, J.; Lancioni, C.; Purcaro, G. Solid-Phase Microextraction—Gas Chromatography Analytical Strategies for Pesticide Analysis. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Sousa, J.; Do Nascimento, H.O.; De Oliveira Gomes, H.; Do Nascimento, R.F. Pesticide Residues in Groundwater and Surface Water: Recent Advances in Solid-Phase Extraction and Solid-Phase Microextraction Sample Preparation Methods for Multiclass Analysis by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnezhad, N.; Matin, A.A.; Samadi, N.; Shomali, A.; Valizadeh, H. Ionic Liquid-Bonded Fused Silica as a New Solid-Phase Microextraction Fiber for the Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Bisphenol A as an Endocrine Disruptor. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Yang, P.; Pang, R.; Yuan, Y.; Ge, L.; Zhang, H. Polymeric Ionic Liquid Based Fused Silica Fiber by Chemical Binding for Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction of Organophosphate Esters in Water Samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 1094–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J.; Shang, Q. Electrochemical in Situ Fabrication of Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes on a Titanium Wire as a Fiber Coating for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Crystals 2021, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Shen, X.-F.; Yang, C.; Pang, Y.-H. In Situ Growth of Covalent Organic Framework on Titanium Fiber for Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction of 11 Phthalate Esters in Vegetables. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazipour, S.; Raoof, J.B.; Ghani, M. Template-Directed Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Metal Organic Framework 199-Derived Highly Porous Copper Nano-Foam Fiber for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Some Antibiotics Prior to Their Quantification by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1660, 462677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, M.; Masoum, S.; Ghoreishi, S.M. Three-Dimensional Pd/Pt Bimetallic Nanodendrites on a Highly Porous Copper Foam Fiber for Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction of BTEX Prior to Their Quantification by GC-FID. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z. Flower-like Layered Double Hydroxide-modified Stainless-steel Fibers for Online In-tube Solid-phase Microextraction of Sudan Dyes. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-X.; Yu, L.-Q.; Sun, Y.-N.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-M.; Lv, Y.-K. Hollow Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-7 Coated Stainless Steel Fiber for Solid Phase Microextraction of Volatile Biomarkers in Headspace Gas of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1181, 338901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poryan, G.; Noori, M.; Talebpour, Z.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. A Polyacrylate Cotton-Based Pipette Tip Micro-Solid-Phase ExtractionTechnique Coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for Carvedilol Determination in Aqueous Media. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2024, 20, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varona, M.; Shimelis, O.I.; Anderson, J.L. Modification of Polyacrylate Sorbent Coatings with Carbodiimide Crosslinker Chemistry for Sequence-Selective DNA Extraction Using Solid-Phase Microextraction. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3200–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, J.; Grześkowiak, T.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. A Polydimethylsiloxane/Deep Eutectic Solvent Sol-Gel Thin Film Sorbent and Its Application to Solid-Phase Microextraction of Parabens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 339666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhong, D.; Li, Y.; Wu, D. Inhibition of Water Adsorption into Polar Solid-Phase Microextraction Materials with Ultrathin Polydimethylsiloxane Coating for Thermal Desorption-Gas Chromatography Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1578, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ren, X.; Gao, Y.; Mu, M.; Zhu, S.; Li, D.; Tian, S.; Qin, P.; Lu, M. Poly (Divinylbenzene) as a Fiber Coating for Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from River Water. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7574–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenti, L.; Scortichini, S.; Pacetti, D.; Cespi, M.; Fiorini, D. Polydimethylsiloxane/Divinylbenzene Overcoated Fiber and Its Application to Extract and Analyse Wine Volatile Compounds by Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry: Direct Immersion, Headspace or Both? Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavir, K.; Eor, P.; Kloskowski, A.; Anderson, J.L. Polymeric Metal-containing Ionic Liquid Sorbent Coating for the Determination of Amines Using Headspace Solid-phase Microextraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2620–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y. A Double-Functionalized Polymeric Ionic Liquid Used as Solid-Phase Microextraction Coating for Efficient Aromatic Amine Extraction and Detection with Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Sun, M. Recent Advances on Graphene and Graphene Oxide as Extraction Materials in Solid-Phase (Micro)Extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 168, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.T.; Martins, R.O.; Lanças, F.M. Advances and Applications of Hybrid Graphene-Based Materials as Sorbents for Solid Phase Microextraction Techniques. Molecules 2024, 29, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, M. Solid Supports and New Advanced Materials Used in Microextraction Processes Metal-Organic Framework-Based Solid-Phase Microextraction for Air Samples Analysis: A Mini-Review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 181, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaykhaii, M.; Hashemi, S.H.; Gębicki, J. Applications of Metal Organic Framework Adsorbents for Pipette-Tip Micro Solid-Phase Extraction. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 179, 117877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, G.D.T.M.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Dispersive (Micro)Solid Phase Extraction: A Review. Separations 2021, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Ishizaki, A.; Saito, K.; Ehara, K. Developments and Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based In-Tube Solid Phase Microextraction Technique for Efficient Sample Preparation. Molecules 2024, 29, 4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; O’Keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Feng, Z.; Ma, K.; Ding, X.; et al. Efficient and Rapid Adsorption of Thorium by Sp2c-COF with One-Dimensional Regular Micropores Channels. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhashmi, S.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Mavridis, A.; Nair, R.R.; Zhao, X.; D’Agostino, C. Diffusion and Adsorption in Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) Probed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Methods. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 41, 102245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Yao, Y.; Meng, L.; Duan, E.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Photocatalytic and Electrocatalytic Extraction of Uranium by COFs: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 18230–18250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Hollow Rh-COF@COF S-Scheme Heterojunction for Photocatalytic Nicotinamide Cofactor Regeneration. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6619–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gong, H.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z. Fabrication a Sensor Based on Sulfonate-Based COF for Humidity Sensing. Mater. Lett. 2022, 328, 133123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Q.-H.; Ye, X.-L.; Wang, G.-E.; Xu, G. Dangling Bond Formation on COF Nanosheets for Enhancing Sensing Performances. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 4824–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tao, H.; Tao, H.; Shuai, Q.; Huang, L. In Situ Growth of Hierarchical Porous Covalent Organic Framework Coating for Enhanced Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1739, 465519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Xu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Lian, Y.; Zhao, R.-S. Ketoenamine Covalent Organic Framework Coating for Efficient Solid-Phase Microextraction of Trace Organochlorine Pesticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8008–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, S.; Deng, X.; Yang, N.; Qin, M.; Zhang, X.; Yao, X.; An, C.; Zhou, P.; Lu, X. A Durable Hydrophobicity Hydrazone Covalent Organic Framework Coating for Solid Phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Food and Environmental Sample. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wu, M.; Lin, C.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z. Efficient and Selective Solid-Phase Microextraction of Polychlorinated Biphenyls by Using a Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework as Functional Coating. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1681, 463419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Shen, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, B. The Preparation of Covalent Bonding COF-TpBD Coating in Arrayed Nanopores of Stainless Steel Fiber for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; You, J. A New 3D COF with Excellent Fluorescence Response for Water and Good Adsorption Performance for Polychlorinated Biphenyls. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analytes | Linear Range (µg L−1) | R2 | LODs (μg∙L−1) | RSDs | EFs * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inter-Day (%, n = 5) | Fiber-to-Fiber (%, n = 3) | |||||
| 3-MP | 5–1000 | 0.9938 | 0.17 | 5.87 | 3.68 | 243 |
| 2,6-DMP | 1–200 | 0.9953 | 0.15 | 7.11 | 5.20 | 861 |
| 2-NP | 5–1000 | 0.9984 | 0.52 | 8.89 | 8.05 | 493 |
| 2,4-DMP | 2–400 | 0.9963 | 0.33 | 3.94 | 7.46 | 689 |
| 2,4-DCP | 2–400 | 0.9966 | 0.07 | 4.98 | 2.14 | 2405 |
| Analytes | Lake Water | Caohe River Water | Tap Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found (μg∙L−1) | Recoveries (%) | Found (μg∙L−1) | Recoveries (%) | Found (μg∙L−1) | Recoveries (%) | |
| 3-MP | ND * | 100.46 | ND | 100.56 | ND | 90.38 |
| 2,6-DMP | ND | 111.65 | ND | 110.85 | ND | 100.34 |
| 2-NP | ND | 100.25 | ND | 106.61 | ND | 84.76 |
| 2,4-DMP | ND | 91.38 | ND | 108.55 | ND | 113.19 |
| 2,4-DCP | ND | 122.06 | ND | 102.32 | ND | 124.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, B. The Preparation of Robust Gully-like Surface of Stainless Steel Fiber-Bonded TFPA–TTA–COF with Nano Pores for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds in Water. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050354
Wei W, Shi Y, Zhang K, Li B. The Preparation of Robust Gully-like Surface of Stainless Steel Fiber-Bonded TFPA–TTA–COF with Nano Pores for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds in Water. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(5):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Wanqian, Yu Shi, Keqing Zhang, and Baohui Li. 2025. "The Preparation of Robust Gully-like Surface of Stainless Steel Fiber-Bonded TFPA–TTA–COF with Nano Pores for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds in Water" Nanomaterials 15, no. 5: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050354
APA StyleWei, W., Shi, Y., Zhang, K., & Li, B. (2025). The Preparation of Robust Gully-like Surface of Stainless Steel Fiber-Bonded TFPA–TTA–COF with Nano Pores for Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenolic Compounds in Water. Nanomaterials, 15(5), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15050354






