Rayleigh–Ritz Approximation of the Acoustic Vibrations of Clamped Superquadrics—Application to Free Core–Shell Objects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Superquadrics with Rigid Boundary Conditions
3.2. Thickness Breathing Vibration of Core–Shell Slabs
3.3. 3D Core–Shell
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maynard, J. Resonant Ultrasound Spectroscopy. Phys. Today 1996, 49, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, W.M.; Migliori, A.; Bell, T.M.; Reinert, R.A. On the normal modes of free vibration of inhomogeneous and anisotropic elastic objects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 90, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.; Tisdale, W.A.; Wood, V. Nanocrystal phononics. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.; Hartland, G.V. The Science of Nanostructure Acoustic Vibrations. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2025, 76, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Portalès, H.; Walls, M.; Beaunier, P.; Goubet, N.; Tremblay, N.; Margueritat, J.; Saviot, L.; Courty, A. Versatile and robust synthesis process for the fine control of the chemical composition and core-crystallinity of spherical core-shell Au@Ag nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 95604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebbe, M.; Kuttner, C.; Mayer, M.; Maennel, M.; Pazos-Perez, N.; König, T.A.; Fery, A. Silver-Overgrowth-Induced Changes in Intrinsic Optical Properties of Gold Nanorods: From Noninvasive Monitoring of Growth Kinetics to Tailoring Internal Mirror Charges. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 9513–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernier, C. Étude de Nanocristaux Métalliques Anisotropes par Spectroscopies Optique et Vibrationnelle. Ph.D. Thesis, Sorbonne Université, Paris, France, 2024. Available online: https://theses.fr/2024SORUS300 (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Vernier, C.; Portalès, H. Impact of tip curvature and edge rounding on the plasmonic properties of gold nanorods and their silver-coated counterparts. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 161, 124711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestoklon, M.; Saviot, L.; Goupalov, S.V. Application of perturbation theory to finding vibrational frequencies of a spheroid. Phys. Rev. B 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, D.B.; Saviot, L. Phonons in an inhomogeneous continuum: Vibrations of an embedded nanoparticle. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 94305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, E. Application of group theory to free oscillations of an anisotropic rectangular parallelepiped. J. Phys. Earth 1987, 35, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviot, L. Free vibrations of anisotropic nano-objects with rounded or sharp corners. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.M.Y.; Mork, A.J.; Willard, A.P.; Tisdale, W.A. Including surface ligand effects in continuum elastic models of nanocrystal vibrations. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 44711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurus, N.N.; Milekhin, A.G.; Sklyar, R.I.; Saidzhonov, B.M.; Vasiliev, R.B.; Adichtchev, S.V.; Surovtsev, N.V.; Latyshev, A.V.; Zahn, D.R.T. Phonons in Core–Shell CdSe/CdS Nanoplatelets Studied by Vibrational Spectroscopies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 7107–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, T.; Yu, K.; Hartland, G.V. Mass loading effects in the acoustic vibrations of gold nanoplates. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 16208–16213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, J.J.; Jonas, U.; Steffen, W.; Fytas, G.; Penciu, R.S.; Economou, E.N. The spectrum of vibration modes in soft opals. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 121104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviot, L.; Champagnon, B.; Duval, E.; Kudriavtsev, I.A.; Ekimov, A.I. Size dependence of acoustic and optical vibrational modes of CdSe nanocrystals in glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 197, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, F. New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 2012, 20, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elishakoff, I.; Amato, M.; Ankitha, A.P.; Marzani, A. Rigorous implementation of the Galerkin method for stepped structures needs generalized functions. J. Sound Vib. 2021, 490, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

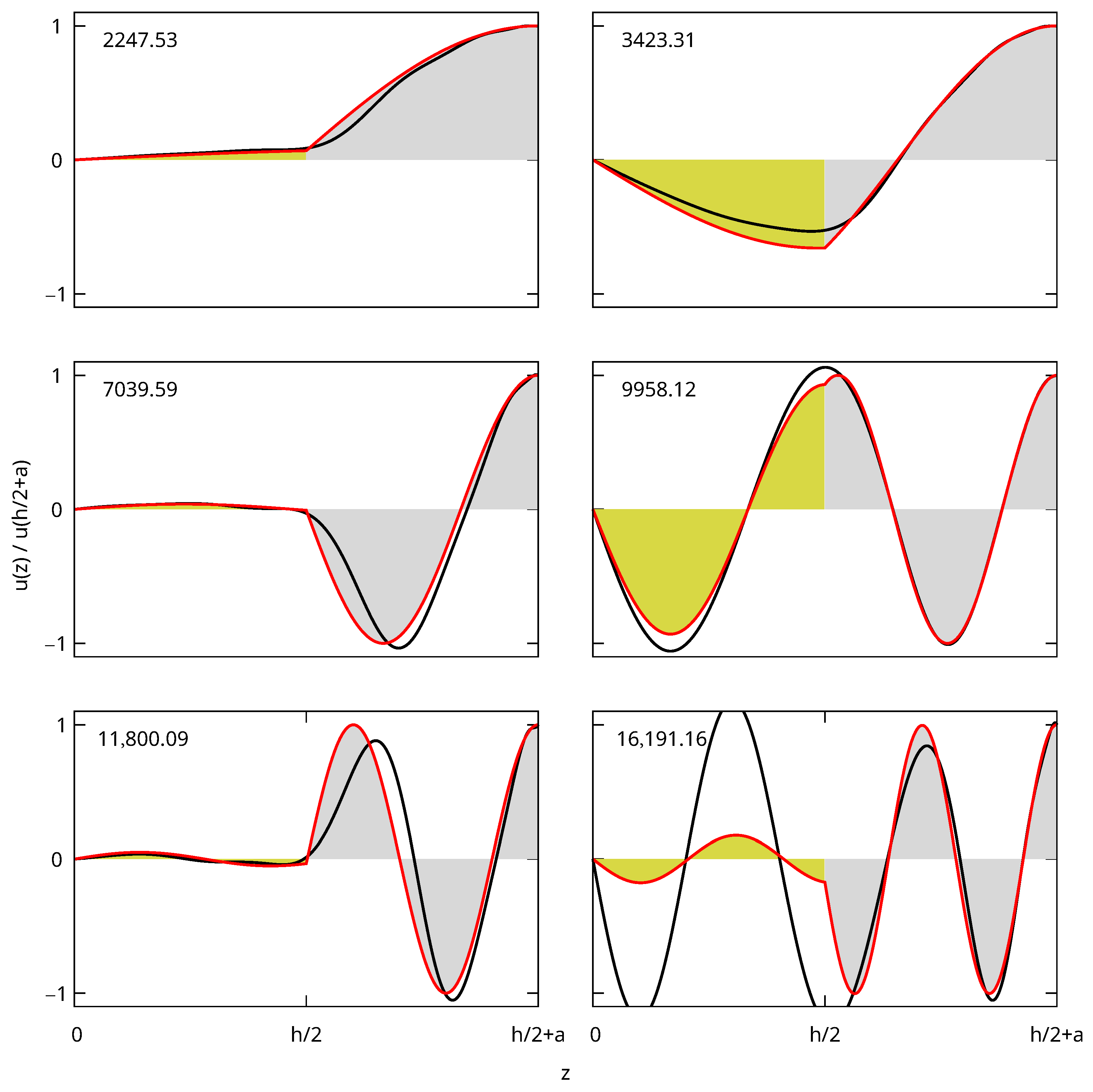
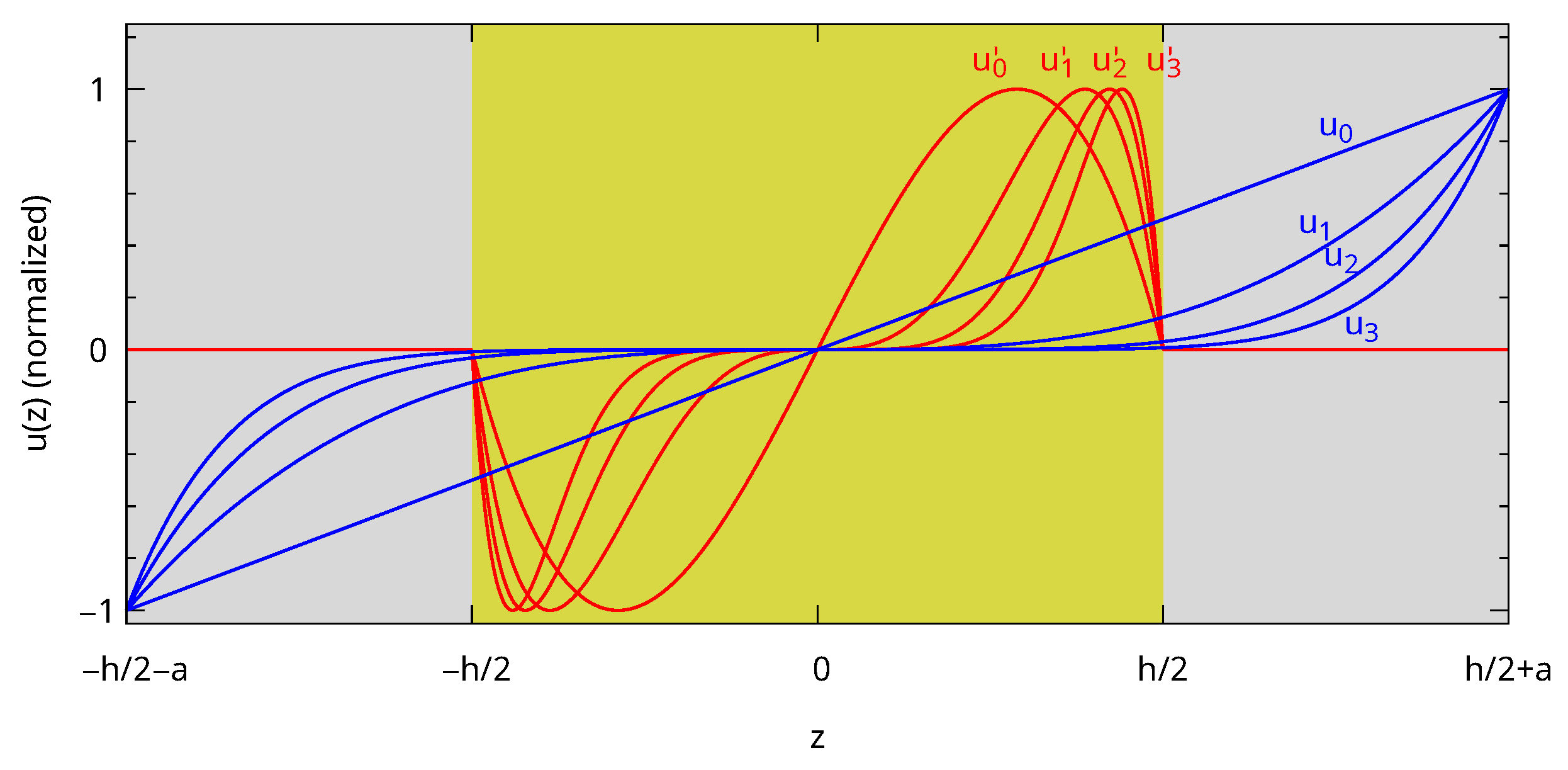
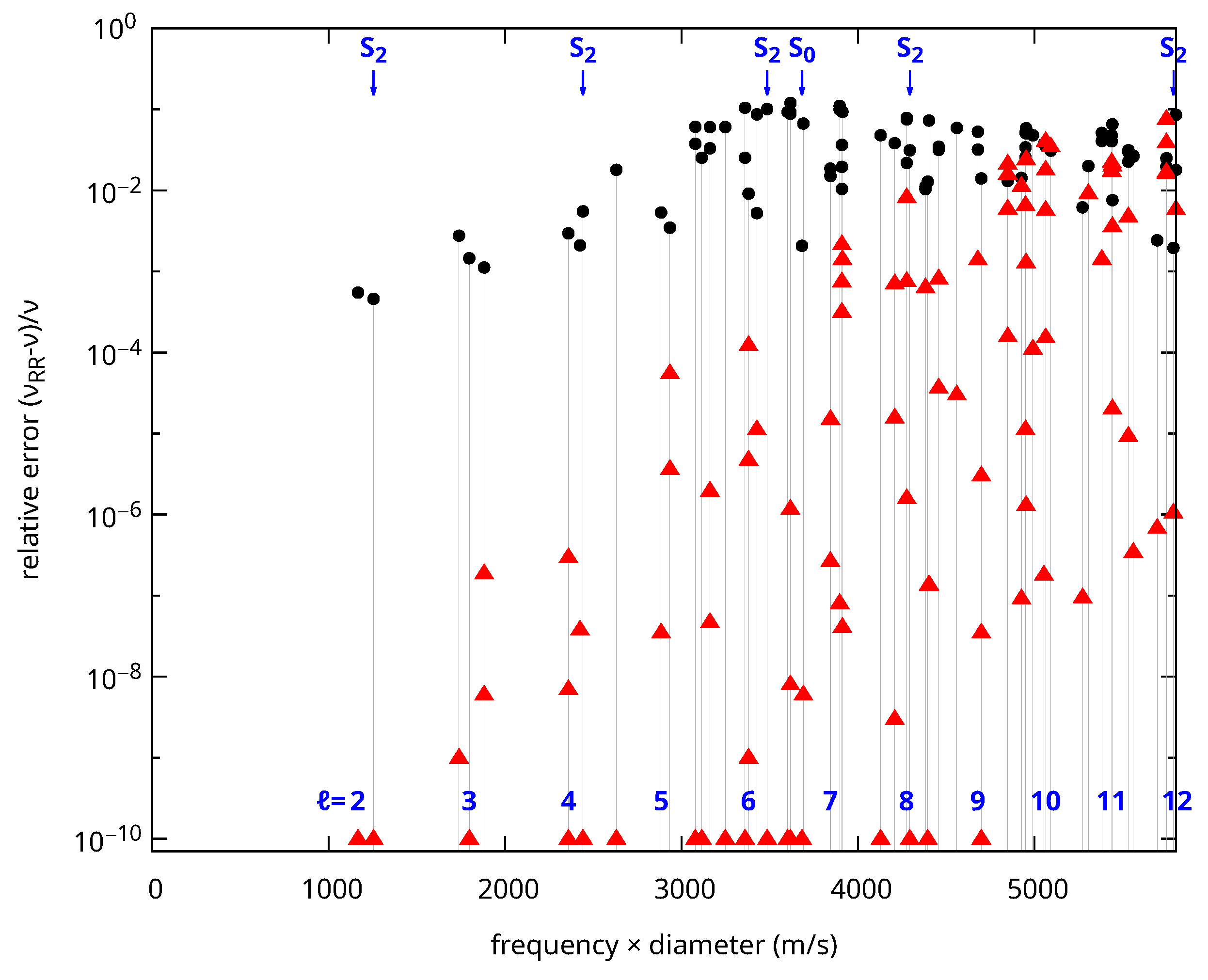
| Method | Frequency × Total Thickness (m/s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 11 | 2608.98 | 3490.04 | 9059.21 | 9973.30 | 16,066.04 | 34,164.95 | |
| 7 | 13 | 2539.65 | 3472.34 | 8263.32 | 9969.51 | 15,393.52 | 17,773.62 | |
| 8 | 15 | 2533.52 | 3470.00 | 8259.65 | 9966.11 | 14,698.40 | 16,991.05 | |
| ⇓ | 9 | 17 | 2471.79 | 3456.12 | 7927.41 | 9962.83 | 13,944.58 | 16,599.73 |
| 10 | 19 | 2453.82 | 3453.18 | 7821.38 | 9962.68 | 13,356.83 | 16,568.04 | |
| 11 | 21 | 2445.02 | 3451.14 | 7787.45 | 9961.65 | 13,323.51 | 16,560.45 | |
| 12 | 23 | 2412.39 | 3445.44 | 7645.69 | 9961.65 | 12,953.16 | 16,556.57 | |
| analytic | 2247.53 | 3423.31 | 7039.59 | 9958.12 | 11,800.09 | 16,191.16 | ||
| 22 | 23 | 2247.53 | 3423.31 | 7039.59 | 9958.12 | 11,800.09 | 16,191.26 | |
| 20 | 21 | 2247.53 | 3423.31 | 7039.59 | 9958.12 | 11,800.10 | 16,191.58 | |
| 18 | 19 | 2247.53 | 3423.31 | 7039.60 | 9958.12 | 11,800.10 | 16,196.30 | |
| 16 | 17 | 2247.53 | 3423.31 | 7039.61 | 9958.14 | 11,802.25 | 16,273.71 | |
| ⇑ | 14 | 15 | 2247.54 | 3423.31 | 7039.82 | 9958.20 | 11,838.04 | 16,316.39 |
| 12 | 13 | 2247.64 | 3423.31 | 7041.55 | 9958.96 | 11,890.71 | 16,557.73 | |
| 10 | 11 | 2248.41 | 3423.31 | 7042.05 | 9979.64 | 12,185.18 | 16,644.00 | |
| 8 | 9 | 2254.85 | 3423.44 | 7188.40 | 9991.92 | 16,590.86 | 20,576.40 | |
| 6 | 7 | 2313.28 | 3430.40 | 9743.33 | 11,191.98 | 17,406.92 | 43,458.30 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
S, S.; Marco de Lucas, M.d.C.; Saviot, L. Rayleigh–Ritz Approximation of the Acoustic Vibrations of Clamped Superquadrics—Application to Free Core–Shell Objects. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241865
S S, Marco de Lucas MdC, Saviot L. Rayleigh–Ritz Approximation of the Acoustic Vibrations of Clamped Superquadrics—Application to Free Core–Shell Objects. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(24):1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241865
Chicago/Turabian StyleS, Sajana, María del Carmen Marco de Lucas, and Lucien Saviot. 2025. "Rayleigh–Ritz Approximation of the Acoustic Vibrations of Clamped Superquadrics—Application to Free Core–Shell Objects" Nanomaterials 15, no. 24: 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241865
APA StyleS, S., Marco de Lucas, M. d. C., & Saviot, L. (2025). Rayleigh–Ritz Approximation of the Acoustic Vibrations of Clamped Superquadrics—Application to Free Core–Shell Objects. Nanomaterials, 15(24), 1865. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15241865






