Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Bisphenol A for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of 3-Chloroaniline from Water Matrices: Material Synthesis and Sorption Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Instrumentations
2.3. Synthesis of MSNs
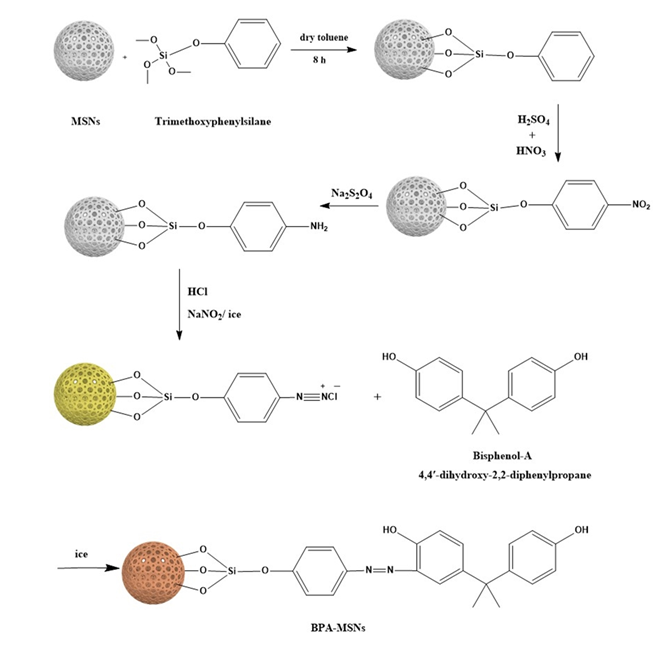
2.4. Functionalization of MSNs with Bisphenol-A Moiety
2.5. Adsorption and D-SPE Procedure
3. Results
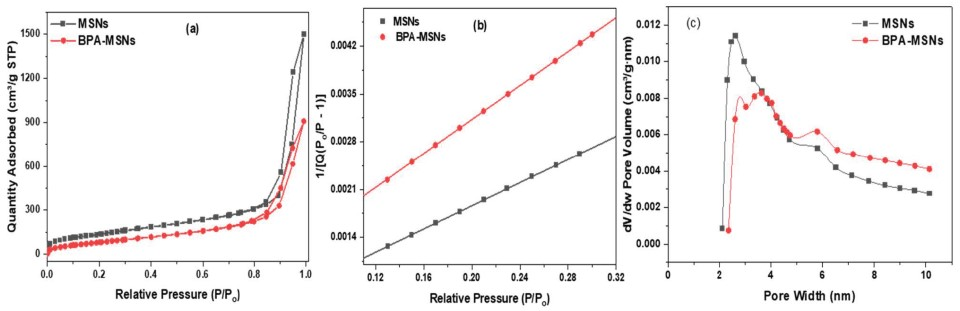
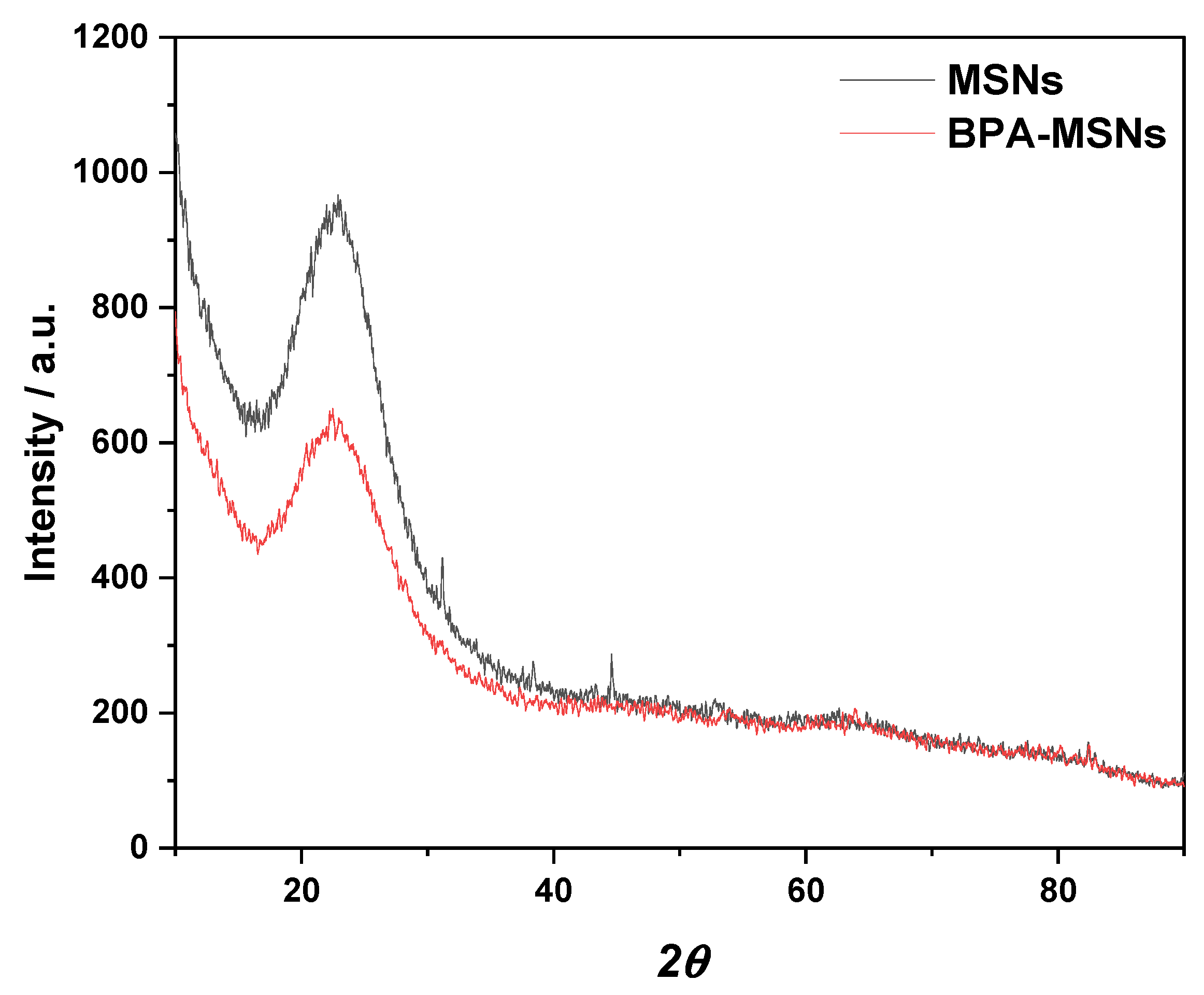
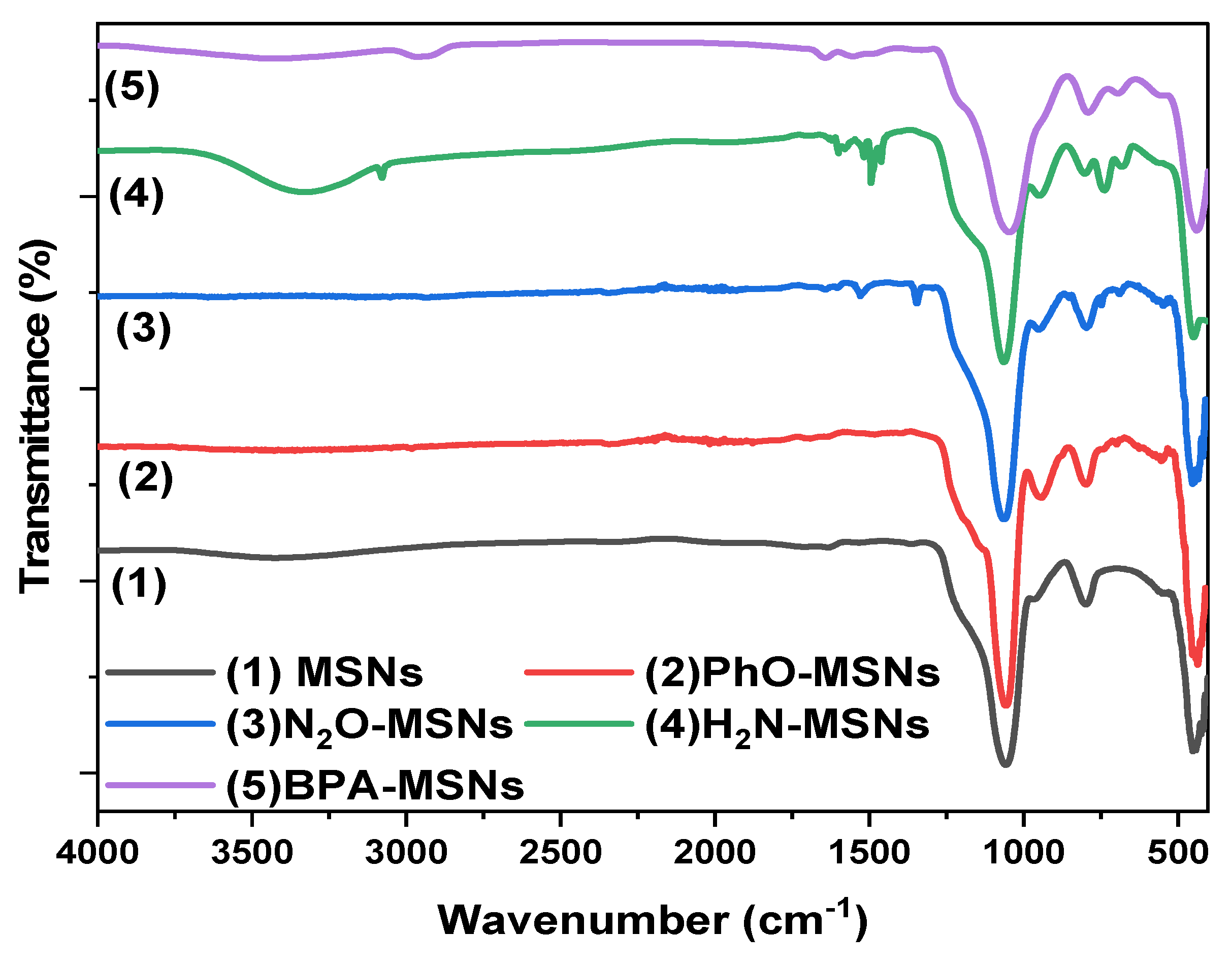
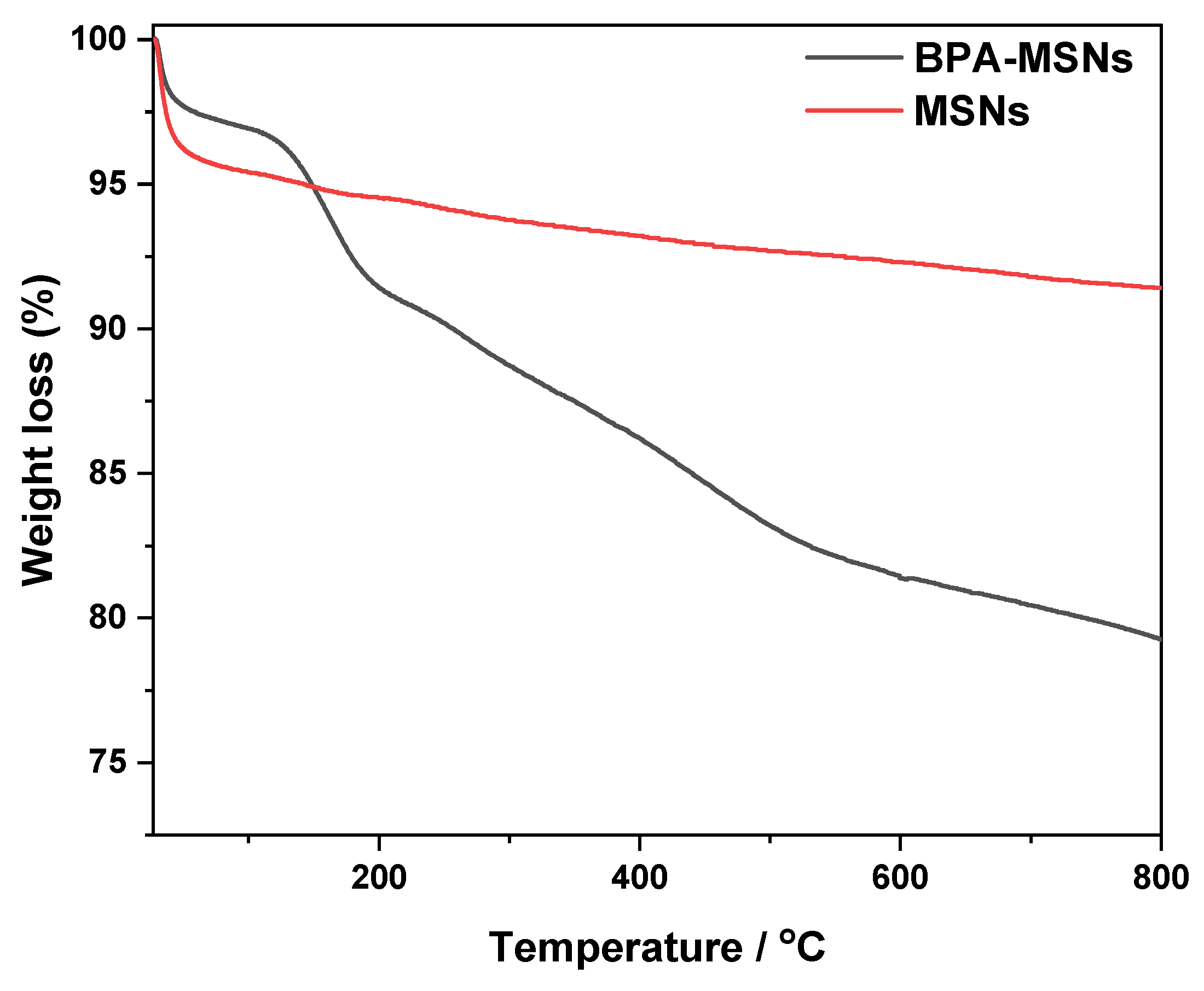
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Sorbent
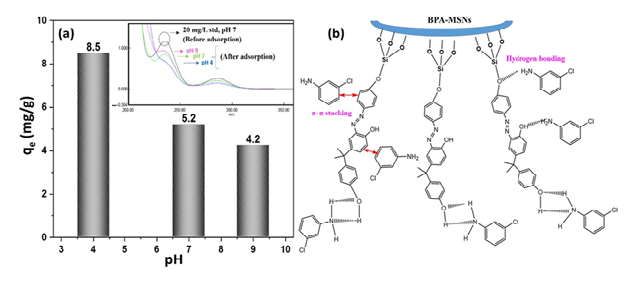
3.2. Adsorption Performance and the Influence of Solution pH
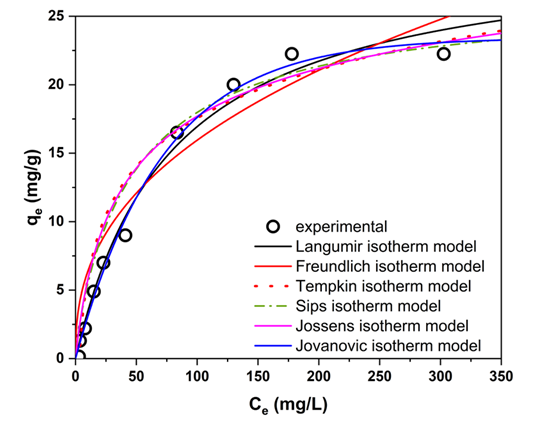
3.3. Equilibrium Isotherm Analysis and Surface Interaction Mechanisms
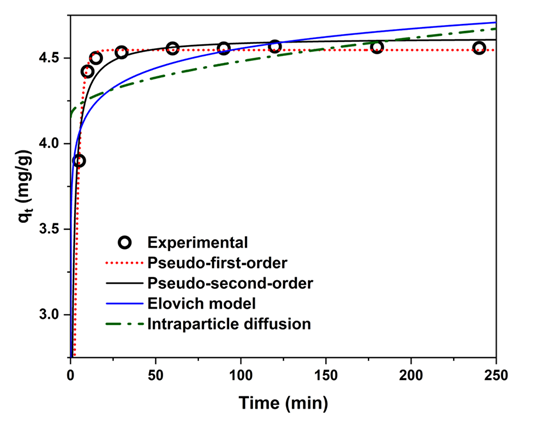
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics and Rate-Limiting Steps
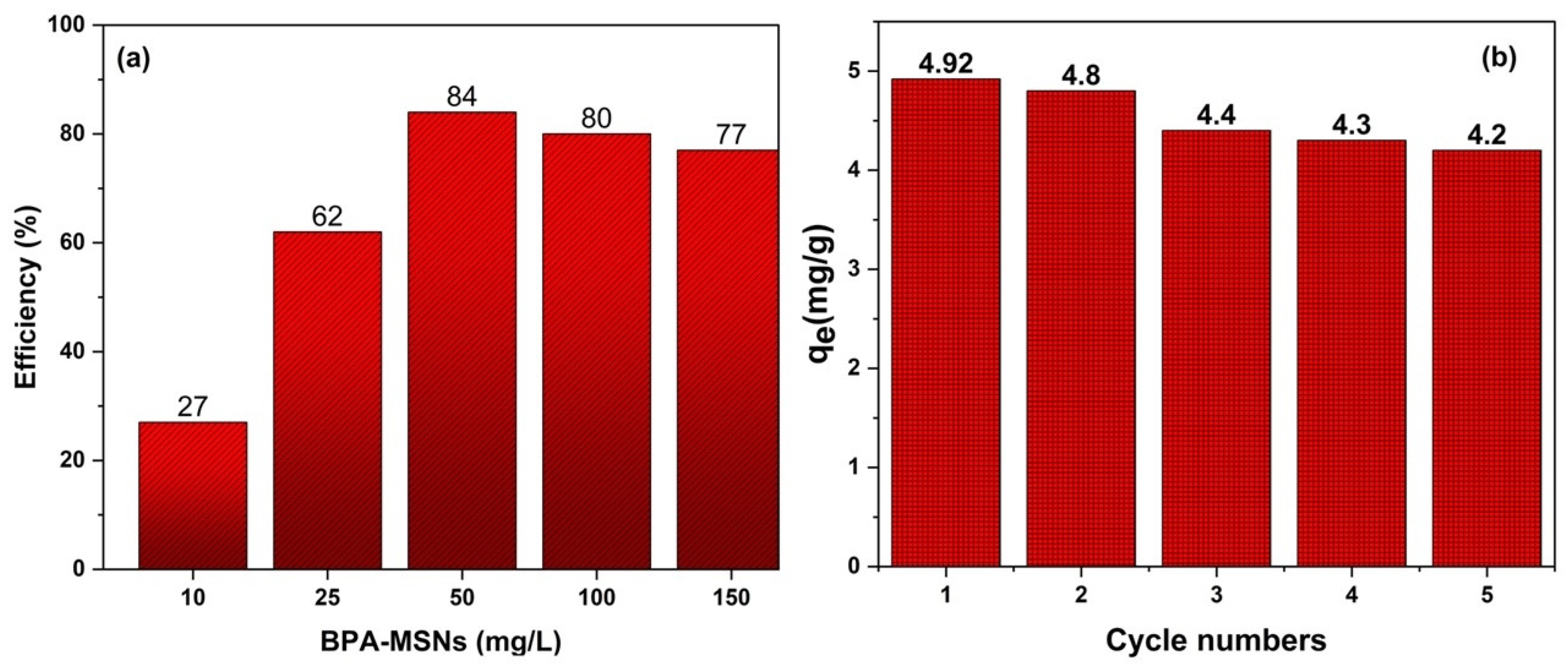
3.5. BPA-MSNs as D-SPE Sorbent for 3-CA: Calibration and Real-Sample Application
3.6. Comparative Performance and Reusability of BPA-MSNs as Sorbent for 3-CA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| 3-CA | 3-Chloroaniline |
| AADs | Aromatic amine derivatives |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| BPA-MSNs | Bisphenol A–functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| CTAC | Cetyltrimethylammonium chloride |
| D-SPE | Dispersive solid-phase extraction |
| EDS/EDX | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| FESEM | Field-emission scanning electron microscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MSNs | Mesoporous silica nanoparticles |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| qmax | Maximum adsorption capacity |
| SDA | Structure-directing agent |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| UV–Vis | Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Freeman, H.S. Aromatic Amines: Use in Azo Dye Chemistry. Front. Biosci. 2013, 18, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfouse, E.; Schwarzbauer, J.; Robert, D. Pollutants in Buildings, Water and Living Organisms, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-19471-2. [Google Scholar]
- Özge, E.; Krupčíková, S.; Goellner, A.; Vrana, B.; Melis, M.; Melymuk, L. Tracking Aromatic Amines from Sources to Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujar, N.K.; Premakshi, H.G.; Shruti, L.; Pattar, S.V.; Manisha, M.; Kamanavalli, C.M. Biodegradation of Chlorpropham and Its Major Products by Bacillus licheniformis NKC-1. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, E.R.A.; de Oliveira, G.A.R.; de Oliveira, D.P. The Impact of Aromatic Amines on the Environment: Risks and Damages. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2012, 4, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Occupational Exposures of Hairdressers and Barbers and Personal Use of Hair Colourants; Some Hair Dyes, Cosmetic Colourants, Industrial Dyestuffs and Aromatic Amines; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Vol. 57; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1993; Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/89 (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Rebelo, D.; Antunes, S.C.; Rodrigues, S. The Silent Threat: Exploring the Ecological and Ecotoxicological Impacts of Chlorinated Aniline Derivatives and Their Metabolites on the Aquatic Ecosystem. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcia, A.D.; Samperi, R. Determination of Chloroaniline Traces in Environmental Waters by Selective Extraction with Two Traps in Tandem and Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced Removal of p-Chloroaniline from Aqueous Solution by a Carboxylated Polymeric Sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Removal of p-Chloroaniline from Polluted Waters Using a Cathodic Electrochemical Ceramic Membrane Reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noormohammadi, F.; Faraji, M.; Pourmohammad, M. Determination of Aromatic Amines in Environmental Water Samples by Deep Eutectic Solvent-Based Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Followed by HPLC-UV. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupčíková, S.; Marek, S.; Kalousková, P.; Jakub, U.; Zdeněk, Š.; Melymuk, L.; Melis, M.; Vrana, B. Investigation of Occurrence of Aromatic Amines in Municipal Wastewaters Using Passive Sampling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosetti, F.; Chiuminatto, U.; Zampieri, D.; Mazzucco, E.; Marengo, E.; Gennaro, M.C. A New On-Line Solid Phase Extraction High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Study the Sun Light Photodegradation of Mono-Chloroanilines in River Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3427–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Fattore, E.; Benfenati, E. Determination of Aromatic Amines by Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry in Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 791, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X. Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Followed by Reversed Phase-High Performance Liquid Chromatography for the Determination of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers at Trace Levels in Landfill Leachate and Environmental Water Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 615, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, N.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A. Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction of Aromatic Amines Based on an Efficient Sorbent Made from Poly(1,8-Diaminonaphthalene) and Magnetic Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Composite. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1499, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSuhaimi, A.O. Sustainable Solid-Phase Extractant Based on Spent Coffee Waste-Derived Activated Carbon Functionalized with 1,10-Phenanthroline-5-Amine for Trace Metals from Groundwater Samples. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, O.S.; Hussein, B.H.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Mgaidi, A. Mixture of Illite-Kaolinite for Efficient Water Purification: Removal of As(III) from Aqueous Solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 79, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, O.S.; Hussein, B.H.M.; Ouf, A.M.; Hussein, M.A.; Mgaidi, A. An Organified Mixture of Illite-Kaolinite for the Removal of Congo Red from Wastewater. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2018, 12, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousi, N.; Rosenberg, E.; Deliyanni, E.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Samanidou, V. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Organic Compounds Based on Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. Molecules 2020, 25, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Aguinaga, V.; Domini, C.E.; Acebal, C.C. Current Trends in Sample Preparation for the Determination of Primary Aromatic Amines in Environmental Samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 37, e00197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankovych, H.; Vaclavikova, M.; Melnyk, I. A Review on Adsorbable Organic Halogens Treatment Technologies: Approaches and Application. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Ihsanullah, I. Novel materials for dispersive (micro) solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.K.; Adio, S.O. Applications of Nanomaterials in Miniaturized Extraction Techniques. In Nanomaterials in Chromatography; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 157–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; Cárdenas, S.; Lucena, R. Dispersive Micro-Solid Phase Extraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 112, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ścigalski, P.; Kosobucki, P. Recent Materials Developed for Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction. Molecules 2020, 25, 4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.H.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Sidik, S.M.; Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Jusoh, R.; Jusoh, N.W.C.; Hameed, B.H. Amino Modified Mesostructured Silica Nanoparticles for Efficient Adsorption of Methylene Blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 386, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfhaid, L.H.K. Adsorption of Paracetamol in Contaminated Water through pH-Responsive Polymer-Brush-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, H.A. Nanoparticles Used for Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4816849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, F.; Ma, X.; Yue, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; You, J. Quaternary Ammonium-Functionalized MCM-48 Mesoporous Silica as a Sorbent for the Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1557, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.; Raichur, A.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Chun, J. Facile Approach for the Synthesis of Spherical Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles from Sodium Silicate. Mater. Lett. 2021, 283, 128765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMohaimadi, K.M.; Albishri, H.M.; Thumayri, K.A.; AlSuhaimi, A.O.; Mehdar, Y.T.H.; Hussein, B.H.M. Facile Hydrothermal Assisted Basic Catalyzed Sol Gel Synthesis for Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle from Alkali Silicate Solutions Using Dual Structural Templates. Gels 2024, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinfar, M.; Nychka, J.A. A Review of Sodium Silicate Solutions: Structure, Gelation, and Syneresis. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 322, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, O.V.; Baklanova, O.N.; Gulyaeva, T.I.; Trenikhin, M.V.; Drozdov, V.A. Poly(ethylene glycol) as Structure Directing Agent in Sol–Gel Synthesis of Amorphous Silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 190, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.M.; Mabrouk, M.; Soliman, I.E.; Beherei, H.H.; Tohamy, K.M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Prepared by Different Methods for Biomedical Applications: Comparative Study. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 15, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Hui, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Spheres: Effect of the Cooling Process. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMohaimadi, K.M.; Albishri, H.M.; Althumayri, K.; AlSuhaimi, A.O.; Hussein, B.H.M. Preparation of Phenanthroline-2-Carbaldehyde Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Nanochelator for Solid Phase Extraction of Trace Metals from Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2025, 18, 792024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyawan, H.; Yuwana, M.; Balgis, R. PEG-Templated Mesoporous Silicas Using Silicate Precursor and Their Applications in Desiccant Dehumidification Cooling Systems. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 218, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Using the Sol–Gel Approach: Adjusting Architecture and Composition for Novel Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joselevich, M.; Williams, F.J. Synthesis and Characterization of Diazonium Functionalized Nanoparticles for Deposition on Metal Surfaces. Langmuir 2008, 24, 11711–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agho, O.B.; Okele, A.I.; Adams, D.A.; Obadahun, J.; Enyeribe, C. Application of Bisphenol as a Coupler in the Synthesis of Azo Dyes and Its Assessments on Vegetable Tanned Leather. Anal. Chem. Indian J. 2016, 16, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Nuti, S.; Fernández-Lodeiro, A.; Galhano, J.; Oliveira, E.; Duarte, M.P.; Capelo-Martínez, J.L.; Fernández-Lodeiro, J. Tailoring Mesoporous Silica-Coated Silver Nanoparticles and Polyurethane-Doped Films for Enhanced Antimicrobial Applications. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, S.; Aboalhassan, A.; Lill, H.; Bald, D.; El-Khamisy, S.; Ebeid, E.-Z. Efficient Loading and Encapsulation of Anti-Tuberculosis Drugs using Multifunctional Mesoporous Silicate Nanoparticles Running Title: Mesoporous Silicate Nanoparticles as Smart Drug Delivery System. J. Nanosci. Curr. Res. 2016, 1, 1000103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, E.N.; Sysoev, S.V.; Tsyrendorzhieva, I.P.; Rakhlin, V.I.; Kosinova, M.L. Trimethyl(phenyl)silane—A Precursor for Gas Phase Processes of SiCx:H Film Deposition: Synthesis and Characterization. Mod. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, S.; Basbas, N.; Tighadouini, S.; Bacquet, M. New Polysiloxane Surfaces Modified with Ortho-, Meta- or Para-Nitrophenyl Receptors for Copper Adsorption. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2014, 4, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolete, G.; Purcăreanu, B.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Ficai, D.; Oprea, O.-C.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Chircov, C.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Vasilievici, G.; Ficai, A.; et al. A Comparative Loading and Release Study of Vancomycin from a Green Mesoporous Silica. Molecules 2022, 27, 5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, O.V.; Baklanova, O.N.; Gulyaeva, T.I. Porous structure of PEG-mediated silica controlled by solution pH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 307, 110468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Saadati-Moshtaghin, H.R.; Zonoz, F.M.; Targhoo, A. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Wells-Dawson Heteropoly Acid Nanoparticles for Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Aromatic Amines in Water Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1483, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Gao, P.; Yu, Y.; Gao, J.; Fei, Z. Effective Adsorption of Chloroanilines from Aqueous Solution by m-Phenylenediamine Modified Hyper-Cross-Linked Resin: Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 124996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkin, M.J.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of the Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1940, 12, 327–356. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jossens, L.; Prausnitz, J.M.; Fritz, W.; Schlünder, E.U.; Myers, A.L. Thermodynamics of multi-solute adsorption from dilute aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1978, 33, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, D.S. Physical Adsorption of Gases: II. Practical Application of Derived Isotherms for Monolayer and Multilayer Adsorption. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1969, 235, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudziński, W.; Wojciechowski, B.W. On the Jovanović Model of Adsorption: II. The Role of Surface Heterogeneity. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1977, 255, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, I.; Guiochon, G. Derivation and Application of a Jovanović–Freundlich Isotherm Model for Single-Component Adsorption on Heterogeneous Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Selim, H.; Shahawy, A.E. Chitosan/MCM-48 Nanocomposite as a Potential Adsorbent for Removing Phenol from Aqueous Solution. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23417–23430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloester stoffe, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.Y.; McKay, G.; Yeung, K.L. Selective Adsorbents from Ordered Mesoporous Silica. Langmuir. 2003, 19, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, R.S.; Chen, M.L. Application of the Elovich Equation to the Kinetics of Metal Sorption with Solvent-Impregnated Resins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghamdi, K.; AlSuhaimi, A.O.; AlMuhaimadi, K.M.; Mehdar, Y.T.; Alharbi, S.K.; Almalky, M.A.; Hussein, B.H. Applications of Lactobacillus bulgaricus (Lactic Acid Bacteria) as dispersive solid phase sorbent for sample preparation of heavy metals from aqueous samples. Green Anal. Chem. 2025, 15, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Hernandez, R.; Fortela, D.L.B.; Sharp, W.; Chistoserdov, A.; Gang, D.; Zappi, M.E. Formulation of a Simulated Wastewater Influent Composition for Use in the Research of Technologies for Managing Wastewaters Generated during Manned Long-Term Space Exploration and Other Similar Situations—Literature-Based Composition Development. BioTech 2023, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cashin, V.B.; Eldridge, D.S.; Yu, A.; Zhao, D. Surface Functionalization and Manipulation of Mesoporous Silica Adsorbents for Improved Removal of Pollutants: A Review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo Treviño, M.J.; Zarazúa, S.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Nanosorbents as Materials for Extraction Processes of Environmental Contaminants and Others. Molecules 2022, 27, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A. Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. TrACTrend Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioi, S.; Polati, S.; Roz, M.; Rinaudo, C.; Gianotti, V.; Gennaro, M.C. Sorption Studies of Chloroanilines on Kaolinite and Montmorillonite. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanik, B.; Słomkiewicz, P.; Garnuszek, M.; Rogala, P.; Banaś, D.; Kubala-Kukuś, A.; Stabrawa, I. Effect of Temperature on Halloysite Acid Treatment for Efficient Chloroaniline Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Clays Clay Miner. 2017, 65, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsehli, B.R. Removal of 3-Chloroaniline from Aqueous Solution by Treated Coffee Waste: Isotherm Modelling and Thermodynamic Studies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 3389–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.S.; Flowers, T.H.; Duncan, H.J. Adsorption of 3-Chloroaniline on Potato Skin in Aqueous Solution. Indian J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 2016, 1972395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Awual, M.R.; Angove, M.J. A Review on Nickel (II) Adsorption in Single and Binary Component Systems and Future Path. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALOthman, Z.A. A Review: Fundamental Aspects of Silicate Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2012, 5, 2874–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

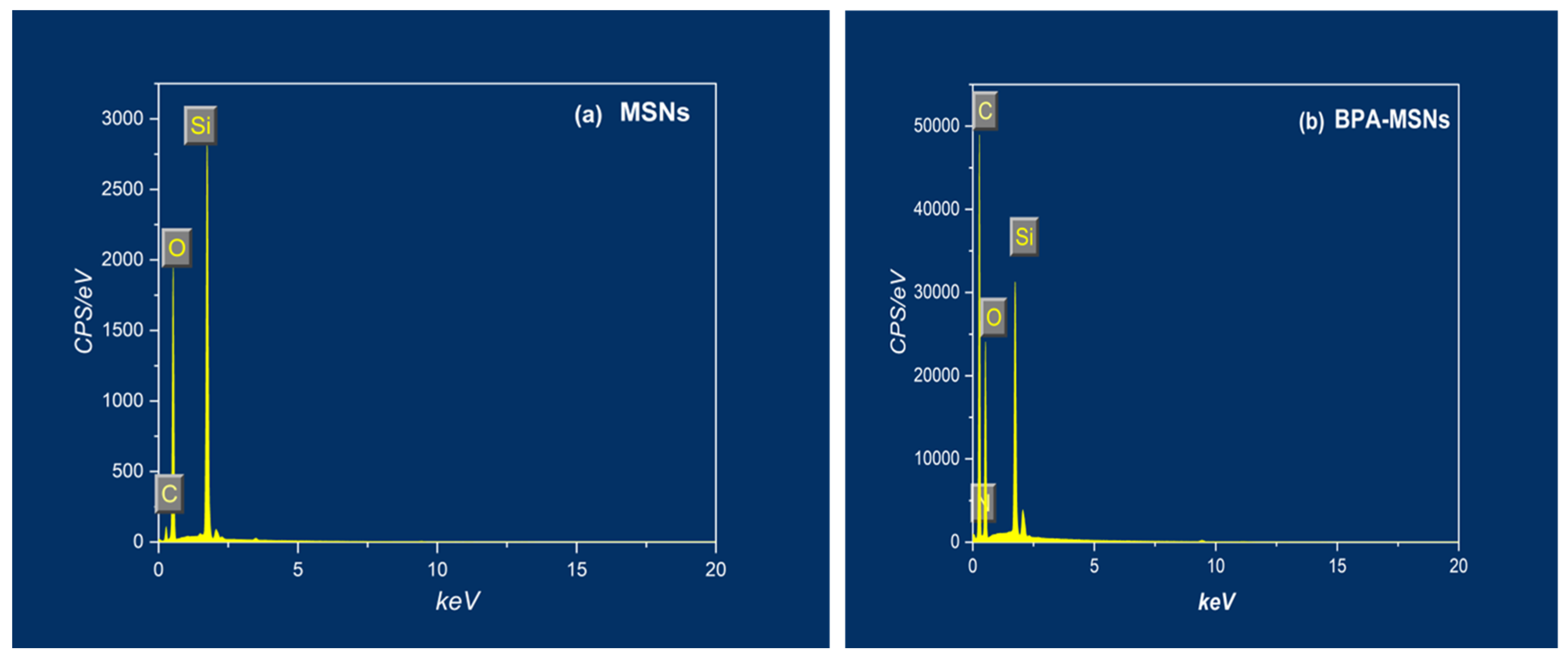
| Sample | Percentage of Weight (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | O | C | N | |
| MSNs | 32.1 | 52.81 | 15.12 | 0.0 |
| BPA-MSNs | 8.15 | 27.29 | 60.31 | 4.25 |
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Volume of Pores (cm3/g) | Most Probable Pore Diameter (nm) | Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSNs | 503 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 17 |
| BPA-MSNs | 334 | 1.4 | 3.6 | 15 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameters | R2 | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | (mg g−1) | (L mg−1) | 30.26 | 0.0127 | |
| Freundlich | (mg g−1 (mg L−1)(1/n)) | 2.52 | 2.1 | ||
| Temkin , | (J mol−1) | (L mg−1) | 0.31 | 5.1 | |
| Sips | (mg g−1) | (L mg−1) | 26.58 | 0.0158 | |
| Jossens | (L g−1) | (L mg−1) | 0.86 | 0.067 | |
| Jovanovic | (mg g−1) | (L mg−1) | 23.44 | 0.014 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | (mg g−1) | (min−1) | 4.55 | 0.39 |
| Pseudo-second-order | (mg g−1) | (g mg−1 min−1) | 4.65 | 0.29 |
| Elovich model | (mg g−1 min−1) | (g mg−1) | 1.38 × 109 | 6.03 |
| Intraparticle diffusion | (mg g−1 min0.5) | C | 0.027 | 4.24 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Linear range | 0.05–15.0 mg/L |
| Calibration equation | A = 0.0593 C − 0.000273 |
| R2 | 0.999 |
| LOD (mg/L) | 0.016 |
| LOQ (mg/L) | 0.05 |
| Preconcentration factor (PF) | 20 (50 mL sample, 2.5 mL eluent) |
| Actual PF | 9.54 |
| Recovery (%) | 73–85 |
| Precision (RSD, %) | 2.38–5.26 |
| Sample | Added (mg L−1) | Found (mg L−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottled water | 1 | 0.86 ± 0.04 | 85 | 3.53 |
| 5 | 4.20 ± 0.12 | 84 | 2.38 | |
| Ground water | 1 | 0.81 ± 0.05 | 82 | 3.67 |
| 5 | 4.05 ± 0.14 | 80 | 3.13 | |
| Tap water | 1 | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 76 | 5.26 |
| 5 | 3.72 ± 0.19 | 74 | 3.65 | |
| Synthetic municipal wastewater * | 1 | 1.1 ± 0.06 | 76 | 5.45 |
| 5 | 5.65 ± 0.31 | 74 | 5.48 |
| Adsorbent | qm (mg g−1), or Efficiency (%) | Conditions (pH, T) | Reusability (Cycles, % Retention) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaolinite | <0.4 | 5.0–5.5 | Not reported | [70] |
| Na-montmorillonite | <0.5 | 8.8–9.3 | Not reported | [70] |
| Halloysites | (5.5%) | <5, (60 °C) | Not reported | [71] |
| Acid-activated halloysite | (21.3%) | (<5, 60 °C) | Not reported | [71] |
| Coffee waste | 45.77 | 7 (25 °C) | Not regenerable | [72] |
| Fresh potato peel | 0.14 | 3–9 (30 °C) | Not reported | [73] |
| BPA-MSNs | 30.2 | 6 (25 °C) | Five cycles, >92% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, S.K.; Alsehli, B.R.; AlSuhaimi, A.O.; Thumayri, K.A.; AlMohaimadi, K.M.; Mehdar, Y.T.H.; Almalki, M.A.; Hussein, B.H.M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Bisphenol A for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of 3-Chloroaniline from Water Matrices: Material Synthesis and Sorption Optimization. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231751
Alharbi SK, Alsehli BR, AlSuhaimi AO, Thumayri KA, AlMohaimadi KM, Mehdar YTH, Almalki MA, Hussein BHM. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Bisphenol A for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of 3-Chloroaniline from Water Matrices: Material Synthesis and Sorption Optimization. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(23):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231751
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Sultan K., Bandar R. Alsehli, Awadh O. AlSuhaimi, Khaled A. Thumayri, Khaled M. AlMohaimadi, Yassin T. H. Mehdar, Manal A. Almalki, and Belal H. M. Hussein. 2025. "Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Bisphenol A for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of 3-Chloroaniline from Water Matrices: Material Synthesis and Sorption Optimization" Nanomaterials 15, no. 23: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231751
APA StyleAlharbi, S. K., Alsehli, B. R., AlSuhaimi, A. O., Thumayri, K. A., AlMohaimadi, K. M., Mehdar, Y. T. H., Almalki, M. A., & Hussein, B. H. M. (2025). Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Bisphenol A for Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction of 3-Chloroaniline from Water Matrices: Material Synthesis and Sorption Optimization. Nanomaterials, 15(23), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15231751







