Cost-Effective Fabrication of Silica–Silver Microspheres with Enhanced Conductivity for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
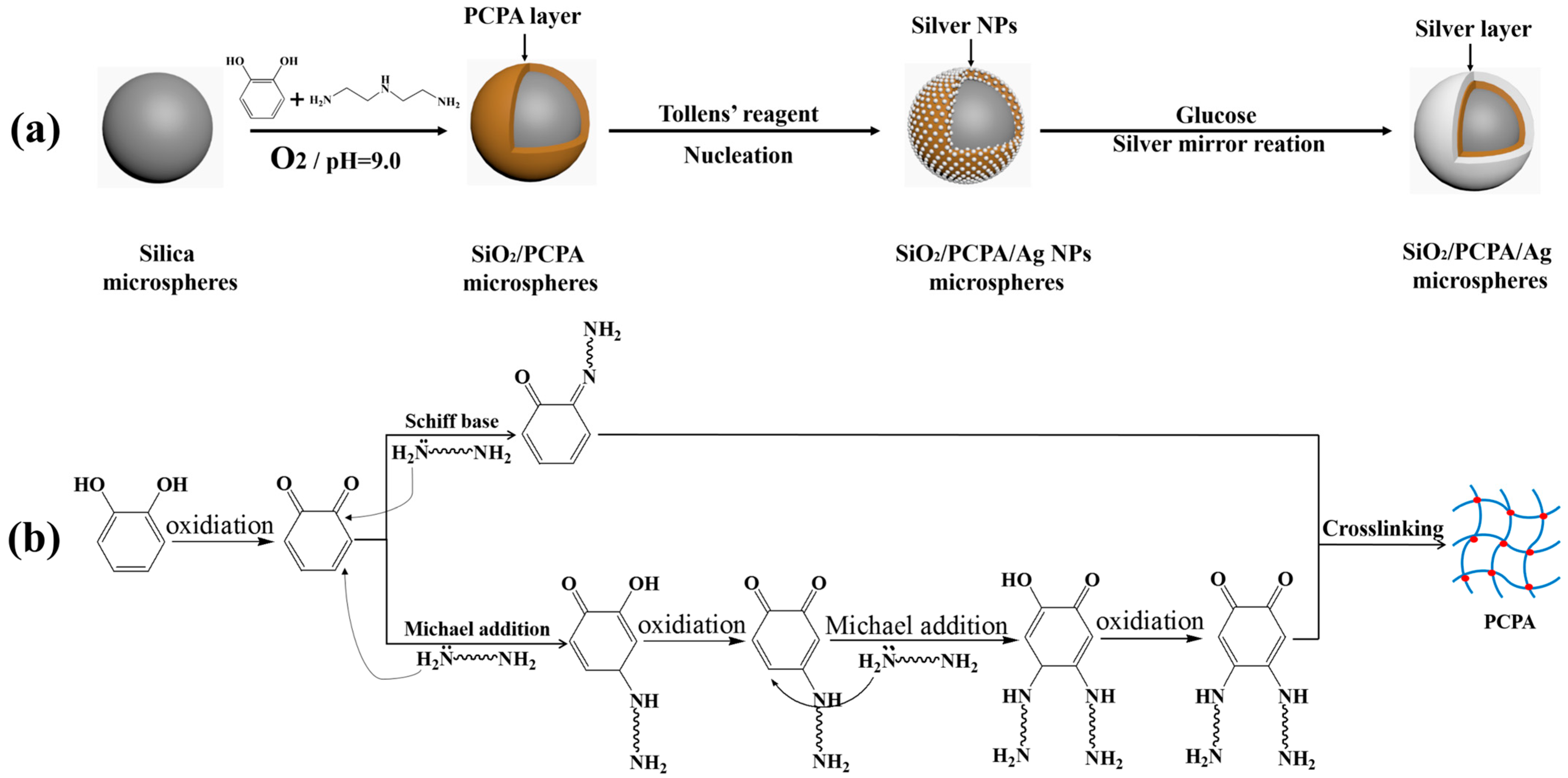
2.2. Preparation of PCPA Modified Silica Microspheres
2.3. Electroless Plating of Silver on the SiO2/PCPA Surface
2.4. Fabrication of SiO2/PCPA/Ag Filled Silicone Rubber
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
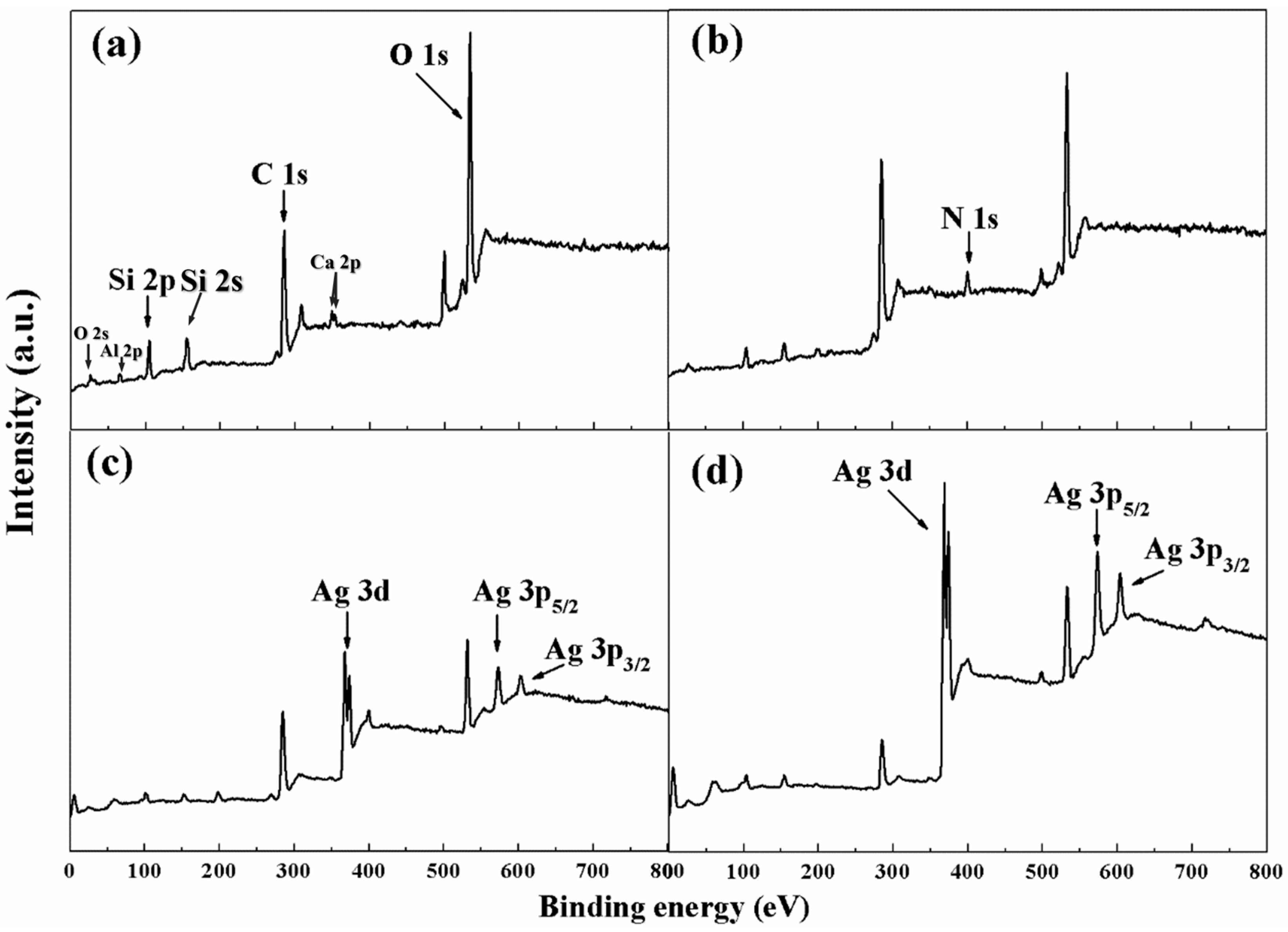
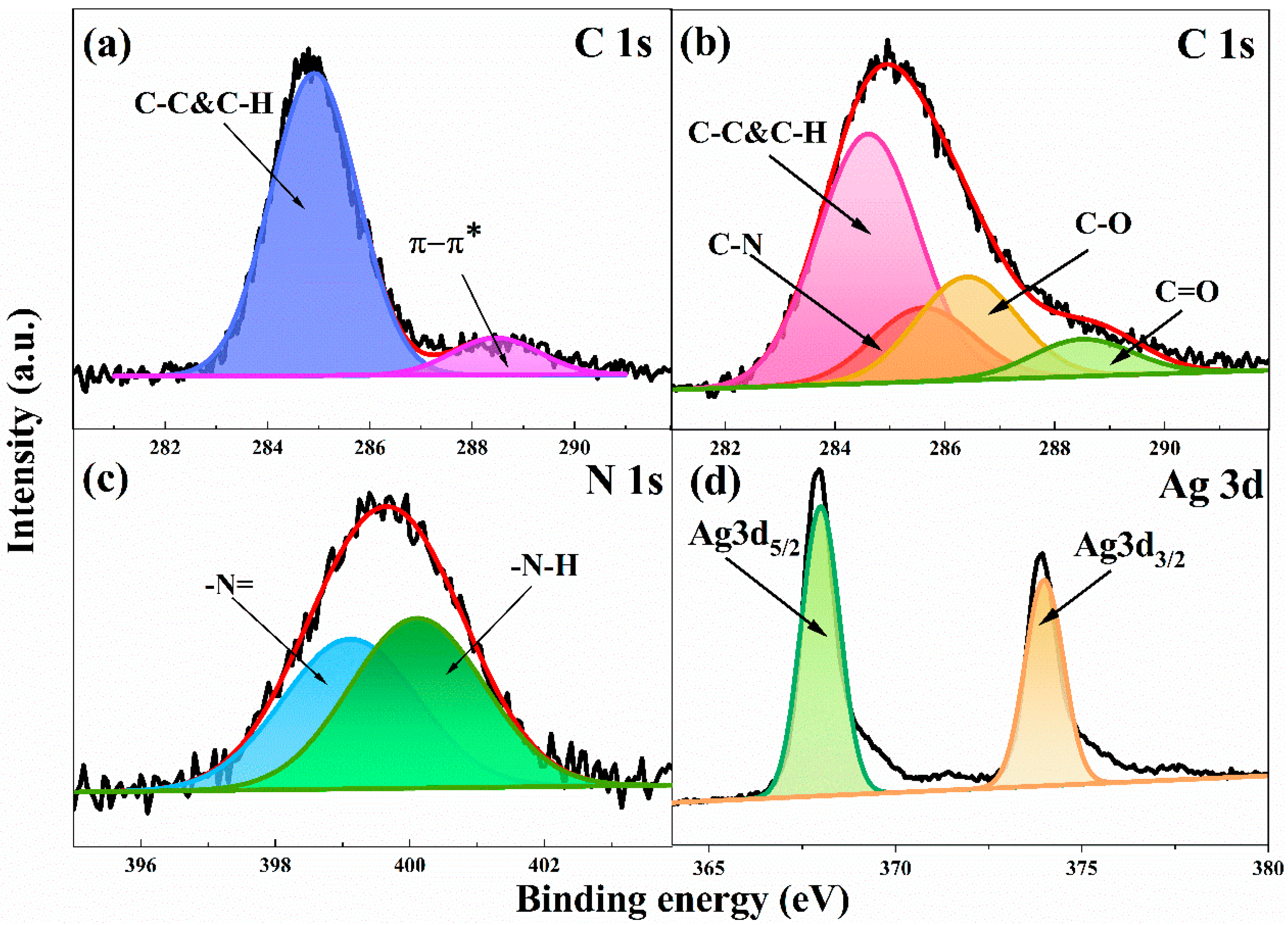
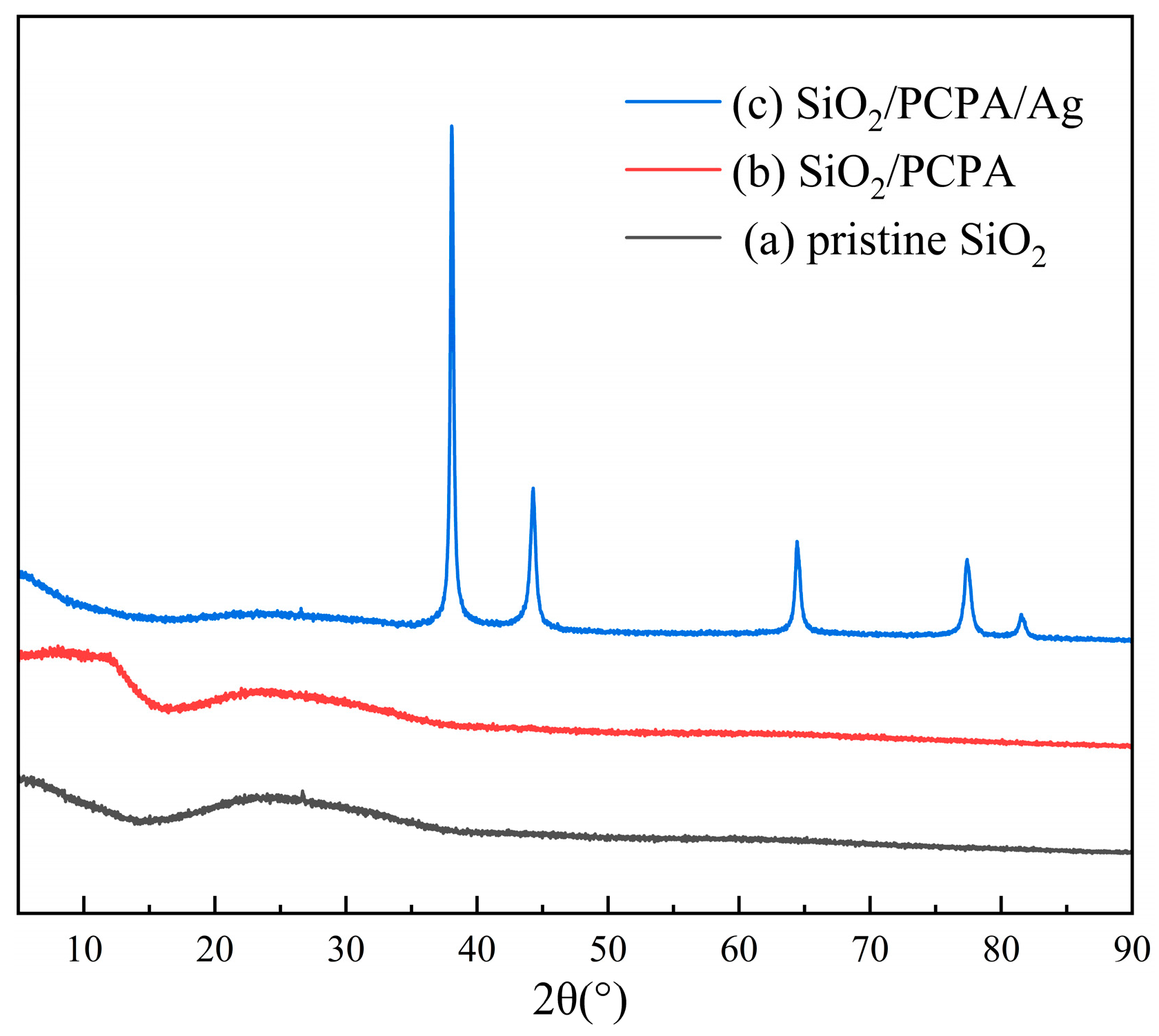
3.1. PCPA Coordination on the Surface of SiO2 Microspheres
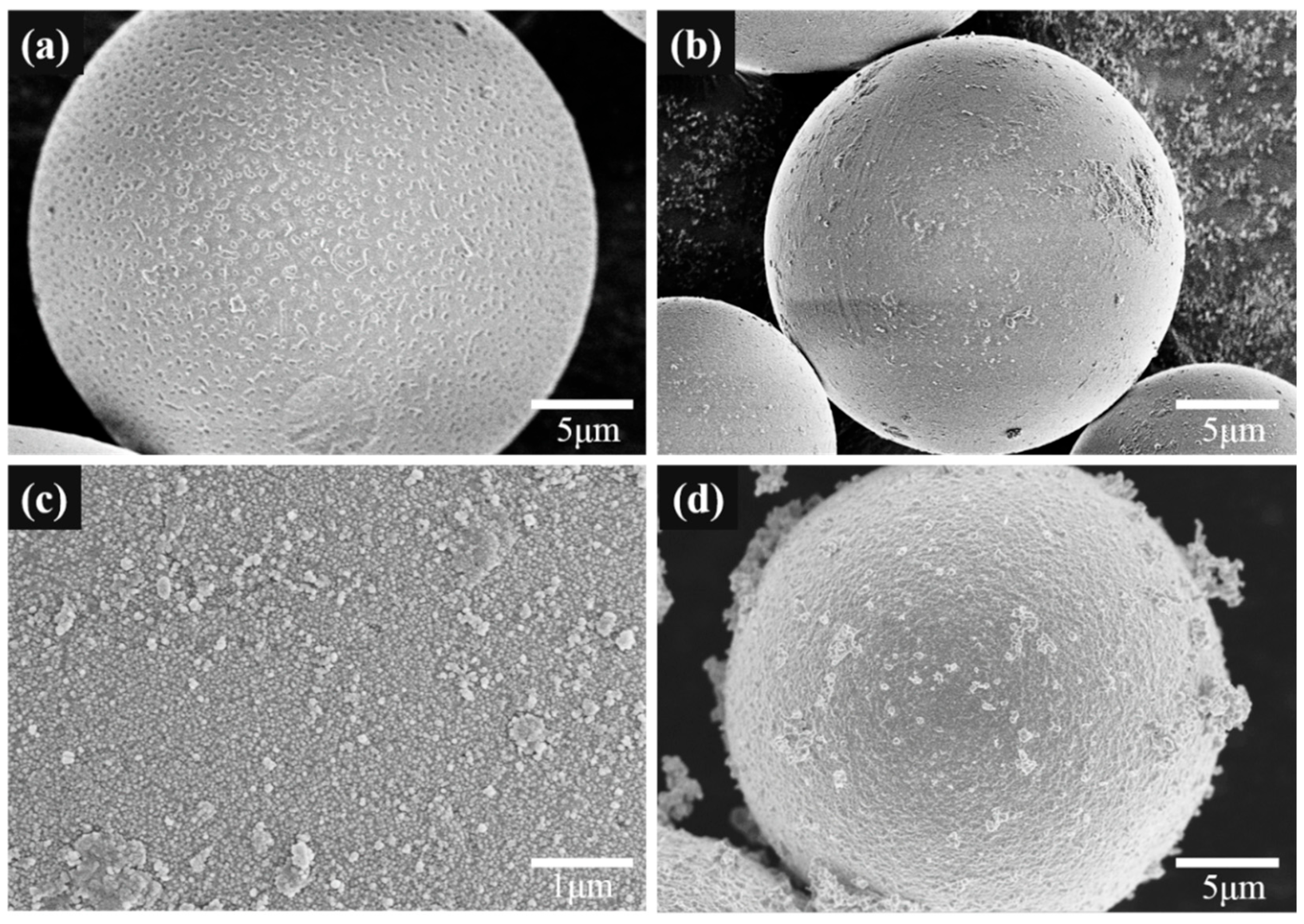
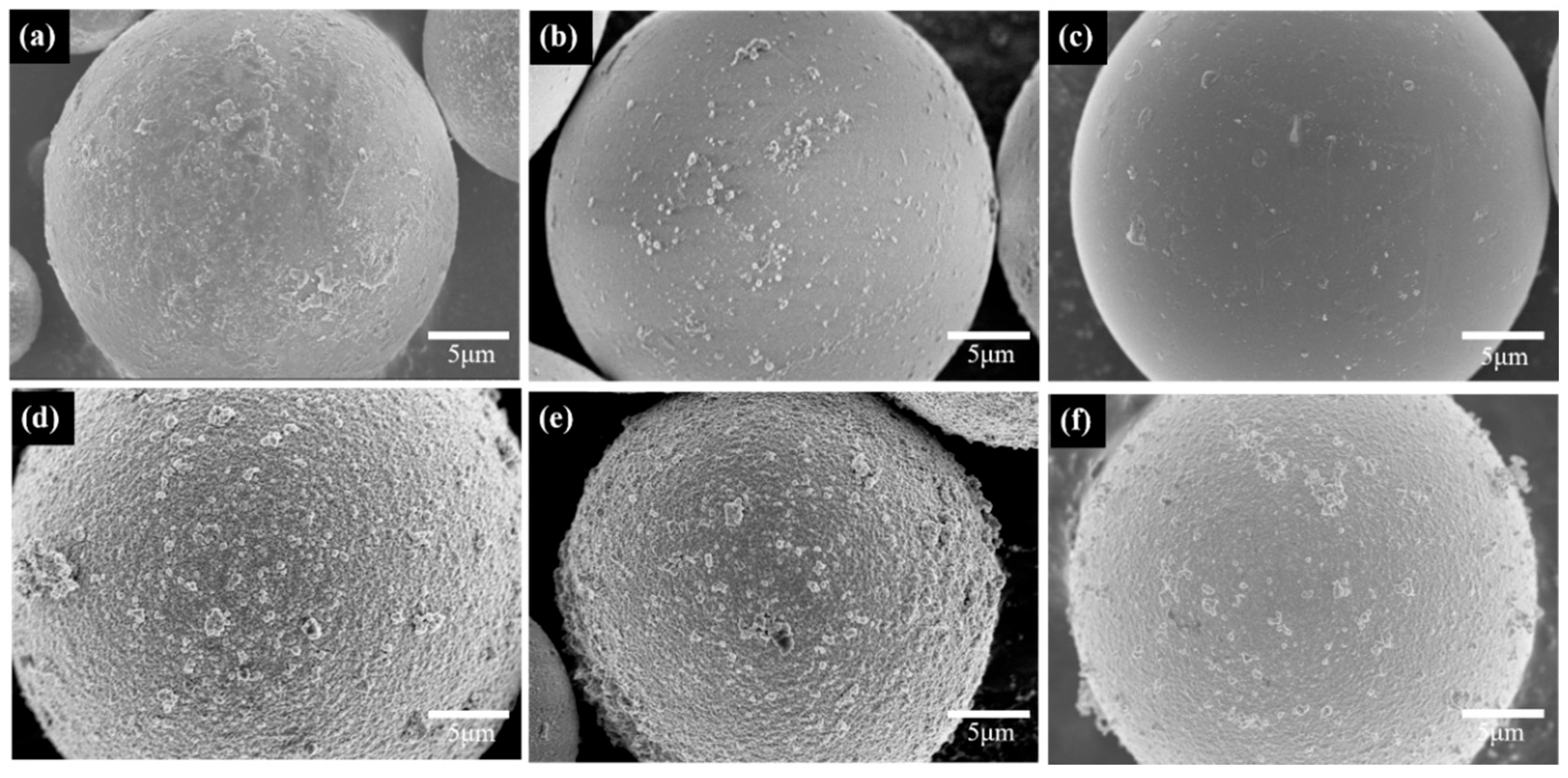
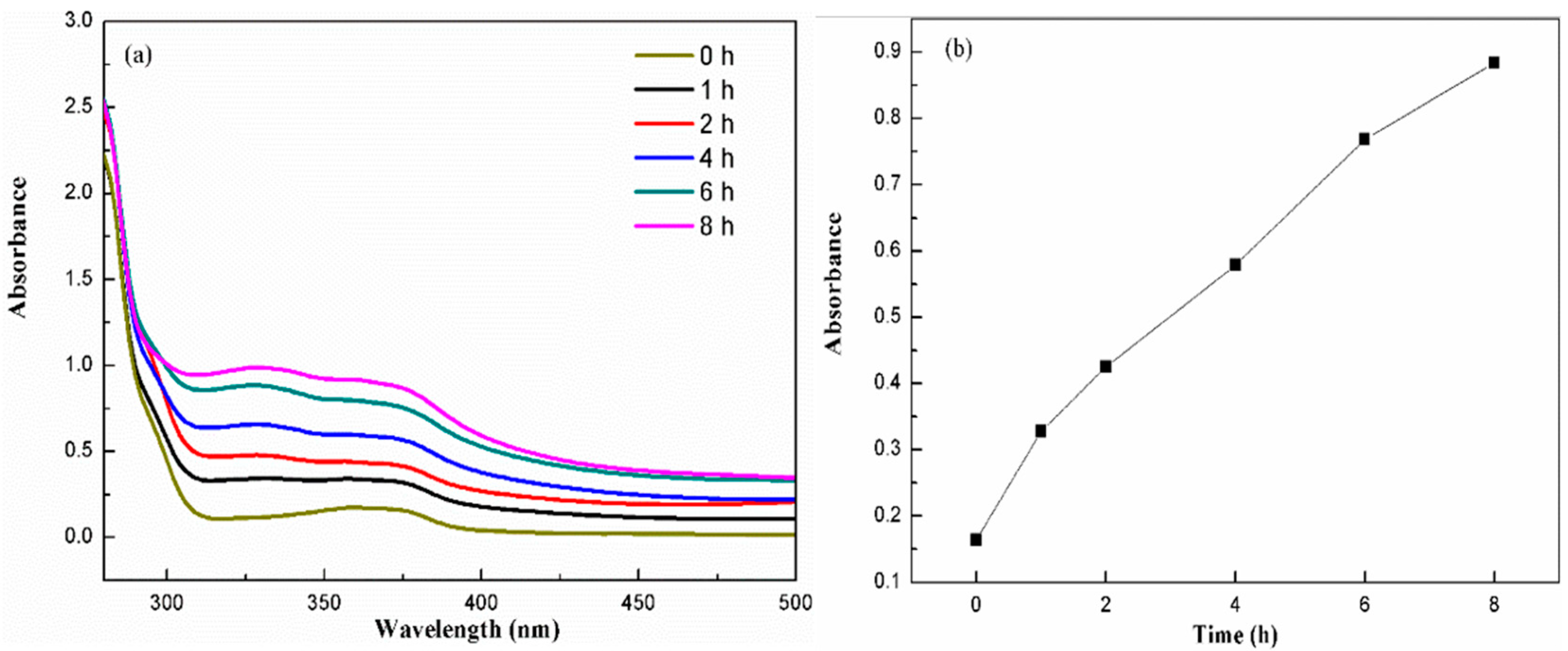
3.2. Electroless Plating of Silver on the Surface of SiO2/PCPA
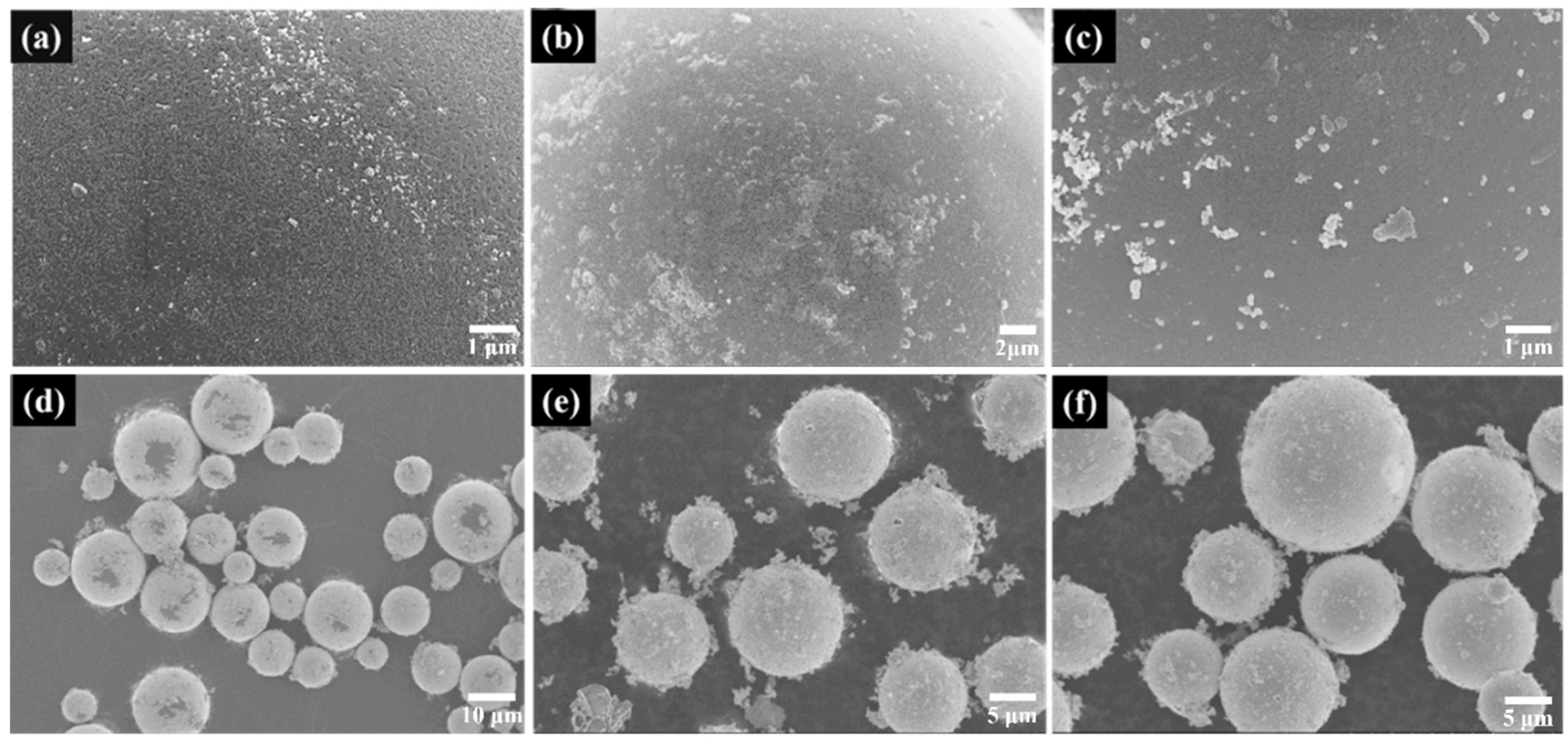
3.3. Fabrication of Silicone Rubber Composites Filled with SiO2/PCPA/Ag Microspheres
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhao, W.; Tan, L.L.; Li, Y.R.; Qin, L.; Li, S.D. Review of polymer-based composites for electromagnetic shielding application. Molecules 2023, 28, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.D.L. Materials for electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 255, 123587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Yang, Q.X.; Liao, J.L.; Zhu, Y.F.; Li, X.; Yang, W.T.; Fu, Y.Q. A novel 3D silver nanowires@polypyrrole sponge loaded with water giving excellent microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W.D.; Lu, X.F.; Wang, C. One-dimensional metallic, magnetic, and dielectric nanomaterials-based composites for electromagnetic wave interference shielding. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9595–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoush, W.M.; El-Tantawy, A.; Morsi, K.; El-Nikhaily, A.E. Novel cubic boron nitride-reinforced Cu/Ni alloy elemental metal matrix composites for electromagnetic radiation shielding applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 8676–8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Y.; Wu, M.; Kuga, S.; Huang, Y. Graphite nanosheet-based carbon foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 16784–16792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R.K.; Tan, W.K.; Kar, K.K.; Matsuda, A. Recent progress on carbon-based composite materials for microwave electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2021, 177, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tao, W.T.; Liao, X.J.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.Q.; He, H.W.; Wang, X. Cellulose nanofiber/MXene/FeCo composites with gradient structure for highly absorbed electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.F.; Dai, M.Y.; Guo, Q.; Yin, D.W.; Hu, S.Q.; Hu, N.G.; Zheng, X.; Huang, J.T. Construction of sandwich-structured Cu-Ni wood-based composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Ru, X.H.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.P.; Yang, C.H.; Zheng, S.R.; Gong, L.; Zhang, X.G.; Duan, H.J.; Liu, Z.G. Flexible sandwich-structured silicone rubber/MXene/Fe3O4 composites for tunable electromagnetic interference shielding. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 11766–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Dai, Z.; Bu, F.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J. Preparation and properties of flexible electromagnetic shielding composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasinghe, D.; Aslani, F. A review on recent advancement of electromagnetic interference shielding novel metallic materials and processes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicyilmaz, A.S.; Bedeloglu, A.C. Electromagnetic interference shielding thermoplastic composites reinforced with carbon based hybrid materials: A review. Compos. Interfaces 2022, 29, 1413–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z.; Wei, W.; Lin, Z.H.; Chang, J.J.; Hao, Y. Flexible nanocomposite conductors for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.T. Mechanical performance and electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of composites based on Ag-plating cellulose micro-nano fibers and epoxy. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.X.; Yan, B.; Xie, Y.J.; Qian, H.; Wang, X.G.; Huang, Q.X.; He, Y.H.; Jin, S.M.; Zeng, H.B. Regenerable urchin-like Fe3O4@PDA-Ag hollow microspheres as catalyst and adsorbent for enhanced removal of organic dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 350, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.Y.; Liu, L.H.; Su, G.; Zhao, L.; Peng, H.L.; Xue, J.R.; Tang, A.P. Enhanced adsorption performance, separation, and recyclability of magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@PGMA-g-TETA-CSSNa microspheres for heavy metal removal. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bermany, E.; Mekhalif, A.T.; Banimuslem, H.A.; Abdali, K.; Sabri, M.M. Effect of green synthesis bimetallic Ag@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles on absorption behavior and electrical properties of PVA-PEO nanocomposites for optoelectronic applications. Silicon 2023, 15, 4095–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Ni, H.S.; Li, X.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, H.X. Eco-friendly fabrication of highly stable silica aerogel microspheres with core-shell structure. Polymers 2023, 15, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Q.; Yap, B.S.M.; Wang, R.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T.; Fu, G.D. Catecholamine-induced electroless metallization of silver on silica@polymer hybrid nanospheres and their catalytic applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3116–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jundale, R.B.; Bari, A.H.; Kulkarni, A.A. Insights into the synthesis and kinetics of silver-on-silica core-shell particles. Langmuir 2023, 39, 9681–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Han, J.L.; Chen, C.C.; Jiang, M.D.; Hsu, J.S.; Chan, C.H.; Hsieh, K.H. Immobilization of silver nanoparticles on silica microspheres. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.J.; Jiang, Y.W.; Xiao, H.S.; Jiang, B.F.; Zhang, H.; Peng, M.Y.; Dong, G.P.; Yu, X.; Yang, J. Sol-gel preparation of Ag-silica nanocomposite with high electrical conductivity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chi, B.; Guan, J.G.; Liu, Y.Q. Facile method to synthesize silver nanoparticles on the surface of hollow glass microspheres and their microwave shielding properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18645–18651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, S.R.; English, D.S.; Hu, E.L.; Barbara, P.F.; Belcher, A.M. Selection of peptides with semiconductor binding specificity for directed nanocrystal assembly. Nature 2000, 405, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.D.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, H.L.; Ju, Y.M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.J.; Meng, Y.; Wei, Y.J.; Chen, G. Improved electrochemical properties of tavorite LiFeSO4F by surface coating with hydrophilic poly-dopamine via a self-polymerization process. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6523–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Ai, K.L.; Lu, L.H. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.J.; Cai, C.; Guo, J.; Fan, H.S.; Zhu, C.Z.; Dong, H.X.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Mussel inspired modification of polypropylene separators by catechol/polyamine for Li-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5602–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, M.Z.; Li, L.; Shao, X.M.; Tian, M.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.Q.; Wang, W.C. Fabrication of highly conductive silver-coated aluminum microspheres based on poly(catechol/polyamine) surface modification. Polymers 2022, 14, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, L.H.; Nie, H.Y.; Biesinger, M.C. Defining the nature of adventitious carbon and improving its merit as a charge correction reference for XPS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 653, 159319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, R.; Ma, Y.; Chen, R.; Shi, N.; Fan, Q.; Huang, W. One-step electrochemical synthesis of graphene/polyaniline composite film and its applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 2989–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Hallböök, F.; Temperton, R.H.; Sun, J.; Rämisch, L.; Gericke, S.M.; Ehn, A.; Zetterberg, J.; Blomberg, S. In situ ambient pressure photoelectron spectroscopy study of the plasma–surface interaction on metal foils. Langmuir 2024, 40, 13950–13956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tang, X.H.; Cai, J.H.; Wu, H.; Shen, J.B.; Guo, S.Y. Construction, mechanism and prospective of conductive polymer composites with multiple interfaces for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. Carbon 2021, 177, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Ding, Y.Q.; Yu, N.; Gao, Q.; Fan, X.; Wei, X.; Zhang, G.C.; Ma, Z.L.; He, X.H. Lightweight and stiff carbon foams derived from rigid thermosetting polyimide foam with superior electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Carbon 2020, 158, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.L.; Cao, M.S.; Lu, M.M.; Bi, S.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Fan, L.Z. Flexible graphene/polymer composite films in sandwich structures for effective electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2014, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorakhpurwalla, H.D.; McGinty, R.J.; Watson, C.A. Microwave dissipation loss in high-moisture grain. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1975, 20, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Chen, C.H. Plane-wave shielding characteristics of anisotropic laminated composites. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 1993, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, A.J.; Hubing, T.H. Analysis and comparison of plane wave shielding effectiveness decompositions. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2014, 56, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Ye, F.; Yin, X.W.; Li, W.; Li, H.J.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, K.Z.; Xie, K.Y.; Li, X.H.; Fu, Q.G.; et al. Carbon nanotube–multilayered graphene edge plane core–shell hybrid foams for ultrahigh-performance electromagnetic-interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.J.; Zhu, P.L.; Yu, S.H.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.P.; Liao, W.H. Anticorrosive, ultralight, and flexible carbon-wrapped metallic nanowire hybrid sponges for highly efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Small 2018, 14, 1800534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Qin, F. Clarification of basic concepts for electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 225108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Sheng, S.; Hu, C.; Xie, H.; Huang, B.; Lou, P.; Fei, H.F.; Zhang, Z. Lightweight flexible and efficient electromagnetic shielding composites based on silver-coated glass microspheres. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 11516–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, K.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Guan, J. Ultralow content silver densely-coated glass microsphere for high performance conducting polymer-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 140, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qin, Y.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, J. Light-weight carbon fiber/silver-coated hollow glass spheres/epoxy composites as highly effective electromagnetic interference shielding material. J. Reinf. Plast. Comp. 2021, 41, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.; Parameswarreddy, G.; Sarathi, R.; Arunachalam, K.; Suematsue, H.; Verma, R.; Sharma, A. Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of silver-coated hollow glass microsphere-graded short carbon fiber epoxy composite. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 6142–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Guo, F.; Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, G. Gradient structure design of lightweight and flexible silicone rubber nanocomposite foam for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Roy, S.; Chen, Y.; Chua, E.K.; See, K.Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, M. Mussel-inspired polydopamine coated hollow carbon microspheres, a novel versatile filler for fabrication of high performance syntactic foams. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18644–18652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
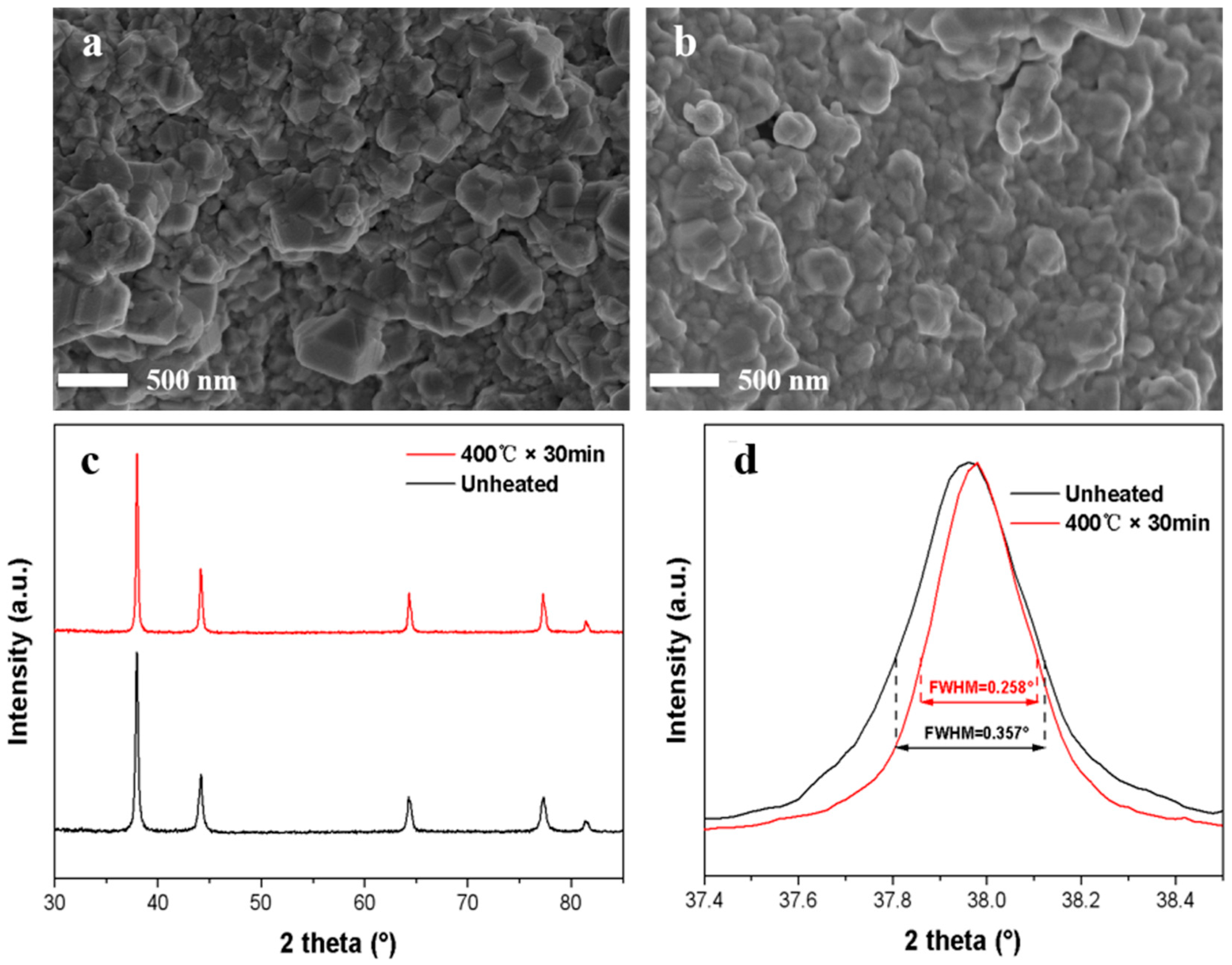
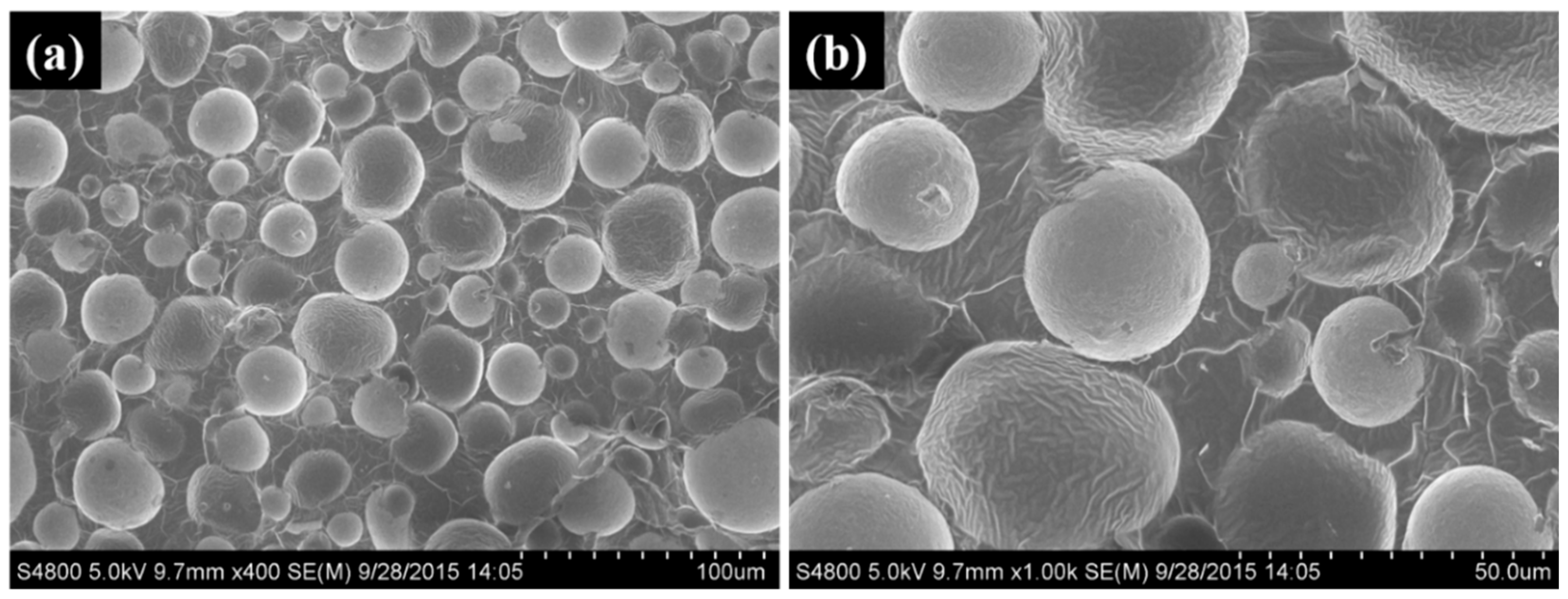
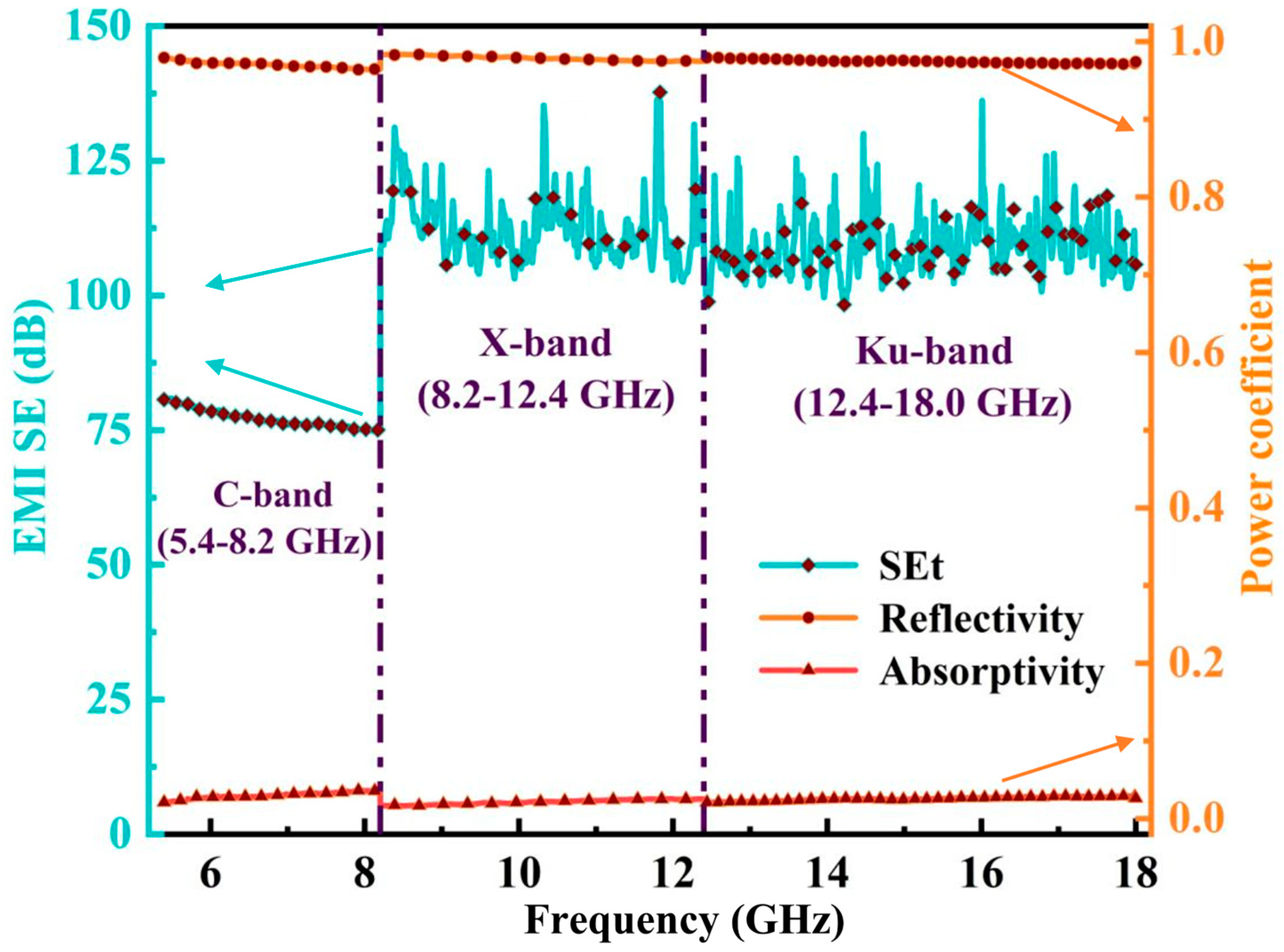
| Sample | Electrical Conductivity (S/cm) | Electrical Resistivity (Ω·cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-heat treatment | 1005 | 0.995 × 10−3 |
| 200 °C × 30 min | 1029 | 0.972 × 10−3 |
| 200 °C × 2 h | 1466 | 0.682 × 10−3 |
| 300 °C × 30 min | 1044 | 0.958 × 10−3 |
| 300 °C × 1.5 h | 1513 | 0.661 × 10−3 |
| 400 °C × 30 min | 1612 | 0.620 × 10−3 |
| 500 °C × 30 min | 524 | 1.908 × 10−3 |
| Sample | Substrate | Filler Content | Thickness (mm) | Frequency (GHz) | SE (dB) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/GM | PDMS | 77.7 wt% | 2 | 8.2–12.4 | 100 | [42] |
| Ag/GM | epoxy | - | 8.2–12.4 | 50 | [43] | |
| Carbon fiber + Ag@HGMs | epoxy | 15 wt% + 50 wt% | 1 | 8.2–12.4 | 88.1 | [44] |
| Ag@HGM + short carbon fiber | epoxy | 1 wt% + 5 wt% | 2 | 8.2–12.4 | 34.6 | [45] |
| Ag/HGM | epoxy resin adhesive | 50 vol% | - | 2.0–12.0 | 75 | [24] |
| Al/Ag | MVQ | 71.4 wt% | 2 | 8.2–12.4 | 70 | [29] |
| Ag@HGM + Fe3O4@CNT | silicone rubber | 0.51 vol% + 1.6 vol% | 2 | 8.2–12.4 | 59.4 | [46] |
| Ag/hollow carbon microspheres | epoxy resin | 30.5 wt% | 1.5 | 8.2–12.4 | 60.2 | [47] |
| Ag/GM | MVQ | 71.4 wt% | 2 | 5.4–8.2 | 75 | This work |
| Ag/GM | MVQ | 71.4 wt% | 2 | 8.2–18.0 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, M.; Huang, Z.; Wang, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liang, W.; Liang, Y. Cost-Effective Fabrication of Silica–Silver Microspheres with Enhanced Conductivity for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181433
Hao M, Huang Z, Wang W, Lv Z, Zhang T, Liang W, Liang Y. Cost-Effective Fabrication of Silica–Silver Microspheres with Enhanced Conductivity for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(18):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181433
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Mingzheng, Zhonghua Huang, Wencai Wang, Zhaoxia Lv, Tao Zhang, Wenjin Liang, and Yurong Liang. 2025. "Cost-Effective Fabrication of Silica–Silver Microspheres with Enhanced Conductivity for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding" Nanomaterials 15, no. 18: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181433
APA StyleHao, M., Huang, Z., Wang, W., Lv, Z., Zhang, T., Liang, W., & Liang, Y. (2025). Cost-Effective Fabrication of Silica–Silver Microspheres with Enhanced Conductivity for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Nanomaterials, 15(18), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181433






