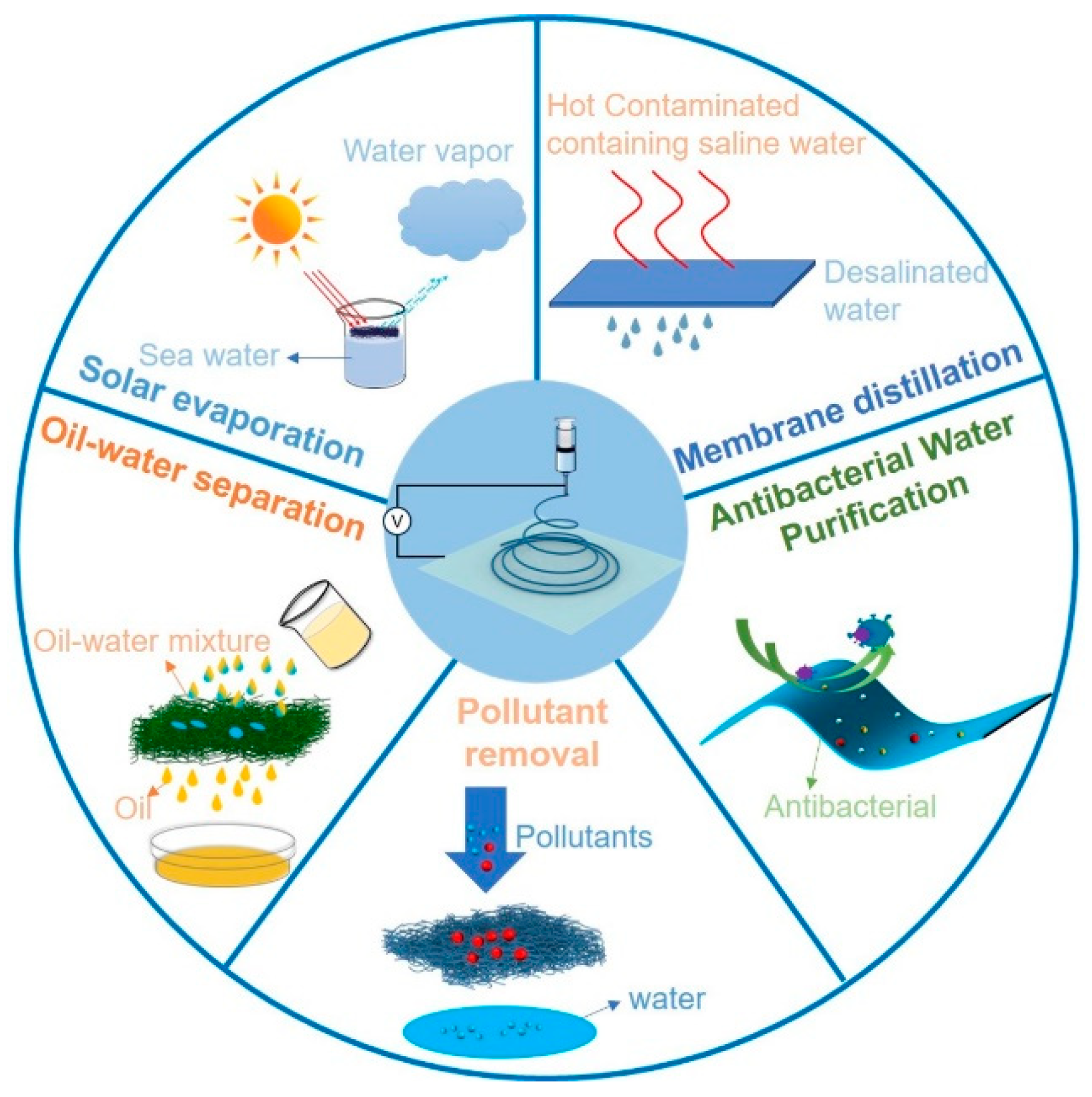
Applications of Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials in Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Membrane Distillation
2.1. Problems and Solutions for Membrane Distillation
2.2. Preparation of Membranes
2.3. Factors
2.3.1. Operational Characteristics
2.3.2. Spinning Solution Properties
2.4. Selection and Modification of Membrane Materials
2.4.1. Material Selection of Membrane
2.4.2. Modification of the Membrane
2.4.3. Inorganic Nanoparticle Modification
2.4.4. Surface Spray Modification
2.4.5. Membrane Surface Chemical Graft
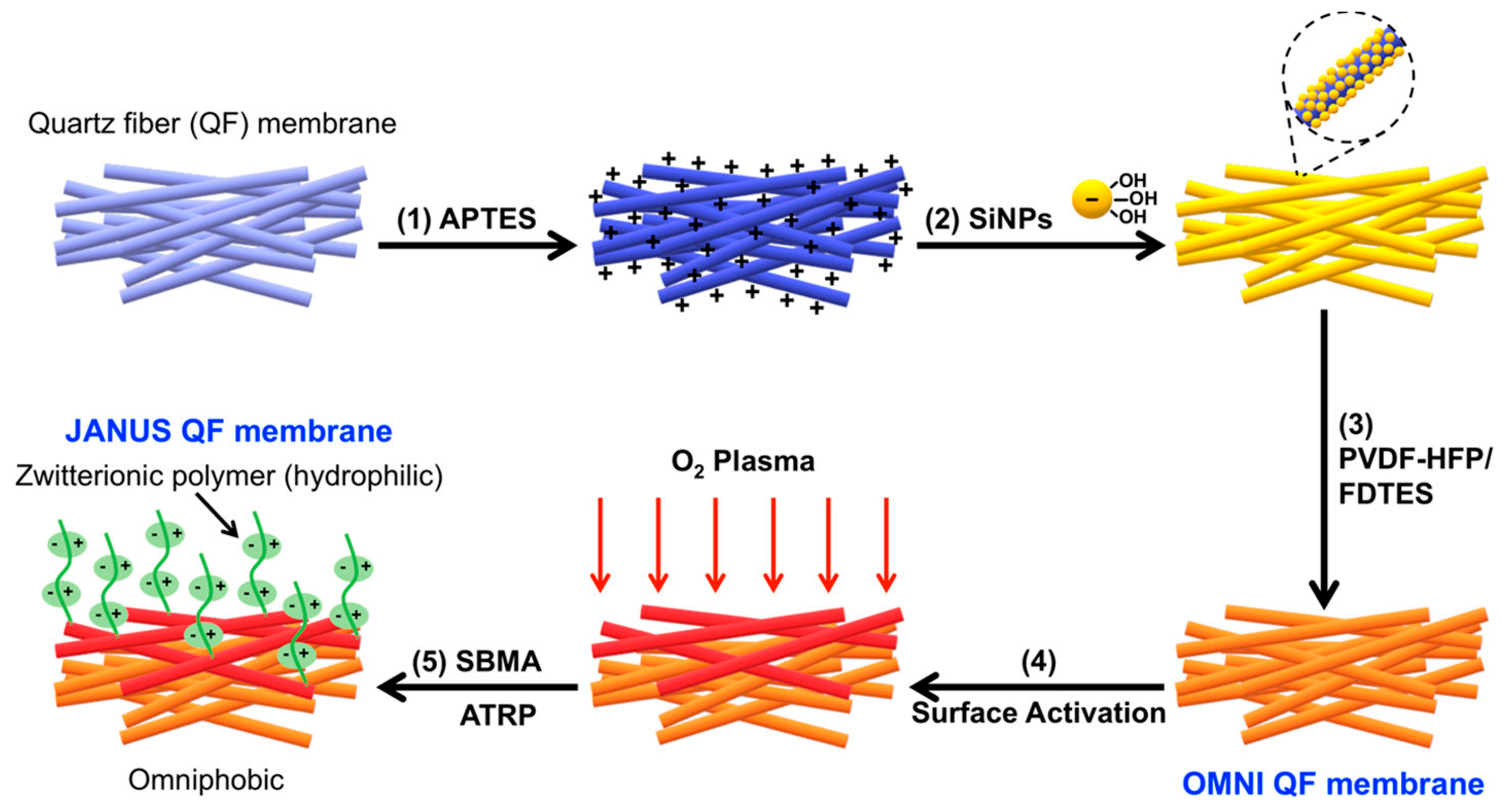
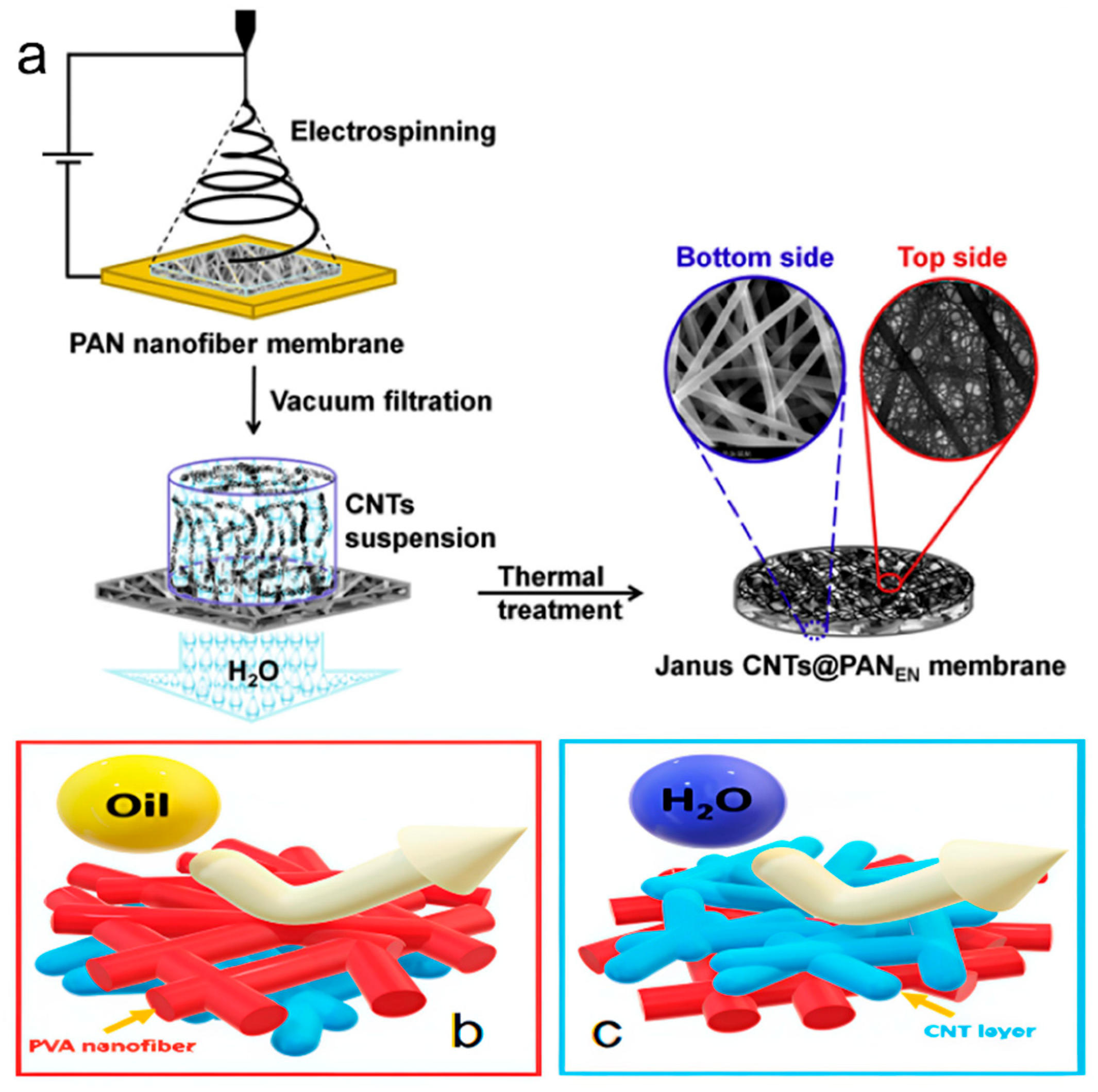
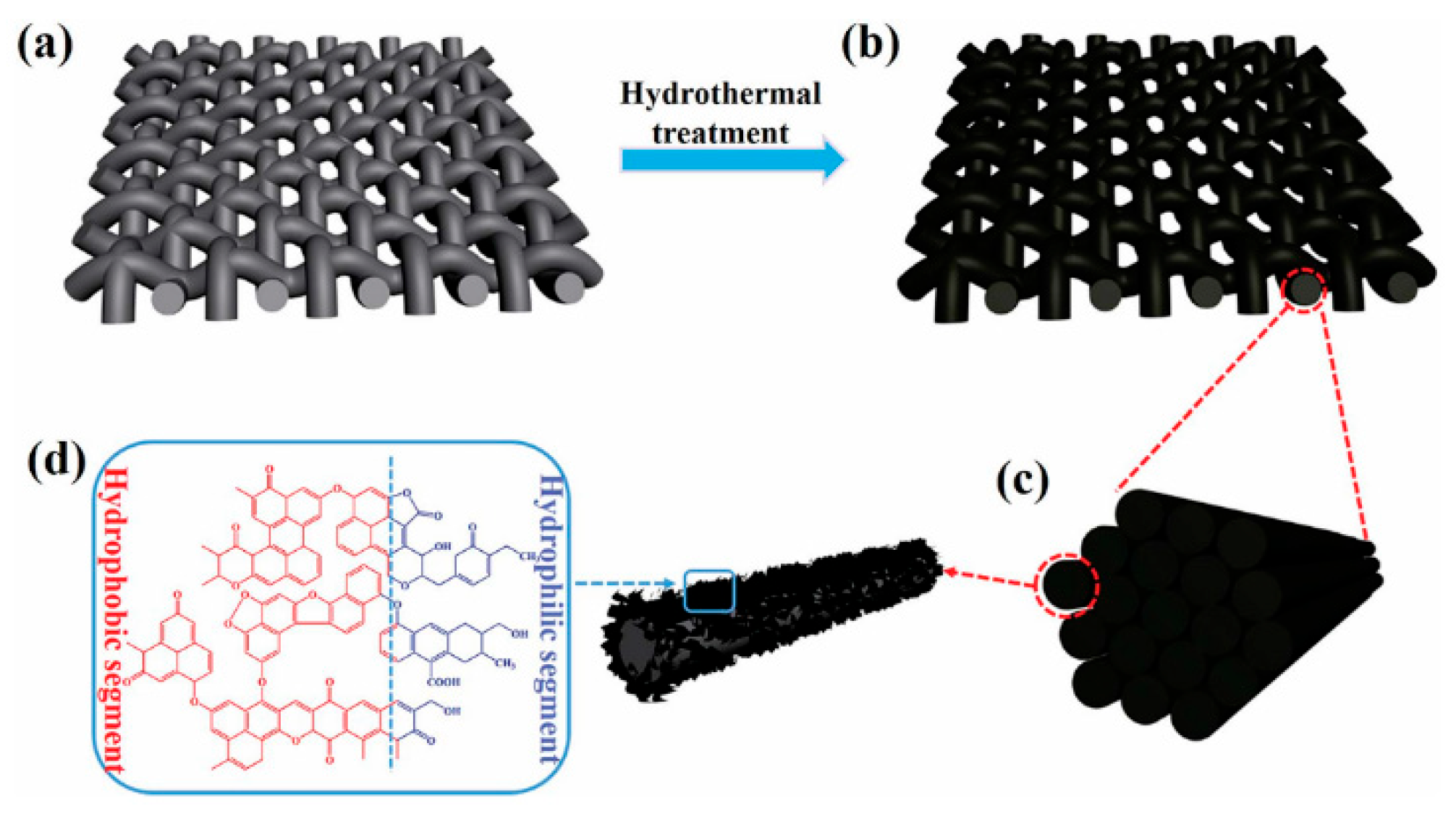
2.4.6. Janus Membrane
2.5. Application
2.5.1. Printing and Dyeing Wastewater Treatment
2.5.2. Desalination
2.5.3. Heavy Metal Recycling
2.5.4. ENM Diversification
2.5.5. Urgent Problems
3. Oil–Water Separation
3.1. Two-Dimensional Oil–Water Separation Membrane
3.1.1. Superhydrophilic/Superoleophobic Membrane
3.1.2. Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Membrane
3.1.3. Switchable Oil–Water Separation Membrane
3.2. The 3D Porous Composites Were Prepared on the Substrate of the Electrospinning Membrane
3.2.1. Three-Dimensional Porous Sponges
3.2.2. Three-Dimensional Porous Aerogels
3.2.3. Three-Dimensional Porous Membrane Scaffolds
4. Solar Evaporation
4.1. Two-Dimensional Solar Thermal Conversion Material
4.1.1. Materials Prepared by Doping Method
4.1.2. Material Prepared by Carbonization Method
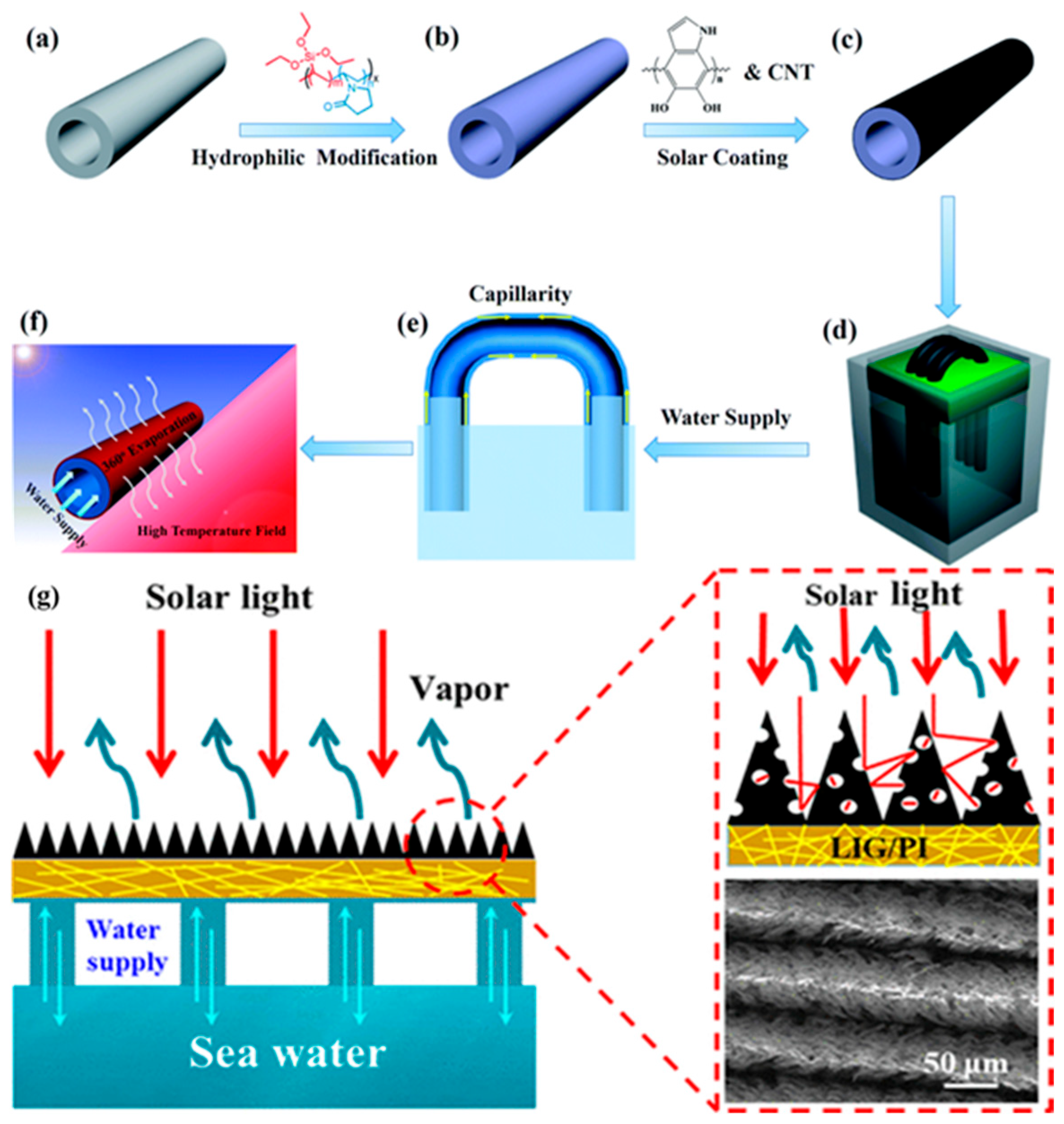
4.2. Three-Dimensional Solar Thermal Conversion Material
4.2.1. Three-Dimensional Porous Carbon-Based Materials
4.2.2. Three-Dimensional Porous Aerogel
5. Pollutant Removal
5.1. Photocatalytic Process
5.2. Adsorption
5.3. Filtering
6. Other Critical Applications
6.1. Antibacterial Water Purification
6.2. Sensors for Water Treatment
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, D.X.; Lin, Y.G.; Guo, X.Y.; Brindha, R.; Wang, R.W.; Radacsi, N.; Jose, R.; Qin, X.H.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nanofibers. Nat. Rev. Method Prime 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Qiao, X.C.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Microcystin in source water: Pollution characteristics and human health risk assessment. Rsc. Adv. 2021, 11, 6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Z.; Yu, M.J.; Ren, R.; Wang, H.; Kong, B.H. Thymol incorporation within chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers by electrospinning: Enhanced antibacterial packaging films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, S. Nonflammable and magnetic sponge decorated with polydimethylsiloxane brush for multitasking and highly efficient oil–water separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Malik, A. Engineered nanomaterials for water decontamination and purification: From lab to products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, X.; She, H.; Yang, Y.; Zha, F. Superhydrophobic meshes that can repel hot water and strong corrosive liquids used for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, K.N.; Mallikarjuna, N.; Kakarla, R.R.; Shukla, S.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membrane-based separation of potential emerging pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 9, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasi, R.A.; Rahman, R.A.; Rasid, R.A. Biofilm and Multimedia Filtration for Rainwater Treatment. J. Sust. Dev. 2009, 2, 196–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Guo, L.; Fan, H.; Meng, L.; Li, Y. Flocculation, coalescence and migration of dispersed phase droplets and oil–water separation in heavy oil emulsion. J. Petrpl. Sci. Eng. 2012, 81, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.D.; Li, M.M.; Duvail, J.L.; Jiang, X.Y.; Yin, H.L. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G. Disintegration of Water Drops in an Electric Field. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1964, 280, 383–397. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Lai, C.; Reneker, D.H.; Qiu, H.; Ye, Y.; Hou, H. Electrospun polymer nanofibres with small diameters. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 161558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.Z.; Li, H.P.; Yang, J.H.; Wan, J.; Yu, D.G. Influence of Working Temperature on the Formation of Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Engineering superhydrophobic surface on poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 44, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; Maab, H.; Alsaadi, A.; Nunes, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Amy, G.L. Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Membrane Distillation Application. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Qi, H.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zeng, J.; Wu, T.; et al. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: From academic research to industrial production. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 154, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Fan, T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Yin, F.; Gao, Y.; Long, Y.Z. Nanofiber aerogel with layered array structure coupled photothermal/magnetothermal effect for continuous seawater desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.L.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.D.; Wu, S.H.; Zhai, H.Y. Electrospun amine-modified polysuccinimide/polycaprolactone nanofiber hydrogel dressings as antibacterial and hemostatic wound dressing applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 252, 114648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Intelligent textiles are looking bright. Science 2024, 384, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhan, L.; Huang, C.Z. Recent insights into functionalized electrospun nanofibrous films for chemo-/bio-sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, X.Y.; Jing, X.F.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, G.S.; Wang, C. Bio-inspired functionalization of electrospun nanofibers with anti-biofouling property for efficient uranium extraction from seawater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Darband, G.B.; Zakeri, A.; Ahmadi, E. Review of superoleophobic surfaces: Evaluation, fabrication methods, and industrial applications. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 17, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issac, M.N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Review of manufacturing three-dimensional-printed membranes for water treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36091–36108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 12, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghali, M.; Jayathilaka, W.A.D.M.; Ramakrishna, S. The Role of Electrospun Nanomaterials in the Future of Energy and Environment. Materials 2021, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Miao, J.L.; Ning, X.; Fan, T.T. Photothermal/magnetothermal coupled polyphenylene sulfide composite membranes for ultra-efficient and continuous seawater desalination. Desalination 2024, 592, 118163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: Mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res. 2018, 139, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.C.; Yu, L.; Pan, Y.Q. Superwetting nanofibrous membranes for effective separation of oil–water emulsions. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 32, 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T.S. Recent advances in membrane distillation processes: Membrane development, configuration design and application exploring. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M. Membranes and theoretical modeling of membrane distillation: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 56–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dow, N.; Duke, M.; Ostarcevic, E.; Gray, S. Identification of material and physical features of membrane distillation membranes for high performance desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Membrane Distillation and Related Operations—A Review. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2005, 34, 35–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning Jets and Polymer Nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qin, X. Nanofiber bundles and nanofiber yarn device and their mechanical properties: A review. Text. Res. J. 2016, 17, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y. Electrospun nanofibers: Fabrication and applications. CIESC J. 2013, 64, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, F. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent 1975504, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, W.J. Method of Dispersing Fluids. U.S. Patent 706691, 12 August 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, S.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Yano, H. Nano-fibrillation of pulp fibers for the processing of transparent nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 2007, 89, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, N.; Li, X.; Gong, P. Preparation of poly(ether sulfone) nanofibers by gas-jet/electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Lin, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. One-step electro-spinning/netting technique for controllably preparing polyurethane nano-fiber/net. Macromol. Rapid. Comm. 2011, 32, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Reagan, M.R.; Kaplan, D.L. Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2009, 61, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essalhi, M.; Khayet, M. Self-sustained webs of polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun nanofibers at different electrospinning times, 1. Desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membrane Sci. 2013, 433, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Polymer Nanofibers by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The Effect of Processing Variables on the Morphology of Electrospun Nanofibers and Textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Park, H.C.; Lee, D.R. Transport properties of electrospun nylon 6 non-woven mats. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 18839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Bang, H.J.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, S.G. The change of bead morphology formed on electrospun polystyrene fibers. Polymer 2003, 44, 4029–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Chun, I. Nanometre diameter fibres of polymer, produced by electrospinning. Nanotechnology 1996, 7, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchitphimon, S.; Wang, R.; Jiraratananon, R. Surface modification of polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF-HFP) hollow fiber membrane for membrane gas absorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudchenko, A.V.; Chen, C.; Cardenas, A.; Rolf, J.; Jassby, D. Frequency-dependent stability of CNT Joule heaters in ionizable media and desalination processes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Novel Janus Membrane for Membrane Distillation with Simultaneous Fouling and Wetting Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13304–13310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; Ghaffour, N.; Alsaadi, A.S. PVDF hollow fiber and nanofiber membranes for fresh water reclamation using membrane distillation. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2045–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger-jrgensen, R.; Meyer, A.S.; Pinelo, M. Recovery of volatile fruit juice aroma compounds by membrane technology: Sweeping gas versus vacuum membrane distillation. Innov. Food. Sci. Emerg. 2011, 12, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Li, F.; Jiang, B. Effect of surfactants on the treatment of radioactive laundry wastewater by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2018, 93, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Bonyadi, S.; Chung, T.S. A stable and hydrophilic substrate for thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Koeman-Stein, N.E.; Creusen, R.J.M.; Zijlstra, M. Membrane distillation of industrial cooling tower blowdown water. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 14, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Gopal, R.; Kaur, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Production of drinking water from saline water by air-gap membrane distillation using polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.I.; Shihj, H.; Huang, M. A study of hydrophobic electrospun membrane applied in seawater desalination by membrane distillation. Fiber. Polym. 2012, 13, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yan, Y. Characterisation of surface wettability based on nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 42, 202–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.; Osman, M.S.; Johnson, D.J. Modelling of air gap membrane distillation and its application in heavy metals removal. Desalination 2017, 424, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
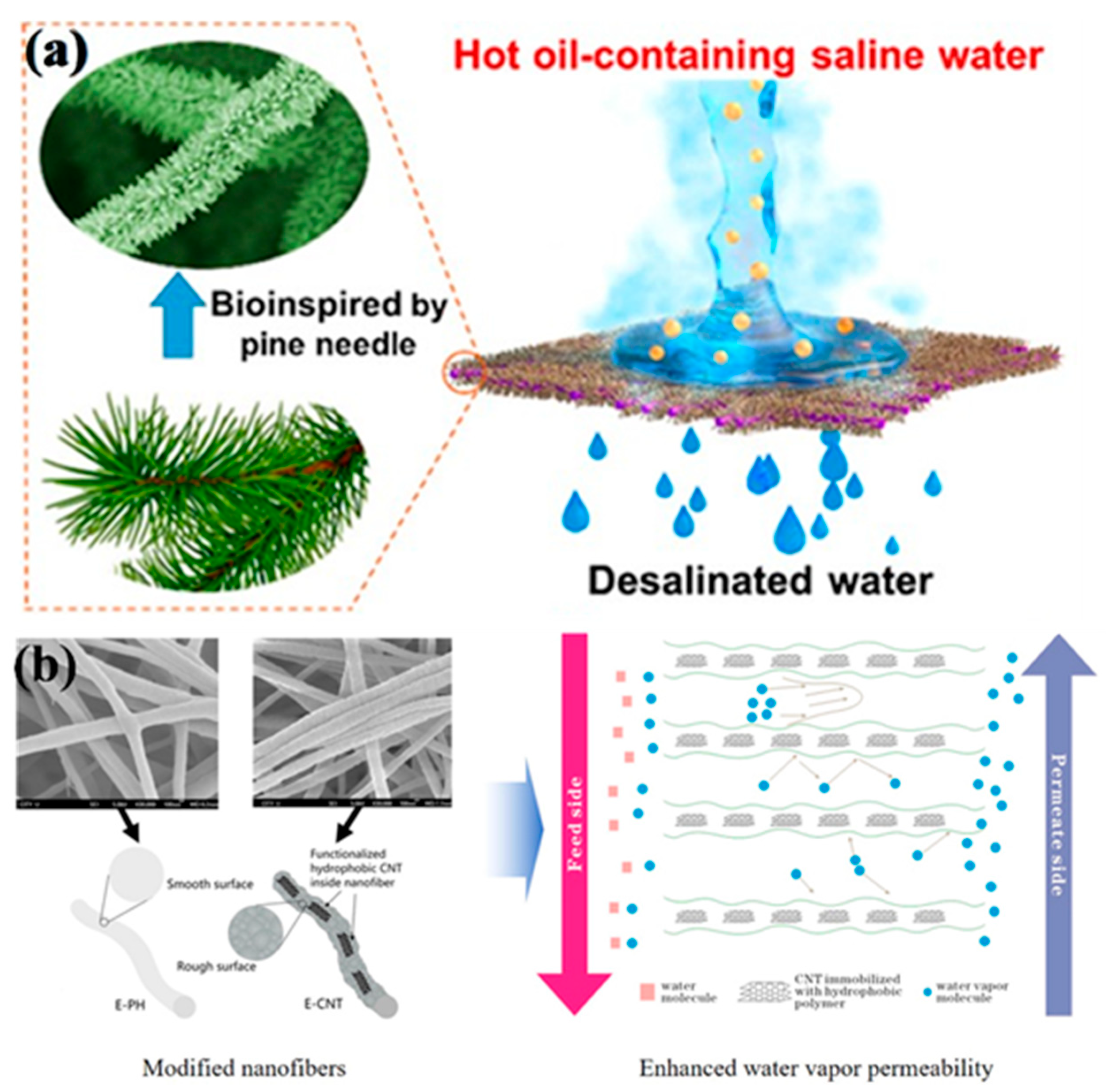
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Omniphobic Nanofibrous Membrane with Pine-Needle-Like Hierarchical Nanostructures: Toward Enhanced Performance for Membrane Distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 47963–47971. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.G.; Lee, E.J.; Jeong, S.; Guo, J.X.; An, A.K.; Guo, H.; Kim, J.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N. Theoretical modeling and experimental validation of transport and separation properties of carbon nanotube electrospun membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Shim, W.G. Superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane containing carbon nanotubes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.-K. Superhydrophobic electrospun nanofiber membrane coated by carbon nanotubes network for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 437, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Tijing, L.D.; Phuntsho, S.; He, T.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. CF4 plasma-modified omniphobic electrospun nanofiber membrane for produced water brine treatment by membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Fejjari, K.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Liao, Y. Engineering hierarchically structured superhydrophobic PTFE/POSS nanofibrous membranes for membrane distillation. Desalination 2020, 486, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Kappl, M.; Butt, H.J.; Sugimoto, T.; Nakamura, Y. Soft Janus colloidal crystal film. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9809–9813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.K. Janus membranes: Exploring duality for advanced separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Du, X.; Tong, T.; Cath, T.Y.; Lee, J. Antiwetting and Antifouling Janus Membrane for Desalination of Saline Oily Wastewater by Membrane Distillation. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18456–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chung, T.S.; O’brien, G.S. Hydrophobic/hydrophilic PVDF/Ultem® dual-layer hollow fiber membranes with enhanced mechanical properties for vacuum membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Edwie, F.; Teoh, M.M.; Chung, T.S. Effects of additives on dual-layer hydrophobic hydrophilic PVDF hollow fiber membranes for membrane distillation and continuous performance. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 68, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Garvia-Payo, M.C. Dual-layered electrospun nanofibrous membranes for membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 426, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
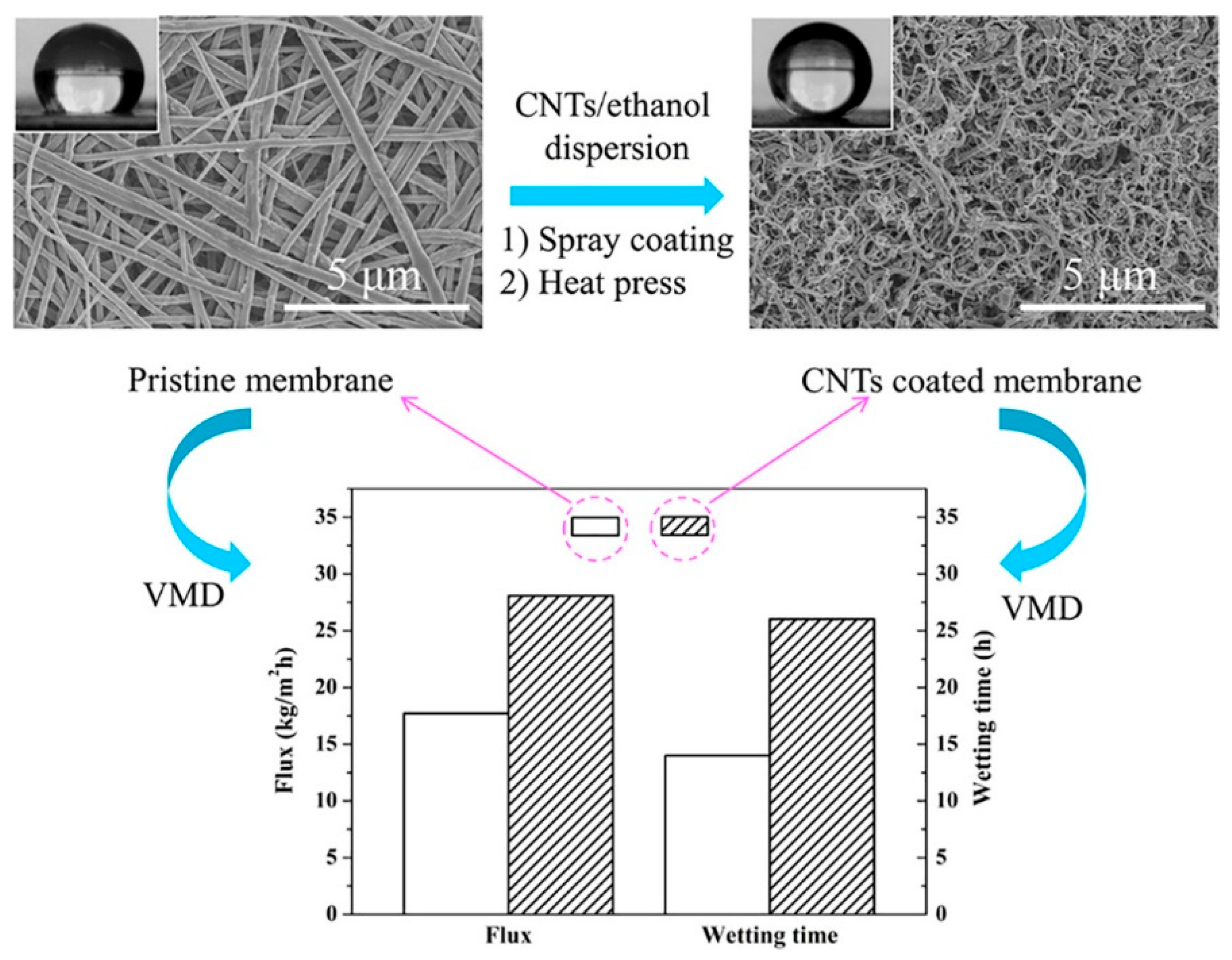
- Francis, L.; Hilal, N. Electrosprayed CNTs on Electrospun PVDF-Co-HFP Membrane for Robust Membrane Distillation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hhuang, Y.X.; Wang, Z.X.; Hou, D.Y. Coaxially electrospun super-amphiphobic silica-based membrane for antisurfactant-wetting membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.Y.; Ding, C.L.; Li, K.L. A novel dual-layer composite membrane with underwater-superoleophobic/hydrophobic asymmetric wettability for robust oil-fouling resistance in membrane distillation desalination. Desalination 2018, 428, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.P.; Hou, D.Y.; Wang, J. Hydrophilic surface coating on hydrophobic PTFE membrane for robust anti-oil-fouling membrane distillation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.; Aexander, S.; Wright, C.J. Superhydrophobic electrospun membrane for heavy metals removal by air gap membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 420, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: Challenges and applications. Desalination 2015, 356, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Zhao, J.; Rao, W. Electrospun fibers for oil–water separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 12868–12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, Y.; Siekierka, A.; Bryjak, M.; Maryska, J. Preparation of various nanofibrous composite membranes using wire electrospinning for oil-water separation. J. Acs. Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.K.; Bae, S.; Jeon, H.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.J.; Lim, G. An underwater superoleophobic nanofibrous cellulosic membrane for oil/water separation with high separation flux and high chemical stability. Nanoscale 2016, 10, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, W.; Mu, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Sacrifice template strategy to the fabrication of a self-cleaning nanofibrous membrane for efficient crude oil-in-water emulsion separation with high flux. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53484–53493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Ejaz, F.; Lalia, B.S.; Hilal, N.; Hashaikeh, R. Underwater superoleophobic cellulose/electrospun pvdf–hfp membranes for efficient oil/water separation. Desalination 2014, 344, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zong, D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic and superwettable nanofibrous skins for highly efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705051.1–1705051.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, T.; Lu, M. Fabrication of special wettability functionalized mg(oh)2@cotton fabric for oil/water mixtures and emulsions separation. Cellulose 2020, 27, 7739–7749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.F. Electrospinning superhydrophobic–superoleophilic fibrous pvdf membranes for high-efficiency water–oil separation. Mater. Lett. 2015, 160, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Facile fabrication of nanofiber- and micro/nanosphere-coordinated pvdf membrane with ultrahigh permeability of viscous water-in-oil emulsions. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 6, 7014–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, J.; Oderinde, O.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, B.; Xiong, R.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Huang, C. Durable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic electrospun nanofibrous membrane for oil-water emulsion separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 532, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Fu, G. Nature-inspired chemistry toward hierarchical superhydrophobic, antibacterial and biocompatible nanofibrous membranes for effective uv-shielding, self-cleaning and oil-water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Gao, F.; Tang, K.; Cao, H. Fabrication of three-dimensional superhydrophobic membranes with high porosity via simultaneous electrospraying and electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2016, 170, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, W.; Shi, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Tang, C.Y. Robust superhydrophobic-superoleophilic polytetrafluoroethylene nanofibrous membrane for oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, M.; Shen, Y. Waste cigarette filter as nanofibrous membranes for on-demand immiscible oil/water mixtures and emulsions separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 549, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, N.; Tan, L.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, X. Bioinspired Superwettable Covalent Organic Framework Nanofibrous Composite Membrane with a Spindle-Knotted Structure for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16545–16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Tian, M.; Wang, R. A high-performance and robust membrane with switchable super-wettability for oil/water separation under ultralow pressure. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 543, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, J.; Xu, J.; Shan, B. Switchable oil/water separation with efficient and robust Janus nanofiber membranes. Carbon 2017, 115, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, A.S.; Baji, A. Electrospun Janus membrane for efficient and switchable oil–water separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800272. [Google Scholar]
- Pornea, A.M.; Puguan, J.M.C.; Deonikar, V.G.; Kim, H. Robust janus nanocomposite membrane with opposing surface wettability for selective oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 236, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Shen, H.; Han, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, X. Mechanically robust janus poly(lactic acid) hybrid fibrous membranes toward highly efficient switchable separation of surfactant-stabilized oil/water emulsions. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50879–50888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Zhou, Y.N.; Luo, Z.H. Smart fiber membrane for ph-induced oil/water separation. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19643–19650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Z.; Yang, D.Z. Beadlike porous fibrous membrane with switchable wettability for efficient oil/water separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 10894–10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Ju, J.; Kang, W.; Naebe, M. Development of smart poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(acrylic acid) tree-like nanofiber membrane for ph-responsive oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 534, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, Z.; Holakooei, P. Durable light-driven three-dimensional smart switchable superwetting nanotextile as a green scaled-up oilwater separation technology. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4962–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaran, S.P.; Reshmi, C.R.; Sagitha, P.; Sujith, A. Polyurethane nanofibrous membranes decorated with reduced graphene oxide–tio2 for photocatalytic templates in water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 55, 5892–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tas, S.; Zhang, K.; De Vos, W.M.; Ma, J.; Vancso, G.J. Thermoresponsive membranes from electrospun mats with switchable wettability for efficient oil/water separations. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 8435–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lai, C.; Hu, H.; Yang, L.; Xin, J.H. Temperature-responsive nanofibers for controllable oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51078–51085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Zhu, L.T.; Luo, Z.H. Electrospun fibrous membrane with enhanced swithchable oil/water wettability for oily water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.A.; Mohsen, G.; Saeid, R.; Jessop, P.G.; Cunningham, M.F. CO2-switchable-hydrophilicity membrane (CO2-shm) triggered by electric potential: Faster switching time along with efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8478–8481. [Google Scholar]
- Che, H.; Huo, M.; Peng, L. CO2-responsive nanofibrous membranes with switchable oil/water wettability. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 9062–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Mei, Q.; Xiao, J.; Du, M.; Zheng, Q. 3d multiscale superhydrophilic sponges with delicately designed pore size for ultrafast oil/water separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1704293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Xie, H.; Huang, H.X.; Turng, L.S. Magnetically driven superhydrophobic silica sponge decorated with hierarchical cobalt nanoparticles for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791. [Google Scholar]
- Karki, H.P.; Kafle, L.; Kim, H.J. Modification of 3D polyacrylonitrile composite fiber for potential oil-water mixture separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 229, 115840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Xing, B.; Hu, W.; Ke, Q.; Zhao, Y. Robust candy-floss-like poly(l-lactide) fibrous filters driven by sodium-dodecyl-benzene-sulfonate for high efficient dye/oil separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Guan, C.; Li, H. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation based on double-layer polylactic acid fibrous membranes loading Chinese ink nanoparticles. Solar. Energy. 2020, 195, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, H.; Xie, M.; Shen, S.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M.; Mo, X.; Xia, Y. Incorporation of gold nanocages into electrospun nanofibers for efficient water evaporation through photothermal heating. Mater. Today Energy 2019, 12, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, T.F.; Wu, C.M.; Chou, M.H.; Guo, Z.L. Melt Electrospun Reduced Tungsten Oxide /Polylactic Acid Fiber Membranes as a Photothermal Material for Light-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2018, 10, 28955–28962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Guo, S.; Zuo, X.; Tian, M.; Zhang, X.; Qu, L.; Miao, J. Smart green cotton textiles with hierarchically responsive conductive network for personal healthcare and thermal management. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 43, 59358–59369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W. Constructing Black Titania with Unique Nanocage Structure for Solar Desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, D.; Cao, M.; Jiang, L. Floatable, Self-Cleaning, and Carbon-Black-Based Superhydrophobic Gauze for the Solar Evaporation Enhancement at the Air–Water Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, S. Scalable, flexible and reusable graphene oxide-functionalized electrospun nanofibrous membrane for solar photothermal desalination. Desalination 2020, 488, 114535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, X. Synthesis of a sulfur-graphene composite as an enhanced metal-free photocatalyst. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Lv, B.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Song, C. Electrospun reduced graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile membrane for high-performance solar evaporation. Sol. Energy 2020, 209, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Jia, C.; Song, J.; Hitz, E.M.; Liu, B.; Huang, H.; et al. Architecting a floatable, durable, and scalable steam generator: Hydrophobic/hydrophilic bifunctional structure for solar evaporation enhancement. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H. Solar evaporation and electricity generation of porous carbonaceous membrane prepared by electrospinning and carbonization. Sol. Energy Mat. Sol. Cells 2020, 215, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Wang, H.; Jian, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Q.S. Extremely black vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays for solar steam generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.W.; Mishnaevsky, L., Jr.; Yi, H.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hu, X.; Warrier, A.; Dai, G.M. Carbon fiber/carbon nanotube reinforced hierarchical composites: Effect of CNT distribution on shearing strength. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 88, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fang, Q.; Xi, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, L. Ultra-robust carbon fibers for multi-media purification via solar-evaporation. Mater. J. Chem. 2019, 7, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.W.; Li, G.; Boriskina, S.V.; Li, H.; Gang, C. Steam generation under one sun enabled by a floating structure with thermal concentration. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Feng, R.; Bernard, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Shang, W.; Tao, P.; Song, C. A Bioinspired, Reusable, Paper-Based System for High-Performance Large-Scale Evaporation. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Xing, B. A flexible and salt-rejecting electrospun film-based solar evaporator for economic, stable and efficient solar desalination and wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2020, 267, 128916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Porous graphene/polyimide membrane with a three-dimensional architecture for rapid and efficient solar desalination via interfacial evaporation. Acs. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 36, 13850–13858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhuo, S.; Shi, L.; Chang, J.; Hong, S.; Ng, K.C.; Wang, P. A 3D Photothermal Structure toward Improved Energy Efficiency in Solar Steam Generation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Song, C.Z.; Huang, X.J. Improved light-harvesting and thermal management for efficient solar-driven water evaporation using 3D photothermal cones. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9874–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Gao, M.; Peh, C.K.N.; Ho, G.W. Recent progress in solar-driven interfacial water evaporation: Advanced designs and applications. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Lin, H.; Han, Q.; Wang, P. Exceptional interfacial solar evaporation via heteromorphic PTFE/CNT hollow fiber arrays. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Cao, L.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Deng, H. Cellular structured CNTs@ SiO2 nanofibrous aerogels with vertically aligned vessels for salt-resistant solar desalination. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malara, A. Discovering biomarkers associated and predicting cardiovascular disease with high accuracy using a novel nexus of machine learning techniques for precision medicine. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, M. Research progress on the TiO2/ACF composite photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants from water. Aids. Rev. 2009, 27, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, M.; Monteserín, C.; Angulo, A.; Pérez-Márquez, A.; Maudes, J.; Murillo, N.; Aranzabe, E.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Vilas, J.L. TiO2-Doped Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane for Photocatalytic Water Treatment. Polymers 2019, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, T.; Li, G.; An, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, Z. Electrospun H4SiW12O40/cellulose acetate composite nanofibrous membrane for photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and methyl orange with different mechanism. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 168, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Feng, G.S.; Yan, L.; Pan, H.J. One-Dimensional Nanostructured TiO2 for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Wastewater. Int. J. Photoenergy 2014, 2014, 563879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
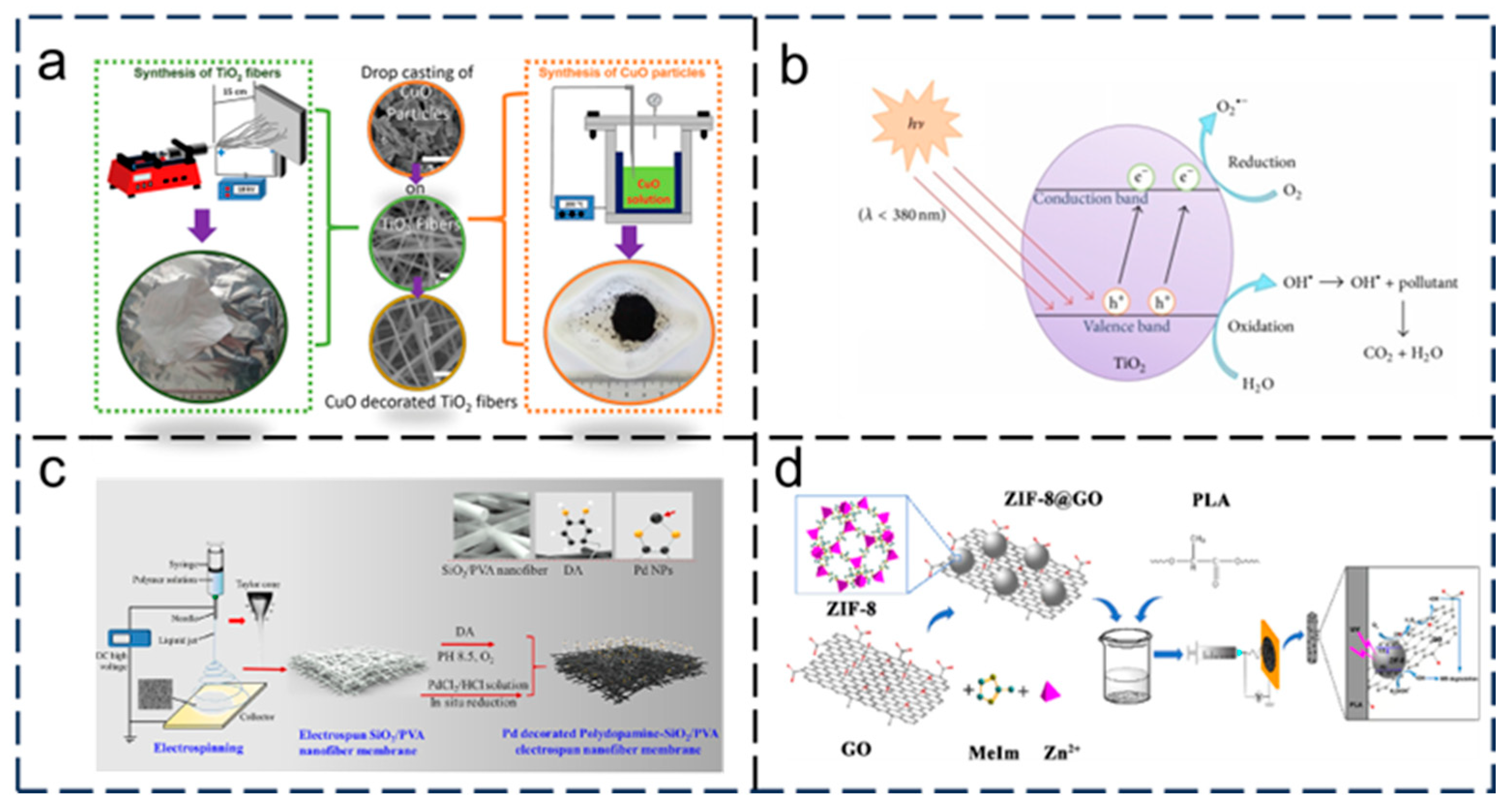
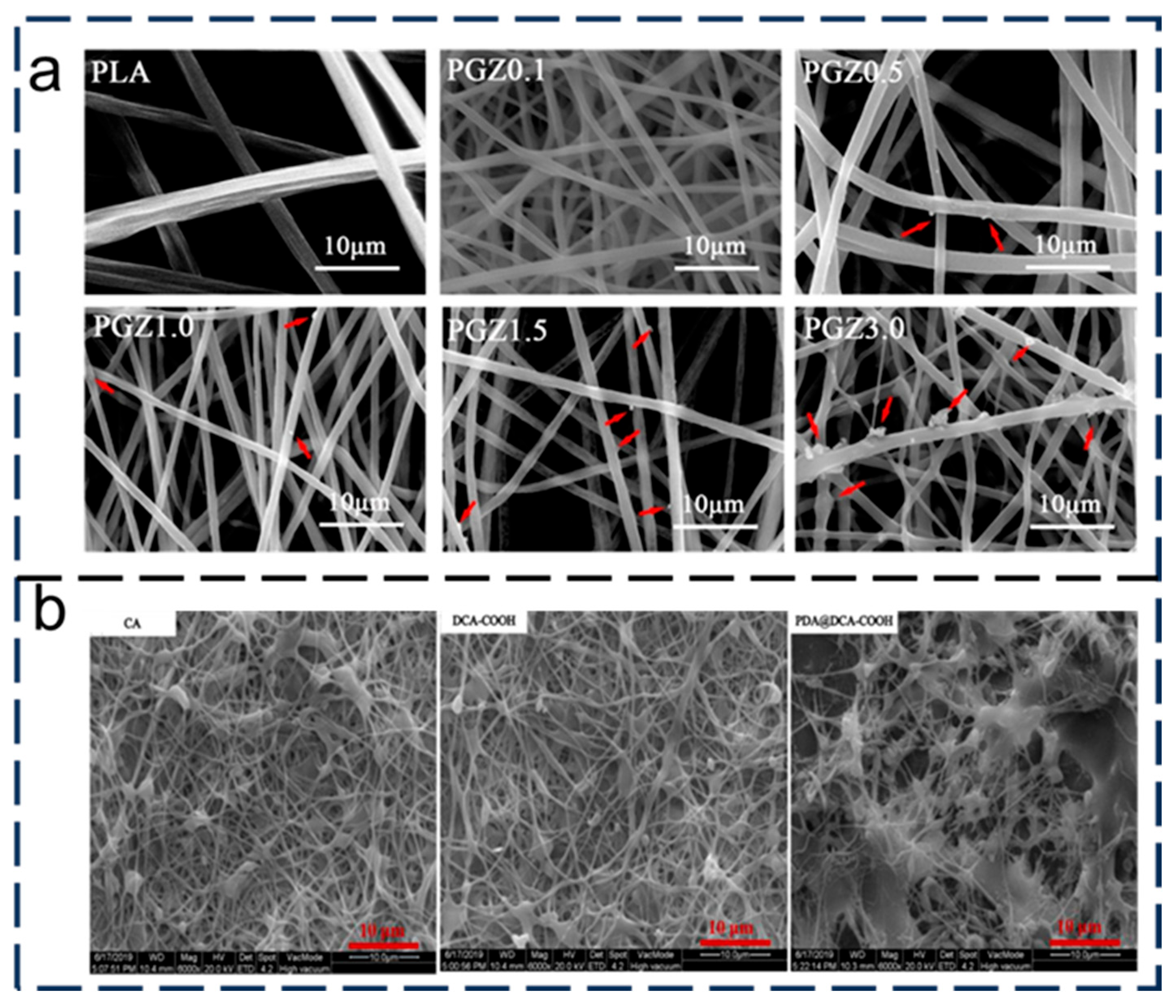
- Büra, C.; Kerimoglu, I.; Beyza, T.; Atakan, D.; Dursun, S.; Kaya, C.I.; Kalem, V.; Akyildiz, H. Hydrothermal/electrospinning synthesis of CuO plate-like particles/TiO2 fibers heterostructures for high-efficiency photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and phenolic pollutants. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 2020, 109, 104919. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. A novel Pd decorated polydopamine-SiO2/PVA electrospun nanofiber membrane for highly efficient degradation of organic dyes and removal of organic chemicals and oils. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122937. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Xu, L.; Mi, Z. Zeolitic Imidazole Framework/Graphene Oxide Hybrid Functionalized Poly(lactic acid) Electrospun Membranes: A Promising Environmentally Friendly Water Treatment Material. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6860–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.; Wang, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Ramkumar, S. Visible Light Photocatalytic Functional TiO2/PVDF Nanofibers for Dye Pollutant Degradation. Part. Part. Syst. Char. 2019, 36, 190091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Environmentally benign modification of breathable nanofibrous membranes exhibiting superior waterproof and photocatalytic self-cleaning properties. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, S.X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yu, D.G. Electrospun Functional Nanofiber Membrane for Antibiotic Removal in Water: Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Lin, C.; Ye, X.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Rapid elimination of trace bisphenol pollutants with porous β-cyclodextrin modified cellulose nanofibrous membrane in water: Adsorption behavior and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 403, 123666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Tan, J.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y. Electrospun membrane of cellulose acetate for heavy metal ion adsorption in water treatment. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 83, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Jo, H.S.; Song, K.Y.; Mali, M.G.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yoon, S.S. Electrically-charged recyclable graphene flakes entangled with electrospun nanofibers for the adsorption of organics for water purification. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19170–19177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akduman, C.; Kumbasar, E.P.; Morsunbul, S. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for adsorption of dye molecules from textile wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, H.; Xing, B. Electrospinning of multifunctional cellulose acetate membrane and its adsorption properties for ionic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Xu, J.; Dai, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, H.; Sun, K.; Liu, R. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase by electrospun fibrous membranes for adsorption and degradation of pentachlorophenol in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246–247, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S.D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Bao, W.; Zhang, K.Q.; Ling, L.Z. Anti-icing properties of superhydrophobic ZnO/PDMS composite coating. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 2016, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, A.I.; Stelzl, K.; Faghih, M.; Gupta, S.S.; Krishnadas, K.R.; Heißler, S.; Pradeep, T. Poly(ether sulfone) Nanofibers Impregnated with β-Cyclodextrin for Increased Micropollutant Removal from Water. ACS Sustaln. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 2942–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.-H.; Chiu, P.-C.; Cho, C.-J.; Veeramuthu, L.; Tung, S.-H.; Satoh, T.; Chiang, W.-H.; Cai, X.; Kuo, C.-C. Facile 3D Boron Nitride Integrated Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Purging Organic Pollutants. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, P.C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Lee, H.R.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chu, S.; et al. Nanofiber air filters with high-temperature stability for efficient PM2. 5 removal from the pollution sources. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Tian, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, T.; Lei, H.; Zhu, G. An electrospun fiber based metal–organic framework composite membrane for fast, continuous, and simultaneous removal of insoluble and soluble contaminants from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22559–22570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Alamry, K.A.; Asiri, A.M.; Mohamed, S.A. Efficient water disinfection using hybrid polyaniline/graphene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
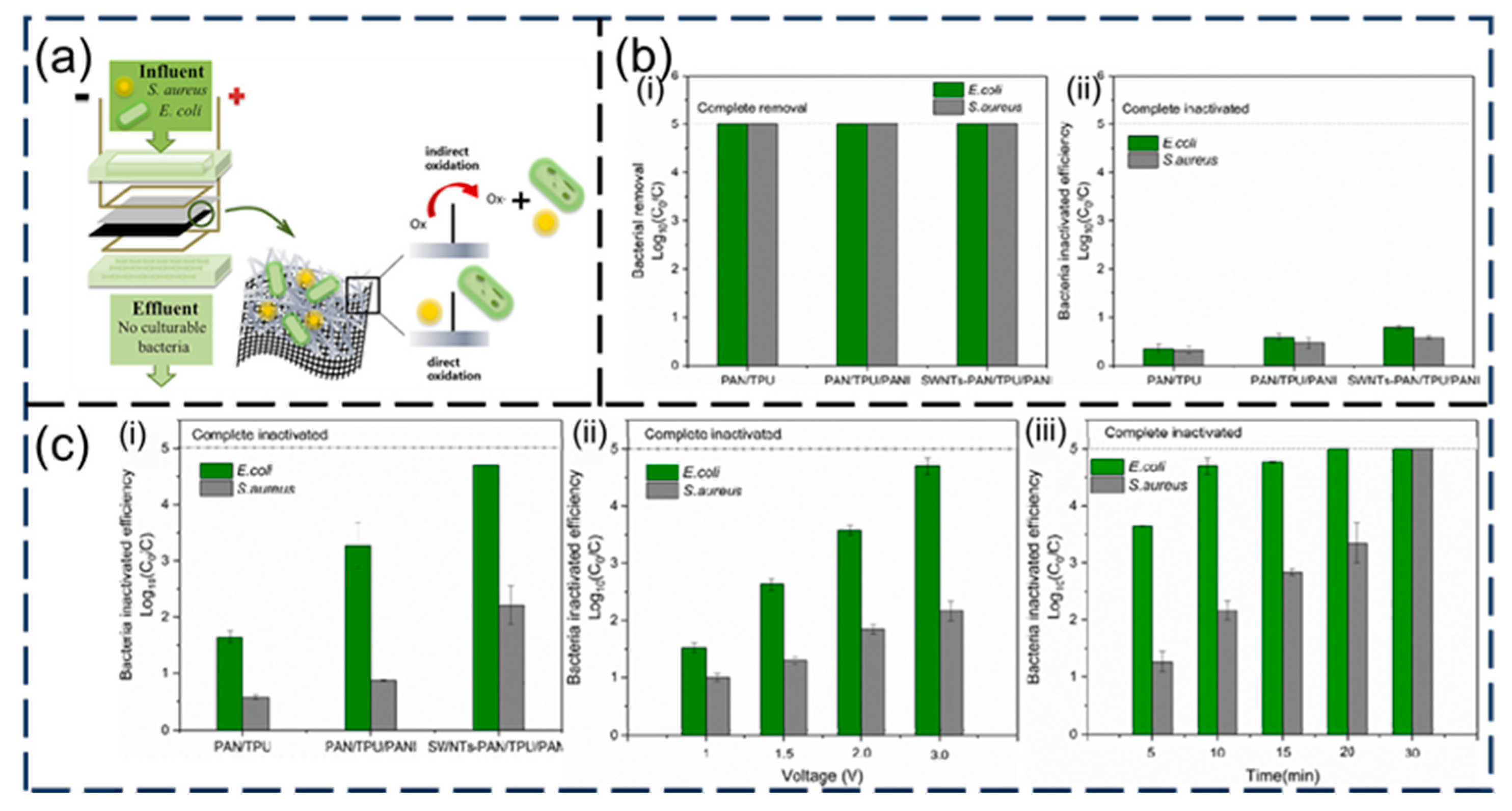
- Xie, L.; Shu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. SWNTs-PAN/TPU/PANI composite electrospun nanofiber membrane for point-of-use efficient electrochemical disinfection: New strategy of CNT disinfection. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
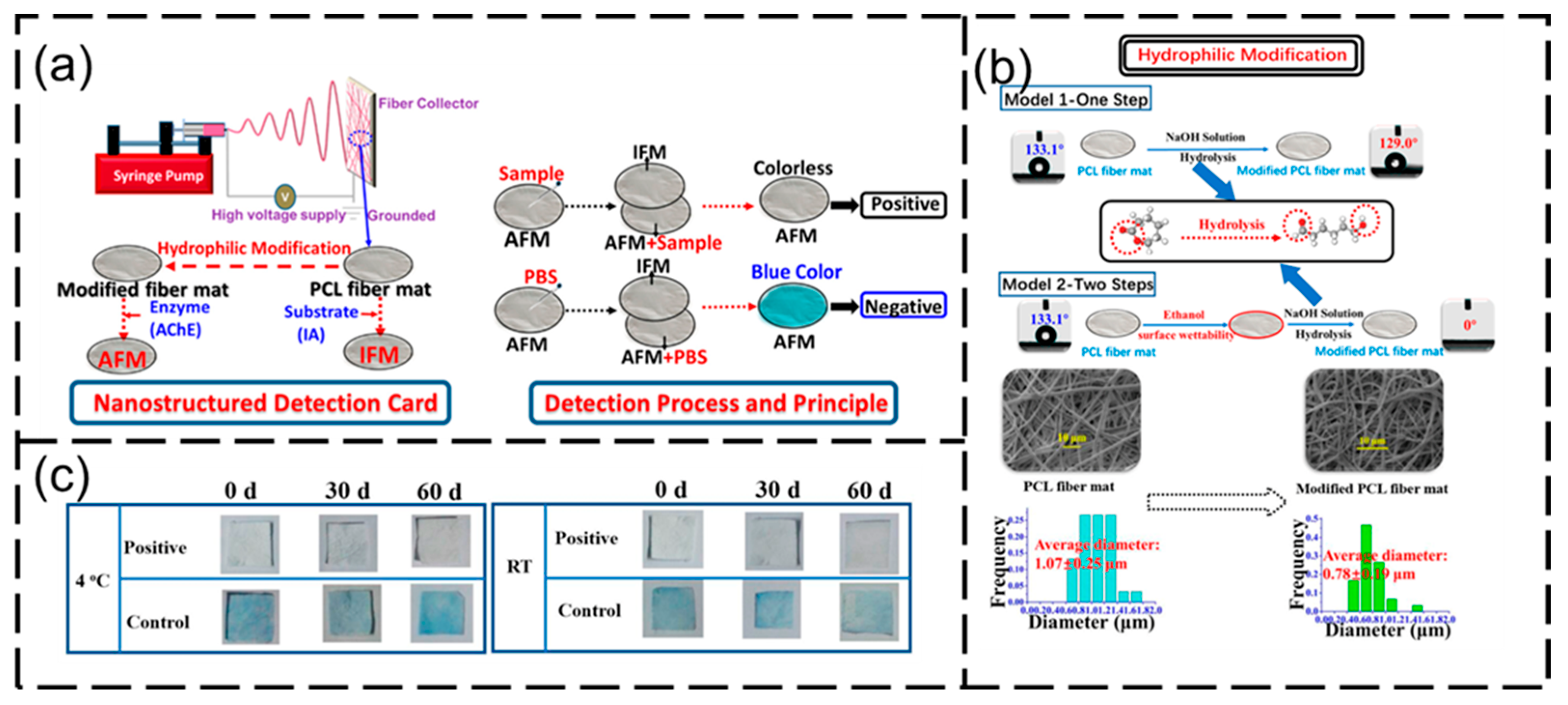
- Feng, K.; Zhai, M.Y.; Wei, Y.S.; Zong, M.H.; Wu, H.; Han, S.Y. Fabrication of nano/micro-structured electrospun detection card for the detection of pesticide residues. Foods 2021, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




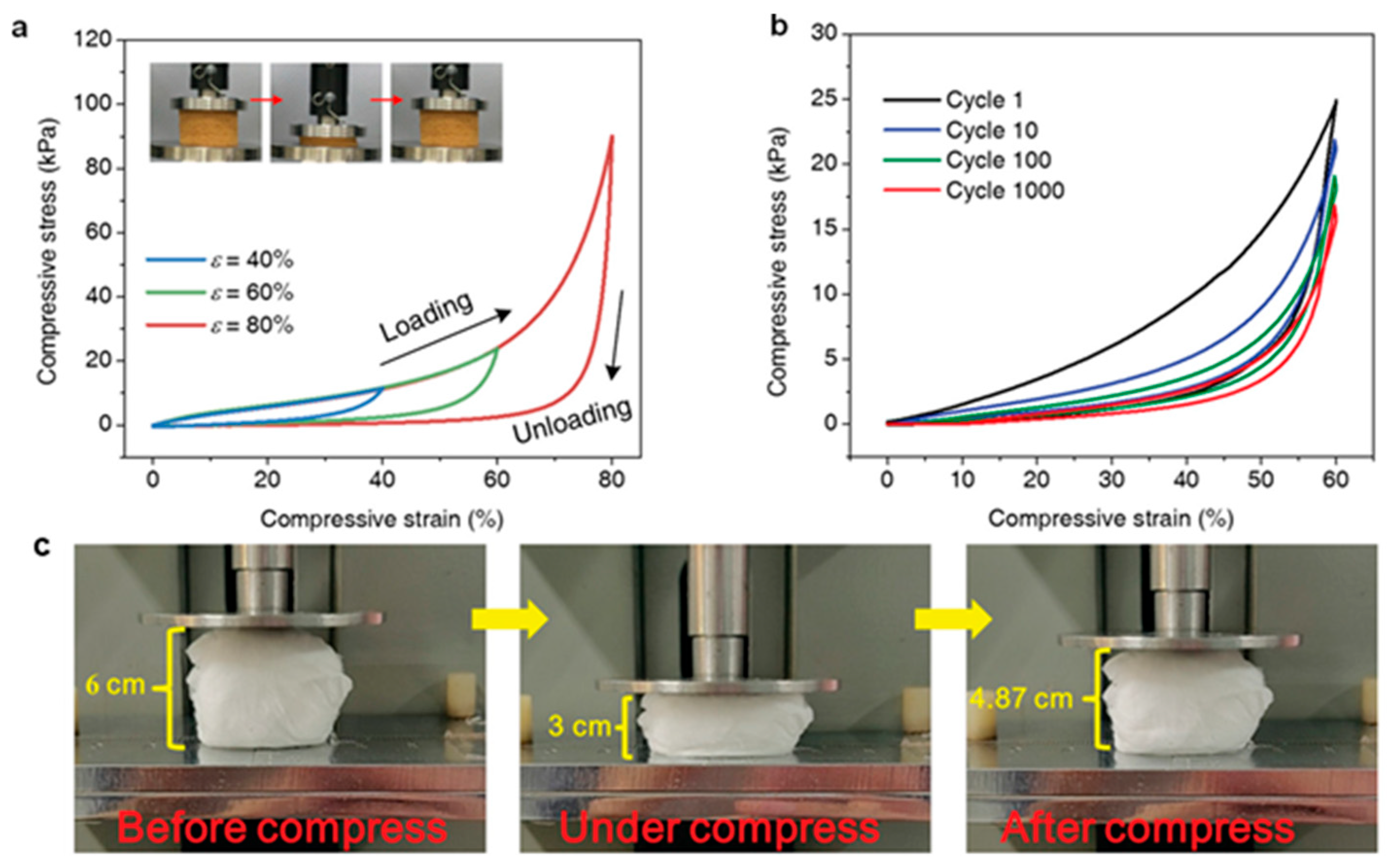
| Sample | Voltage (kV) | Distance (cm) | Feed (mL/h) | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-GP | 20 | 15 | 1.0 | 25 | 3 | |
| PAN | 14 | 1.0 | 20 | 15 | 15 | |
| PEO | 5.5 | 1.0 | 20 | 4–10 | 47 | |
| PS | 15 | 12 | 25 | 13 | 51 | |
| PLLA | 20 | 16 | 0.8 | 21–27 | 8–10 | 56 |
| PAN | 25 | 20 | 1.0 | 25 | 14 | 92 |
| COF-DhaTab/PAN | 20 | 15 | 1.0 | 23 ± 5 | 3 | 101 |
| CNTSX@PANEN | 18 | 18 | 2.0 | 14 | 103 | |
| PLA/CNTS | 20 | 18 | 0.35 | 10 | 106 | |
| PMMA-b-P4VP | 14 | 0.2 | 20 | 107 | ||
| PS | 10 | 15 | 0.5 | 25 | 8 | 108 |
| RC | 15 | 0.5 | 15 | 114 | ||
| PAN | 15 | 14 | 1.0 | 30 | 14 | 121 |
| ink/PLA | 12 | 15 | 0.8 | 15 | 123 | |
| GO/PVA | 15 | 15 | 0.7 | 25 ± 1 | 6 | 129 |
| PAN | 22.5 | 20 | 1.5 | 25 | 1.5 | 133 |
| GF | 16 | 10 | 2.5 | 25 | 20 | 139 |
| SiO2@PVA | 15 | 8 | 152 | |||
| PLA/ZIF-8@GO | 22 | 0.5 | 10 | 153 | ||
| PVDF/TiO2 | 25 | 15 | 4.8 | 13.5 | 154 | |
| PAN | 12.9 | 20 | 1.0 | 20 | 12 | 165 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, A.; Pan, R.; Miao, J.; Lin, Y.; Deng, Y.; Peng, S.; Luo, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Applications of Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials in Water Treatment. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181424
Wang A, Pan R, Miao J, Lin Y, Deng Y, Peng S, Luo X, Wu P, Zhang S, Wu Y, et al. Applications of Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials in Water Treatment. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(18):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181424
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Aiqi, Rui Pan, Jinlei Miao, Yishen Lin, Yuanrou Deng, Siqi Peng, Xiuhuan Luo, Pinhong Wu, Shuting Zhang, Yuanyuan Wu, and et al. 2025. "Applications of Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials in Water Treatment" Nanomaterials 15, no. 18: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181424
APA StyleWang, A., Pan, R., Miao, J., Lin, Y., Deng, Y., Peng, S., Luo, X., Wu, P., Zhang, S., Wu, Y., Xie, J., & Fan, T. (2025). Applications of Advanced Electrospun Nanofibrous Materials in Water Treatment. Nanomaterials, 15(18), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15181424