Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of the Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of the Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
3. Results and Discussion
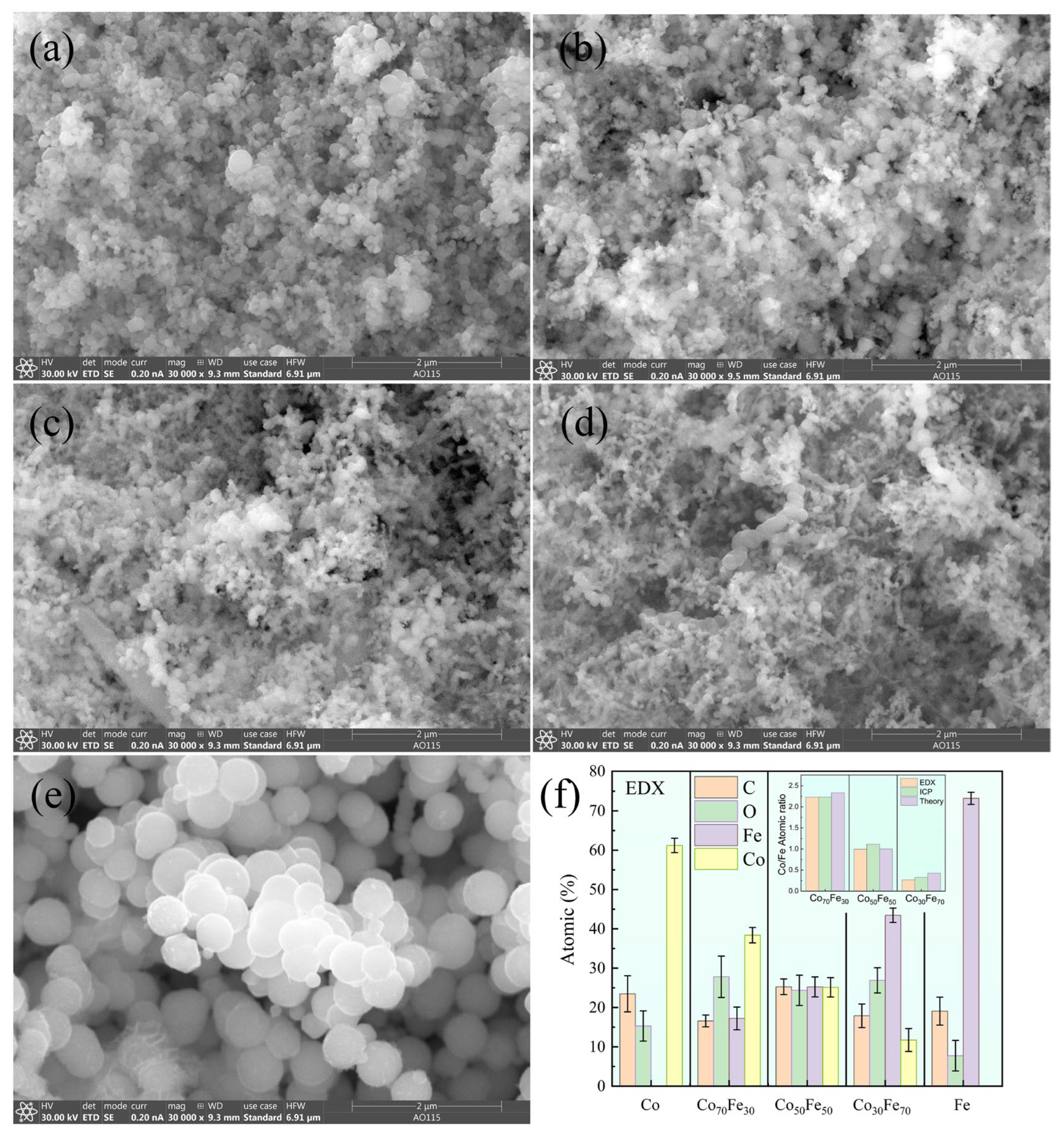
3.1. Morphological and Structural Characterization of the Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
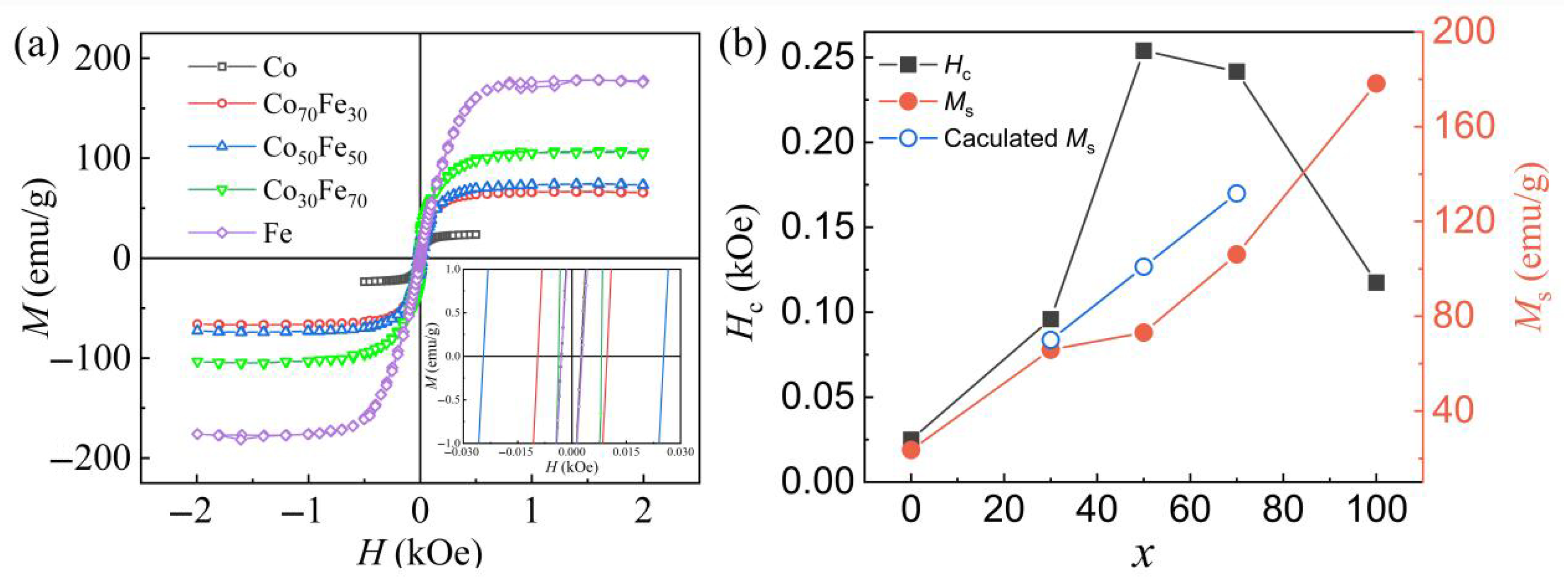
3.2. Static Magnetic Characterization of the Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
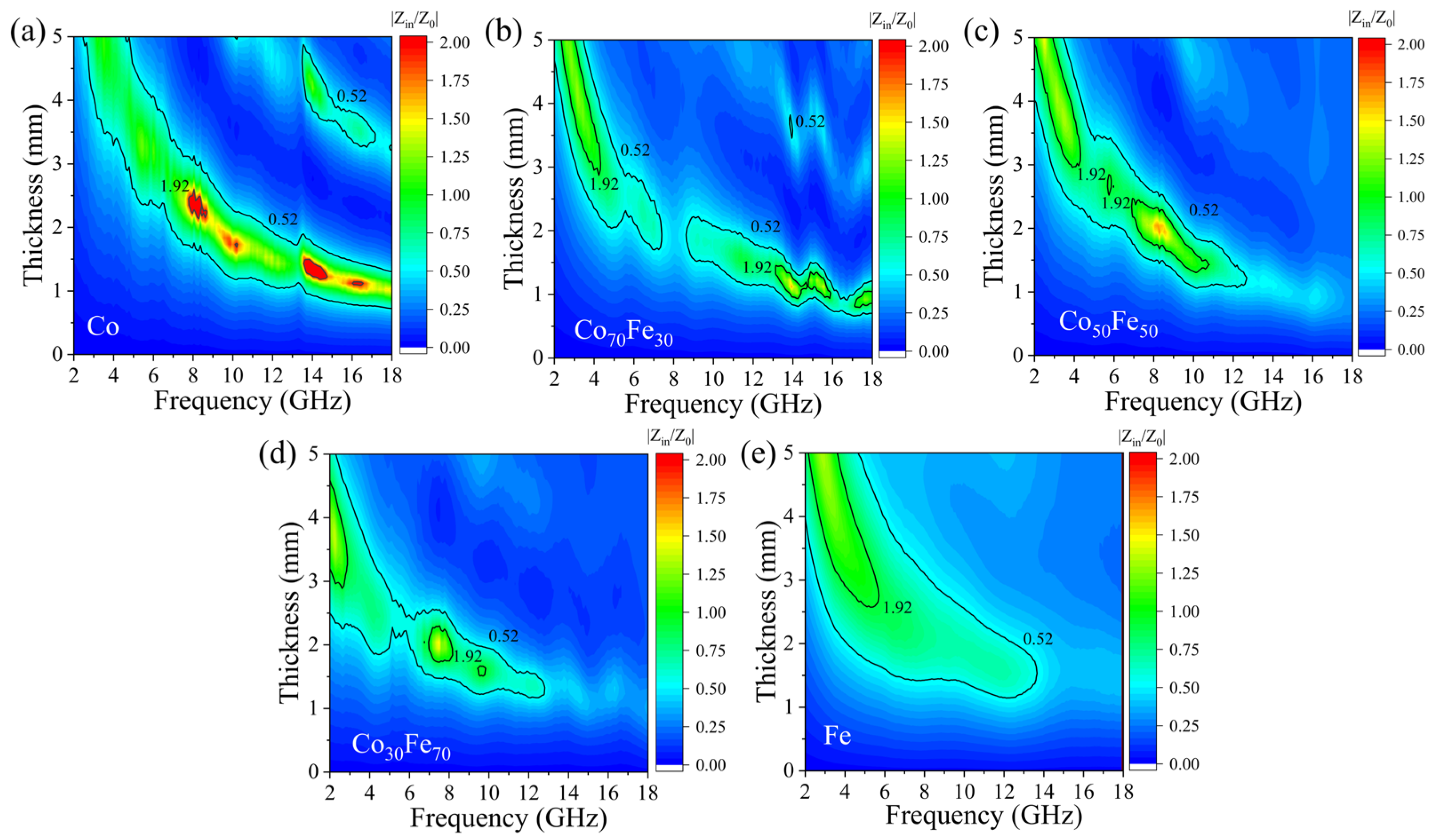
3.3. Microwave Performance Characterization of the Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; He, X.; Yao, J.; Tan, R.; Chen, P.; Yao, B.; Zhou, J.; Yao, Z. Multifunctional Shape Memory Composites for Joule Heating, Self-Healing, and Highly Efficient Microwave Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhan, W.; Su, Y.; Siyal, S.H.; Bai, G.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, A.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Achieving Excellent Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of ZnFe2O4@CNT/Polyvinylidene Fluoride Flexible Composite Membranes by Adjusting Processing Conditions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 133, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Xu, P.; Cui, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Du, Y. Ternary Mo2C/Co/C Composites with Enhanced Electromagnetic Waves Absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.S.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, W.Q.; Fang, X.Y.; Yuan, J. Variable-Temperature Electron Transport and Dipole Polarization Turning Flexible Multifunctional Microsensor beyond Electrical and Optical Energy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.I.; Cao, W.I.; Cao, M.H.; Yuan, J. Assembling Nano–Microarchitecture for Electromagnetic Absorbers and Smart Devices. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong Ng, V.M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, K.; Lee, P.S.; Que, W.; Xu, J.Z.; Kong, L.B. Recent Progress in Layered Transition Metal Carbides and/or Nitrides (MXenes) and Their Composites: Synthesis and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3039–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ning, M.; Li, Z.; Batalu, D.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, W. Sequential Architecture Induced Strange Dielectric-Magnetic Behaviors in Ferromagnetic Microwave Absorber. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Hui, S.; Zhang, L.; Tao, K.; Chen, Q.; Lu, W.; Wu, H. High-Density Dual Atoms Pairs Coupling for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorbers. Small 2025, 21, 2408396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Yang, Z. Customizing Heterointerfaces in Multilevel Hollow Architecture Constructed by Magnetic Spindle Arrays Using the Polymerizing-Etching Strategy for Boosting Microwave Absorption. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.; Wu, B.; Wei, Y.; Dou, S.; Mahmood, N. Facile Synthesis of Fe3O4/GCs Composites and Their Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6101–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.Y.; You, M.C.; Chuang, K.W.; Wu, M.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Anbalagan, A.K.; Lee, C.H. Investigating Anisotropic Magnetoresistance in Epitaxially Strained CoFe Thin Films on a Flexible Mica. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; You, M.C.; Anbalagan, A.K.; Su, G.Y.; Chuang, K.W.; Yang, C.Y.; Lee, C.H. Investigation of a magnetic sensor based on the magnetic hysteresis loop and anisotropic magnetoresistance of cofe thin films epitaxial grown on flexible mica and rigid mgo substrates with strain effect. Micromachines 2025, 16, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Yang, D.; Jia, L.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Gao, C.; Xue, D. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy correlated negative anisotropic magnetoresistance in epitaxial fe30co70 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 042404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xi, L.; Du, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, D. Microwave Absorption Properties of Amorphous Iron Nanostructures Fabricated by a High-Yield Method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 135002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.; Wang, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Shi, X. The Enhanced Microwave Absorption Property of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticles Coated with a Co3Fe7-Co Nanoshell by Thermal Reduction. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 045707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zong, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhao, H.; Feng, J.; He, M.; Li, X.H.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, X. Crystalline-Amorphous Permalloy@Iron Oxide Core-Shell Nanoparticles Decorated on Graphene as High-Efficiency, Lightweight and Hydrophobic Microwave Absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6374–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Han, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, F. Enhanced Microwave Absorption of Fe Nanoflakes after Coating with SiO2 Nanoshell. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 095708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.Q.; Liu, L.X.; Yu, Z.Z. Lightweight Fe@C Hollow Microspheres with Tunable Cavity for Broadband Microwave Absorption. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Yu, Z.Z. Controllable Synthesis of Hollow Microspheres with Fe@Carbon Dual-Shells for Broad Bandwidth Microwave Absorption. Carbon 2019, 147, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.R.; Itoh, M.; Terada, M.; Horikawa, T.; Machida, K.I. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Fe Nanowires in Gigahertz Range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 093101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lv, J.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, J.; Ying, Y.; Qiao, L.; Yu, J.; Che, S. Enhanced and Broadband Microwave Absorption of Flake-Shaped Fe and FeNi Composite with Ba Ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X. Facile Chemical Synthesis, Electromagnetic Response, and Enhanced Microwave Absorption of Cobalt Powders with Controllable Morphologies. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 084707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, H. Synthesis, Dual-Nonlinear Magnetic Resonance and Microwave Absorption Properties of Nanosheet Hierarchical Cobalt Particles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 18333–18340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Xia, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Synthesis and Microwave Absorption Properties of FeCo Nanoplates. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 493, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvpm, S.; Prozorov, R.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical Preparation and Characterization of Nanosized Amorphous Co-Ni Alloy Powders. J. Mater. Chem. 1998, 8, 769–773. [Google Scholar]
- Suslick, K.S.; Choe, S.B.; Cichowlas, A.A.; Grinstaff, M.W. Sonochemical Synthesis of Amorphous Iron. Nature 1991, 353, 414–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.J.; Hudgins, D.M.; Brown, L.W.; Yoon, S.D.; Heiman, D.; Harris, V.G.; Carpenter, E.E. Annealing of Amorphous FexCo100-x Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Modified Aqueous Reduction Using NaBH4. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09A303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, E.K.; Grossmann, P.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Template Free, Large Scale Synthesis of Cobalt Nanowires Using Magnetic Fields for Alignment. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 165606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, Z.; Lv, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, J.; Du, Y. Facile Synthesis of FeCo Alloys with Excellent Microwave Absorption in the Whole Ku-Band: Effect of Fe/Co Atomic Ratio. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Seshadri, G.; Kelber, J.A. A Consistent Method for Quantitative XPS Peak Analysis of Thin Oxide Films on Clean Polycrystalline Iron Surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 119, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Grosvenor, A.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.R.; Smart, R.S.C. Resolving Surface Chemical States in XPS Analysis of First Row Transition Metals, Oxides and Hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Physical Electronics: Chanhassen, MN, USA, 1992; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Grinstaff, M.W.; Salamon, M.B.; Suslick, K.S. Magnetic Properties of Amorphous Iron. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Huang, H.; Dong, X.L.; Zhang, X.F.; Lei, J.P.; Sun, J.P.; Dong, C. Influence of Alloy Components on Electromagnetic Characteristics of Core/Shell-Type Fe–Ni Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 114313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, H.; Du, S.; Wang, Y. A Facile Hydrothermal Synthesis of MnO2 Nanorod–Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites Possessing Excellent Microwave Absorption Properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 88979–88988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramo, S.; Whinnery, J.R.; Van Duzer, T. Fields and Waves in Communication Electronics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lacrevaz, T.; Fléchet, B.; Farcy, A.; Torres, J.; Gros-Jean, M.; Bermond, C.; Vo, T.; Cueto, O.; Blampey, B.; Angénieux, G. Wide band frequency and in situ characterisation of high permittivity insulators (high k) for h.f. integrated passives. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.; Gangopadhyay, K.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Mehta, N.; Biswas, N. Permittivity enhancement of aluminum oxide thin films with the addition of silver nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 5243–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.; Doefman, J. Spontaneous and induced magnetisation in ferromagnetic bodies. Nature 1930, 126, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hui, S.; Xiao, T.; Ge, S.; Hines, W.; Budnick, J.; Taylor, G. Microwave Magnetic Properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 Nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4404–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Yi, H.; Qiao, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, D.; Li, F. Analyses on Double Resonance Behavior in Microwave Magnetic Permeability of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composites Containing Ni Catalyst. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 042507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.J.; Zhou, P.H.; Xie, J.L.; Zhang, L. Characterization and microwave resonance in nanocrystalline FeCoNi flake composite. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 10F905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amikam, A. Exchange resonance modes in a ferromagnetic sphere. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 7762–7764. [Google Scholar]
- Aharoni, A. Effect of surface anisotropy on the exchange resonance modes. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel, C. On the Theory of Ferromagnetic Resonance Absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Suetake, K. Application of Ferrite to Electromagnetic Wave Absorber and its Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1971, 19, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.R.; Itoh, M.; Machida, K.I. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of α-Fe/Fe3B/Y2O3 Nanocomposites in Gigahertz Range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 4017–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Huang, H.; Lv, B.; Lei, J.; Choi, C. Microstructure and Microwave Absorption Properties of Carbon-Coated Iron Nanocapsules. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Che, R. Hollow porous Fe2O3 microspheres wrapped by reduced graphene oxides with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 11167–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xing, H.; Zong, Y.; Ren, Z.; Yu, H.; Zheng, X. Controllable synthesis of mof-derived fexni1x@c composites with dielectric–magnetic synergy toward optimized impedance matching and outstanding microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Amorphous bimetallic nanowires with high-performance microwave absorption: A case for FeCo nanowires. Nano 2019, 1, 1950041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Ji, G.; Wang, M.; Shang, C.; Zhang, H.; Du, Y. Hexagonal-cone like of Fe50Co50 with broad frequency microwave absorption: Effect of ultrasonic irradiation time. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, T.; Yang, S.; Yu, Q.; Yu, B.; Cai, M.; Zhou, F. The synergistic enhancement of microwave absorption performance and corrosion resistance of FeCo by polypyrrole-M16 and TiO2. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2025, 686, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sample | State | RL (dB) | fr (GHz) | dO (mm) | EAB (GHz) | dEAB (mm) | Filled Mass Ratio | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe7Co3 flower | Crystalline | −53.6 | 14.3 | 1.55 | 6.8 | 2.0 | 7:3 | [29] |
| Fe nanoparticle | Amorphous | −53.2 | 6.4 | 2.4 | 3.9 | 1.5–5.0 | 4:1 | [14] |
| CoFe nanowires | Amorphous | −25.9 | 4 | 3 | 5.4 | 1–5 | 4:1 | [51] |
| Hexagonal-cone like Fe50Co50 | Crystalline | −22 | 10.4 | 1.5 | 7.1 | 1.5 | 7:3 | [52] |
| FeCo@TiO2 material @PPy-M16 | Crystalline | −29.8 | / | 1.9 | 10.21 | 2.63 | 1:1 | [53] |
| Co | Amorphous | −41.8 | 3.85 | 4.9 | 2.9 | 1.6 | 1:1 | This work |
| Co70Fe30 | Amorphous | −38.6 | 3.93 | 3.5 | 2.64 | 1.58 | 1:1 | This work |
| Co50Fe50 | Amorphous | −35.6 | 4.25 | 3.3 | 2.55 | 2.55 | 1:1 | This work |
| Co30Fe70 | Amorphous | 34.6 | 3.65 | 3.5 | 2.28 | 2.28 | 1:1 | This work |
| Fe | Amorphous | 42 | 5.02 | 3.2 | 6.25 | 1.85 | 1:1 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; An, C.; Wang, F.; Liang, H.; Hou, Z.; Shen, H.; Wu, H. Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141091
Wang Z, An C, Wang F, Liang H, Hou Z, Shen H, Wu H. Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(14):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141091
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Chao An, Fenglong Wang, Hongsheng Liang, Zhaoyang Hou, Hao Shen, and Hongjing Wu. 2025. "Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 15, no. 14: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141091
APA StyleWang, Z., An, C., Wang, F., Liang, H., Hou, Z., Shen, H., & Wu, H. (2025). Enhanced Microwave Absorption Performance of Amorphous Co100−xFex Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 15(14), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15141091









