Biomimetic Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Surface Modification and Smart Soft Actuator Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
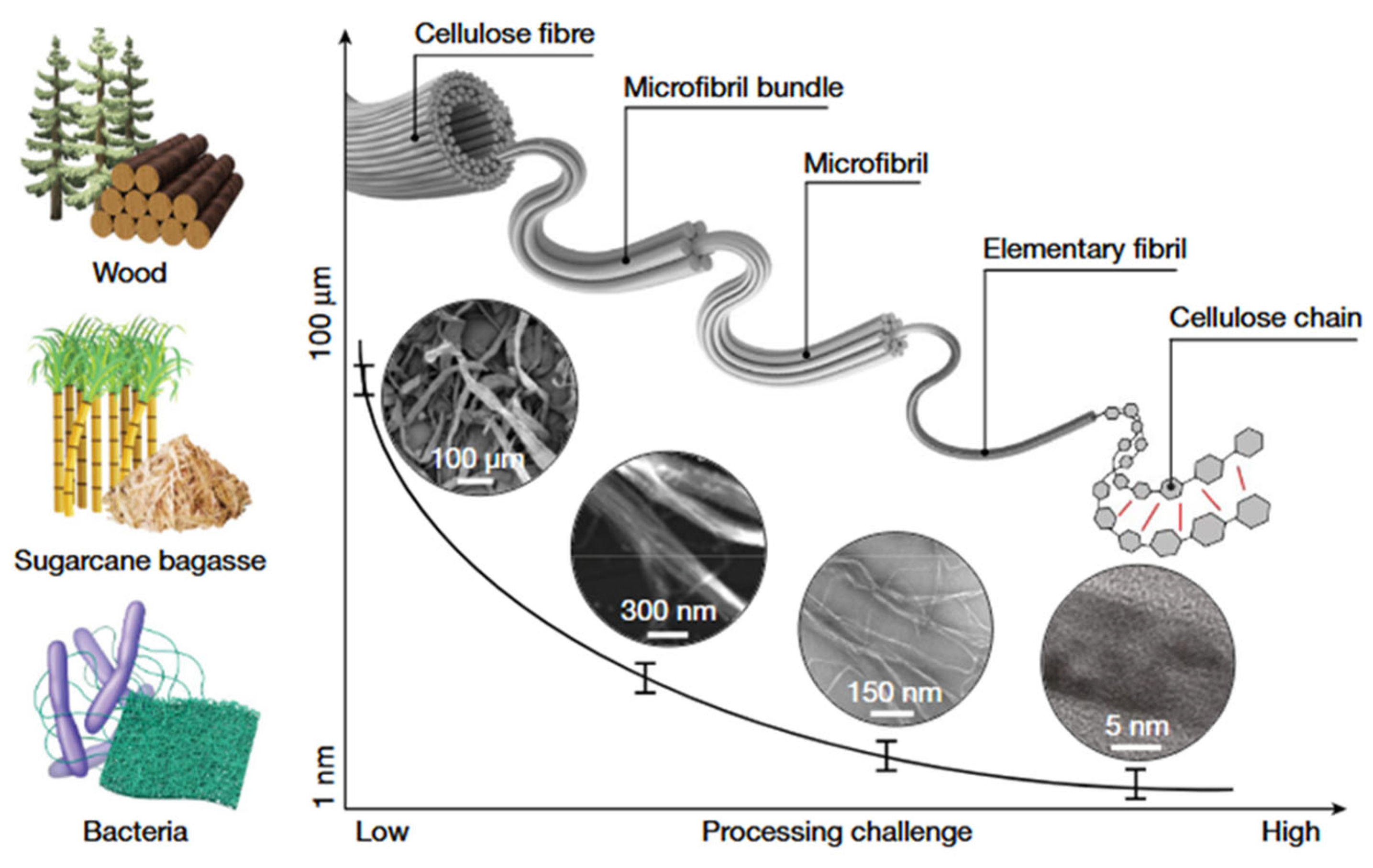

| Preparation Method | Core Process | Dimensions of CNCs | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid hydrolysis | 64% H2SO4, 45 °C, 45–90 min | Length 100–200 nm, diameter 5–20 nm | Reinforced Composites (Hydrogels/Plastics), Pickering emulsion stabilizer | Mature process, high yield (~70%), sulfate ester groups improve dispersibility | Low thermal stability (sulfate decomposition), extensive washing required, equipment corrosion | [19,22] |
| Hydrochloric acid hydrolysis | 6 reflux boil (105 °C), 2–4 h | Low (~14–28 nm) | High thermal stability, no charged groups | Aggregation-prone, poor dispersibility | [23] | |
| Phosphoric acid hydrolysis | 85% H3PO4, 50 °C, 120 min | Moderate (~11 nm) | High thermal stability, excellent dispersibility, suitable for biomaterials | Harsh conditions, larger dimensions | [14,24] | |
| Oxalic acid hydrolysis | 50% (COOH)2, 90 °C, 6 h ultrasonic | Uniform dimensions, tunable aspect ratio | Eco-friendly, high yield (>80%), high thermal stability | Poor dispersibility | [16] | |
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis | Cellulase mildly hydrolyzes high-pressure homogenization | High (~28–50 nm) | Tissue engineering scaffolds, flexible sensor substrates | Mild conditions, eco-friendly, high selectivity | Low efficiency, time-consuming, high cost | [21] |
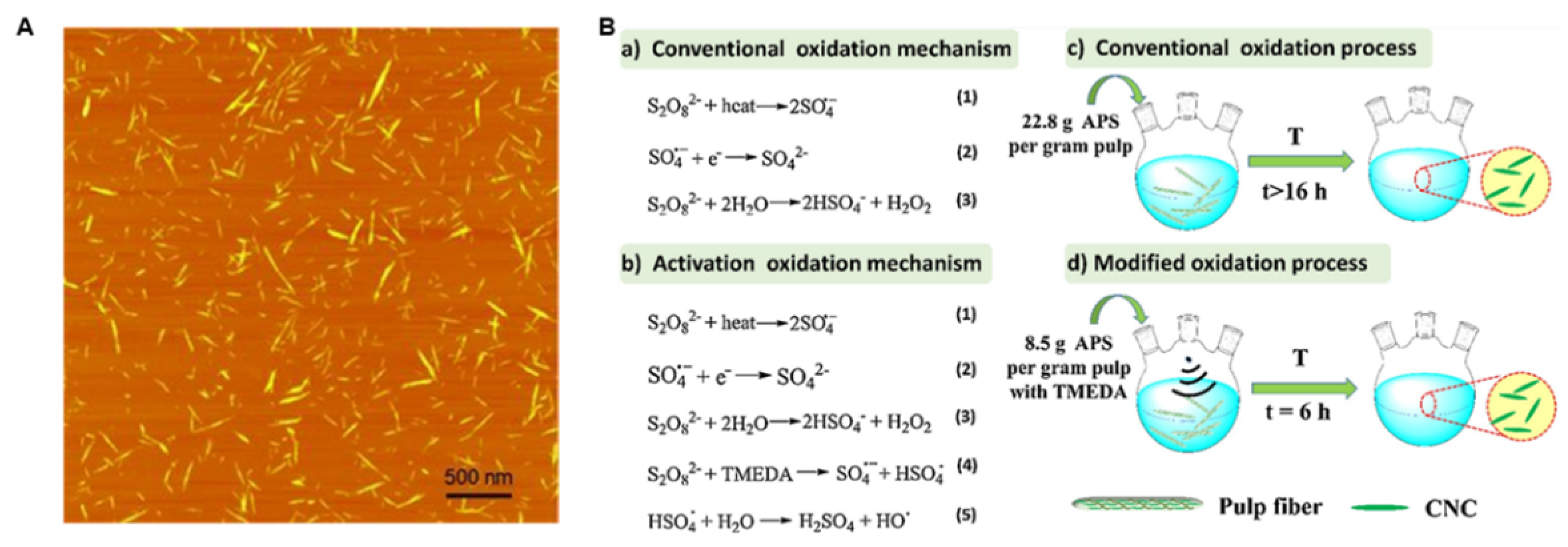
| TEMPO Oxidation | TEMPO/NaClO2 oxidation ultrasonic crushing | Very high (>150, nanofibers) | Biomedical vectors (Targeted Delivery), conductive hydrogel electrodes | High carboxyl content (easy functionalization), excellent dispersibility | Expensive oxidant, over-oxidation/chain scission risk | [20] |
| Mechanical methods | High-pressure homogenization/ball mill, deep delignification pretreatment | Low crystallinity (40–60%), wide size distribution (50–1000 nm) | Rheology Modifiers (Coatings/Food), Aerogel insulation | Green and environmentally friendly, process is safe and non-toxic | Poor uniformity, poor stability, and low efficiency | [18] |
2. CNCs Surface Modification Strategies and Their Effects on Hydrogel Properties
2.1. Surface Modification of CNC
| Modification Type | Modification Method | Method Description | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages | Performance Impact | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Modification | |||||||
| Surfactant Adsorption | Cationic (CTAB), nonionic (PEG) adsorption via electrostatic/hydrophobic interactions | Improves hydrophobicity; enhances polymer compatibility | Drug carriers (hydrophobic drugs); composite compatibilizers | Simple operation, reversible; preserves CNC crystal structure | Weak bonding (easy desorption); poor thermal stability | Dispersibility significant improvement; interfacial compatibility improvement; thermal stability reduction | [49,50] |
| Plasma Treatment | O2, N2 plasma treatment | Introduces polar groups (-COOH, -OH); increases surface roughness | Enhanced composite interfaces; biomedical scaffolds | Eco-friendly (solvent-free); uniform surface modification | High equipment costs; over-treatment may damage CNC structure | Surface activity improvement; interfacial adhesion improvement; thermal stability no change | [51,52] |
| Ultrasound-Assisted Dispersion | High-energy ultrasound deagglomeration | Improves CNC dispersion in solvents/matrices | Nanocomposite dispersion; Pickering emulsion stabilizers | Rapid and efficient; preserves chemical integrity | Prolonged ultrasound reduces aspect ratio; high energy consumption | Dispersibility significant improvement; aspect ratio reduction; crystallinity no change | [11] |
| Chemical Modification | |||||||
| Esterification | Reaction with anhydrides (acetic/EDTA dianhydride) or acyl chlorides | Introduces hydrophobic chains or carboxyl groups | Hydrophobic composites; fluorescent material carriers; flame retardants | Controllable DS (0–63%); dramatically improves organic solvent dispersion | Strong acids/high temperatures may reduce crystallinity; organic solvent pollution | Hydrophobicity improvement; thermal stability improvement; functional sites | [53] |
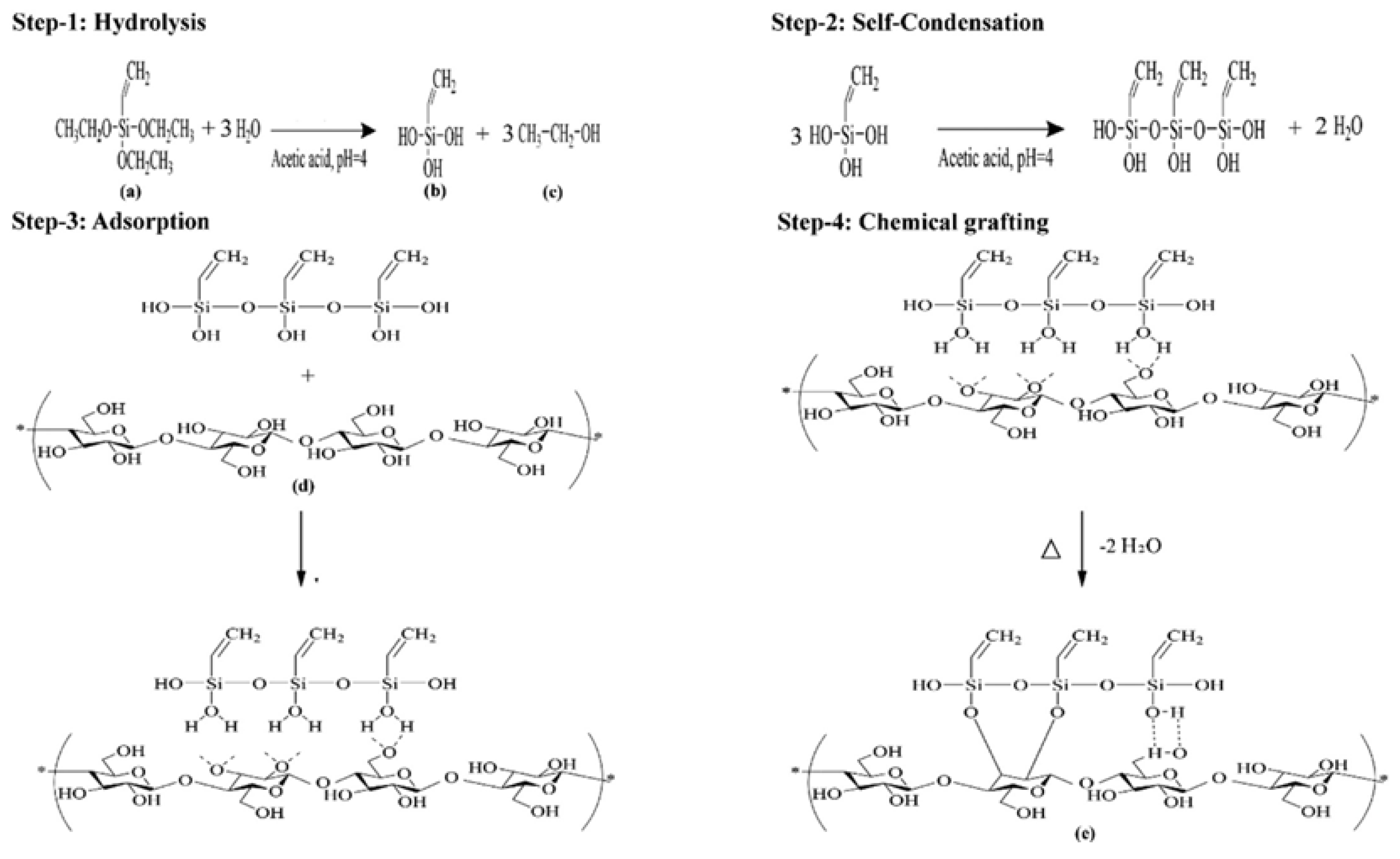
| Silanization | Hydrolysis-condensation of alkoxysilanes (APTES, GPTMS) | Introduces alkyl chains or epoxy groups | Rubber/epoxy reinforcement; sensors | Enhanced thermal stability; provides reactive functional groups | Multi-step reaction; solvent exchange challenges | Thermal stability: Si-O bonds resist high temperatures (>300 °C); interfacial strength improvement; Dispersibility improvement organic compatibility | [54,55] |
| TEMPO Oxidation | NaClO/NaBr/TEMPO system oxidizes C6-OH to -COOH | High-density carboxylation (>1.5 mmol/g) | Metal ion carriers; fluorescent material templates | Mild reaction (pH 10); carboxyl groups enable further functionalization | May cause cellulose chain scission; expensive reagents | Colloidal stability improved; Reactivity: carboxyl supports amidation/esterification; crystallinity (5–10%) | [56] |
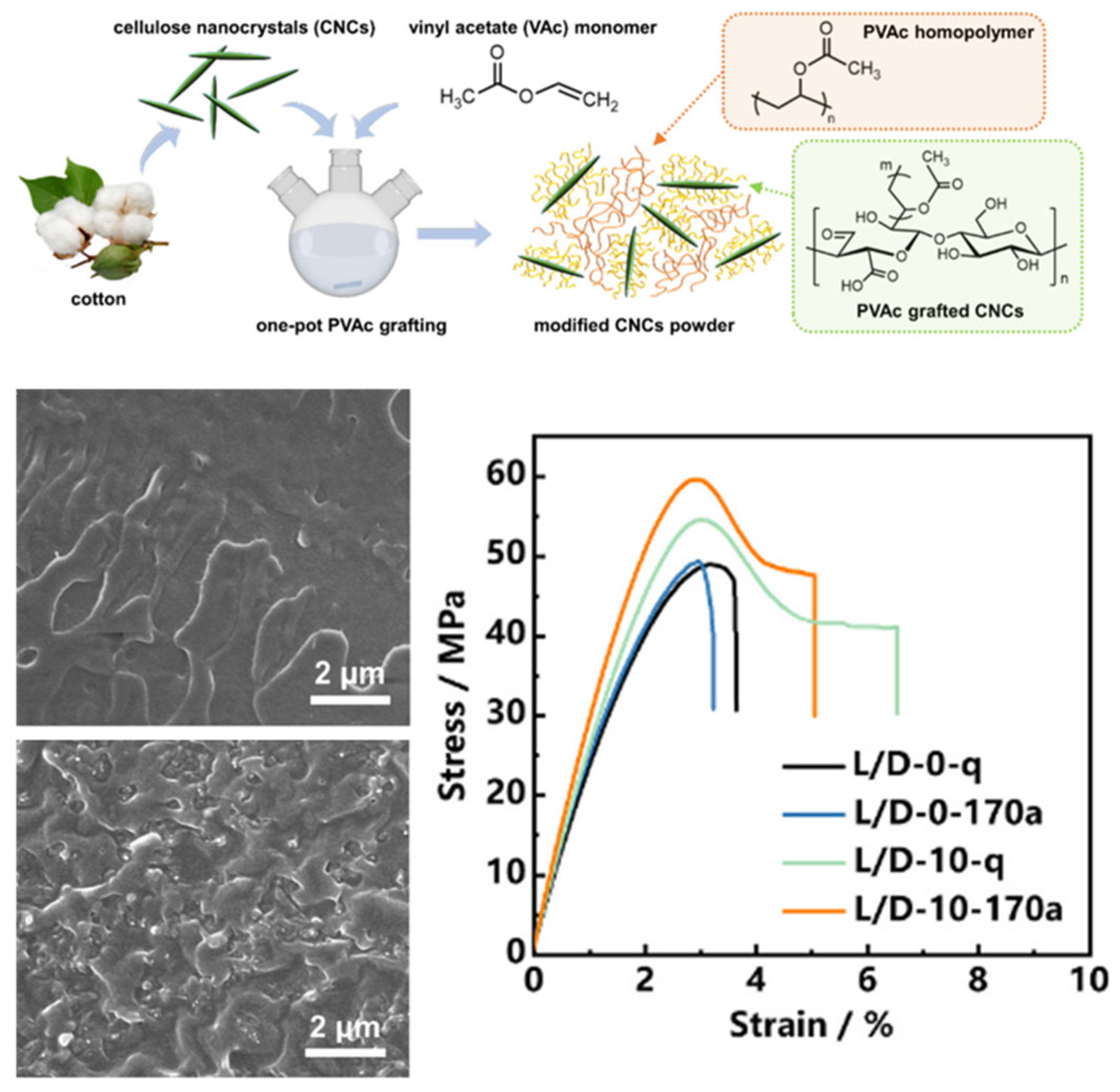
| Polymer Grafting | Grafting to: Pre-synthesized polymers (PCL, PEG) coupled to CNCs; Grafting from: ATRP/RAFT polymerization initiated from CNC surface | Core-shell structures or interpenetrating networks | High-toughness composites; stimuli-responsive gels | High grafting density (“grafting from”); controllable molecular weight | Steric hindrance limits “grafting onto”; complex initiator modification required for “grafting from” | Toughness improved; thermal stability: Polymer layers protect CNCs; dispersibility well | [57,58] |
| Biological Modification | |||||||
| Enzymatic Hydrolysis | Cellulase selectively hydrolyzes amorphous regions | Green CNC preparation | Food packaging; biocompatible materials | Eco-friendly (aqueous phase); mild conditions | Low yield (<30%); slow reaction (>48 h) | Crystallinity > 80%; Size uniformity improvement; thermal stability: Tmax > 300 °C | [59] |
| Enzyme-Assisted Assembly | Laccase/peroxidase modifies surface groups | Enhances interfacial bonding or functionality | Biosensors; tissue engineering scaffolds | High selectivity; excellent biocompatibility | High enzyme cost; complex process | Bioactivity; interfacial bonding improvement | [53] |
2.2. Effect of CNC on Hydrogel Properties
2.2.1. Physical Blending for Improved Mechanical Properties
2.2.2. Chemical Grafting for Hydrogel Functionalization
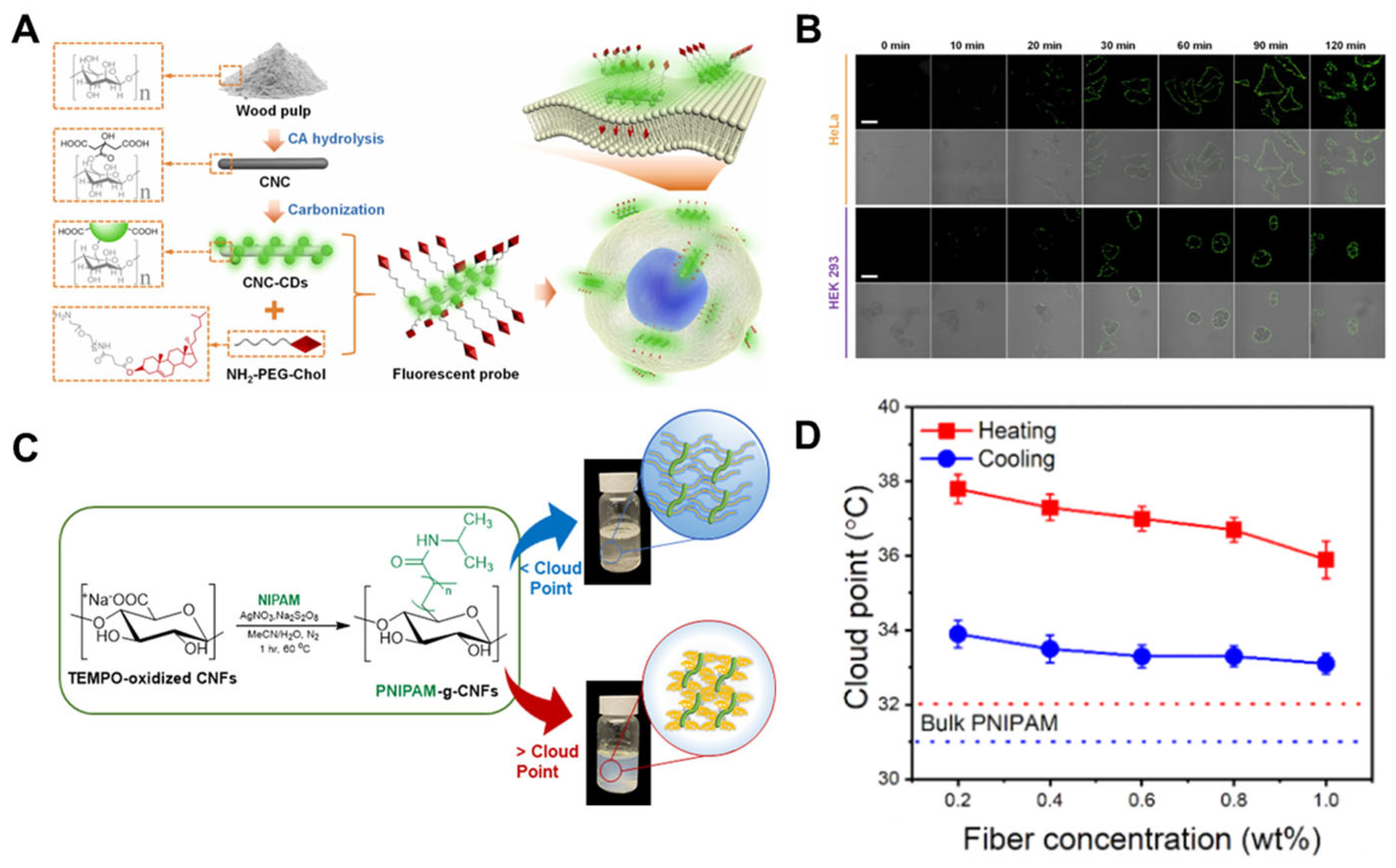
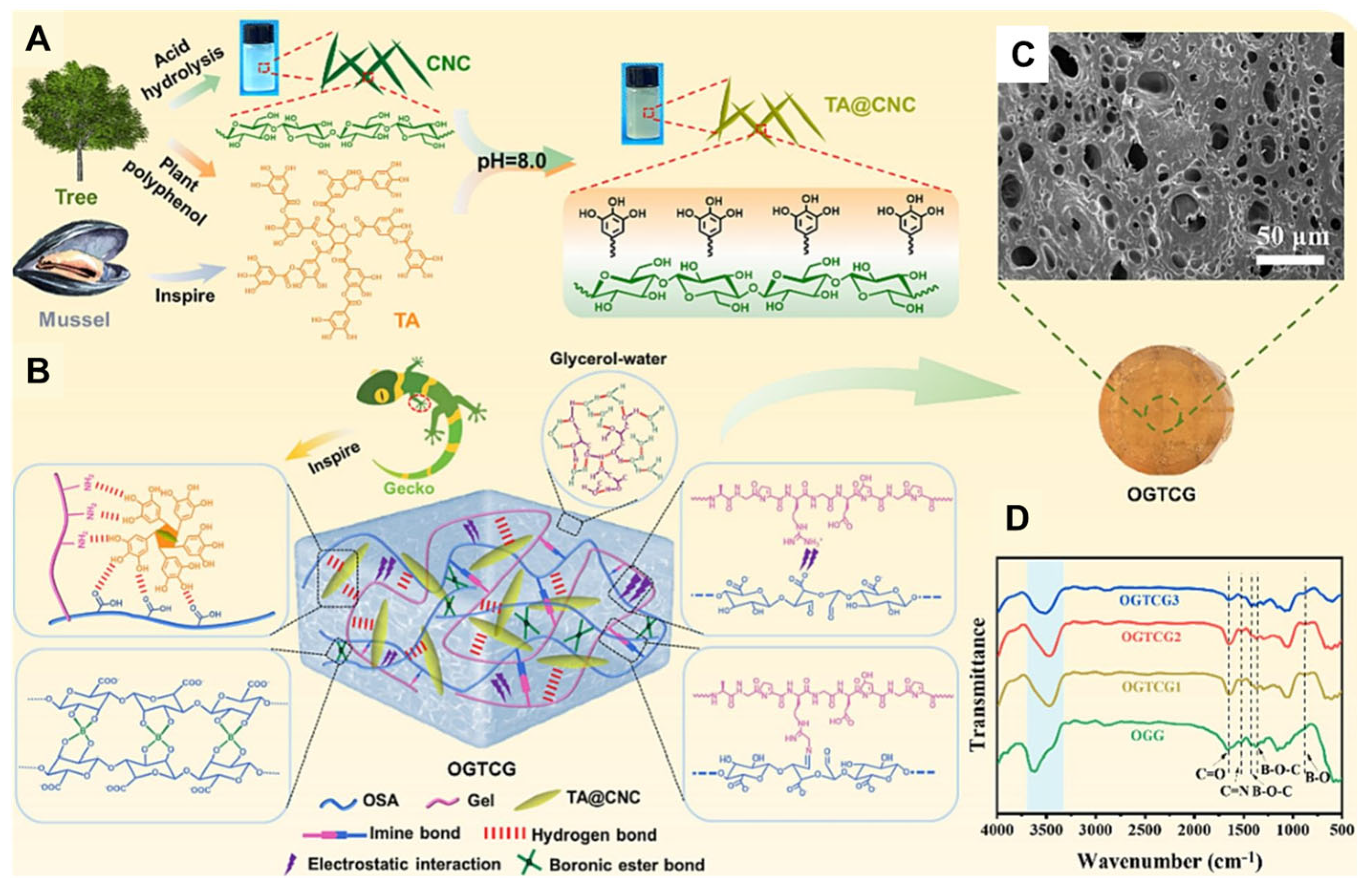
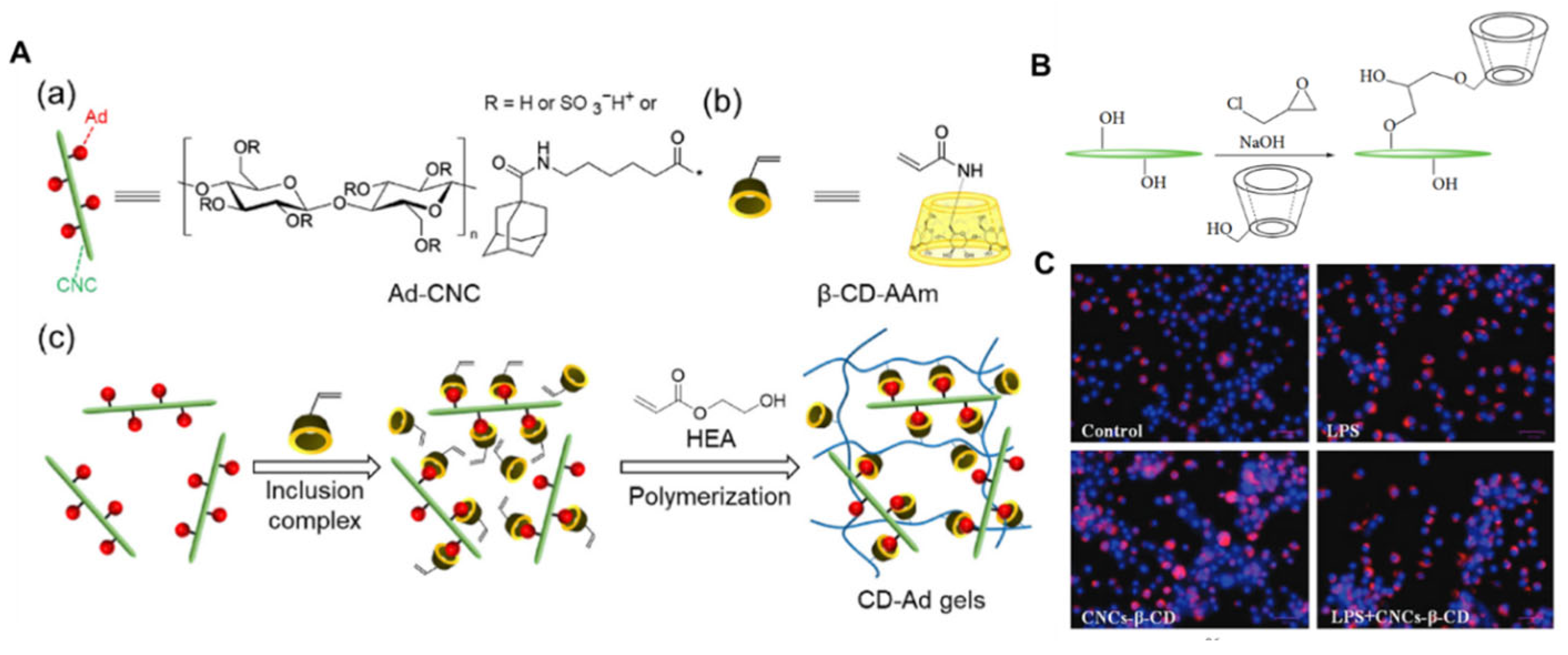
2.2.3. CNC-Hybridized Hydrogels for Biofunctionalization
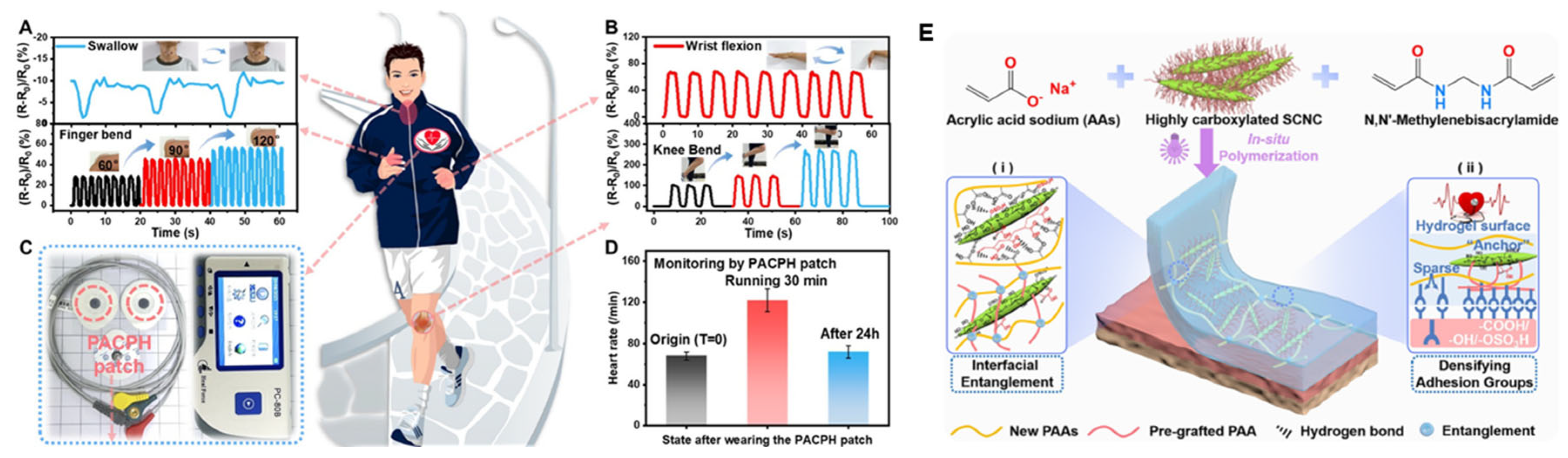
3. Bioinspired Structural Design and Intelligent Actuation Behavior
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ionov, L. Hydrogel-based actuators: Possibilities and limitations. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Nelson, B.J.; Yang, G.-Z. New materials for next-generation robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaau0448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Q. Fabricating water-resistant and stimuli responsive smart hydrogels via iminoboronate chemistry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2411234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Li, G. Photo-dissociable Fe3+-carboxylate coordination: A general approach toward hydrogels with shape programming and active morphing functionalities. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 59310–59319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Javaid, M.U.; Pan, C.; Yu, G.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Self-healing stimuli-responsive cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Akkus, O.; Liu, H.; Cao, C. Bio-inspired anisotropic hydrogels and their applications in soft actuators and robots. Matter 2023, 6, 3803–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, C.; Brozena, A.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Xu, L.; Driemeier, C.; Dai, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Isogai, A.; Wågberg, L.; et al. Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 2021, 590, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinchi, L.; Cotana, F.; Fortunati, E.; Kenny, J.M. Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: Technology and applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Saito, T.; Bergström, L.; Isogai, A. Acid-free preparation of cellulose nanocrystals by TEMPO oxidation and subsequent cavitation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, S.; Ge, S.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Green preparation and characterization of size-controlled nanocrystalline cellulose via ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 83, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Hsieh, Y. Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: Rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck-Candanedo, S.; Roman, M.; Gray, D.G. Effect of reaction conditions on the properties and behavior of wood cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarero Espinosa, S.; Kuhnt, T.; Foster, E.J.; Weder, C. Isolation of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals by phosphoric acid hydrolysis. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.; Sattler, S.; Reza, M.; Bismarck, A.; Kontturi, E. Cellulose nanocrystals by acid vapour: Towards more effortless isolation of cellulose nanocrystals. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 202, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Liu, Y. Two characteristic cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) obtained from oxalic acid and sulfuric acid processing. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8351–8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Okita, Y.; Nge, T.T.; Sugiyama, J.; Isogai, A. TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose: Microscopic analysis of fibrous fractions in the oxidized products. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, R.; Tarrés, Q.; Pèlach, M.À.; Mutjé, P.; de la Fuente, E.; Sanchez-Salvador, J.L.; Negro, C.; Delgado-Aguilar, M. Micro- and nanofibrillated cellulose from annual plant-sourced fibers: Comparison between enzymatic hydrolysis and mechanical refining. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pääkkönen, T.; Spiliopoulos, P.; Nonappa; Kontturi, K.S.; Penttilä, P.; Viljanen, M.; Svedström, K.; Kontturi, E. Sustainable high yield route to cellulose nanocrystals from bacterial cellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14384–14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Ni, S.; Rosqvist, E.; Smått, J.; Peltonen, J.; Hou, Q.; Qin, M.; Willför, S.; et al. From biomass to nanomaterials: A green procedure for preparation of holistic bamboo multifunctional nanocomposites based on formic acid rapid fractionation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6592–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynam, J.G.; Kumar, N.; Wong, M.J. Deep eutectic solvents’ ability to solubilize lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose; thermal stability; and density. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Holbery, J.; Li, K. A technique for production of nanocrystalline cellulose with a narrow size distribution. Cellulose 2009, 16, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Balakrishnan, P.; Chandradhara, D.; Poovathankandy, D.; Thomas, S. General scenarios of cellulose and its use in the biomedical field. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 13, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, I.; Chow, W.S. Synthesis of phosphoric acid-treated sugarcane bagasse cellulose nanocrystal and its thermal properties enhancement for poly(lactic acid) nanocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019, 32, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.C.W.; Hrapovic, S.; Lam, E.; Liu, Y.L.; Male, K.B.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Luong, J.H.T. Characteristics and properties of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals prepared from a novel one-step procedure. Small 2011, 7, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, H.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Modified ammonium persulfate oxidations for efficient preparation of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’acierno, F.; Capron, I. Modulation of surface properties of cellulose nanocrystals through adsorption of tannic acid and alkyl cellulose derivatives. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 319, 121159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Johnstone, T.; Quinn, T.M.; Gray, D.G. Reinforcement with cellulose nanocrystals of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by cyclic freezing and thawing. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Huang, J.; Chang, P.R.; Feng, J.; Yu, J. Surface acetylation of cellulose nanocrystal and its reinforcing function in poly (lactic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Sun, X.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Yang, P.; Zhu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, F. A universal strategy to mitigate microphase separation via cellulose nanocrystal hydration in fabricating strong, tough, and fatigue-resistant hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2024, 37, 2416916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rol, F.; Belgacem, M.N.; Gandini, A.; Bras, J. Recent advances in surface-modified cellulose nanofibrils. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Hart, P.; Thakur, V.K. Cellulose-alginate hydrogels and their nanocomposites for water remediation and biomedical applications. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Duan, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, B.; Yang, H.; Hu, N.; Zhong, Q.; Shi, L.; Qi, D. Enhancement of mechanical properties in reactive polyurethane film via in-situ assembly of embedded cellulose nanocrystals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuello, C.; Foulon, L.; Chabbert, B.; Molinari, M.; Aguié-Béghin, V. Langmuir-blodgett procedure to precisely control the coverage of functionalized AFM cantilevers for SMFS measurements: Application with cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9376–9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, K.; Delepierre, G.; King, A.W.T.; Kostiainen, M.A.; Zoppe, J.; Weder, C.; Kontturi, E. Chemical modification of reducing end-Groups in cellulose nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 60, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Way, A.E.; Hsu, L.; Shanmuganathan, K.; Weder, C.; Rowan, S.J. pH-responsive cellulose nanocrystal gels and nanocomposites. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ji, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Xue, Y. Synthesis and characterization of aminosilane grafted cellulose nanocrystal modified formaldehyde-free decorative paper and its CO2 adsorption capacity. Polymers 2019, 11, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, G. Grafting polymers from cellulose nanocrystals via surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hua, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of stereocomplex-type poly (lactic acid) nanocomposites based on the selective nucleation of poly (vinyl acetate) modified cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 347, 122716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Highly efficient grafting of polyvinyl acetate onto cellulose nanocrystals in the aqueous phase. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 3027–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Nidetzky, B. Precision synthesis of reducing-end thiol-modified cellulose enabled by enzyme selection. Polym. J. 2021, 54, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Fujinami, S.; Hoshino, T.; Kamio, E.; Matsuyama, H. Energy dissipation the internal fracture of the silica particle network in inorganic/organic double network ion gels. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.; Siow, L.; Chan, E.; Tey, B.; Lee, Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of palm cellulose to yield nanocrystals with potential roles in lipid and cholesterol digestion and absorption. Cellulose 2025, 32, 1575–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Male, K.B.; Chong, J.H.; Leung, A.C.W.; Luong, J.H.T. Applications of functionalized and nanoparticle-modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, J. Biological-chemical modification of cellulose nanocrystal to prepare highly compatible chitosan-based nanocomposites. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5267–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lindström, M.E.; Li, J. Tunicate cellulose nanocrystals: Preparation, neat films and nanocomposite films with glucomannans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neisi, E.; Dadkhah Tehrani, A.; Shamloei, H.R. Development of cellulose nanowhisker–gallic acid antioxidant bioconjugate via covalent conjugation and supramolecular interactions: A comparative study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Liu, L.; Cao, H.; Lu, B.; Nie, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; An, X. Polydopamine modified cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) for efficient cellulase immobilization towards advanced bamboo fiber flexibility and tissue softness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abitbol, T.; Marway, H.; Cranston, E.D. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nord. Pulp. Pap. Res. J. 2014, 29, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.K.; Letchford, K.; Wasserman, B.Z.; Ye, L.; Hamad, W.Y.; Burt, H.M. The use of nanocrystalline cellulose for the binding and controlled release of drugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Panaitescu, D.M.; Vizireanu, S.; Nicolae, C.A.; Frone, A.N.; Casarica, A.; Carpen, L.G.; Dinescu, G. Treatment of Nanocellulose by Submerged Liquid Plasma for Surface Functionalization. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanis, A.; Valdés, J.H.; María Guadalupe, N.-V.; Lopez, R.; Mendoza, R.; Mathew, A.P.; Díaz de León, R.; Valencia, L. Plasma surface-modification of cellulose nanocrystals: A green alternative towards mechanical reinforcement of ABS. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 17417–17424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Gan, L.; Huang, J. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals towards new materials development. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Behrooz, R.; Bahramifar, N.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Bacher, M.; Edler, M.; Griesser, T. Surface chemical functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, A.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Functionalized cellulose nanocrystals as biobased nucleation agents in poly (l-lactide) (PLLA)-Crystallization and mechanical property effects. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogai, A.; Hänninen, T.; Fujisawa, S.; Saito, T. Review: Catalytic oxidation of cellulose with nitroxyl radicals under aqueous conditions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 86, 122–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, A.L.; Raquez, J.M.; Duquesne, E.; Siqueira, G.; Habibi, Y.; Dufresne, A.; Dubois, P. Poly (ɛ-caprolactone) based nanocomposites reinforced by surface-grafted cellulose nanowhiskers via extrusion processing: Morphology, rheology, and thermo-mechanical properties. Polymer 2011, 52, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzior, S.A.; Zoppe, J.O.; Berry, R.M.; Cranston, E.D. Recent advances and an industrial perspective of cellulose nanocrystal functionalization through polymer grafting. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltramino, F.; Blanca Roncero, M.; Vidal, T.; Valls, C. A novel enzymatic approach to nanocrystalline cellulose preparation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kim, S.H.; Sun, F.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; Diao, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Li, R.; et al. Bio-inspired hydrogen bonding cross-linking strategy for DIW-printed carbon-based conductive hydrogels in wearable self-powered sensing systems. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2025, 7, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.S.; Ludueña, L.N.; Ponce, A.; Alvarez, V.A. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/cellulose nanowhiskers nanocomposite hydrogels for potential wound dressings. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Z.; Pei, Z.; Ma, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wei, D. Self-healing nanocomposite hydrogels based on modified cellulose nanocrystals by surface-initiated photoinduced electron transfer ATRP. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5305–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-rocha, O.L.; Campbell, S.; Woodcock, N.; Pinaud, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Champagne, P.; Cunningham, M.F. Non-covalent polymer surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals using block copolymers. Macromol. React. Eng. 2022, 16, 2100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhali, K.; Daver, F.; Cass, P.; Adhikari, B. Surface modification of the cellulose nanocrystals through vinyl silane grafting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 200, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Thakur, V.K. Surface modification of cellulose using silane coupling agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, R.S.; Das, P. Bioinspired nanocomposites of sodium carboxymethylcellulose and polydopamine-modified cellulose nanocrystals for UV-protective packaging. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 16580–16594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, F.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.; Sun, R.; Liu, C.; Xiao, H. A cellulose nanocrystal-carbon dots@cholestrol fluorescent probe for imaging of plasma membrane with extended time scale. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2024, 405, 135371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.J.; Ayurini, M.; Browne, C.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Simon, G.P.; Hooper, J.F.; Garnier, G. Thermoresponsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) grafted from cellulose nanofibers via silver-promoted decarboxylative radical polymerization. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 1610–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, X.; Yue, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, L. Antifreeze proteins and surface-modified cellulose nanocrystals for designing anti-freezing conductive hydrogel sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 350, 123056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, H.; Ding, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Tao, K.; Xie, X.; Wu, J. Hydrogel- and organohydrogel-based stretchable, ultrasensitive, transparent, room-temperature and real-time NO2 sensors and the mechanism. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1921–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Lin, R.; Tang, C.; Jing, X. Tannic acid-coated cellulose nanocrystal-reinforced transparent multifunctional hydrogels with UV-filtering for wearable flexible sensors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 323, 121385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myat, M.N.; Sugawara, A.; Asoh, T.-A.; Takashima, Y.; Harada, A.; Uyama, H. Composite hydrogels with host–guest interaction using cellulose nanocrystal as supramolecular filler. Polymer 2023, 277, 125979. [Google Scholar]
- Sunasee, R.; Carson, M.; Despres, H.W.; Pacherille, A.; Nunez, K.D.; Ckless, K. Analysis of the immune and antioxidant response of cellulose nanocrystals grafted with β-cyclodextrin in myeloid cell lines. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 4751827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, A.; Hu, H.; Ye, T.; Ding, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Wu, J.; et al. Deep-learning enabled active biomimetic multifunctional mydrogel electronic skin. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 16160–16173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
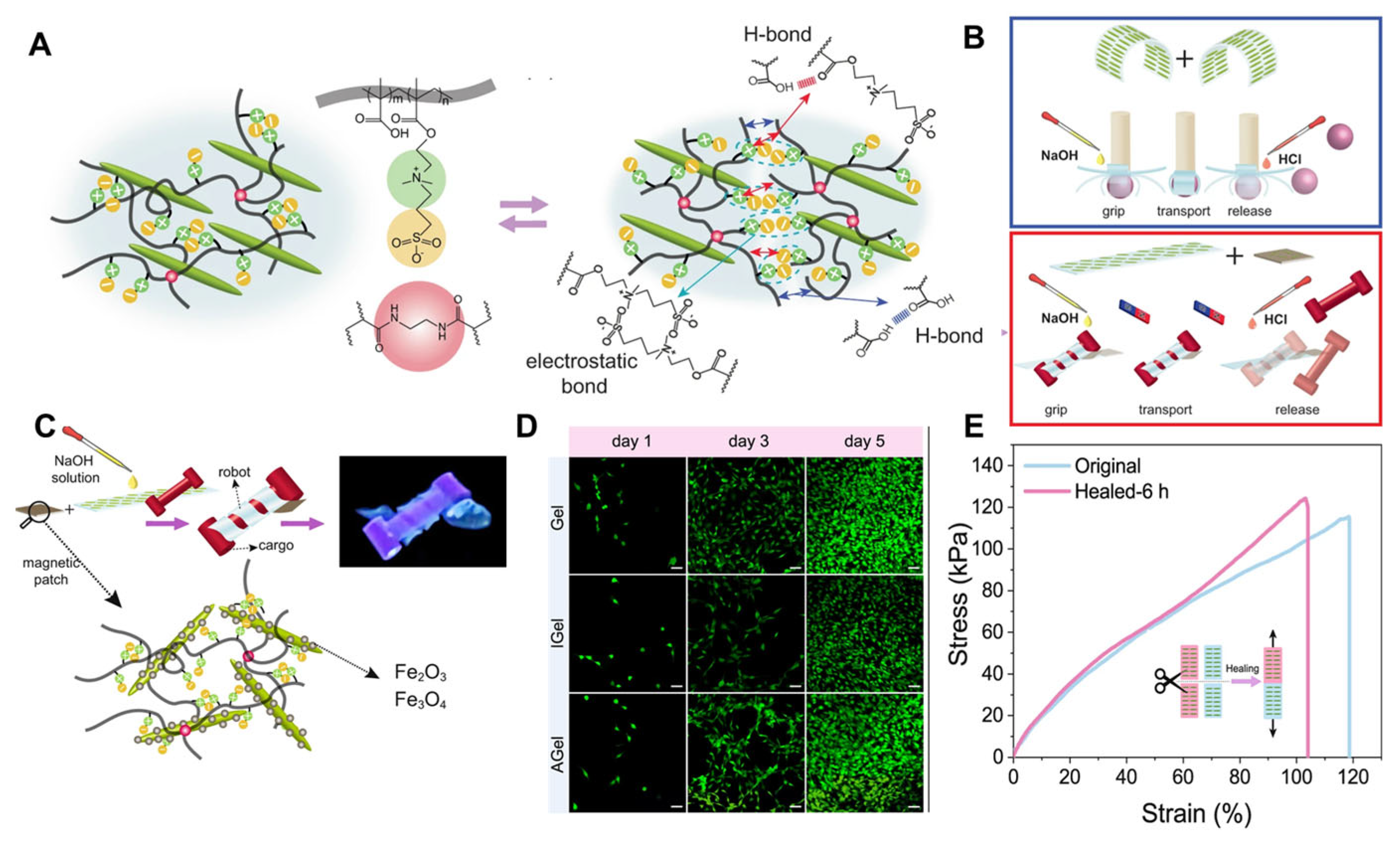
- Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zong, L. Fabrication of a tough, long-lasting adhesive hydrogel patch via the synergy of interfacial entanglement and adhesion group densification. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
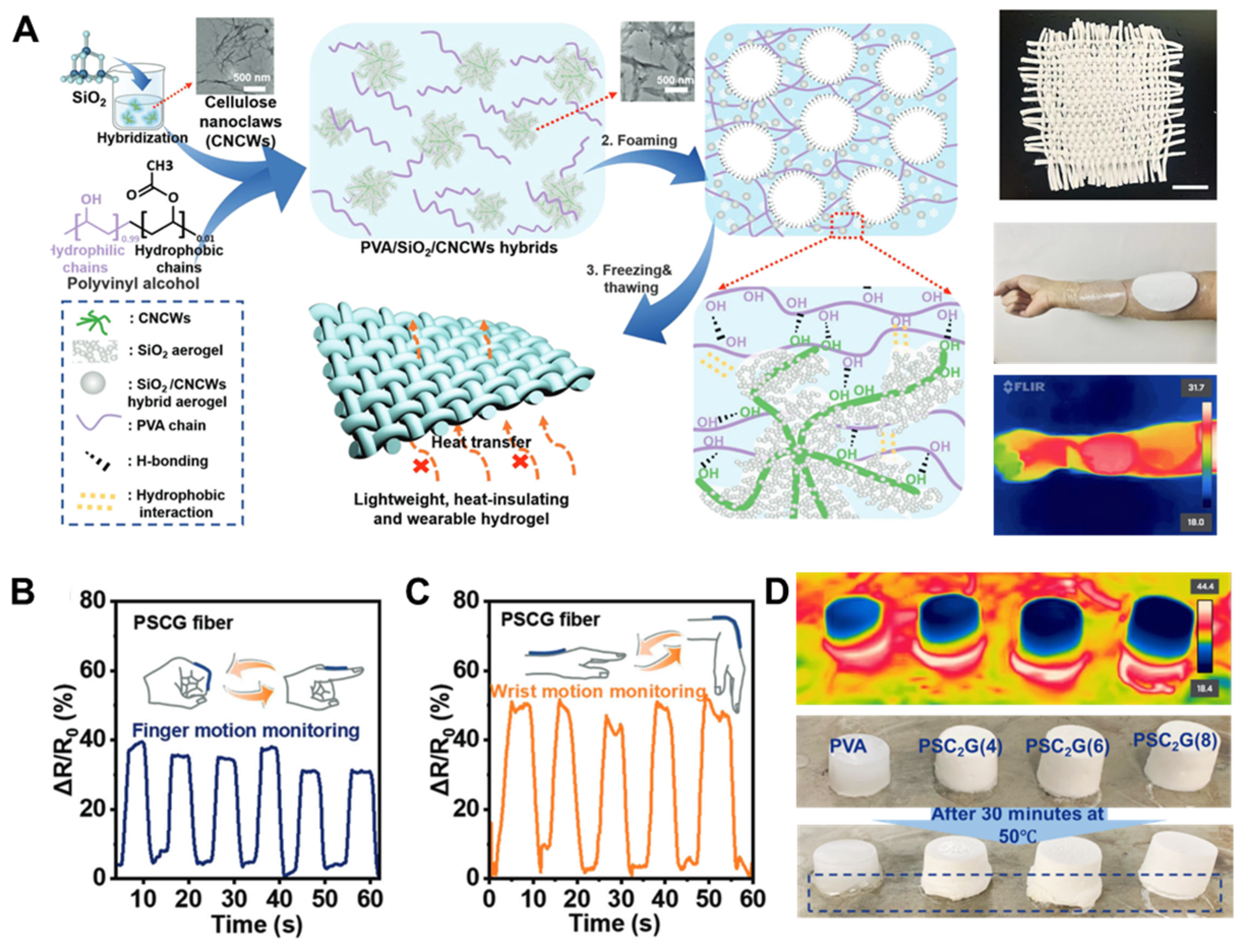
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zong, L. Ultralight, heat-insulated, and tough PVA hydrogel hybridized with SiO2@cellulose nanoclaws aerogel via the synergy of hydrophilic and hydrophobic interfacial interactions. Small 2023, 19, 2303044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zong, L. Biomimetic multiscale oriented PVA/NRL hydrogel enabled multistimulus responsive and smart shape memory actuator. Small 2024, 20, e2311240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Du, J.; Mao, Y. Hydrogel-based continuum soft robots. Gels 2025, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J. Naturally sourced hydrogels: Emerging fundamental materials for next-generation healthcare sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2992–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Mao, Y.; Zheng, T.; Cui, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, T.; Chang, C. Electric field-induced dual-gradient heterojunction diodes toward ultrasensitive self-towered ionic skin. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, e2500949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wu, P. A supramolecular biomimetic skin combining a wide spectrum of mechanical properties and multiple sensory capabilities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.L.; Du, C.; Dai, Y.; Daab, M.; Matejdes, M.; Breu, J.; Hong, W.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Light-steered locomotion of muscle-like hydrogel by self-coordinated shape change and friction modulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.Y.; Zhu, Q.L.; Cheng, H.L.; Wen, X.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Muscle-like hydrogels with fast isochoric responses and their applications as soft robots: A minireview. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, L.E.; Garbonova, G.; Pfukwa, R.; Klumperman, B. Synthesis of thermoresponsive PNIPAm-b-PVP-b-PNIPAm hydrogels via aqueous RAFT polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 3569–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabpour, Z.; Abedi, F.; Salehi, M.; Baharnoori, S.M.; Soleimani, M.; Djalilian, A.R. Hydrogel-based skin regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chang, C. Triple physically cross-linked hydrogel artificial muscles with high-stroke and high-work capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, D.; Gong, C.; Chang, C. Bioinspired shape memory hydrogel artificial muscles driven by solvents. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13712–13720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
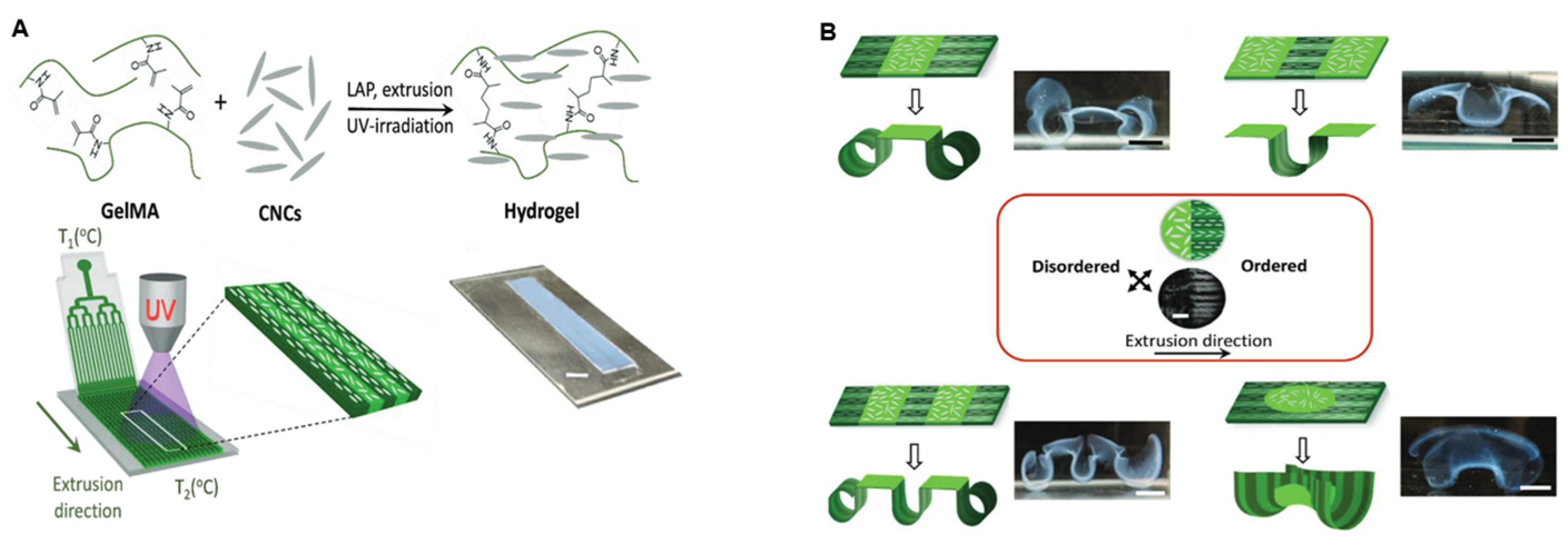
- Müller, L.A.E.; Zingg, A.; Arcifa, A.; Zimmermann, T.; Nyström, G.; Burgert, I.; Siqueira, G. Functionalized cellulose nanocrystals as active reinforcements for light-actuated 3D-printed structures. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 18210–18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chiappone, A.; Roppolo, I.; Shao, F.; Fantino, E.; Lorusso, M.; Rentsch, D.; Dietliker, K.; Pirri, C.F.; Grützmacher, H. All-in-one cellulose nanocrystals for 3D printing of nanocomposite hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorkian, A.; Morozova, S.M.; Kheiri, S.; Khuu, N.; Chen, H.; Young, E.; Yan, N.; Kumacheva, E. Actuation of three-dimensional-printed nanocolloidal hydrogel with structural anisotropy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseri, R.; Bouzari, N.; Huang, J.; Golzar, H.; Jankhani, S.; Tang, X.; Mekonnen, T.H.; Aghakhani, A.; Shahsavan, H. Programmable nanocomposites of cellulose nanocrystals and zwitterionic hydrogels for soft robotics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Pressure/temperature dual-responsive cellulose nanocrystal hydrogels for on-demand schemochrome patterning. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
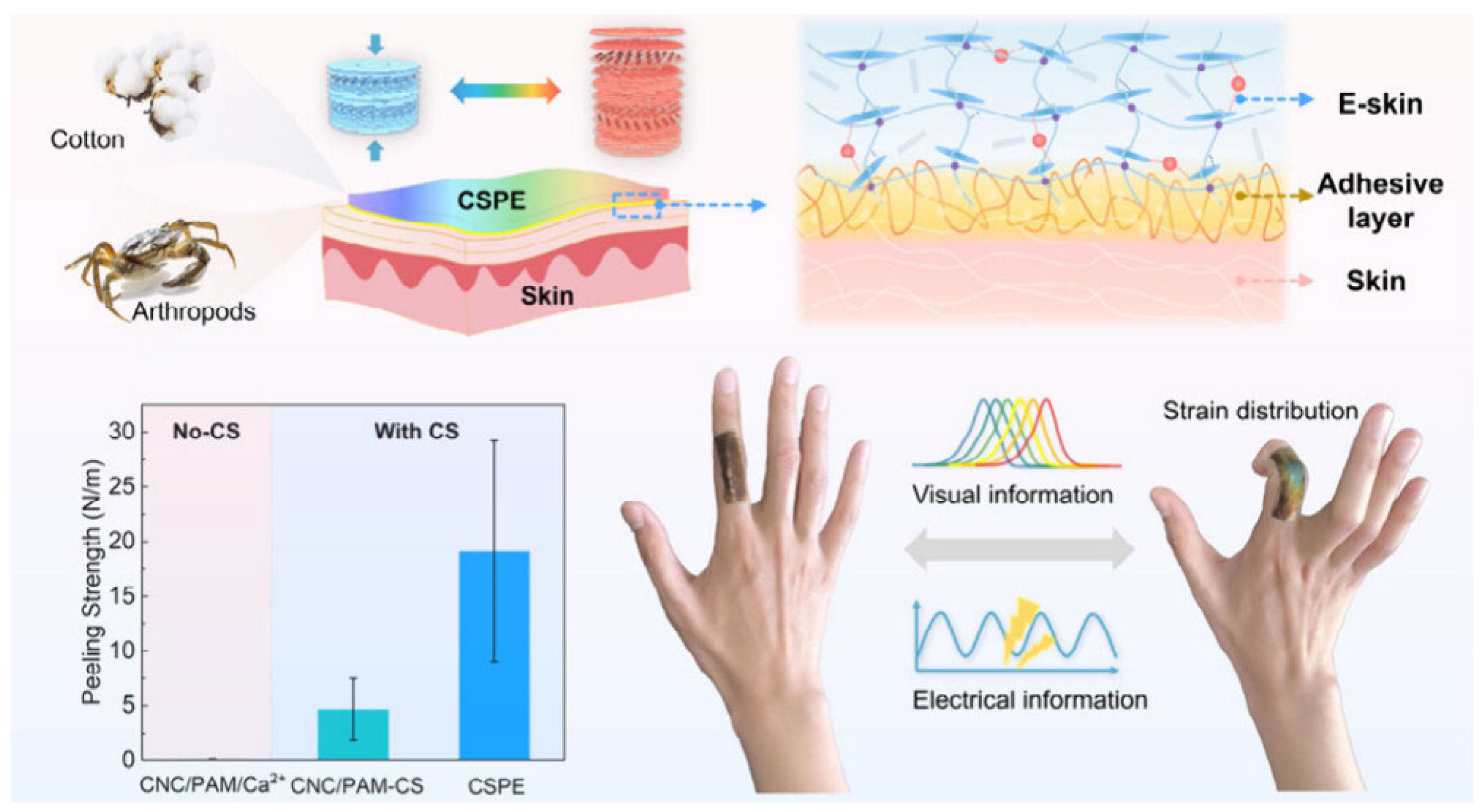
- Wang, X.; Geng, M.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, M. Skin-Adherent, Cellulose-Based Photonic Patch for Visual Strain Mapping. ACS Mater. Lett. 2025, 7, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Zong, L. Biomimetic Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Surface Modification and Smart Soft Actuator Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130996
Cui Y, Wang Z, Zhao M, Wang Z, Zong L. Biomimetic Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Surface Modification and Smart Soft Actuator Applications. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130996
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yuzhu, Zekai Wang, Mingliang Zhao, Zhihui Wang, and Lu Zong. 2025. "Biomimetic Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Surface Modification and Smart Soft Actuator Applications" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130996
APA StyleCui, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, M., Wang, Z., & Zong, L. (2025). Biomimetic Cellulose Nanocrystals Composite Hydrogels: Recent Progress in Surface Modification and Smart Soft Actuator Applications. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130996







