Recent Advances on the Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Through Interfacial Polymerization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Evaluation Parameters for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Effectiveness
3. Strategies of Positively-Charged NF Membrane by Interfacial Polymerization
3.1. Monomer Engineering
3.2. Additive Incorporation
3.3. Surface Modification
| Membrane | Mixture Concentration (ppm) | RMg2+ (%) | RLi+ (%) | MLR | PWP (LMH/bar) | SLi,Mg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSf/PEI/TMC/QTHIM | 2000 | 92.2 | 46.0 | - | 32.5 | 4.5 | [91] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/QBPD | 2000 | 94.7 | 37.0 | 50 | 13.6 | 5.9 | [92] |
| PAN/PIP/TMC/[MimAP][TFf2N] | 2000 | 81.9 | −45.2 | 20 | 6.3 | 8.1 | [89] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/HMTAB | 2000 | 93.9 | 37.0 | 50 | 16.3 | 10.2 | [93] |
| PES/PEI/TMC/TQAIL | 10,500 | 92.8 | 26.6 | - | 22.2 | 10.5 | [94] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/DETA | - | 93.9 | 31.0 | 24 | 2.8 | 11.4 | [90] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/PEI | 2000 | - | - | 150 | 8.3 | 12.3 | [85] |
| PES/PEI/TMC/DABIL | 10,500 | 91.0 | 18.6 | - | 16.9 | 12.9 | [95] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/Cyclen | 2000 | 86.3 | 50.7 | 20 | 1.3 | 15.3 | [96] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/QEDTP | 2000 | 95.0 | 55.0 | 120 | 21.0 | 15.6 | [28] |
| PES/PIP/TMC/ARG | 2000 | 91.5 | 9.5 | 20 | 47.0 | 17.1 | [97] |
| PES/PIP-HMAH/TMC/ATA | 2000 | 95.7 | 18.1 | 20 | 9.4 | 19.2 | [98] |
| PES/PIP/TMC/Am-CDs | 2000 | - | - | 20 | 3.8 | 21.4 | [99] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/QTHEED | 2000 | 94.3 | −22.8 | 60 | 23.1 | 21.7 | [100] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/DCA | 1000 | 96.0 | 37.0 | 20 | 10.9 | 23.3 | [101] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/1-AI | 2000 | 97.1 | - | 20 | 19.8 | 27.7 | [30] |
| PES/SWCNT-PDA/PIP/TMC/PEI | 2000 | 98.5 | 46.2 | 20 | 7.4 | 35.9 | [102] |
| PES/PEI/TMC/DHTAB | 2000 | 95.4 | 65.4 | - | 6.7 | 58.0 | [103] |
| PES, PSf/PA/G-AS-Fe | 2000 | 86.6 | 22.7 | 20 | 55.7 | 81.5 | [104] |
| PAN/PEI/TMC/BTPB | 2000 | 98.9 | 30.6 | - | ~50.0 | 81.6 | [105] |
| PAN/PEI/TMC/BTAB | 2000 | 99.2 | ~30.0 | 20 | 50.0 | 95.9 | [106] |
| PES/PEI/TMC/PEI | 2000 | 99.5 | - | 50 | 2.1 | 150.0 | [88] |
| PAN/PEI/TMC/TC | 2000 | 99.1 | 30.6 | 20 | ~37.0 | 167.0 | [107] |
| PSf/PEI/TMC/SBI | 2000 | 91.0 | 46.4 | 100 | 16.0 | / | [108] |
3.4. Interlayer Integration
| Membrane | Mixture Concentration (ppm) | RMg2+ (%) | RLi+ (%) | MLR | PWP (LMH/bar) | SLi,Mg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSF/ZIF-8/PA | 2000 | 97.3 | 43.0 | - | 21.8 | 4.0 | [109] |
| PSf/UIO-66-NH2/PA | 2000 | 97.0 | 35.9 | 15.3 | - | 32.2 | [110] |
| PES/zwitterion-g-C3N4/PA | 2000 | 97.9 | ~30.0 | 48 | 9.1 | 37.8 | [111] |
| PSf/CP8/PA | 2000 | 98.5 | 13.9 | 8.1 | 39.0 | [112] | |
| PES/PIP/SDS/TMC | 2000 | 96.8 | 37.8 | - | 11.0 | 42.1 | [113] |
| PSf/160A/PA | 2000 | 98.2 | ~25.0 | 7.5 | - | 45.8 | [114] |
| PSf/polyphenol-PEI/PA | 2000 | 93.6 | 28.8 | - | 18.6 | 50.7 | [107] |
| PSf-NoriaPG-PEI/PA | 2000 | 98.5 | - | 30.9 | 22.5 | 88.6 | [115] |
| PSf/RA-PEI/PA | 2000 | 93.6 | 28.8 | 20 | 16.7 | 92.8 | [116] |
- (i)
- Compared to traditional hydrophobic porous substrates, the hydrophilic interlayer is conducive to the adsorption of amine monomers at the interface, thereby increasing the storage of amines at the interface, making more amines available for IP. This is considered to minimize the formation of defects in the PA layer, thereby improving the rejection performance [117,118].
- (ii)
- During the IP process, amine monomers will continuously diffuse from the aqueous phase to the organic phase. Therefore, the diffusion rate from the amine reservoir (i.e., interlayer or substrate) to the organic phase is crucial for the performance of the PA layer. Studies have shown that due to the interaction between the interlayer and the amine monomers (such as covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds), the interlayer exhibits a reduced amine desorption rate or slower amine diffusion [117,119]. The slow amine diffusion limits the available amine monomers that can enter the organic phase to react with TMC, thereby forming a thinner PA layer [120]. At the same time, it can also provide a more uniform pore structure for the IP process, which, in turn, makes the distribution of monomer solutions in the IP reaction more uniform. Many scholars have combined the intermediate layer with the base membrane through the electrophilic coupling reaction of diazonium salts to regulate the diffusion behavior of amine monomers in the oil phase, allowing them to react with acyl chlorides, thereby endowing the interfacial polymerization polyamide dense layer with optimized selective pore structure and reduced internal negative charge [110,112,114]. As shown in Figure 7a, Zhao et al. [112] introduced a double-rigid twisted (porous organic polymer) POP intermediate layer onto the base membrane, and the modified membrane has a narrow pore size distribution, a small average pore size, and a lithium–magnesium separation factor of up to 78.56.
- (iii)
- In the magnesium–lithium separation system, due to the synergistic effect between size sieving and Donnan equilibrium, compared to the negatively charged intermediate layer, the positively charged intermediate layer can endow the nanofiltration membrane with appropriate pore size and surface charge density, thereby achieving higher Mg2+/Li+ separation selectivity [115]. This is mainly because there is no strong interaction between the positively charged intermediate layer and the amine monomer, thus allowing for the rapid release of a large number of amine monomers from the intermediate layer. These amine monomers diffuse into the IP reaction zone and react with TMC to form a dense PA layer with a smaller average pore size and a narrower pore size distribution. Conversely, for the negatively charged intermediate layer, the strong electrostatic interaction between the amine monomer and the intermediate layer inhibits the release of amine monomers from the intermediate layer, slowing down the diffusion of amine monomers to the IP reaction zone, resulting in a more porous PA layer for the negatively charged intermediate layer nanofiltration membrane. For example, Chen et al. [121] used catechol (CA), hydroquinone (HQ), and pyrogallol (PG) to crosslink PEI to form nanoscale aggregates on a PSf substrate to prepare a positively charged hydrophilic polyphenol intermediate layer, and by controlling the distribution and diffusion of PIP, a highly crosslinked PA layer was formed. Compared to the original membrane (TFC-0), the modified membrane’s PA layer thickness is reduced (35-50 nm), the average pore size is smaller (as shown in Figure 7d), the rejection rate for Mg2+ is higher, and the lithium–magnesium separation factor is 50.7.
3.5. Substrate Functionalization
4. Fundamental Characteristics of NF Membrane for Mg2+/Li+ Separation
4.1. Pore Size and Distribution
4.2. Zeta Potential
4.3. Hydrophilicity
4.4. Thickness of the Separation Layer
5. Summary and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [MimAP][TFf2N] | amine-functionalized ionic liquid 1-(3-aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| 160A | 160-Aromatic-NH2 |
| 1-AI | 1-Aminopyridinium iodide |
| Am-CDs | amine-functionalized carbon dots |
| AMN | aminomalononitrile |
| ARG | arginine monohydrochloride |
| ATA | acryloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride |
| BNNS | boron nitride nanosheets |
| BTAB | 3-bromopropyl trimethylammonium bromide |
| BTPB | 3-bromopropyl triphenyl phosphonium bromide |
| CDs | cyclodextrins |
| CNC-COOK | carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal |
| CP8 | The PSf substrates modified using TTSBI/BAPF interlayers in which C and 8 represented cross-link and the pH values of the diazonium reagent solution. |
| Cyclen | 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane |
| DA18C6 | diazo-18-crown-6 |
| DABIL | N1-(6-aminohexyl)-N1,N1,N6,N6,N6-pentamethylhexane-1,6-diaminium bromide |
| DAGH | 1,3-diaminoguanidine hydrochloride |
| DAPP | 1,4-bis(3-aminopropyl) piperazine |
| DCA | 4,7,10-Trioxygen-1,13-tridecanediamine |
| DDP | dodecyl phosphate |
| DETA | diethylenetriamine |
| DHTAB | 3,5-dimethylhydrazine-benzyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| EDA | ethylenediamine |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| g-C3N4 | nano graphitic carbon nitride |
| g-C3N5 | amine-rich graphitic carbon nitride |
| GEM | Gemini electrolyte monomer |
| GO | graphene oxide |
| GRT | Girard’s Reagent T |
| HACC | hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan |
| HMAH | 3-[n-tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]—2-hydroxypropanesulfonic |
| HMTAB | 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,3,5,7-tetraazaadamantane-1-ium bromide |
| IPC | isophthaloyl chloride |
| MWCNTs-COOK | potassium carboxylate functionalized multi-wall carbon nanotubes |
| PA | polyamide |
| PAA | polyallylamine |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PDA | polydopamine |
| PE | polyethylene |
| PEI | polyethyleneimine |
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| PHF | polyhydroxylated fullerene |
| PIP | piperazine |
| PSf | polysulfone |
| QBPD | quaternized bipyridine |
| QBPIP | quaternized-bis piperazine |
| QEDTP | quaternized N, N, N’, N’-tetrakis (2-hydroxypropyl) ethylenediamine |
| QSPIP | quaternized-spiral piperazine |
| QTHIM | quaternized tetrahydroxyethyl imidazolium |
| SBI | spirocyclic diamine |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| TBB | 1,3,5-tris(bromoethyl)benzene |
| TC | 2, 3-epoxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride |
| TET | trimesoyl chloride |
| TG | triaminoguanidine |
| TMC | trimesoyl chloride |
| TQAIL | triple-quaternary ammonium based ionic liquid |
| β-CD | β-Cyclodextrin |
| γ-CDs | γ-cyclodextrins |
References
- Peng, H.Y.; Lau, S.K.; Yong, W.F. Recent advances of thin film composite nanofiltration membranes for Mg2+/Li+ separation. Adv. Membr. 2024, 4, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, L.; Tang, H. Lithium extraction from water lithium resources through green electrochemical-battery approaches: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, L.; Chao, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, G.; Zhu, W. Progress in electrochemical lithium ion pumping for lithium recovery. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 59, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, X.; Wang, P.; Yu, T.; Du, X.; Hao, X.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Electrochemical technologies for lithium recovery from liquid resources: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hong, J.; Qian, X.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H.; Tao, X.; Xu, Z.; Ni, Q.-Q. Materials for lithium recovery from salt lake brine. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 16–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineral Commodity Summaries 2025; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2025; p. 212.
- Khalil, A.; Mohammed, S.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Lithium recovery from brine: Recent developments and challenges. Desalination 2022, 528, 115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, B.; Makuei, F.; Albijanic, B.; Dyer, L. The beneficiation of lithium minerals from hard rock ores: A review. Miner. Eng. 2019, 131, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yun, R.; Xiang, X. Recent advances in magnesium/lithium separation and lithium extraction technologies from salt lake brine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 256, 117807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sha, Z. Review on the electrochemical extraction of lithium from seawater/brine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 850, 113389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Jia, C.; Sun, L.; Tong, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Tang, J. Advances and promotion strategies of membrane-based methods for extracting lithium from brine. Desalination 2023, 566, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; He, L. Highly selective lithium recovery from high Mg/Li ratio brines. Desalination 2020, 474, 114185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Darling, S.B. Sharpening Nanofiltration: Strategies for Enhanced Membrane Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39948–39966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, X.; Wang, G.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, H.; et al. Mix-charged polyamide membranes via molecular hybridization for selective ionic nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 644, 120051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Oatley, D.L.; Williams, P.M.; Wright, C.J. Positively charged nanofiltration membranes: Review of current fabrication methods and introduction of a novel approach. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Teow, Y.H.; Ang, W.L.; Chung, Y.T.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes review: Recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2015, 356, 226–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hudson-Smith, N.V.; Frand, S.D.; Cahill, M.S.; Davis, L.S.; Feng, Z.V.; Haynes, C.L.; Hamers, R.J. Influence of the Spatial Distribution of Cationic Functional Groups at Nanoparticle Surfaces on Bacterial Viability and Membrane Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 10814–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Januszewski, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Fu, R.; Elimelech, M.; Huang, X. Tailored design of nanofiltration membranes for water treatment based on synthesis–property–performance relationships. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 672–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, J.M.M.; Boom, J.P.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Strathmann, H. Retention measurements of nanofiltration membranes with electrolyte solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 145, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; He, B.; Cui, Z. Preparation and characterization of positively charged polyamide composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for lithium and magnesium separation. Desalination 2015, 369, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, J.E.; King, R.S.; Majerle, R.J.; Petersen, R.J. Interfacial Synthesis in the Preparation of Reverse Osmosis Membranes. J. Macromol. Sci.—Chem. 1981, 15, 727–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ma, P.; Zhu, C.; He, Q.; Deng, X. Preliminary study on recovering lithium chloride from lithium-containing waters by nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yao, Z.; Jiao, L.; Waheed, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L. Separation mechanism, selectivity enhancement strategies and advanced materials for mono-/multivalent ion-selective nanofiltration membrane. Adv. Membr. 2022, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, C.; Zhou, A.; He, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. A positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane modified by EDTA for LiCl/MgCl2 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Qian, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, C.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.; Teng, K.; Wang, Z. Positive charged PEI-TMC composite nanofiltration membrane for separation of Li+ and Mg2+ from brine with high Mg2+/Li+ ratio. Desalination 2019, 449, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G. Sub–10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Gao, Y.-B.; Gai, J.-G. Guanidinium-functionalized nanofiltration membranes integrating anti-fouling and antimicrobial effects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 6442–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q. High performance Mg2+/Li+ separation membranes modified by a bis-quaternary ammonium salt. Desalination 2022, 526, 115519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Q. Polyester Nanofiltration Membranes for Efficient Cations Separation. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2309406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
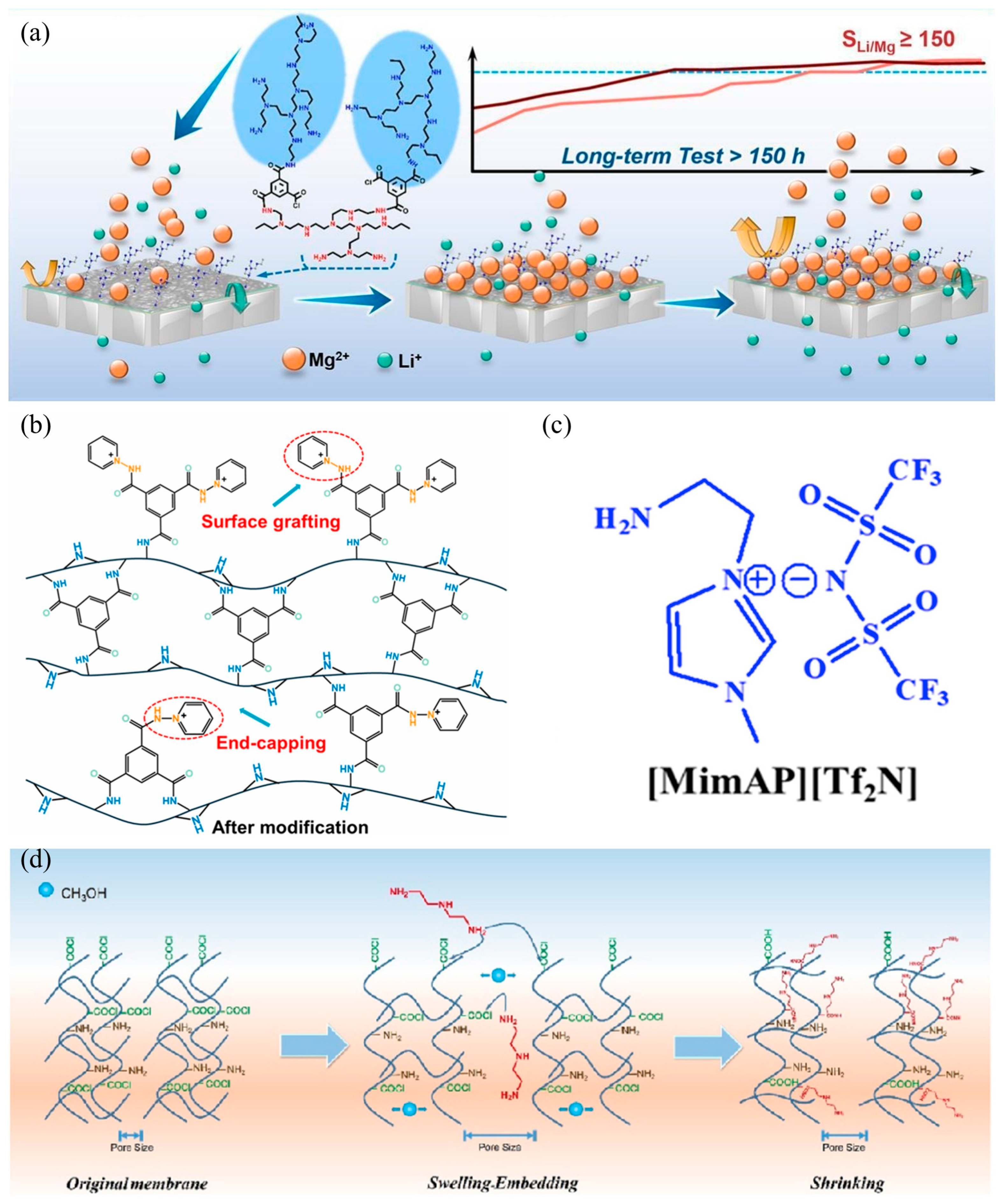
- Li, K.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, B. Capping-grafting synergistic strategy for the preparation of high-performance Mg2+/Li+ separation nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, N.; Yin, S. Based on high cross-linked structure design to fabricate PEI-based nanofiltration membranes for Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 693, 122351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, K.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, B. Advanced Mg2+/Li+ separation nanofiltration membranes fabricated with Girard’s reagent T based on functional end-capping strategy. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 695, 122483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Jin, D.; Xu, R.; Zhong, J. Enhancing ion separation efficiency: Janus charged nanofiltration membrane fabricated via polyethyleneimine-manipulated interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 706, 122930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-S.; Gao, Y.-W.; Zhu, Y.-K.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.-S.; Yin, Y.-H.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, C.-B. Fabrication of self-cleaning nanofiltration membranes through interfacial polymerization using PEI@CoPc monomer for Mg2+/Li+ separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 153807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Guan, K.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Mai, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhang, P.; Gonzales, R.R.; Matsuyama, H. Fine-tuning polyamide nanofiltration membrane for ultrahigh separation selectivity of Mg2+ and Li+. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 688, 122133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Ultrahighly Li-selective nanofiltration membranes prepared via tailored interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 700, 122728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Q. Quaternization-spiro design of chlorine-resistant and high-permeance lithium separation membranes. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. Designing Gemini-Electrolytes for Scalable Mg2+/Li+ Separation Membranes and Modules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Guanidyl-incorporated nanofiltration membrane with high performance in Mg/Li separation by in situ nanobubble cooperation with polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Di, N.; Zha, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S. Positively Charged Polyamine Nanofiltration Membrane for Precise Ion–Ion Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 48695–48704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Luo, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Jing, K.; Lin, L.; Qiao, Z.; Xu, J.; Yan, F.; Wan, D.; et al. Thin film composite membranes prepared from diaminoguanidine hydrochloride for Mg2+/Li+ separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 635, 157605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Impact of acyl chloride monomers on the structure and performance of polyamide nanofiltration membranes for lithium-magnesium separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 722, 123858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhao, J.; Gu, T.; Long, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Guanidyl-incorporated nanofiltration membranes toward superior Li+/Mg2+ selectivity under weakly alkaline environment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Liu, C.; Mao, X.; Shi, X. Poly(bis(1-methylpiperazin-1-ium-amide) Nanofilm Composite Membrane with Nanochannel-Enabled Microporous Structure and Enhanced Steric Hindrance for Magnesium/Lithium Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2412463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Gonzales, R.R.; Hong, J.; Guan, K.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Mai, Z.; Li, Z.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Matsuyama, H. Fabrication of highly positively charged nanofiltration membranes by novel interfacial polymerization: Accelerating Mg2+ removal and Li+ enrichment. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 668, 121251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, K.; Ye, H.; Tang, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Jason Niu, Q. Advanced Mg2+/Li+ separation nanofiltration membranes by introducing hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan as a co-monomer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 616, 156434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Boutilier, M.S.H.; Kidambi, P.R.; Jang, D.; Hadjiconstantinou, N.G.; Karnik, R. Fundamental transport mechanisms, fabrication and potential applications of nanoporous atomically thin membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, M.L.; Torres, W.R.; Galli, C.I.; Chagnes, A.; Flexer, V. Environmental impact of direct lithium extraction from brines. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, L.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Zou, M.; Ma, R.; Yuan, Q.; Duan, X. Large-area graphene-nanomesh/carbon-nanotube hybrid membranes for ionic and molecular nanofiltration. Science 2019, 364, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; Xu, Z.-K. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13398–13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Xie, Y.; Hou, J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Chen, V.; Darling, S.B. Janus Membranes: Creating Asymmetry for Energy Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Darling, S.B.; Shao, L. Porous Janus materials with unique asymmetries and functionality. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 626–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, Z. Dually Charged MOF-Based Thin-Film Nanocomposite Nanofiltration Membrane for Enhanced Removal of Charged Pharmaceutically Active Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7619–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ren, L.-F.; Shao, J. Fouling- and chlorine- resistant bilayer heterostructured Janus charged nanofiltration membranes constructed via novel electrospray polymerization-based method. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 690, 122178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Shibo, B.; Jiawang, L.; Ming, W.; Yan, Z.; Yingfei, H. Crown ether-functionalized nanofiltration membranes with high ions selectivity for Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 714, 123372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Ren, X.-K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S. Nanofiltration membrane with crown ether as exclusive Li+ transport channels achieving efficient extraction of lithium from salt lake brine. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.-H.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Yan, Y.; Subramani, A.; Huang, X.; Hurwitz, G.; Ghosh, A.K.; Jawor, A. Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: A new concept for reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 294, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S. Nanofiltration membrane comprising structural regulator Cyclen for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation. Desalination 2023, 556, 116575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, B.; Shao, R.; Min, C.; Xu, Z.; Deng, H. Extra-thin composite nanofiltration membranes tuned by γ-cyclodextrins containing amphipathic cavities for efficient separation of magnesium/lithium ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Z.; Li, T.; Hussein, I.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S. Aza-crown ether-coupled polyamide nanofiltration membrane for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 695, 122484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xu, S.-J.; Xu, Z.-L.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Dong, Z.-Q. Novel thin-film nanocomposite membrane with water-soluble polyhydroxylated fullerene for the separation of Mg2+/Li+ aqueous solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Hai, C.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dong, S.; Ma, L.; He, X.; Xu, Q. High-flux polyamide nanofiltration membranes tuning by polydopamine-modified boron nitride nanosheets: Accelerating Mg2+/Li+ separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Han, C.; Huo, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, N. Efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation nanofiltration membranes modified by amine-functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Huo, K.; Han, C.; Zhang, Q. Structure and positive charge regulation in nanofiltration membrane by novel nanomaterial g-C3N5 for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 707, 122984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, S. Positively charged zwitterion-carbon nitride functionalized nanofiltration membranes with excellent separation performance of Mg2+/Li+ and good antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, L.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Jin, P.; Volodine, A.; Dewil, R.; et al. Intercalation of small molecules in the selective layer of polyamide nanofiltration membranes facilitates the separation of Mg2+/Li+. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Fang, R. Development of an Environmentally Friendly nanofiltration membrane for efficient Lithium-Magnesium separation using ZIF-8-NH2 grafted polyamide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, F.; Ghoreyshi, A.A.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Rahimpour, A. A highly permeable UiO-66-NH2/polyethyleneimine thin-film nanocomposite membrane for recovery of valuable metal ions from brackish water. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 151, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, A.; Islam, M.A.; Jashni, E.; Khalili, A.; Cho, J.-Y.; Sadrzadeh, M. Efficient Lithium Recovery from Water Using Polyamide Thin-Film Nanocomposite (TFN) Membrane Modified with Positively Charged Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 66514–66531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y. Novel polyamide nanofiltration membrane PEI-(β-CD@g-C3N5)/TMC based on microfiltration substrate for efficient separation of lithium and magnesium. Desalination 2024, 592, 118136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hong, J.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H.; Ni, Q.-Q. MWCNTs-COOK-assisted high positively charged composite membrane: Accelerating Li+ enrichment and Mg2+ removal. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 212, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wu, L.-K.; Xu, Z.-L.; Hedar, M.; Luo, L.-H.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Li, H.-X.; Tong, Y.-H.; Xu, S.-J. Efficient separation of Li+/Mg2+ via positively charged TFN membrane based on the PEI interlayer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 284, 119523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Shen, Q.; Kawabata, Y.; Segawa, J.; Cao, X.; Guan, K.; Istirokhatun, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Matsuyama, H. Graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-assembled membranes with intrinsic functionalized nanochannels for high-performance nanofiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y.; Deng, B. Probing the Contributions of Interior and Exterior Channels of Nanofillers toward the Enhanced Separation Performance of a Thin-Film Nanocomposite Reverse Osmosis Membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J.; et al. Extreme Li-Mg selectivity via precise ion size differentiation of polyamide membrane. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, C.; Ju, T.; Wei, M.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Engineering transport highways in microporous membranes for lithium extraction: The double role of covalent organic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 680, 121759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, F.J.; von Krbek, L.K.S.; Nitschke, J.R. Strategies for binding multiple guests in metal–organic cages. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xing, F.; Zhu, S. Synthesis of 1,8-anthraquinone functionalized aza 18/20-crown-5 macrocycles and their chromogenic ion-pair recognition of hydroxides in DMSO. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Shen, B.; He, X.; Ghazi, Z.A.; Khan, N.A.; Sin, H.; Khattak, A.M.; Li, L.; et al. Microporous membranes comprising conjugated polymers with rigid backbones enable ultrafast organic-solvent nanofiltration. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yan, F.; Wang, J. Regulating the interfacial polymerization process toward high-performance polyamide thin-film composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nulens, I.; Ben Zvi, A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Ramon, G.Z. Re-thinking polyamide thin film formation: How does interfacial destabilization dictate film morphology? J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 656, 120593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Kecheng, G.; Aiwen, Z.; Liheng, D.; Siyu, Z.; Wenming, F.; Mengyang, H.; Ping, X.; Pengfei, Z.; Zhan, L.; et al. Multifunctional role of surfactant in fabricating polyamide nanofiltration membranes for Li+/Mg2+ separation. Desalination 2024, 594, 118295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, M.; Fei, Z.; Li, J.; Ren, Z.; Hou, Y. Synergistic regulation of macrocyclic polyamine-based polyamide nanofiltration membranes by the interlayer and surfactant for divalent ions rejection and mono-/di-ions sieving. Desalination 2022, 544, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lee, K.-R.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Elimelech, M.; Jin, J.; Lin, S. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane with highly uniform sub-nanometre pores for sub-1 Å precision separation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Ma, T.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, G.; An, Q.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Q.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, L. Constructing a selective blocked-nanolayer on nanofiltration membrane via surface-charge inversion for promoting Li+ permselectivity over Mg2+. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, N.; Sun, J.; Lee, K.-R.; An, Q.-F.; Liu, C.-M.; Zhao, Q. Phosphonium Modification Leads to Ultrapermeable Antibacterial Polyamide Composite Membranes with Unreduced Thickness. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, G.; Tong, Y.; Ding, K.; Wang, Z.; Meng, C.; Gao, C. Polyethyleneimine modified polyamide composite nanofiltration membrane for separation of lithium and magnesium. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 103894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Guo, F.; Wang, L.; Zhen, H.; Zhang, N.; Yin, S.; Zhou, G.; Ruan, X.; He, G.; Jiang, X. Nanofiltration membrane with modified nano-gradient structure and positive charge for Li separation from high Mg/Li ratio brine. Desalination 2024, 577, 117394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, Y.; Feng, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Yao, H.; Wang, X. A novel nanofiltration membrane with [MimAP][Tf2N] ionic liquid for utilization of lithium from brines with high Mg2+/Li+ ratio. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 117997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, Y.; Kang, G.; Cao, Y. Improving Mg2+/Li+ separation performance of polyamide nanofiltration membrane by swelling-embedding-shrinking strategy. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 669, 121321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Ni, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Q. High-permeance Mg2+/Li+ separation nanofiltration membranes intensified by quadruple imidazolium salts. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 667, 121178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Q. Fabrication of high performance Mg2+/Li+ nanofiltration membranes by surface grafting of quaternized bipyridine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Peng, H.; Zhao, Q. High flux Mg2+/Li+ nanofiltration membranes prepared by surface modification of polyethylenimine thin film composite membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 579, 152161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Wen, H.; Liao, D.; Liu, C. Fouling-resistant ionic graft-polyamide nanofiltration membrane with improved permeance for lithium separation from MgCl2/LiCl mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyekwo, F.; Wen, H.; Liao, D.; Liu, C. Nanofiltration Membranes Modified with a Clustered Multiquaternary Ammonium-Based Ionic Liquid for Improved Magnesium/Lithium Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 32420–32432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Jin, Y.; Kang, G.; Cao, Y. Polyamide nanofiltration membranes with rigid–flexible microstructures for high-efficiency Mg2+/Li+ separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, A.; Rahimpour, A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Tailored l-Arginine modified Poly(piperazine-amide) nanofiltration membrane with enhanced water permeability for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 728, 124140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, H.; Hu, D.; Feng, X. Grafting modification of thin-film composite membrane with quaternary ammonium polyelectrolyte for Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, W.-S.; Kong, W.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. Dual integration of amine-functionalized carbon dots endowed nanofiltration membranes with highly efficient biofouling/ acid/chlorine resistance for effective Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 696, 122542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, K.; Zhou, G.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Kou, W. High positively charged composite nanofiltration membranes modified by a novel bis-quaternary ammonium monomer for Li+ extraction from high Mg2+/Li+ ratio salt lakes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Chen, S.; Chen, P.; Gao, F.; Lu, J.; Hou, Y.; He, Q.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Q. Space-Confined Synthesis of Thinner Ether-Functionalized Nanofiltration Membranes with Coffee Ring Structure for Li+/Mg2+ Separation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2404150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. Dual-skin layer nanofiltration membranes for highly selective Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Shi, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, M.; Wang, G.; Qiu, T.; Jiang, Z. Quaternary ammonium engineered polyamide membrane with high positive charge density for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Liang, M.; Ji, Y.; Cui, Z.; Younas, M.; Li, J.; He, B. A nanofiltration membrane with positively and negatively charged groups by grafted p-aminosalicylic acid-Fe(III) chelation for Li+/Mg2+ efficient separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wan, Y.; Pan, G.; Yu, H.; Tang, G.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Quaternary phosphonium-polyamide membranes for efficient lithium extraction from brine sources. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 349, 127787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Sun, J.; Tang, G.; Pan, G.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Highly selective Mg2+/Li+ separation membranes prepared by surface grafting of a novel quaternary ammonium bromide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, G.; Liu, Y. Positively charged nanofiltration membranes for efficient Mg2+/Li+ separation from high Mg2+/Li+ ratio brine. Adv. Membr. 2023, 3, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Enhanced Mg2+/Li+ separation by nanofiltration membrane through surface modification using spirocyclic diamine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 364, 132515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Ji, D.; Feng, H.; Lin, W.; Wang, C.; Wei, L.; Shu, W.; Xiao, C. Fabrication of positively charged composite nanofiltration membranes with “multilayer interlocking” structure based on ZIF-8 layer anchored constrained growth strategy for Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yuan, S.; Jia, C.; Hu, P.; Zhao, S.; Ren, Y.; You, M.; Zhao, S.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Hyperbranched polymer wrapped UIO-66-NH2 as covalent intermediate layer to enhance polyamide membrane for Li+/Mg2+ separation and acid/alkaline stability. Desalination 2025, 593, 118212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Bi, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Qi, F.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S. Nanofiltration membrane with a zwitterion-g-C3N4 composite interlayer for Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cui, W.; Shen, Q.; Yao, Z.; Fang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L. Porous organic polymer interlayers modulated nanofiltration membranes for ultra-permselective Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 690, 122207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Jin, X.-G.; Xu, Z.-L.; Wu, L.-K.; Tong, Y.-H.; Li, H.-X.; Ping, H.-H.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, S.-J. Surfactant-interlayer assisted interfacial polymerization for constructing Janus nanofiltration membranes: Enhanced Li+/Mg2+ separation efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 712, 123235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Wang, M.; Wu, M.; Yang, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, P.; You, M.; Zhao, S.; et al. Asymmetric polyamide nanofilm boosted by protonated dendrimer porous intermediate layer for Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 701, 122743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, F.; Wei, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, S.; Xie, T.; Sun, H.; Li, P.; Niu, Q.J. An interlayer-based positive charge compensation strategy for the preparation of highly selective Mg2+/Li+ separation nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 684, 121882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Jiang, C.; Li, J.; Miao, C.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Hou, Y. Ultra-fast interlayer construction strategy for the preparation of NF membranes with high Li+/Mg2+ separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.-w.; Guo, H.; Yao, Z.; Ma, X.-h.; Song, X.; Feng, S.-P.; Tang, C.Y. Tannic Acid/Fe3+ Nanoscaffold for Interfacial Polymerization: Toward Enhanced Nanofiltration Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9341–9349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Constructing interlayer to tailor structure and performance of thin-film composite polyamide membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jian, M.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Thin-Film Nanocomposite Forward-Osmosis Membranes on Hydrophilic Microfiltration Support with an Intermediate Layer of Graphene Oxide and Multiwall Carbon Nanotube. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34464–34474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Jin, H.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhao, S.; Lan, H.; Xie, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, H.; Niu, Q.J.; Yang, C. Dual-electric layer nanofiltration membranes based on polyphenol/PEI interlayer for highly efficient Mg2+/Li+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Geng, N. Effect of Interlayer Construction on TFC Nanofiltration Membrane Performance: A Review from Materials Perspective. Membranes 2023, 13, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-l.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, A.-q.; Wang, X.-m.; Yang, H.-w.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.F. Exploring the interactions of organic micropollutants with polyamide nanofiltration membranes: A molecular docking study. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 577, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Surface Modification of Water Purification Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4662–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, N.; Qian, X.; Shi, J.; Jing, M.; Teng, K.; Xu, Z. Ultra-thin double Janus nanofiltration membrane for separation of Li+ and Mg2+: “Drag” effect from carboxyl-containing negative interlayer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 230, 115567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-L.; Fu, P.; Lin, W.-T.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Luo, X.-W.; Yu, Y.-H.; Xu, Z.-K.; Wan, L.-S. High-performance thin-film composite (TFC) membranes with 2D nanomaterial interlayers: An overview. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Hoek, E.M.V. Impacts of support membrane structure and chemistry on polyamide–polysulfone interfacial composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 336, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Lu, D.; Jin, H.; Xia, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, C.Y. Inhibiting Polyamide Intrusion of Thin Film Composite Membranes: Strategies and Environmental Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10860–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Lai, G.S.; Zhao, Y.; Torres, J.; Wang, R. Unraveling the role of support membrane chemistry and pore properties on the formation of thin-film composite polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 640, 119805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Sotto, A.; Molina, S.; Arsuaga, J.M.; García-Calvo, E.; Keiski, R.L. Preparation of loose polypiperazine amide membranes. Effect of the nanocomposite sublayer on the NF process performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Feng, C.; Lopez, R.; Coronell, O. Identifying facile and accurate methods to measure the thickness of the active layers of thin-film composite membranes—A comparison of seven characterization techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zeng, G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Feng, Z.; Tang, B.; Yu, X.; et al. Nanofiltration membrane based on a dual-reinforcement strategy of support and selective layers for efficient Mg2+/Li+ separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hong, J.; Qian, X.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H.; Ni, Q.-Q. “Bridge” graphene oxide modified positive charged nanofiltration thin membrane with high efficiency for Mg2+/Li+ separation. Desalination 2020, 488, 114522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Ling, K.; Zhou, F.; Guo, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; et al. Aligned amino-functionalized γ-cyclodextrin nanofiltration membrane via customized interfacial polymerization for precise Li+/Mg2+ separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 132092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B.; Zhu, X. Janus membrane with tailored upper and lower surface charges for ion penetration manipulation in high-performance nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 667, 121191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Guan, K.; Zhou, S.; Song, Q.; Shi, Y.; Fu, W.; Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Hu, M.; Mai, Z.; et al. Ternary-coordination-regulated polyamide nanofiltration membranes for Li+/Mg2+ separation. Desalination 2024, 581, 117577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Xu, N.; Dou, P.; Liu, C. Facile design of the nanofiltration membrane with Cu2+-incorporated aminated polyethylene substrate for highly selective magnesium/lithium separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 704, 122820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Wang, N.; Zhao, S.; Hu, P.; Jiang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, X.; You, M.; Lou, X.; Niu, Q.J. Polyamide nanofiltration membrane fine-tuned via mixed matrix ultrafiltration support to maximize the sieving selectivity of Li+/Mg2+ and Cl−/SO42−. Desalination 2022, 538, 115929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Van der Bruggen, B. A critical review on thin-film nanocomposite membranes enabled by nanomaterials incorporated in different positions and with diverse dimensions: Performance comparison and mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 661, 120952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Hong, J.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H.; Ni, Q.-Q. Positively charged nanofiltration membrane based on (MWCNTs-COOK)-engineered substrate for fast and efficient lithium extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 270, 118796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Lau, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M. Synthesis and characterization of thin film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane with hydrophilic nanocomposite support to reduce internal concentration polarization. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar-Mahboub, M.; Pakizeh, M. Development of a novel thin film composite membrane by interfacial polymerization on polyetherimide/modified SiO2 support for organic solvent nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 119, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Designed strategies of nanofiltration technology for Mg2+/Li+ separation from salt-lake brine: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2022, 546, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yao, Y.; Xu, J.; Ang, E.H.; Xu, G.; Liao, J.; Sotto, A.; Shen, J. Strategies for lithium extraction from salt lakes by nanofiltration and selective-electrodialysis and analysis of differences between the two methods. Desalination 2024, 586, 117749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritt, C.L.; Werber, J.R.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Kulik, H.J.; Elimelech, M. Ionization behavior of nanoporous polyamide membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 30191–30200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epsztein, R.; DuChanois, R.M.; Ritt, C.L.; Noy, A.; Elimelech, M. Towards single-species selectivity of membranes with subnanometre pores. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Dai, L.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Z. Li+/Mg2+ separation by membrane separation: The role of the compensatory effect. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y. Thickness-dependent ion rejection in nanopores. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Lu, L. Mg2+-Channel-Inspired Nanopores for Mg2+/Li+ Separation: The Effect of Coordination on the Ionic Hydration Microstructures. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9201–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendse, A.; Cetindag, S.; Lin, M.-H.; Rackovic, A.; Debbarma, R.; Almassi, S.; Chaplin, B.P.; Berry, V.; Shan, J.W.; Kim, S. Charged Layered Boron Nitride-Nanoflake Membranes for Efficient Ion Separation and Water Purification. Small 2019, 15, 1904590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-l.; Zhao, Y.-y.; Wang, X.-m.; Wen, X.-h.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y.F. Effect of varying piperazine concentration and post-modification on prepared nanofiltration membranes in selectively rejecting organic micropollutants and salts. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Meng, N.; Jian, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Graphene oxide incorporated thin film nanocomposite membrane at low concentration monomers. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, R.; Fan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Preparation of thin film composite nanofiltration membrane with improved structural stability through the mediation of polydopamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, P.-F.; Li, X.; Gan, B.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Park, H.-D.; Tang, C.Y. A Critical Review on Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes with Interlayered Structure: Mechanisms, Recent Developments, and Environmental Applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15563–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, J.; Peinemann, K.V. Multilayer composite membranes for gas separation based on crosslinked PTMSP gutter layer and partially crosslinked Matrimid® 5218 selective layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V.; Srebnik, S. Mathematical model of charge and density distributions in interfacial polymerization of thin films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
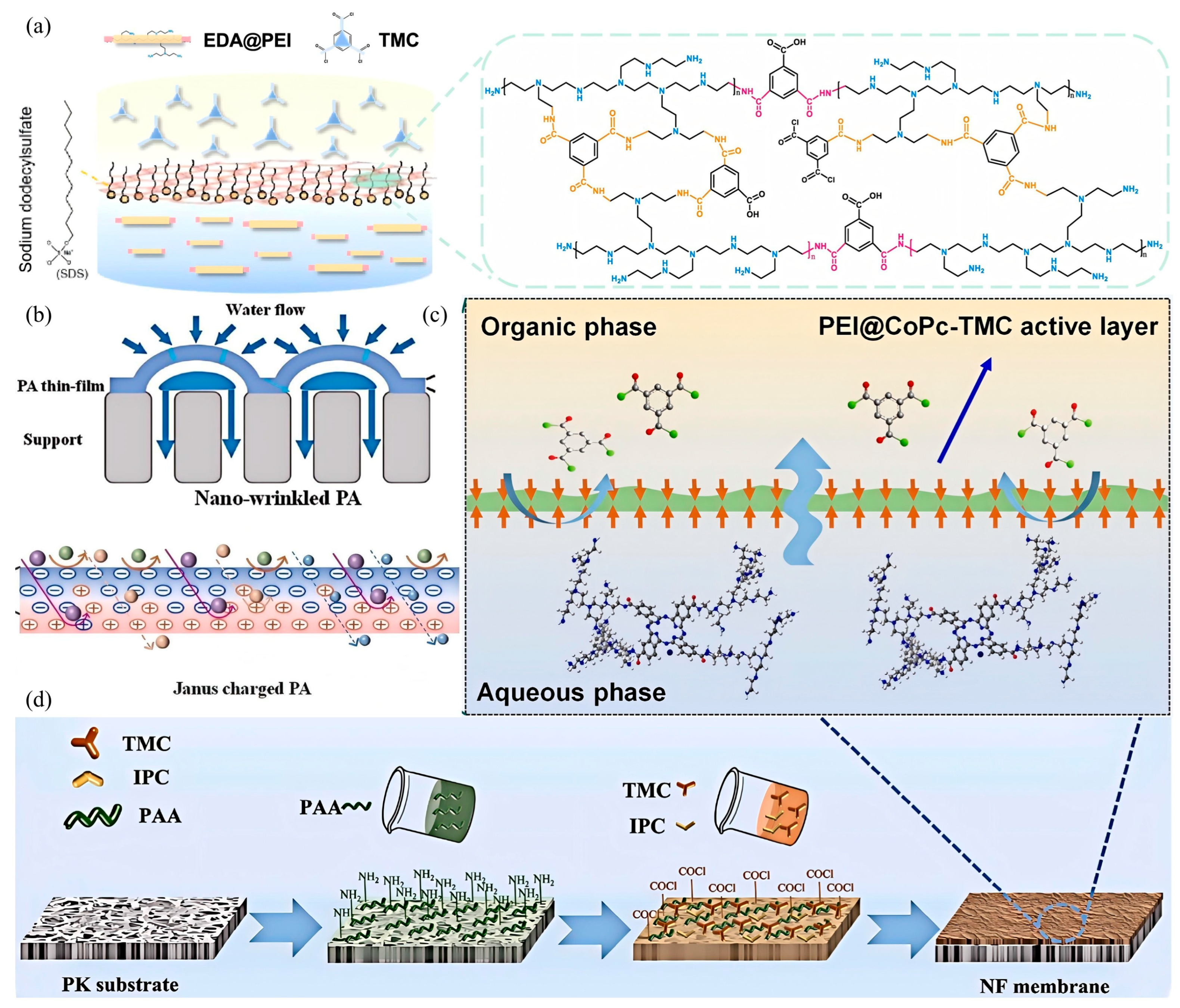
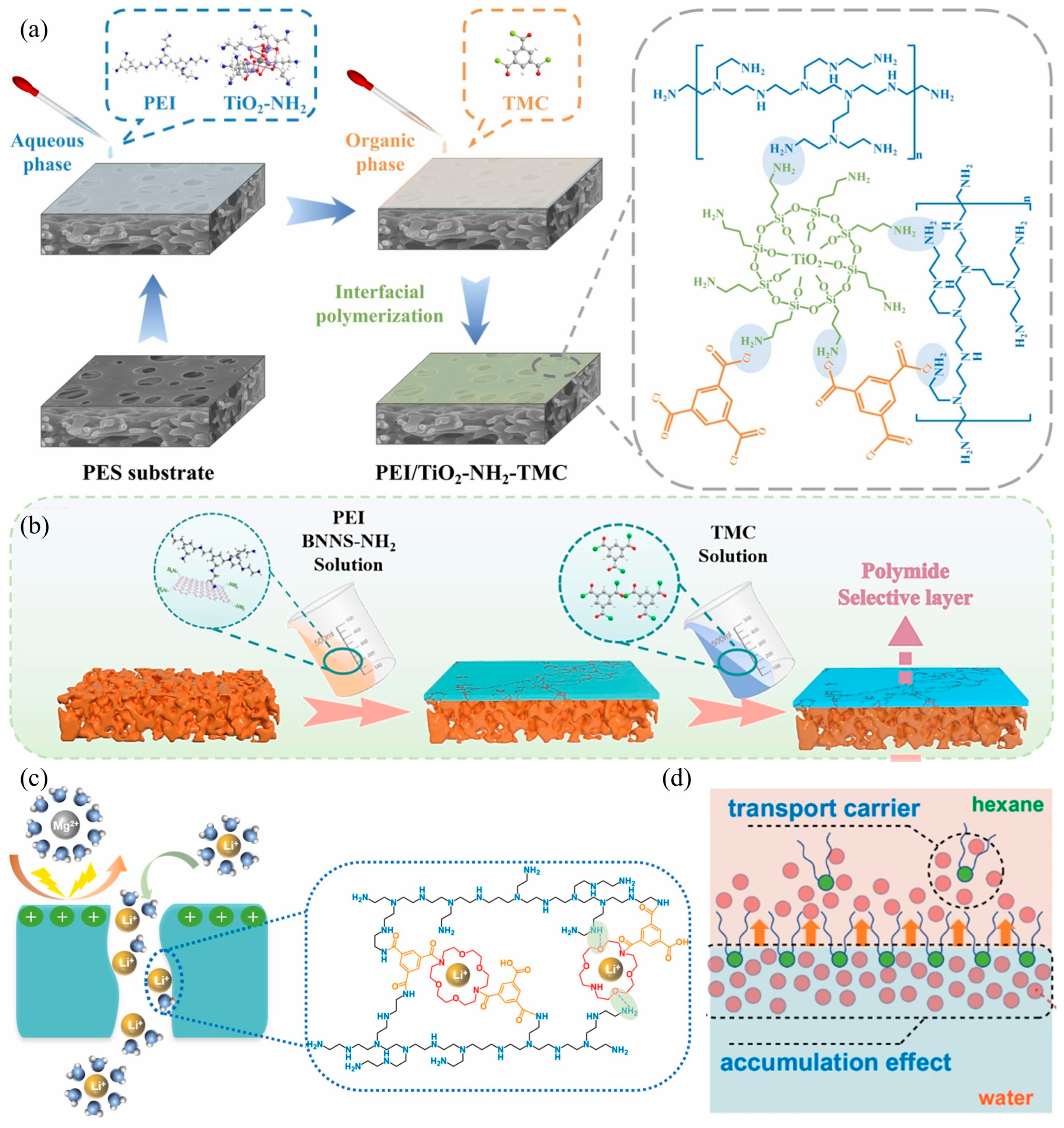
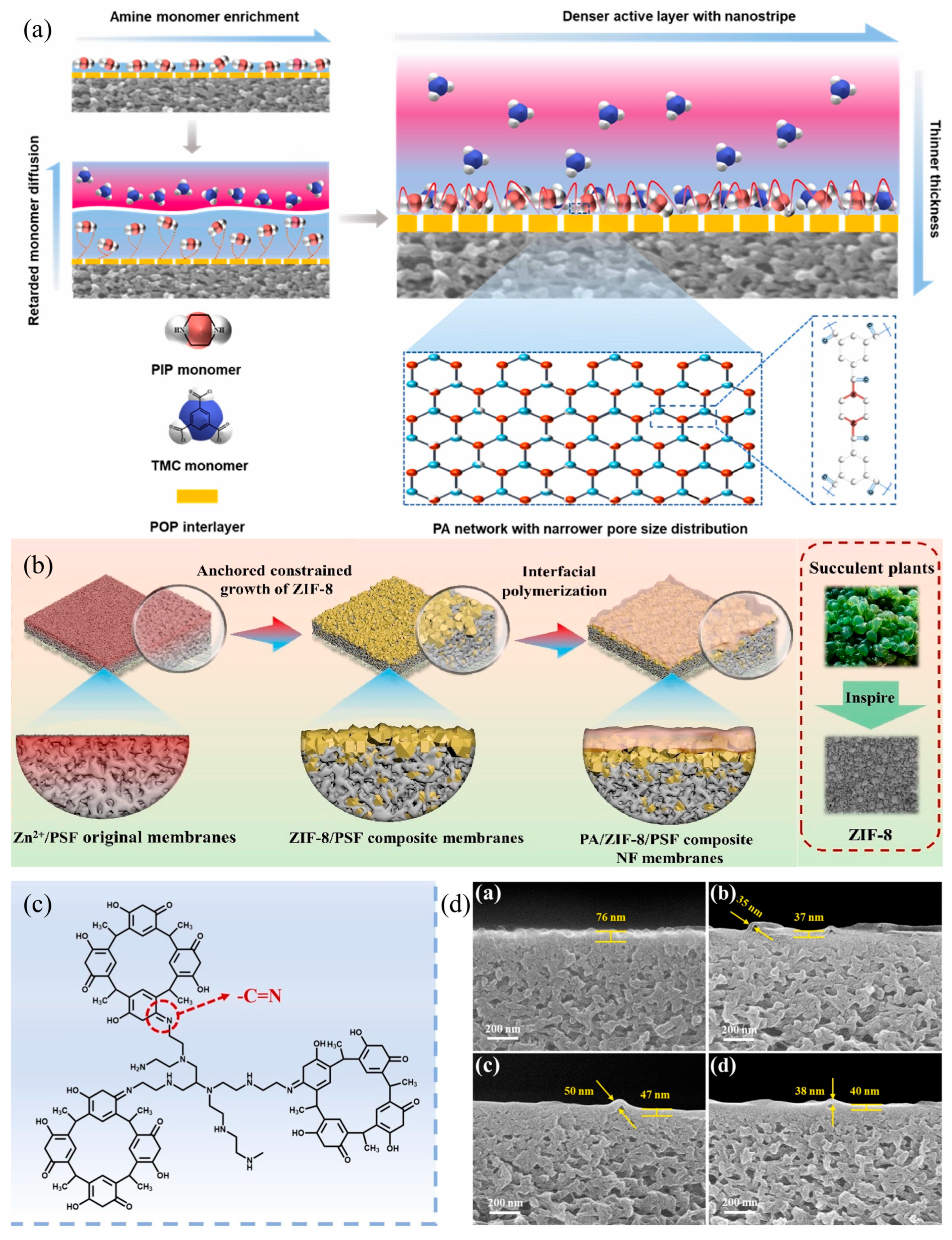
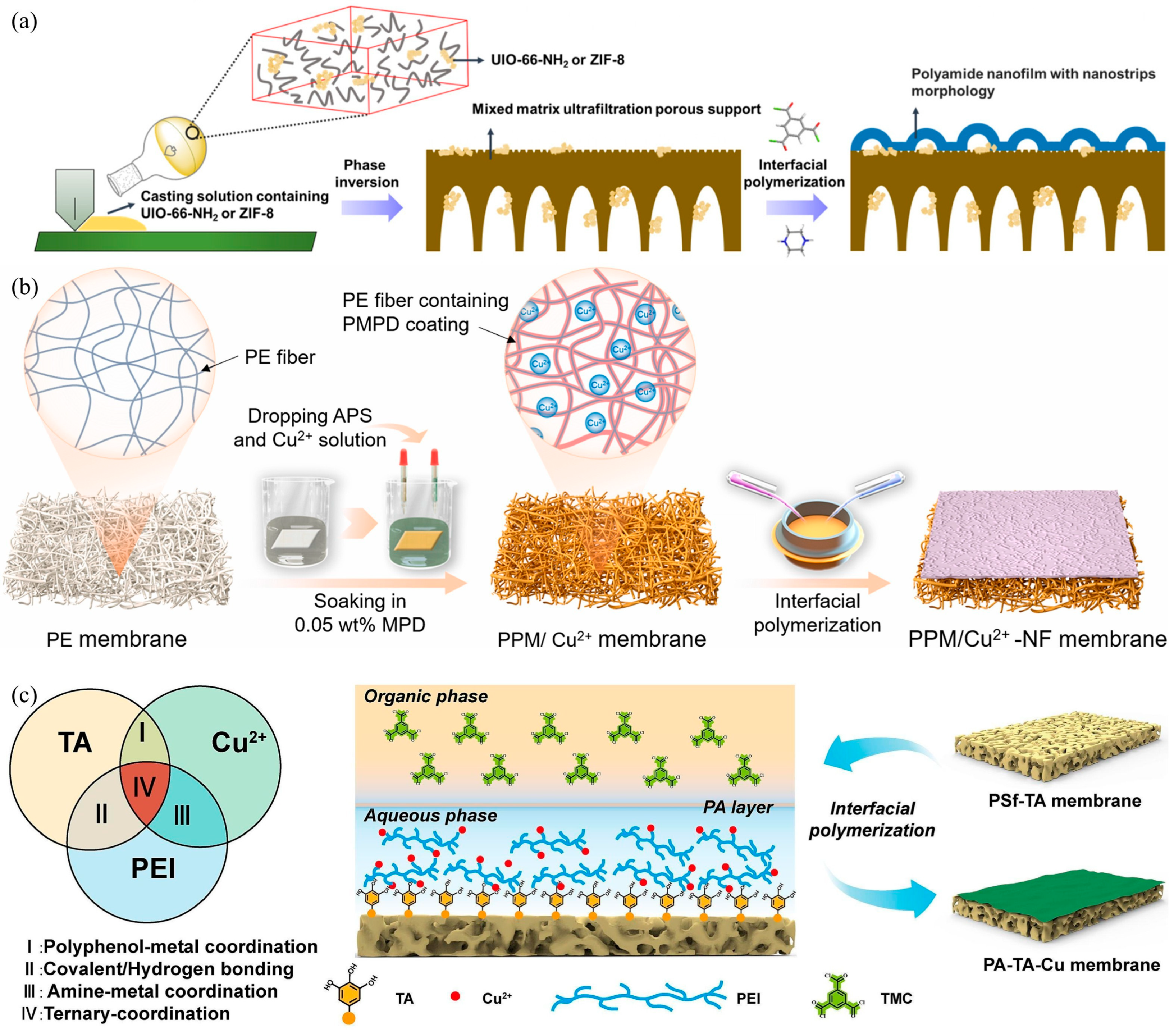
| Membrane | Mixture Concentration (ppm) 1 | RMg2+ (%) 2 | RLi+ (%) 3 | MLR 4 | PWP (LMH/bar) 5 | SLi,Mg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN/DAPP/TMC | 2000 | 70.4 | 21.8 | 20 | 2.6–2.8 | 2.6 | [20] |
| PSF/QSPIP/TMC | 2000 | ~93.0 | ~30.0 | 40 | ~20.0 | ~8.7 | [37] |
| PSF/GEM/TMC | 2000 | 94.8 | 40.0 | 100 | 17.5 | 13.1 | [38] |
| PES/1,3-diaminoguanidine-PEI/TMC | 2000 | 96.7 | 62.7 | 20 | 22.4 | 13.6 | [39] |
| PSF@PDA/PEI/TBB | 2000 | 94.7 | 42.8 | 20 | 4.2 | 16.7 | [40] |
| PES/PEI/TMC | 2000 | 94.8 | 30.6 | 20 | 5.0 | 20.0 | [25] |
| PSF/PEI@GRT/TMC | 2000 | 97.2 | - | 20 | 115.0 | 22.7 | [32] |
| PES/DAGH/TMC | 2500 | 95.0 | 36.1 | 10 | 12.2 | 23.3 | [41] |
| PSF/PIP-PEI/TMC | 2100 | 98.5 | 21.0 | 20 | 16.0 | 24.0 | [33] |
| PSF/TET/TMC | 2000 | 95.5 | 27.0 | 50 | 18.0 | 28.0 | [29] |
| PES/PEI/TPC | 2000 | >97.0 | <38.0 | 20 | 4.8 | 30.9 | [42] |
| PAN/TG/TMC | 2000 | 98.7 | 59.2 | 120 | 3.0 | 36.4 | [43] |
| PSF/PIP/TMC | 2000 | >99.0 | <11.3 | 20 | 6.8 | 45.3 | [36] |
| PES/QBPIP/TMC | 2000 | 98.8 | 12.3 | 31.2 | 28.3 | 76.9 | [44] |
| PSF/EDA@PEI/TMC | 2000 | 99.2 | 36.7 | 60 | 5.2 | 80.6 | [31] |
| PK/PAA/IPC | 2000 | 99.1 | 23.3 | 20 | 7.4 | 82.8 | [45] |
| PSf/PIP, HACC/TMC | 2000 | 94.3 | −4.0 | 13.9 | 15.7 | 115.0 | [46] |
| PK/PAA/TMC-IPC | 2000 | 99.3 | <55.0 | 20 | 9.3 | 117.0 | [35] |
| Monomers and Additives into PA | Substrate Membrane | Mixture Concentration (ppm) | RMg2+ (%) | RLi+ (%) | MLR | PWP (LMH/bar) | SLi,Mg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEI/TMC+Cyclen | PSf | 2000 | 90.4 | 22.0 | 20 | 14.0 | 8.7 | [58] |
| PEI/TMC+γ-CDs | PES | 2000 | 96.0 | - | 30 | 4.8 | 10.8 | [59] |
| PEI/TMC+DA18C6 | PSf | 2000 | 96.3 | 43.4 | 20 | 10.4 | 11.2 | [60] |
| PIP/TMC+PHF | PES | 2000 | 89.9 | 16.3 | 21.4 | 6.7 | 13.1 | [61] |
| PEI/TMC+PDA@BNNSs-NH2 | PSf | 2000 | 94.0 | <35.0 | 75 | 8.5 | 15.6 | [62] |
| PEI/TMC+TiO2-NH2 | PES | 2000 | 94.6 | - | 20 | 57.9 | 16.3 | [63] |
| PEI/TMC+g-C3N5 | PES | 2000 | 94.5 | 32.8 | 20 | 58.6 | 18.2 | [64] |
| BAPP/TMC+g-C3N4@MBCN | PES | 2000 | 97.4 | - | 73 | - | 23.9 | [65] |
| PEI/TMC+AMN | PES | 2000 | 91.8 | 32.1 | 50 | 13.0 | 26.7 | [66] |
| PEI+ZIF-8-NH2/TMC | MCE | 2000 | 91.3 | 23.7 | - | - | 33.1 | [67] |
| PEI/TMC+UiO-66-NH2 | PAN | 2000 | 97.4 | 4.1 | 20 | 30.6 | 36.9 | [68] |
| PIP/TMC+F-SiO2 | PES | 2000 | 95.7 | −63.2 | 20 | 56.0 | 37.9 | [69] |
| PEI/TMC+β-CD@g-C3N5 | PES | 2000 | ~97.8 | ~30.0 | 20 | 8.9 | 38.5 | [70] |
| PEI/TMC+MWCNTs-COOK | PES | 2000 | 98.6 | 21.6 | 20 | 12.2 | 58.0 | [71] |
| BAPP/TMC+g-C3N4 | PES | 2000 | 96.1 | 42.3 | 73 | 17.0 | 102.0 | [72] |
| Membrane | Mixture Concentration (ppm) | RMg2+ (%) | RLi+ (%) | MLR | PWP (LMH/bar) | SLi,Mg | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES-MXene/PEI/TMC | 2000 | 89.7 | 21.4 | - | 16.1 | 15.8 | [132] |
| PEI/TMC/CNC-COOK | 2000 | 95.1 | 20.9 | 20 | 11.1 | 16.1 | [133] |
| PES@γ-CD/TPC/PEI | 2000 | >90.0 | <25.0 | 30 | 6.5 | 22.5 | [134] |
| PES/GO/PA | - | 95.9 | 67.6 | 23 | - | 23.5 | [135] |
| PSf-CuCl2/PEI/TMC | 2000 | 96.0 | −7.1 | - | 4.8 | 26.5 | [136] |
| PE-Cu2+/PEI/TMC | 2000 | ~98.0 | 39.1 | - | 16.0 | 33.0 | [137] |
| PSf-ZIF-8/PEI/TMC | 2000 | 97.3 | 43.0 | - | 47.2 | 47.6 | [109] |
| PES@MWCNTs-COOK/PEI/TMC | 2000 | 98.6 | 21.5 | 20 | 12.2 | 58.6 | [71] |
| PSf@UiO-66-NH2/PIP/TMC | 2000 | 97.9 | −66.7 | 30.6 | 50.2 | 78.6 | [138] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, X.; Meng, C.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, G. Recent Advances on the Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Through Interfacial Polymerization. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130967
Zeng X, Meng C, Xu Z, Li X, Zhu H, Li G. Recent Advances on the Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Through Interfacial Polymerization. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(13):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130967
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Xinyu, Chunchun Meng, Zihan Xu, Xinwu Li, Haochen Zhu, and Guangming Li. 2025. "Recent Advances on the Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Through Interfacial Polymerization" Nanomaterials 15, no. 13: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130967
APA StyleZeng, X., Meng, C., Xu, Z., Li, X., Zhu, H., & Li, G. (2025). Recent Advances on the Positively-Charged Nanofiltration Membranes for Mg2+/Li+ Separation Through Interfacial Polymerization. Nanomaterials, 15(13), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15130967








