A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Lubricant in the Sizing Agent on the Properties of a Basalt Fiber and Epoxy Resin Composite Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
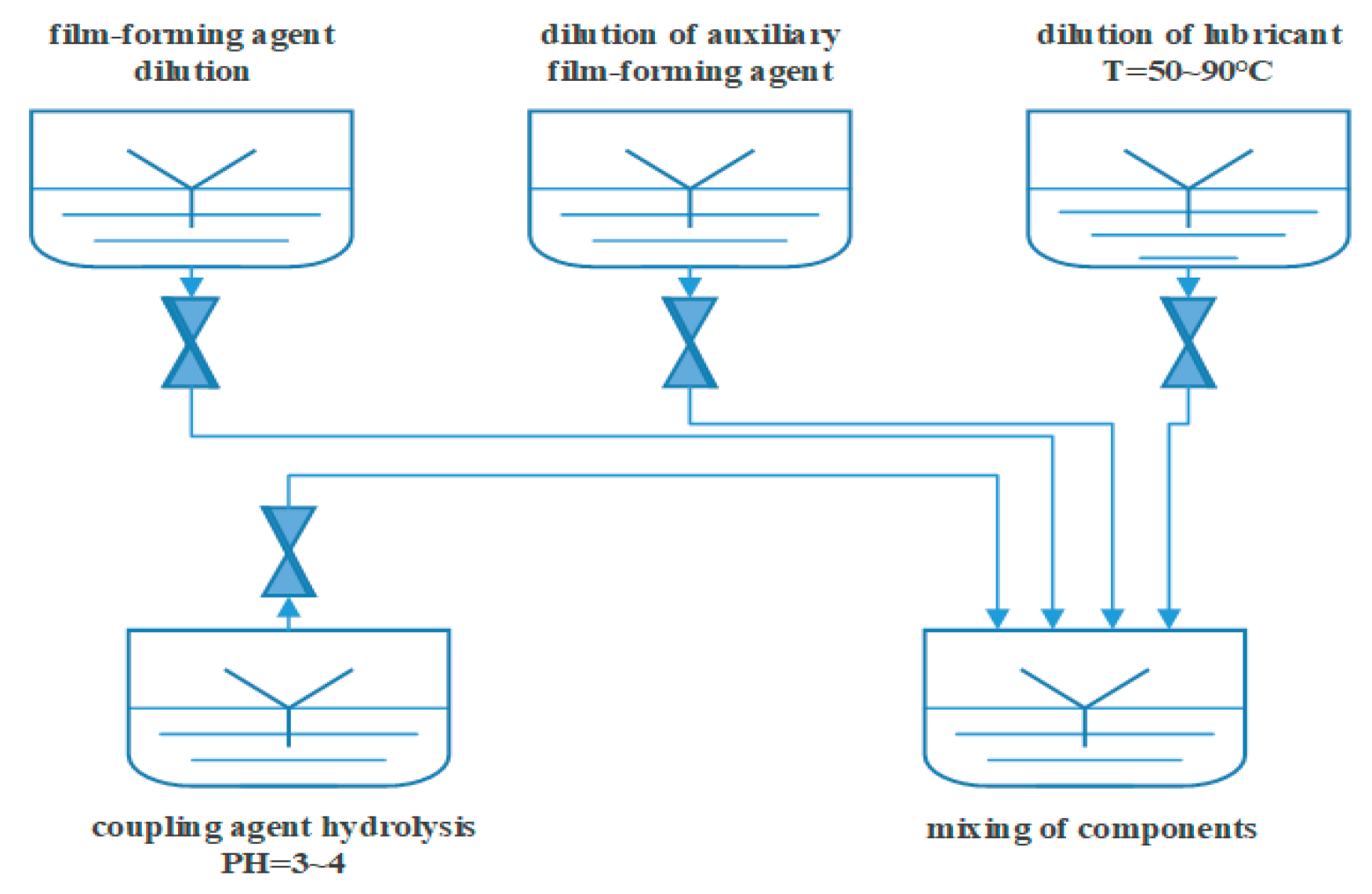
2.2. Sizing Agent Preparation
2.3. Epoxy–Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer Preparation
2.4. Characterization and Testing
2.4.1. Evaluation of the Physical and Chemical Properties of the Sizing Agent
2.4.2. BF Performance Evaluation
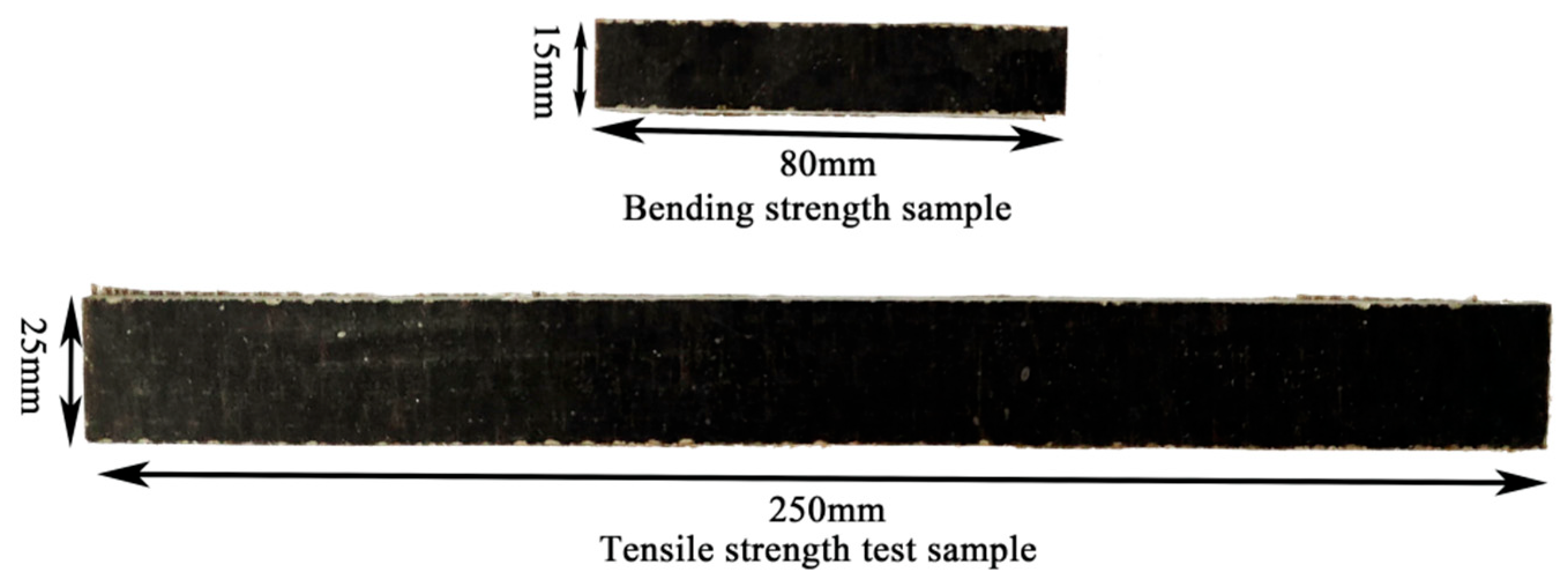
2.4.3. Epoxy–BFRP Composite Material Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Lubricants on the Physical and Chemical Properties of the Sizing Agent
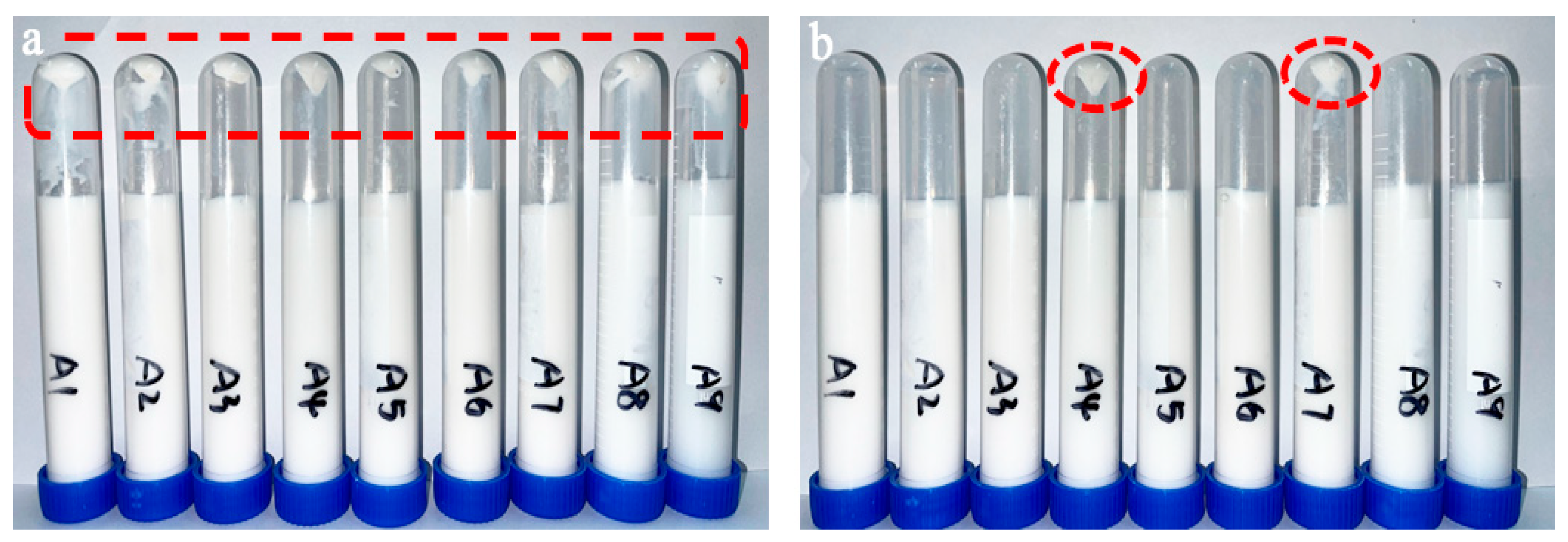
3.1.1. Emulsion Stability
3.1.2. Emulsion Size and Distribution
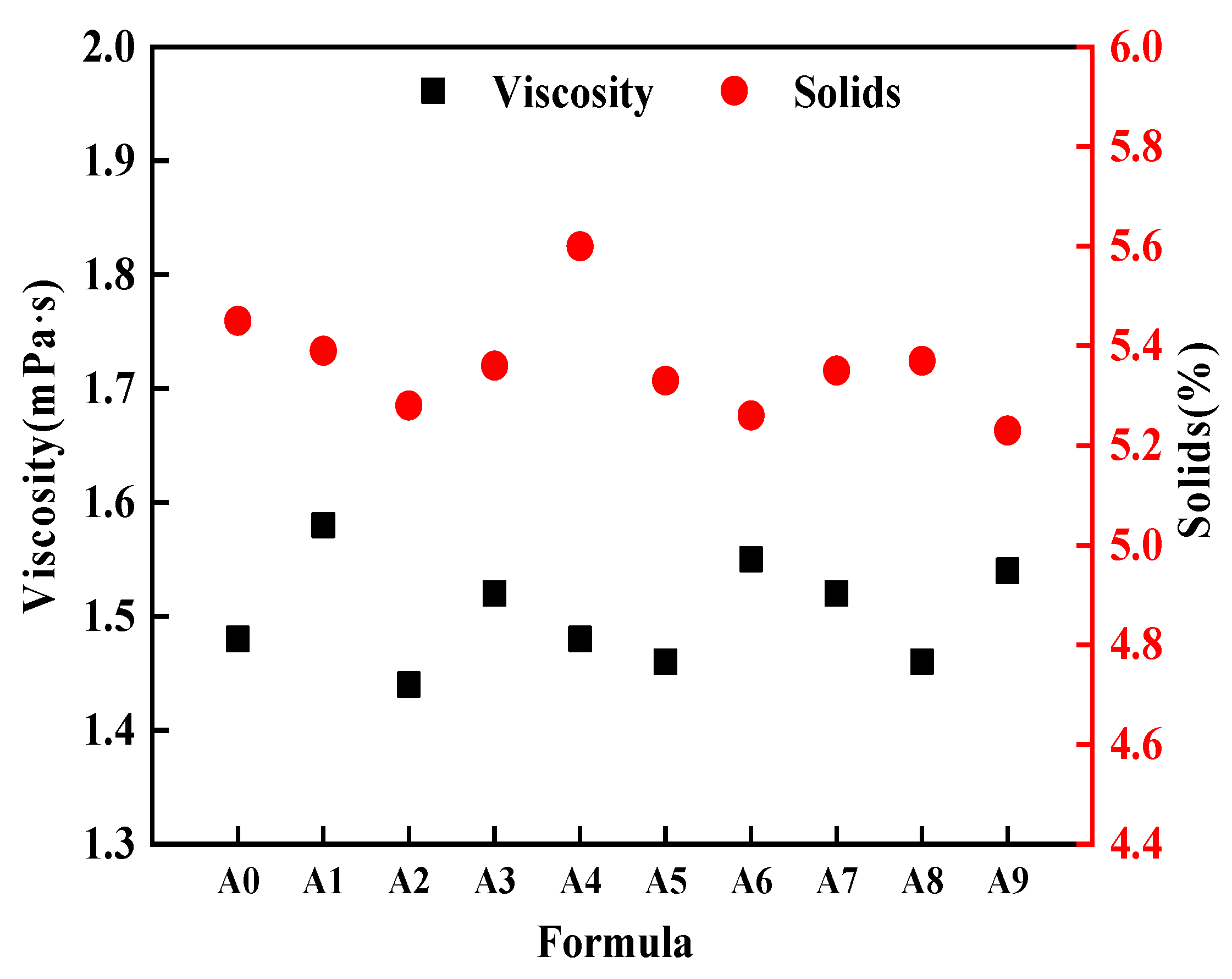
3.1.3. Emulsion Solid Content and Viscosity
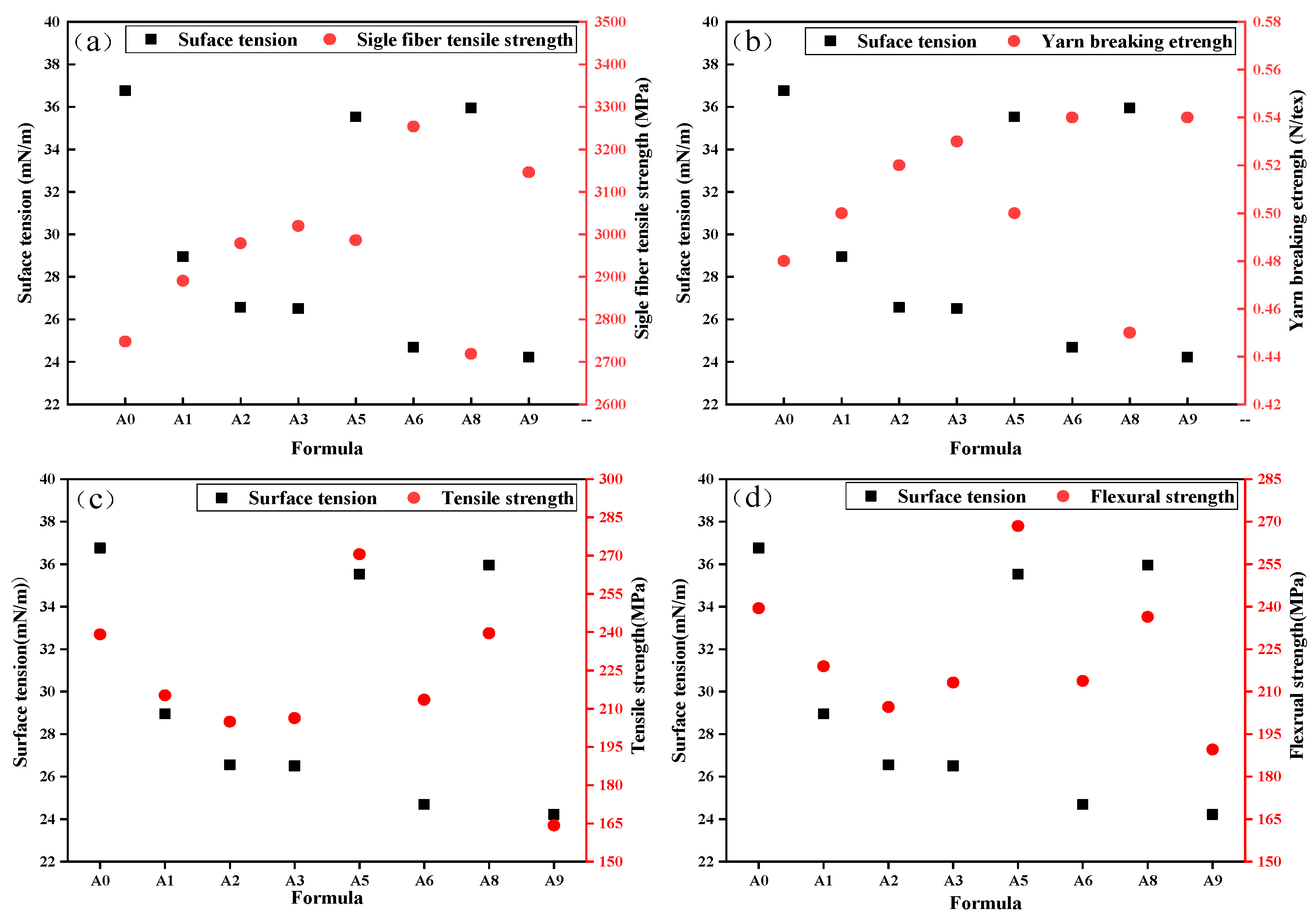
3.1.4. Emulsion Surface Tension
3.2. Effect of Lubricants on BF Performances
3.2.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Parameters
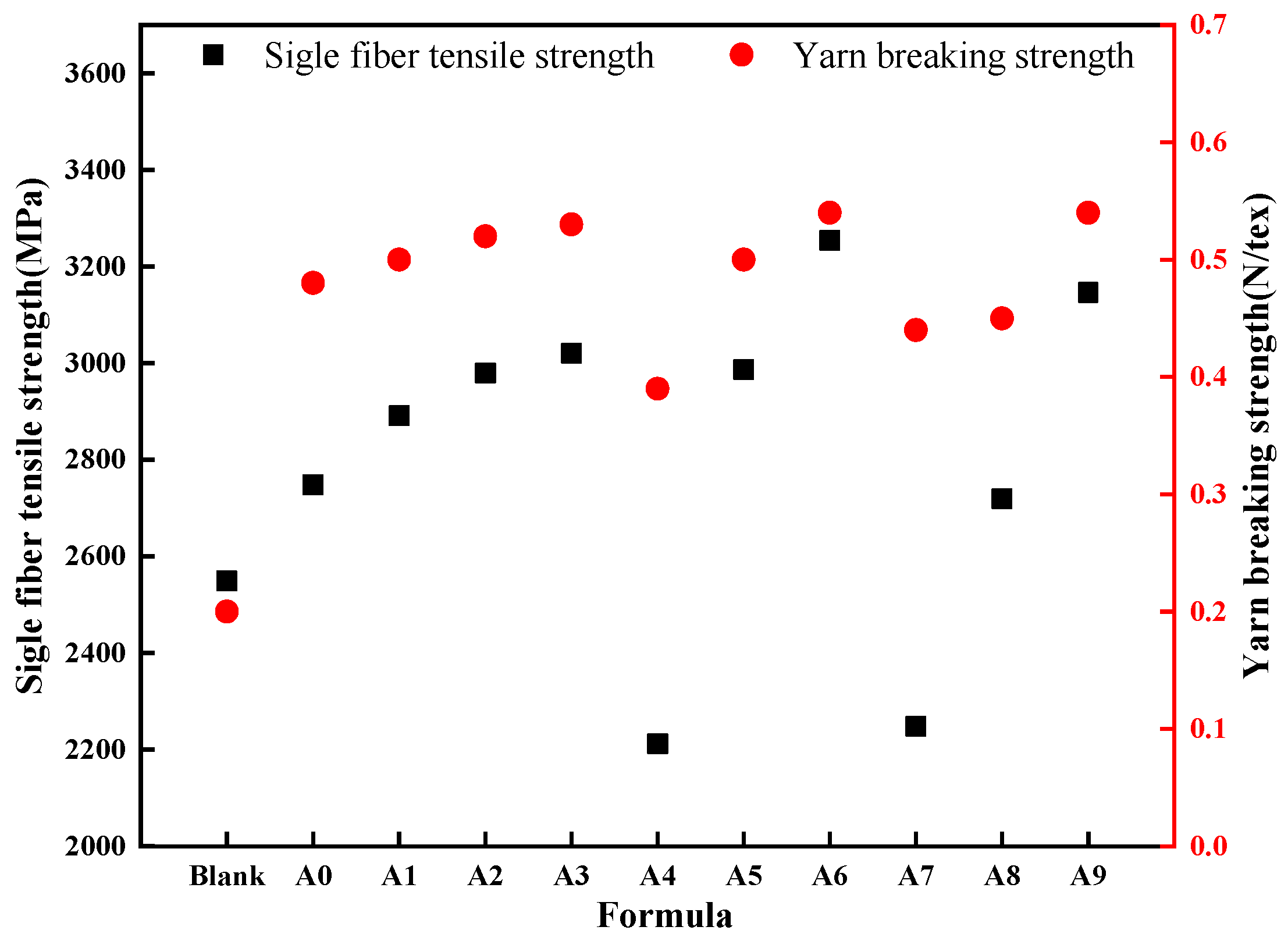
3.2.2. Mechanical Performance
3.3. Effect of Lubricants on Epoxy–BFRP Performances
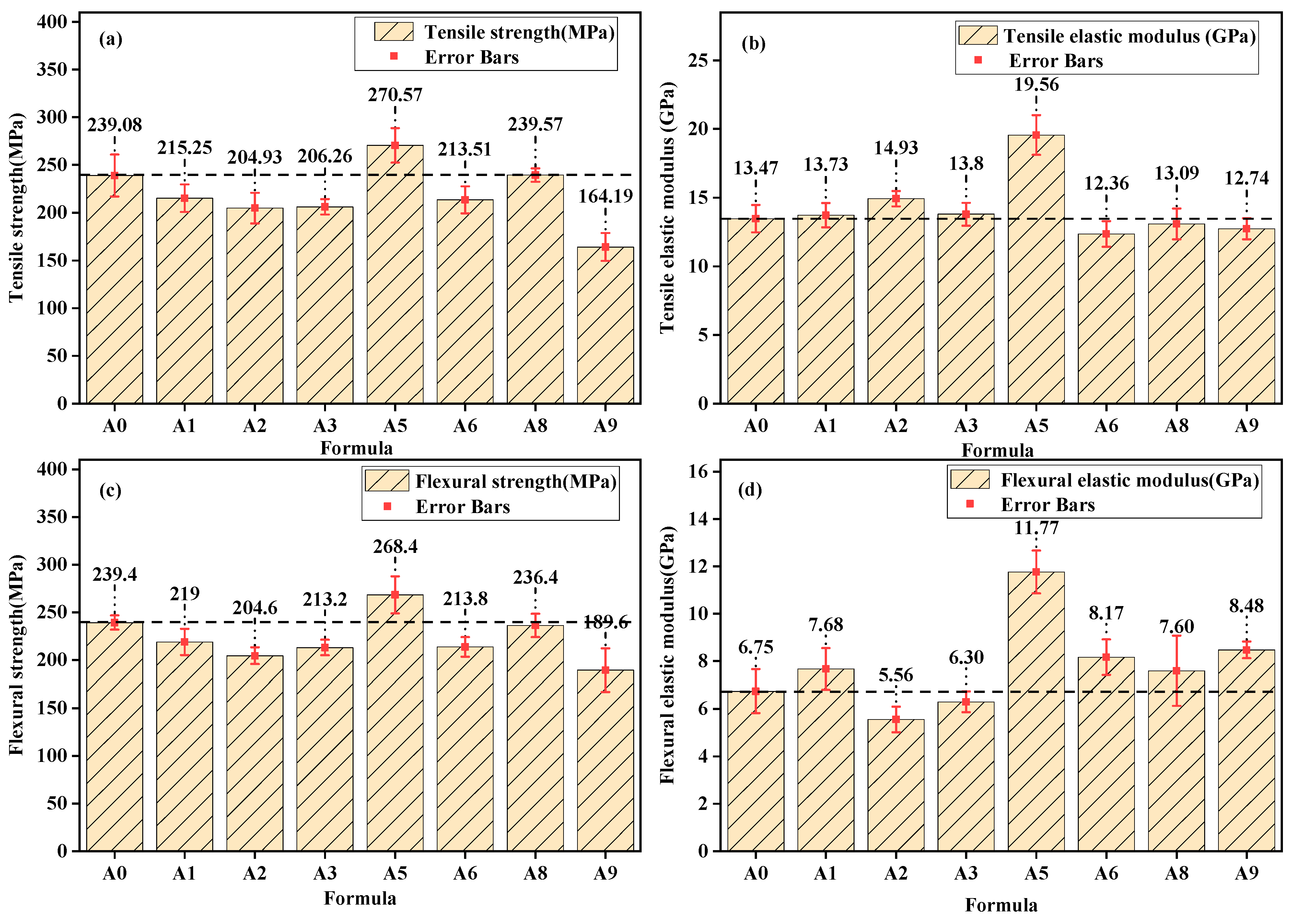
3.3.1. Mechanical Properties of Epoxy–BFRP
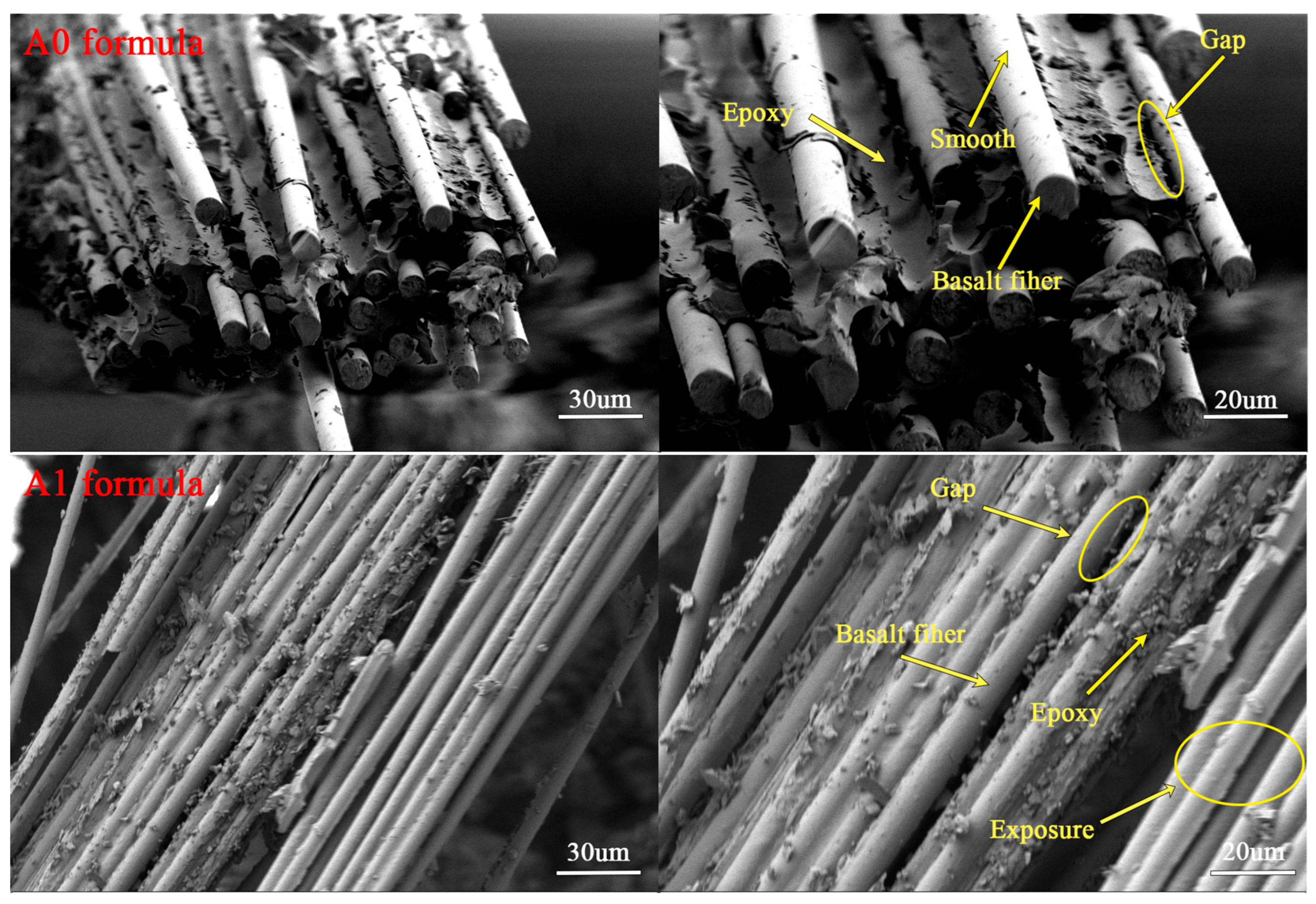
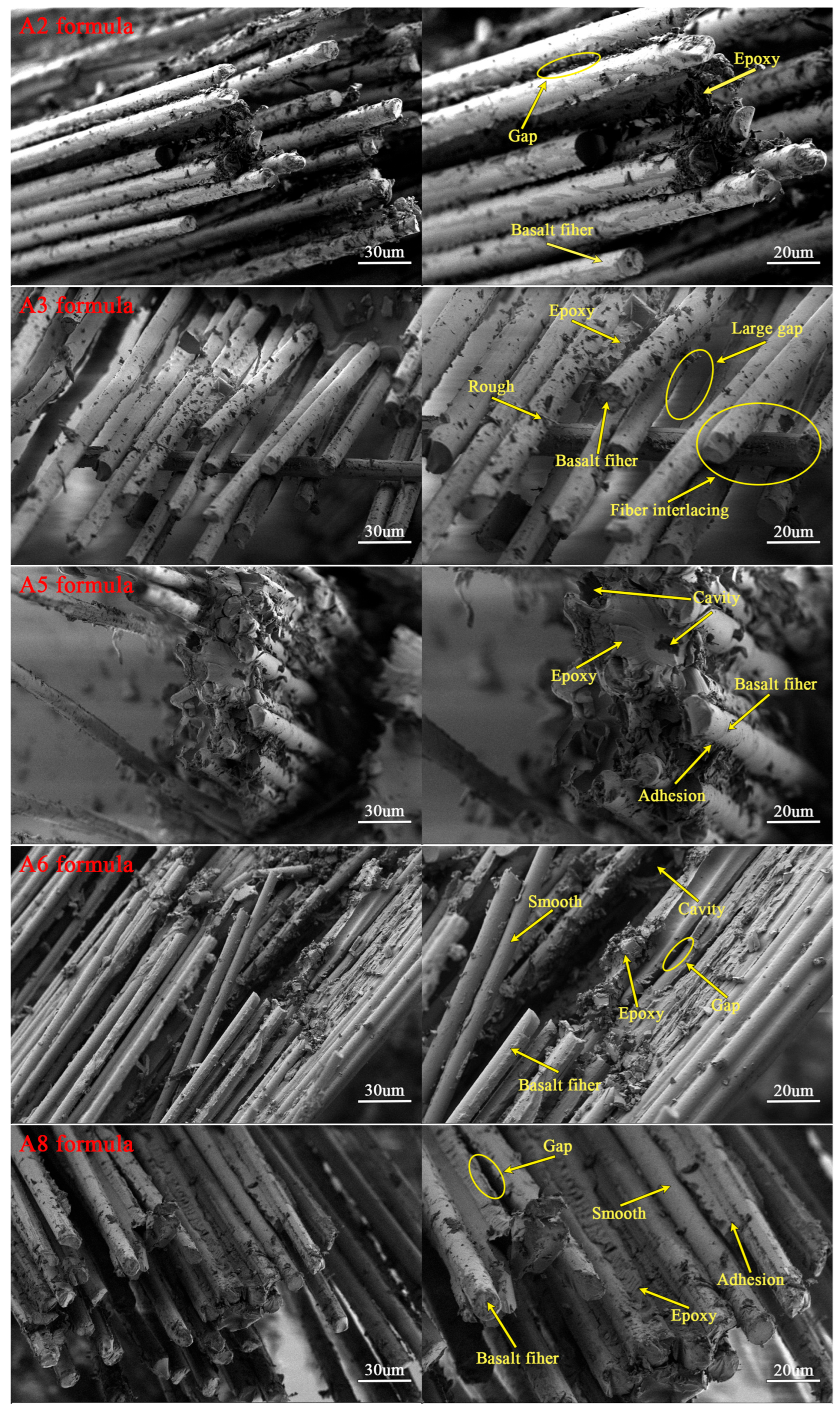
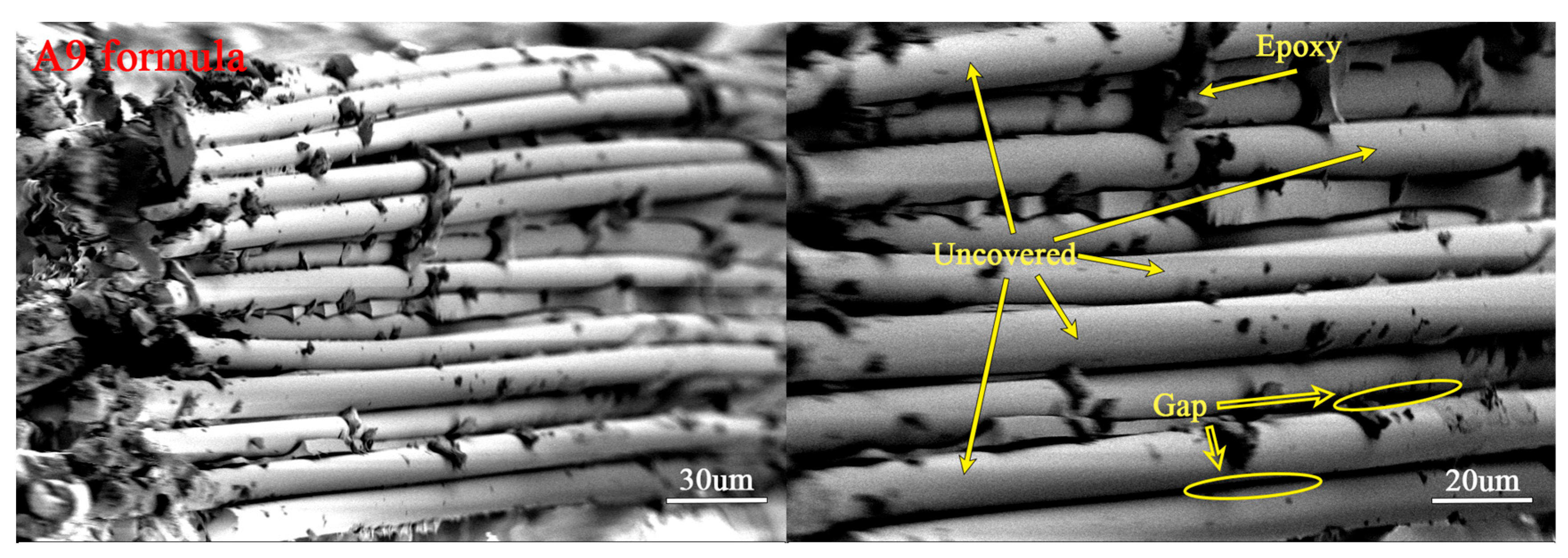
3.3.2. Morphology of Epoxy–BFRP
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The lubricant components presented a significant influence on physical and chemical parameters of the sizing agent, as well as the properties of BF and its epoxy resin composite materials.
- (2)
- Imidazoline-type lubricant II (L-5) exhibited antagonistic effects with lubricant L-2, leading to poor stability of the impregnating emulsion. Imidazoline-type lubricant III (L-6) can markedly reduce the surface tension of the sizing agent, yielding superior mechanical properties of the fibers.
- (3)
- Imidazoline-type lubricant II (L-4) can partially reduce the viscosity of the impregnating emulsion, and the Epoxy–BFRP exhibited significant differences in the interface bonding performance between fibers and the matrix resin obtained by the A5 and A8 formulations. Specifically, for the A5 lubricant combination (L-1 0.30%, L-2 0.70%, L-4 0.30%), the tensile strength, tensile modulus, and flexural strength of the resulting Epoxy–BFRP increased by 13.2%, 45.2%, and 12%, respectively, which indicated excellent microscale interface properties.
- (4)
- The particle size of the sizing agent emulsion can affect the mechanical properties of BF. A sizing agent emulsion with an excessively large particle size can lead to phenomena such as fly fibers and uneven coating of the BF after treatment, thereby degrading the mechanical properties of the BF.
- (5)
- Epoxy–BFRP shows a positive correlation trend with the surface tension of the sizing agent emulsion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. A review on basalt fibre and its composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 74, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshaid, H.; Mishra, R. A green material from rock: Basalt fiber—A review. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hui, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, Z. Study of melting properties of basalt based on their mineral components. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 116, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overkamp, T.; Mahltig, B.; Kyosev, Y. Strength of basalt fibers influenced by thermal and chemical treatments. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 47, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. The influences of silane coupling agents on the heat and moisture resistance of basalt fibre-reinforced composites. High Volt. 2023, 8, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, V.; Mittal, G.; Rhee, K.Y.; Park, S.-J.; Hui, D. A short review on basalt fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 73, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, M.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Gamma ray shielding property of tungsten powder modified continuous basalt fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39 (Suppl. S4), E2106–E2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaznov, A.N.; Atyasova, E.V.; Shundrina, I.K.; Samoilenko, V.V.; Firsov, V.V.; Zubkov, A.S. Thermomechanical characterization of BFRP and GFRP with different degree of conversion. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Xi, X.-Y.; Ma, P.-C. Factors governing the tensile strength of basalt fibre. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 119, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-J. Interfacial behaviors of basalt fiber-reinforced polymeric composites: A short review. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1414–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.R. A review of interphase formation and design in fibre-reinforced composites. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoglu, M.; Ziaee, S.; Mcknight, S.H.; Palmese, G.R.; Gillespie, J.J.W. Investigation of properties of fiber/matrix interphase formed due to the glass fiber sizings. J. Mater. Sci. 2001, 36, 3041–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.L. The interface region in glass fibre-reinforced epoxy resin composites: 3. Characterization of fibre surface coatings and the interphase. Composites 1995, 26, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathusha, M.S.; Din, I.U.; Umer, R.; Khan, K.A. In-situ monitoring of crack growth and fracture behavior in composite laminates using embedded sensors of rGO coated fabrics and GnP paper. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 365, 114850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, I.U.; Bathusha, M.S.; Khan, K.A. Effects of Liquid Rubber-Modified Epoxy on the Fracture Toughness of rGO-Coated Fabric Piezoresistive Composites. Compos. Commun. 2025, 56, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J. A review of the analysis and characterisation of polymeric glass fibre sizings. Polym. Test. 2020, 85, 106421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Xi, X.-Y.; Qi, M.-G.; Zheng, Q.-B.; Ma, P.-C. Optimization on the formulation of sizing to enhance the mechanical properties of basalt fiber. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, C.; Lemoine, P.; Boyd, A.; Archer, E.; McIlhagger, A. The effect of fibre sizing on the modification of basalt fibre surface in preparation for bonding to polypropylene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Fu, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H. Effect of Sizing Agent on the Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Performance of Basalt Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Nam, I.; Kim, H. Thermal stability and physical properties of epoxy composite reinforced with silane treated basalt fiber. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, C.; Dogan, M. The effects of silane coupling agents on the mechanical properties of basalt fiber reinforced poly (butylene terephthalate) composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 146, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, J.; Han, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z. Silane coupling agent impact on surface features of modification of basalt fibers and the rheological properties of basalt fiber reinforced asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7690.1-2013; Reinforcements—Test method for yarns—Part 1: Determination of linear density. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 9914.1-2013; Test Method for Reinforcement Products Part 1: Determination of Moisture Content. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 9914.2-2013; Test Method for Reinforcement Products Part 1: Determination of Combustible-Matter Content for Glass Fibre. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- DB51/T 2321-2017; Test Method for Tensile Properties of Basalt Fiber Monofilament. Sichuan Provincial Fiber Inspection Bureau: Chengdu, China, 2017.
- GB/T 7690.3-2013; Reinforcements—Test Method for Yarns—Part 3: Determination of Breaking Force and Breaking Elongation for Glass Fibre. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- GB/T 1447-2005; Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Tensile Properties. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- GB/T 1449-2005; Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Flexural Properties. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.




| Formula | Lubricant-I | Proportion | Lubricant-II | Proportion | Lubricant-III | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A1 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-5 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A2 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-4 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A3 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-6 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A4 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-5 | 0.30% |
| A5 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-4 | 0.30% |
| A6 | L-1 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-6 | 0.30% |
| A7 | L-5 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A8 | L-4 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| A9 | L-6 | 0.30% | L-2 | 0.70% | L-3 | 0.30% |
| Formula | Linear Density (tex) | Diameter (µm) | Moisture Content (%) | Combustible Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 213.37 | 15.89 | 0.0913 | 0.9834 |
| A0 | 243.53 | 15.73 | 0.0865 | 2.0030 |
| A1 | 235.67 | 15.99 | 0.0697 | 1.0818 |
| A2 | 225.32 | 15.88 | 0.0714 | 1.4393 |
| A3 | 251.20 | 16.12 | 0.0784 | 1.0974 |
| A4 | 247.93 | 16.98 | 0.0844 | 2.1004 |
| A5 | 253.42 | 16.38 | 0.0765 | 1.0768 |
| A6 | 236.64 | 15.56 | 0.0697 | 1.4348 |
| A7 | 245.91 | 16.45 | 0.0897 | 1.0446 |
| A8 | 255.57 | 16.88 | 0.0810 | 1.0768 |
| A9 | 245.91 | 16.45 | 0.0897 | 2.0196 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Lai, C.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Xie, B.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Zou, L. A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Lubricant in the Sizing Agent on the Properties of a Basalt Fiber and Epoxy Resin Composite Material. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110838
He J, Lai C, Li J, Yang N, Xie B, Li X, Deng Y, Zou L. A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Lubricant in the Sizing Agent on the Properties of a Basalt Fiber and Epoxy Resin Composite Material. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110838
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiajun, Chuan Lai, Junlan Li, Ning Yang, Bin Xie, Xiaolong Li, Yuanfang Deng, and Like Zou. 2025. "A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Lubricant in the Sizing Agent on the Properties of a Basalt Fiber and Epoxy Resin Composite Material" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110838
APA StyleHe, J., Lai, C., Li, J., Yang, N., Xie, B., Li, X., Deng, Y., & Zou, L. (2025). A Comprehensive Study of the Effect of Lubricant in the Sizing Agent on the Properties of a Basalt Fiber and Epoxy Resin Composite Material. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110838







