Preparation and Performance of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blend-Modified Fiber Membranes via Centrifugal Spinning for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
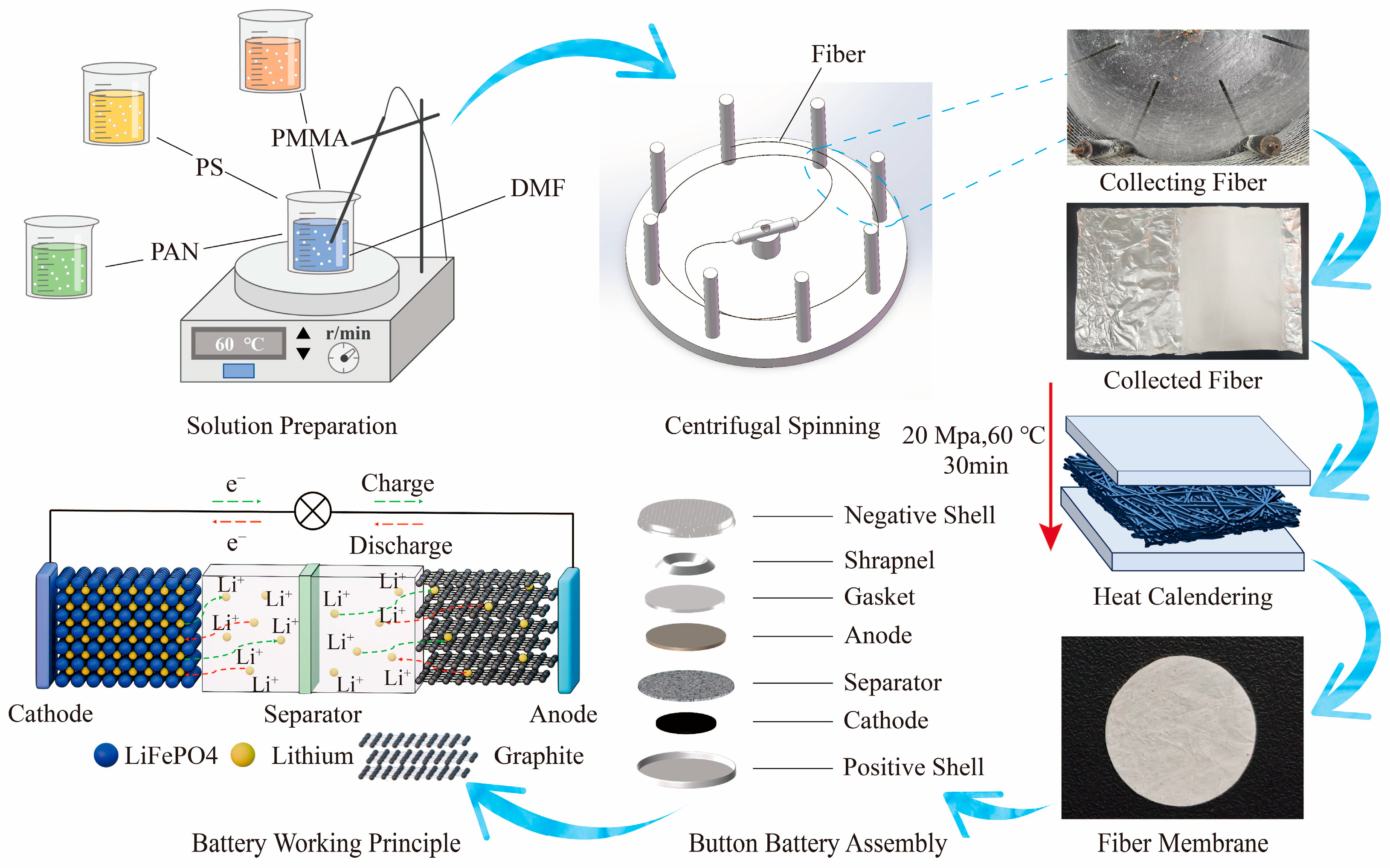
2.2. Preparation of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blended Modified Fibrous Membranes
2.3. Microscopic Morphology and Performance Characterization
2.4. Battery Performance
3. Results and Discussion
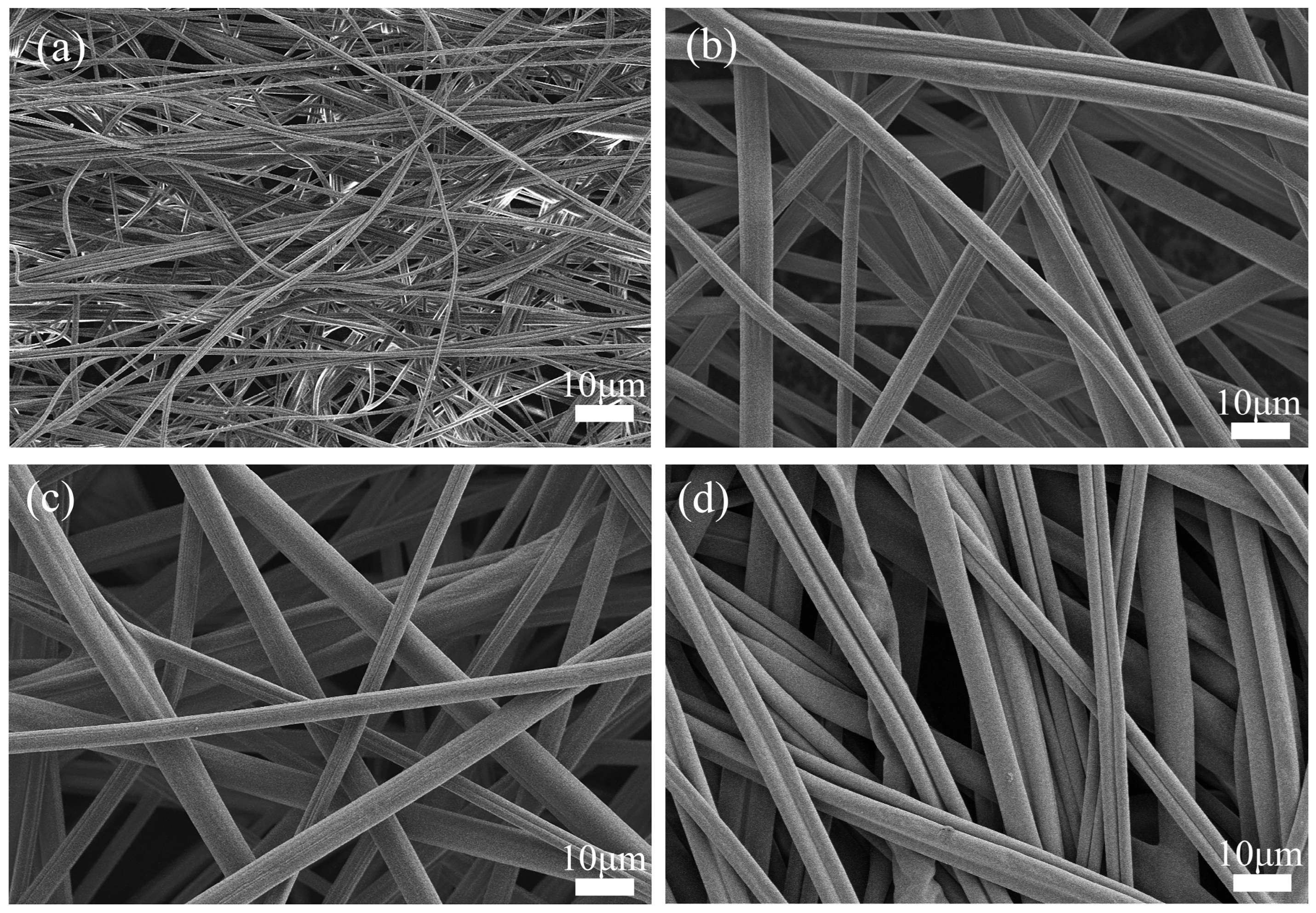
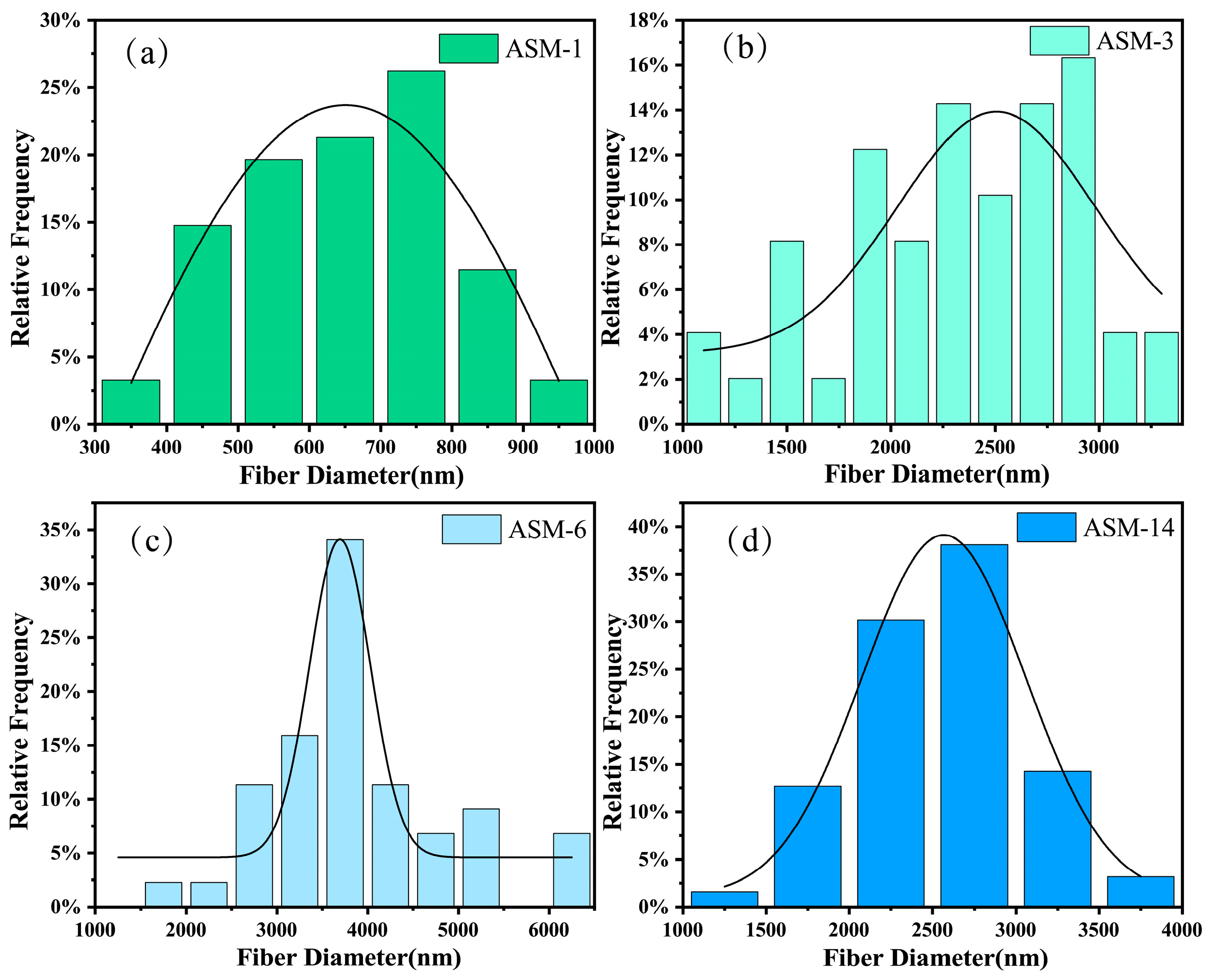
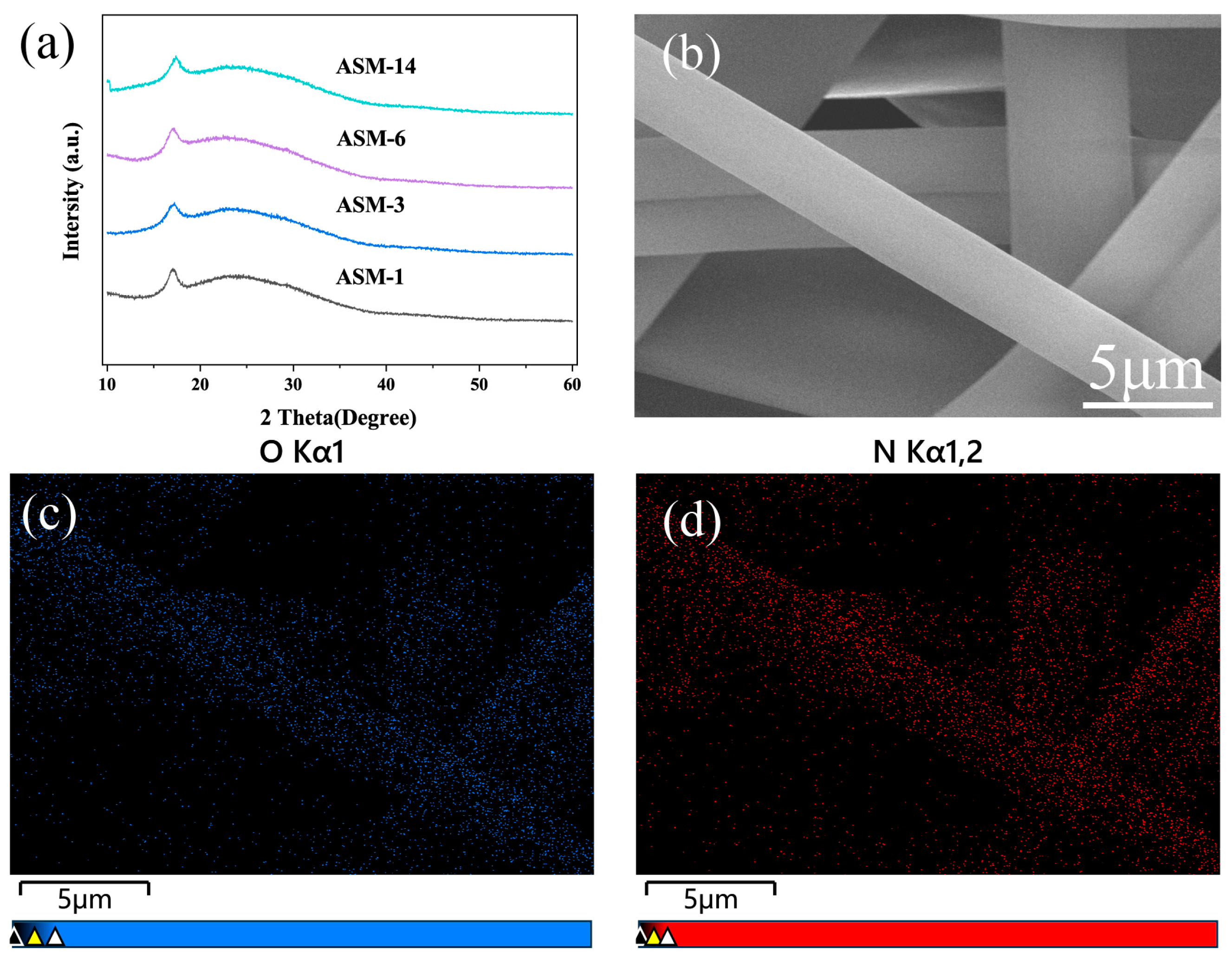
3.1. Microstructure, Elemental Distribution, and X-Ray Diffraction of the Membranes
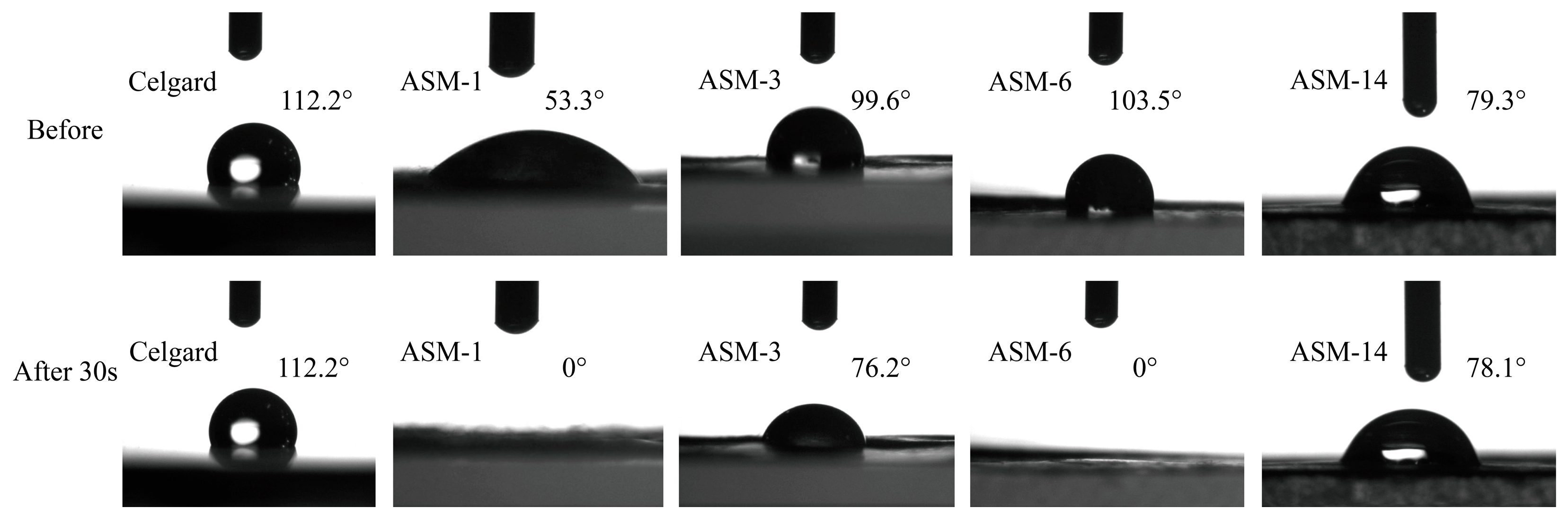
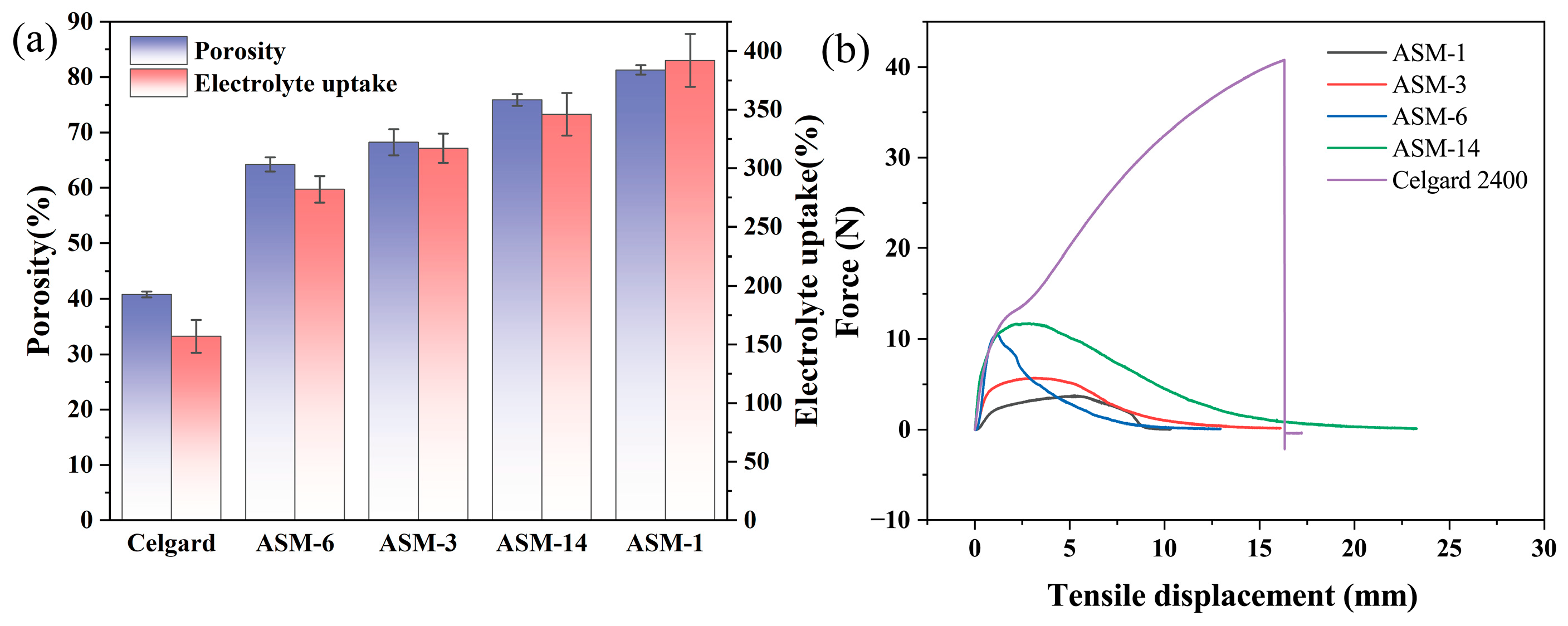
3.2. Contact Angle, Porosity, Electrolyte Uptake, and Tensile Strength
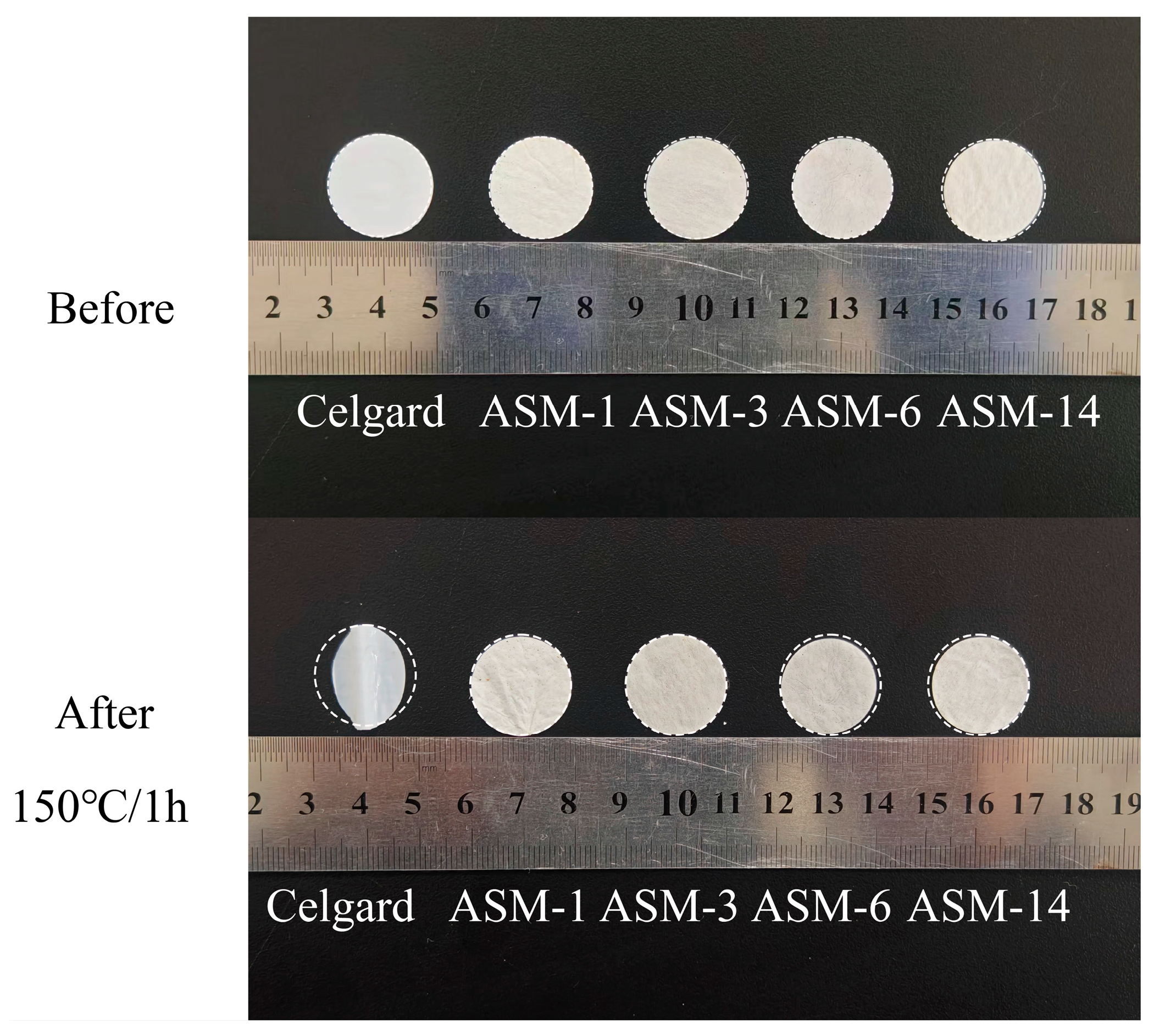
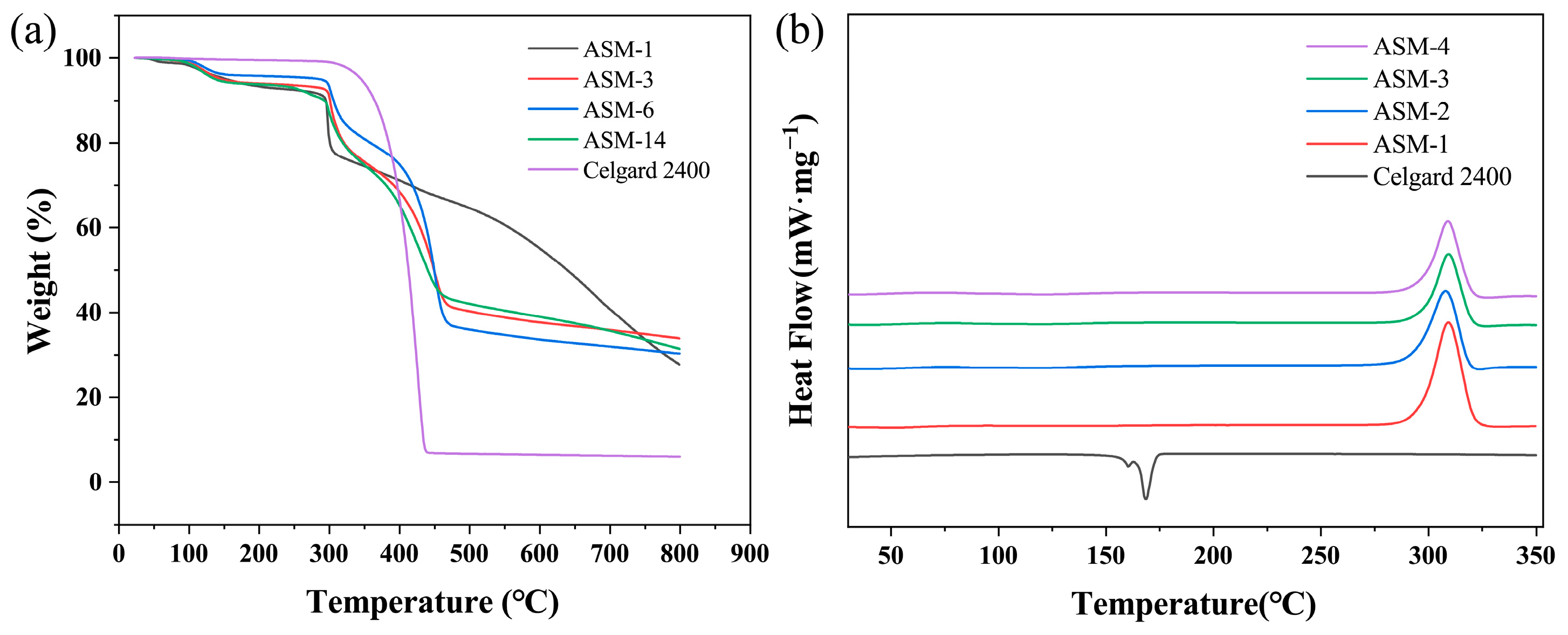
3.3. Thermal Stability and Dimensional Thermal Stability
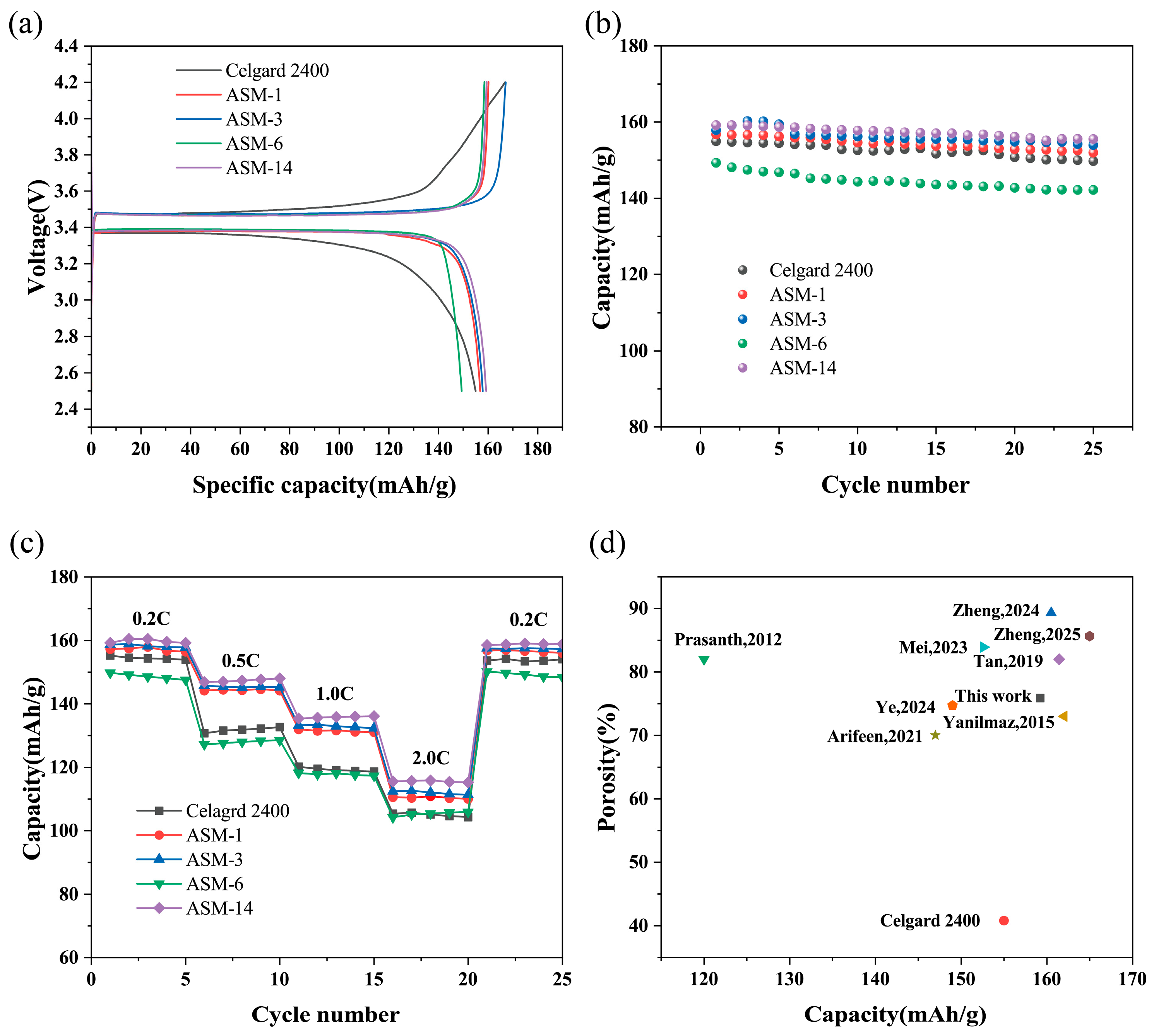
3.4. Electrochemical Performance of the Battery
3.5. Comparison of Overall Separator Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, P.; Liu, X.; Qu, J.; Zhao, J.; Huo, Y.; Qu, Z.; Rao, Z. Recent advances of thermal safety of lithium ion battery for energy storage. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 31, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Y.; Sun, J. Progress of enhancing the safety of lithium ion battery from the electrolyte aspect. Nano Energy 2019, 55, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey, C.P.; Hall, D.S. Prospects for lithium-ion batteries and beyond—A 2030 vision. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagadec, M.F.; Zahn, R.; Wood, V. Characterization and performance evaluation of lithium-ion battery separators. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xiao, P.; Luo, M.; Nie, S.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. Eco-Friendly Lithium Separators: A Frontier Exploration of Cellulose-Based Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Khan, M.A.; Zou, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Recent progress in advanced electrode materials, separators and electrolytes for lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 20564–20620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kim, P.J. A roadmap of battery separator development: Past and future. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 31, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Kang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ju, J.; Wu, D.; Li, L.; Hassan, B.S.; Cheng, B. A review on separators for lithiumsulfur battery: Progress and prospects. J. Power Sources 2016, 331, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, J.; Liu, D.; Xie, Z.; Qu, D.; Li, K.; Deng, T.; Tang, H. Advanced separators for lithium-ion and lithium–sulfur batteries: A review of recent progress. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 3023–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Lamprou, D.; Zhao, M. Electrospinning technologies for the delivery of Biopharmaceuticals: Current status and future trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 651, 123641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, S.; Surendran, A.; Ghosh, S.; Anandhan, S.; Venimadhav, A. Electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) fluoride separator for sodium ion battery with high coulombic efficiency. Solid State Ion. 2016, 292, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Manuel, J.; Choi, H.; Park, W.H.; Ahn, J.-H. Partially oxidized polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membrane as a thermally stable separator for lithium ion batteries. Polymer 2015, 68, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, T.; Zhao, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Wu, H. A heatproof separator for lithium-ion battery based on nylon66 nanofibers. Ionics 2016, 22, 731–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Jiang, P.; Chen, W.; Qian, G.; He, D.; Lu, X. Bifunctional Al2O3/polyacrylonitrile membrane to suppress the growth of lithium dendrites and shuttling of polysulfides in lithium-sulfur batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 428, 140955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, C.; Deng, L.; Zhang, W.; Peng, L.; Dai, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, P. Core-shell structured ceramic nonwoven separators by atomic layer deposition for safe lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Wang, Z.; Reddy, V.S.; Nagy, Z.K.; Vass, P.; Buzgo, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Radacsi, N. The history of electrospinning: Past, present, and future developments. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Schossig, J.; Towolawi, A.; Xu, K.; Bayiha, E.; Mohanakanthan, M.; Savastano, D.; Jayaraman, D.; Zhang, C.; Lu, P. High-speed electrospinning of ethyl cellulose nanofibers via Taylor cone optimization. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2024, 2, 2454–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arican, F.; Uzuner-Demir, A.; Polat, O.; Sancakli, A.; Ismar, E. Fabrication of gelatin nanofiber webs via centrifugal spinning for N95 respiratory filters. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kántor, J.; Farmos, R.L.; Gergely, A.L. Optimization of Oil Sorbent Thermoplastic Elastomer Microfiber Production by Centrifugal Spinning. Polymers 2023, 15, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihova, M.; Ince, A.E.; Cicmancova, V.; Hromadko, L.; Castkova, K.; Pavlinak, D.; Vojtova, L.; Macak, J.M. Water-born 3D nanofiber mats using cost-effective centrifugal spinning: Comparison with electrospinning process: A complex study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Gultekinoglu, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Recent developments in the use of centrifugal spinning and pressurized gyration for biomedical applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotech. 2024, 16, e1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, H.; Ning, X.; Du, Y.; Xie, H.; Wu, T.; Qu, J. Efficient fabrication of fabric-based Janus interfacial evaporator via melt centrifugal spinning for simultaneous solar evaporation, pollutant degradation, antibacterial action, and thermoelectric output. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 105, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Liang, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Ding, X. Water-stable CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum-dot luminous fibers fabricated by centrifugal spinning for dual white light illumination and communication. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Xu, B.; Wan, J.; Chen, J. Preparation of CNT/CNF/PDMS/TPU Nanofiber-Based Conductive Films Based on centrifugal spinning method for strain sensors. Sensors 2024, 24, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihova, M.; Cihalova, K.; Pouzar, M.; Kuthanova, M.; Jelinek, L.; Hromadko, L.; Cicmancova, V.; Heger, Z.; Macak, J.M. Biopolymeric fibers prepared by centrifugal spinning blended with ZnO nanoparticles for the treatment of Acne vulgaris. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B. Research on rotary nozzle structure and flow field of the spinneret for centrifugal spinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihova, M.; Lepcio, P.; Cicmancova, V.; Frumarova, B.; Hromadko, L.; Bureš, F.; Vojtova, L.; Macak, J.M. The centrifugal spinning of vitamin doped natural gum fibers for skin regeneration. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, X.; Fei, P.; Li, F. Centrifugal spinning of lignin amine/cellulose acetate nanofiber for heavy metal ion adsorption. Fibers Polym. 2022, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Na, B.; Huang, Y.; Xie, X. Poly (vinylidene fluoride)/poly (acrylonitrile) blend fibrous membranes by centrifugal spinning for high-performance lithium ion battery separators. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 44515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.; Xu, F.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Mao, Y.; Lozano, K. Fibrous cellulose membrane mass produced via forcespinning® for lithium-ion battery separators. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B. Highly porous fibers prepared by centrifugal spinning. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, G.; Fu, K.; Lee, H.; Zhang, X. Parameter study and characterization for polyacrylonitrile nanofibers fabricated via centrifugal spinning process. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 3834–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Mei, S.-q.; Liu, T.; Yang, L.-y.; Fan, L.-l. Preparation and tensile conductivity of carbon nanotube/polyurethane nanofiber conductive films based on the centrifugal spinning method. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 135708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, H.N.; Nguyen, D.K.; Vo, P.P.; Hayashi, K.; Kinashi, K.; Sakai, W.; Tsutsumi, N.; Huynh, D.P. Facile and scalable fabrication of porous polystyrene fibers for oil removal by centrifugal spinning. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15992–16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lu, L.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, B. Fabrication of centrifugally spun prepared poly (lactic acid)/gelatin/ciprofloxacin nanofibers for antimicrobial wound dressing. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 35328–35335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, P.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q. High-speed centrifugal spinning polymer slip mechanism and PEO/PVA composite fiber preparation. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.; Arifeen, W.U.; Choi, J.; Yoo, K.; Ko, T. Surface-modified electrospun polyacrylonitrile nano-membrane for a lithium-ion battery separator based on phase separation mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Deng, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, G. Designing polyimide/polyacrylonitrile/polyimide sandwich composite separator for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Guo, K.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Guo, B.; Guo, D.; Liu, G.; Wu, N. A CNC-Modified PAN Separator Improving the Cycle Stability of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Coatings 2025, 15, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bi, Z.; Wan, Y.; Guo, X. Composition regulation of polyacrylonitrile-based polymer electrolytes enabling dual-interfacially stable solid-state lithium batteries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 665, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Deng, Y.; Cao, Q.; Jing, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Gel electrolytes based on polyacrylonitrile/thermoplastic polyurethane/polystyrene for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 2019, 25, 3673–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanilmaz, M.; Zhang, X. Polymethylmethacrylate/polyacrylonitrile membranes via centrifugal spinning as separator in Li-ion batteries. Polymers 2015, 7, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjuban, S.M.H.; Rahman, M.; Duza, S.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Patel, D.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Lozano, K. Recent advances in centrifugal spinning and their applications in tissue engineering. Polymers 2023, 15, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Fan, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, Y. Orientation gradient architecture of nanofibrous separator towards mechanical enhancement and ion transport acceleration for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 441, 141794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; De Guzman, M.R.; Ye, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, F.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Gong, D.; Fu, Q. Mechanically enhanced battery separator prepared by hot-pressing electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride@ polymethyl methacrylate membranes with different fiber orientations in adjacent layers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2024, 64, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchiers, J.; Reddy, N.K.; Sharma, V. Extensibility-enriched spinnability and enhanced sorption and strength of centrifugally spun polystyrene fiber mats. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S.; Kyu, K.B. Crosslinkings of polyacrylonitrile using NCO terminated urethanes. Polymer 1997, 38, 5211–5216. [Google Scholar]
- Jyothi, N.K.; Kumar, K.V.; Murthy, P.N. FTIR, XRD and DC conductivity studies of proton conducting gel polymer electrolytes based on polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res 2014, 6, 5214–5219. [Google Scholar]
- Elrasheedy, A.; Rabie, M.; El-Shazly, A.; Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Hamid, S.; El Kady, M.F. Numerical investigation of fabricated mwcnts/polystyrene nanofibrous membrane for dcmd. Polymers 2021, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Mei, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Preparation and performance of bicomponent polyacrylonitrile/polymethyl methacrylate lithium-ion battery separator by centrifugal spinning. Polymer 2024, 307, 127226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakar, S.; Soykan, C.; Özacar, M. Polystyrene/Polyacrylonitrile/Polyindole based quasi solid electrolytes for DSSCs: Boosting both efficiency and stability. Mater. Res. Bull. 2025, 181, 113108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, R.; Aravindan, V.; Srinivasan, M. Novel polymer electrolyte based on cob-web electrospun multi component polymer blend of polyacrylonitrile/poly (methyl methacrylate)/polystyrene for lithium ion batteries—Preparation and electrochemical characterization. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Liu, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y. Preparation and performance of a PU/PAN lithium-ion battery separator based on a centrifugal spinning method. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, H.; Ye, F.; Zhang, X.; Ge, Y. Oriented PAN/PVDF/PAN laminated nanofiber separator for lithium-ion batteries. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifeen, W.U.; Choi, J.; Yoo, K.; Shim, J.; Ko, T.J. A nano-silica/polyacrylonitrile/polyimide composite separator for advanced fast charging lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number | PAN Solution Mass Fraction (%) | Stirring Time (h)/Temperature (°C) | Needle Inner Diameter (G) | Rotating Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 22/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 2 | 20 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 3 | 20 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 4 | 20 | 9/80 | 24 | 4500 |
| 5 | 18 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 6 | 18 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 7 | 18 | 9/80 | 24 | 4500 |
| 8 | 16 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 9 | 16 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 10 | 16 | 9/80 | 24 | 4500 |
| Number | PAN/PS/PMMA Ratio | Stirring Time (h)/Temperature (°C) | Needle Inner Diameter (G) | Rotating Speed (r/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10:0:0 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 2 | 9:1:0 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 3 | 8:2:0 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 4 | 8:2:0 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 5 | 8:2:0 | 9/80 | 24 | 4500 |
| 6 | 7:3:0 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 7 | 7:3:0 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 8 | 7:3:0 | 9/80 | 24 | 4500 |
| 9 | 6:4:0 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 10 | 8:2:0.5 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 11 | 8:2:0.5 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 12 | 8:2:1 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 13 | 8:2:1 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 14 | 8:2:2 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 15 | 8:2:2 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| 16 | 8:2:3 | 9/80 | 26 | 4500 |
| 17 | 8:2:3 | 9/80 | 28 | 4500 |
| Sample | Celgard 2400 | ASM-1 | ASM-3 | ASM-6 | ASM-14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter distribution (nm) | - | 500–800 | 2000–3000 | 3000–4000 | 2000–3000 |
| Porosity (%) | 40.82 | 81.27 | 68.23 | 64.21 | 75.87 |
| Electrolyte uptake (%) | 157 | 392 | 317 | 282 | 346 |
| Contact angle (°) | 112.2 | 53.3 | 99.6 | 103.5 | 79.3 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 163.16 | 7.52 | 11.44 | 20.96 | 23.48 |
| Thermal shrinkage ratio (%) | 28.9 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 3.18 | 2.85 |
| Initial discharge capacity (mAh/g) | 155 | 157 | 158 | 149 | 159 |
| Capacity retention after cycling (mAh/g) | 150 | 152 | 154 | 142 | 156 |
| Capacity retention (%) | 96.77 | 96.82 | 97.47 | 95.3 | 98.11 |
| Discharge capacity at 2.0 C (mAh/g) | 106 | 111 | 113 | 106 | 116 |
| Separator Material | Porosity (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Capacity (mAh/g) | Method/Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celgard 2400 | 40.82 | 125.17 | 155 (0.2 C) | / | / |
| PAN-PMMA | 89.28 | 10.85 | 160.5 (0.2 C) | CS/100mL/h | [50] |
| PAN-PS-PMMA | 80–84 | / | 120 (0.1 C) | ES/12mL/h | [52] |
| PAN-TPU-PS | 82 | 10.8 | 161.44 (0.1 C) | ES/0.5mL/h | [41] |
| PMMA-PAN | 73 | / | 162 (0.2 C) | CS | [42] |
| PU-PAN | 83.9 | / | 152.6 (0.2 C) | CS/100mL/h | [53] |
| PAN-PVDF-PAN | 85.64 | 11.03 | 165 (0.5 C) | ES/0.6mL/h | [54] |
| PAN-PI-SiO2 | 70 | 18.9 | 147 (1 C) | ES/1.8 mL/h | [55] |
| PVDF-PMMA | 74.68 | 22.09 | 149 (0.2 C) | ES/1.4mL/h | [45] |
| PAN-PS-PMMA | 75.87 | 23.48 | 159 (0.2 C) | CS/100mL/h | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, S.; Luo, F.; Xie, Y.; Xu, B.; Zheng, Q. Preparation and Performance of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blend-Modified Fiber Membranes via Centrifugal Spinning for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110789
Mei S, Luo F, Xie Y, Xu B, Zheng Q. Preparation and Performance of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blend-Modified Fiber Membranes via Centrifugal Spinning for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials. 2025; 15(11):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110789
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Shunqi, Feng Luo, Yi Xie, Bin Xu, and Quan Zheng. 2025. "Preparation and Performance of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blend-Modified Fiber Membranes via Centrifugal Spinning for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Nanomaterials 15, no. 11: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110789
APA StyleMei, S., Luo, F., Xie, Y., Xu, B., & Zheng, Q. (2025). Preparation and Performance of PAN/PS/PMMA Ternary Blend-Modified Fiber Membranes via Centrifugal Spinning for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials, 15(11), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15110789





